Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
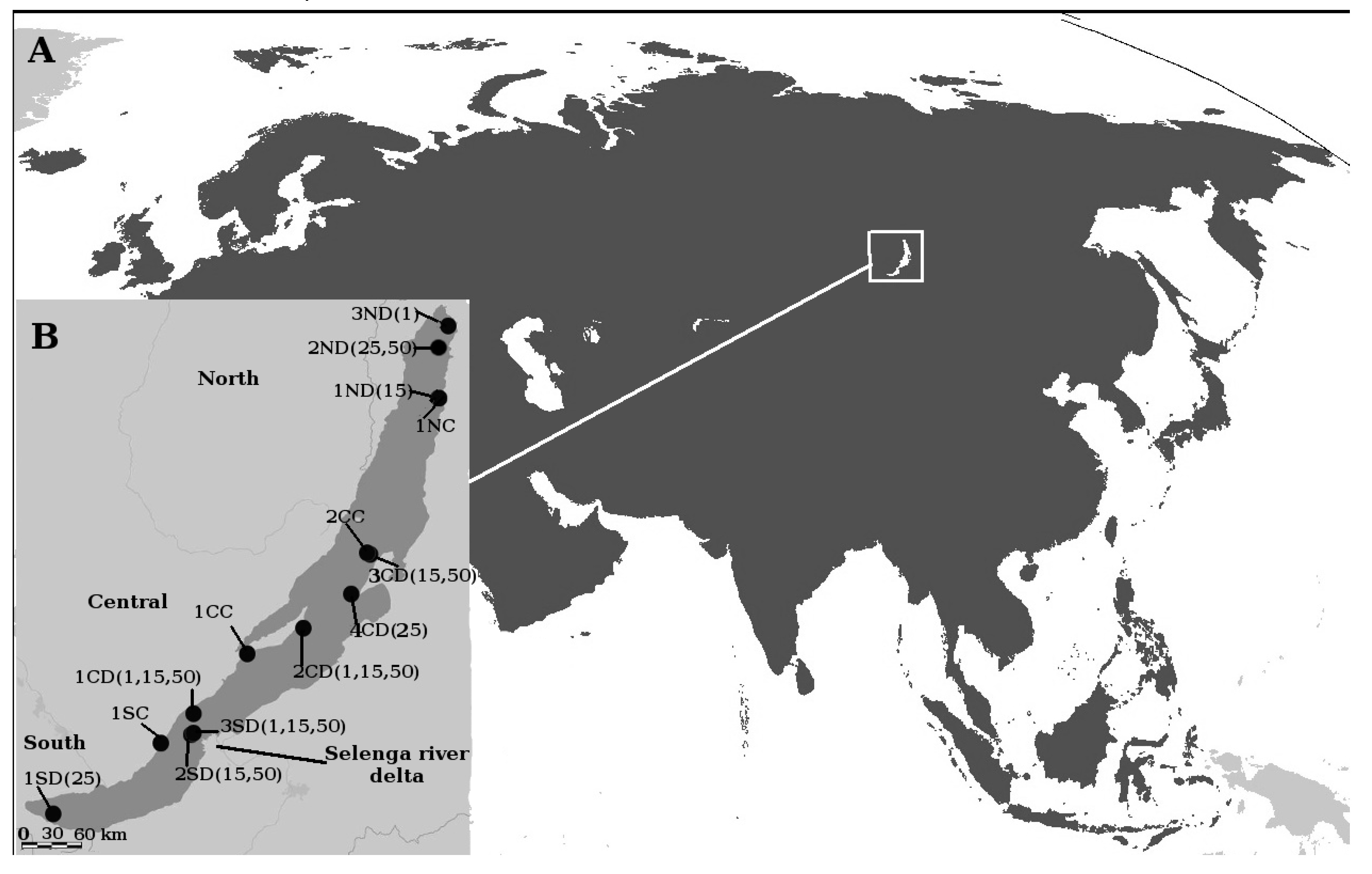
2.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Sequencing of 18S rRNA Genes
2.2. V4-Amplicon Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
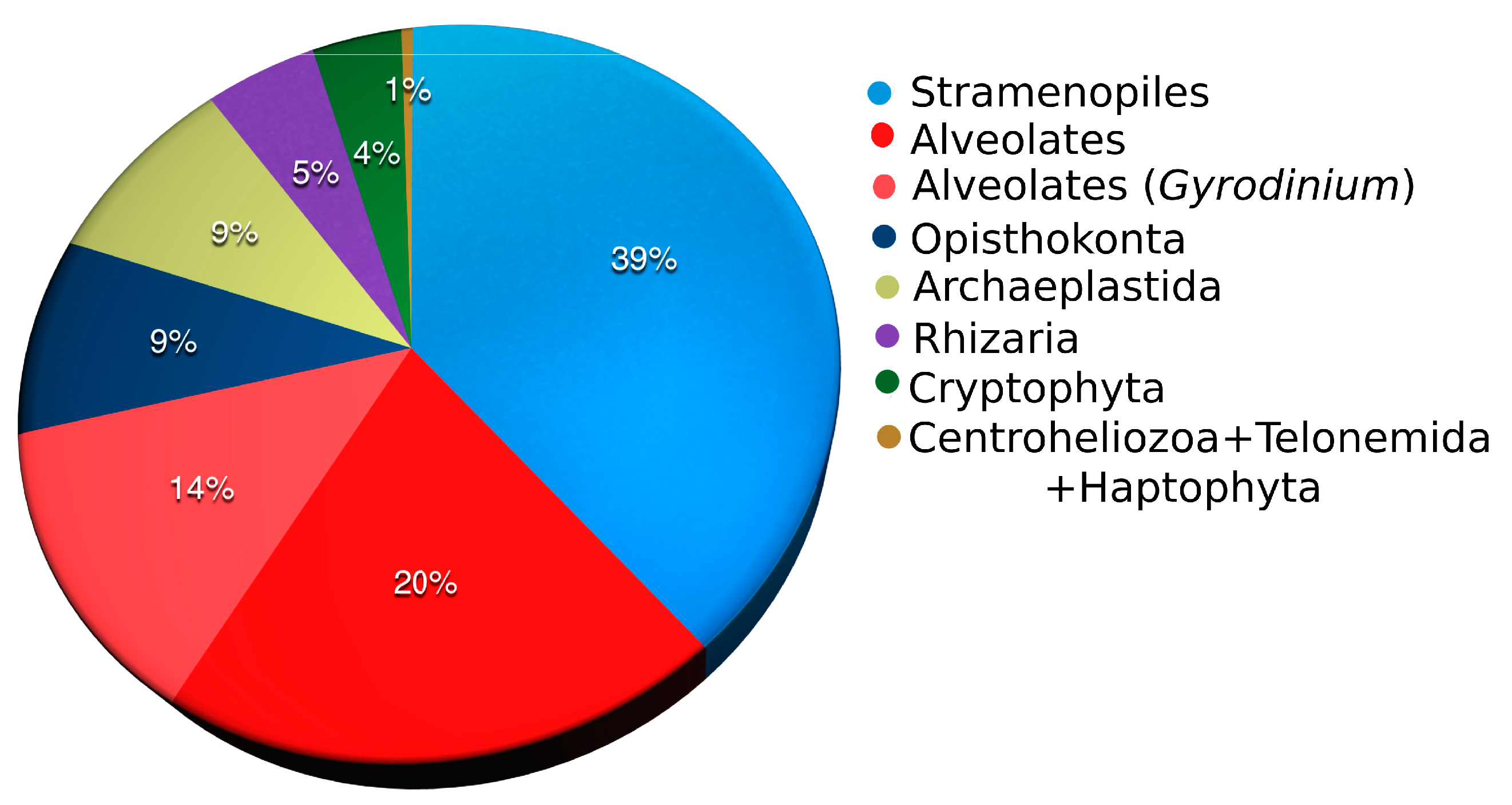
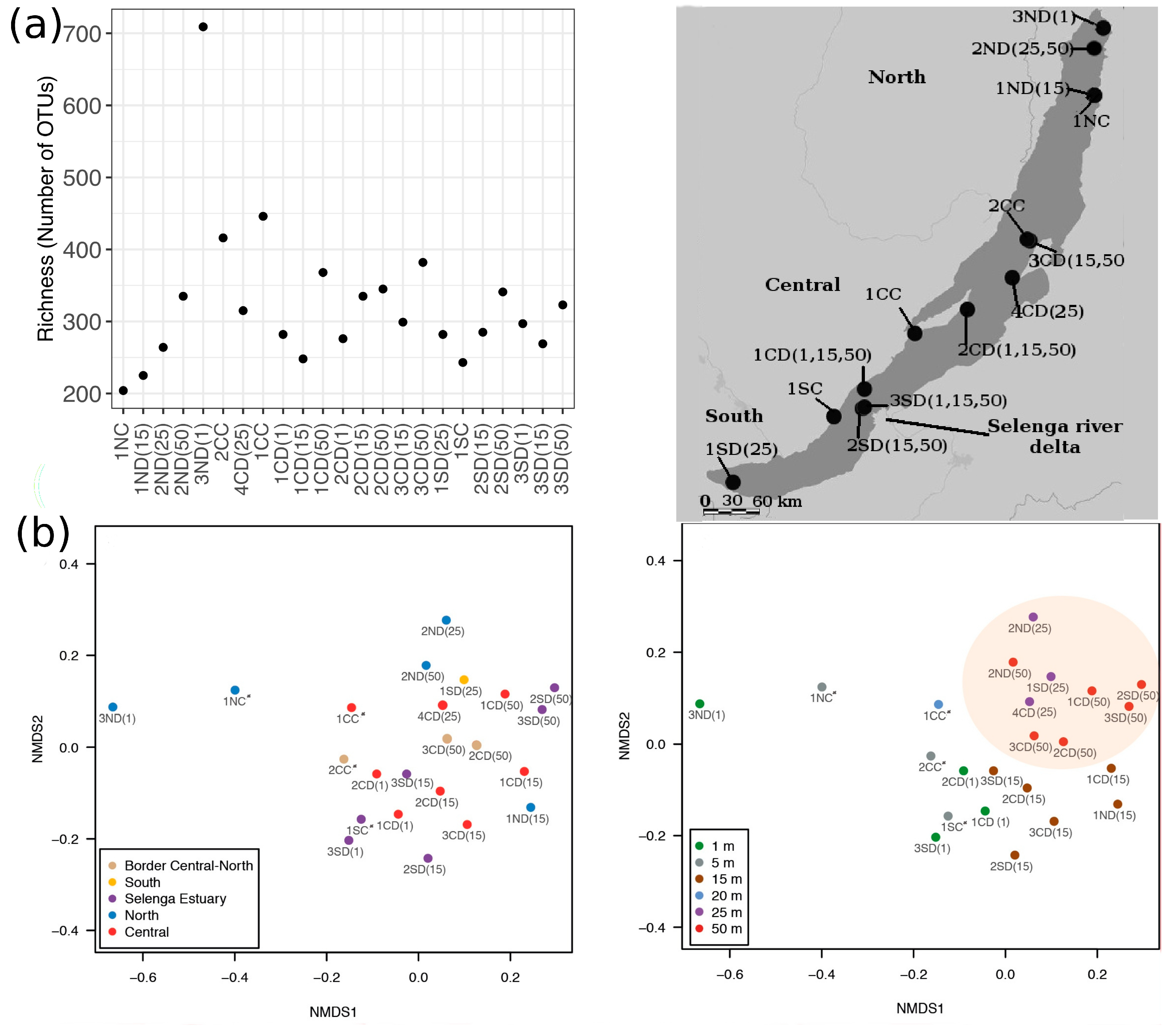
3.1. Protist Composition
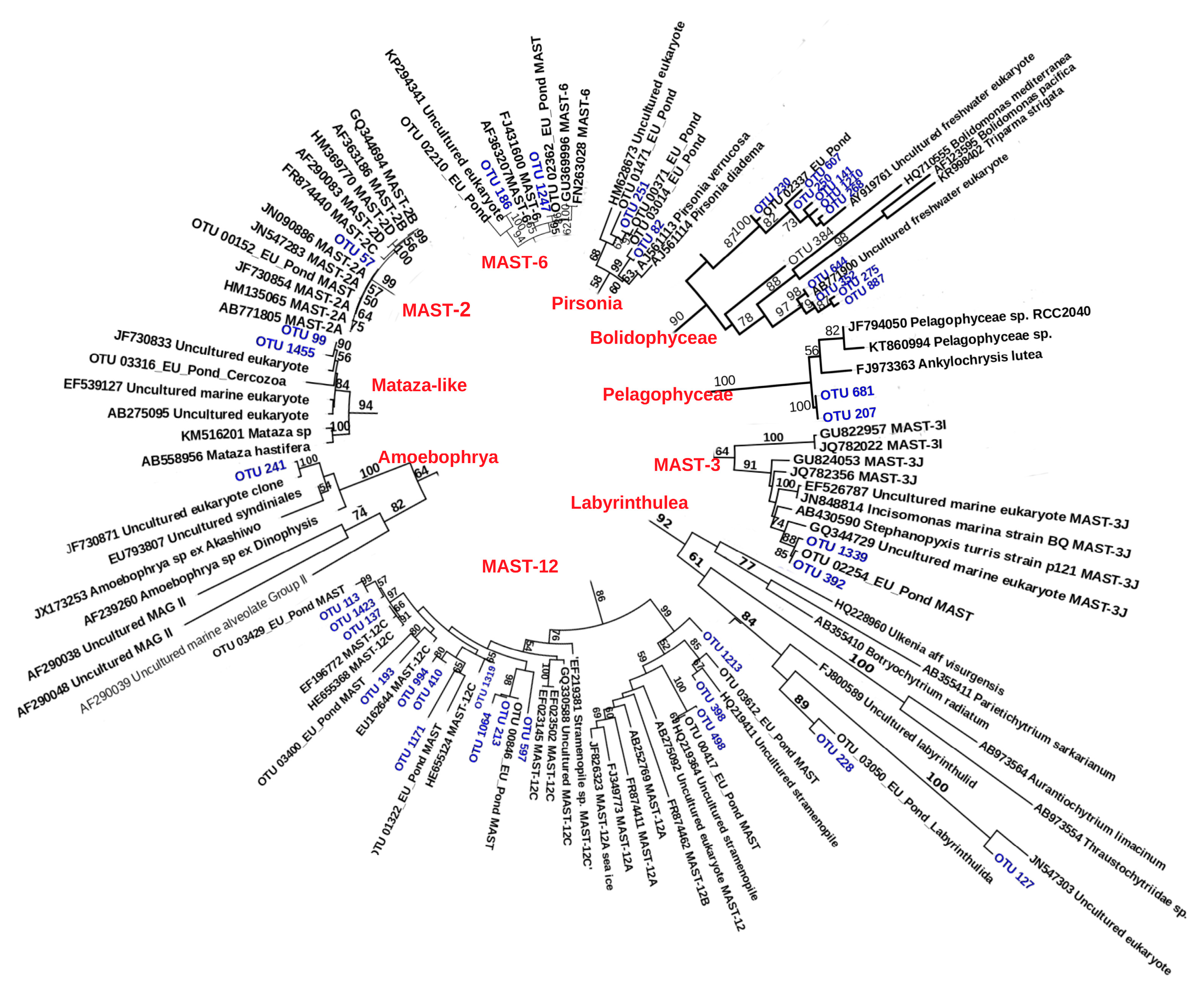
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships
3.3. Presence of Species Flocks
3.4. Potentially Endemic Baikal OTUs
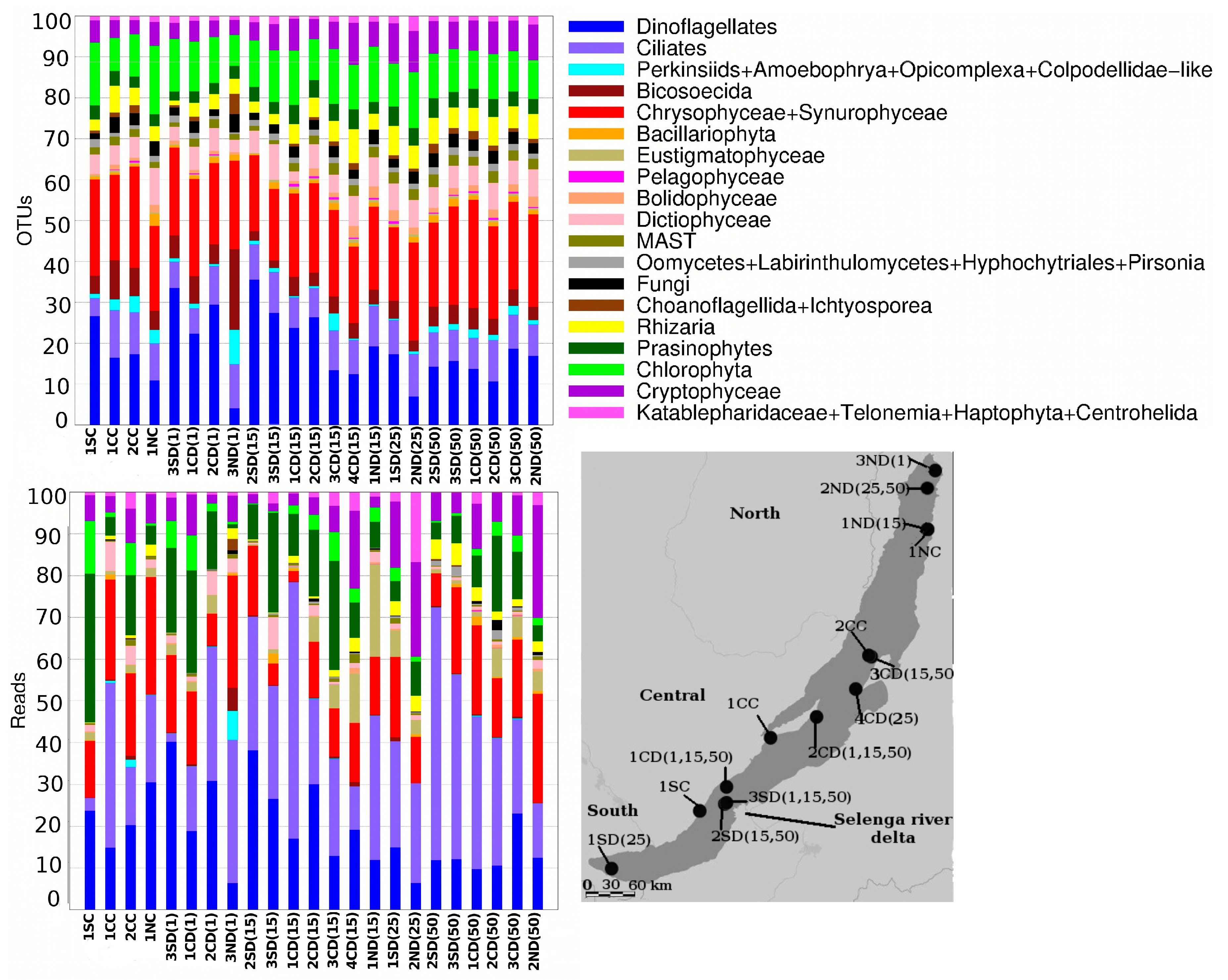
3.5. Community Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Freshwater and Marine Lineages in Lake Baikal
4.2. Did Lake Baikal Protists Radiate?
4.3. Potential Endemism within Baikal Protists
4.4. Community Structure of Small Baikal Protists
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logares, R.; Haverkamp, T.H.; Kumar, S.; Lanzén, A.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Quince, C.; Kauserud, H. Environmental microbiology through the lens of high-throughput DNA sequencing: Synopsis of current platforms and bioinformatics approaches. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 91, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrós-Alió, C.; Acinas, S.G.; Logares, R.; Massana, R. Marine microbial diversity as seen by high-throughput sequencing. In Microbial Ecology of the Oceans, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 47–97. ISBN 978-1-119-10718-7. [Google Scholar]
- de Vargas, C.; Audic, S.; Henry, N.; Decelle, J.; Mahé, F.; Logares, R.; Lara, E.; Berney, C.; Le Bescot, N.; Probert, I.; et al. Eukaryotic plankton diversity in the sunlit global ocean. Science 2015, 348, 1261605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaulot, D.; Eikrem, W.; Viprey, M.; Moreau, H. The diversity of small eukaryotic phytoplankton (≤ 3 μm) in marine ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massana, R. Eukaryotic Picoplankton in Surface Oceans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepère, C.; Domaizon, I.; Debroas, D. Unexpected importance of potential parasites in the composition of the freshwater small-eukaryote community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Álvarez, R.; Catalan, J.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Camarero, L.; Casamayor, E.O.; Catalan, J. High planktonic diversity in mountain lakes contains similar contributions of autotrophic, heterotrophic and parasitic eukaryotic life forms. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.; Thénot, A. Genetic diversity of small eukaryotes in lakes differing by their trophic status. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5935–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; Moreira, D.; López-García, P. The extent of protist diversity: Insights from molecular ecology of freshwater eukaryotes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 2005, 272, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.A.; Vepritskiy, A.A.; Gouliamova, D.E.; Nierzwicki-Bauer, S.A. The molecular diversity of fresh-water picoeukaryotes from an oligotrophic lake reveals diverse, distinctive and globally dispersed lineages. Environ. Microb. 2005, 7, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, A.; Filker, S.; Breiner, H.; Stoeck, T. Eukaryotic communities in a meromictic lake. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Jardillier, L.; Deschamps, P.H.; Moreira, D.; Restoux, G.; Bertolino, P.; López-García, P. Complex communities of small protists and unexpected occurrence of typical marine lineages in shallow freshwater systems. Environ. Microb. 2015, 17, 3610–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahoon, A.B.; Huffman, A.G.; Krager, M.M.; Crowell, R.M. A meta-barcoding census of freshwater planktonic protists in Appalachia–Natural Tunnel State Park, Virginia, USA. MBMG 2018, 2, e26939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentendu, G.; Buosi, P.R.; Cabral, A.F.; Trevizan Segóvia, B.; Ramos Meira, B.; Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Velho, L.F.; Ritter, C.D.; Dunthorn, M. Protist Biodiversity and Biogeography in Lakes from Four Brazilian River–Floodplain Systems. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2019, 66, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debroas, D.; Domaizon, I.; Humbert, J.-F.; Jardillier, L.; Lepère, C.; Oudart, A.; Taïb, N. Overview of freshwater microbial eukaryotes diversity: A first analysis of publicly available metabarcoding data. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Bronner, G.; Lepère, C.; Kong, F.; Shi, X. Temporal and spatial variations in the composition of freshwater photosynthetic picoeukaryotes revealed by MiSeq sequencing from flow cytometry sorted samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2286–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerlander, B.; Breiner, H.-W.; Filker, S.; Sommaruga, R.; Sonntag, B.; Stoeck, T. High diversity of protistan plankton communities in remote high mountain lakes in the European Alps and the Himalayan mountains. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timoshkin, O.A. Main Tendencies in Research of Ancient Lake Biodiversity; most Interesting Recent Discoveries in Biodiversity of Lake Baikal. In Index of Animal Species Inhabiting Lake Baikal and Its Catchment Area; Timoshkin, O.A., Ed.; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 1423–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Mats, V.D.; Shcherbakov, D.Y.; Efimova, I.M. Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic history of the Lake Baikal depression and formation of its unique biodiversity. Strat. Geo Correl. 2011, 19, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbakov, D.Y. Molecular phylogenetic studies on the origin of biodiversity in Lake Baikal. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Izmest’eva, L.R.; Moore, M.V.; Katz, S.L.; Dennis, B.; Silow, E.A. Sixty years of environmental change in the world’s largest freshwater lake—Lake Baikal, Siberia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovskaya, G.I. Ecological monitoring of phytoplankton in Lake Baikal. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Logacheva, N.F. Structural Changes in Phytoplankton of the Littoral Zone of Lake Baikal. Hydrobiol. J. 2017, 53, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkina, L.A. New species of the family Colepidae (Prostomatida, Ciliophora) from Lake Baikal. Zool. Zh. 1995, 74, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pronin, N.M. List of parasitofauna species. In Lake Baikal: Evolution and Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Kozhova, O.M., Izmest’eva, L.R., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, NL, USA, 1998; pp. 417–447. ISBN 9789057820014. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikovskiy, M.S.; Lang-Bertalot, H.; Kuznetsova, I.V. Lake Baikal: Hotspot of Endemic Diatoms: II. Iconographia Diatomologic; Koeltz Scientific Books: Oberreifenberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783874294904. [Google Scholar]
- Annenkova, N.V.; Hansen, G.; Moestrup, Ø.; Rengefors, K. Recent adaptive radiation in a marine and freshwater dinoflagellate species flock. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Berney, C.; Hartikainen, H.; Mahamdallie, S.H.; Gardner, M.; Boenigk, J.; Cavalier-Smith, T.; Bass, D. High throughput sequencing of microbial eukaryotes in Lake Baikal reveals ecologically differentiated communities and novel evolutionary radiations. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, I.S.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Bukin, Y.U.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Petrova, D.P.; Sakirko, M.V.; Likhoshway, E.V. Co-occurrence Networks Among Bacteria and Microbial Eukaryotes of Lake Baikal During a Spring Phytoplankton Bloom. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Stoeck, T.; Bass, D.; Nebel, M.; Christen, R.; Jones, M.D.; Breiner, H.W.; Richards, T.A. Multiple marker parallel tag environmental DNA sequencing reveals a highly complex eukaryotic community in marine anoxic water. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R. Workflow for Analysing MiSeq Amplicons Based on Uparse v1.5. 2017. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.259579 (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Nikolenko, S.I.; Korobeynikov, A.I.; Alekseyev, M.A. BayesHammer: Bayesian clustering for error correction in single-cell sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Ijaz, U.Z.; D’Amore, R.; Hall, N.; Sloan, W.T.; Quince, C. Insight into biases and sequencing errors for amplicon sequencing with the Illumina MiSeq platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, D.A.; Hu, S.K. Are We Overestimating Protistan Diversity in Nature? Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. JMB 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logares, R. Available online: https://github.com/ramalok (accessed on 10 June 2017).
- Pernice, M.C.; Logares, R.; Guillou, L.; Massana, R. General patterns of diversity in major marine microeukaryote lineages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massana, R.; Gobet, A.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Chambouvet, A.; Christen, R.; Claverie, J.-M.; Decelle, J.; et al. Marine protist diversity in European coastal waters and sediments as revealed by high-throughput sequencing. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4035–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R. Available online: https://github.com/ramalok/filtering.blast.results (accessed on 25 June 2017).
- European Nucleotide Archive Home Page. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2019. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Schluter, D. The Ecology of Adaptive Radiation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, S. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R.; Mangot, J.F.; Massana, R. Rarity in aquatic microbes: Placing protists on the map. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, L.N.; Zhuang, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, S. Phylogenetic analysis guided by intragenomic SSU rDNA polymorphism refines classification of “Alexandrium tamarense” species complex. Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinomiya, M.; dos Santos, A.; Gourvil, P.; Yoshikawa, S.; Kamiya, M.; Ohki, K.; Audic, S.; de Vargas, C.; Noël, M.-H.; Vaulot, D.; et al. Diversity and oceanic distribution of the Parmales (Bolidophyceae), a picoplanktonic group closely related to diatoms. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2419–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevia-Orube, J.; Orive, E.; David, H.; Díez, A.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Miguel, I.; Seoane, S. Molecular and morphological analyses of solitary forms of brackish Thalassiosirioid diatoms (Coscinodiscophyceae), with emphasis on their phenotypic plasticity. Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishniac, H.A.; Hempfling, W.P. Cryptococcus vishniacii sp. nov., an Antarctic yeast. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1979, 29, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, R.; Ni, Y. Habitat-specificity and diversity of culturable cold-adapted yeasts of a cold-based glacier in the Tianshan Mountains, northwestern China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2311–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khublaryan, M.G. Surface waters: Rivers, Streams, Lakes and Wetlands. In Types and Properties of Water—Volume 1; Khublaryan, M.G., Ed.; EOLS Publishers Co. Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-84826-922-4. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, K. Speciation in ancient lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1997, 12, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabanov, E.; Douglas, W.; Kuzmin, M.; Sideleva, V.; Khursevich, G.; Prokopenko, A.; Solotchina, E.; Tkachenko, L.; Fedenya, S.; Kerber, E.; et al. Ecological collapse of Lake Baikal and Lake Hovsgol ecosystems during the Last Glacial and consequences for aquatic species diversity. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2004, 209, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovskaya, G.I. Phytoplankton. In Limnology of Northern Baikal. Novosibirsk; Galazii, G.I., Bogdanov, V.T., Eds.; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1983; pp. 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, T.L.; Strobeck, C. Multiple fossil calibrations, nuclear loci and mitochondrial genomes provide new insight into biogeography and divergence timing for true seals (Phocidae, Pinnipedia). J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Yeves, P.J.; Zemskaya, T.I.; Rosselli, R.; Coutinho, F.H.; Zakharenko, A.S.; Blinov, V.V.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Genomes of Novel Microbial Lineages Assembled from the Sub-Ice Waters of Lake Baikal. AEM 2017, 84, e02132-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annenkova, N.V.; Hansen, G.; Rengefors, K. Closely related dinoflagellate species in vastly different habitats—An example of a marine-freshwater transition. Eur. J. Phycol. Accepted.
- Logares, R.; Bråte, J.; Bertilsson, S.; Clasen, J.L.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K.; Rengefors, K. Infrequent marine–freshwater transitions in the microbial world. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielhagen, R.F.; Erlenkeuser, H.; Siegert, C.H. History of freshwater runoff across the Laptev Sea (Arctic) during the last deglaciation. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2005, 48, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirst, G.O.; Wiencke, C. Ecophysiology of polar algae. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segerstrale, S.G. Immigration of glacial relicts into northern Europe. Boreas 1976, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereshchagin, G.Y. Origines et histoire de la faune et de la flora du lac Baikal. Int. Rev. D Gesamten. Hydrobiol. 1940, 5, 390–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-González, I.; Sanchez-Jimenez, A.; Singer, D.; Murciano, A.; Díez-Hermano, S.; Lara, E.; Martín-Cereceda, M. Rain-Fed Granite Rock Basins Accumulate a High Diversity of Dormant Microbial Eukaryotes. Microb. Ecol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilets, S.; Losos, J.B. Adaptive Radiation: Contrasting theory with data. Science 2009, 323, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, I.; Martens, K. Adaptive, pre-adaptive and non-adaptive components of radiations in ancient lakes: A review. Org. Divers. Evol. 2004, 4, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelbrink, B.; Jovanovska, E.; Levkov, Z.; Ognjanova-Rumenova, N.; Wilke, T.; Albrecht, C. Diatoms do radiate: Evidence for a freshwater species flock. J. Evol. Biol. 2018, 31, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikovskiy, M.S.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Metzeltin, D.; Witkowski, A. Lake Baikal: Hotspot of Endemic Diatoms: I. Iconographia Diatomologica; Koeltz Scientific Books: Koenigstein, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-905-997-09-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.L.; Kociolek, J.P.; Zhang, R.L.; Wang, L.Q. Oricymba tianmuensis sp. nov., a new cymbelloid species (Bacillariophyceae) from Tianmu Mountain Zhejiang Province, China. Phytotaxa 2015, 236, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kociolek, J.P.; Hamsher, S.E.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Bramburger, A.J. Are there species flocks in freshwater diatoms? A review of past reports and a look to the future. Hydrobiologia 2017, 792, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessudova, A.Y.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Tomberg, I.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Silica-Scaled Chrysophytes in Large Tributaries of Lake Baikal. Cryptogam. Algol. 2018, 39, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, A.R.D.; Kobayashi, T. Highly efficient concerted evolution in the ribosomal DNA repeats: Total rDNA repeat variation revealed by whole-genome shotgun sequence data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Dong, J.; Liu, X.; Massana, R. Extremely high copy numbers and polymorphisms of the rDNA operon estimated from single cell analysis of oligotrich and peritrich ciliates. Protist 2013, 164, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryavtsev, A.; Gladkikh, A. Two new species of Ripella (Amoebozoa, Vannellida) and unusual intragenomic variability in the SSU rRNA gene of this genus. Eur. J. Protistol. 2017, 61, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annenkova, N.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Denikina, N.N.; Belikov, S.I. Identification of dinoflagellates from the Lake Baikal on the basis of molecular genetic data. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2009, 426, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursevich, G.K.; Karabanov, E.B.; Prokopenko, A.A.; Williams, D.F.; Kuzmin, M.I.; Fedenya, S.A.; Gvozdkov, A.N.; Kerber, E.V. Detailed diatom biostratigraphy of Baikal sediment during the Brunhes Chron and climatic factors of species formation. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2011, 42, 108–129. [Google Scholar]
- Stelbrink, B.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Clewing, C.; Sitnikova, T.Y.; Prozorova, L.A.; Albrecht, C. Conquest of the deep, old and cold: An exceptional limpet radiation in Lake Baikal. Biol. Lett. 2015, 11, 20150321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, K.A.; Rynearson, T.A. Evidence for environmental and ecological selection in a microbe with no geographic limits to gene flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2651–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherbakov, D.Y.; Kovalenkova, M.V.; Maikova, O.O. Some results of molecular phylogenetic studies of Baikal endemic invertebrates. Russ. J. Genet. Appl. Res. 2017, 7, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychenko, O.S.; Sukhanova, L.V.; Azhikina, T.L.; Skvortsov, T.A.; Belomestnykh, T.V.; Sverdlov, E.D. Differences in Brain Transcriptomes of Closely Related Baikal Coregonid Species. J. BioMed Biotechnol. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teterina, V.I.; Sukhanova, L.V.; Kirilchik, S.V. Molecular divergence and speciation of Baikal oilfish (Comephoridae): Facts and hypotheses. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 2010, 56, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meixner, M.J.; Lüter, C.; Eckert, C.; Itskovich, V.; Janussen, D.; von Rintelen, T.; Bohne, A.V.; Meixner, J.M.; Hess, W.R. Phylogenetic analysis of freshwater sponges provide evidence for endemism and radiation in ancient lakes. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 2007, 45, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidding, B.; Michel, E.; Natyaganova, A.V.; Sherbakov, D.Y. Molecular evidence reveals a polyphyletic origin and chromosomal speciation of Lake Baikal’s endemic asellid isopods. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, A.W. New genera of symbiotic protozoans in lake Baikal. In News about Fauna of Baikal; Galaziy, G.I., Ed.; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russian, 1982; pp. 25–32. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kozhov, M. Lake Baikal and Its Life; Junk, W., Ed.; Martinus Nijhof Publishers: Hague, The Netherlands, 1963; p. 344. [Google Scholar]
- Fietz, S.; Bleiß, W.; Hepperle, D.; Koppitz, H.; Krienitz, L.; Nicklisch, A. First record of Nannochloropsis limnetica (Eustigmatophyceae) in the autotrophic picoplankton from lake baikal. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Tsang, A.; Roy, J. Microbial community coalescence for microbiome engineering. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
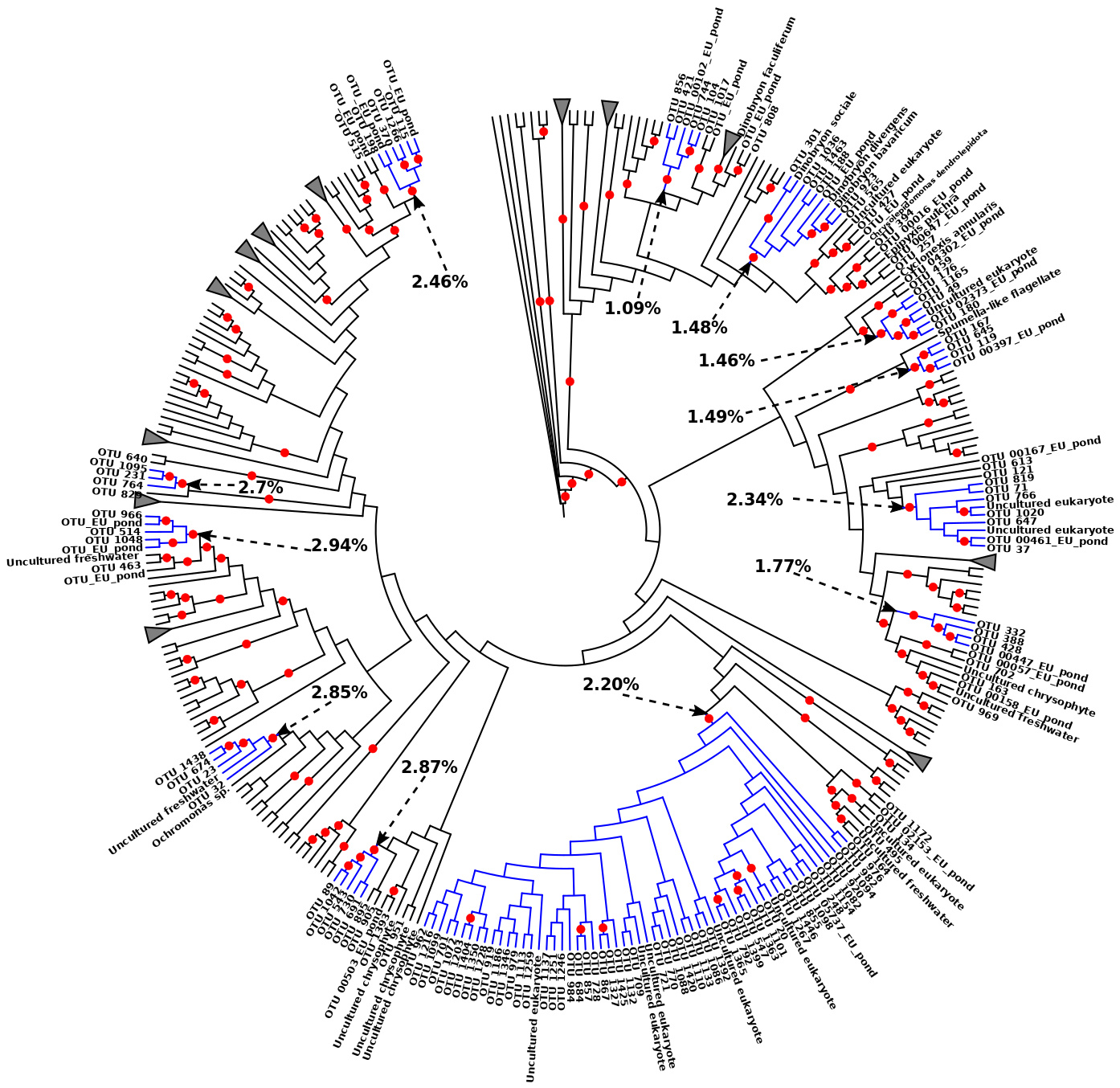

| Phylum | Taxon | Number of Potential Species Flocks |
|---|---|---|
| Stramenopiles | Chrysophyceae | 11 |
| Dictyochophyceae | 5 | |
| Bicosoecida | 4 | |
| Bolidophyceae | 2 | |
| Alveolata | Ciliata | 4 |
| Perkinsiidae | 5 | |
| Opisthokonta | Choanoflagellatea | 2 |
| Chytridiomycota | 2 | |
| Rozellida | 1 | |
| Archaeplastida | Chlorophyta | 4 |
| Rhizaria | Thecofilosea | 1 |
| Sarcomonadea | 1 | |
| Novel Clade 10 | 1 | |
| Hacrobia | Cryptophyceae | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Annenkova, N.V.; Giner, C.R.; Logares, R. Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040543
Annenkova NV, Giner CR, Logares R. Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(4):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040543
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnnenkova, Nataliia V., Caterina R. Giner, and Ramiro Logares. 2020. "Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake" Microorganisms 8, no. 4: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040543
APA StyleAnnenkova, N. V., Giner, C. R., & Logares, R. (2020). Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake. Microorganisms, 8(4), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040543





