Baikalomycins A-C, New Aquayamycin-Type Angucyclines Isolated from Lake Baikal Derived Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Culture Conditions and Routine Procedures
2.2. Sampling and Actinobacteria Isolation
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Screening the Culture Conditions for Biological Activity of Streptomyces sp. IB2016I91-2A
2.5. LC-MS and LC-HRMS Analysis
2.6. Isolation and Purification of Compounds 1–5
2.7. Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics
2.8. Gene Disruption of the Glycosyltransferase Genes baiGT2 and baiGT3
2.9. Cloning of the bai Gene Cluster Using Transformation-Associated Recombination (TAR) Technique
2.10. Biological Activity Assays
2.11. Anticancer Activities of Isolated Compounds
3. Results and Discussion
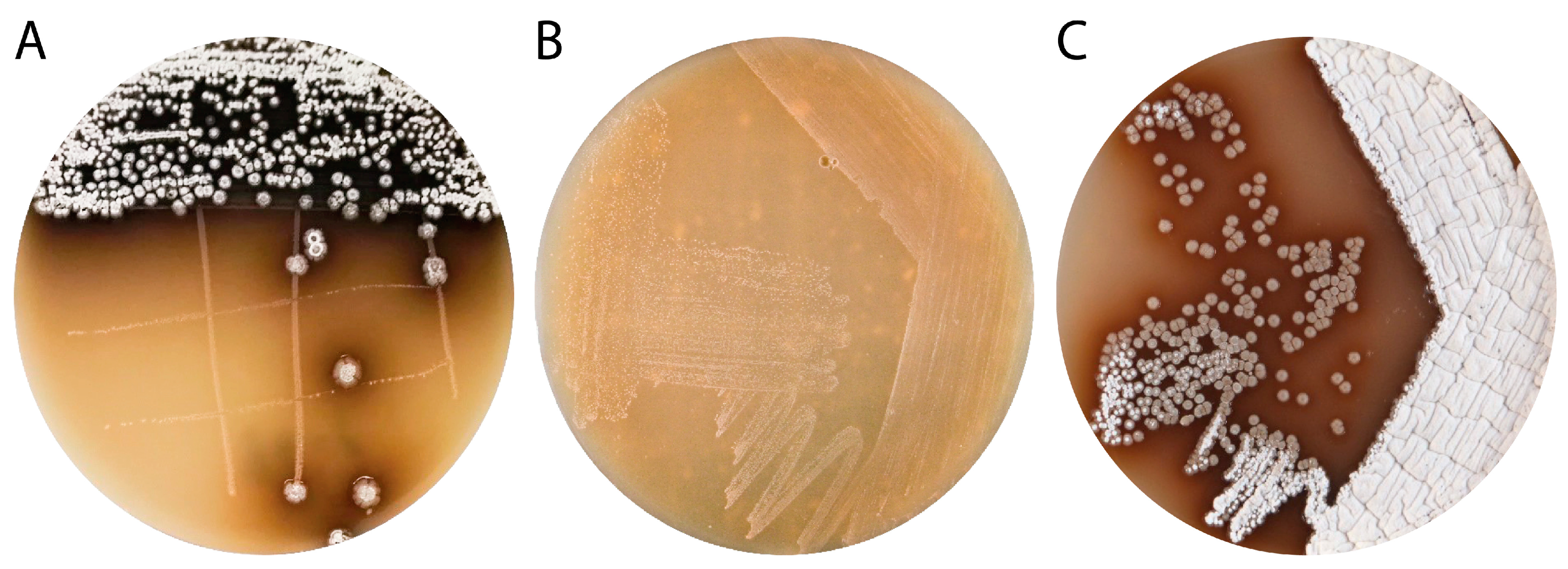
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A
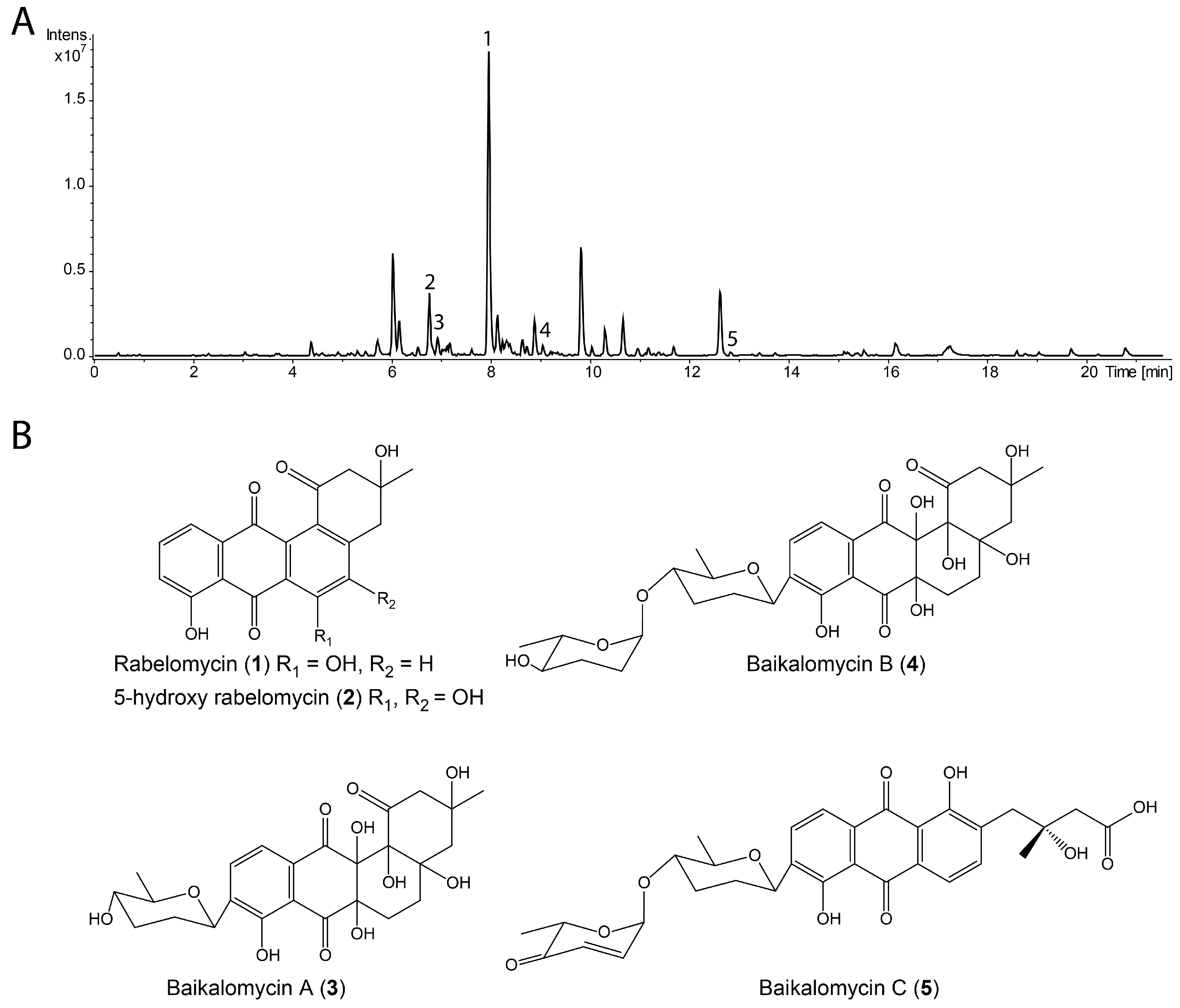
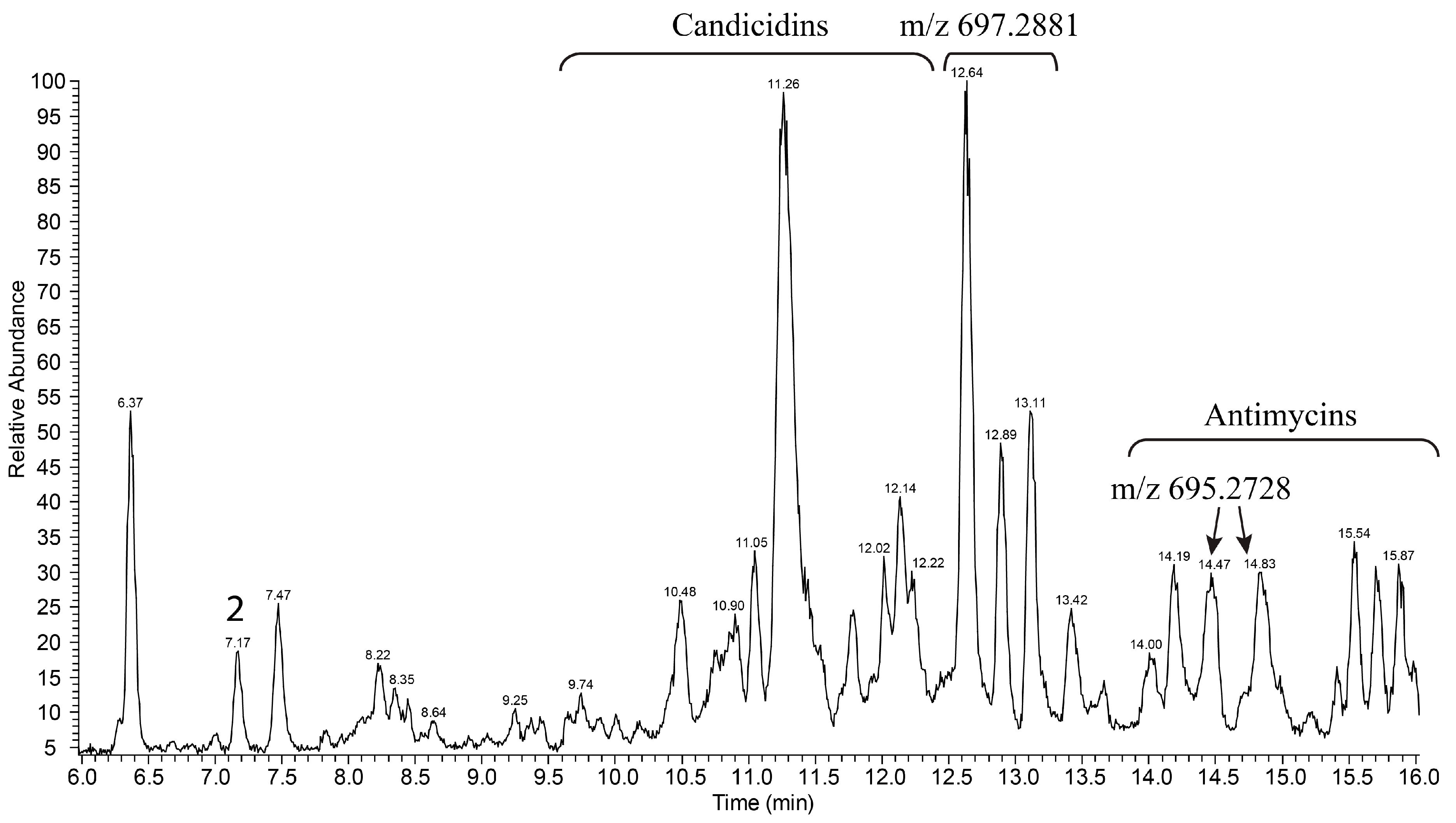
3.2. Production and Isolation of Baikalomycins
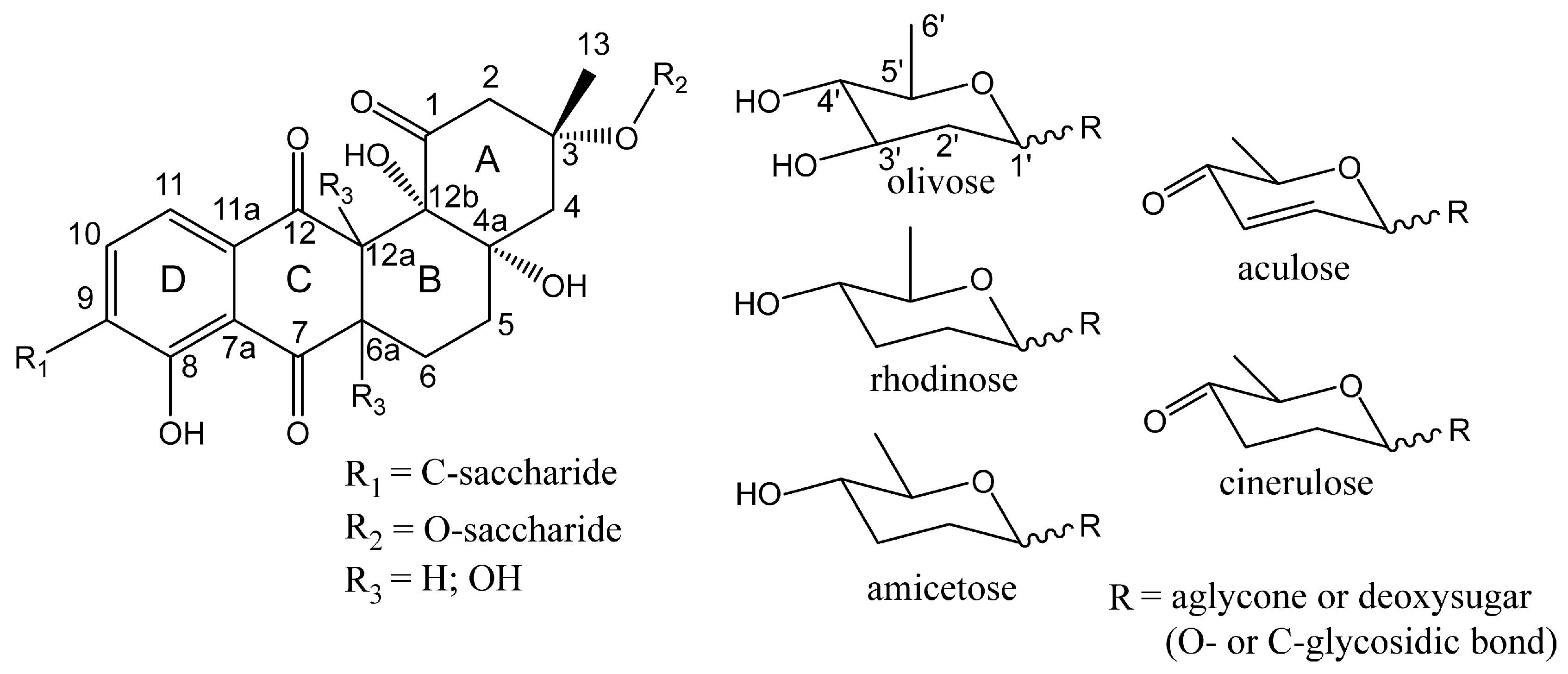
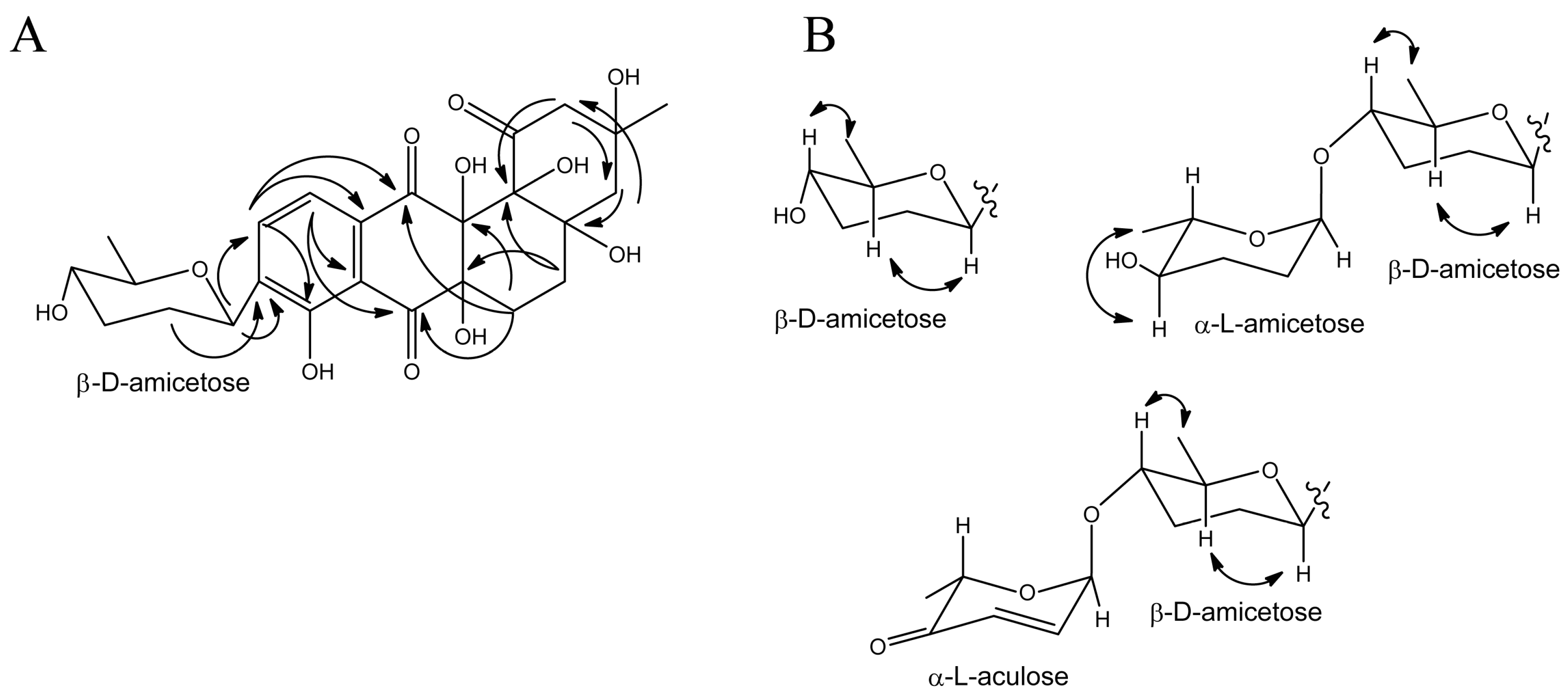
3.3. Structure Elucidation of Baikalomycins
3.4. Biological Activities of Baikalomycins
3.5. Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A Genome Sequencing and Analysis
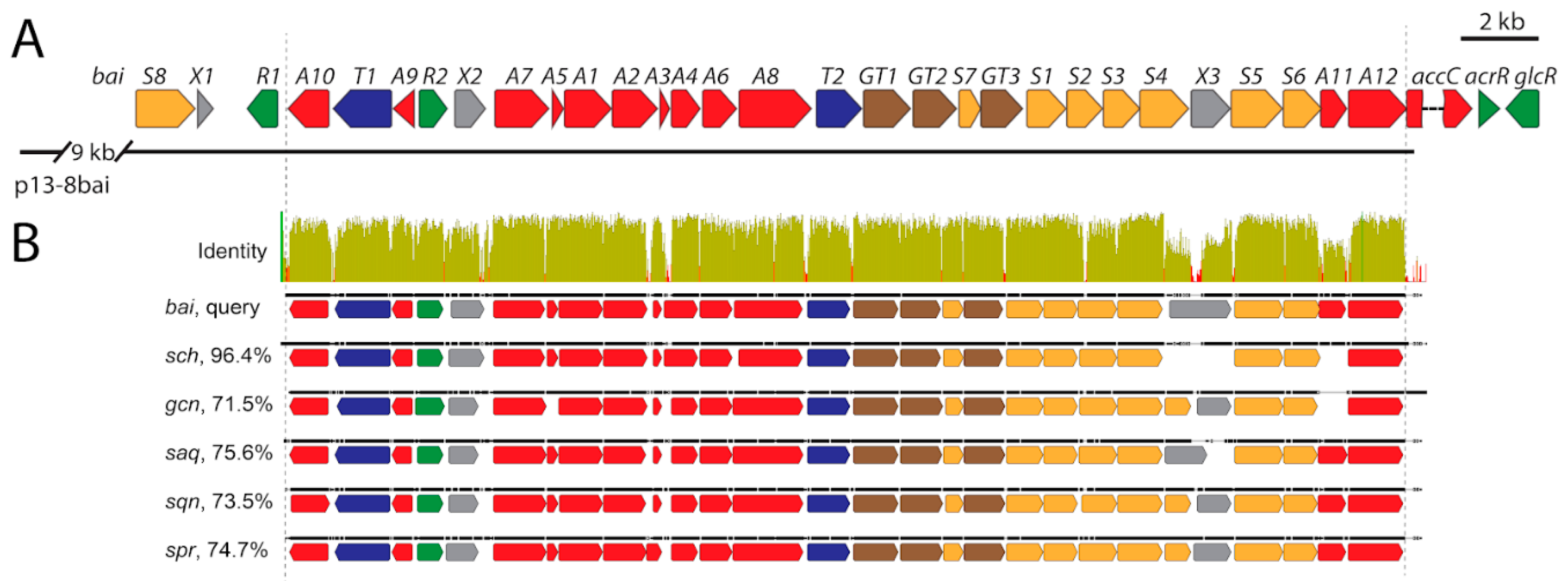
3.6. Identification of Baikalomycins Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
3.6.1. Genes Putatively Involved in Biosynthesis of Aglycone Core
3.6.2. Genes Putatively Involved in Deoxysugars Biosynthesis and Attachment
3.6.3. Genes Involved in Regulation, Resistance, and with Unknown Functions
3.7. Inactivation of Genes Encoding Glycosyltransferases in bai Cluster
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohr, J.; Thiericke, R. Angucycline group antibiotics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1992, 9, 103–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharel, M.K.; Pahari, P.; Shepherd, M.D.; Tibrewal, N.; Nybo, S.E.; Shaaban, K.A.; Rohr, J. Angucyclines: Biosynthesis, mode-of-action, new natural products, and synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 264–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y. Cyclization of aromatic polyketides from bacteria and fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 839–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, N.; Kakinuma, K.; Ikekawa, N.; Tanaka, H.; Omura, S. Biosynthesis of vineomycins A1 and B2. J. Antibiot. 1982, 35, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulowski, K.; Wendt-Pienkowski, E.; Han, L.; Yang, K.; Vining, L.C.; Hutchinson, C.R. Functional Characterization of the jadI gene as a cyclase forming angucyclinones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostash, B.; Rebets, Y.; Yuskevich, V.; Luzhetskyy, A.; Tkachenko, V.; Fedorenko, V. Targeted disruption of Streptomyces globisporus lndF and lndL cyclase genes involved in landomycin E biosynthesis. Folia Microbiol. 2003, 48, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Halley, K.A. Biosynthesis of the benz[a]anthraquinone antibiotic PD 116198: Evidence for a rearranged skeleton. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 5092–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, E.; Ogasawara, Y.; Liu, H.-W. A biosynthetic pathway for BE-7585A, a 2-thiosugar-containing angucycline-type natural product. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7405–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshahawi, S.I.; Shaaban, K.A.; Kharel, M.K.; Thorson, J.S. A comprehensive review of glycosylated bacterial natural products. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7591–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezaki, M.; Kondo, S.; Maeda, K.; Umezawa, H.; Ohno, M. The structure of aquayamycin. Tetrahedron 1970, 26, 5171–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Imoto, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Miura, K.; Dobashi, T.; Matsuda, N.; Sawa, T.; Naganawa, H.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. Saquaymycins, new aquayamycin-group antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 1985, 38, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizawa, R.; Iinuma, H.; Naganawa, H.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Yamaizumi, J.; Umezawa, K. Isolation of novel saquayamycins as inhibitors of farnesyl-protein transferase. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Antal, N.; Fiedler, H.-P.; Stackebrandt, E.; Beil, W.; Ströch, K.; Zeeck, A. Retymicin, galtamycin B, saquayamycin Z and ribofuranosyllumichrome, novel secondary metabolites from Micromonospora sp. Tü 6368. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yang, T.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, A.; Ma, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Cytotoxic angucycline class glycosides from the deep sea actinomycete Streptomyces lusitanus SCSIO LR32. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, K.A.; Ahmed, T.A.; Leggas, M.; Rohr, J. Saquayamycins G-K, cytotoxic angucyclines from Streptomyces sp. Including two analogues bearing the aminosugar rednose. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, A.; Luzhetskyy, A.; Hardter, U.; Bechthold, A. Cloning and sequencing of the biosynthetic gene cluster for saquayamycin Z and galtamycin B and the elucidation of the assembly of their saccharide chains. Chembiochem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2009, 10, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Yarborough, R.; Schwartz, J.; Patel, M.G.; Horan, A.C.; Gullo, V.P.; Das, P.R.; Puar, M.S. Sch 47554 and Sch 47555, two novel antifungal antibiotics produced from a Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakagawa, K.; Hara, C.; Tokuyama, S.; Takada, K.; Imamura, N. Saprolmycins A-E, new angucycline antibiotics active against Saprolegnia parasitica. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, M.S.; Kharel, M.K.; Hitron, J.A.; Baig, I.; Rohr, J. Moromycins A and B, isolation and structure elucidation of C-glycosylangucycline-type antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. KY002. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Lu, X.; Ke, A.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, J.; Hao, W.; Zhu, J.; Fan, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Three novel members of angucycline group from Streptomyces sp. N05WA963. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, N.; Kakinuma, K.; Ikekawa, N.; Tanaka, H.; Omura, S. The structure of vineomycin B2. J. Antibiot. 1981, 34, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, N.; Sawa, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Sawa, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Naganawa, H.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. Amicenomycins A and B, New Antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. MJ384-46F6. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, A.; Qu, X.; Liu, F.; Li, X.; Li, E.; Xie, W. Angucycline glycosides from an intertidal sediments strain Streptomyces sp. and their cytotoxic activity against hepatoma carcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkel, T.; Zeeck, A. Derivatives of saquayamycins A and B. Regio- and diastereoselective addition of alcohols to the l-aculose moiety. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maskey, R.P.; Helmke, E.; Laatsch, H. Himalomycin A and B: Isolation and structure elucidation of new fridamycin type antibiotics from a marine streptomyces isolate. J. Antibiot. 2003, 56, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mulzer, M.; Shi, P.; Beuning, P.J.; Coates, G.W.; O’Doherty, G.A. De novo asymmetric synthesis of fridamycin E. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6592–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Q.; Luo, M.; Sun, A.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Ju, J. Identification of the grincamycin gene cluster unveils divergent roles for GcnQ in different hosts, tailoring the l-rhodinose moiety. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3254–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.M.; Weidenbach, S.; Rohr, J. Two cooperative glycosyltransferases are responsible for the sugar diversity of saquayamycins isolated from Streptomyces sp. KY 40-1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, D.B.; Oh, T.-J.; Vu, T.T.H.; Sthapit, B.; Liou, K.; Lee, H.C.; Yoo, J.-C.; Sohng, J.K. Angucyclines Sch 47554 and Sch 47555 from Streptomyces sp. SCC-2136: Cloning, sequencing, and characterization. Mol. Cells 2006, 22, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Fidan, O.; Yan, R.; Gladstone, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, D.; Zhan, J. New insights into the glycosylation steps in the biosynthesis of sch47554 and sch47555. Chembiochem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2018, 19, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, T.; Moriyama, A.; Nakagawa, K.; Imamura, N. Cloning and identification of saprolmycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. TK08046. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, K.F.; Wilde, L.C. Streptomyces albus G mutants defective in the SalGI restriction-modification system. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1980, 116, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flett, F.; Mersinias, V.; Smith, C.P. High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 155, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouprina, N.; Larionov, V. Transformation-associated recombination (TAR) cloning for genomics studies and synthetic biology. Chromosoma 2016, 125, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieser, T.; Bibb, M.J.; Buttner, M.J.; Chater, K.F.; Hopwood, D.A. Practical Streptomyces Genetics; John Innes Foundation: Norwich, UK, 2000; p. 613. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989; p. 1659. [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorf, B.; Röpstorf, P.; Riedel, F. Relationships and origin of endemic Lake Baikal gastropods (Caenogastropoda: Rissooidea) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 26, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Pryer, K.M.; Miao, V.P.W.; Palmer, J.D. Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Running, W. Computer Software Reviews. Chapman and Hall Dictionary of Natural Products on CD-ROM. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 1993, 33, 934–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Weißbach, U.; Reillo, C.S.; Braña, A.F.; Méndez, C.; Rohr, J.; Salas, J.A. Identification of two genes from Streptomyces argillaceus encoding glycosyltransferases involved in transfer of a disaccharide during biosynthesis of the antitumor drug mithramycin. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Pyshkin, A.V. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F. GenDB-an open source genome annotation system for Prokaryote genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinform 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Blin, K.; Duddela, S.; Krug, D.; Kim, H.U.; Bruccoleri, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; Müller, R.; Wohlleben, W.; et al. antiSMASH 3.0-a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilyk, O.; Sekurova, O.; Zotchev, S.B.; Luzhetskyy, A. Cloning and heterologous expression of the grecocycline biosynthetic gene cluster. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritacco, F.V.; Eveleigh, D.E. Molecular and phenotypic comparison of phaeochromycin-producing strains of Streptomyces phaeochromogenes and Streptomyces ederensis. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Wellington, E.M.; Sneath, P.H.; Sackin, M.J. Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1983, 129, 1743–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olano, C.; Méndez, C.; Salas, J.A. Antitumor compounds from marine actinomycetes. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 210–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Cheng, X.C.; Halley, K.A. Biosynthesis of dehydrorabelomycin and PD 116740: Prearomatic deoxygenation as evidence for different polyketide synthases in the formation of benz[a]anthraquinones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10066–10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-C.; Parker, W.L.; Slusarchyk, D.S.; Greenwood, G.L.; Graham, S.F.; Meyers, E. Isolation, characterization, and structure of rabelomycin, a new antibiotic. J. Antibiot. 1970, 23, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paululat, T.; Kulik, A.; Hausmann, H.; Karagouni, A.D.; Zinecker, H.; Imhoff, J.F.; Fiedler, H.-P. Grecocyclines: New Angucyclines from Streptomyces sp. Acta 1362. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2344–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, J.; Zeeck, A. Metabolic products of microorganisms. 240 Urdamycins, new angucycline antibiotics from Streptomyces fradiae. II Structural studies of urdamycins B to F. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzenkämpfer, M.; Walker, M.; Zeeck, A.; Schimana, J.; Fiedler, H.-P. Simocyclinones, novel cytostatic angucyclinone antibiotics produced by Streptomyces antibioticus Tü 6040 II. Structure elucidation and biosynthesis. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotso, S.; Mahmud, T.; Zabriskie, T.M.; Santosa, D.A.; Sulastri; Proteau, P.J. Angucyclinones from an Indonesian Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinovskaya, N.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Romanenko, L.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuznetsova, T.A. New angucyclines and antimicrobial diketopiperazines from the marine mollusk-derived actinomycete Saccharothrix espanaensis An 113. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, N.; Qin, S.; Laatsch, H. Kiamycin, a unique cytotoxic angucyclinone derivative from a marine Streptomyces sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, M.; Hoppstädter, J.; Breinig, F.; Kiemer, A.K. Yeast-mediated mRNA delivery polarizes immuno-suppressive macrophages towards an immuno-stimulatory phenotype. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, S.; Bicz, J.; Song, L.; Deeth, R.J.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ochi, K.; Challis, G.L. Structure and biosynthesis of scabichelin, a novel tris-hydroxamate siderophore produced by the plant pathogen Streptomyces scabies 87.22. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 4686–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, N.N.; Mekhanikova, I.V.; Chebykin, E.P.; Vodneva, E.V.; Timoshkin, O.A.; Suturin, A.N. Chemical element composition and amphipod concentration function in Baikal littoral zone. Water Resour. 2017, 44, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, G.P.; Oh, T.-J.; Lee, H.C.; Sohng, J.K. Squalene-hopene cyclase (Spterp25) from Streptomyces peucetius: Sequence analysis, expression and functional characterization. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürtler, H.; Pedersen, R.; Anthoni, U.; Christophersen, C.; Nielsen, P.H.; Wellington, E.M.; Pedersen, C.; Bock, K. Albaflavenone, a sesquiterpene ketone with a zizaene skeleton produced by a streptomycete with a new rope morphology. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Tsuda, M.; Omura, S.; Oikawa, H.; Ikeda, H. Identification and functional analysis of genes controlling biosynthesis of 2-methylisoborneol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7422–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, H.; Haag, S. Cloning and characterization of a polyketide synthase gene from Streptomyces fradiae Tü2717, which carries the genes for biosynthesis of the angucycline antibiotic urdamycin A and a gene probably involved in its oxygenation. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6126–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patrikainen, P.; Kallio, P.; Fan, K.; Klika, K.D.; Shaaban, K.A.; Mäntsälä, P.; Rohr, J.; Yang, K.; Niemi, J.; Metsä-Ketelä, M. Tailoring enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of angucyclines contain latent context-dependent catalytic activities. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, B.; Hoffmeister, D.; Weitnauer, G.; Westrich, L.; Haag, S.; Schneider, P.; Decker, H.; Künzel, E.; Rohr, J.; Bechthold, A. Two new tailoring enzymes, a glycosyltransferase and an oxygenase, involved in biosynthesis of the angucycline antibiotic urdamycin A in Streptomyces fradiae Tü2717. Microbiology 2000, 146, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Xie, Z.; Pu, Y.; Pei, S.; Li, F.; Qin, S. Genomic sequence-based discovery of novel angucyclinone antibiotics from marine Streptomyces sp. W007. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 332, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexeev, I.; Sultana, A.; Mäntsälä, P.; Niemi, J.; Schneider, G. Aclacinomycin oxidoreductase (AknOx) from the biosynthetic pathway of the antibiotic aclacinomycin is an unusual flavoenzyme with a dual active site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6170–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebets, Y.; Ostash, B.; Luzhetskyy, A.; Hoffmeister, D.; Braňa, A.; Mendez, C.; Salas, J.A.; Bechthold, A.; Fedorenko, V. Production of landomycins in Streptomyces globisporus 1912 and S. cyanogenus S136 is regulated by genes encoding putative transcriptional activators. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 222, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, L.; Nodwell, J.R. The TetR family of regulators. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. Mmbr 2013, 77, 440–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.A.; Brzoska, A.J.; Wilson, N.L.; Eijkelkamp, B.A.; Brown, M.H.; Paulsen, I.T. Roles of DHA2 family transporters in drug resistance and iron homeostasis in Acinetobacter spp. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmu, K.; Ishida, K.; Mäntsälä, P.; Hertweck, C.; Metsä-Ketelä, M. Artificial reconstruction of two cryptic angucycline antibiotic biosynthetic pathways. Chembiochem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2007, 8, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test Strain | MIC, μM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | |
| Erwinia persicina DSMZ 19328 | >500 | 250 | n.t. | 31 | 125 |
| Pseudomonas putida KT2440 | >500 | >500 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Candida glabrata DSMZ 11226 | >500 | >500 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Staphylococcus carnosus DSMZ 20501 | >500 | >500 | 62 | 62 | 125 |
| Mycobacteriaum smegmatis DSMZ 43286 | >500 | >500 | 250 | 31 | 125 |
| Compound | A549 | Huh7.5 | MCF7 | SW620 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 58.51 ± 5.15 | inactive | 53.19 ± 3.36 | inactive |
| 4 | 46.26 ± 0.52 | inactive | inactive | inactive |
| 5 | 42.43 ± 3.71 | 7.62 ± 0.47 | 13.35 ± 1.33 | 3.87 ± 0.69 |
| 1 | 9.78 ± 0.49 | 7.21 ± 0.70 | 21.94 ± 1.59 | 7.82 ± 0.40 |
| 2 | 9.11 ± 0.59 | 11.91 ± 2.94 | 27.39 ± 2.17 | 13.43 ± 0.72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voitsekhovskaia, I.; Paulus, C.; Dahlem, C.; Rebets, Y.; Nadmid, S.; Zapp, J.; Axenov-Gribanov, D.; Rückert, C.; Timofeyev, M.; Kalinowski, J.; et al. Baikalomycins A-C, New Aquayamycin-Type Angucyclines Isolated from Lake Baikal Derived Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050680
Voitsekhovskaia I, Paulus C, Dahlem C, Rebets Y, Nadmid S, Zapp J, Axenov-Gribanov D, Rückert C, Timofeyev M, Kalinowski J, et al. Baikalomycins A-C, New Aquayamycin-Type Angucyclines Isolated from Lake Baikal Derived Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(5):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050680
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoitsekhovskaia, Irina, Constanze Paulus, Charlotte Dahlem, Yuriy Rebets, Suvd Nadmid, Josef Zapp, Denis Axenov-Gribanov, Christian Rückert, Maxim Timofeyev, Jörn Kalinowski, and et al. 2020. "Baikalomycins A-C, New Aquayamycin-Type Angucyclines Isolated from Lake Baikal Derived Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A" Microorganisms 8, no. 5: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050680
APA StyleVoitsekhovskaia, I., Paulus, C., Dahlem, C., Rebets, Y., Nadmid, S., Zapp, J., Axenov-Gribanov, D., Rückert, C., Timofeyev, M., Kalinowski, J., Kiemer, A. K., & Luzhetskyy, A. (2020). Baikalomycins A-C, New Aquayamycin-Type Angucyclines Isolated from Lake Baikal Derived Streptomyces sp. IB201691-2A. Microorganisms, 8(5), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050680





