Z/I1 Hybrid Virulence Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance genes in S. Typhimurium from Australian Food Animal Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Strains
2.2. DNA Extraction, Sequencing and Genome Assembly
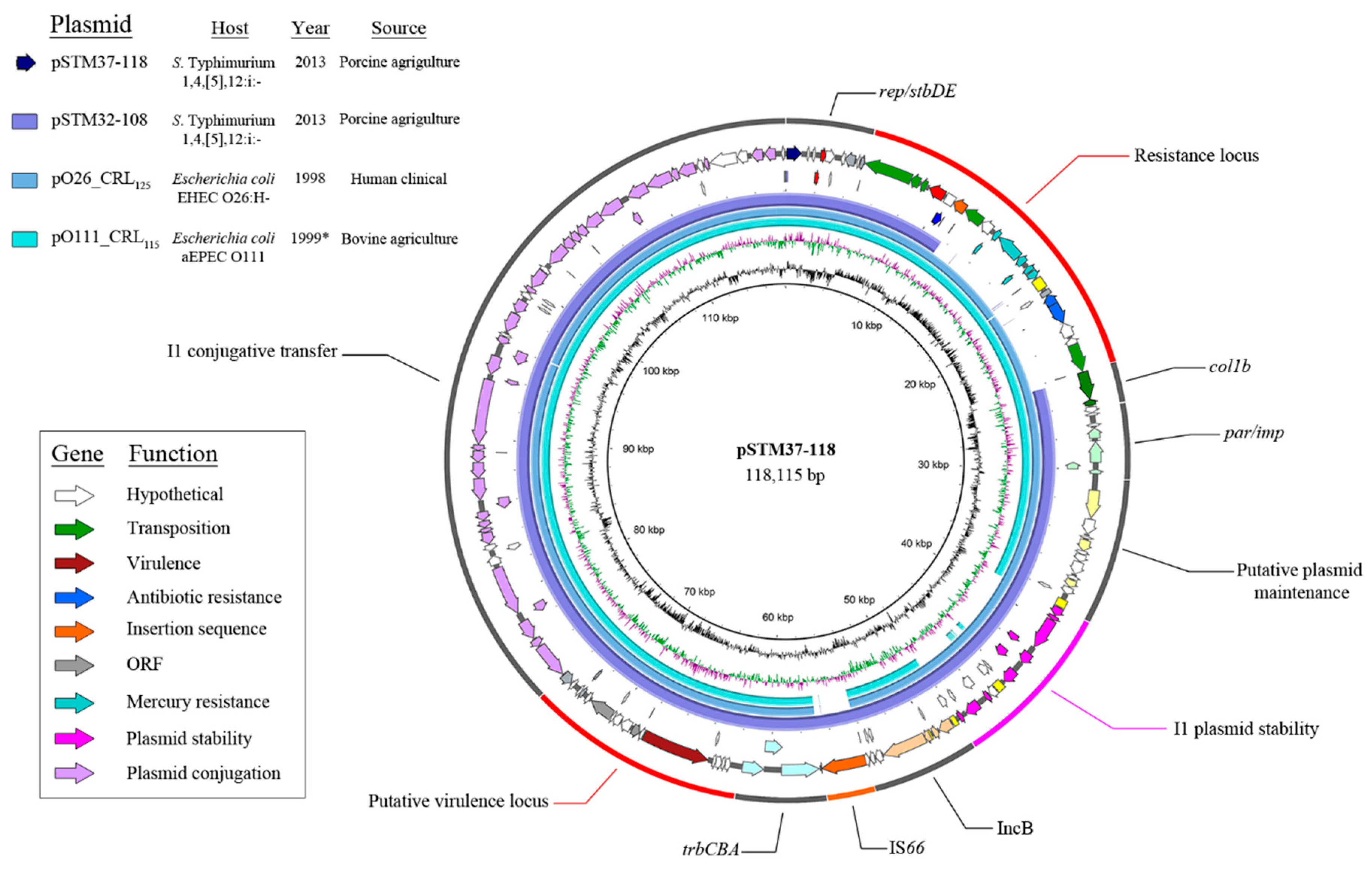
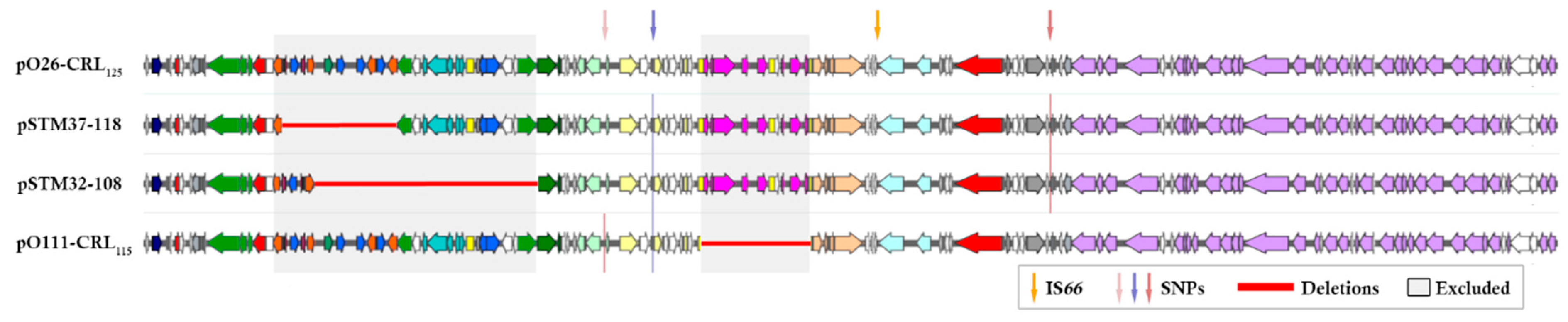
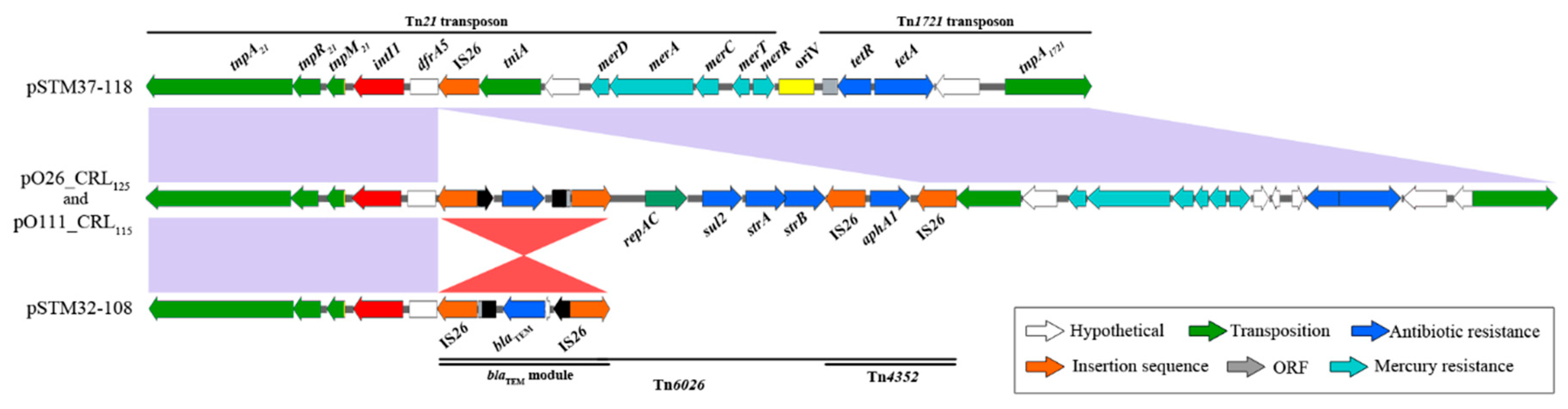
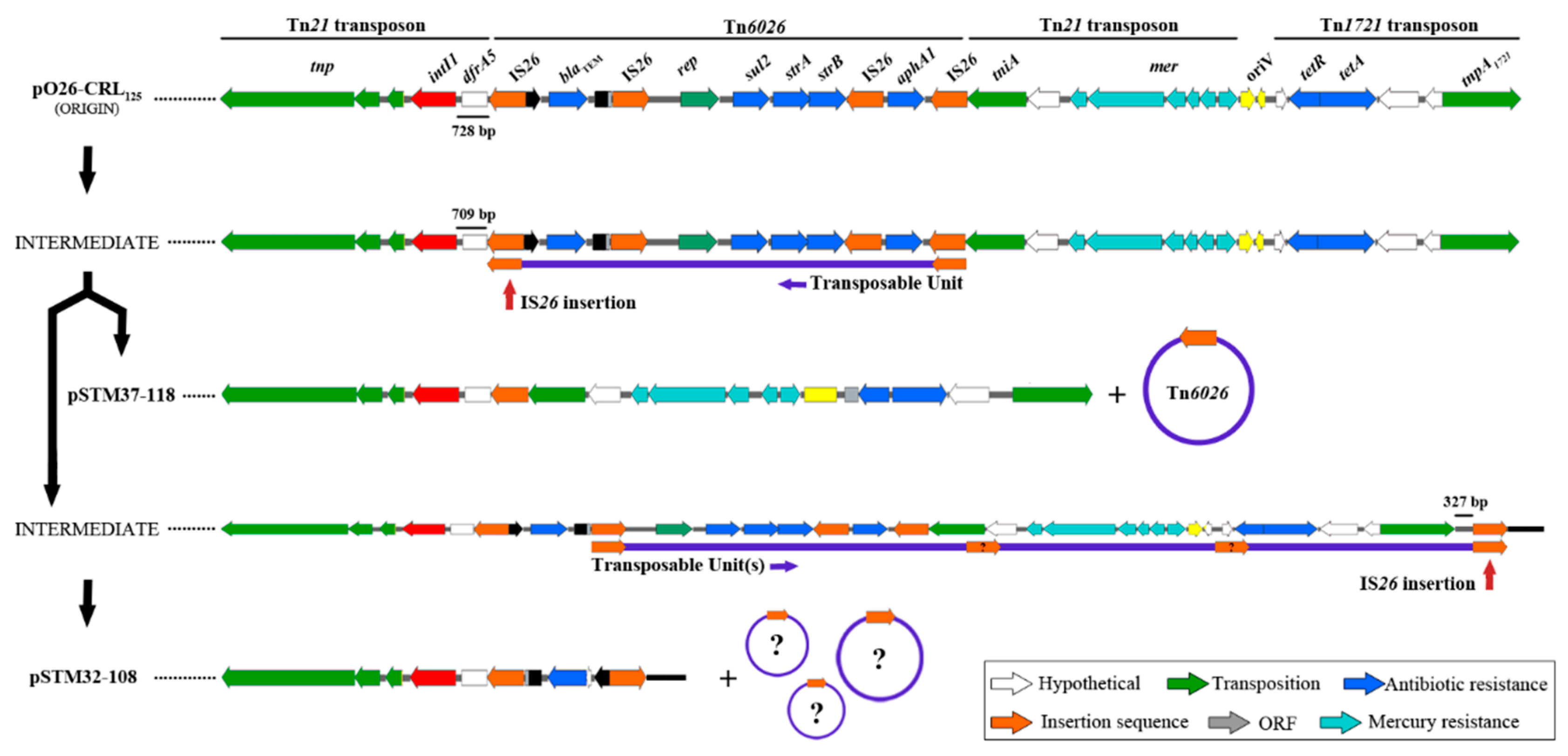
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bannas, P.; Fraedrich, K.; Treszl, A.; Bley, T.A.; Herrmann, J.; Habermann, C.R.; Derlin, T.; Henes, F.O.; Wenzel, U.; Adam, G.; et al. Shiga Toxin-Producing E. Coli O104:H4 Outbreak 2011 in Germany: Radiological Features of Enterohemorrhagic Colitis. Rofo 2013, 185, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J.D. Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Combination of Virulence with Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierard, D.; De Greve, H.; Haesebrouck, F.; Mainil, J. O157:H7 and O104:H4 Vero/Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli outbreaks: Respective role of cattle and humans. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardefeldt, L.; Gilkerson, J.; Billman-Jacobe, H.; Stevenson, M.; Thursky, K.; Browning, G.; Bailey, K. Antimicrobial labelling in Australia: a threat to antimicrobial stewardship? Aust. Vet. J. 2018, 96, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelheim, K.A.; Hornitzky, M.A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Kuzevski, A. Antibiotic resistance among verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli (VTEC) and non-VTEC isolated from domestic animals and humans. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.; Jordan, D.; Wong, H.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Toleman, M.A.; Wakeham, D.L.; Gordon, D.M.; Turnidge, J.D.; Mollinger, J.L.; Gibson, J.S.; et al. First detection of extended-spectrum cephalosporin- and fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli in Australian food-producing animals. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015, 3, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, C.J.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Zingali, T.; Liu, M.; Darling, A.E.; Chapman, T.A.; Djordjevic, S.P. Porcine commensal Escherichia coli: A reservoir for class 1 integrons associated with IS26. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, A.K.; Liu, X.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Hall, R.M. Transposons related to Tn1696 in IncHI2 plasmids in multiply antibiotic resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium from Australian animals. Microb. Drug Resist. 2010, 16, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, F.E.; Kuzevski, A.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Hornitzky, M.A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Walker, M.J. Distribution of class 1 integrons with IS26-mediated deletions in their 3’-conserved segments in Escherichia coli of human and animal origin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Kirkwood, R.N.; Laird, T.; Saputra, S.; Mitchell, T.; Singh, M.; Linn, B.; Abraham, R.J.; Pang, S.; Gordon, D.M.; et al. Dissemination and persistence of extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistance encoding IncI1-blaCTXM-1 plasmid among Escherichia coli in pigs. The ISME J. 2018, 12, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billman-Jacobe, H.; Liu, Y.; Haites, R.; Weaver, T.; Robinson, L.; Marenda, M.; Dyall-Smith, M. pSTM6-275, a conjugative IncHI2 plasmid of Salmonella that confers antibiotic and heavy metal resistance under changing physiological conditions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02357-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, R.A.; Holt, K.E.; Hall, R.M. pCERC3 from a commensal ST95 Escherichia coli: A ColV virulence-multiresistance plasmid carrying a sul3-associated class 1 integron. Plasmid 2016, 84, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyall-Smith, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Billman-Jacobe, H. Genome Sequence of an Australian Monophasic Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Typhimurium Isolate (TW-Stm6) Carrying a Large Plasmid with Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00793-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, C.; Beatson, S.A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Walker, M.J. Multiple antibiotic resistance gene recruitment onto the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli virulence plasmid. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, C.; Hassan, K.A.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Paulsen, I.T.; Walker, M.J.; Djordjevic, S.P. Sequences of Two Related Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Virulence Plasmids Sharing a Unique IS26-Related Molecular Signature Isolated from Different Escherichia coli Pathotypes from Different Hosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.; Trott, D.J.; Jordan, D.; Gordon, D.M.; Groves, M.D.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Smith, M.G.; Zhang, R.; Chapman, T.A. Phylogenetic and molecular insights into the evolution of multidrug-resistant porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Australia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saputra, S.; Jordan, D.; Mitchell, T.; Wong, H.S.; Abraham, R.J.; Kidsley, A.; Turnidge, J.; Trott, D.J.; Abraham, S. Antimicrobial resistance in clinical Escherichia coli isolated from companion animals in Australia. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 211, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Djordjevic, S.P. Genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli ST58 causing urosepsis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy Chowdhury, P.; McKinnon, J.M.; Liu, M.Y.; Djordjevic, S.P. Multidrug resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli ST405 with a novel, composite IS26 transposon in a unique chromosomal location. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, M.L.; Reid, C.J.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Bushell, R.N.; Esbert, N.; Tivendale, K.A.; Noormohammadi, A.H.; Islam, S.; Marenda, M.S.; Browning, G.F.; et al. Whole genome sequence analysis of Australian avian pathogenic Escherichia coli that carry the class 1 integrase gene. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OzFoodNet. OzFoodNet quarterly report, 1 January to 31 March 2015. Commun. Dis. Intell. Q. Rep. 2017, 41, E186–E193. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, T.; Valcanis, M.; Mercoulia, K.; Sait, M.; Tuke, J.; Kiermeier, A.; Hogg, G.; Pointon, A.; Hamilton, D.; Billman-Jacobe, H. Longitudinal study of Salmonella 1,4,[5],12:i:- shedding in five Australian pig herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 136, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, E.; Tietze, E.; Helmuth, R.; Junker, E.; Blank, K.; Prager, R.; Rabsch, W.; Appel, B.; Fruth, A.; Malorny, B. Pork Contaminated with Salmonella enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:i:-, an Emerging Health Risk for Humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4601–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Kirchner, M.; Guerra, B.; Granier, S.A.; Lucarelli, C.; Porrero, M.C.; Jakubczak, A.; Threlfall, E.J.; Mevius, D.J. Multiresistant Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- in Europe: a new pandemic strain? Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switt, A.I.; Soyer, Y.; Warnick, L.D.; Wiedmann, M. Emergence, distribution, and molecular and phenotypic characteristics of Salmonella enterica serotype 4,5,12:i. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.; Holds, G.; Hogg, G.; Valcanis, M.; Kiermeier, A. Longitudinal study of an Australian pig farm infected with monophasic Salmonella Typhimurium-like PT193 (1, 4,[5], 12: i:-PT193) using MLVA. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on the Epidemiology and Control of Hazards in Pork Production Chain, Porto, Portugal, 7–10 September 2015; pp. 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treangen, T.J.; Ondov, B.D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Chiaretto, G.; Bertini, A.; Villa, L.; Fortini, D.; Ricci, A.; Carattoli, A. Multilocus sequence typing of IncI1 plasmids carrying extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in Escherichia coli and Salmonella of human and animal origin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, C.J.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Djordjevic, S.P. Tn6026 and Tn6029 are found in complex resistance regions mobilised by diverse plasmids and chromosomal islands in multiple antibiotic resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid 2015, 80, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy Chowdhury, P.; Charles, I.G.; Djordjevic, S.P. A role for Tn6029 in the evolution of the complex antibiotic resistance gene loci in genomic island 3 in enteroaggregative hemorrhagic Escherichia coli O104:H4. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi, A.M.; Lucarelli, C.; Owczarek, S.; Luzzi, I.; Villa, L. Characterization of the plasmid-borne quinolone resistance gene qnrB19 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4019–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liakopoulos, A.; Mevius, D.; Ceccarelli, D. A Review of SHV Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamases: Neglected Yet Ubiquitous. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmer, C.J.; Moran, R.A.; Hall, R.M. Movement of IS26-Associated Antibiotic Resistance Genes Occurs via a Translocatable Unit That Includes a Single IS26 and Preferentially Inserts Adjacent to Another IS26. MBio 2014, 5, e01801–e01814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, C. Transmissible ST3-IncHI2 Plasmids Are Predominant Carriers of Diverse Complex IS26-Class 1 Integron Arrangements in Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangat, C.S.; Bekal, S.; Irwin, R.J.; Mulvey, M.R. A Novel Hybrid Plasmid Carrying Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovar Dublin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02601–e02616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Hopkins, J.D.; Syvanen, M. Direct involvement of IS26 in an antibiotic resistance operon. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porse, A.; Schonning, K.; Munck, C.; Sommer, M.O. Survival and Evolution of a Large Multidrug Resistance Plasmid in New Clinical Bacterial Hosts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2860–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enne, V.I.; Livermore, D.M.; Stephens, P.; Hall, L.M. Persistence of sulphonamide resistance in Escherichia coli in the UK despite national prescribing restriction. Lancet 2001, 357, 1325–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grape, M.; Sundstrom, L.; Kronvall, G. Sulphonamide resistance gene sul3 found in Escherichia coli isolates from human sources. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerum, A.M.; Sandvang, D.; Andersen, S.R.; Seyfarth, A.M.; Porsbo, L.J.; Frimodt-Moller, N.; Heuer, O.E. Detection of sul1, sul2 and sul3 in sulphonamide resistant Escherichia coli isolates obtained from healthy humans, pork and pigs in Denmark. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 106, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, M.; Marathe, N.P.; Gillings, M.R.; Flach, C.F.; Kristiansson, E.; Joakim Larsson, D.G. Discovery of the fourth mobile sulfonamide resistance gene. Microbiome. 2017, 5, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.; Chin, J.J.; Fahy, V.A.; Barton, M.D.; Smith, M.G.; Trott, D.J. Antimicrobial use in the Australian pig industry: results of a national survey. Aust. Vet. J. 2009, 87, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.H.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Chan, E.W.; Chen, S. Dissemination of IncI2 Plasmids That Harbor the blaCTX-M Element among Clinical Salmonella Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5026–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhi, C.P.; Chen, X.J.; Guo, Z.W.; Liu, W.L.; Luo, J.; Huang, X.Y.; Zeng, L.; Huang, J.W.; Xia, Y.B.; et al. Characterization of oqxAB in Escherichia coli Isolates from Animals, Retail Meat, and Human Patients in Guangzhou, China. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire Martín, I.; AbuOun, M.; La Ragione, R.M.; Reichel, R.; Woodward, M.J. Sequence analysis of a CTX-M-1 IncI1 plasmid found in Salmonella 4,5,12:i:-, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae on a UK pig farm. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2098–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, T.L.; Callaway, T.R.; Norman, K.N.; Scott, H.M.; Loneragan, G.H.; Ison, S.A.; Beier, R.C.; Harhay, D.M.; Norby, B.; Nisbet, D.J. Transferability of antimicrobial resistance from multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in the USA to E. coli and Salmonella Newport recipients. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Worden, P.; Monahan, L.G.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Burke, C.M.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Charles, I.G.; Darling, A.E. Evaluation of ddRADseq for reduced representation metagenome sequencing. PeerJ. 2017, 5, e3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMaere, M.Z.; Darling, A.E. Sim3C: Simulation of Hi-C and Meta3C proximity ligation sequencing technologies. Gigascience 2018, 7, gix103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wyrsch, E.R.; Hawkey, J.; Judd, L.M.; Haites, R.; Holt, K.E.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Billman-Jacobe, H. Z/I1 Hybrid Virulence Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance genes in S. Typhimurium from Australian Food Animal Production. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090299
Wyrsch ER, Hawkey J, Judd LM, Haites R, Holt KE, Djordjevic SP, Billman-Jacobe H. Z/I1 Hybrid Virulence Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance genes in S. Typhimurium from Australian Food Animal Production. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(9):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090299
Chicago/Turabian StyleWyrsch, Ethan R., Jane Hawkey, Louise M. Judd, Ruth Haites, Kathryn E. Holt, Steven P. Djordjevic, and Helen Billman-Jacobe. 2019. "Z/I1 Hybrid Virulence Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance genes in S. Typhimurium from Australian Food Animal Production" Microorganisms 7, no. 9: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090299
APA StyleWyrsch, E. R., Hawkey, J., Judd, L. M., Haites, R., Holt, K. E., Djordjevic, S. P., & Billman-Jacobe, H. (2019). Z/I1 Hybrid Virulence Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance genes in S. Typhimurium from Australian Food Animal Production. Microorganisms, 7(9), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090299






