Phytoplankton and Bacterial Community Structure in Two Chinese Lakes of Different Trophic Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sample Collection
2.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Phytoplankton
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions
3.2. Phytoplankton Community Composition in the Two Lakes
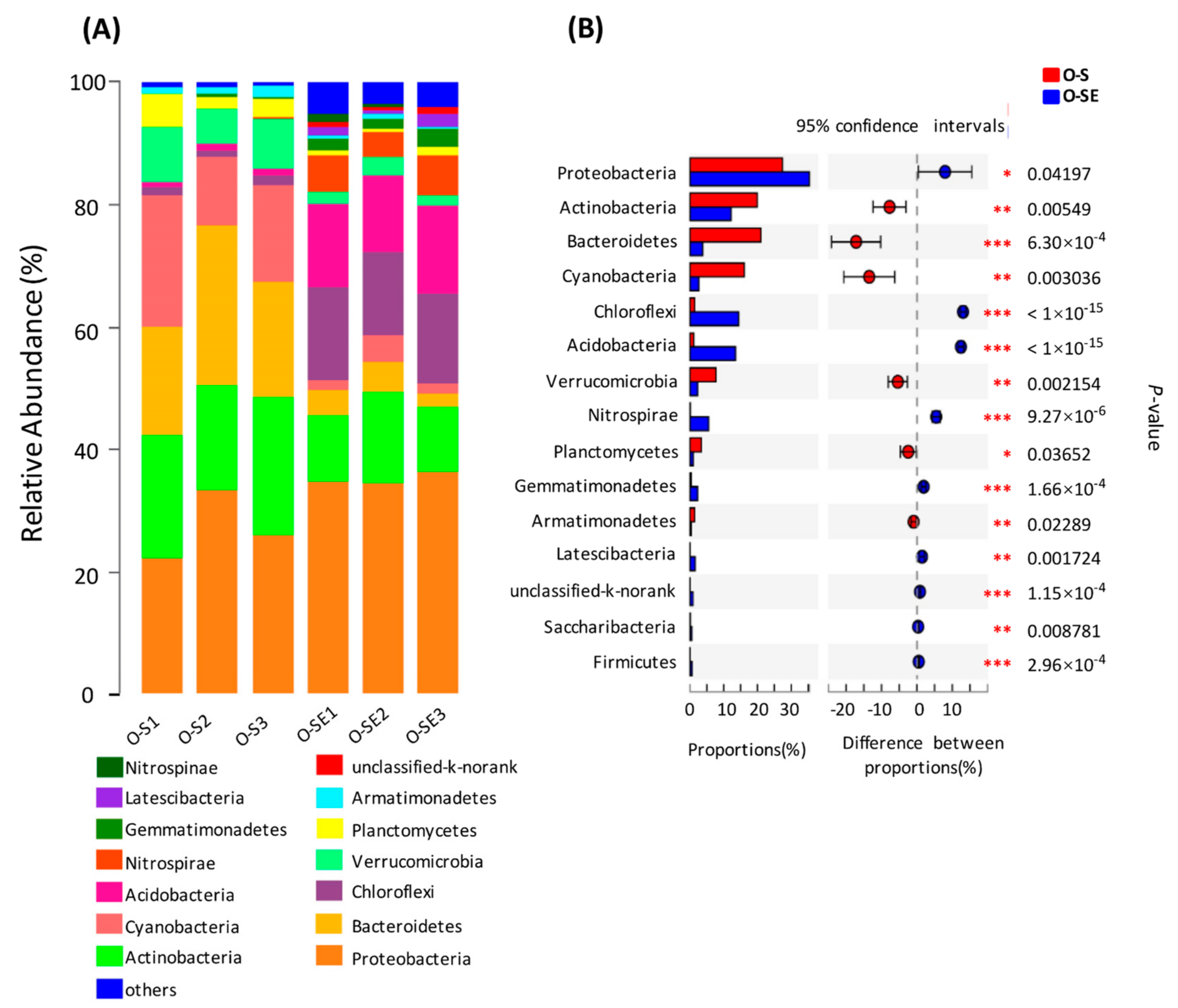
3.3. Bacterial Community Structure in the Two Lakes
3.4. Comparative Analysis of the Bacterial Communities in the Water and Sediment
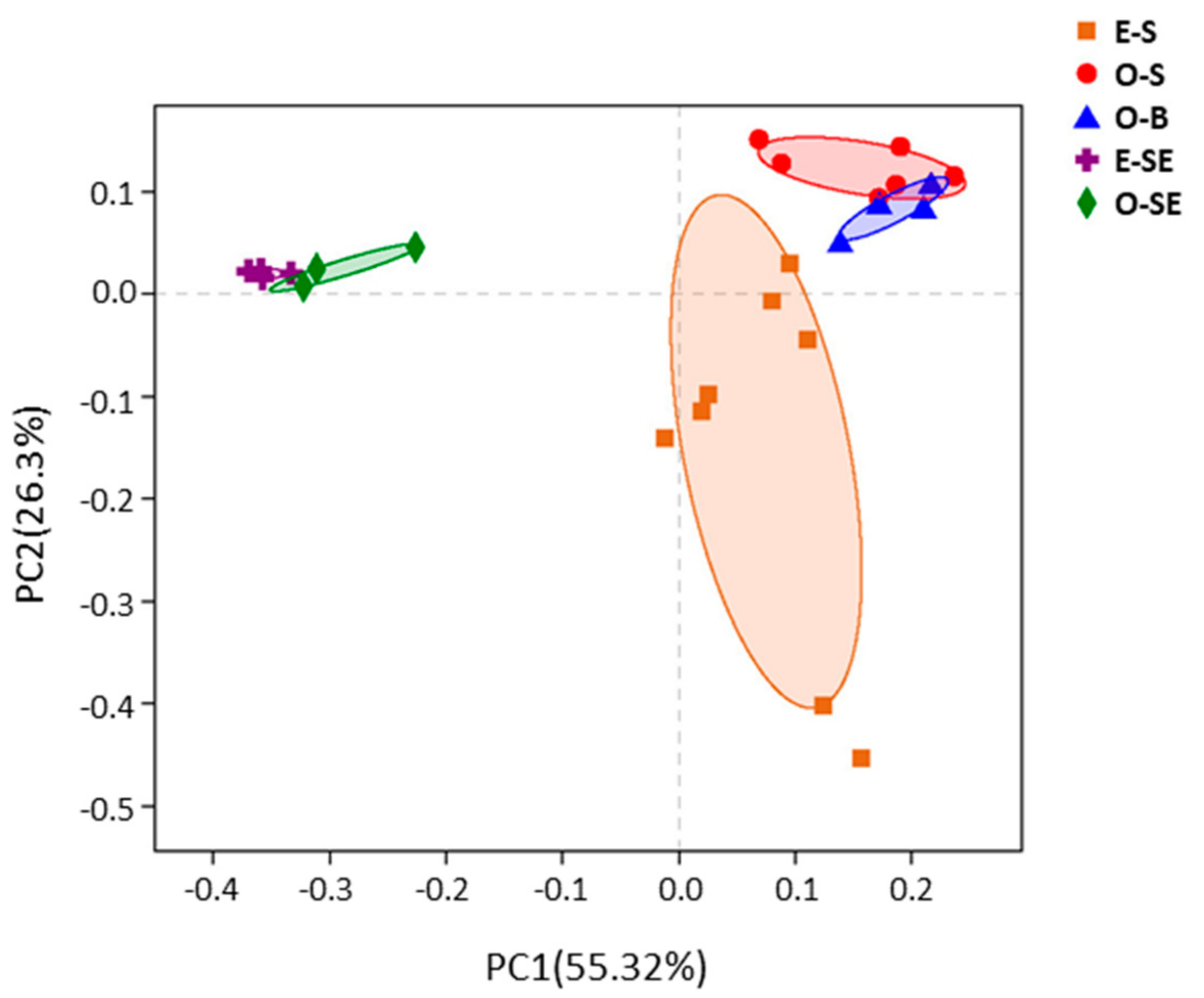
3.5. Principal Co-ordinates Analysis
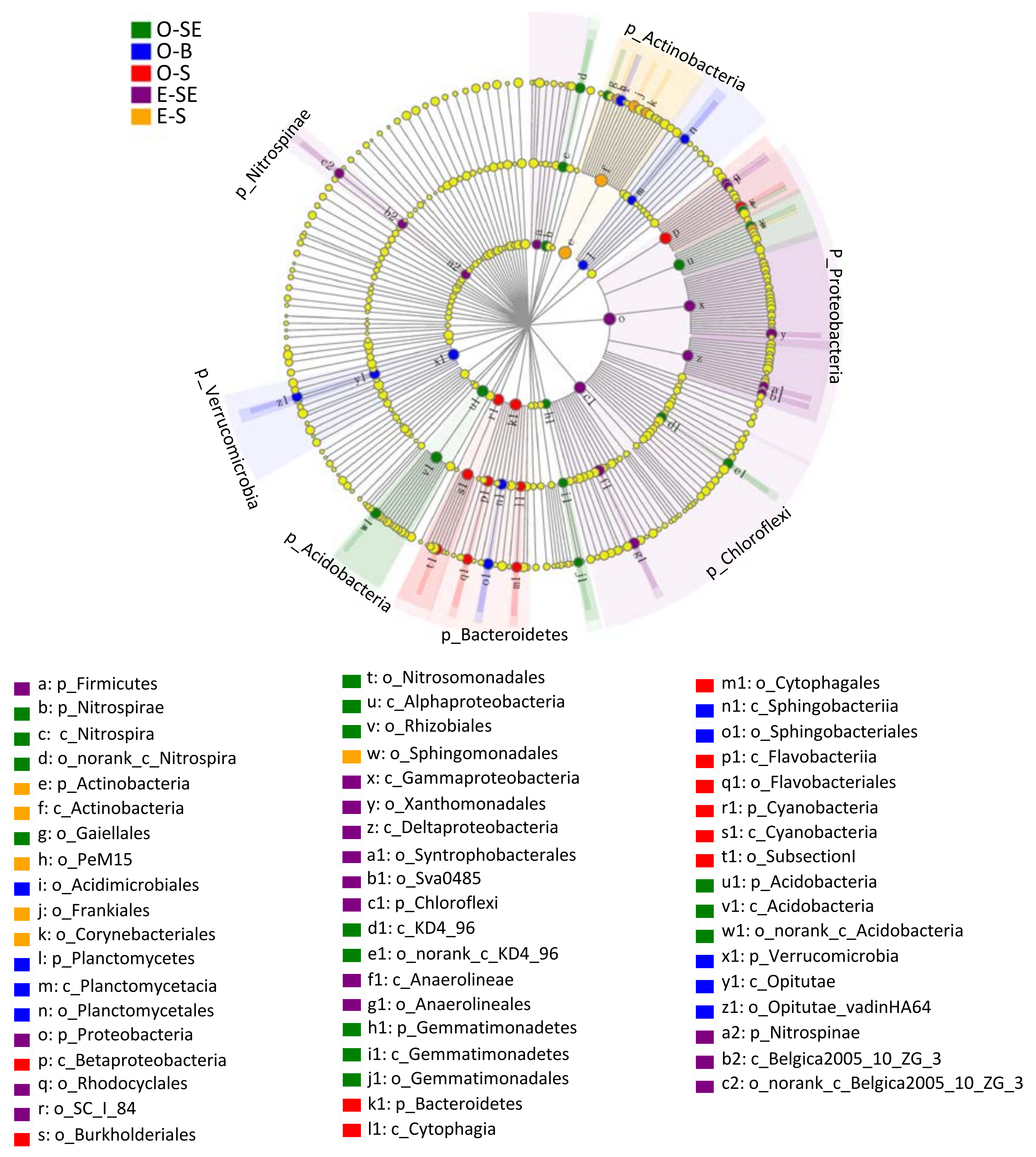
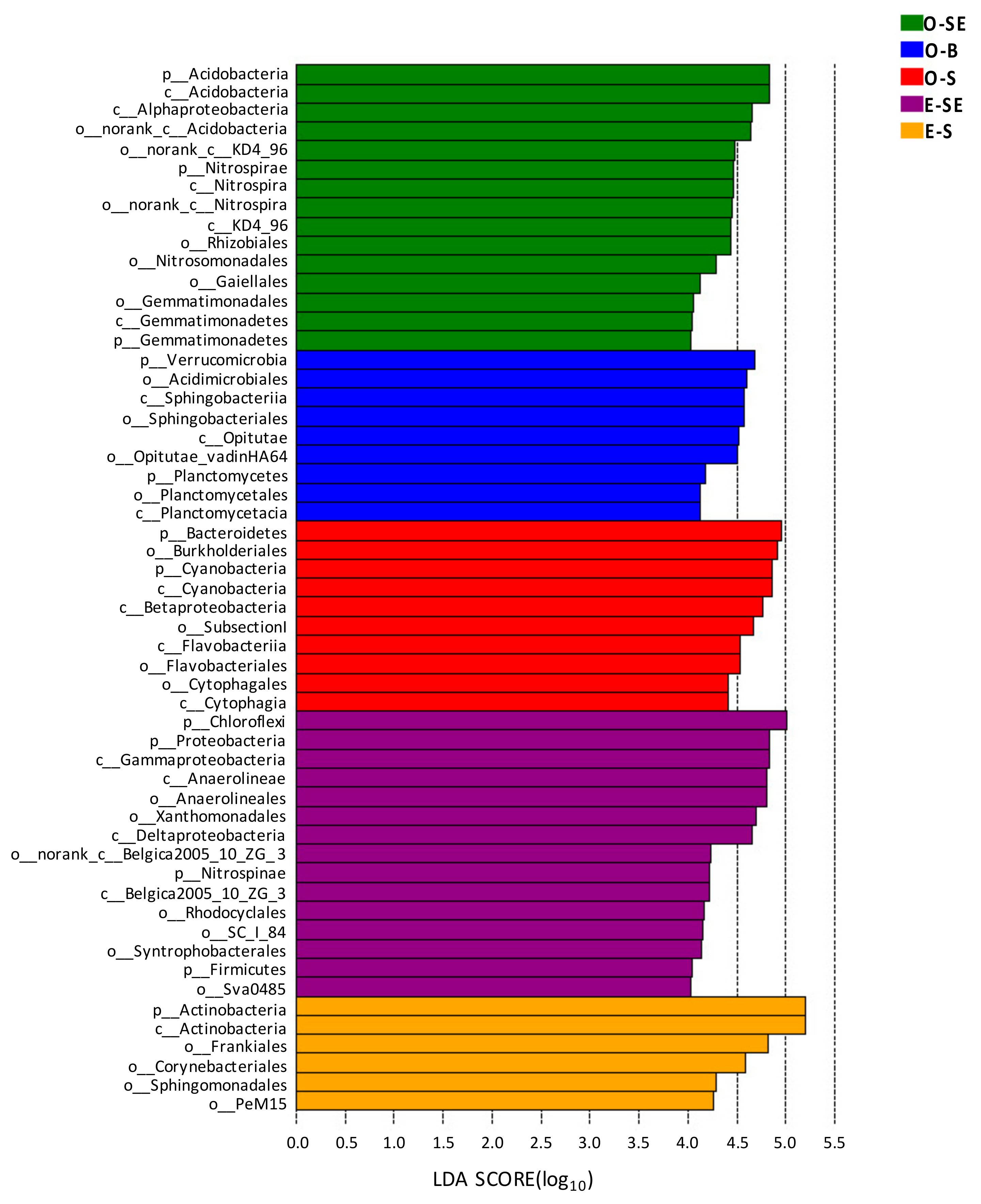
3.6. LEfSe Analysis Based on Community Abundance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falkowski, P.G.; Tom, F.; Delong, E.F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Berben, T.; Melton, E.D.; Overmars, L.; Vavourakis, C.D.; Muyzer, G. Microbial diversity and biogeochemical cycling in soda lakes. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, K.; Yang, S.H.; Wan, M.T.; Yang, C.C.; Baatar, B.; Chiu, C.Y.; Tsai, J.W.; Liu, W.C.; Tang, S.L. Bacterial Community in Water and Air of Two Sub-Alpine Lakes in Taiwan. Microbes. Environ. 2018, 33, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.Y.; Zheng, B.H.; Jiang, X. Comparison among the microbial communities in the lake, lake wetland, and estuary sediments of a plain river network. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J. Bacterioplankton Growth on Fractions of Dissolved Organic-Carbon of Different Molecular-Weights from Humic and Clear Waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Lean, D.R.S.; Pick, F.R. Photosynthetic Response of Lake Plankton to Nutrient Enrichment - a Test for Nutrient Limitation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadro, S.; Nelson, C.E.; Melack, J.M. Linking diel patterns in community respiration to bacterioplankton in an oligotrophic high-elevation lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer-Natan, O.; Ofek-Lalzar, M.; Sher, D.; Sukenik, A. Particle-Associated Microbial Community in a Subtropical Lake During Thermal Mixing and Phytoplankton Succession. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paver, S.F.; Hayek, K.R.; Gano, K.A.; Fagen, J.R.; Brown, C.T.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Crabb, D.B.; Rosario-Passapera, R.; Giongo, A.; Triplett, E.W.; et al. Interactions between specific phytoplankton and bacteria affect lake bacterial community succession. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2489–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hannen, E.J.; Mooij, W.M.; van Agterveld, M.P.; Gons, H.J.; Laanbroek, H.J. Detritus-dependent development of the microbial community in an experimental system: Qualitative analysis by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.J. Interactions between Bacteria and Algae in Aquatic Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1982, 13, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, C.R.; Salvitti, L.R.; Whereat, E.B.; Coyne, K.J. Community-Level and Species-Specific Associations between Phytoplankton and Particle-Associated Vibrio Species in Delaware’s Inland Bays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5703–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, K.; Tobiesen, A. Bacterivory in Algae - a Survival Strategy during Nutrient Limitation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Langeland, K.A.; Maceina, M.J.; Haller, W.T.; Shireman, J.V.; Jones, J.R. Trophic State Classification of Lakes with Aquatic Macrophytes. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1983, 40, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösel, S.; Grossart, H.P. Contrasting dynamics in activity and community composition of free-living and particle-associated bacteria in spring. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 66, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, B.; Reveilliez, J.P.; Mary, I.; Ravet, V.; Bronner, G.; Mangot, J.F.; Domaizon, I.; Debroas, D. Diversity and dynamics of free-living and particle-associated. 2011, 77, 461–476. [Google Scholar]
- Allgaier, M.; Grossart, H.P. Seasonal dynamics and phylogenetic diversity of free-living and particle-associated bacterial communities in four lakes in northeastern Germany. 2006, 45, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Heil, C.A.; Hollander, D.; Revilla, M.; Hoare, A.; Alexander, J.; Murasko, S. Evidence for dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus uptake during a cyanobacterial bloom in Florida Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 280, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, E.S.; Kamst-Van Agterveld, M.P.; Zwart, G. Distribution of typical freshwater bacterial groups is associated with pH, temperature, and lake water retention time. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8201–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klein, J.J.M.; Overbeek, C.C.; Jorgensen, C.J.; Veraart, A.J. Effect of Temperature on Oxygen Profiles and Denitrification Rates in Freshwater Sediments. Wetlands 2017, 37, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, F.; Das Purkayastha, S.; Sen, A.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Misra, B.B. Diversity of methanogenic archaea in freshwater sediments of lacustrine ecosystems. J. Basic. Microb. 2018, 58, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y. Bacterial communities in sediments of the shallow Lake Dongping in China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.X.; Xu, M.; Qiu, S.; Shen, R.C. Spatial patterns of benthic bacterial communities in a large lake. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2015, 100, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.Z.; Xie, S.G.; Liu, Y. Distribution of sediment bacterial and archaeal communities in plateau freshwater lakes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Liu, Y.Q.; Jiao, N.Z.; Zhu, L.P.; Wang, J.B.; Hu, A.Y.; Liu, X.B. Vertical variation of bacterial community in Nam Co, a large stratified lake in central Tibetan Plateau. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. G. 2016, 109, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, E.R.; Mohn, W.W. Psychrotolerant bacteria isolated from Arctic soil that degrade polychlorinated biphenyls at low temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4823–4829. [Google Scholar]
- Demnerova, K.; Stiborova, H.; Leigh, M.B.; Pieper, D.; Mackova, M. Bacteria degrading PCBs and CBs isolated from long-term PCB contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2003, 3, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, L.J.; Zhao, D.Y. Spatial distribution of bacterial communities in sediment of a eutrophic lake revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and multivariate analysis. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Hui, L.I.; Bo-Zhong, M.U. RFLP Analysis of 16S rRNA Genes of Bacterial Community in Water Sample of a Petroleum Reservoir. J. Microbiol. 2005, 25, 1–5. Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-WSWX200506000.htm (accessed on 27 November 2019).
- Neufeld, J.D.; Mohn, W.W. Unexpectedly High Bacterial Diversity in Arctic Tundra Relative to Boreal Forest Soils, Revealed by Serial Analysis of Ribosomal Sequence Tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5710–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Zuo, J.E.; Sun, Y.J.; Jian-Ping, L.I. Study on Microbial Community in Methanogenic Granular Sludge by FISH and DGGE. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2006, 27, 2268–2272. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, D.P.; Brockman, F.J.; Fredrickson, J.K. Use of 16S rDNA clone libraries to study changes in a microbial community resulting from ex situ perturbation of a subsurface sediment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 20, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.B.; Taylor, D.R.; Mills, A.L. Characterization of microbial community structure using Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD). J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 35, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofle, M.G.; Flavier, S.; Christen, R.; Botel, J.; Labrenz, M.; Brettar, I. Retrieval of nearly complete 16S rRNA gene sequences from environmental DNA following 16S rRNA-based community fingerprinting. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.Z.; Gong, Y.H.; Zhou, C.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Z.; Ning, K. Comparison and Interpretation of Taxonomical Structure of Bacterial Communities in Two Types of Lakes on Yun-Gui plateau of China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parulekar, N.N.; Kolekar, P.; Jenkins, A.; Kleiven, S.; Utkilen, H.; Johansen, A.; Sawant, S.; Kulkarni-Kale, U.; Kale, M.; Saebo, M. Characterization of bacterial community associated with phytoplankton bloom in a eutrophic lake in South Norway using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequence analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.T.; Peng, X.; Deng, G.H.; Sheng, H.F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.W.; Tam, N.F.Y. Illumina Sequencing of 16S rRNA Tag Revealed Spatial Variations of Bacterial Communities in a Mangrove Wetland. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, Z.; Xie, S.G.; Liu, Y. Distribution of bacterial communities across plateau freshwater lake and upslope soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-unseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.J.; Wei, Y.X. The freshwater algae of China--Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Sciencep: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rother, A.J. The annual cycle of growth and reproduction of planktonic blue-green algae in the Salopian meres. Queen Mary Univ. Lond. 1977. Available online: http://qmro.qmul.ac.uk/xmlui/handle/123456789/1905 (accessed on 27 November 2019).
- Brittain, S.M.; Wang, J.; Babcock-Jackson, L.; Carmichael, W.W.; Rinehart, K.L.; Culver, D.A. Isolation and characterization of microcystins, cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins from a Lake Erie strain of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Great. Lakes Res. 2000, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnecke, F.; Amann, R.; Pernthaler, J. Actinobacterial 16S rRNA genes from freshwater habitats cluster in four distinct lineages. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcher, M.M.; Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T. Spatiotemporal distribution and activity patterns of bacteria from three phylogenetic groups in an oligomesotrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.A.; van der Gast, C.J.; Woodward, K.; Newsham, K.K. Significant changes in the bacterioplankton community structure of a maritime Antarctic freshwater lake following nutrient enrichment. Microbiologyopen 2005, 151, 3237–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Garcia, S.L.; McMahon, K.D.; Grossart, H.P.; Warnecke, F. Successful enrichment of the ubiquitous freshwater acI Actinobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.L.; McMahon, K.D.; Martinez-Garcia, M.; Srivastava, A.; Sczyrba, A.; Stepanauskas, R.; Grossart, H.P.; Woyke, T.; Warnecke, F. Metabolic potential of a single cell belonging to one of the most abundant lineages in freshwater bacterioplankton. Isme J. 2013, 7, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Sekiguchi, Y. Cultivation of Uncultured Chloroflexi Subphyla: Significance and Ecophysiology of Formerly Uncultured Chloroflexi ‘Subphylum I’ with Natural and Biotechnological Relevance. Microbes Environ. 2009, 24, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Rash, B.A.; Rainey, F.A.; Moe, W.M. Isolation of novel bacteria within the Chloroflexi capable of reductive dechlorination of 1,2,3-trichloropropane. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, L.A.; Castelle, C.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Sharon, I.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Williams, K.H.; Tringe, S.G.; Banfield, J.F. Community genomic analyses constrain the distribution of metabolic traits across the Chloroflexi phylum and indicate roles in sediment carbon cycling. Microbiome 2013, 1, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, E.; Schmidt, M.L.; Berry, M.A.; Biddanda, B.A.; Burtner, A.; Johengen, T.H.; Palladino, D.; Denef, V.J. Verrucomicrobia are prevalent in north-temperate freshwater lakes and display class-level preferences between lake habitats (vol 13, e0195112, 2018). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, W.; Fischer, A.; Smida, J.; Stackebrandt, E. Verrucomicrobium spinosum, a Eubacterium Representing an Ancient Line of Descent. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1987, 10, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.L.; White, J.D.; Denef, V.J. Phylogenetic conservation of freshwater lake habitat preference varies between abundant bacterioplankton phyla. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.M.; Stevens, S.L.R.; Chan, L.K.; Bertilsson, S.; del Rio, T.G.; Tringe, S.G.; Malmstrom, R.R.; McMahon, K.D. Ecophysiology of Freshwater Verrucomicrobia Inferred from Metagenome-Assembled Genomes. Msphere 2017, 2, e00277-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jain, S.; Dick, G.J. Genomic and Transcriptomic Resolution of Organic Matter Utilization Among Deep-sea Bacteria in Guaymas Basin Hydrothermal Plumes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Damsté, J.S.S. Acidobacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Pankratov, T.A.; Belova, S.E.; Kulichevskaya, I.S.; Liesack, W. Phylogenetic Analysis and In Situ Identification of Bacteria Community Composition in an Acidic Sphagnum Peat Bog. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2110–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkebaeva, Y.M.; Kim, Y.; Liesack, W.; Dedysh, S.N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of the Bacteria Diversity in Surface and Subsurface Peat Layers of a Northern Wetland, with Focus on Poorly Studied Phyla and Candidate Divisions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. Isme J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, H.F.; He, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Zhou, H.W. Comparison of the Levels of Bacterial Diversity in Freshwater, Intertidal Wetland, and Marine Sediments by Using Millions of Illumina Tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Q.Y.; Xie, S.G.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xie, P.; Wang, S.R.; Niu, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, W.J. Sources of organic matter affect depth-related microbial community composition in sediments of Lake Erhai, Southwest China. J. Limnol. 2015, 74, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Yao, T.D.; Jiao, N.Z.; Liu, X.B.; Kang, S.C.; Luo, T.W. Seasonal Dynamics of the Bacterial Community in Lake Namco, the Largest Tibetan Lake. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
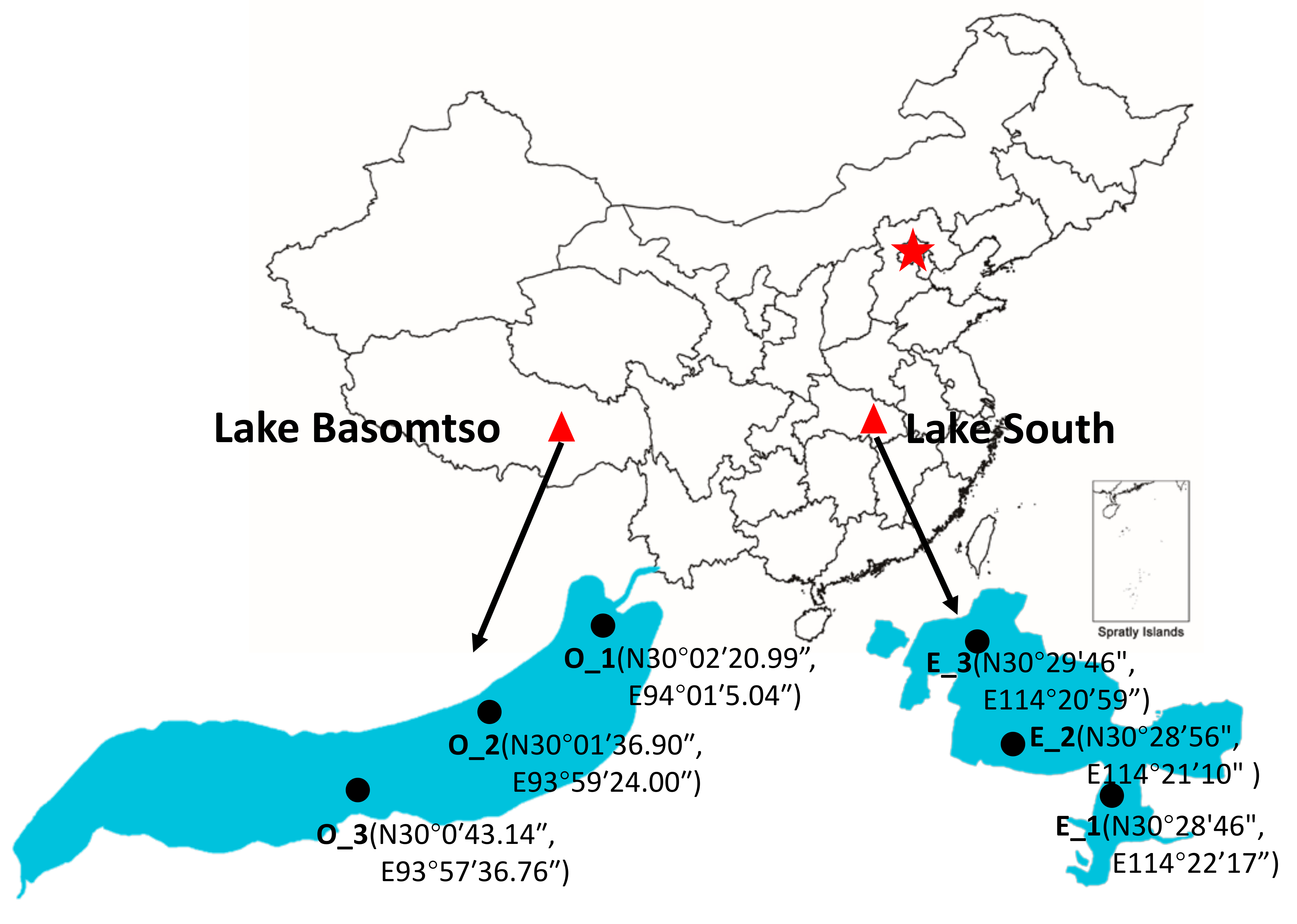
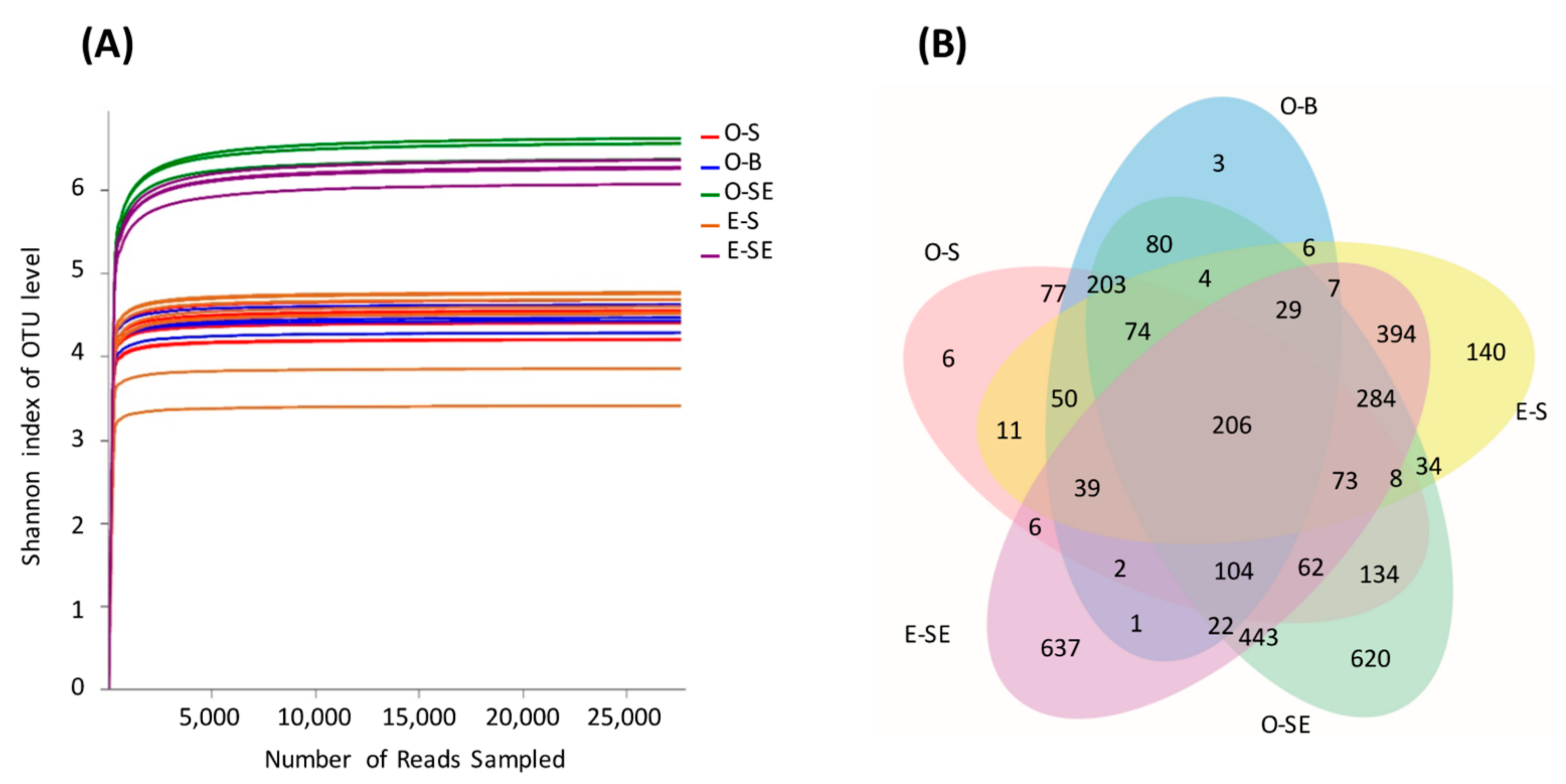
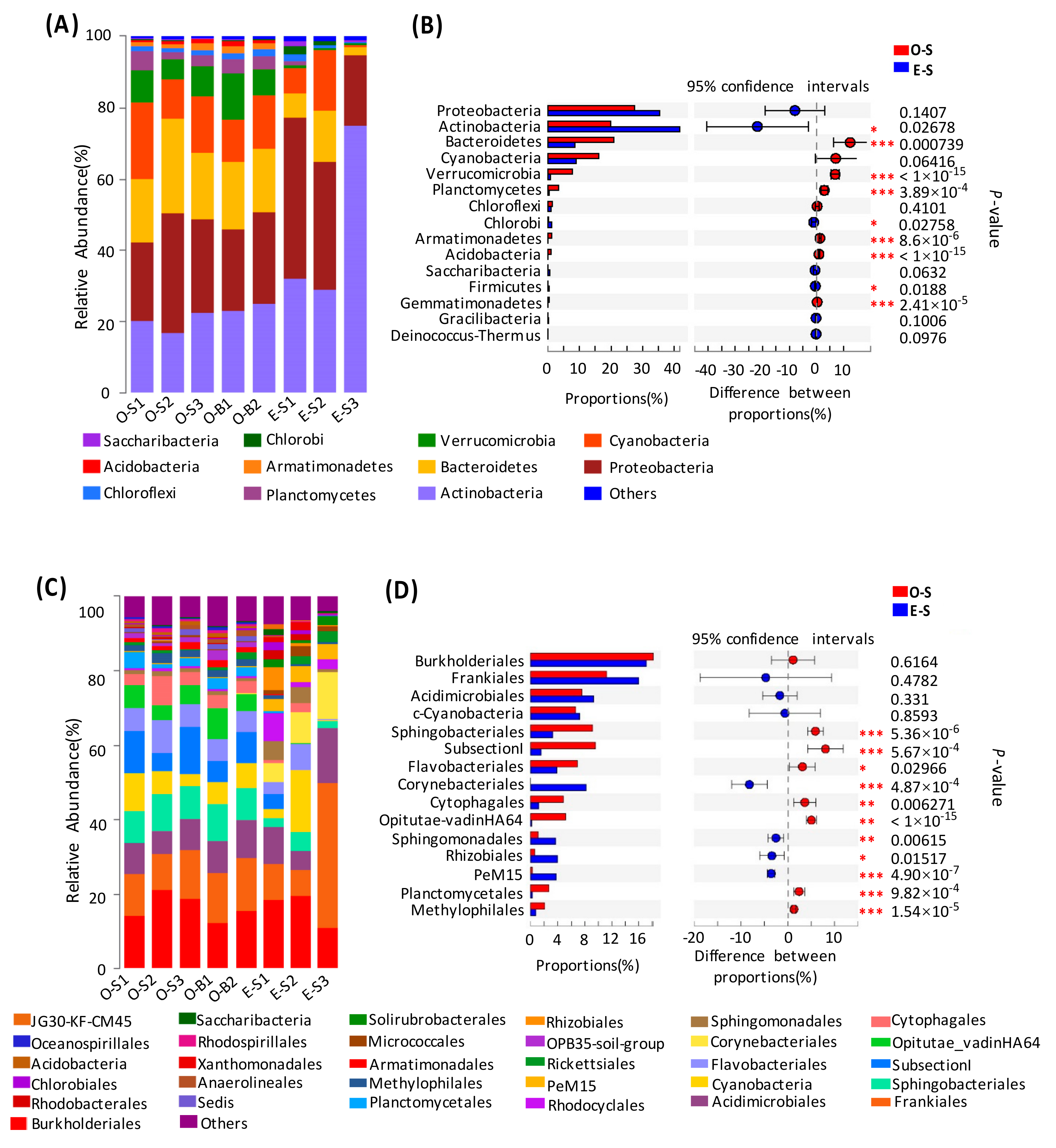
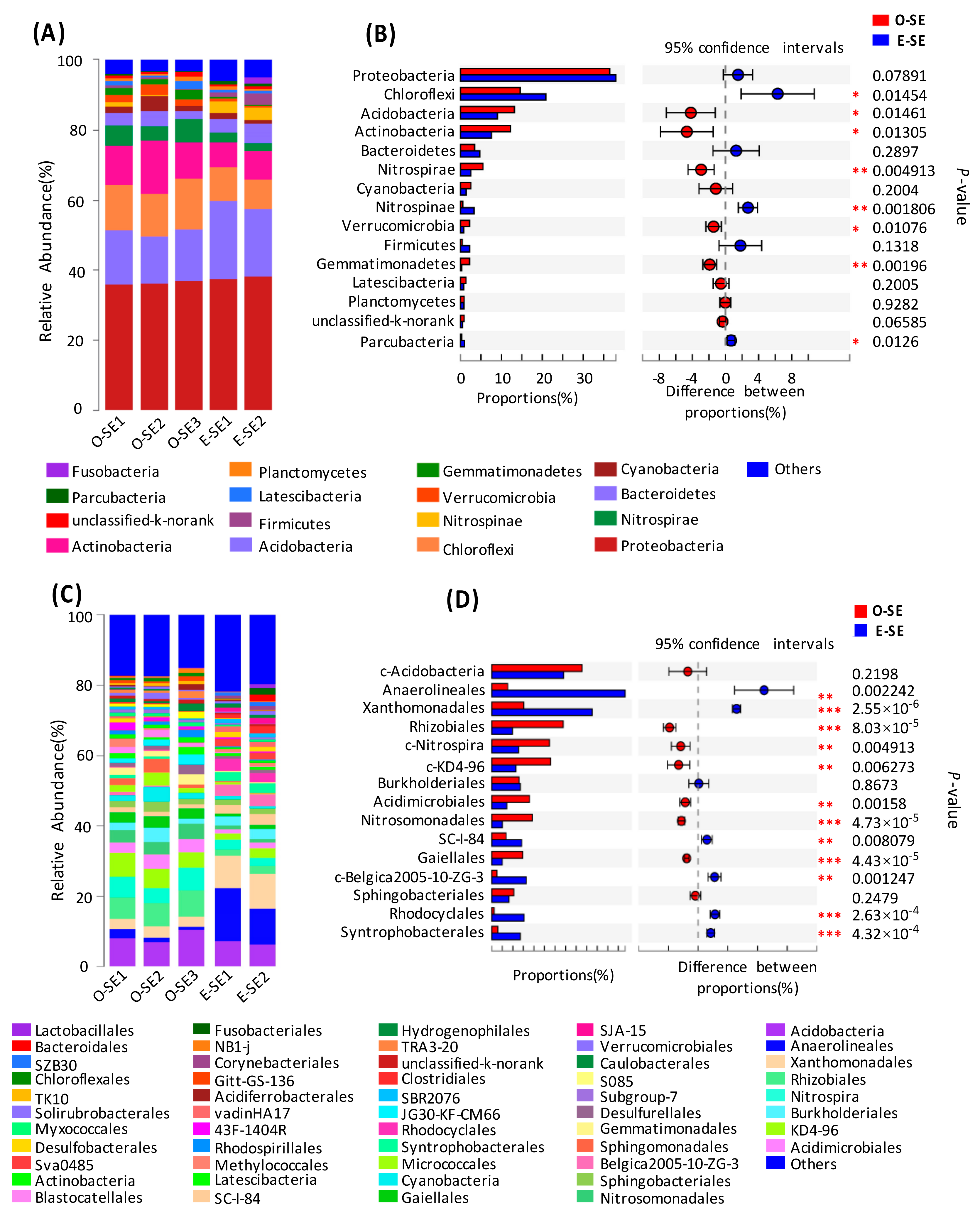
| Environmental Parameters | Oligotrophic (Lake Basomtso) | Eutrophic (Lake South) |
|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | 12.6 ± 0.62 | 29.4 ± 0.08 *** |
| pH | 7.42 ± 0.07 | 8.80 ± 0.06 *** |
| DO (mg/L) | 7.46 ± 0.22 | 8.45 ± 0.60 |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.62 ± 0.97 | 6.73 ± 0.24 ** |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.01 ± 0.002 | 0.13 ± 0.04 ** |
| Chl-a (μg/L) | 0.60 ± 0.08 | 220.54 ± 18.20 *** |
| Total phytoplankton density (cells/L) | 3933 | 4.82 × 108 |
| Sample Nature | Sample ID | Assigned Reads | 97% Similarity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTUs | Shannon | Chao1 | Coverage | |||
| Water | O-S1 | 4,1086 | 518 | 3.426241 | 239.5462 | 0.998772 |
| O-S2 | 3,6344 | 587 | 3.753438 | 275.2587 | 0.998930 | |
| O-S3 | 4,3431 | 514 | 3.470968 | 244.3997 | 0.998709 | |
| O-B1 | 4,1275 | 556 | 3.652926 | 258.7321 | 0.998741 | |
| O-B2 | 3,7534 | 519 | 3.532502 | 230.0804 | 0.998993 | |
| E-S1 | 3,1767 | 636 | 3.837348 | 281.7246 | 0.998898 | |
| E-S2 | 3,1891 | 632 | 3.548155 | 318.5813 | 0.998657 | |
| E-S3 | 4,4184 | 441 | 2.575510 | 209.3030 | 0.998883 | |
| Sediment | O-SE1 | 3,3418 | 1885 | 6.539644 | 2041.603 | 0.992609 |
| O-SE2 | 2,7443 | 1659 | 6.419282 | 1806.995 | 0.990854 | |
| O-SE3 | 3,3654 | 1545 | 6.337208 | 1675.043 | 0.994295 | |
| E-SE1 | 3,0407 | 1941 | 6.274548 | 1914.850 | 0.992344 | |
| E-SE2 | 3,6831 | 1889 | 6.129345 | 1902.770 | 0.994143 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, C.; Jia, J.; Wang, C.; Han, M.; Dong, C.; Huo, B.; Li, D.; Liu, X. Phytoplankton and Bacterial Community Structure in Two Chinese Lakes of Different Trophic Status. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120621
Feng C, Jia J, Wang C, Han M, Dong C, Huo B, Li D, Liu X. Phytoplankton and Bacterial Community Structure in Two Chinese Lakes of Different Trophic Status. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(12):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120621
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Cui, Jingyi Jia, Chen Wang, Mengqi Han, Chenchen Dong, Bin Huo, Dapeng Li, and Xiangjiang Liu. 2019. "Phytoplankton and Bacterial Community Structure in Two Chinese Lakes of Different Trophic Status" Microorganisms 7, no. 12: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120621
APA StyleFeng, C., Jia, J., Wang, C., Han, M., Dong, C., Huo, B., Li, D., & Liu, X. (2019). Phytoplankton and Bacterial Community Structure in Two Chinese Lakes of Different Trophic Status. Microorganisms, 7(12), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120621






