Composition and Functional Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bacterioplankton Community in the Huangshui River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
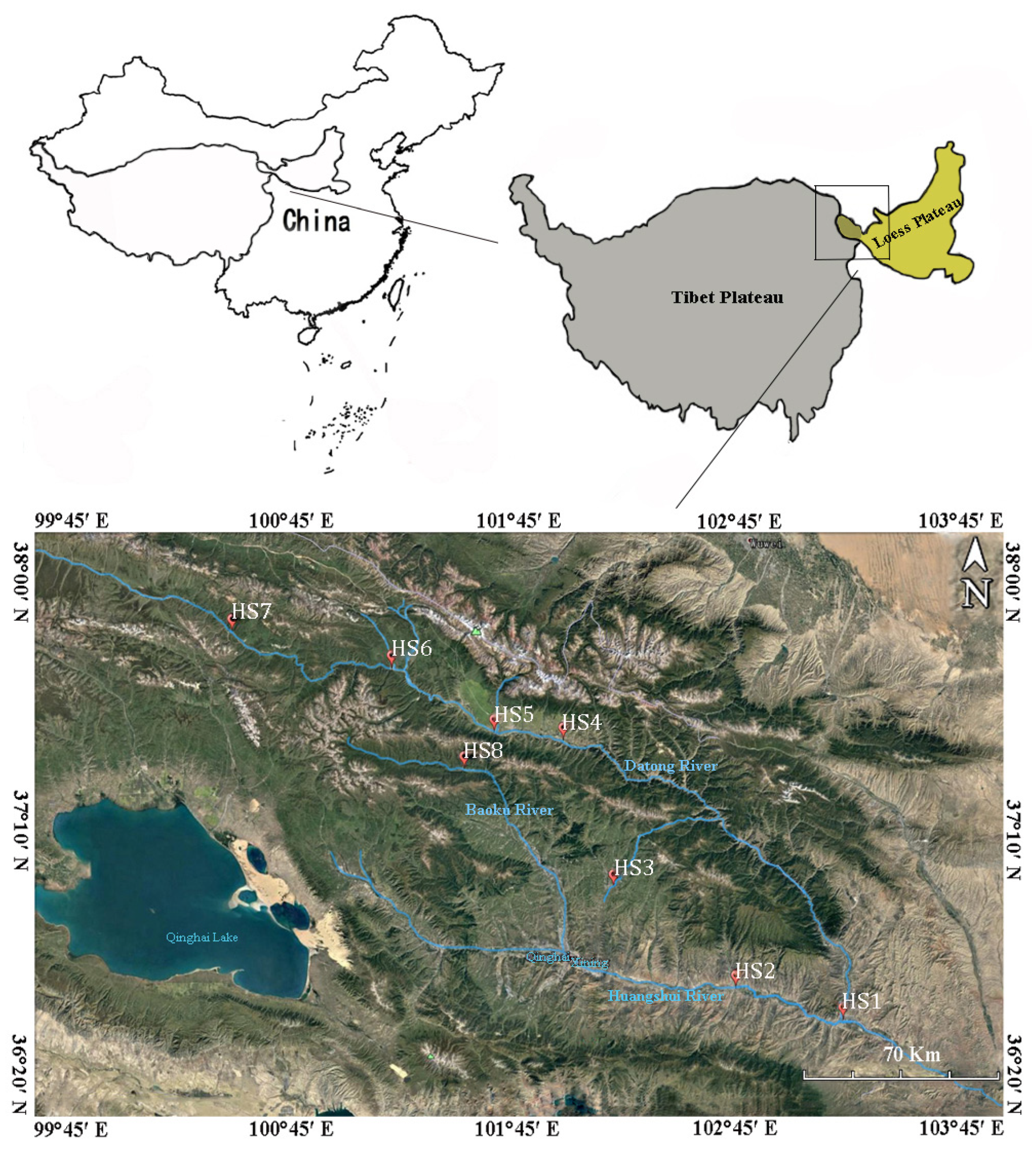
2.1. Study Sites and Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Illumina Miseq Sequencing
2.4. Processing of Sequencing Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Functional Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Characteristics
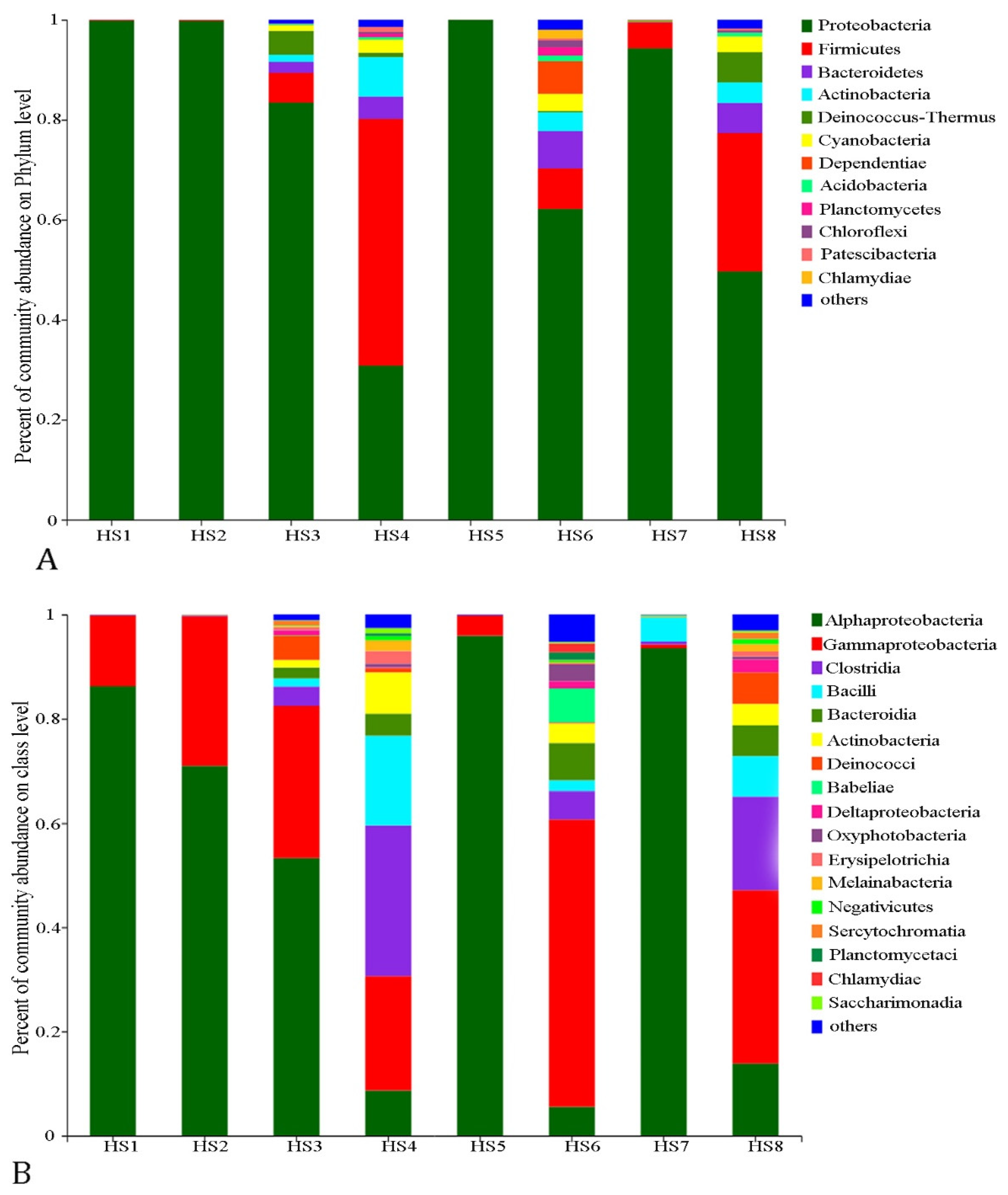
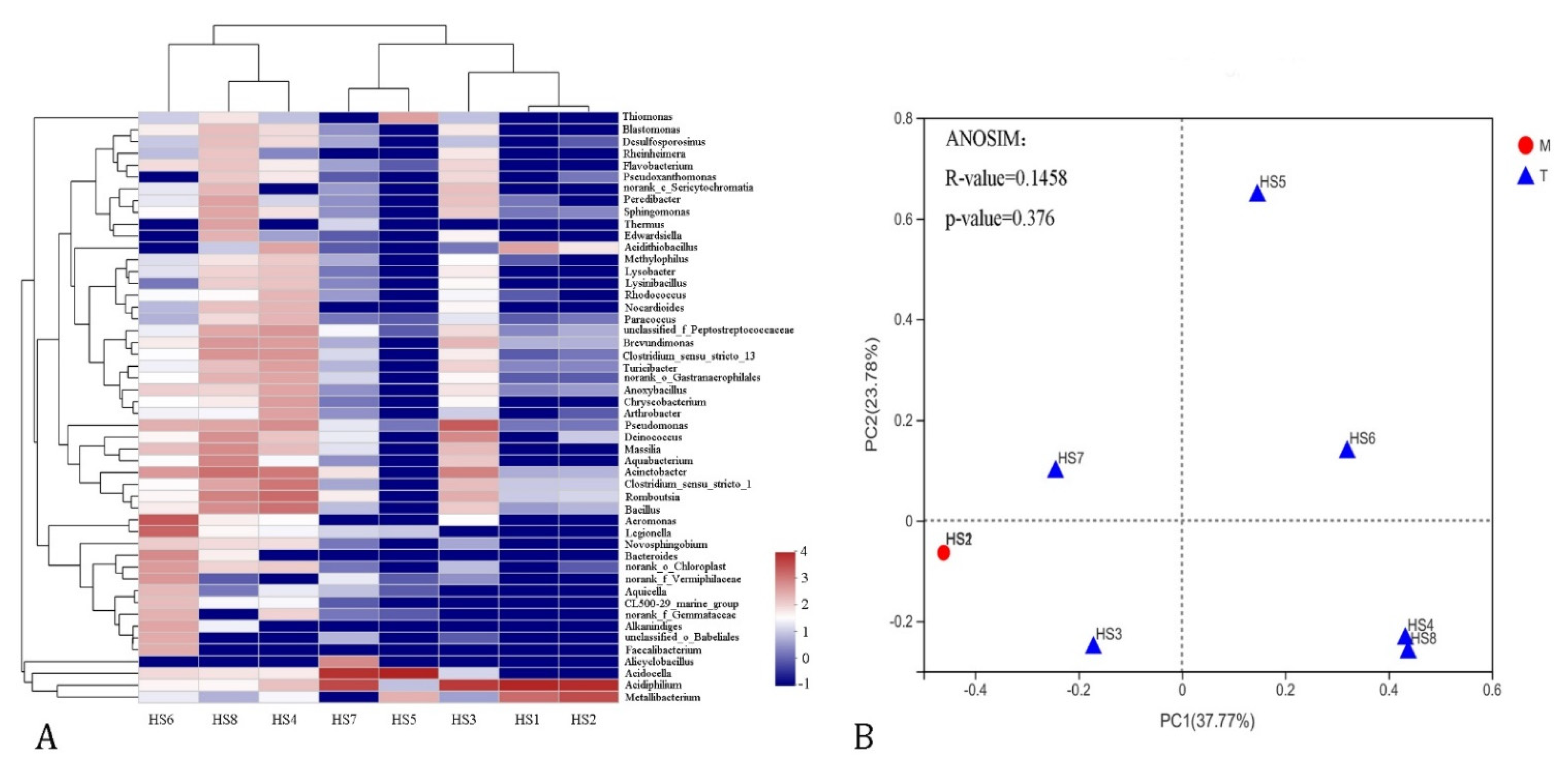
3.2. Diversity and Structure of the Bacterioplankton Communities
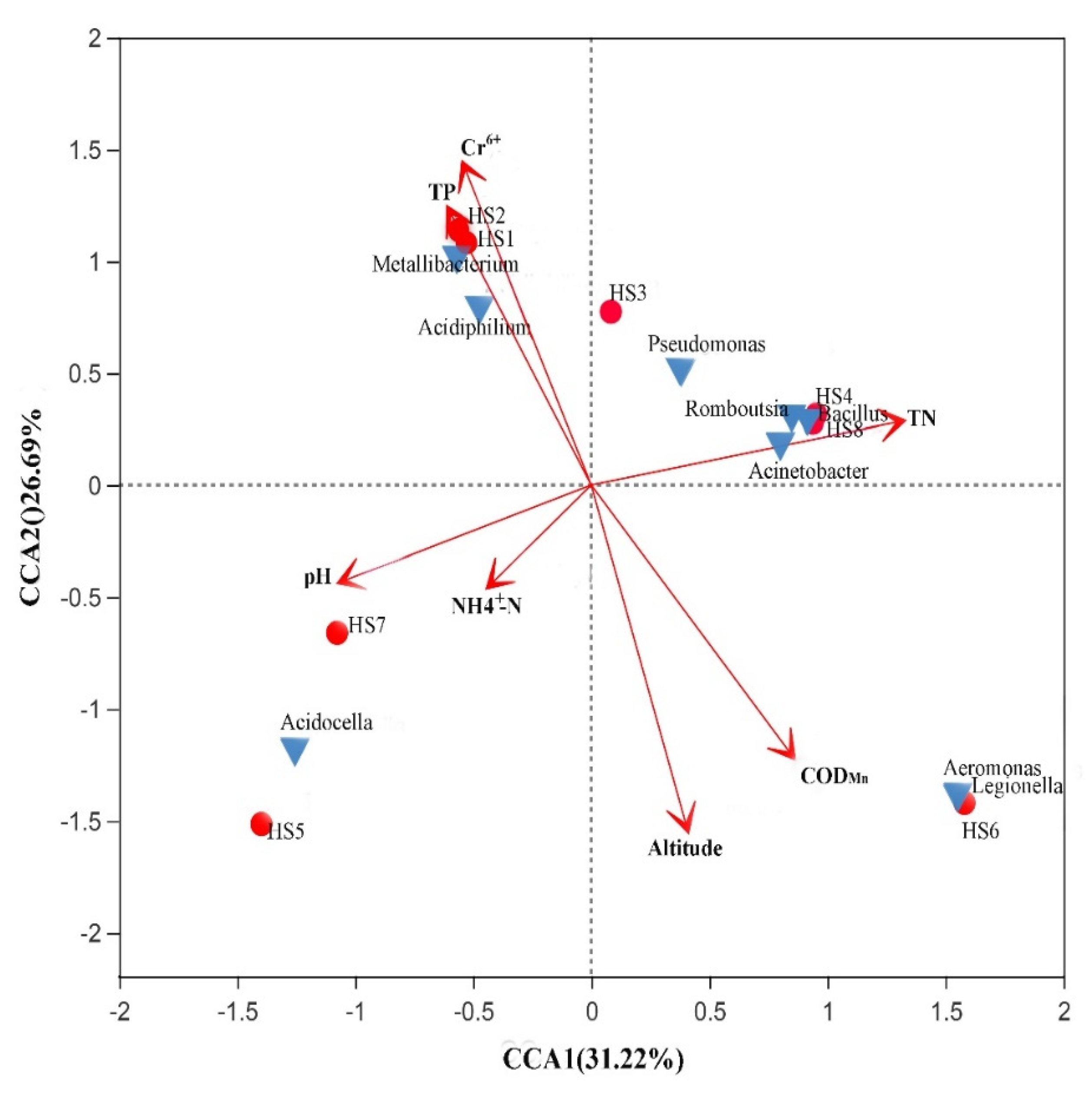
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Bacterioplankton Communities and Environmental Factors
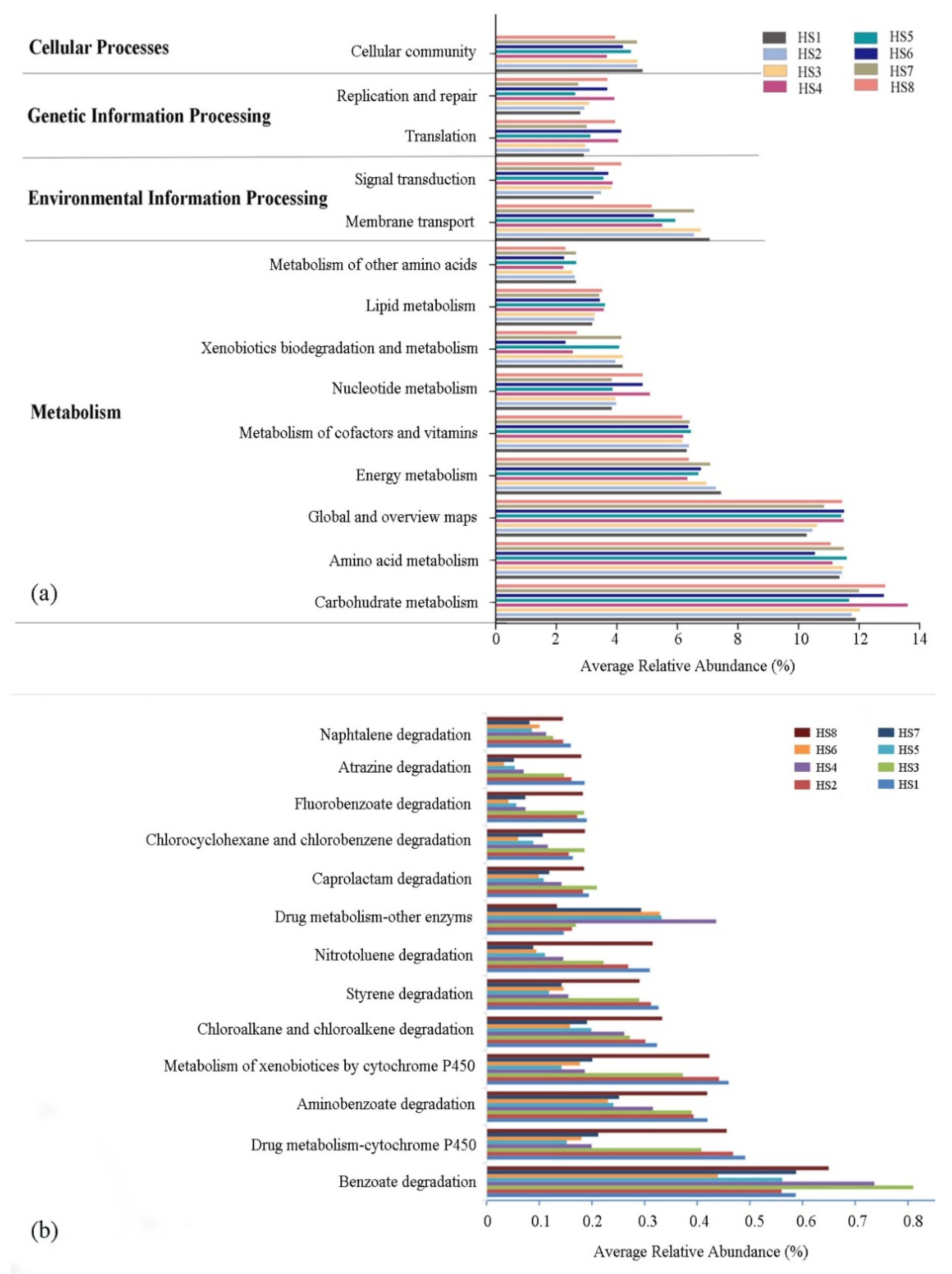
3.4. Functional Prediction by PICRUSt2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuhrman, J.A. Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 2009, 459, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, H.; Tang, F.; Koide, R.T.; Cui, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Insam, H.; Zhang, Q. Relative roles of competition, environmental selection and spatial processes in structuring soil bacterial communities in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 117, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernthaler, J. Predation on prokaryotes in the water column and its ecological implications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Dittel, A.I.; Malmstrom, R.R.; Cottrell, M.T. Biogeography of major bacterial groups in the Delaware Estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Huang, L.; He, Z.; Chen, L.; Hua, Z.; Jia, P.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, J. Predicting taxonomic and functional structure of microbial communities in acid mine drainage. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.; Terada, A.; Ribeiro, D.C.; Corral, A.M.; Brito, A.G.; Smets, B.F.; Nogueira, R. Structure and activity of lacustrine sediment bacteria involved in nutrient and iron cycles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 77, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, A.; Filker, S.; Breiner, H.W.; Stoeck, T. Protistan diversity in a permanently stratified meromictic lake (Lake Alatsee, SW Germany). Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simek, K.; Hornák, K.; Jezbera, J.; Nedoma, J.; Znachor, P.; Hejzlar, J.; Sed’a, J. Spatio-temporal patterns of bacterioplankton production and community composition related to phytoplankton composition and protistan bacterivory in a dam reservoir. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 51, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Xi, B.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, X. Municipal wastewater effluent influences dissolved organic matter quality and microbial community composition in an urbanized stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.; Robson, A. A summary of river water quality data collected within the Land–Ocean Interaction Study: Core data for eastern UK rivers draining to the North Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 251, 585–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Jiang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.S.; Dong, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z. Responses of bacterial communities in seagrass sediments to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-induced stress. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, T.C.; Schmitz Fontes, M.L.; Harrison, D.P.; Van-Dongen-Vogels, V.; Eyre, B.D.; Ralph, P.J.; Seymour, J.R. Bacterioplankton Dynamics within a Large Anthropogenically Impacted Urban Estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Ji, F.Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, Q.K.; Li, Q. Microbial and metabolic characterization of a denitrifying phosphorus-uptake/side stream phosphorus removal system for treating domestic sewage. Biodegradation 2014, 25, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besaury, L.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Quillet, L. Abundance, activity, and diversity of archaeal and bacterial communities in both uncontaminated and highly copper-contaminated marine sediments. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-Y.; Bao, Y.-X.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Zhang, L.-L.; Ge, B.-M. Research progress on ecology of natural wetland zoobenthos in China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 959. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Chen, A.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Ma, G.; Ma, Q. Impacts of urbanization on water quality and macrobenthos community structure upstream in the Huangshui river. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3570–3576. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.; Li, N.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Bai, L. Community structure analysis of macrobenthos in the upper reaches of Huangshui river in Qinghai Province. J. Qinghai Univ. 2019, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Yan, C. Effects of eco-environmental construction projects on soil and water loss in Huangshui River basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 33, 217–305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Dong, X.; Xin, W.-R.; Zhang, F.-C.; Yang, X.-Y. Analysis of factors of soil erosion and some ways of rehabilitation in Huangshui River of Qinghai Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 15, 200–202. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackebrandt, E.; GOEBEL, B.M. Taxonomic note: A place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.J.; Xu, Z.; Amir, A.; Peddada, S.; Bittinger, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozupone, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Birmingham, A. Effects of Library Size Variance, Sparsity, and Compositionality on the Analysis of Microbiome Data; PeerJ PrePrints: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 2167–9843. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Chao, A. Estimating and comparing microbial diversity in the presence of sequencing errors. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, H.; Watanabe, M.; Nakahara, T.; Xu, B.; Uchiyama, H. Succession of bacterial community structure along the Changjiang River determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and clone library analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5142–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.L.V.; Knight, R. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, F.; Qu, X.D.; Elser, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, L.M. Taxonomic and Functional Differences between Microbial Communities in Qinghai Lake and Its Input Streams. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.S.; Huang, J.; Long, D.F.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, J.J. Diversity and community structure of ectomycorrhizal fungi associated with Larix chinensis across the alpine treeline ecotone of Taibai Mountain. Mycorrhiza 2017, 27, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Yi, Y.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.F. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the sediment microbial communities of Baiyangdian shallow lake. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Song, C.; Meng, S.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Qu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G. Spatial distribution of planktonic bacterial and archaeal communities in the upper section of the tidal reach in Yangtze River. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, A.L.; Markussen, T.N.; Stibal, M.; Olsen, N.S.; Elberling, B.; Bælum, J.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Jacobsen, C.S. Upstream freshwater and terrestrial sources are differentially reflected in the bacterial community structure along a small Arctic river and its estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, A. Environment-driven geographical distribution of bacterial communities and identification of indicator taxa in Songhua River. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Tian, J.Q.; Bai, C.M.; Xiang, M.C.; Sun, J.Z.; Liu, X.Z. The biogeography of fungal communities in wetland sediments along the Changjiang River and other sites in China. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian-Qian, Z.; Sheng-Long, J.; Ke-Mao, L.; Zhen-Bing, W.; Hong-Tao, G.; Jin-Wen, H.; Shu-Yi, W.; Yao-Yao, L.; Guo-Jie, W.; Ai-Hua, L. Community structure of bacterioplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the upper reaches of the Heihe River in Qinghai Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, L.; Besemer, K.; Fragner, L.; Peter, H.; Weckwerth, W.; Battin, T.J. Altitudinal patterns of diversity and functional traits of metabolically active microorganisms in stream biofilms. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Q.; Chai, Y.H.; Wang, X.S.; Huang, L.Y.; Luo, X.M.; Qiu, C.; Liu, Q.H.; Guan, X.Y. Bacterial community in saline farmland soil on the Tibetan plateau: Responding to salinization while resisting extreme environments. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.S.; Yao, T.D.; Pearce, D.A.; Jiao, N.Z.; Zeng, Y.H.; Guo, B.X.; Liu, Y.Q. Bacteria in the lakes of the Tibetan Plateau and polar regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, A.N.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Jiang, X.; Dang, C.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Xie, S. Integrated biogeography of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial communities in the Yangtze River. Microbiome 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percent, S.F.; Frischer, M.E.; Vescio, P.A.; Duffy, E.B.; Milano, V.; McLellan, M.; Stevens, B.M.; Boylen, C.W.; Nierzwicki-Bauer, S.A. Bacterial community structure of acid-impacted lakes: What controls diversity? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Li, D.; Zeng, S.; He, M. Changes of microbial composition during wastewater reclamation and distribution systems revealed by high-throughput sequencing analyses. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, A.; André, S.; Viana, P.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial residues and bacterial community composition in urban wastewater. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1875–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böckelmann, U.; Manz, W.; Neu, T.R.; Szewzyk, U. Characterization of the microbial community of lotic organic aggregates (‘river snow’) in the Elbe River of Germany by cultivation and molecular methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2000, 33, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, B.; Huber, I.; Amann, R.; Ludwig, W.; Simon, M. α-and β-Proteobacteria control the consumption and release of amino acids on lake snow aggregates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, H.; Stübner, M.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Phylogeny of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes from oxic habitats of a tidal flat ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 54, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Rolfe, S.; Hallberg, K.B.; Iversen, E. Isolation and phylogenetic characterization of acidophilic microorganisms indigenous to acidic drainage waters at an abandoned Norwegian copper mine. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Xining Section of the Huangshui River. J. Salt Lake Res. 2017, 25, 8–12+59. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.I.; Shih, H.Y.; Lee, C.M.; Yang, T.C.; Lay, J.J.; Lin, Y.E. In vitro efficacy of copper and silver ions in eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Acinetobacter baumannii: Implications for on-site disinfection for hospital infection control. Water Res. 2008, 42, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J.C.; Murinda, S.E. Bacterial community composition and structure in an Urban River impacted by different pollutant sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pablos, M.; Rodriguez-Calleja, J.M.; Santos, J.A.; Otero, A.; Garcia-Lopez, M.L. Occurrence of motile Aeromonas in municipal drinking water and distribution of genes encoding virulence factors. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Dittel, A.I.; Findlay, S.E.; Fischer, D. Changes in bacterial activity and community structure in response to dissolved organic matter in the Hudson River, New York. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wei, Z.; Li, F. Spatial heterogeneity in a deep artificial lake plankton community revealed by PCR-DGGE fingerprinting. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, B.; Yuan, R.; Li, C.; Li, Y. Characteristics of aquatic bacterial community and the influencing factors in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Lu, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and water pollution sources in the Huangshui River Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Xie, W.; Wan, X.S.; Kao, S.-J.; Phelps, T.J.; Zhang, C. Population dynamics of methanogens and methanotrophs along the salinity gradient in Pearl River Estuary: Implications for methane metabolism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yan, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Wei, X.; Mei, Z.; Liu, X. The composition, localization and function of low-temperature-adapted microbial communities involved in methanogenic degradations of cellulose and chitin from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau wetland soils. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Y.Z.; Lai, Z.N.; Li, X.H.; Peng, S.Y.; Wang, C. Structural and functional shifts of bacterioplanktonic communities associated with spatiotemporal gradients in river outlets of the subtropical Pearl River Estuary, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandifer, P.A.; Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Ward, B.P. Exploring connections among nature, biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health and well-being: Opportunities to enhance health and biodiversity conservation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernli, D.; Jørgensen, P.S.; Morel, C.M.; Carroll, S.; Harbarth, S.; Levrat, N.; Pittet, D. Mapping global policy discourse on antimicrobial resistance. BMJ Glob. Health 2017, 2, e000378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abia, A.L.K.; Alisoltani, A.; Keshri, J.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E. Metagenomic analysis of the bacterial communities and their functional profiles in water and sediments of the Apies River, South Africa, as a function of land use. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Site | HS1 | HS2 | HS3 | HS4 | HS5 | HS6 | HS7 | HS8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | 13 | 14 | 13 | 17.20 | 16.00 | 9.30 | 6.80 | 9.30 |
| pH | 8.47 | 8.34 | 8.42 | 8.35 | 8.46 | 8.39 | 8.39 | 8.34 |
| Altitude (m) | 1728 | 1960 | 2630 | 2741 | 2838 | 3096 | 3436 | 2942 |
| DO (mg/L) | / | / | 6.20 | 7.80 | 6.30 | 6.90 | 7.30 | 7.10 |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.06 | 1.70 | 2.41 | 2.39 | 1.54 | 1.83 | 1.33 | 1.94 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Cr6+ (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | / | / | 1.60 | 2.08 | 2.24 | 2.00 | 1.60 | 2.96 |
| Cu (mg/mL) | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Pb (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Cd (mg/mL) | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Hg (mg/mL) | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| As (mg/mL) | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.49 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.75 |
| Sampling Site | Sequence Number | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS1 | 69,445 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 423.91 | 175.63 | 99.90% |
| HS2 | 56,403 | 0.69 | 0.58 | 184.05 | 104.15 | 99.93% |
| HS3 | 63,972 | 2.47 | 0.27 | 464.03 | 469.37 | 99.83% |
| HS4 | 56,234 | 4.34 | 0.03 | 382.38 | 383.50 | 99.96% |
| HS5 | 67,826 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 111.46 | 58.33 | 99.97% |
| HS6 | 59,560 | 5.05 | 0.06 | 1765.84 | 1764.35 | 99.67% |
| HS7 | 65,202 | 1.535 | 0.32 | 979.80 | 610.00 | 99.61% |
| HS8 | 58,962 | 4.97 | 0.02 | 640.05 | 641.02 | 99.91% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Hao, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Guan, H.; Zhang, J.; Jian, S.; et al. Composition and Functional Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bacterioplankton Community in the Huangshui River, China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112260
Zhang Q, Wu Z, Zhao J, Wang G, Hao J, Wang S, Lin Y, Guan H, Zhang J, Jian S, et al. Composition and Functional Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bacterioplankton Community in the Huangshui River, China. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(11):2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112260
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qianqian, Zhenbing Wu, Juan Zhao, Guojie Wang, Jingwen Hao, Shuyi Wang, Yaoyao Lin, Hongtao Guan, Jinyong Zhang, Shenglong Jian, and et al. 2021. "Composition and Functional Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bacterioplankton Community in the Huangshui River, China" Microorganisms 9, no. 11: 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112260
APA StyleZhang, Q., Wu, Z., Zhao, J., Wang, G., Hao, J., Wang, S., Lin, Y., Guan, H., Zhang, J., Jian, S., & Li, A. (2021). Composition and Functional Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bacterioplankton Community in the Huangshui River, China. Microorganisms, 9(11), 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112260






