Successful Use of Heterologous CMV-Reactive T Lymphocyte to Treat Severe Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection in a Liver Transplanted Patient: Correlation of the Host Antiviral Immune Reconstitution with CMV Viral Load and CMV miRNome
Abstract
1. Introduction
Case Presentation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells (DCs)
2.2. Preparation of CMV-Reactive T Cell and Analysis of T-Cell Subsets
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Interferon-γ Detection
2.5. Monitoring of CMV-DNA Load
2.6. CMV Genotyping Resistance Testing
2.7. Analysis of CMV Encoded miRNAs
2.8. Cellular miRNA Profiling
2.9. Data Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CMV-Reactive T Cells Generation
3.2. CMV-Reactive T Cells Recovery
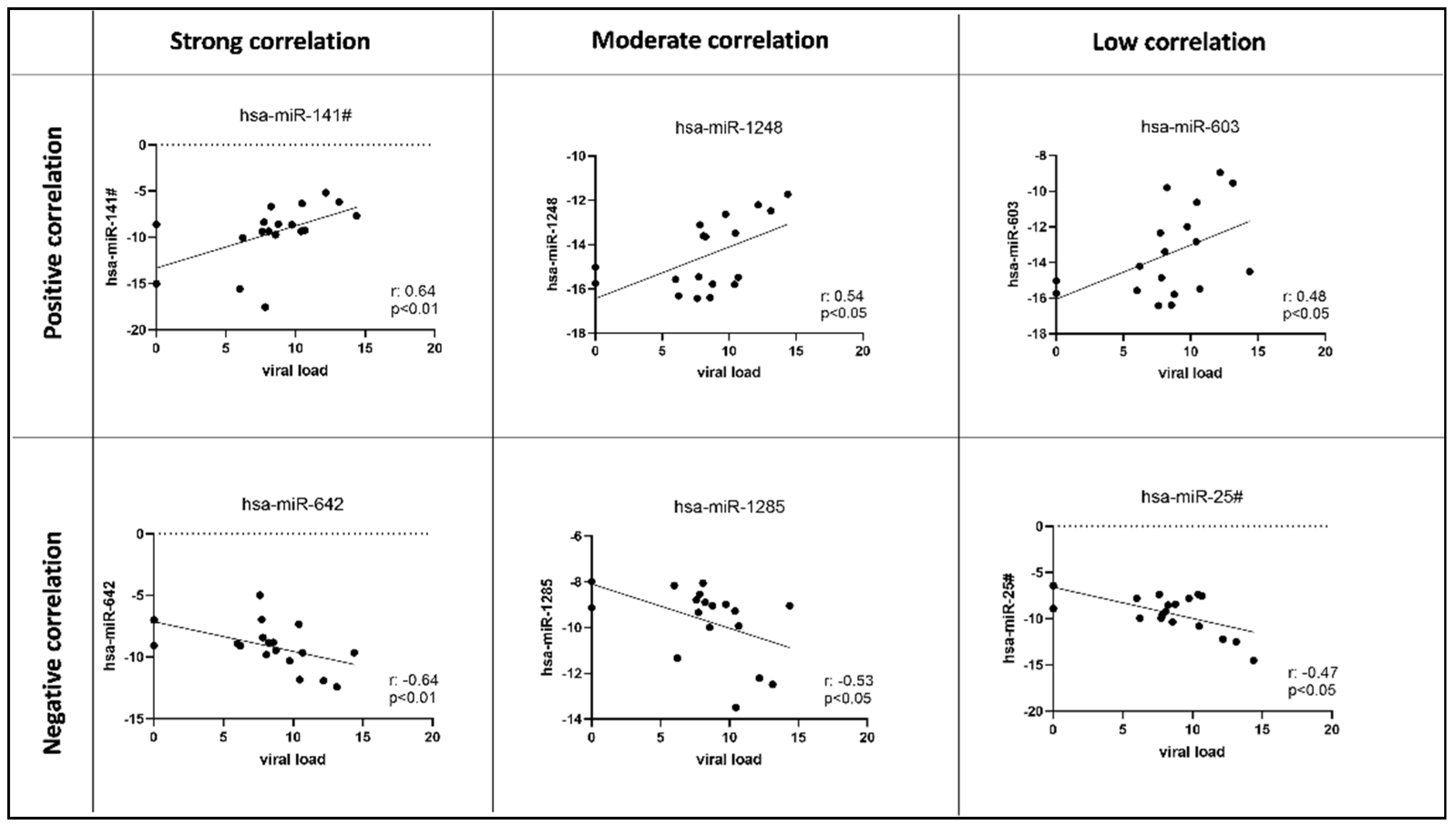
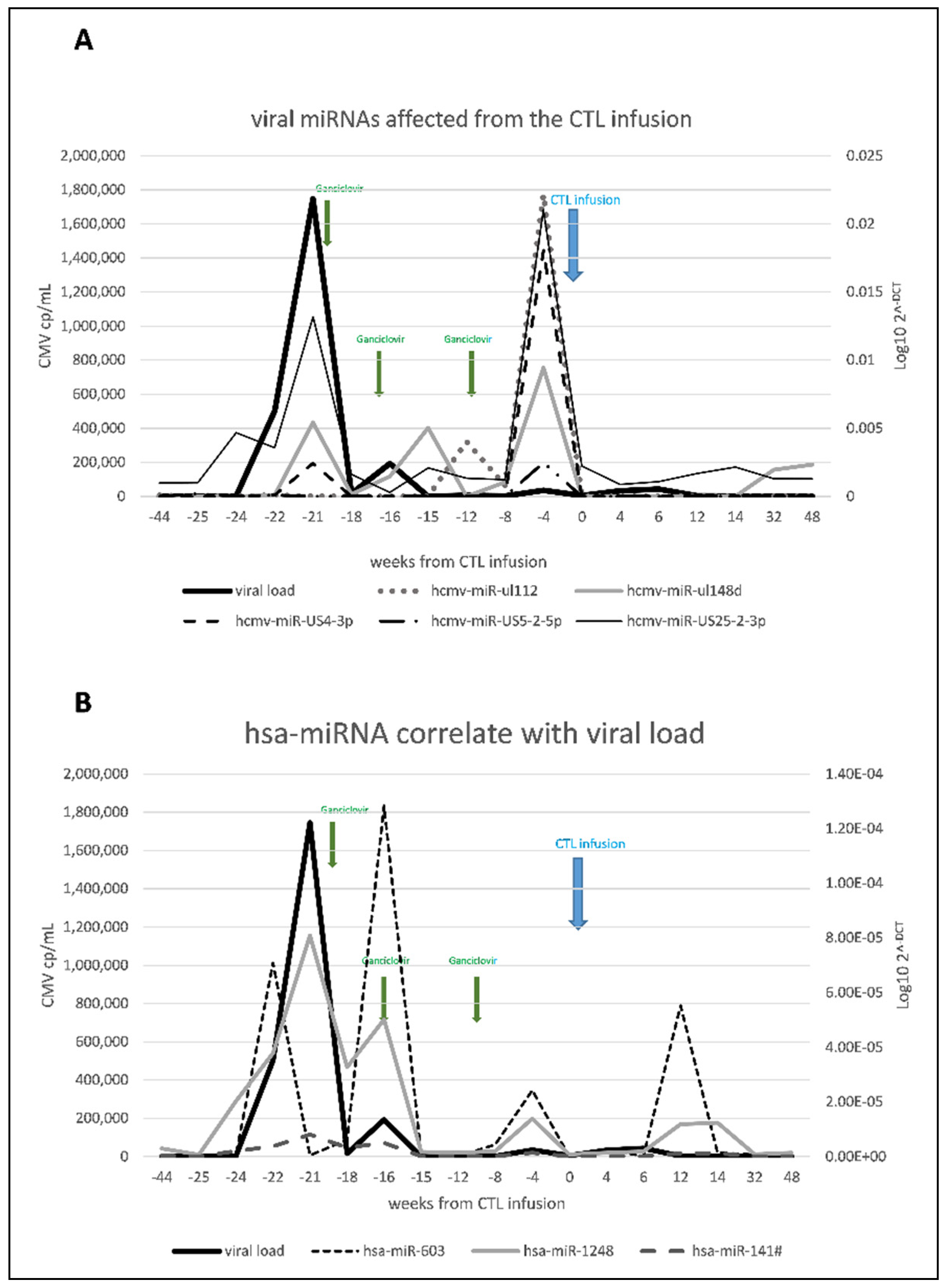
3.2.1. Host Cellular miRNome Evaluation
3.2.2. CMV miRNome Evaluation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, E.C.; Bowden, R.A.; Dandliker, P.S.; Lilleby, K.E.; Meyers, J.D. Treatment of cytomegalovirus pneumonia with ganciclovir and intravenous cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin in patients with bone marrow transplants. Ann. Intern. Med. 1988, 109, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.K.; Khanna, R. Human cytomegalovirus: Clinical aspects, immune regulation, and emerging treatments. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C.; Sterneck, M.; Weiss, K.H.; Templin, S.; Zopf, S.; Denk, G.; Eurich, D.; Pratschke, J.; Weiss, J.; Braun, F.; et al. Prevention and Management of CMV Infections after Liver Transplantation: Current Practice in German Transplant Centers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razonable, R.R.; Hayden, R.T. Clinical utility of viral load in management of cytomegalovirus infection after solid organ transplantation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, G.A.; Silveira, F.P.; Langston, A.A.; Pereira, M.R.; Avery, R.K.; Uknis, M.; Wijatyk, A.; Wu, J.; Boeckh, M.; Marty, F.M.; et al. Maribavir for Refractory or Resistant Cytomegalovirus Infections in Hematopoietic-cell or Solid-organ Transplant Recipients: A Randomized, Dose-ranging, Double-blind, Phase 2 Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, F.M.; Winston, D.J.; Chemaly, R.F.; Mullane, K.M.; Shore, T.B.; Papanicolaou, G.A.; Chittick, G.; Brundage, T.M.; Wilson, C.; Morrison, M.E.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial of Oral Brincidofovir for Cytomegalovirus Prophylaxis in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligat, G.; Cazal, R.; Hantz, S.; Alain, S. The human cytomegalovirus terminase complex as an antiviral target: A close-up view. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, L.J.; Melaragno, J.I.; Brennan, D.C. Letermovir for the management of cytomegalovirus infection. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusser, P.; Einsele, H.; Lee, J.; Volin, L.; Rovira, M.; Engelhard, D.; Finke, J.; Cordonnier, C.; Link, H.; Ljungman, P.; et al. Randomized multicenter trial of foscarnet versus ganciclovir for preemptive therapy of cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2002, 99, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; Engelhard, D.; Link, H.; Biron, P.; Brandt, L.; Brunet, S.; Cordonnier, C.; Debusscher, L.; de Laurenzi, A.; Kolb, H.J.; et al. Treatment of interstitial pneumonitis due to cytomegalovirus with ganciclovir and intravenous immune globulin: Experience of European Bone Marrow Transplant Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einsele, H.; Ehninger, G.; Hebart, H.; Wittkowski, K.M.; Schuler, U.; Jahn, G.; Mackes, P.; Herter, M.; Klingebiel, T.; Loffler, J.; et al. Polymerase chain reaction monitoring reduces the incidence of cytomegalovirus disease and the duration and side effects of antiviral therapy after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1995, 86, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, S.; Dumontier, N.; Biard, L.; Schnepf, N.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Peffault de Latour, R.; Scieux, C.; Robin, M.; Meunier, M.; Xhaard, A.; et al. Response to antiviral therapy in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation according to the donor CMV serological status. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 289.e1–289.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almyroudis, N.G.; Jakubowski, A.; Jaffe, D.; Sepkowitz, K.; Pamer, E.; O'Reilly, R.J.; Papanicolaou, G.A. Predictors for persistent cytomegalovirus reactivation after T-cell-depleted allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2007, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, E.A.; Greenberg, P.D.; Gilbert, M.J.; Finch, R.J.; Watanabe, K.S.; Thomas, E.D.; Riddell, S.R. Reconstitution of cellular immunity against cytomegalovirus in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow by transfer of T-cell clones from the donor. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peggs, K.S. Adoptive T cell immunotherapy for cytomegalovirus. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einsele, H.; Roosnek, E.; Rufer, N.; Sinzger, C.; Riegler, S.; Loffler, J.; Grigoleit, U.; Moris, A.; Rammensee, H.G.; Kanz, L.; et al. Infusion of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T cells for the treatment of CMV infection not responding to antiviral chemotherapy. Blood 2002, 99, 3916–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meij, P.; Jedema, I.; Zandvliet, M.L.; van der Heiden, P.L.; van de Meent, M.; van Egmond, H.M.; van Liempt, E.; Hoogstraten, C.; Kruithof, S.; Veld, S.; et al. Effective treatment of refractory CMV reactivation after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with in vitro-generated CMV pp65-specific CD8+ T-cell lines. J. Immunother. 2012, 35, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Han, W.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, X.J. Cytomegalovirus-Specific T-Cell Transfer for Refractory Cytomegalovirus Infection After Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation: The Quantitative and Qualitative Immune Recovery for Cytomegalovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaya, A.; Gimenez, E.; Pascual, M.J.; Gago, B.; Pinana, J.L.; Hernandez-Boluda, J.C.; Vazquez, L.; Garcia, M.; Serrano, D.; Hernandez, M.; et al. An investigation of the utility of plasma Cytomegalovirus (CMV) microRNA detection to predict CMV DNAemia in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 209, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.E.; Redeker, A.; Arens, R.; van Baarle, D.; van den Berg, S.P.H.; Benedict, C.A.; Cicin-Sain, L.; Hill, A.B.; Wills, M.R. CMV immune evasion and manipulation of the immune system with aging. Geroscience 2017, 39, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Qi, Y.; He, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Guo, X.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ruan, Q. Human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-US25-1-5p inhibits viral replication by targeting multiple cellular genes during infection. Gene 2015, 570, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, W.; Gao, S.J.; Lu, C. KSHV microRNAs: Tricks of the Devil. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micklethwaite, K.; Hansen, A.; Foster, A.; Snape, E.; Antonenas, V.; Sartor, M.; Shaw, P.; Bradstock, K.; Gottlieb, D. Ex vivo expansion and prophylactic infusion of CMV-pp65 peptide-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007, 13, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienzle, N.; Sculley, T.B.; Poulsen, L.; Buck, M.; Cross, S.; Raab-Traub, N.; Khanna, R. Identification of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response to the novel BARF0 protein of Epstein-Barr virus: A critical role for antigen expression. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6614–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, L.E.; Blyth, E.; Simms, R.M.; Micklethwaite, K.P.; Ma, C.K.; Burgess, J.S.; Antonenas, V.; Shaw, P.J.; Gottlieb, D.J. Cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be efficiently expanded from granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized hemopoietic progenitor cell products ex vivo and safely transferred to stem cell transplantation recipients to facilitate immune reconstitution. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.; Boivin, G. Human cytomegalovirus resistance to antiviral drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allice, T.; Busca, A.; Locatelli, F.; Falda, M.; Pittaluga, F.; Ghisetti, V. Valganciclovir as pre-emptive therapy for cytomegalovirus infection post-allogenic stem cell transplantation: Implications for the emergence of drug-resistant cytomegalovirus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevillotte, M.; von Einem, J.; Meier, B.M.; Lin, F.M.; Kestler, H.A.; Mertens, T. A new tool linking human cytomegalovirus drug resistance mutations to resistance phenotypes. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Z.; Weber, F.; Croce, C.; Liu, C.G.; Liao, X.; Pellett, P.E. Human cytomegalovirus infection alters the expression of cellular microRNA species that affect its replication. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9065–9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedade, D.; Azevedo-Pereira, J.M. The Role of microRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Herpesvirus Infection. Viruses 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, E.; Clancy, L.; Simms, R.; Ma, C.K.; Burgess, J.; Deo, S.; Byth, K.; Dubosq, M.C.; Shaw, P.J.; Micklethwaite, K.P.; et al. Donor-derived CMV-specific T cells reduce the requirement for CMV-directed pharmacotherapy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2013, 121, 3745–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macesic, N.; Langsford, D.; Nicholls, K.; Hughes, P.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Clancy, L.; Blyth, E.; Micklethwaite, K.; Withers, B.; Majumdar, S.; et al. Adoptive T cell immunotherapy for treatment of ganciclovir-resistant cytomegalovirus disease in a renal transplant recipient. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, T.; Wilkie, G.M.; Jones, M.M.; Higgins, C.D.; Urquhart, G.; Wingate, P.; Burns, D.; McAulay, K.; Turner, M.; Bellamy, C.; et al. Allogeneic cytotoxic T-cell therapy for EBV-positive posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease: Results of a phase 2 multicenter clinical trial. Blood 2007, 110, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 indicates the timepoints of drug resistance mutations analysis. The upper part of the figure shows the immunosuppressant therapy administrated during the timeline.
indicates the timepoints of drug resistance mutations analysis. The upper part of the figure shows the immunosuppressant therapy administrated during the timeline.
 indicates the timepoints of drug resistance mutations analysis. The upper part of the figure shows the immunosuppressant therapy administrated during the timeline.
indicates the timepoints of drug resistance mutations analysis. The upper part of the figure shows the immunosuppressant therapy administrated during the timeline.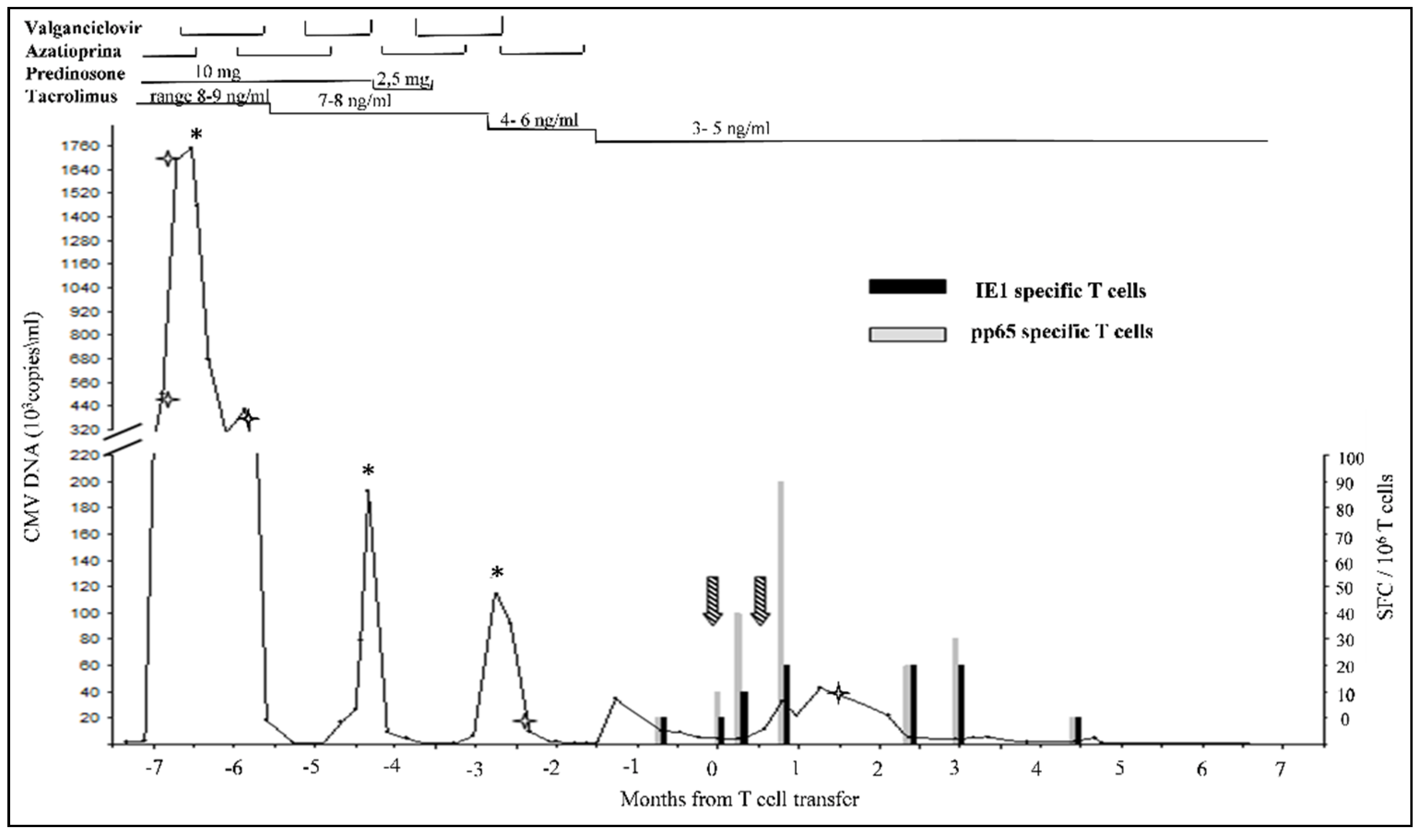
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miele, M.; Gallo, A.; Di Bella, M.; Timoneri, F.; Barbera, F.; Sciveres, M.; Riva, S.; Grossi, P.; Conaldi, P.G. Successful Use of Heterologous CMV-Reactive T Lymphocyte to Treat Severe Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection in a Liver Transplanted Patient: Correlation of the Host Antiviral Immune Reconstitution with CMV Viral Load and CMV miRNome. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040684
Miele M, Gallo A, Di Bella M, Timoneri F, Barbera F, Sciveres M, Riva S, Grossi P, Conaldi PG. Successful Use of Heterologous CMV-Reactive T Lymphocyte to Treat Severe Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection in a Liver Transplanted Patient: Correlation of the Host Antiviral Immune Reconstitution with CMV Viral Load and CMV miRNome. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040684
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiele, Monica, Alessia Gallo, Mariangela Di Bella, Francesca Timoneri, Floriana Barbera, Marco Sciveres, Silvia Riva, Paolo Grossi, and Pier Giulio Conaldi. 2021. "Successful Use of Heterologous CMV-Reactive T Lymphocyte to Treat Severe Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection in a Liver Transplanted Patient: Correlation of the Host Antiviral Immune Reconstitution with CMV Viral Load and CMV miRNome" Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040684
APA StyleMiele, M., Gallo, A., Di Bella, M., Timoneri, F., Barbera, F., Sciveres, M., Riva, S., Grossi, P., & Conaldi, P. G. (2021). Successful Use of Heterologous CMV-Reactive T Lymphocyte to Treat Severe Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection in a Liver Transplanted Patient: Correlation of the Host Antiviral Immune Reconstitution with CMV Viral Load and CMV miRNome. Microorganisms, 9(4), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040684





