Multiple New Strains of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) from the North Atlantic Revealed a High Toxin Profile Variability of Azadinium spinosum and a New Non-Toxigenic Az. cf. spinosum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Work
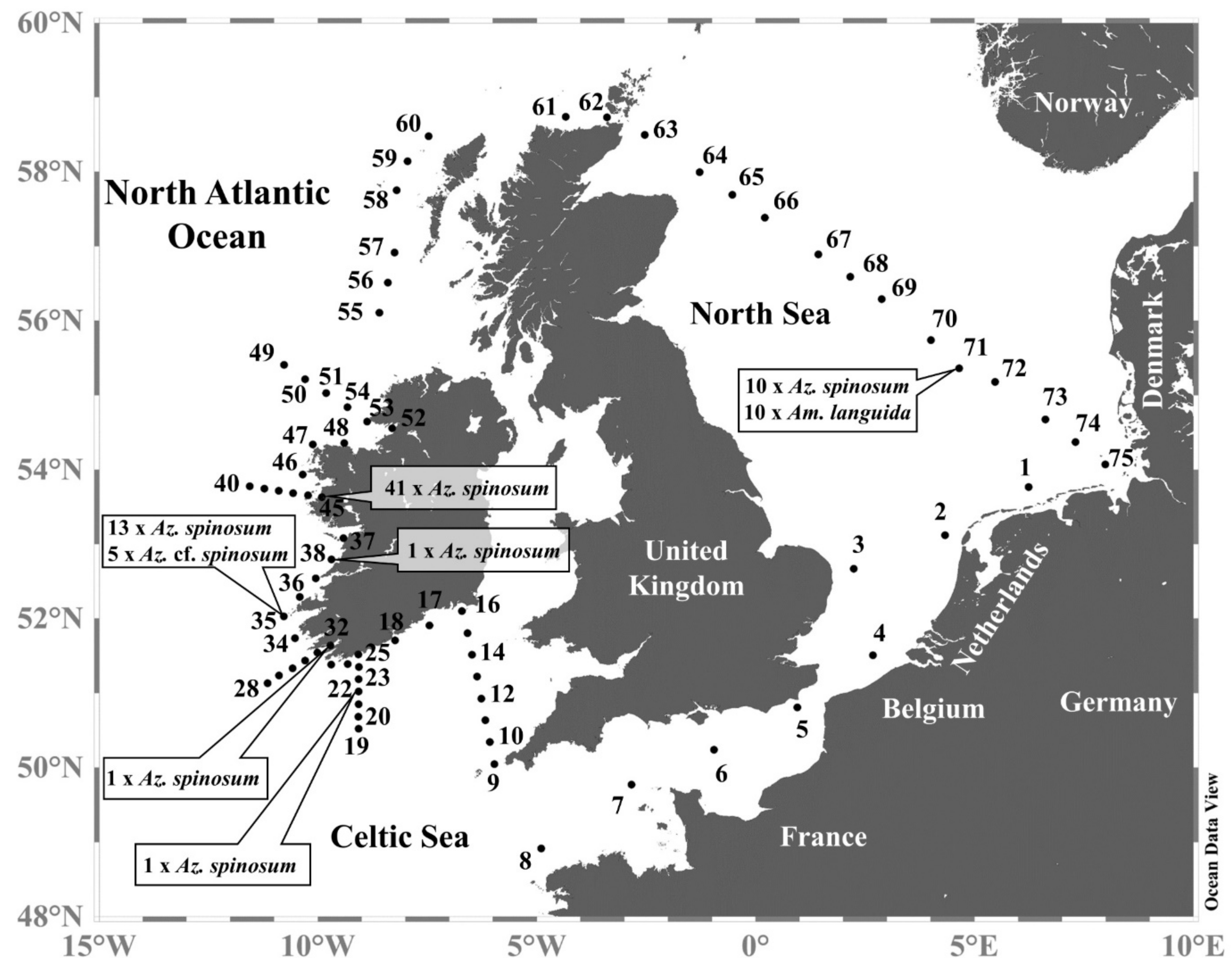
2.1.1. Sampling
2.1.2. On Board Microscopy
2.1.3. On-Board Isolation and Culture
2.2. Characterization of Amphidomataceae Strains
2.2.1. Culture Growth, Sampling, and Extraction
2.2.2. Microscopy
2.2.3. Molecular Phylogeny
PCR Amplification and DNA Sequencing
Phylogenetic Analyses
qPCR Assay Specificity of Newly Obtained Strains
2.2.4. Chemical Analysis of Azaspiracids
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
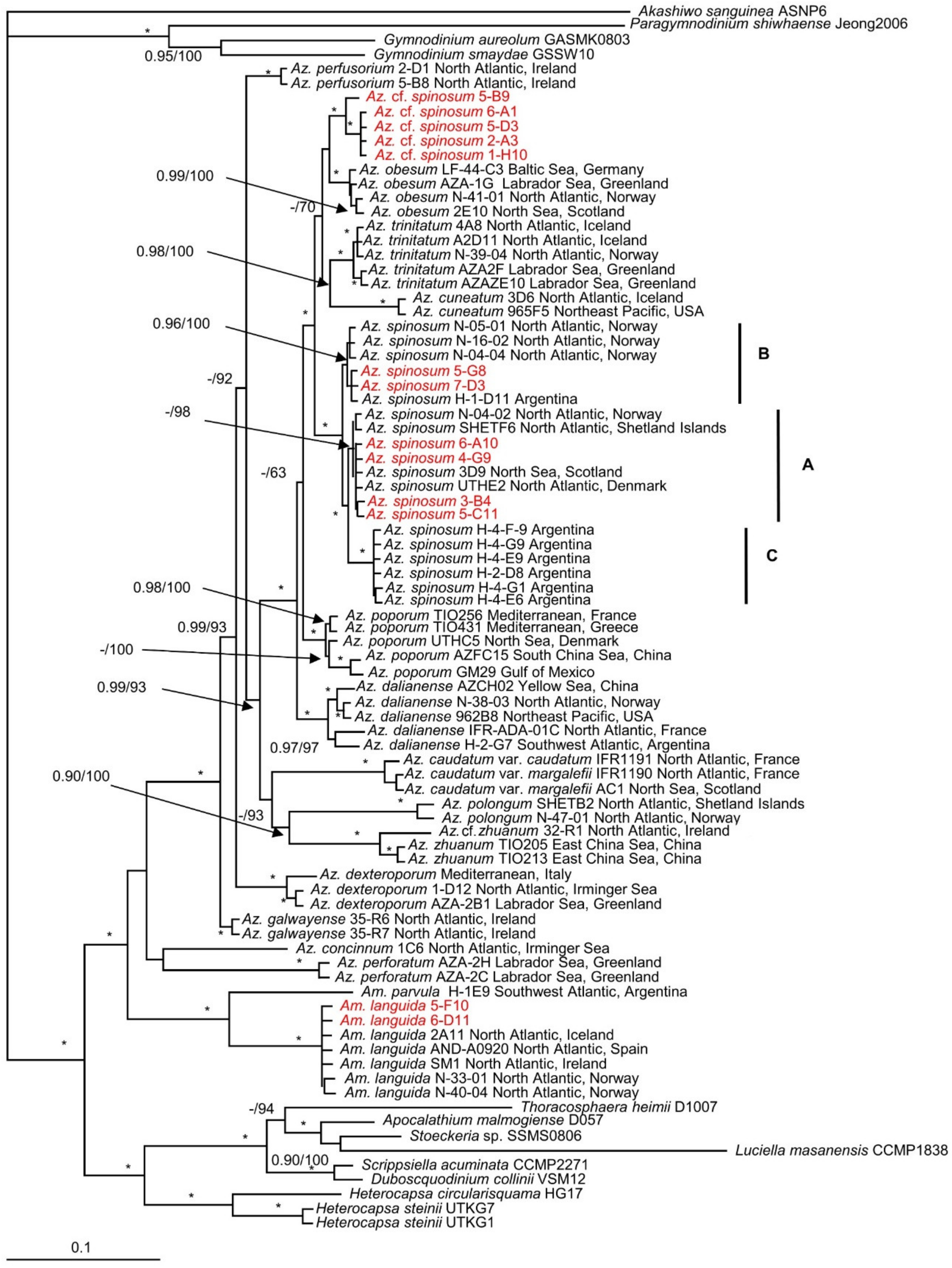
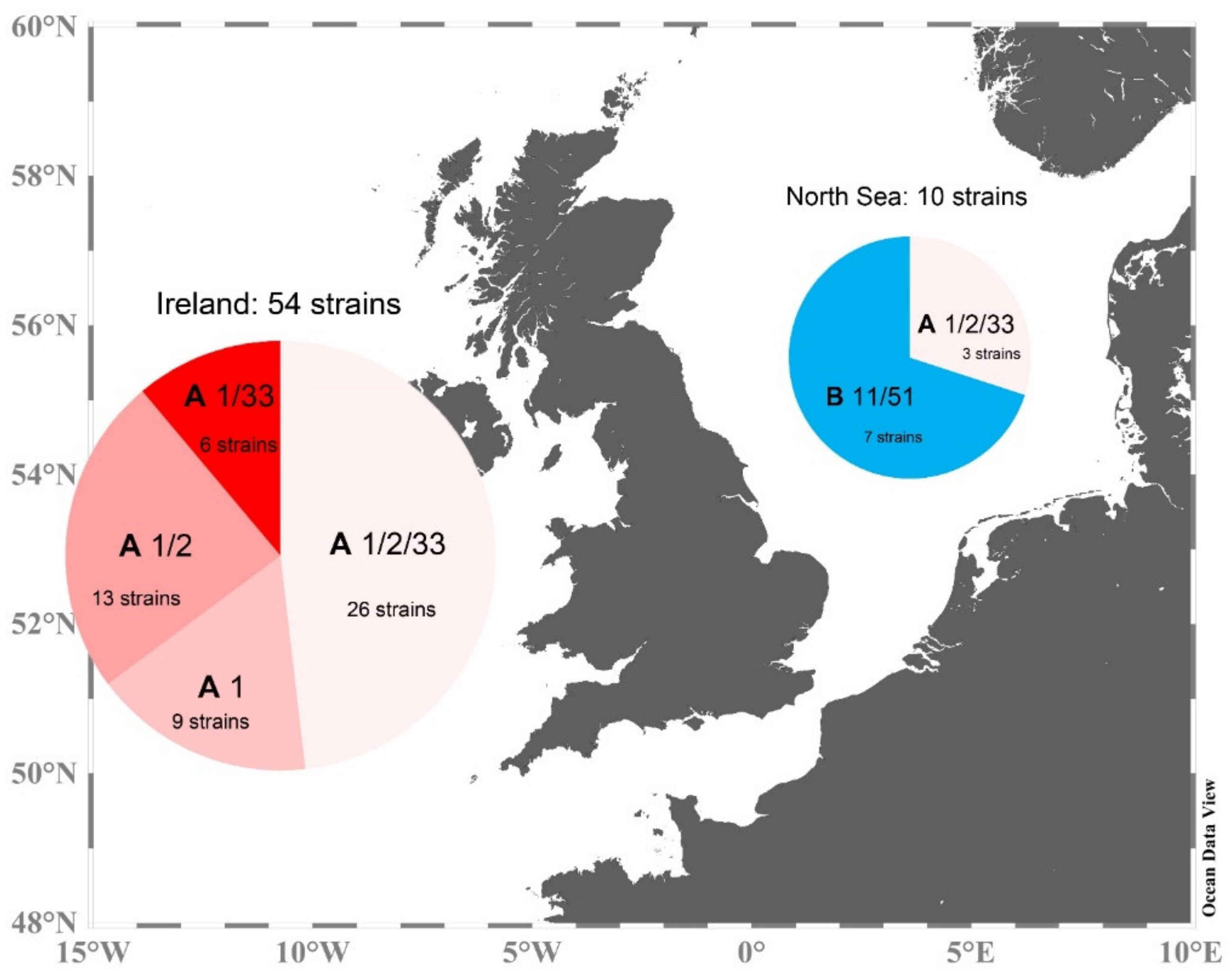
3.1. Phylogeny of Strains
qPCR Assay Specificity with Newly Obtained Strains
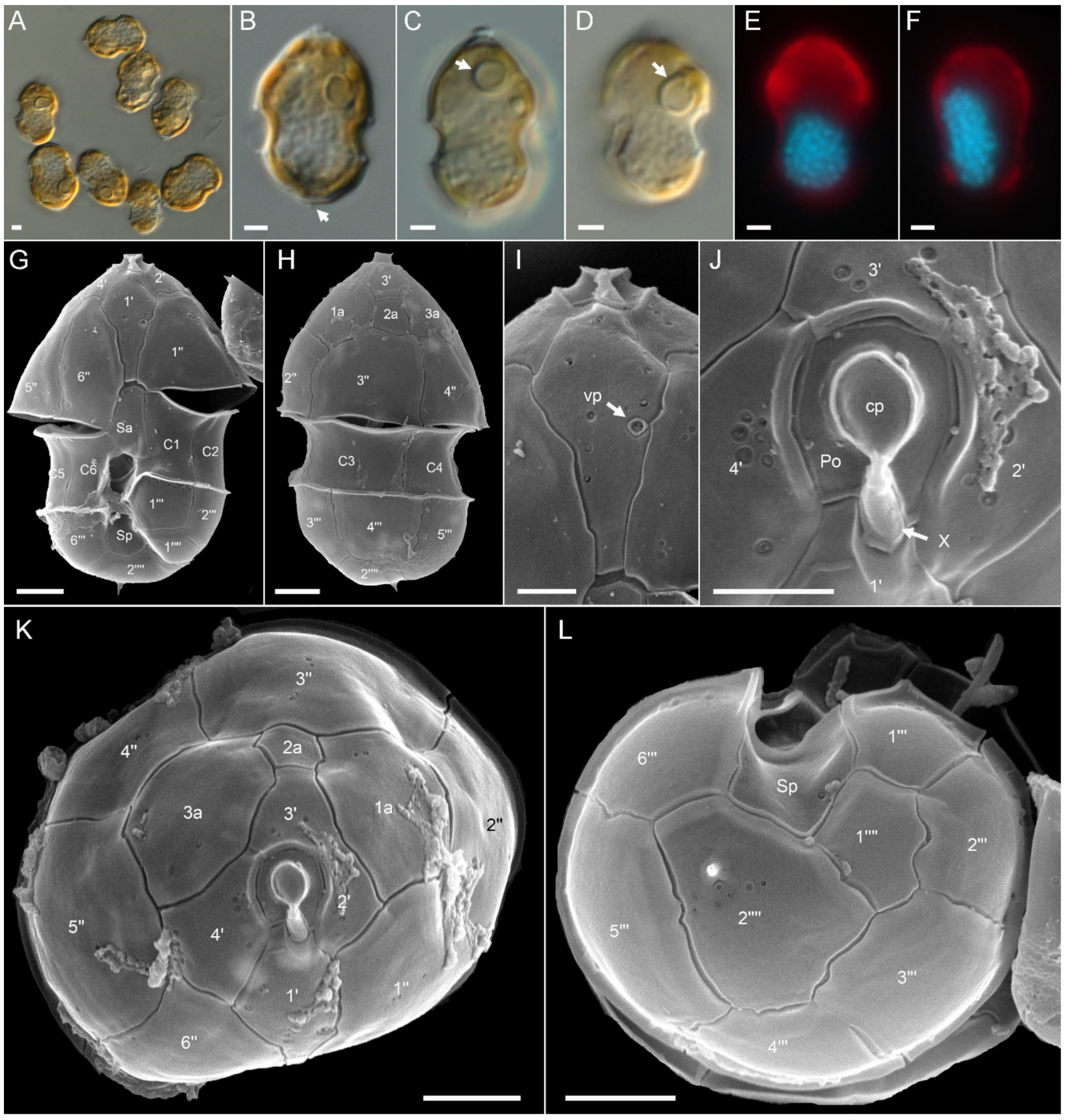
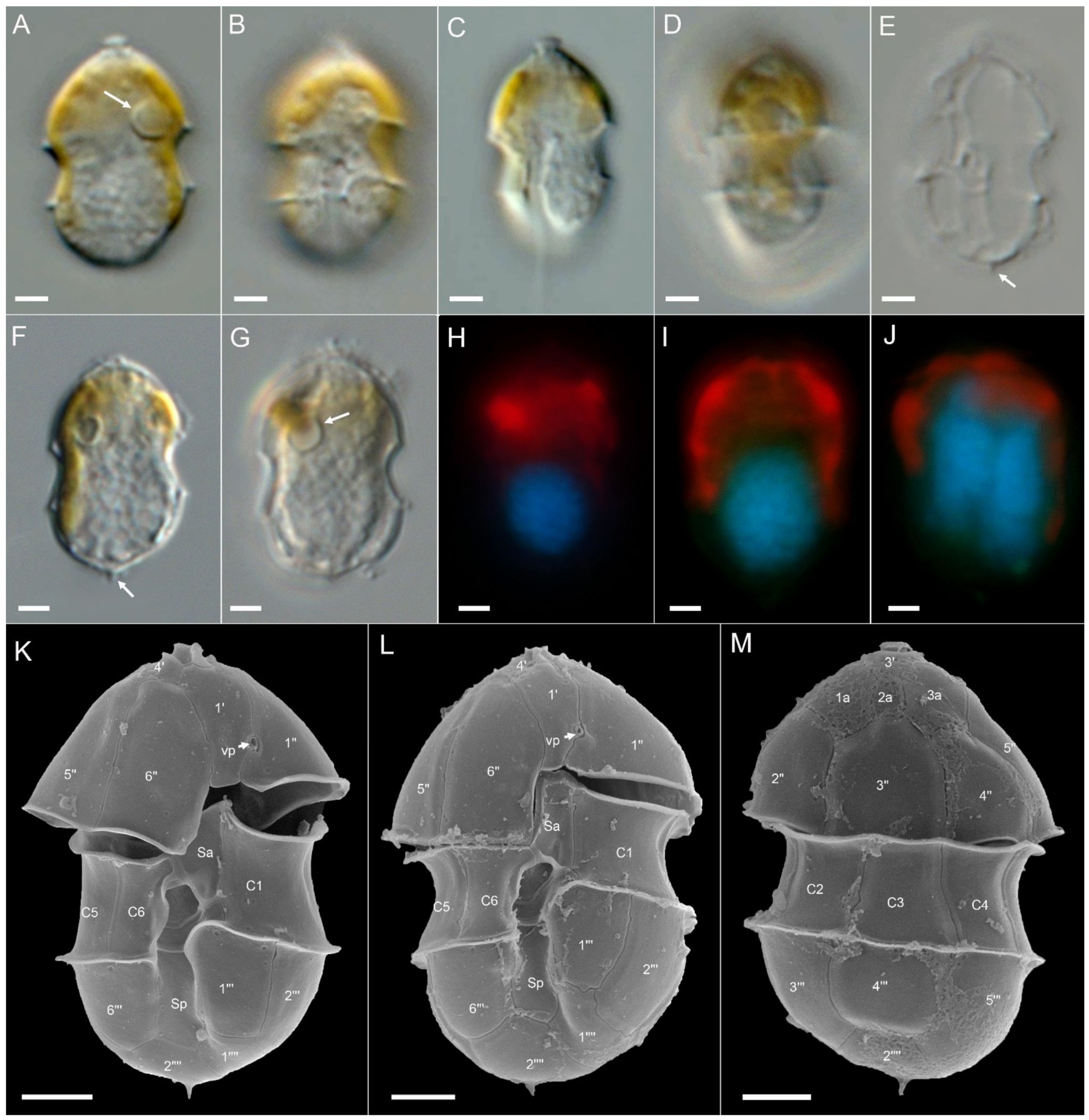
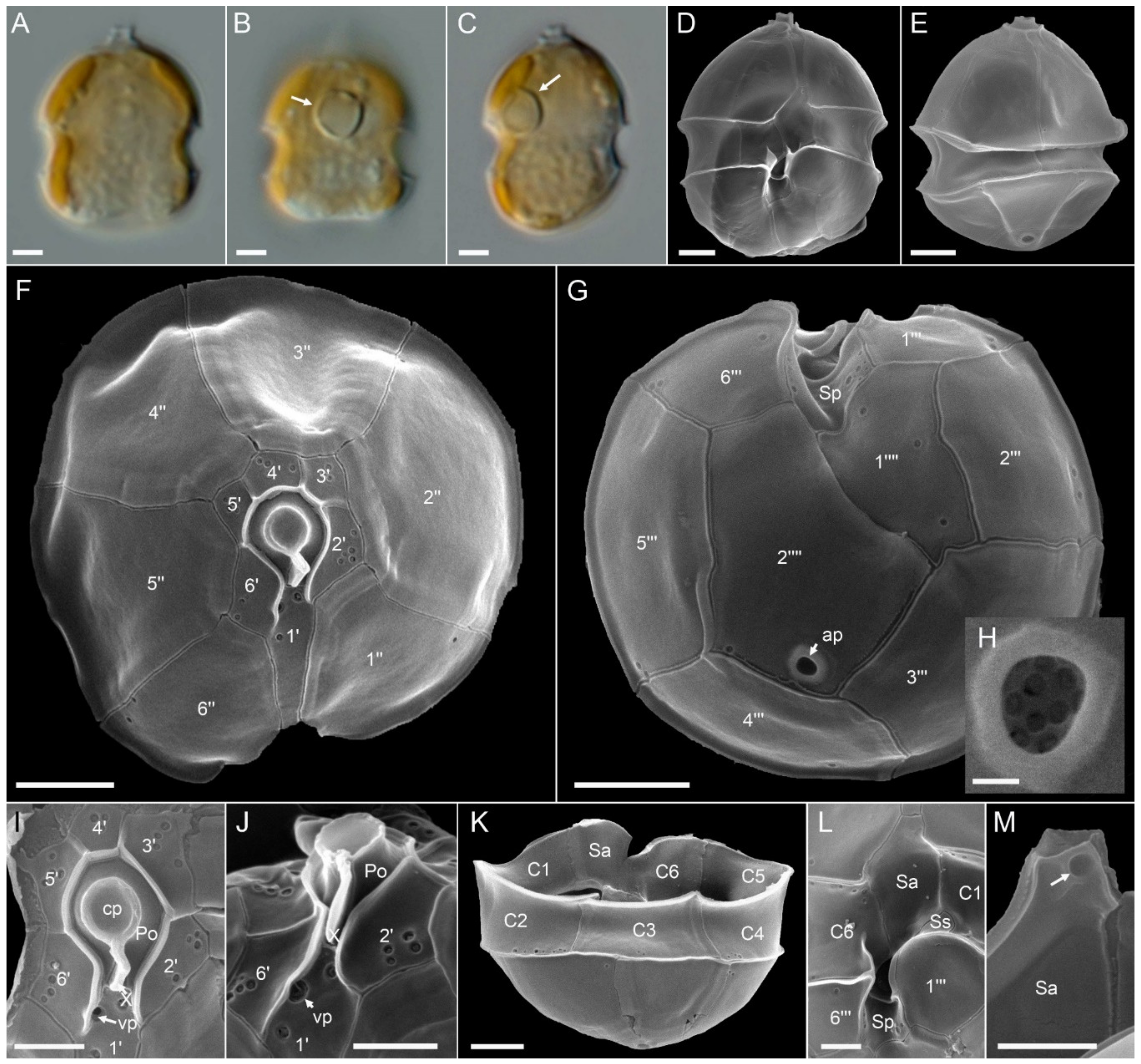
3.2. Morphological Identification
Azadinium spinosum
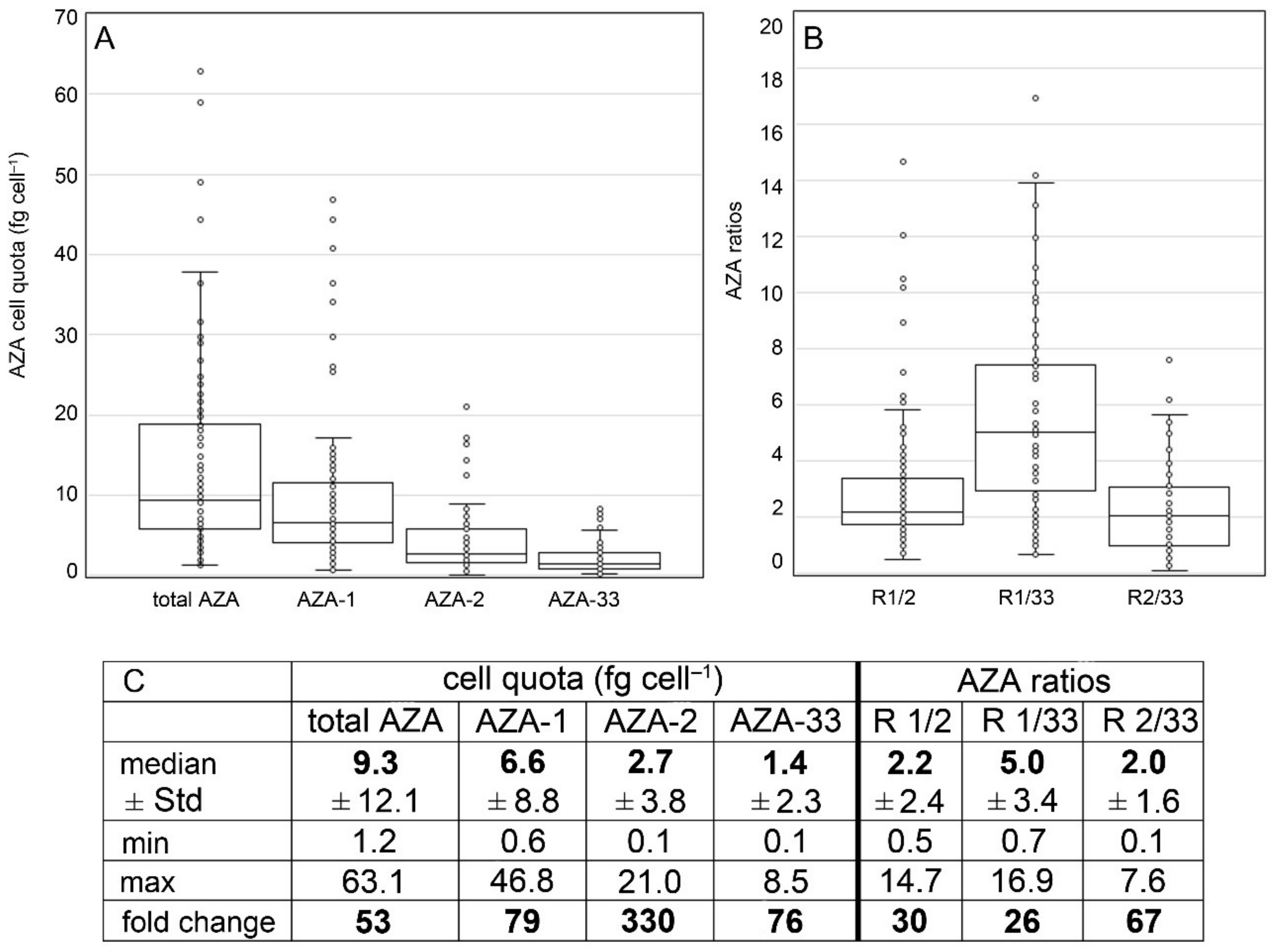
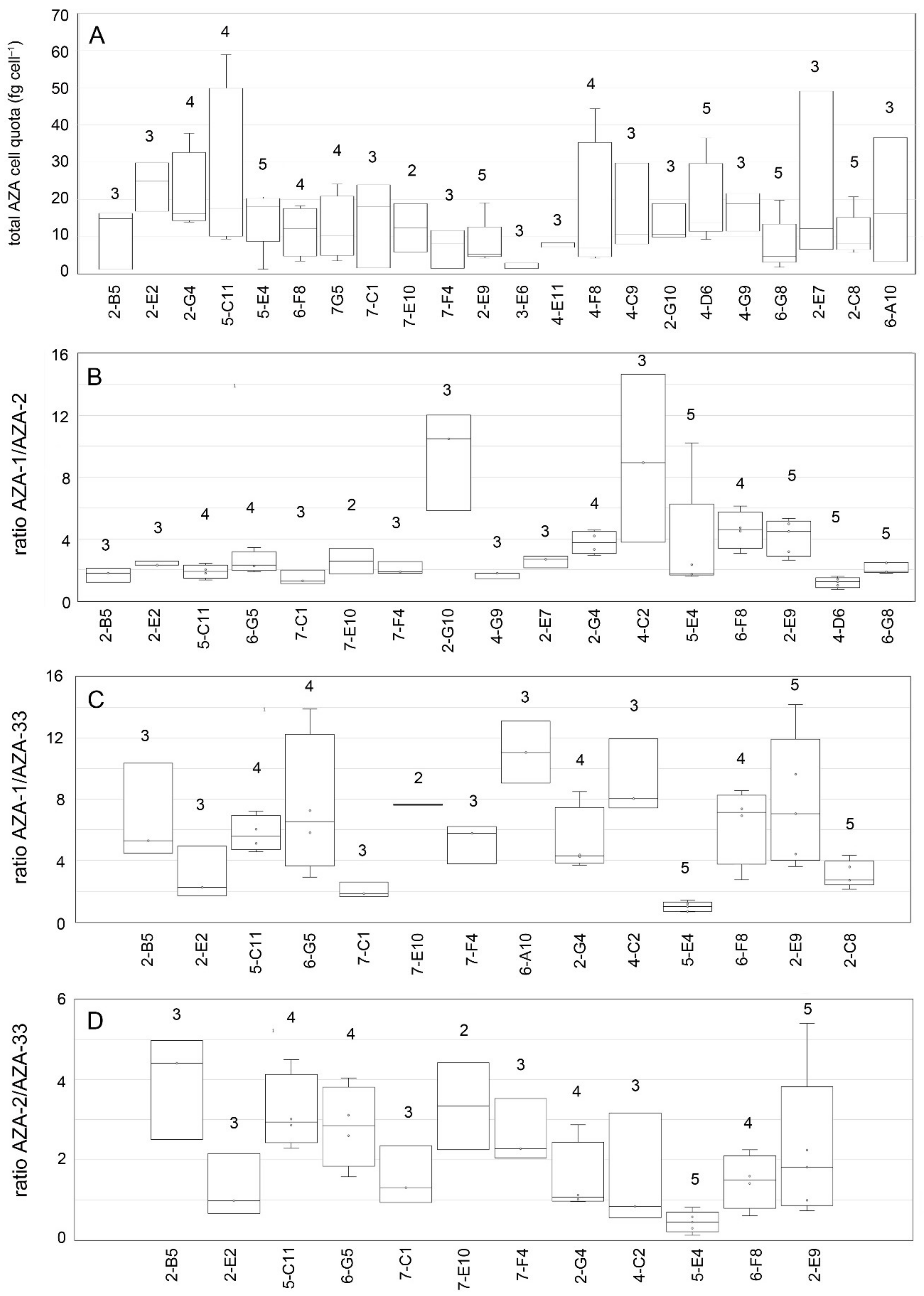
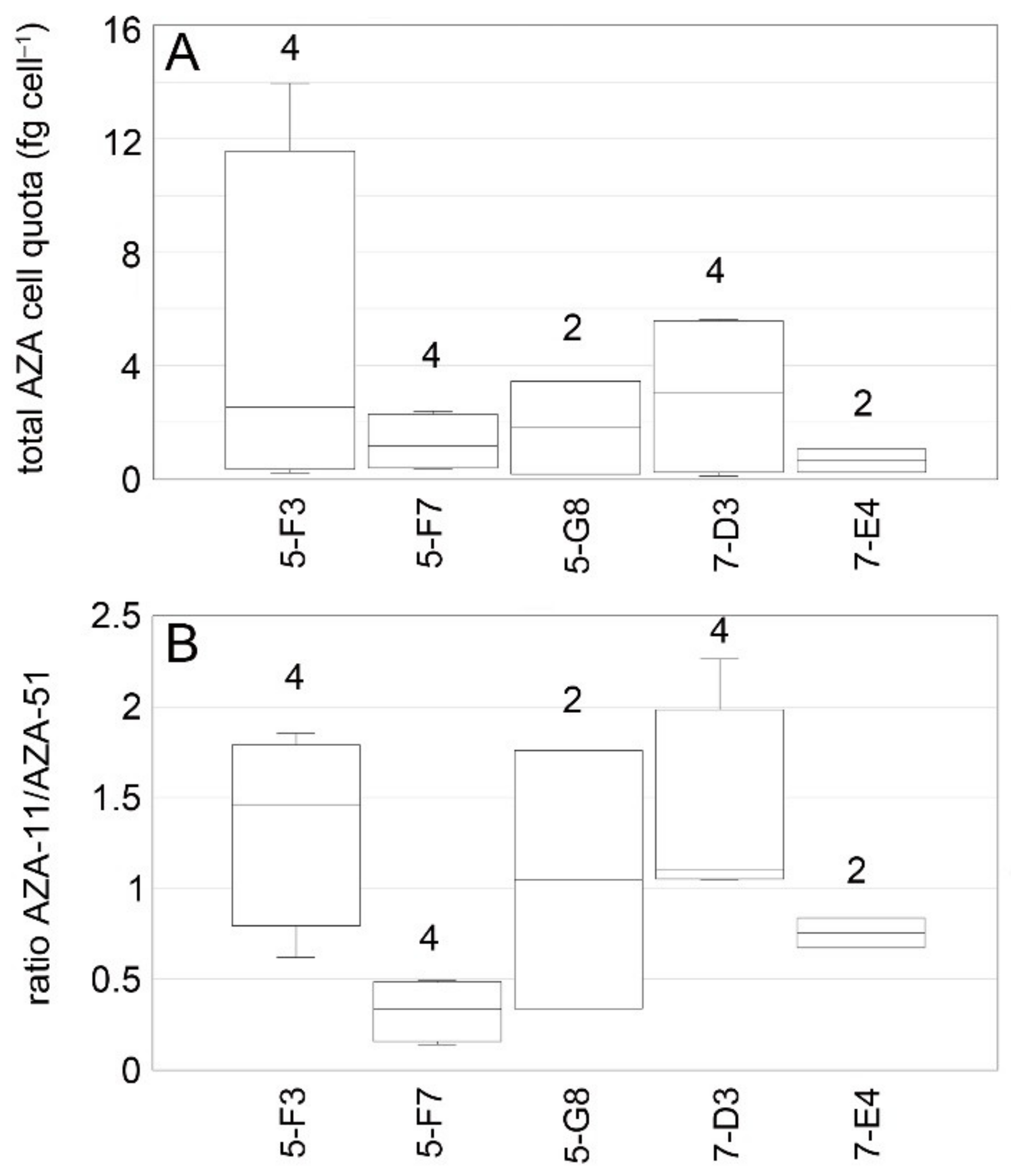
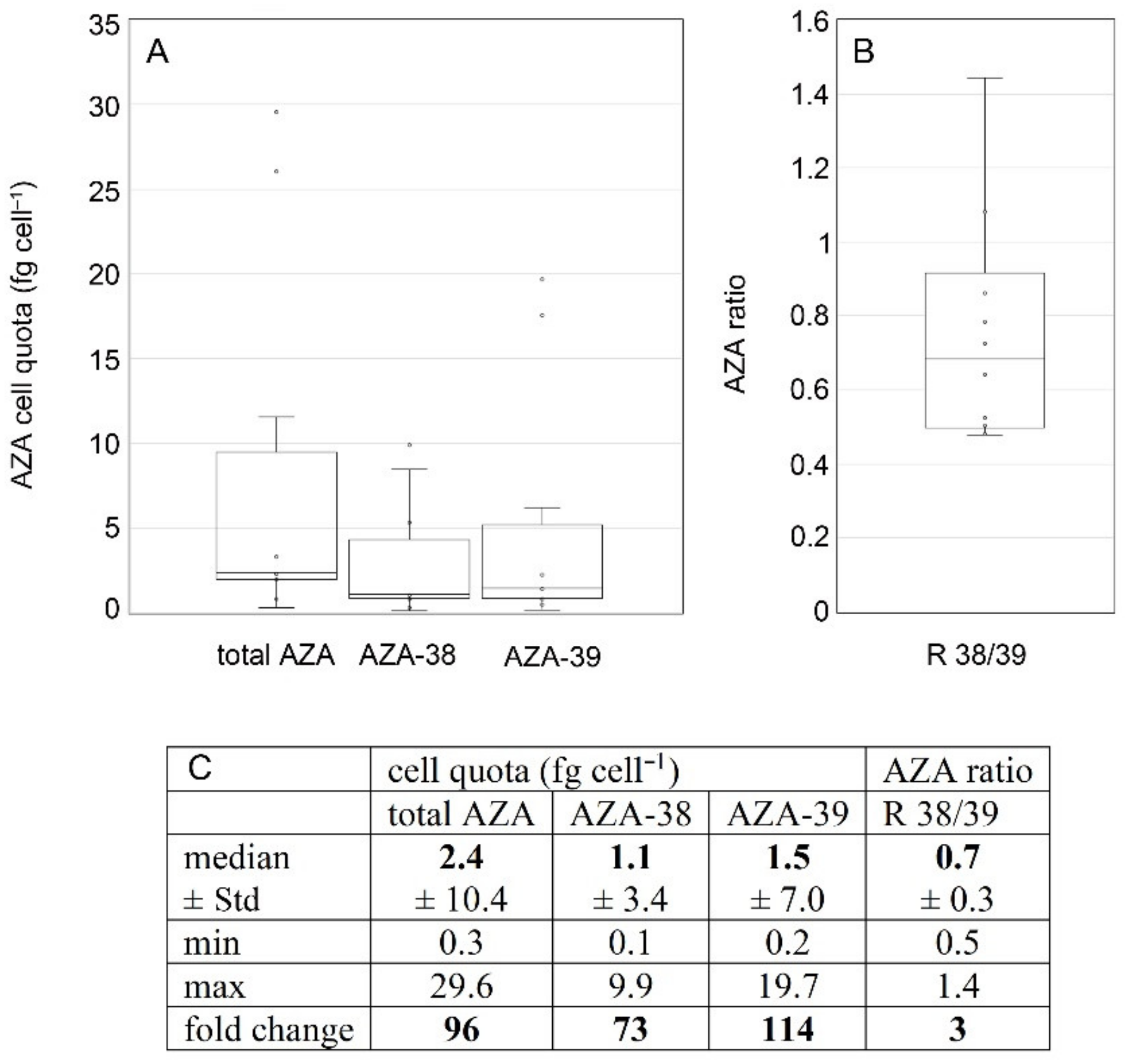
3.3. Toxins
4. Discussion
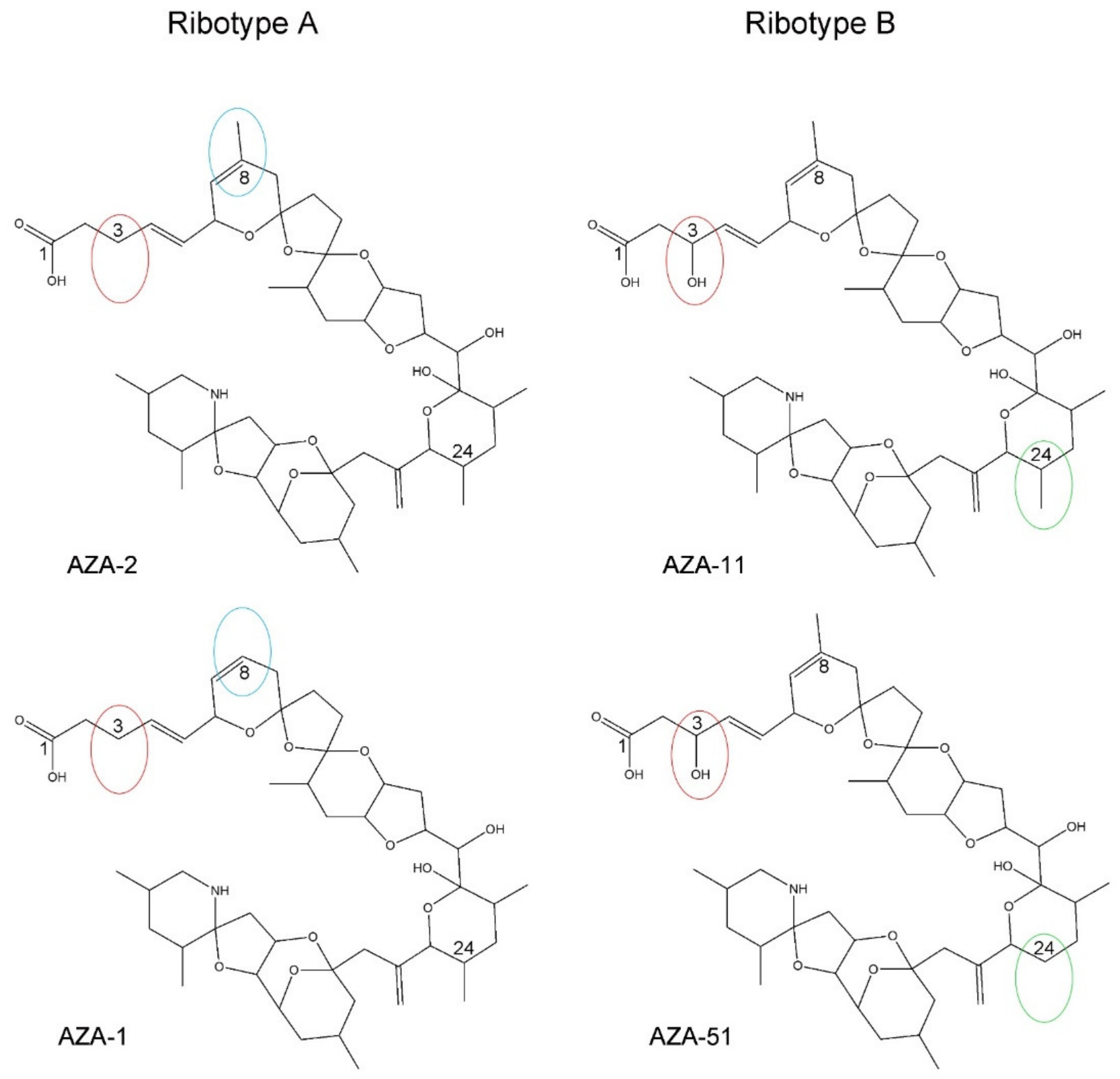
4.1. Azadinium spinosum Ribotype A and B
4.2. Toxin Profile Variability of Ribotype A
4.3. Cell Quota Variability
4.4. Non-Toxigenic Az. cf. spinosum
4.5. Amphidoma languida
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMahon, T.; Silke, J. West coast of Ireland; winter toxicity of unknown aetiology in mussels. Harmful Algae News 1996, 14, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Ofuji, K.; James, K.; Furey, A.; Yasumoto, T. New toxic events caused by Irish mussels. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and International Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 468–469. [Google Scholar]
- Twiner, M.; Hess, P.; Doucette, G.J. Azaspiracids: Toxicology, pharmacology, and risk assessment. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 823–855. [Google Scholar]
- Twiner, M.J.; Rehmann, N.; Hess, P.; Doucette, G.J. Azaspiracid shellfish poisoning: A review on the chemistry, ecology, and toxicology with emphasis on human health impacts. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; O’Neilla, A.; Maskreya, B.H.; Coatesa, L.; Swanb, S.C.; Alvesa, M.T.; Kellya, R.J.; Hatfielda, R.G.; Rowland-Pilgrima, S.J.; Lewisa, A.M.; et al. Variability and profiles of lipophilic toxins in bivalves from Great Britain during five and a half years of monitoring: Azaspiracids and yessotoxins. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.J.; Furey, A.; Lehane, M.; Ramstad, H.; Aune, T.; Hovgaard, P.; Morris, P.; Higman, W.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. First evidence of an extensive northern European distribution of azaspiracid poisoning (AZP) toxins in shellfish. Toxicon 2002, 40, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braña Magdalena, A.; Lehane, M.; Krys, S.; Fernández, M.L.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. The first identification of azaspiracids in shellfish from France and Spain. Toxicon 2003, 42, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Biré, R.; Hess, P. Confirmation by LC-MS/MS of azaspiracids in shellfish from the Portuguese north-west coast. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Goya, A.B. Occurrence and profiles of lipophilic toxins in shellfish harvested from Argentina. Toxicon 2015, 102, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Royer, F.; Savar, V. First report on azaspiracid and yessotoxin groups detection in French shellfish. Toxicon 2008, 52, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Moore, L.; Bill, B.D.; Adams, N.G.; Harrington, N.; Borchert, J.; Da Silva, D.A.M.; Eberhard, B.T.L. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins and other lipophilic toxins of human health concern in Washington State. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1815–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Guo, M.; Xing, L.; Yang, S. Determination of azaspiracid-1 in shellfishes by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2010, 28, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueoka, R.; Ito, A.; Izumikawa, M.; Maeda, S.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K.; Yoshida, M.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Matsunaga, S. Isolation of azaspiracid-2 from a marine sponge Echinoclathria sp. as a potent cytotoxin. Toxicon 2009, 53, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Ávalos, P.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. First identification of azaspiracid and spirolides in Mesodesma donacium and Mulinia edulis from Northern Chile. Toxicon 2010, 55, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rivera, A.; O’Callaghan, K.; Moriarty, M.; O’Driscoll, D.; Hamilton, B.; Lehane, M.; James, K.J.; Furey, A. First evidence of azaspiracids (AZAs): A family of lipophilic polyether marine toxins in scallops (Argopecten purpuratus) and mussels (Mytilus chilensis) collected in two regions of Chile. Toxicon 2010, 55, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.; Torgersen, T.; Dahl, E.; Naustvoll, L. Confirmation of azaspiracids in mussels in Norwegian coastal areas, and full profile at one location. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Molluscan Shellfish Safety; Marine Institute: Galway, Ireland, 2006; pp. 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann, U.; Jaén, D.; Fernández, L.; Gottschling, M.; Witt, M.; Blanco, J.; Krock, B. Amphidoma languida (Amphidomataceae, Dinophyceae) with a novel azaspiracid toxin profile identified as the cause of molluscan contamination at the Atlantic coast of southern Spain. Harmful Algae 2017, 62, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, R.; Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Kilcoyne, J.; Burson, A.; Cantwell, C.; Hess, P.; Jauffrais, T.; Silke, J. The role of Azadinium spinosum (Dinophyceae) in the production of Azaspiracid Shellfish Poisoning in mussels. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcoyne, J.; Jauffrais, T.; Twiner, M.; Doucette, G.; Aasen Bunæs, J.A.; Sosa, S.; Krock, B.; Séchet, V.; Nulty, C.; Salas, R.; et al. Azaspiracids—Toxicological Evaluation, Test Methods and Identification of the Source Organisms (ASTOX 2); Marine Institute: Galway, Ireland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, D. New insights and perspectives from 20 years of monitoring algal events in Irish coastal waters. In Proceedings of the 11th Irish Shellfish Safety Workshop; Clarke, D., Gilmartin, M., Eds.; Marine Environment and Health Series, No. 41; Marine Institute: Galway, Ireland, 2020; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann, U.; Elbrächter, M.; Krock, B.; John, U.; Cembella, A. Azadinium spinosum gen. et sp. nov. (Dinophyceae) identified as a primary producer of azaspiracid toxins. Eur. J. Phycol. 2009, 44, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Krock, B.; Ciminiello, P.; Percopo, I.; Tillmann, U.; Soprano, V.; Zingone, A. Mediterranean Azadinium dexteroporum (Dinophyceae) produces AZA-35 and six novel azaspiracids: A structural study by a multi-platform mass spectrometry approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Voß, D.; Koch, B.P.; Salas, R.; Witt, M.; Potvin, E.; Jeong, H.J. New azaspiracids in Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae): Proposed structures. Toxicon 2012, 60, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Söhner, S.; Nézan, E.; Krock, B. First record of Azadinium from the Shetland Islands including the description of A. polongum sp. nov. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Salas, R.; Jauffrais, T.; Hess, P.; Silke, J. AZA: The producing organisms—Biology and trophic transfer. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 773–798. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann, U.; Edvardsen, B.; Krock, B.; Smith, K.F.; Paterson, R.F.; Voß, D. Diversity, distribution, and azaspiracids of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) along the Norwegian coast. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Gottschling, M.; Krock, B.; Smith, K.F.; Guinder, V. High abundance of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) during the 2015 spring bloom of the Argentinean Shelf and a new, non-toxigenic ribotype of Azadinium spinosum. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmann, U.; Wietkamp, S.; Gu, H.; Clarke, D.; Smith, K. qPCR assays for Amphidomataceae: State of the art and new challenges. In Harmful Algae 2018—From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae; Hess, P., Ed.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Nantes, France, 2020; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Toebe, K.; Joshi, A.R.; Messtorff, P.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Molecular discrimination of taxa within the dinoflagellate genus Azadinium, the source of azaspiracid toxins. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Gottschling, M.; Nézan, E.; Krock, B. First record of Azadinium dexteroporum and Amphidoma languida (Amphidomataceae, Dinophyceae) from the Irminger Sea off Iceland. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2015, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Krock, B.; Giannakourou, A.; Venetsanopoulou, A.; Pagou, K.; Tillmann, U.; Gu, H. Sympatric occurrence of two Azadinium poporum ribotypes in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Harmful Algae 2018, 78, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, J.D. The Dinoflagellates of the British Isles; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann, U.; Salas, R.; Gottschling, M.; Krock, B.; O’Driscoll, D.; Elbrächter, M. Amphidoma languida sp. nov. (Dinophyceae) reveals a close relationship between Amphidoma and Azadinium. Protist 2012, 163, 701–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietkamp, S.; Krock, B.; Clarke, D.; Voß, D.; Salas, R.; Kilcoyne, J.; Tillmann, U. Distribution and abundance of azaspiracid-producing dinophyte species and their toxins in North Atlantic and North Sea waters in summer 2018. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, R.; Tillmann, U.; Gu, H.; Wietkamp, S.; Krock, B.; Clarke, D. Morphological and molecular characterization of multiple new Azadinium strains revealed a high diversity of non-toxigenic species of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) including two new Azadinium species in Irish waters, North East Atlantic. Phycol. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Wisotzki, A. Physical oceanography during HEINCKE cruise HE516. Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven. PANGEA 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.D.; Selvin, R.C.; Claus, W.; Guillard, R.R.L. Media for the culture of oceanic ultraphytoplankton. J. Phycol. 1987, 23, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlin, L.K.; Elwood, H.J.; Stickel, S.; Sogin, M.L. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene 1988, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Sako, Y.; Ishida, Y. Analysis of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species using sequences of the 5.8S ribosomal DNA and internal transcribed spacer regions. J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholin, C.A.; Herzog, M.; Sogin, M.; Anderson, D.M. Identification of group- and strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Trefault, N.; Krock, B.; Parada-Pozo, G.; De la Iglesia, R.; Vásquez, M. Identification of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) in the Southeast Pacific: Morphology, molecular phylogeny, and azaspiracid profile characterization. J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 350–367. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucl. Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. ModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inderence under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boc, A.; Diallo, A.B.; Makarenkov, V. T-REX: A web server for inferring, validating and visualizing phylogenetic trees and networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Alpermann, T.J.; Voß, D.; Zielinski, O.; Cembella, A. Phycotoxin composition and distribution in plankton fractions from the German Bight and Western Danish Coast. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietkamp, S.; Krock, B.; Gu, H.; Voß, D.; Klemm, K.; Tillmann, U. Occurrence and distribution of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) in Danish coastal waters of the North Sea, the Limfjord, and the Kattegat/Belt area. Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 101637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Borel, M.; Barrera, F.; Lara, R.; Krock, B.; Almandoz, G.; Trefault, N. Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from the Argentine continental shelf, Southwestern Atlantic, produces azaspiracid-2 and azaspiracid-2 phosphate. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Tebben, J.; Trefaults, N.; Gu, H. Two novel azaspiracids from Azadinium poporum, and a comprehensive compilation of azaspiracids produced by Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2019, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcoyne, J.; Nulty, C.; Jauffrais, T.; McCarron, P.; Hervé, F.; Foley, B.; Rise, F.; Crain, S.; Wilkins, A.L.; Twiner, M.J.; et al. Isolation, structure elucidation, relative LC-MS response, and in vitro toxicity of azaspiracids from the dinoflagellate Azadinium spinosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcoyne, J.; McCoy, A.; Burrell, S.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U. Effect of temperature, growth media, and photoperiod on growth and toxin production of Azadinium spinosum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Witt, M.; Gu, H. Azaspiracid variability of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from the China Sea. Harmful Algae 2014, 36, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Luo, Z.; Krock, B.; Witt, M.; Tillmann, U. Morphology, phylogeny and azaspiracid profile of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from the China Sea. Harmful Algae 2013, 21–22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauffrais, T.; Séchet, V.; Herrenknecht, C.; Truquet, P.; Véronique, S.; Tillmann, U.; Hess, P. Effect of environmental and nutritional factors on growth and azaspiracid production of the dinoflagellate Azadinium spinosum. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Bill, B.D.; Adams, N.G.; Tillmann, U.; Sloan, C.; Lu, D.; Trainer, V.L. The effect of temperature and salinity on growth rate and azaspiracid concentration in two strains of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from Puget Sound, Washington State. Harmful Algae 2019, 89, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Jiang, B.; Chen, H.; Gu, H. Growth and toxin production of Azadinium poporum strains in batch cultures under different nutrient conditions. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2016, 127, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wietkamp, S.; Tillmann, U.; Clarke, D.; Toebe, K. Molecular determination and quantification of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Amphidoma languida (Amphidomataceae, Dinophyceae). J. Plankton Res. 2019, 41, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.; Salas, R.; Hynes, P.; McCarthy, A.; Walsh, D.; Silke, J. PCR assays for the detection of ASP, DSP, PSP and AZP toxigenic producing phytoplanktonic species in Irish coastal waters. In Harmful Algae 2018–From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algaeon; Hess, P., Ed.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Nantes, France, 2020; pp. 9–24. [Google Scholar]




| Genus | Species | No. of Strains | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azadinium | caudatum var. margalefii | 1 | Salas et al. 2021 [35] |
| Azadinium | cf. zhuanum | 1 | Salas et al. 2021 [35] |
| Azadinium | galwayense | 3 | Salas et al. 2021 [35] |
| Azadinium | perfusorium | 26 | Salas et al. 2021 [35] |
| Azadinium | spinosum ribotype A | 60 | this paper |
| Azadinium | spinosum ribotype B | 7 | this paper |
| Azadinium | cf. spinosum | 5 | this paper |
| Amphidoma | languida | 10 | this paper |
| Strains | 7-D3 (B) | H-4-G1 (C) | 1-H10 (cf.) | 5-B9 (cf.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D9 (A) | no | no | Helix IV | Helix IV |
| 7-D3 (B) | no | Helix IV | Helix IV | |
| H-4-G1 (C) | Helix IV | Helix IV | ||
| 1-H10 (cf.) | no |
| F-Primer | Probe | R-Primer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | CATCTCCCTGACACAAAGACGA | AGGAGTCCTTTTGGGCG | GGAAACTCCTGAAGGG-CTTGT |
| ribotype A | --------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- |
| ribotype B | --------------------------------------------- | --------------------C------------ | ---------------T--------G----------------- |
| ribotype C | --------------------------------------------- | C--A---------------------------- | ---------------T--------TCA-------CCA |
| Az. cf. spinosum | --------------------------------------------- | T-A----------G----------------- | T-------------T----------------A--------- |
| Toxin Profile Confirmation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Toxin Profile | ca. 2 Months Later | ca. 5 Months Later | >1 Year |
| AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-33 | 12 | 11 | 4 |
| AZA-1 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
| AZA-1, AZA-2 | 6 | 6 | 2 |
| AZA-1, AZA-33 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| AZA-11, AZA-51 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| cf. spinosum (none) | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Ribotype A | Groups: Toxin Profile (1, 2, 3, 4) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DF, n | H | p | |
| total AZA | 3, n = 125 | 9.81 | 0.0203 |
| AZA-1 | 3, n = 125 | 2.16 | 0.5417 |
| AZA-2 | 1, n = 94 | 1.05 | 0.3043 |
| AZA-33 | 1, n = 76 | 0.51 | 0.4740 |
| R 1/2 | 1, n = 94 | 3.68 | 0.0549 |
| R 1/33 | 1, n = 76 | 0.03 | 0.8652 |
| Groups: Strains | |||
| total AZA | 21, n = 79 | 26.37 | 0.1927 |
| R 1/2 | 16, n = 62 | 46.29 | 0.0001 |
| R 1/33 | 13, n = 51 | 35.82 | 0.0006 |
| R 2/33 | 11, n = 43 | 24.82 | 0.0097 |
| Ribotype B | Groups: Strains | ||
| DF, n | H | p | |
| total AZA | 4, n = 16 | 1.09 | 0.8956 |
| AZA-11 | 4, n = 16 | 2.91 | 0.5727 |
| AZA-51 | 4, n = 16 | 0.97 | 0.9157 |
| R 11/51 | 4, n = 16 | 8.60 | 0.0718 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tillmann, U.; Wietkamp, S.; Gu, H.; Krock, B.; Salas, R.; Clarke, D. Multiple New Strains of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) from the North Atlantic Revealed a High Toxin Profile Variability of Azadinium spinosum and a New Non-Toxigenic Az. cf. spinosum. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010134
Tillmann U, Wietkamp S, Gu H, Krock B, Salas R, Clarke D. Multiple New Strains of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) from the North Atlantic Revealed a High Toxin Profile Variability of Azadinium spinosum and a New Non-Toxigenic Az. cf. spinosum. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleTillmann, Urban, Stephan Wietkamp, Haifeng Gu, Bernd Krock, Rafael Salas, and Dave Clarke. 2021. "Multiple New Strains of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) from the North Atlantic Revealed a High Toxin Profile Variability of Azadinium spinosum and a New Non-Toxigenic Az. cf. spinosum" Microorganisms 9, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010134
APA StyleTillmann, U., Wietkamp, S., Gu, H., Krock, B., Salas, R., & Clarke, D. (2021). Multiple New Strains of Amphidomataceae (Dinophyceae) from the North Atlantic Revealed a High Toxin Profile Variability of Azadinium spinosum and a New Non-Toxigenic Az. cf. spinosum. Microorganisms, 9(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010134






