Evolution and Genetic Diversity of Primate Cytomegaloviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Primate species | CMV species | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Common Name | Official name /Common Name (Abbreviation) | |
| Great apes | |||
| Homo sapiens | Human | Human betaherpesvirus 5 * | [11] |
| Pan paniscus | Bonobo | Pan paniscus cytomegalovirus (PpanCMV1, PpanCMV2) | [33] |
| Pan troglodytes | Chimpanzee | Panine betaherpesvirus 2 (CCMV) * | [34] |
| Pan troglodytes ellioti | Nigeria–Cameroon chimpanzee | Panine betaherpesvirus 2 (CCMV1, CCMV2) | [33] |
| Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii | Eastern chimpanzee | Panine betaherpesvirus 2 (CCMV1, CCMV2) | [33] |
| Pan troglodytes troglodytes | Central chimpanzee | Panine betaherpesvirus 2 (CCMV1, CCMV2) | [33] |
| Pan troglodytes verus | West African chimpanzee | Panine betaherpesvirus 2 (CCMV1, CCMV2) | [35] |
| Pongo pygmaeus pygmaeus | Orang–utan | Pongo pygmaeus cytomegalovirus (PpygCMV1) | [35] |
| Gorilla beringei beringei | Mountain gorilla | Gorilla beringei cytomegalovirus (GberCMV1, GberCMV2) | [33,36] |
| Gorilla beringei graueri | Eastern lowland gorilla | Gorilla graueri cytomegalovirus (GgraCMV1, GgraCMV2) | [33] |
| Gorilla gorilla gorilla | Western lowland gorilla | Gorilla gorilla cytomegalovirus (GgorCMV1, GgorCMV2) | [35] |
| Old World Monkeys | |||
| Colobus guereza | Mantled guereza | Colobus guereza cytomegalovirus (CgueCMV) | [37] |
| Colobus polykomos | Black–and–white colobus | Colobus polykomos cytomegalovirus (CpolCMV) | [7] |
| Pilocolobus badius | Western red colobus | Piliocolobus badius cytomegalovirus (PbadCMV) | [9] |
| Cercopithecus aethiops | Grivet | Cercopithecine betaherpesvirus 5 (SCMV) * | [38] |
| Cercopithecus campbelli | Campbell’s monkey | Cercopithecus campbelli cytomegalovirus (CcamCMV) | [9] |
| Cercopithecus cephus | Moustached monkey | Cercopithecus cephus cytomegalovirus (CcepCMV) | AY728178.1 |
| Cercopithecus diana | Diana monkey | Cercopithecus diana cytomegalovirus (CdiaCMV) | [9] |
| Cercopithecus kandti | Golden monkey | Cercopithecus kandti cytomegalovirus (CkanCMV) | [36] |
| Cercocebus agilis | Agile mangabey | Cercocebus agilis cytomegalovirus (CagiCMV) | AY608713.1 |
| Cercocebus atys | Sooty mangabey | Cercocebus atys cytomegalovirus (CatyCMV) | [9] |
| Macaca fascicularis | Crab–eating macaque | Macacine betaherpesvirus 8 (CyCMV) * | [8] |
| Macaca mulatta | Rhesus macaque | Macacine betaherpesvirus 3 (RhCMV) * | [39] |
| Papio anubis | Olive baboon | Papiine betaherpesvirus 3 (BaCMV) | [40] |
| Papio cynocephalus | Yellow baboon | Papio cynocephalus cytomegalovirus (PcynCMV) | [40] |
| Papio ursinus | Chacma baboon | Papiine betaherpesvirus 4 (BaCMV) * | [43] |
| Mandrillus leucophaeus | Drill | Mandrilline betaherpesvirus 1 (MleuCMV) * | [43] |
| Mandrillus sphinx | Mandrill | Mandrillus sphinx cytomegalovirus (MsphCMV) | [35] |
| New World Monkeys | |||
| Sapajus apella | Tufted capuchin | Sapajus apella cytomegalovirus (SapeCMV) | [10] |
| Cebus albifrons | White–fronted capuchin | Cebine betaherpesvirus 1 (CalbCMV) | [10] |
| Cebus capucinus | White–headed capuchin | Cebine betaherpesvirus 1 (CcapCMV) | [10] |
| Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis | Black–capped squirrel monkey | Saimiri boliviensi cytomegalovirus (SbolCMV) | [10] |
| Saimiri sciureus | Squirrel monkey | Saimiriine betaherpesvirus 4 (SMCMV) * | [38] |
| Saimiri sciureus albigena | Colombian common squirrel monkey | Saimiri albigena cytomegalovirus (SalbCMV) | [10] |
| Aotus trivirgatus | Three–striped night monkey | Aotine betaherpesvirus 1 (OMCMV) * | [38] |
| Aotus vociferans | Spix’s night monkey | Aotus vociferans cytomegalovirus (AvocCMV) | [10] |
| Aotus nancimaae | Nancy Ma’s night monkey | Aotus nancymaae cytomegalovirus (AnanCMV) | [10] |
| Pithecia pithecia | White–faced saki | Pithecia pithecia cytomegalovirus (PpitCMV) | [10] |
| Alouatta macconelli | Guyanan red howler | Alouatta macconelli cytomegalovirus (AmacCMV) | [10] |
| Alouatta palliata | Mantled howler | Alouatta palliata cytomegalovirus (ApalCMV) | [10] |
| Alouatta seniculus | Venezuelan red howler | Alouatta seniculus cytomegalovirus (AsenCMV) | [10] |
| Ateles paniscus | Red–facied spider monkey | Ateles paniscus cytomegalovirus (ApanCMV) | [10] |
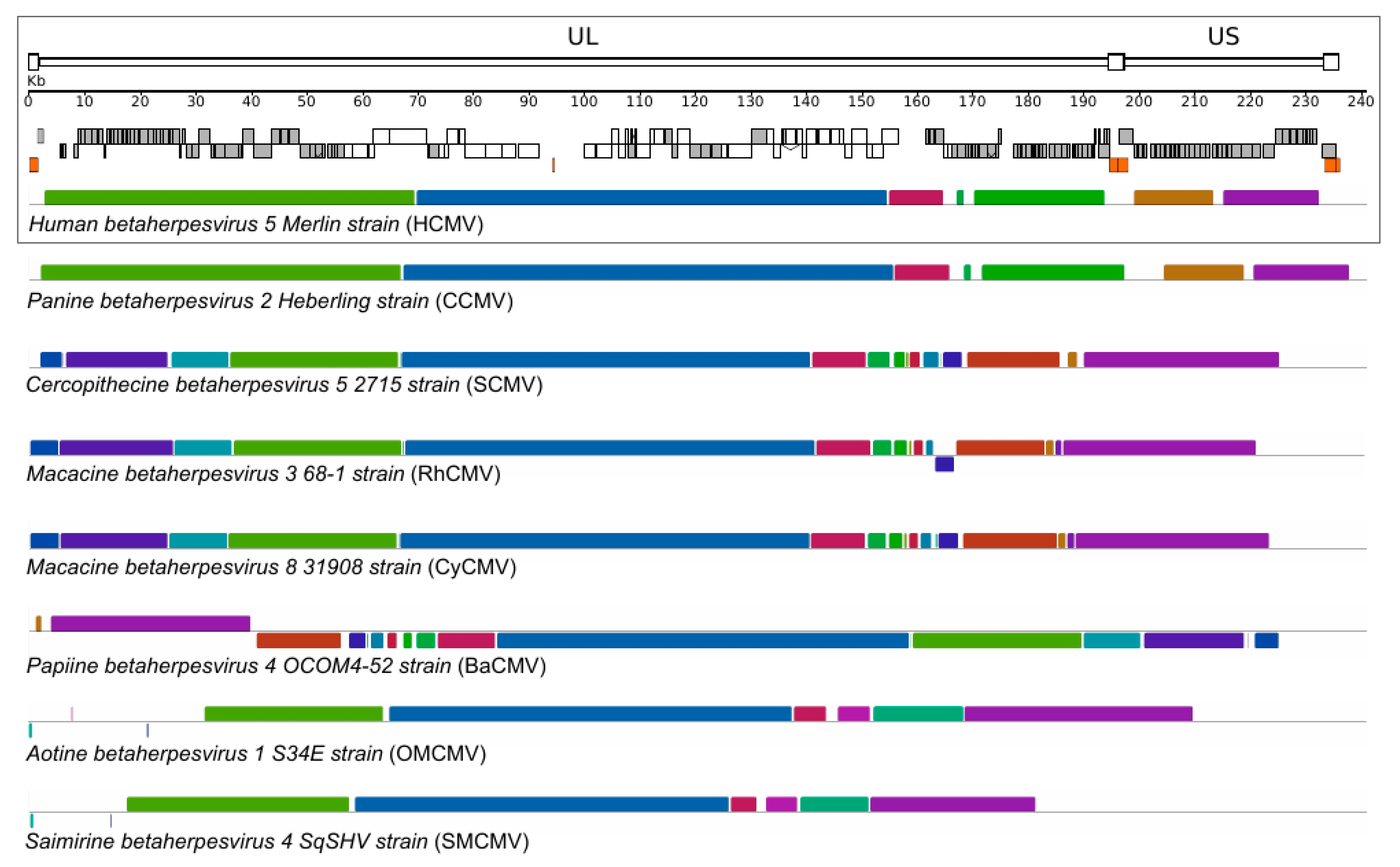
2. Diversity and Host–Specificity of Primate CMVs
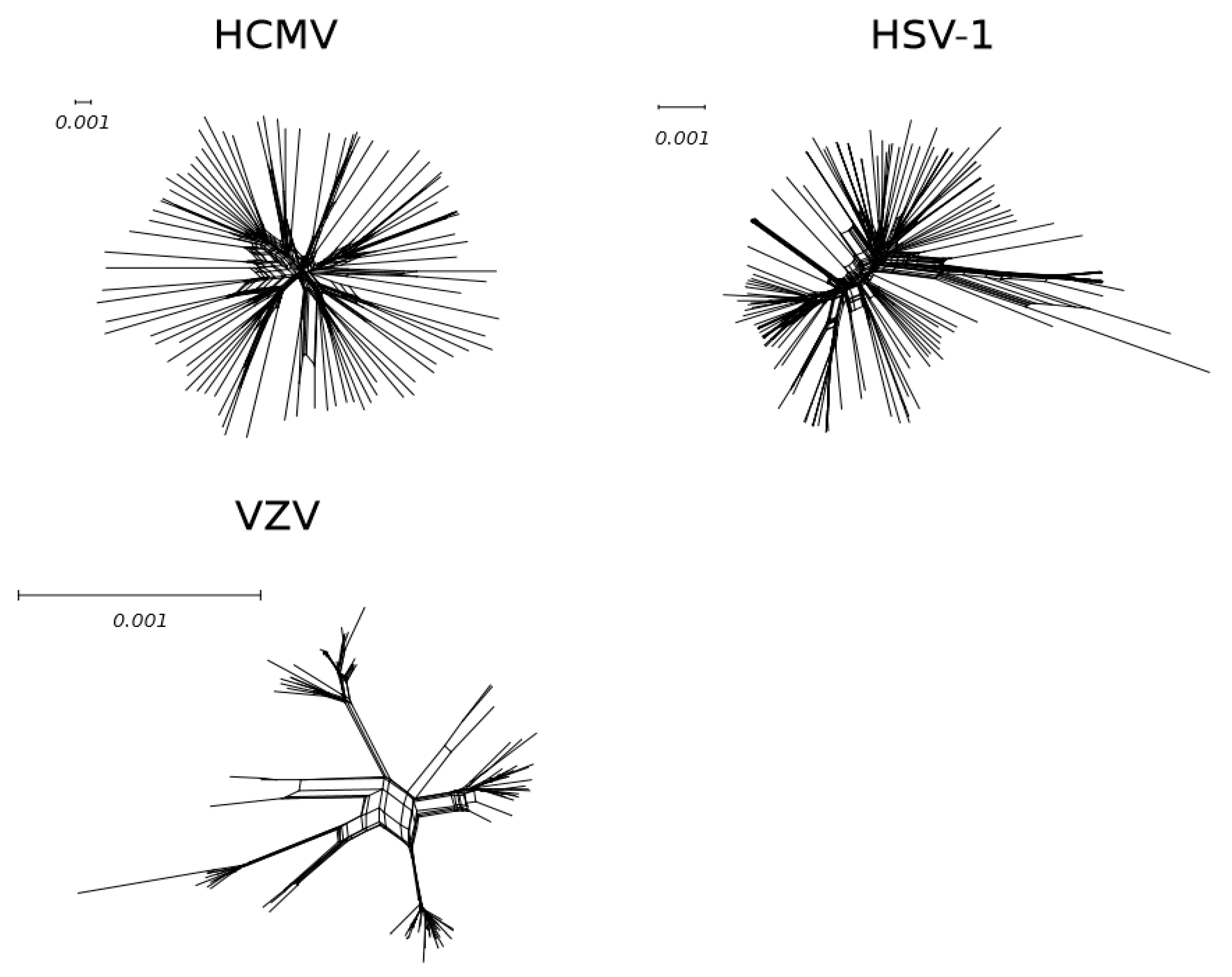
3. High Population–Level Diversity of Circulating HCMV Strains
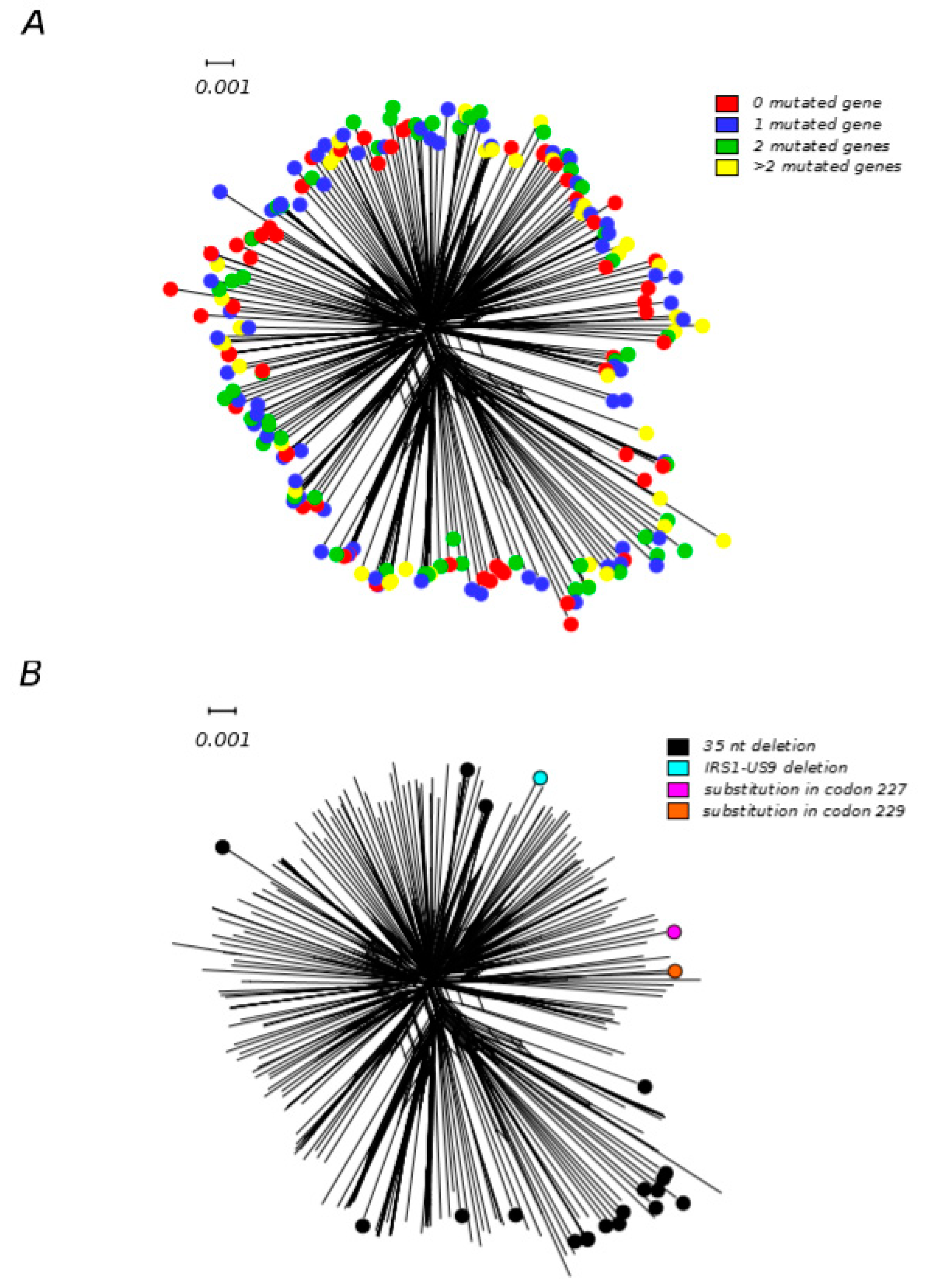
4. Frequency and Origin of Gene–Disrupting Mutations in HCMV Strains
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davison, A.J.; Eberle, R.; Ehlers, B.; Hayward, G.S.; McGeoch, D.J.; Minson, A.C.; Pellett, P.E.; Roizman, B.; Studdert, M.J.; Thiry, E. The Order Herpesvirales. Arch. Virol. 2008, 154, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.J. Comparative Analysis of the Genomes. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, J.L.; Barry, P.A. B-Virus (Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1) Infection in Humans and Macaques: Potential for Zoonotic Disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenzel, M.; Osborn, K.; Shima, A.; Klieforth, R.; Maalouf, G. Naturally occurring fatal herpes simplex virus 1 infection in a family of white-faced saki monkeys (Pithecia pithecia pithecia). J. Med. Primatol. 2003, 32, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, C.; Ochiai, Y.; Taniuchi, Y.; Takano, T.; Ueda, F.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Hondo, R. Specific Detection and Identification of Herpes B Virus by a PCR-Microplate Hybridization Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1869–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.C.; Stewart, J.; Haig, D.M. Malignant catarrhal fever: A review. Veter J. 2009, 179, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Metzger, S.; Nowak, K.; De Nys, H.M.; Boesch, C.; Wittig, R.; Jarvis, M.; Leendertz, F.H.; Ehlers, B. Absence of Frequent Herpesvirus Transmission in a Nonhuman Primate Predator-Prey System in the Wild. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10651–10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burwitz, B.J.; Malouli, D.; Bimber, B.N.; Reed, J.S.; Ventura, A.B.; Hancock, M.H.; Uebelhoer, L.S.; Bhusari, A.; Hammond, K.B.; Trethewy, R.G.E.; et al. Cross-Species Rhesus Cytomegalovirus Infection of Cynomolgus Macaques. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoh, A.E.; Murthy, S.; Koffi, C.A.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Leendertz, F.H.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Ehlers, B. Cytomegaloviruses in a Community of Wild Nonhuman Primates in Taï National Park, Côte D’Ivoire. Viruses 2017, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Donato, D.; Pouliquen, J.-F.; Ruiz-Garcia, M.; Lavergne, A.; Lacoste, V. DNA Polymerase Sequences of New World Monkey Cytomegaloviruses: Another Molecular Marker with Which to Infer Platyrrhini Systematics. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00980-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, A.; Cunningham, C.; Hector, R.; Hassan-Walker, A.F.; Lee, L.; Addison, C.; Dargan, D.J.; McGeoch, D.J.; Gatherer, D.; Emery, V.; et al. Genetic content of wild-type human cytomegalovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Yu, N.; Grimwood, J.; Schmutz, J.; Dickson, M.; Jarvis, M.; Hahn, G.; Nelson, J.A.; Myers, R.M.; Shenk, T.E. Coding potential of laboratory and clinical strains of human cytomegalovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14976–14981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeoch, D.J.; Rixon, F.J.; Davison, A.J. Topics in herpesvirus genomics and evolution. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, E.; Van Loock, M. Functional annotation of human cytomegalovirus gene products: An update. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z. MicroRNAs expressed by human cytomegalovirus. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple Alignment of Conserved Genomic Sequence with Rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple Genome Alignment with Gene Gain, Loss and Rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhair, M.; Smit, G.S.A.; Wallis, G.; Jabbar, F.; Smith, C.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Griffiths, P. Estimation of the worldwide seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckh, M.; Geballe, A.P. Cytomegalovirus: Pathogen, paradigm, and puzzle. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins-McMillen, D.; Buehler, J.C.; Peppenelli, M.; Goodrum, F. Molecular Determinants and the Regulation of Human Cytomegalovirus Latency and Reactivation. Viruses 2018, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Baraniak, I.; Reeves, M.B. The pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. J. Pathol. 2014, 235, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicklal, S.; Emery, V.; Lazzarotto, T.; Boppana, S.B.; Gupta, R.K. The “Silent” Global Burden of Congenital Cytomegalovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, J.; Touma, J.; Rahbar, A.; Söderberg-Naucler, C.; Vetvik, K. A Review of the Potential Role of Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Infections in Breast Cancer Carcinogenesis and Abnormal Immunity. Cancers 2019, 11, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauclér, C.S.; Geisler, J.; Vetvik, K. The emerging role of human cytomegalovirus infection in human carcinogenesis: A review of current evidence and potential therapeutic implications. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4333–4347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caposio, P.; Orloff, S.L.; Streblow, D.N. The role of cytomegalovirus in angiogenesis. Virus Res. 2010, 157, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, G.; Moss, A.C. Cytomegalovirus in inflammatory bowel disease: Pathogen or innocent bystander? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistuba-Hamprecht, K.; Frasca, D.; Blomberg, B.B.; Pawelec, G.; Derhovanessian, E. Age-associated alterations in γδ T-cells are present predominantly in individuals infected with Cytomegalovirus. Immun. Ageing 2013, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Larbi, A.; Özcelik, D.; Solana, R.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Attig, S.; Wikby, A.; Strindhall, J.; Franceschi, C.; Pawelec, G. Cytomegalovirus Infection: A Driving Force in Human T Cell Immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1114, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, T.; Hò, G.-G.T.; Pump, W.C.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Doeding, C. Battle between Host Immune Cellular Responses and HCMV Immune Evasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcami, A. Viral mimicry of cytokines, chemokines and their receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSharry, B.P.; Avdic, S.; Slobedman, B. Human Cytomegalovirus Encoded Homologs of Cytokines, Chemokines and their Receptors: Roles in Immunomodulation. Viruses 2012, 4, 2448–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, C.; Beisser, P.S.; Bruggeman, C.A. Molecular mimicry by cytomegaloviruses. Function of cytomegalovirus-encoded homologues of G protein-coupled receptors, MHC class I heavy chains and chemokines. Intervirology 1999, 42, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, S.; O’Brien, K.; Agbor, A.; Angedakin, S.; Arandjelovic, M.; Ayimisin, E.A.; Bailey, E.; Bergl, R.A.; Brazzola, G.; Dieguez, P.; et al. Cytomegalovirus distribution and evolution in hominines. Virus Evol. 2019, 5, vez015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, A.; Dolan, A.; Akter, P.; Addison, C.; Dargan, D.J.; Alcendor, D.; McGeoch, D.J.; Hayward, G.S. The human cytomegalovirus genome revisited: Comparison with the chimpanzee cytomegalovirus genome FN1. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leendertz, F.H.; Deckers, M.; Schempp, W.; Lankester, F.; Boesch, C.; Mugisha, L.; Dolan, A.; Gatherer, D.; McGeoch, D.J.; Ehlers, B. Novel cytomegaloviruses in free-ranging and captive great apes: Phylogenetic evidence for bidirectional horizontal transmission. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, T.S.; Gilardi, K.V.; Barry, P.A.; Ssebide, B.J.; Kinani, J.F.; Nizeyimana, F.; Noheri, J.B.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Mudakikwa, A.; Cranfield, M.R.; et al. Detection of viruses using discarded plants from wild mountain gorillas and golden monkeys. Am. J. Primatol. 2016, 78, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prepens, S.; Kreuzer, K.-A.; Leendertz, F.H.; Nitsche, A.; Ehlers, B. Discovery of herpesviruses in multi-infected primates using locked nucleic acids (LNA) and a bigenic PCR approach. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.J.; Holton, M.; Dolan, A.; Dargan, D.J.; Gatherer, D.; Hayward, G.S. Comparative genomics of primate cytomegaloviruses. Cytomegaloviruses Mol. Pathog. Interv. 2013, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, S.G.; Strelow, L.I.; Franchi, D.C.; Anders, D.G.; Wong, S.W. Complete Sequence and Genomic Analysis of Rhesus Cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6620–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, E.L.; White, G.; Saliki, J.T.; Eberle, R. Isolation and characterization of an endogenous cytomegalovirus (BaCMV) from baboons. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, P.A.; William Chang, W. Primate betaherpesviruses. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Itell, H.L.; Kaur, A.; Deere, J.D.; Barry, P.A.; Permar, S.R. Rhesus monkeys for a nonhuman primate model of cytomegalovirus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, E.L.; Sherrod, C.J.; Texier, J.R.; Conrad, T.M.; Dittmer, D.P. Complete Genome Sequences of Mandrillus leucophaeus and Papio ursinus Cytomegaloviruses. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00781-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, P.H.; Hartley, J.W.; Rowe, W.P. Isolation of a Cytomegalovirus from African Green Monkey. Exp. Boil. Med. 1963, 112, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.S.; Kilpatrick, B.; Lakeman, A.; Alford, C.A. Genetic analysis of a cytomegalovirus-like agent isolated from human brain. J. Virol. 1978, 26, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.J.; Zeng, L.C.; Ahmed, K.; Roy, M. Cytomegalovirus-related sequence in an atypical cytopathic virus repeatedly isolated from a patient with chronic fatigue syndrome. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.; Ahmed, K.N.; Zeng, L.C.; Olsen, J.-C.; Seward, J.G.; Seehrai, J.S. African green monkey origin of the atypical cytopathic ‘stealth virus’ isolated from a patient with chronic fatigue syndrome. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1995, 4, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, M.G.; Jenkins, F.J.; George, K.S.; Nalesnik, M.A.; Starzl, T.E.; Rinaldo, C.R. Detection of Infectious Baboon Cytomegalovirus after Baboon-to-Human Liver Xenotransplantation. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2825–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeoch, D.J.; Cook, S.; Dolan, A.; Jamieson, F.E.; Telford, E.A. Molecular Phylogeny and Evolutionary Timescale for the Family of Mammalian Herpesviruses. J. Mol. Boil. 1995, 247, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.; Marsh, A.K.; Willer, D.O.; Ambagala, A.P.N.; Dzamba, M.; Chan, J.K.; Pilon, R.; Fournier, J.; Brudno, M.; Antony, J.M.; et al. A novel strain of cynomolgus macaque cytomegalovirus: Implications for host-virus co-evolution. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.K.; Willer, D.O.; Ambagala, A.P.N.; Dzamba, M.; Chan, J.K.; Pilon, R.; Fournier, J.; Sandstrom, P.; Brudno, M.; Macdonald, K.S. Genomic Sequencing and Characterization of Cynomolgus Macaque Cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12995–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, A.E.; Shenk, T. Efficient replication of rhesus cytomegalovirus variants in multiple rhesus and human cell types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19950–19955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perot, K.; Walker, C.M.; Spaete, R.R. Primary chimpanzee skin fibroblast cells are fully permissive for human cytomegalovirus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 3281–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Maul, G.G. Mouse Cytomegalovirus Crosses the Species Barrier with Help from a Few Human Cytomegalovirus Proteins. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7510–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Child, S.J.; Brennan, G.; Braggin, J.E.; Geballe, A.P. Species Specificity of Protein Kinase R Antagonism by Cytomegalovirus TRS1 Genes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3880–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fioretti, A.; Furukawa, T.; Santoli, D.; Plotkin, S.A. Nonproductive Infection of Guinea Pig Cells with Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. 1973, 11, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFemina, R.L.; Hayward, G.S. Differences in Cell Type-specific Blocks to Immediate Early Gene Expression and DNA Replication of Human, Simian and Murine Cytomegalovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsmore, V.; Reid, G.G.; Stow, N.D. Detection of human cytomegalovirus DNA replication in non-permissive Vero and 293 cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocarski, E., Jr. Betaherpes viral genes and their functions. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, A.K.; Ambagala, A.P.; Perciani, C.T.; Russell, J.; Chan, J.K.; Janes, M.; Antony, J.M.; Pilon, R.; Sandstrom, P.; Willer, D.O.; et al. Examining the Species-Specificity of Rhesus Macaque Cytomegalovirus (RhCMV) in Cynomolgus Macaques. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ambagala, A.P.; Marsh, A.K.; Chan, J.K.; Mason, R.; Pilon, R.; Fournier, J.; Sandstrom, P.; Willer, D.O.; Macdonald, K.S. Establishment of an immortal cynomolgus macaque fibroblast cell line for propagation of cynomolgus macaque cytomegalovirus (CyCMV). Arch. Virol. 2012, 158, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaletskaya, A.; Bartle, L.M.; Chittenden, T.; McCormick, A.L.; Mocarski, E.S.; Goldmacher, V.S. A cytomegalovirus-encoded inhibitor of apoptosis that suppresses caspase-8 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7829–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckman, B.J.; Rainish, B.L.; Chase, M.C.; Borton, J.A.; Nelson, J.A.; Jarvis, M.; Johnson, D.C. Characterization of the Human Cytomegalovirus gH/gL/UL128-131 Complex That Mediates Entry into Epithelial and Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2007, 82, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcendor, D.; Zong, J.; Dolan, A.; Gatherer, D.; Davison, A.J.; Hayward, G.S. Patterns of divergence in the vCXCL and vGPCR gene clusters in primate cytomegalovirus genomes. Virology 2009, 395, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarborough, J.A.; Paul, J.R.; Spencer, J. Evolution of the ability to modulate host chemokine networks via gene duplication in human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 51, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurak, I.; Brune, W. Induction of apoptosis limits cytomegalovirus cross-species infection. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, U.; Handke, W.; Jurak, I.; Brune, W. Mutations in the M112/M113-Coding Region Facilitate Murine Cytomegalovirus Replication in Human Cells. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7994–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sironi, M.; Cagliani, R.; Forni, D.; Clerici, M. Evolutionary insights into host–pathogen interactions from mammalian sequence data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozzi, A.; Biolatti, M.; Cagliani, R.; Forni, D.; Dell’Oste, V.; Pontremoli, C.; Vantaggiato, C.; Pozzoli, U.; Clerici, M.; Landolfo, S.; et al. Past and ongoing adaptation of human cytomegalovirus to its host. PLoS Pathog. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, W.; Chou, C.; Li, H.; Hai, R.; Patterson, D.; Stolc, V.; Zhu, H.; Liu, F. Functional profiling of a human cytomegalovirus genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14223–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, M.S.; Bankier, A.T.; Beck, S.; Bohni, R.; Brown, C.M.; Černý, R.; Horsnell, T.; Hutchison, C.A.; Kouzarides, T.; Martignetti, J.A.; et al. Analysis of the Protein-Coding Content of the Sequence of Human Cytomegalovirus Strain AD169. Hantaviruses 1990, 154, 125–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, T.A.; Tom, E.; Kemble, G.W.; Duke, G.M.; Mocarski, E.S.; Spaete, R.R. Human cytomegalovirus clinical isolates carry at least 19 genes not found in laboratory strains. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, N.M.; Wilkie, G.S.; Hage, E.; Camiolo, S.; Holton, M.; Hughes, J.; Maabar, M.; Vattipally, S.B.; Dhingra, A.; Gompels, U.A.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus Genomes Sequenced Directly from Clinical Material: Variation, Multiple-Strain Infection, Recombination, and Gene Loss. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, N.M.; Musonda, K.G.; Escriva, E.; Njenga, M.; Agbueze, A.; Camiolo, S.; Davison, A.J.; Gompels, U.A. Multiple-Strain Infections of Human Cytomegalovirus with High Genomic Diversity Are Common in Breast Milk from Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Infected Women in Zambia. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijmons, S.; Thys, K.; Ngwese, M.M.; Van Damme, E.; Dvorak, J.; Van Loock, M.; Li, G.; Tachezy, R.; Busson, L.; Aerssens, J.; et al. High-Throughput Analysis of Human Cytomegalovirus Genome Diversity Highlights the Widespread Occurrence of Gene-Disrupting Mutations and Pervasive Recombination. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7673–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzette, N.; Pokalyuk, C.; Gibson, L.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Schleiss, M.R.; Hamprecht, K.; Yamamoto, A.Y.; Mussi-Pinhata, M.M.; Britt, W.J.; Jensen, J.D.; et al. Limits and patterns of cytomegalovirus genomic diversity in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4120–E4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijmons, S.; Thys, K.; Corthout, M.; Van Damme, E.; Van Loock, M.; Bollen, S.; Baguet, S.; Aerssens, J.; Van Ranst, M.; Maes, P. A Method Enabling High-Throughput Sequencing of Human Cytomegalovirus Complete Genomes from Clinical Isolates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, E.; Wilkie, G.S.; Linnenweber-Held, S.; Dhingra, A.; Suárez, N.M.; Schmidt, J.J.; Kay-Fedorov, P.C.; Mischak-Weissinger, E.; Heim, A.; Schwarz, A.; et al. Characterization of Human Cytomegalovirus Genome Diversity in Immunocompromised Hosts by Whole-Genome Sequencing Directly from Clinical Specimens. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, D.; Pontremoli, C.; Clerici, M.; Pozzoli, U.; Cagliani, R.; Sironi, M. Recent Out-of-Africa Migration of Human Herpes Simplex Viruses. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2020, msaa001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontremoli, C.; Forni, D.; Clerici, M.; Cagliani, R.; Sironi, M. Possible European origin of circulating Varicella-zoster virus strains. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 221, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of Phylogenetic Networks in Evolutionary Studies. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2005, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, L.; Riquelme, I.; Buchegger, K.; Abanto, M.; Ili, C.; Brebi, P. A reliable Epstein-Barr Virus classification based on phylogenomic and population analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Sauerbrei, A. Evolution and world-wide distribution of varicella–zoster virus clades. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiara, M.; Manzari, C.; Lionetti, C.; Mechelli, R.; Anastasiadou, E.; Buscarinu, M.C.; Ristori, G.; Salvetti, M.; Picardi, E.; D’Erchia, A.M.; et al. Geographic Population Structure in Epstein-Barr Virus Revealed by Comparative Genomics. Genome Boil. Evol. 2016, 8, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegner, F.; Lassalle, F.; Depledge, D.P.; Balloux, F.; Breuer, J. Co-evolution of sites under immune selection shapes Epstein-Barr Virus population structure. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2019, 36, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpara, M.L.; Gatherer, D.; Ochoa, A.; Greenbaum, B.; Dolan, A.; Bowden, R.J.; Enquist, L.W.; Legendre, M.; Davison, A.J. Evolution and Diversity in Human Herpes Simplex Virus Genomes. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 1209–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassalle, F.; Depledge, D.P.; Reeves, M.B.; Brown, A.C.; Christiansen, M.T.; Tutill, H.J.; Williams, R.J.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Holdstock, J.; Atkinson, C.; et al. Islands of linkage in an ocean of pervasive recombination reveals two-speed evolution of human cytomegalovirus genomes. Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrel, S.; Désiré, N.; Marlet, J.; Dacheux, L.; Seang, S.; Caumes, E.; Bourhy, H.; Agut, H.; Boutolleau, D. Genetic Diversity within Alphaherpesviruses: Characterization of a Novel Variant of Herpes Simplex Virus 2. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12273–12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudini, J.; Roy, S.; Houldcroft, C.J.; Bryant, J.M.; Depledge, D.P.; Tutill, H.; Veys, P.; Williams, R.; Worth, A.J.J.; Tamuri, A.U.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus haplotype reconstruction reveals high diversity due to superinfection and evidence of within-host recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5693–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, S.; Monte, P.D.; Rossini, G.; Landini, M.P. Genetic polymorphisms among human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) wild-type strains. Rev. Med. Virol. 2004, 14, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.A.; Dyer, A.P.; Milne, R.S.; Sevilla-Reyes, E.; Gompels, U.A. A Role for Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein O (gO) in Cell Fusion and a New Hypervariable Locus. Virology 2002, 293, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzette, N.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Jensen, J.D.; Gibson, L.; Kowalik, T.F. Extensive Genome-Wide Variability of Human Cytomegalovirus in Congenitally Infected Infants. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangherlin, L.M.; De Paula, F.N.; Icimoto, M.; Ruiz, L.G.P.; Nogueira, M.L.; Braz, A.S.; Juliano, L.; Da Silva, M.C.C. Positively Selected Sites at HCMV gB Furin Processing Region and Their Effects in Cleavage Efficiency. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolitz, J.; Schwing, C.; Chang, J.; Van Ryk, N.; Nawaz, F.; Wei, D.; Cicala, C.; Arthos, J.; Fauci, A.S. Signal peptide of HIV envelope protein impacts glycosylation and antigenicity of gp120. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2443–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargan, D.J.; Douglas, E.; Cunningham, C.; Jamieson, F.; Stanton, R.J.; Baluchova, K.; McSharry, B.P.; Tomasec, P.; Emery, V.; Percivalle, E.; et al. Sequential mutations associated with adaptation of human cytomegalovirus to growth in cell culture. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijmons, S.; Van Ranst, M.; Maes, P. Genomic and Functional Characteristics of Human Cytomegalovirus Revealed by Next-Generation Sequencing. Viruses 2014, 6, 1049–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.; Gatherer, D.; Hilfrich, B.; Baluchova, K.; Dargan, D.J.; Thomson, M.; Griffiths, P.D.; Wilkinson, G.W.G.; Schulz, T.F.; Davison, A.J. Sequences of complete human cytomegalovirus genomes from infected cell cultures and clinical specimens. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 91, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zárate, S.; Pond, S.L.K.; Shapshak, P.; Frost, S.D.W. Comparative Study of Methods for Detecting Sequence Compartmentalization in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6643–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: Hypothesis Testing Using Phylogenies. Mod. Infect. Dis. Epidemiol. 2005, 21, 125–181. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Park, A.; Kang, S.; Lee, E.; Lee, T.A.; Ra, E.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Park, B. Human cytomegalovirus-encoded US9 targets MAVS and STING signaling to evade type I interferon immune responses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolatti, M.; Gugliesi, F.; Dell’Oste, V.; Landolfo, S. Modulation of the innate immune response by human cytomegalovirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 64, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Edlich, F.; Bermejo, G.A.; Norris, K.L.; Youle, R.J.; Tjandra, N. Structural mechanism of Bax inhibition by cytomegalovirus protein vMIA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20901–20906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coaquette, A.; Bourgeois, A.; Dirand, C.; Varin, A.; Chen, W.; Herbein, G. Mixed Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B Genotypes in Immunocompromised Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, L.; Tong, Y.; Kumar, D.; Pang, X.; Åsberg, A.; Hartmann, A.; Rollag, H.; Jardine, A.; Pescovitz, M.; Humar, A. Analysis and clinical correlation of genetic variation in cytomegalovirus. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2011, 14, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houldcroft, C.J.; Bryant, J.M.; Depledge, D.P.; Margetts, B.K.; Simmonds, J.; Nicolaou, S.; Tutill, H.J.; Williams, R.; Worth, A.J.J.; Marks, S.D.; et al. Detection of Low Frequency Multi-Drug Resistance and Novel Putative Maribavir Resistance in Immunocompromised Pediatric Patients with Cytomegalovirus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cagliani, R.; Forni, D.; Mozzi, A.; Sironi, M. Evolution and Genetic Diversity of Primate Cytomegaloviruses. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050624
Cagliani R, Forni D, Mozzi A, Sironi M. Evolution and Genetic Diversity of Primate Cytomegaloviruses. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(5):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCagliani, Rachele, Diego Forni, Alessandra Mozzi, and Manuela Sironi. 2020. "Evolution and Genetic Diversity of Primate Cytomegaloviruses" Microorganisms 8, no. 5: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050624
APA StyleCagliani, R., Forni, D., Mozzi, A., & Sironi, M. (2020). Evolution and Genetic Diversity of Primate Cytomegaloviruses. Microorganisms, 8(5), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050624







