Not That Close to Mommy: Horizontal Transmission Seeds the Microbiome Associated with the Marine Sponge Plakina cyanorosea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Processing of the Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Analyses of Sponge-Enriched OTUs
2.6. Global Analyses of Homoscleromorpha-Associated Prokaryotic Microbiota
2.7. Molecular Sponge Identification
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Sponge Taxonomy
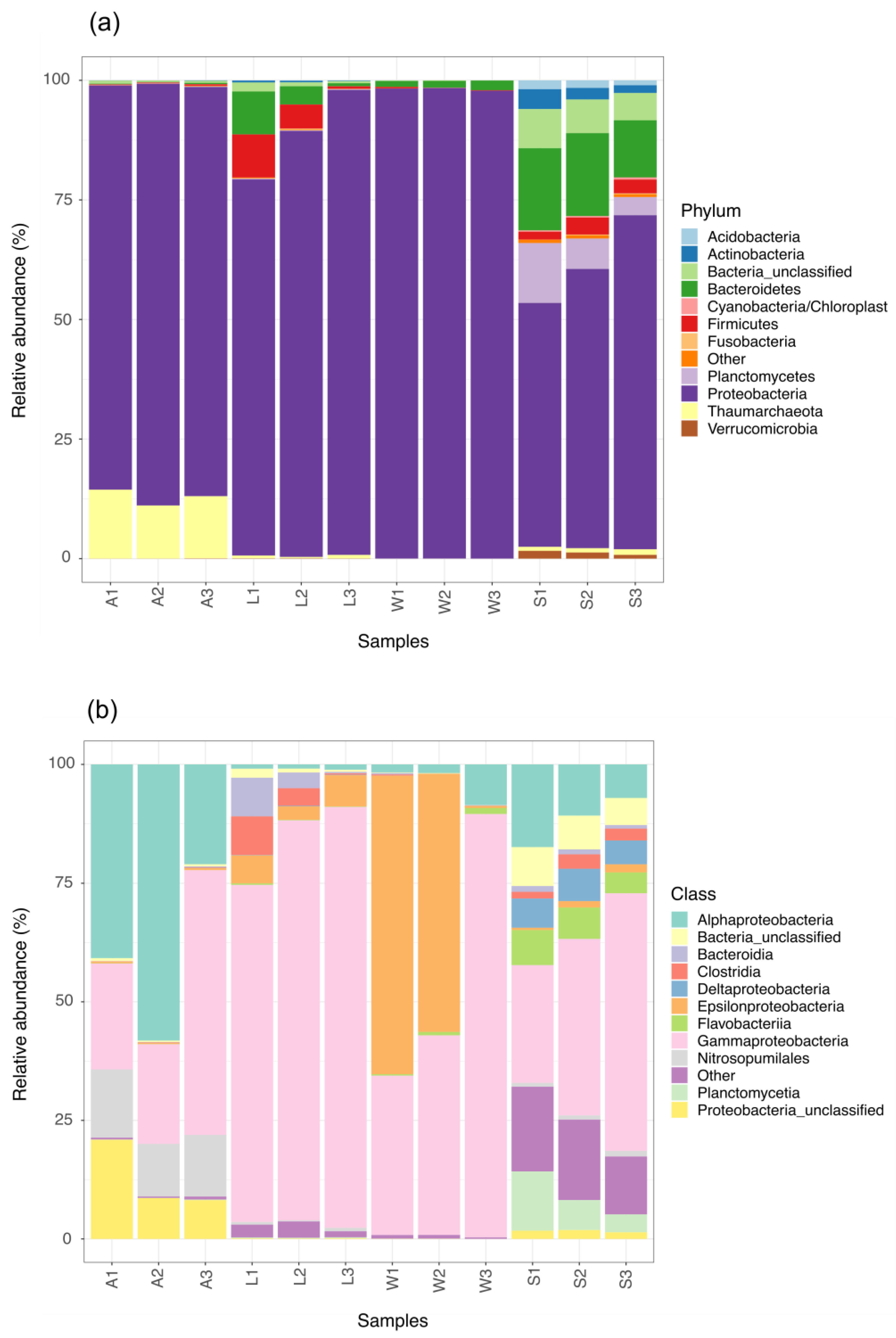
3.2. Prokaryotic Community Composition
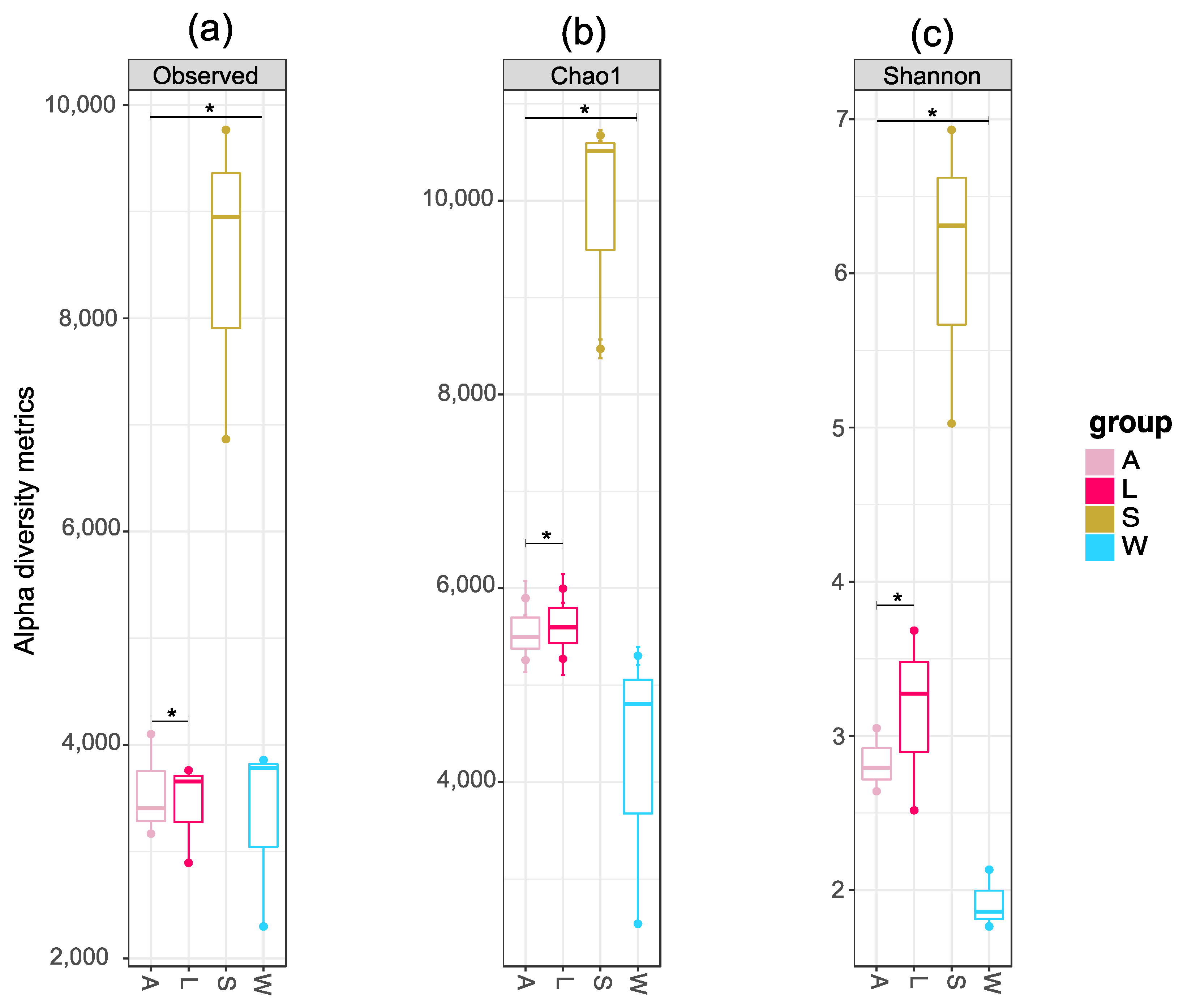
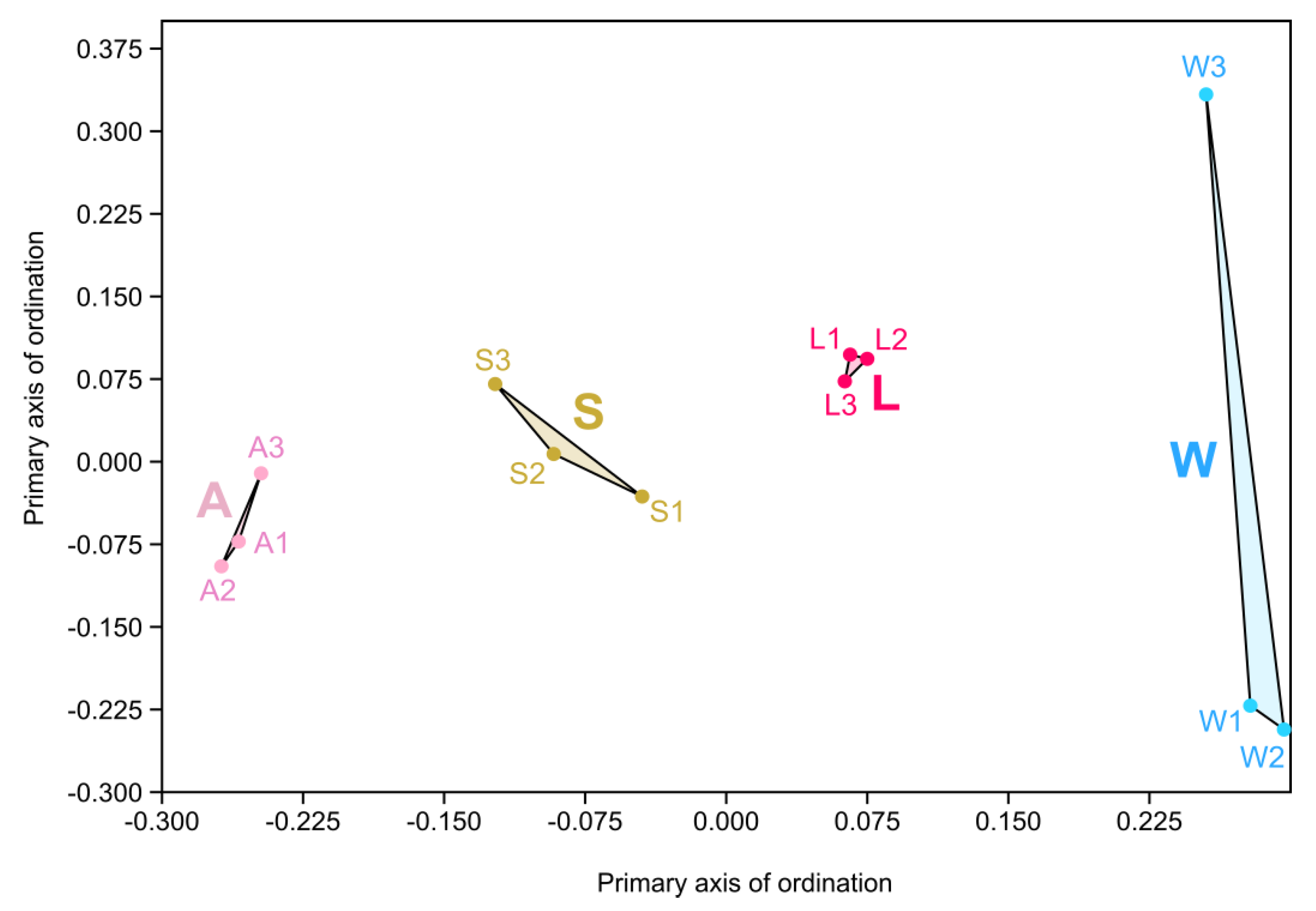
3.3. Prokaryotic Community Diversity and Structure
3.4. OTU-Level and Core Microbiota Analyses
3.5. Global Analyses of Homoscleromorpha-Associated Prokaryotic Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, L.A. Evolving as a holobiont. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2002168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Role of microorganisms in the evolution of animals and plants: The hologenome theory of evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The hologenome concept of evolution after 10 years. Microbiome 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, M.; Bulgheresi, S. A complex journey: Transmission of microbial symbionts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.C.; Marchesi, J.R.; Mougel, C.; Selosse, M.A. Host-microbiota interactions: From holobiont theory to analysis. Microbiome 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijenhoek, R.C. Genetics and evolution of deep-sea chemosynthetic bacteria and their invertebrate hosts. In The Vent and Seep Biota, 1st ed.; Steffen, K., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2010; Volume 33, pp. 15–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.L.; Skophammer, R.G.; Regus, J.U. Evolutionary transitions in bacterial symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10800–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E.; Werren, J.H. Holes in the hologenome: Why host-microbe symbioses are not holobionts. mBio 2016, 7, e02099-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, D. The epidemiology and evolution of symbionts with mixed-mode transmission. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2013, 44, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, K.L. Holobionts and their hologenomes: Evolution with mixed modes of inheritance. Genet. Mol. 2018, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-associated microorganisms: Evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita, L.; Rix, L.; Slaby, B.M.; Franke, A.; Hentschel, U. The sponge holobiont in a changing ocean: From microbes to ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jonas, L.; Lin, H.; Hill, R.T. Microbially mediated nutrient cycles in marine sponges. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, R.W.; Freeman, C.J. Sponge–microbe symbioses: Recent advances and new directions. In Advances in Marine Biology, 1st ed.; Lesser, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 62, pp. 57–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Thomas, T. The sponge hologenome. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Taylor, M.W.; Behnam, F.; Lücker, S.; Rattei, T.; Whalan, S.; Wagner, M. Deep sequencing reveals exceptional diversity and modes of transmission for bacterial sponge symbionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2070–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turon, M.; Cáliz, J.; Garate, L.; Casamayor, E.O.; Uriz, M.J. Showcasing the role of seawater in bacteria recruitment and microbiome stability in sponges. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ou, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J. Structure and dynamics of microbiomes associated with the marine sponge Tedania sp. during its life cycle. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristán-Soriano, O.; Winkler, M.; Erwin, P.; Weisz, J.; Harriott, O.; Heussler, G.; Hill, M. Ontogeny of symbiont community structure in two carotenoid-rich, viviparous marine sponges: Comparison of microbiomes and analysis of culturable pigmented heterotrophic bacteria. Environ. Microbial. Rep. 2019, 11, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, J.R.; Diéz-Vives, C.; Astudillo-García, C.; Archie, E.A.; Montoya, J.M. Vertical transmission of sponge microbiota is inconsistent and unfaithful. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Hopke, J.; Horn, M.; Friedrich, A.B.; Wagner, M.; Hacker, J.; Moore, B.S. Molecular evidence for a uniform microbial community in sponges from different oceans. Appl. Environ. Microbial. 2002, 68, 4431–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Tsai, P.; Simister, R.L.; Deines, P.; Botte, E.; Ericson, G.; Webster, N.S. ‘Sponge-specific’ bacteria are widespread (but rare) in diverse marine environments. ISME J. 2013, 7, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitinho-Silva, L.; Bayer, K.; Cannistraci, C.V.; Giles, E.C.; Ryu, T.; Seridi, L.; Hentschel, U. Specificity and transcriptional activity of microbiota associated with low and high microbial abundance sponges from the Red Sea. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, S.; Angermeier, H.; Schiller, R.; Lindquist, N.; Hentschel, U. Molecular microbial diversity survey of sponge reproductive stages and mechanistic insights into vertical transmission of microbial symbionts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7694–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, S.; Tsai, P.; Bell, J.; Fromont, J.; Ilan, M.; Lindquist, N.; Webster, N. Assessing the complex sponge microbiota: Core, variable and species-specific bacterial communities in marine sponges. ISME J. 2012, 6, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipkema, D.; de Caralt, S.; Morillo, J.A.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Smidt, H.; Uriz, M.J. Similar sponge-associated bacteria can be acquired via both vertical and horizontal transmission. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3807–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieth, R.A.; Gauthier, M.E.A.; Bayes, J.; Green, K.M.; Degnan, S.M. Ontogenetic changes in the bacterial symbiont community of the tropical demosponge Amphimedon queenslandica: Metamorphosis is a new beginning. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazave, E.; Lape’bie, P.; Renard, E.; Vacelet, J.; Rocher, C. Molecular Phylogeny Restores the Supra-Generic Subdivision of Homoscleromorph Sponges (Porifera, Homoscleromorpha). PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazave, E.; Lapébie, P.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Vacelet, J.; Renard, E.; Cárdenas, P.; Borchiellini, C. No longer Demospongiae: Homoscleromorph sponges revisited by molecular phylogeny, Linnaean classification and the PhyloCode. Hydrobiologia 2012, 687, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C. Phylum Homoscleromorpha. In Animal Evolution: Interrelationships of the Living Phyla, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; Volume 53, pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, E.; Gazave, E.; Fierro-Constain, L.; Schenkelaars, Q.; Ereskovsky, A.; Vacelet, J.; Borchiellini, C. Porifera (sponges): Recent knowledge and new perspectives. eLS 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, A.L.; Darris, C.E.; Chetyrkin, S.V.; Pedchenko, V.K.; Boudko, S.P.; Brown, K.L.; Hudson, B.G. Collagen IV and basement membrane at the evolutionary dawn of metazoan tissues. eLife 2017, 6, e24176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belahbib, H.; Renard, E.; Santini, S.; Jourda, C.; Claverie, J.M.; Borchiellini, C.; Le Bivic, A. New genomic data and analyses challenge the traditional vision of animal epithelium evolution. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ereskovsky, A.V.; Lavrov, D.V.; Willenz, P. Five new species of Homoscleromorpha (Porifera) from the Caribbean Sea and re-description of Plakina Jamaicensis. J. Mar. 2014, 94, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boury-Esnault, N.; Lavrov, D.V.; Ruiz, C.A.; Pérez, T. The integrative taxonomic approach applied to Porifera: A case study of the Homoscleromorpha. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2013, 53, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E. Marine caves in the Mediterranean Sea (No. RefW-14-59632). AUTh 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.N.A. World Porifera Database. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/porifera/porifera.php?p=stats (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Ruiz, C.; Muricy, G.; Lage, A.; Domingos, C.; Chenesseau, S.; Pérez, T. Descriptions of new sponge species and genus, including aspiculate Plakinidae, overturn the Homoscleromorpha classification. Zool. J. Linnean Soc. 2017, 179, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, M.; Ruiz, C.; Lage, A.; Perez, T. New cave-dwelling Plakina (Plakinidae, Homoscleromorpha, Porifera) from Martinique Island (French Antilles). Zootaxa 2020, 4729, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, A.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E.; Muricy, G. Taxonomy of Plakina (Porifera: Homoscleromorpha) from Aegean submarine caves, with descriptions of three new species and new characters for the genus. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 49, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Ivanišević, J.; Chevaldonné, P.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Thomas, O.P.; Pérez, T. Integrative taxonomic description of Plakina kanaky, a new polychromatic sponge species from New Caledonia (Porifera: Homoscleromorpha). Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, A.; Muricy, G.; Ruiz, C.; Perez, T. New sciaphilic plakinids (Porifera, Homoscleromorpha) from the Central-Western Pacific. Zootaxa 2018, 4466, 8–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, T.; Alvim, J.; Padula, V.; Muricy, G. Spongivory by nudibranchs on the coast of Rio de Janeiro state, southeastern Brazil. Spixiana 2015, 38, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Domingos, C.; Lage, A.; Muricy, G. Overview of the biodiversity and distribution of the Class Homoscleromorpha in the Tropical Western Atlantic. J. Mar. 2016, 96, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muricy, G.; Domingos, C.; Lage, A.; Lanna, E.; Hardoim, C.C.; Laport, M.S.; Zilberberg, C. Integrative taxonomy widens our knowledge of the diversity, distribution and biology of the genus Plakina (Homosclerophorida: Plakinidae). Invertebr. Syst. 2019, 33, 367–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laport, M.S.; Bauwens, M.; de Oliveira Nunes, S.; Willenz, P.; George, I.; Muricy, G. Culturable bacterial communities associated to Brazilian Oscarella species (Porifera: Homoscleromorpha) and their antagonistic interactions. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, B.F.R.; Cavalcanti, M.D.A.; de Oliveira Nunes, S.; Lobo, L.A.; Domingues, R.M.C.P.; Muricy, G.; Laport, M.S. Paraclostridium is the main genus of anaerobic bacteria isolated from new species of the marine sponge Plakina in the Brazilian Southeast coast. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Silva, J.; Silva-Oliveira, T.; Muricy, G.; Laport, M.S. Bacillus strains associated to homoscleromorpha sponges are highly active against multidrug resistant bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Villegas-Plazas, M.; Thomas, O.P.; Junca, H.; Pérez, T. Specialized microbiome of the cave-dwelling sponge Plakina kanaky (Porifera, Homoscleromorpha). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, H.; Budd, A.F.; Levitan, D.R.; Jara, J.; Kersanach, R.; Knowlton, N. Geographic differences in species boundaries among members of the Montastraea annularis complex based on molecular and morphological markers. Evolution 2004, 58, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprill, A.; McNally, S.; Parsons, R.; Weber, L. Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Sahl, J.W. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbial. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathi, L.; Shetty, S.; Blake, T.; Salojarvi, J. Microbiome R Package. 2017. Available online: http://microbiome.github.io (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical theory of communication. BSTJAN 1948, 27, 379–423, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Mcglinn, D. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5–1. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 11 August 2020).
- Moitinho-Silva, L.; Nielsen, S.; Amir, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Ackermann, G.L.; Cerrano, C.; Steinert, G. The sponge microbiome project. Gigascience 2017, 6, gix077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dat, T.T.H.; Steinert, G.; Cuc, N.T.K.; Smidt, H.; Sipkema, D. Archaeal and bacterial diversity and community composition from 18 phylogenetically divergent sponge species in Vietnam. Peer J. 2018, 6, e4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laport, M.S.; Pinheiro, U.; Rachid, C.T.C.C. Freshwater Sponge Tubella variabilis Presents Richer Microbiota Than Marine Sponge Species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Lurgi, M.; Björk, J.R.; Easson, C.; Astudillo-García, C.; Chaves-Fonnegra, A. Diversity, structure and convergent evolution of the global sponge microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Franco, C.M.; Sorokin, S.J.; Zhang, W. Development of a multilocus-based approach for sponge (phylum Porifera) identification: Refinement and limitations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, G.; Busch, K.; Bayer, K.; Kodami, S.; Arbizu, P.M.; Kelly, M.; Millis, S.; Erpenbeck, D.; Dohrmann, M.; Wörheide, G.; et al. Compositional and quantitative insights into bacterial and archaeal communities of South Pacific deep-sea sponges (Demospongiae and Hexactinellida). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitinho-Silva, L.; Díez-Vives, C.; Batani, G.; Esteves, A.I.; Jahn, M.T.; Thomas, T. Integrated metabolism in sponge–microbe symbiosis revealed by genome-centered metatranscriptomics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1651–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, F.U.; Webster, N.S.; Herbold, C.W.; Behnam, F.; Domman, D.; Albertsen, M.; Mooshammer, M.; Markert, S.; Turaev, D.; Becher, D.; et al. Characterization of a thaumarchaeal symbiont that drives incomplete nitrification in the tropical sponge Ianthella Basta. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3831–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, K.H.; Eam, B.; Faulkner, D.J.; Haygood, M.G. Vertical transmission of diverse microbes in the tropical sponge Corticium Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steger, D.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Whalan, S.; Hentschel, U.; De Nys, R.; Wagner, M.; Taylor, M.W. Diversity and mode of transmission of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in marine sponges. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, M.; Uriz, M.J. New insights into the archaeal consortium of tropical sponges. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Franco, T.; Califano, G.; Dowd, S.E.; Pohnert, G.; Costa, R. Draft genome sequence of Vibrio sp. strain Vb278, an antagonistic bacterium isolated from the marine sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00521-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, J.D.; Pramanik, A.; Webster, N.S.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Gachhui, R.; Mukherjee, J. Draft Genome Sequence of Pseudoalteromonas sp. Strain NW 4327 (MTCC 11073, DSM 25418), a Pathogen of the Great Barrier Reef Sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00001-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai-Kawada, F.E.; Yakym, C.J.; Helmkampf, M.; Hagiwara, K.; Ip, C.G.; Antonio, B.J.; Armstrong, E.; Ulloa, W.J.; Awaya, J.D. Draft genome sequence of marine sponge symbiont Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea IPB1, isolated from Hilo, Hawaii. Gen. Announc. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnosti, C. Microbial extracellular enzymes and the marine carbon cycle. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnosti, C.; Wietz, M.; Brinkhoff, T.; Hehemann, J.H.; Probandt, D.; Zeugner, L.; Amann, R. The biogeochemistry of marine polysaccharides: Sources, inventories, and bacterial drivers of the carbohydrate cycle. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.T.; Lee, J. Global distribution and prevalence of Arcobacter in food and water. Zoonoses Public Health. 2015, 62, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fera, M.T.; Maugeri, T.L.; Gugliandolo, C.; Beninati, C.; Giannone, M.; La Camera, E.; Carbone, M. Detection of Arcobacter spp. in the coastal environment of the Mediterranean Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, T.L.; Irrera, G.P.; Lentini, V.; Carbone, M.; Fera, M.T.; Gugliandolo, C. Detection and enumeration of Arcobacter spp. in the coastal environment of the Straits of Messina (Italy). New Microbiol. 2005, 28, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Collado, L.; Inza, I.; Guarro, J.; Figueras, M.J. Presence of Arcobacter spp. in environmental waters correlates with high levels of fecal pollution. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fera, M.T.; Gugliandolo, C.; Lentini, V.; Favaloro, A.; Bonanno, D.; La Camera, E.; Maugeri, T.L. Specific detection of Arcobacter spp. in estuarine waters of Southern Italy by PCR and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diéguez, A.L.; Romalde, J.L. Complete genome sequence of Arcobacter sp. strain LFT 1.7 isolated from Great Scallop (Pecten maximus) Larvae. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01617-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bonilla, E.; Brandão, P.F.; Pérez, T.; Junca, H. Stable and enriched Cenarchaeum symbiosum and uncultured Betaproteobacteria HF1 in the microbiome of the Mediterranean sponge Haliclona fulva (Demospongiae: Haplosclerida). Microb. Ecol. 2018, 77, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, C.A.; González-Aravena, M.; Font, A.; Hestetun, J.T.; Hajdu, E.; Trefault, N.; Malmberg, M.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E. High similarity in the microbiota of cold-water sponges of the Genus Mycale from two different geographical areas. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balvočiūtė, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT—how do these taxonomies compare? BMC Genomics. 2017, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.; Mitchell, A.L.; Tarkowska, A.; Finn, R.D. Benchmarking taxonomic assignments based on 16S rRNA gene profiling of the microbiota from commonly sampled environments. GigaScience. 2018, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquer, A.; Uriz, M.J.; Galand, P.E. Removing environmental sources of variation to gain insight on symbionts vs. transient microbes in high and low microbial abundance sponges. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 3008–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Caralt, S.; Uriz, M.J.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Wijffels, R.H. Embryo development of Corticium candelabrum (Demospongiae: Homosclerophorida). Invertebr. Biol. 2007, 126, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Riesgo, A. Reproductive output in a Mediterranean population of the homosclerophorid Corticium candelabrum (Porifera, Demospongiae), with notes on the ultrastructure and behavior of the larva. Mar. Ecol. 2008, 29, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloeckner, V.; Hentschel, U.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Schmitt, S. Unique and species-specific microbial communities in Oscarella lobularis and other Mediterranean Oscarella species (Porifera: Homoscleromorpha). Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitinho-Silva, L.; Steinert, G.; Nielsen, S.; Hardoim, C.C.P.; Wu, Y.-C.; López-Legentil, S.; Marchant, R.; Webster, N.; Thomas, T.; Hentschel, U. Predicting the HMA-LMA status in marine sponges by machine learning. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurgi, M.; Thomas, T.; Wemheuer, B.; Webster, N.S.; Montoya, J.M. Modularity and predicted functions of the global sponge-microbiome network. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Swierts, T.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Huang, Y.M.; Ferreira, M.R.S.; Putchakarn, S.; Carvalheiro, L.; van der Ent, E.; Ueng, J.P.; et al. The sponge microbiome within the greater coral reef microbial metacommunity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacelet, J.; Donadey, C. Electron microscope study of the association between some sponges and bacteria. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1977, 30, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Usher, K.M.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisz, J.B.; Lindquist, N.; Martens, C.S. Do associated microbial abundances impact marine demosponge pumping rates and tissue densities? Oecologia 2008, 155, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisz, J.B.; Hentschel, U.; Lindquist, N.; Martens, C.S. Linking abundance and diversity of sponge-associated microbial communities to metabolic differences in host sponges. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.F.; Wu, K.Y.; Prézelin, B.B.; Jovine, R.V. High abundance of Archaea in Antarctic marine picoplankton. Nature 1994, 371, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R. Marine microbes see a sea of gradients. Science 2012, 338, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Schupp, P.J.; Dahllöf, I.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P.D. Host specificity in marine sponge-associated bacteria, and potential implications for marine microbial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Negri, A.P.; Munro, M.M.; Battershill, C.N. Diverse microbial communities inhabit Antarctic sponges. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, E.C.; Kamke, J.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Taylor, M.W.; Hentschel, U.; Ravasi, T.; Schmitt, S. Bacterial community profiles in low microbial abundance sponges. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloeckner, V.; Wehrl, M.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Gernert, C.; Schupp, P.; Pawlik, J.R.; Lindquist, N.L.; Erpenbeck, D.; Wörheide, G.; Hentschel, U. The HMA-LMA dichotomy revisited: An electron microscopical survey of 56 sponge species. Biol. Bull. 2014, 227, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, M.; Dziallas, C.; Coma, R.; Riemann, L. Microbial diversity and putative diazotrophy in high- and low-abundance mediterranean sponges. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5683–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribes, M.; Calvo, E.; Movilla, J.; Logares, R.; Coma, R.; Pelejero, C. Restructuring of the sponge microbiome favors tolerance to ocean acidification. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, B.F.R.; Lopes, I.R.; Canellas, A.L.B.; Muricy, G.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Laport, M.S. Not That Close to Mommy: Horizontal Transmission Seeds the Microbiome Associated with the Marine Sponge Plakina cyanorosea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121978
Oliveira BFR, Lopes IR, Canellas ALB, Muricy G, Dobson ADW, Laport MS. Not That Close to Mommy: Horizontal Transmission Seeds the Microbiome Associated with the Marine Sponge Plakina cyanorosea. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121978
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Bruno F. R., Isabelle R. Lopes, Anna L. B. Canellas, Guilherme Muricy, Alan D. W. Dobson, and Marinella S. Laport. 2020. "Not That Close to Mommy: Horizontal Transmission Seeds the Microbiome Associated with the Marine Sponge Plakina cyanorosea" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121978
APA StyleOliveira, B. F. R., Lopes, I. R., Canellas, A. L. B., Muricy, G., Dobson, A. D. W., & Laport, M. S. (2020). Not That Close to Mommy: Horizontal Transmission Seeds the Microbiome Associated with the Marine Sponge Plakina cyanorosea. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121978






