A Piscibacillus sp. Isolated from A Soda Lake Exhibits Anticancer Activity Against Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Isolation of Bacterial Strain
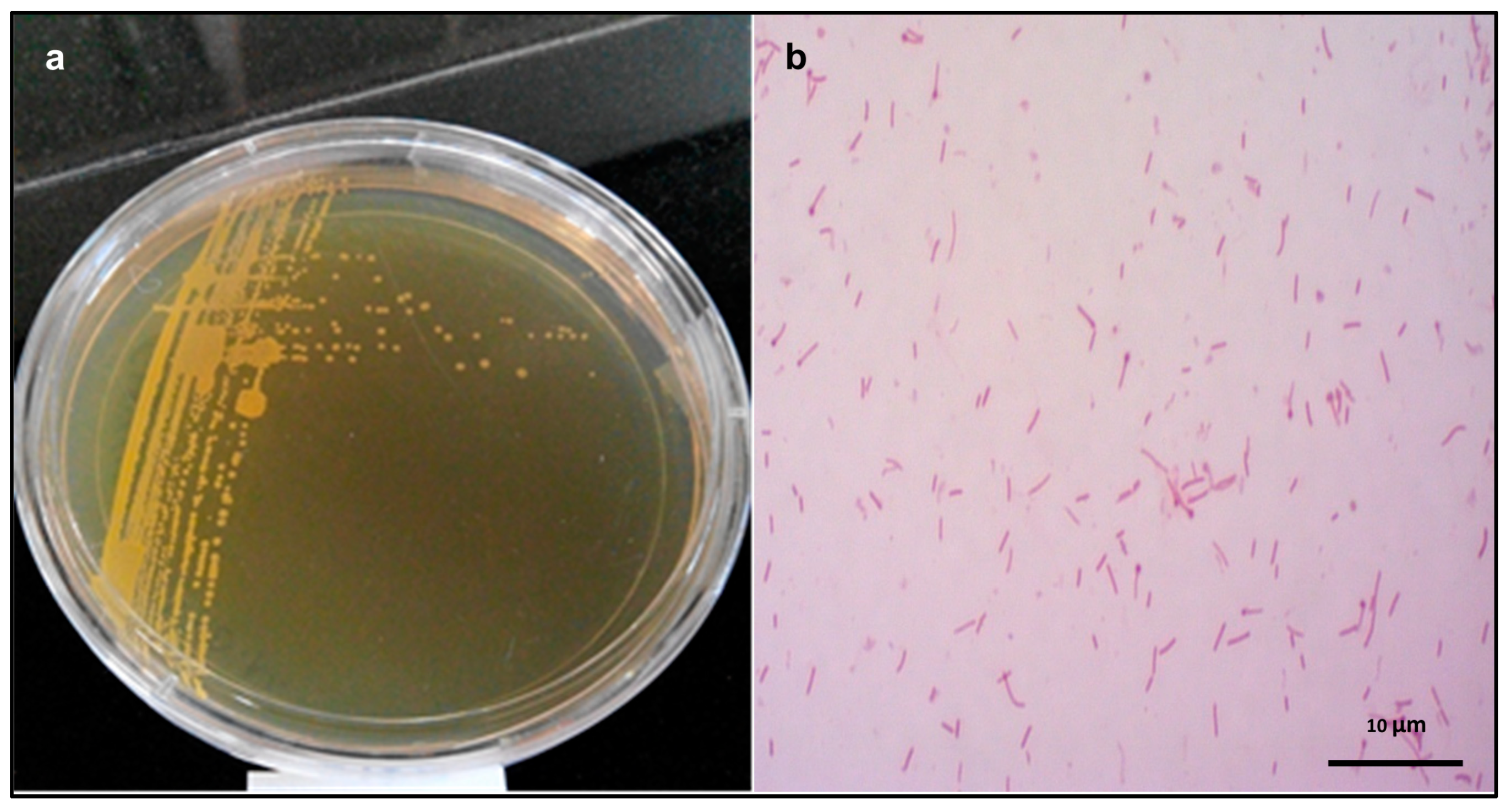
2.2. Morphological Studies of the Isolated Strain
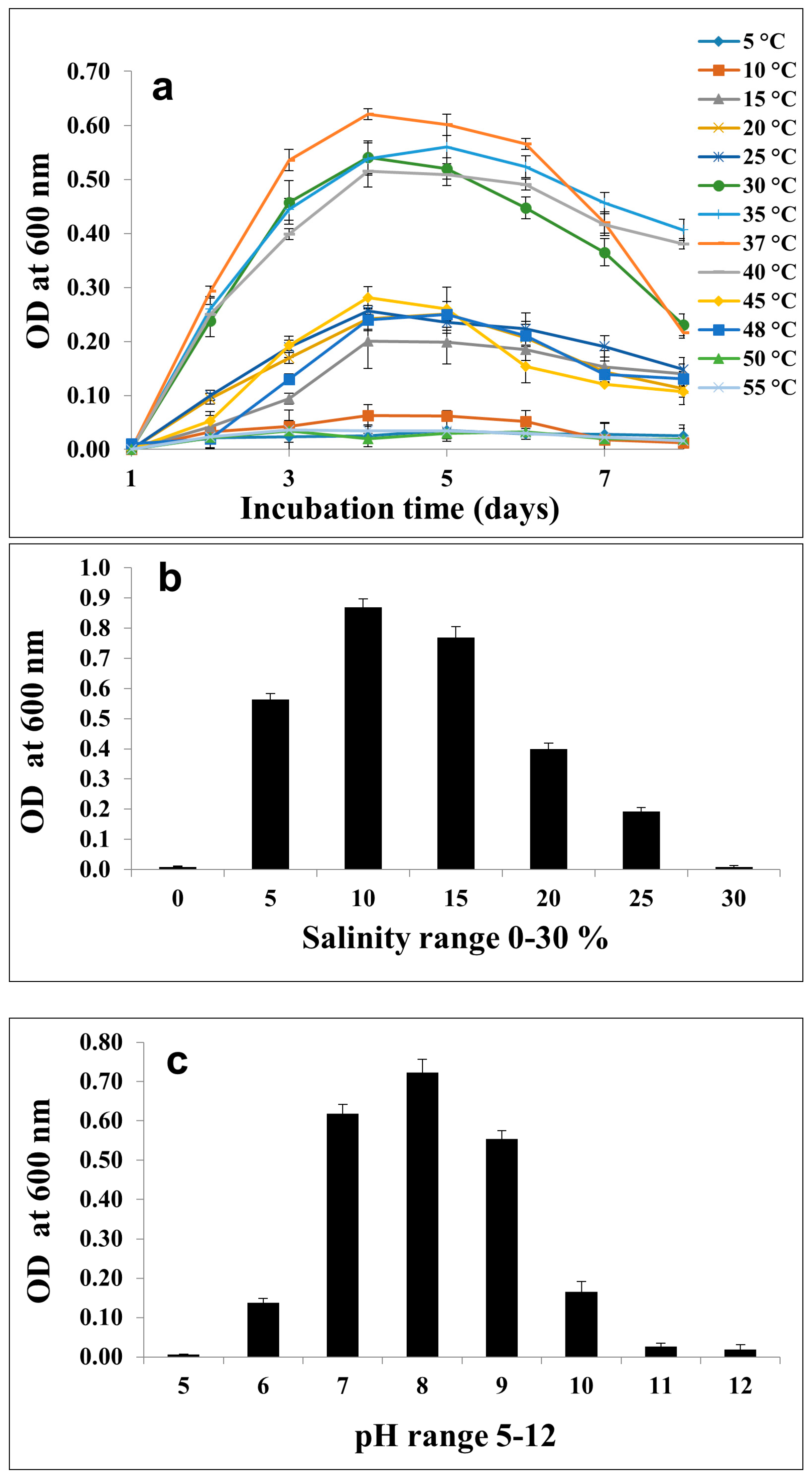
2.3. Metabolic and Growth Characteristics
2.4. Biochemical Characteristics and Enzyme Assays of the Isolated Strain
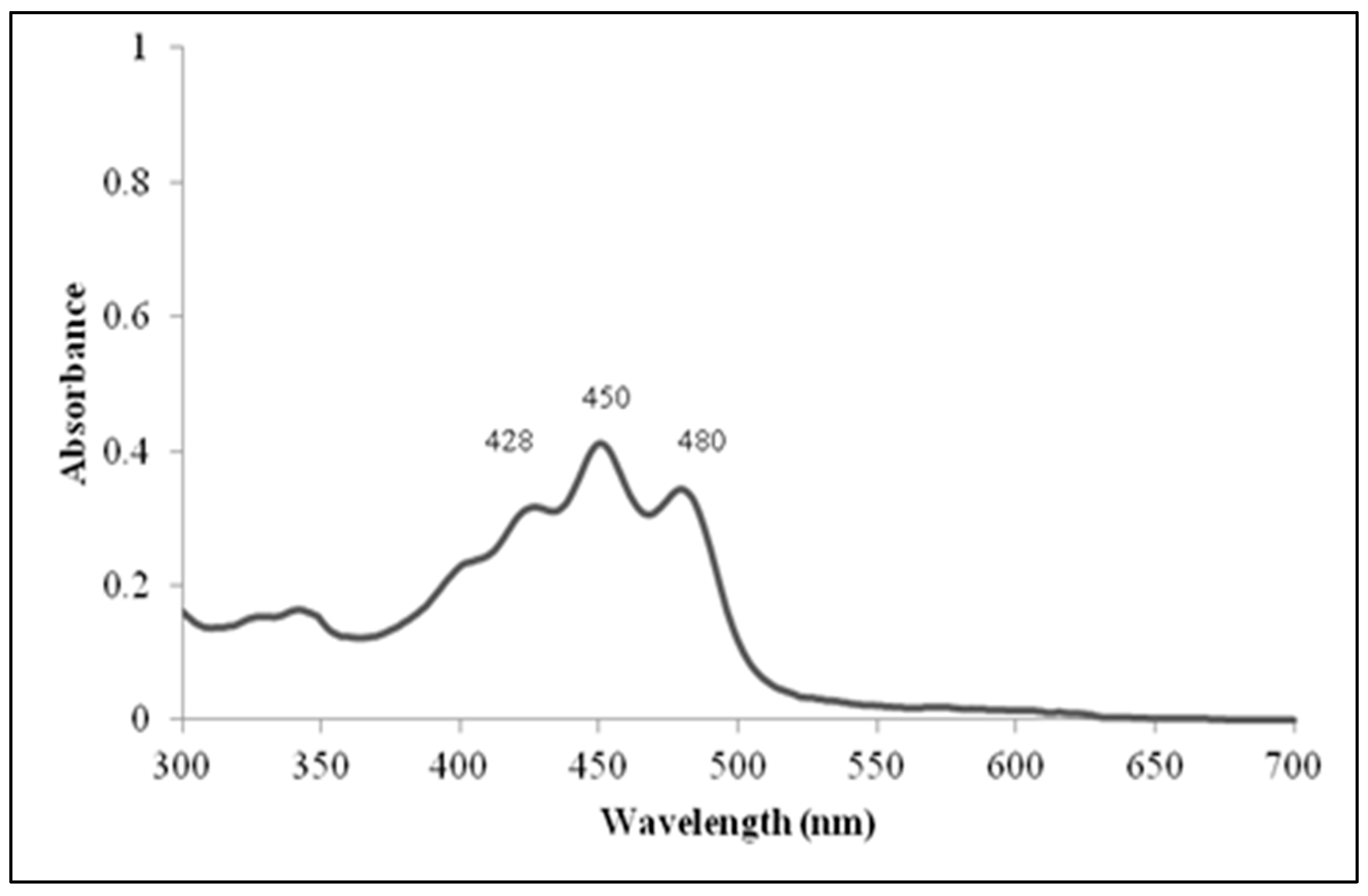
2.5. Pigments Analysis
2.6. Extraction of Genomic DNA
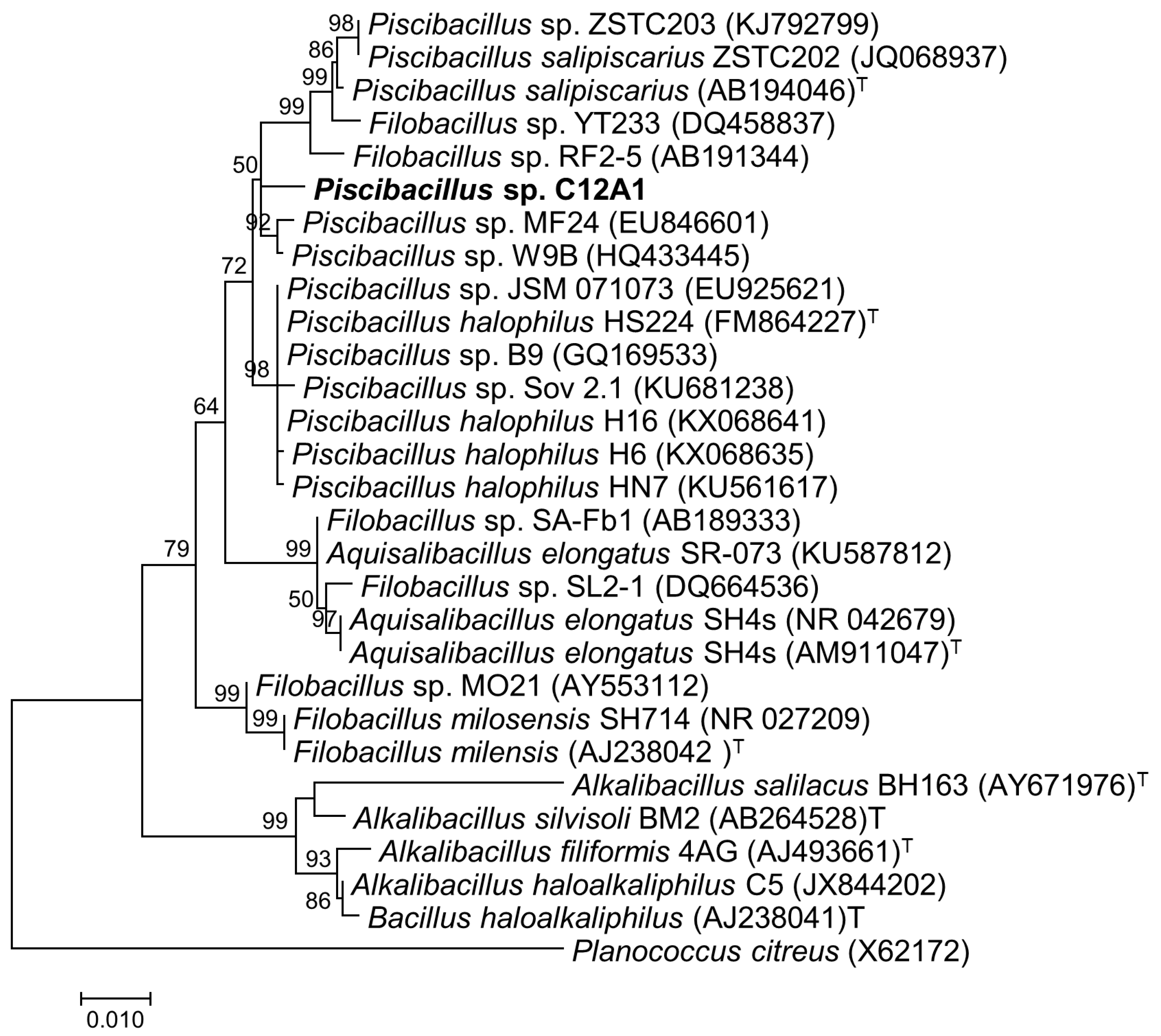
2.7. Amplification of 16S rRNA Gene and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Extraction of Metabolites
2.9. MTT Assay
2.10. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Analysis from MDA-MB-231 Cells
2.11. Scratch Assay for Cell Migration
2.12. Colony Formation Assay for Stemness
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties Sampling Site
3.2. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characterization of the Isolated Strain
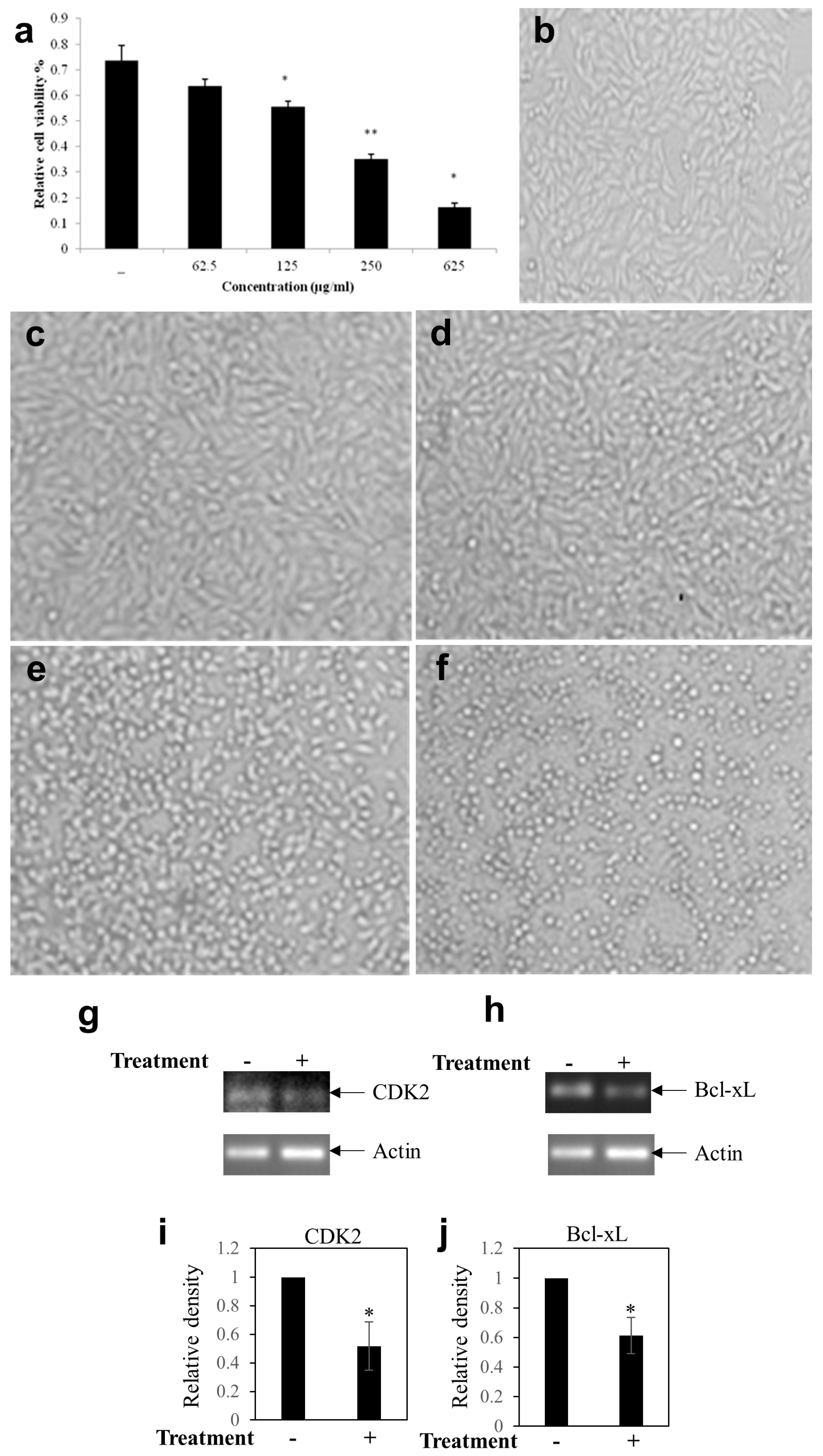
3.3. Effect BEP on Breast Cancer Cells
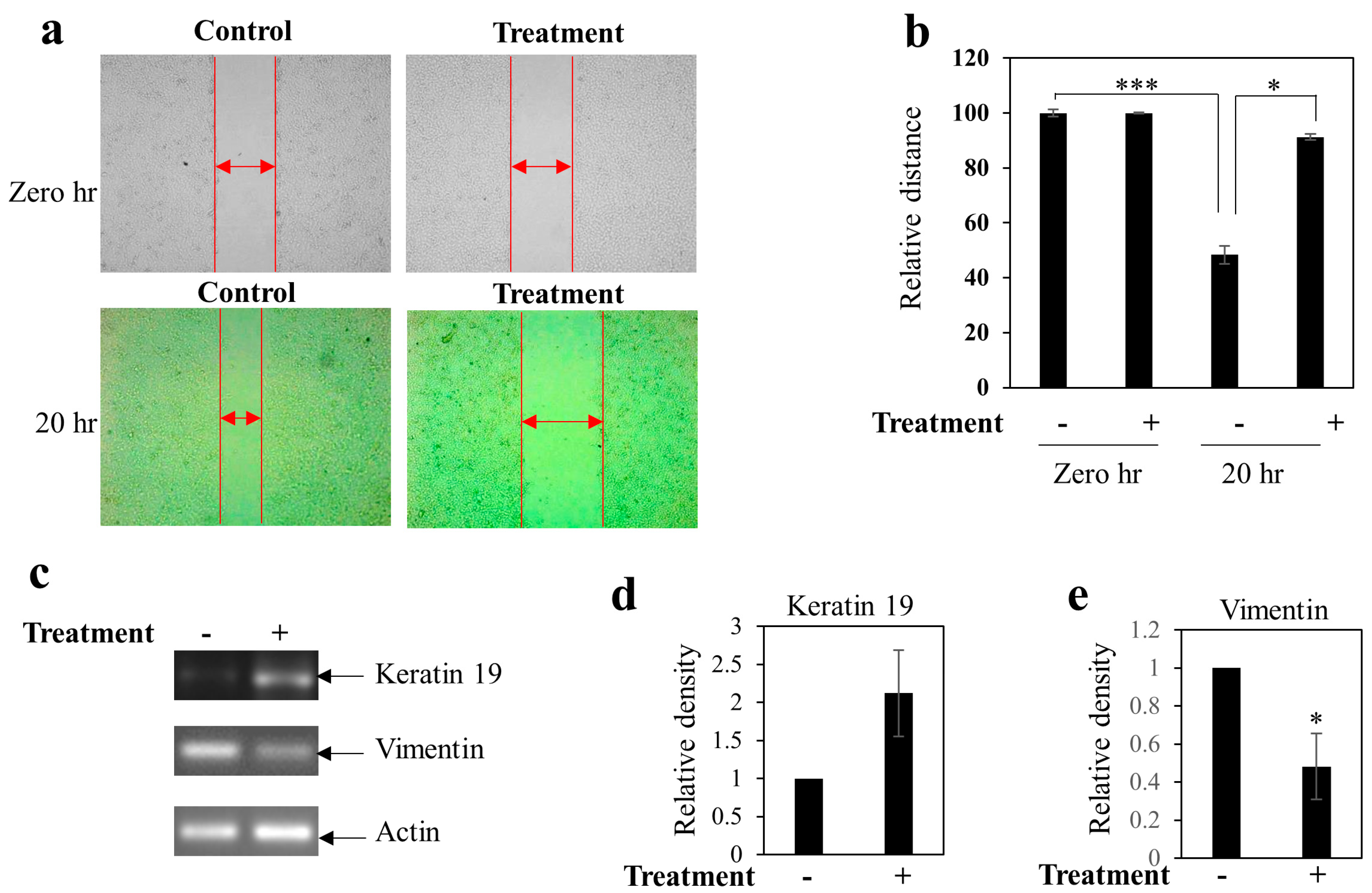
3.4. Effect of BEP on Cell Migration and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition of MDA-MB-231 Cells
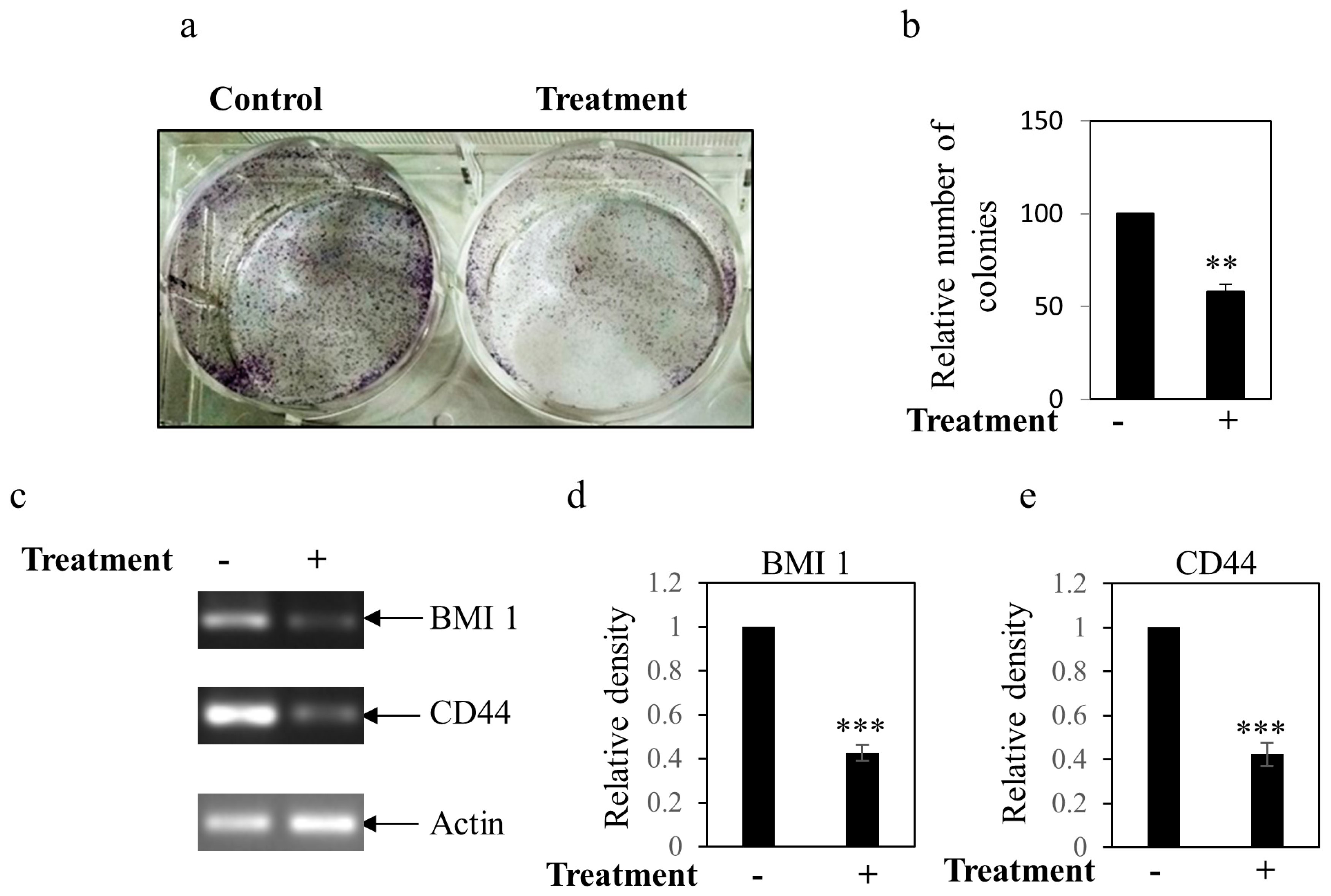
3.5. Influence of BEP on Stemness Property in MDA-MB-231 Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oren, A. Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: Environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, P.A.; Jebakumar, S.R.D. Phylogenetic appraisal of antagonistic, slow growing actinomycetes isolated from hypersaline inland solar salterns at Sambhar salt Lake, India. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Aggarwal, S.; Navani, N.K.; Choudhury, B. Isolation and characterization of a protease-producing novel haloalkaliphilic bacterium Halobiforma sp. strain BNMIITR from Sambhar lake in Rajasthan, India. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.N.; Verma, P.; Kumar, M.; Pal, K.K.; Dey, R.; Gupta, A.; Padaria, J.C.; Gujar, G.T.; Kumar, S.; Suman, A. Diversity and phylogenetic profiling of niche-specific Bacilli from extreme environments of India. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventosa, A.; Nieto, J.J.; Oren, A. Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 504–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ventosa, A.; Márquez, M.C.; Garabito, M.J.; Arahal, D.R. Moderately halophilic gram-positive bacterial diversity in hypersaline environments. Extremophiles 1998, 2, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asker, D.; Ohta, Y. Production of canthaxanthin by extremely halophilic bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 1999, 88, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Rodríguez-Valera, F. The contribution of halophilic Bacteria to the red coloration of saltern crystallizer ponds. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 36, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köcher, S.; Breitenbach, J.; Müller, V.; Sandmann, G. Structure, function and biosynthesis of carotenoids in the moderately halophilic bacterium Halobacillus halophilus. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaei, M.; Emtiazi, G. Isolation of a new Pseudomonas halophila strain possess bacteriorhodopsin-like protein by a novel method for screening of photoactive protein producing bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Hsu, S.; Lin, M.-T.; Hsu, Y. Mass production of C50 carotenoids by Haloferax mediterranei in using extruded rice bran and starch under optimal conductivity of brined medium. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Verma, H.K.; Joshi, S.; Panwar, M.S.; Mandal, C.C. A link between cold environment and cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5953–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranath, D.; Khanna, A. Current status of cancer burden: Global and Indian scenario. Biomed. Res. J. 2014, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlen, P.; Puisieux, A. Metastasis: A question of life or death. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Bu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Lin, X. Phylogenetic analysis and screening of antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of moderately halophilic bacteria isolated from the Weihai Solar Saltern (China). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sersy, N.A.; Abdelwahab, A.E.; Abouelkhiir, S.S.; Abou-Zeid, D.; Sabry, S.A. Antibacterial and Anticancer activity of ε-poly-L-lysine (ε-PL) produced by a marine Bacillus subtilis sp. J. Basic Microbiol. 2012, 52, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, N.; Nishijima, M.; Takadera, T.; Adachi, K.; Sakai, M.; Sano, H. New anticancer antibiotics pelagiomicins, produced by a new marine bacterium Pelagiobacter variabilis. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1997, 50, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donio, M.B.S.; Ronica, F.A.; Viji, V.T.; Velmurugan, S.; Jenifer, J.S.C.A.; Michaelbabu, M.; Dhar, P.; Citarasu, T. Halomonas sp. BS4, A biosurfactant producing halophilic bacterium isolated from solar salt works in India and their biomedical importance. Springerplus 2013, 2, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, E.A.I.F.; Fortes, Z.B.; da Cunha, M.A.A.; Sarilmiser, H.K.; Dekker, A.M.B.; Öner, E.T.; Dekker, R.F.H.; Khaper, N. Levan promotes antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in MCF-7 breast cancer cells mediated by oxidative stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Zeng, X.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W. A new cytotoxic phenazine derivative from a deep sea bacterium Bacillus sp. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, L.I.; Sun, T.; Zhang, H. Isolation and identification of cultivable lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented milk of Tibet in China. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Sarvari, S.; Seyedjafari, E.; Amoozgar, M.A.; Bakhshandeh, B. The effect of moderately halophilic bacteria supernatant on proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2015, 61, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahay, H.; Mahfooz, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, S.; Kaushik, R.; Saxena, A.K.; Arora, D.K. Exploration and characterization of agriculturally and industrially important haloalkaliphilic bacteria from environmental samples of hypersaline Sambhar lake, India. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneegurt, M.A. Media and conditions for the growth of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria and archaea. In Advances in Understanding the Biology of Halophilic Microorganisms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gram, C. The differential staining of Schizomycetes in tissue sections and in dried preparations. Fortschr. Med. 1884, 2, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Amoozegar, M.A.; Sanchez-Porro, C.; Rohban, R.; Hajighasemi, M.; Ventosa, A. Piscibacillus halophilus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from a hypersaline Iranian lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 3095–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, J.A.; Martínez-Cánovas, J.; Quesada, E.; Béjar, V. A detailed phenotypic characterisation of the type strains of Halomonas species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 25, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada, E.; Ventosa, A.; Ruiz-Berraquero, F.; Ramos-Cormenzana, A. Deleya halophila, a new species of moderately halophilic bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1984, 34, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventosa, A.; Quesada, E.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Ruiz-Berraquero, F.; Ramos-Cormenzana, A. Numerical taxonomy of moderately halophilic Gram-negative rods. Microbiology 1982, 128, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, M.J.; Fernández, A.B.; Ghai, R.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Ventosa, A. From metagenomics to pure culture: Isolation and characterization of the moderately halophilic bacterium Spiribacter salinus gen. nov., sp. nov. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3850–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Karan, R.; Kapoor, S.; Singh, S.P.; Khare, S.K. Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing industrially important enzymes. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, Y.-C.; Saratale, G.D.; Chen, W.-M.; Bai, M.-D.; Chang, J.-S. Isolation of cellulose-hydrolytic bacteria and applications of the cellulolytic enzymes for cellulosic biohydrogen production. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2009, 44, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, C.; González, C. Method for simultaneous detection of proteinase and esterase activities in extremely halophilic bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kharangate-Lad, A.; Bhosle, S. Studies on Siderophore and Pigment Produced by an Adhered Bacterial Strain Halobacillus trueperi MXM-16 from the Mangrove Ecosystem of Goa, India. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, C.; Gillings, M.R.; Davison, A.D.; Altavilla, N.; Veal, D.A. PCR amplification of crude microbial DNA extracted from soil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 25, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematic; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.A.; Webster, J.A.; Straus, N. Rapid identification of bacteria on the basis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified ribosomal DNA spacer polymorphisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Software And Services For DNA Analysis. Available online: https://www.sequentix.de (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- Srividya, A.R.; Saritha, G.S.; Suresh, B. Study of the soil isolates for antimicrobial activity. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dikmen, M.; Ozturk, N.; Ozturk, Y. The antioxidant potency of Punica granatum L. Fruit peel reduces cell proliferation and induces apoptosis on breast cancer. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, K.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, T.; Kumar, S.; Mandal, C.C. Simvastatin and MBCD inhibit breast cancer-induced osteoclast activity by targeting osteoclastogenic factors. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, K.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, S.; Gunjan, G.K.; Nag, A.; Mandal, C.C. Colocynth Extracts Prevent Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness of Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, C.C.; Das, F.; Ganapathy, S.; Harris, S.E.; Choudhury, G.G.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) activates NFATc1 transcription factor via an autoregulatory loop involving Smad/Akt/Ca2+ signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, C.C.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N.; Yoneda, T.; Choudhury, G.G.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N. Simvastatin prevents skeletal metastasis of breast cancer by an antagonistic interplay between p53 and CD44. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11314–11327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, C.C.; Ghosh-Choudhury, T.; Yoneda, T.; Choudhury, G.G.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N. Fish oil prevents breast cancer cell metastasis to bone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 402, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ventosa, A. Unusual micro-organisms from unusual habitats: Hypersaline environments. In Symposia-Society for General Microbiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume 66, p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Benlloch, S.; López-López, A.; Casamayor, E.O.; Øvreås, L.; Goddard, V.; Daae, F.L.; Smerdon, G.; Massana, R.; Joint, I.; Thingstad, F. Prokaryotic genetic diversity throughout the salinity gradient of a coastal solar saltern. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanasupawat, S.; Namwong, S.; Kudo, T.; Itoh, T. Piscibacillus salipiscarius gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from fermented fish (pla-ra) in Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobin, B.; Stahly, G.L. The isolation and absorption spectrum maxima of bacterial carotenoid pigments. J. Bacteriol. 1942, 44, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Porro, C.; Martin, S.; Mellado, E.; Ventosa, A. Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohban, R.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Ventosa, A. Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolyses from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | C12A1 | Piscibacillus salipiscarius * | Piscibacillus halophilus ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell size (µm) | 0.3–0.5 × 1.5–3.0 | 0.4–0.5 × 1.5–4.0 | 0.5–0.7 × 2.5–4.0 |
| Gram reaction | + | + | + |
| Spore shape and position | Oval, terminal in swollen sporangia | Oval, terminal in swollen sporangia | Oval, terminal in swollen sporangia |
| Motility | + | + | + |
| NaCl range (optimum) (%, w/v) | 5–25 (10–15) | 2–30 (10–20) | 1–20 (10) |
| Temperature range (optimum) (°C) | 15–48 (37) | 15–48 (37) | 15–55 (35) |
| pH range (optimum) | 6.0–10.0 (8.0) | 5.0–9.0 (7.0) | 7.0–10.0 (7.5) |
| Oxidase | + | + | + |
| Catalase | + | + | + |
| Hydrolysis of: | |||
| Gelatin | + | + | + |
| Starch | − | + | − |
| Skimmed milk | + | + | + |
| Tween 80 | + | − | + |
| Urea | − | − | ND |
| eduction of nitrate | + | − | − |
| Use of citrate | − | − | ND |
| Production of indole | − | − | − |
| Acid production from: | |||
| D-glucose | − | + | − |
| D-maltose | − | − | − |
| D-Xylose | − | − | − |
| D-fructose | − | + | − |
| Glycerol | − | + | − |
| Sucrose | − | + | − |
| Pigment production | + | ND | ND |
| Antibiotic test: | |||
| Tetracycline | S | ND | S |
| Kanamycin | R | ND | R |
| Gentamycin | S | ND | R |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neelam, D.K.; Agrawal, A.; Tomer, A.K.; Bandyopadhayaya, S.; Sharma, A.; Jagannadham, M.V.; Mandal, C.C.; Dadheech, P.K. A Piscibacillus sp. Isolated from A Soda Lake Exhibits Anticancer Activity Against Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7020034
Neelam DK, Agrawal A, Tomer AK, Bandyopadhayaya S, Sharma A, Jagannadham MV, Mandal CC, Dadheech PK. A Piscibacillus sp. Isolated from A Soda Lake Exhibits Anticancer Activity Against Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeelam, Deepesh Kumar, Akhil Agrawal, Anuj Kumar Tomer, Shreetama Bandyopadhayaya, Ankit Sharma, Medicharla V. Jagannadham, Chandi C. Mandal, and Pawan K. Dadheech. 2019. "A Piscibacillus sp. Isolated from A Soda Lake Exhibits Anticancer Activity Against Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells" Microorganisms 7, no. 2: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7020034
APA StyleNeelam, D. K., Agrawal, A., Tomer, A. K., Bandyopadhayaya, S., Sharma, A., Jagannadham, M. V., Mandal, C. C., & Dadheech, P. K. (2019). A Piscibacillus sp. Isolated from A Soda Lake Exhibits Anticancer Activity Against Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Microorganisms, 7(2), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7020034





