Kinematic Locomotion Changes in C57BL/6 Mice Infected with Toxoplasma Strain ME49
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethical Aspects
2.2. Cysts
2.3. Experimental Groups
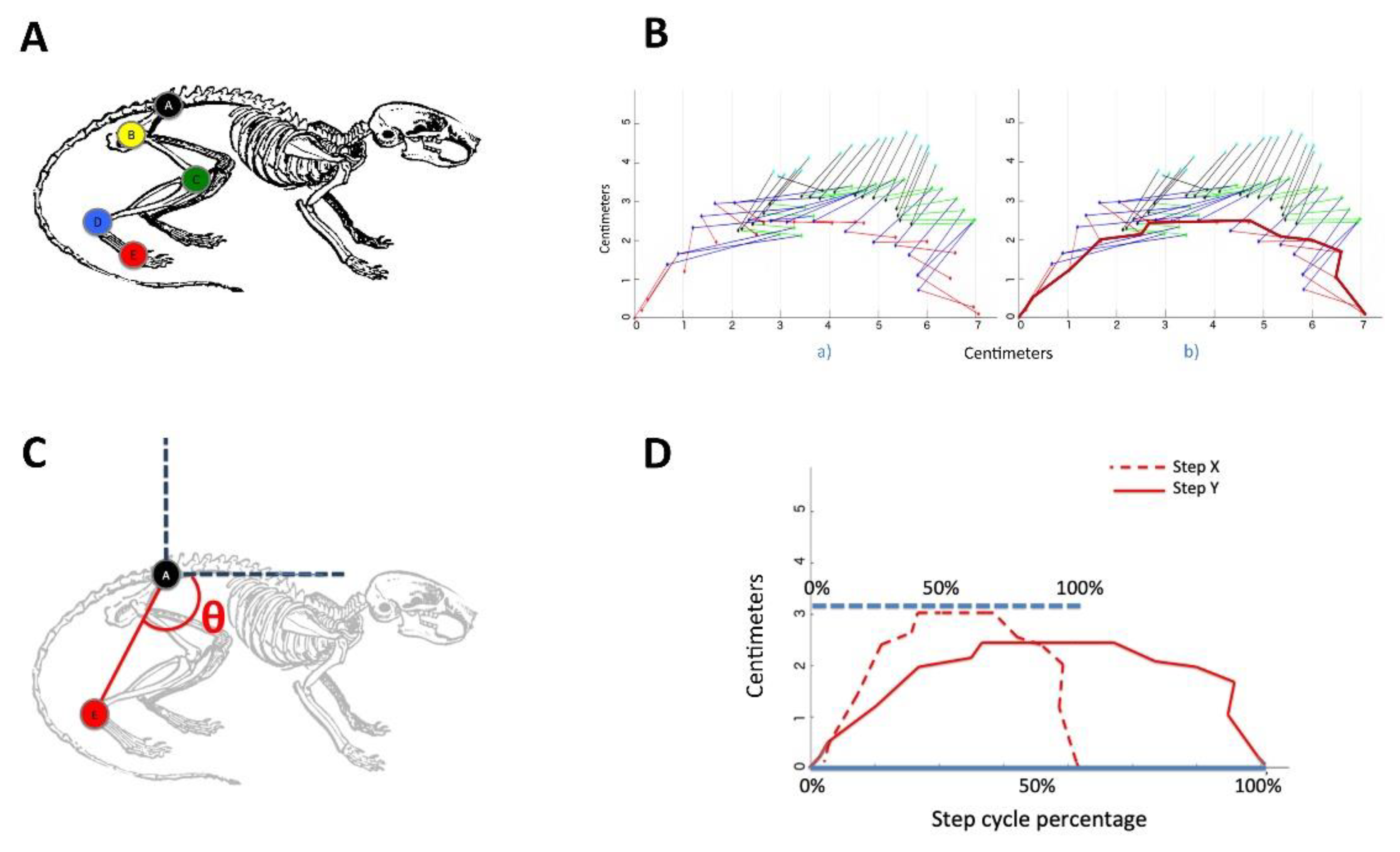
2.4. Locomotion Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Histopathological Samples
2.7. Staining with Hematoxylin and Eosin
3. Results
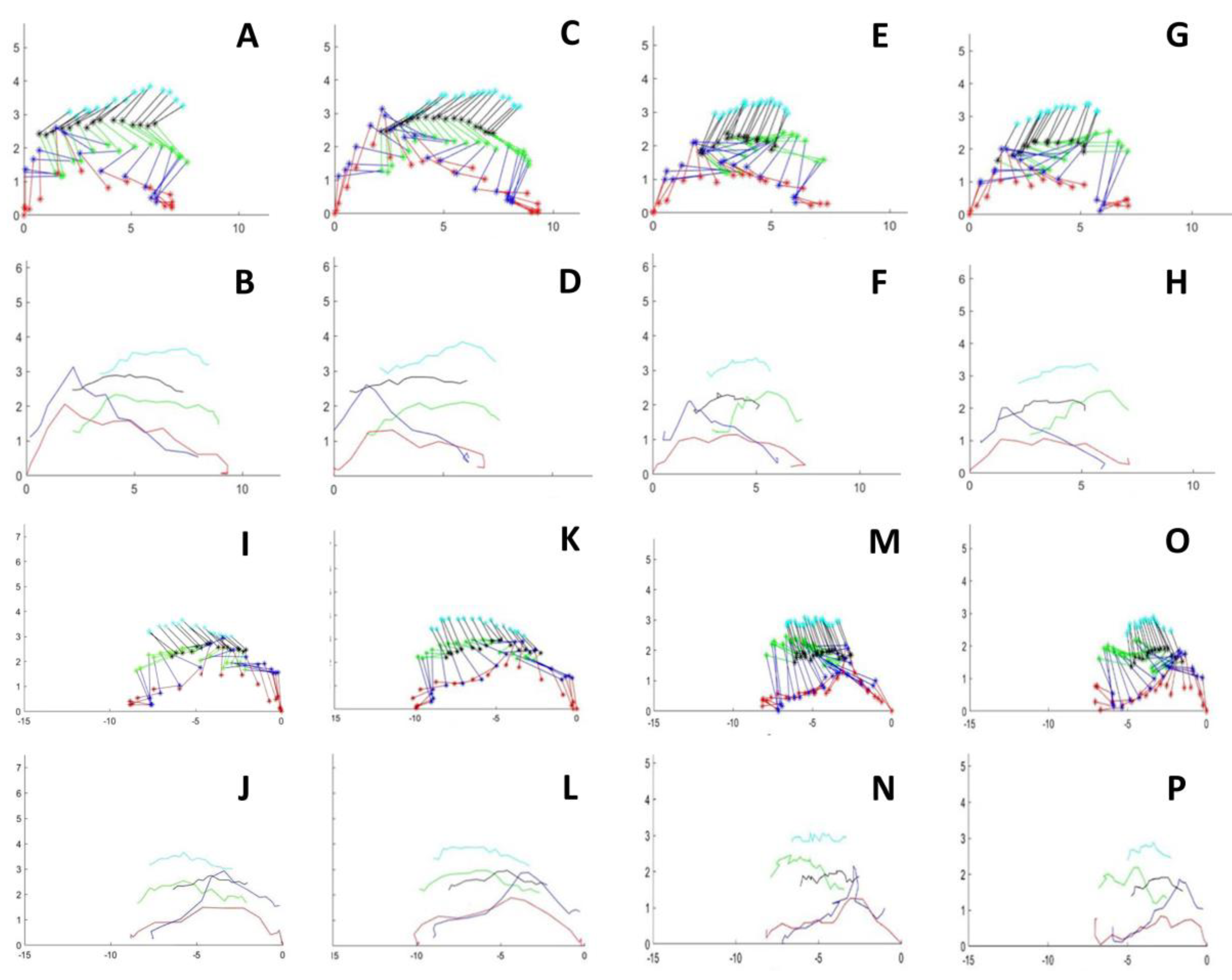
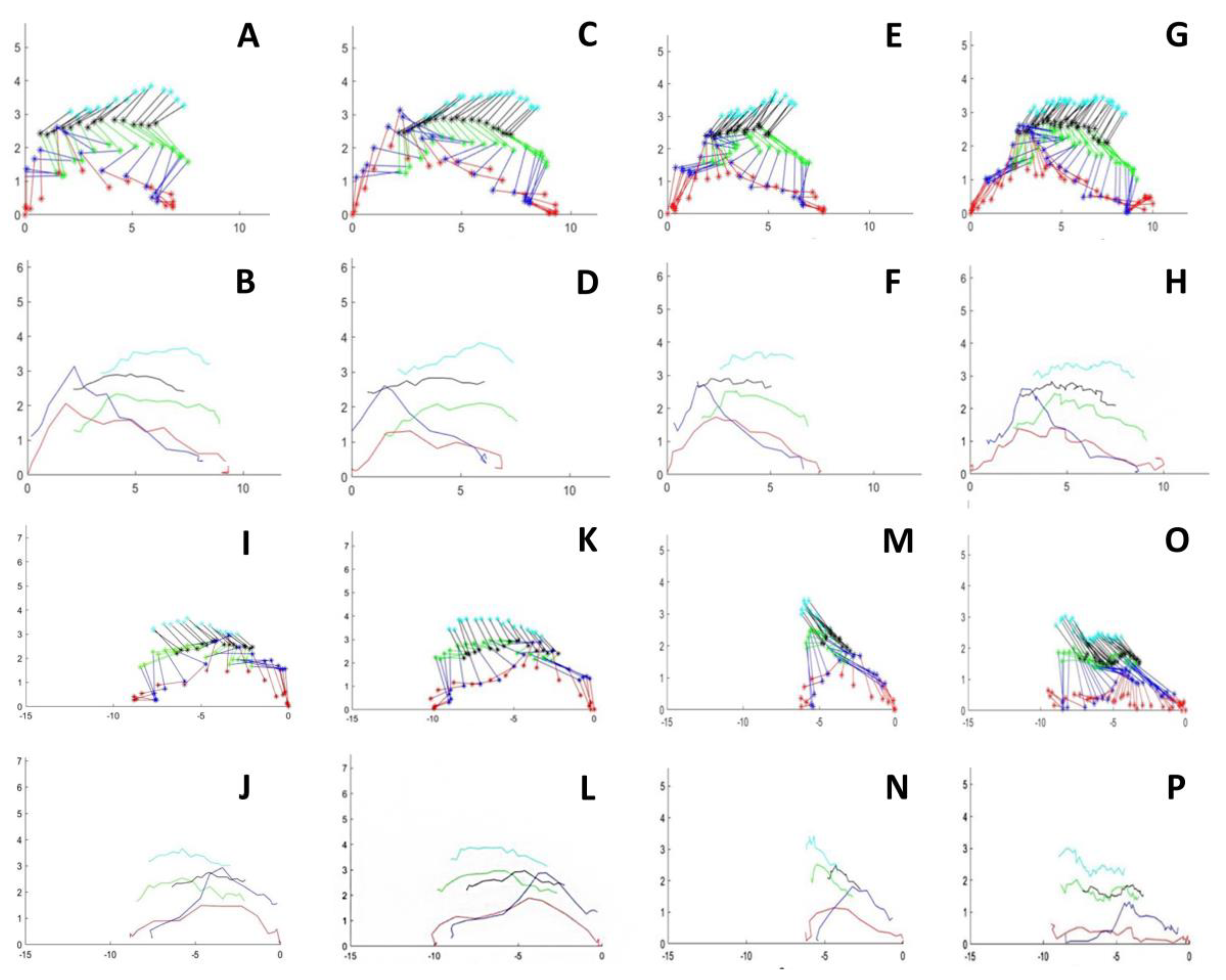
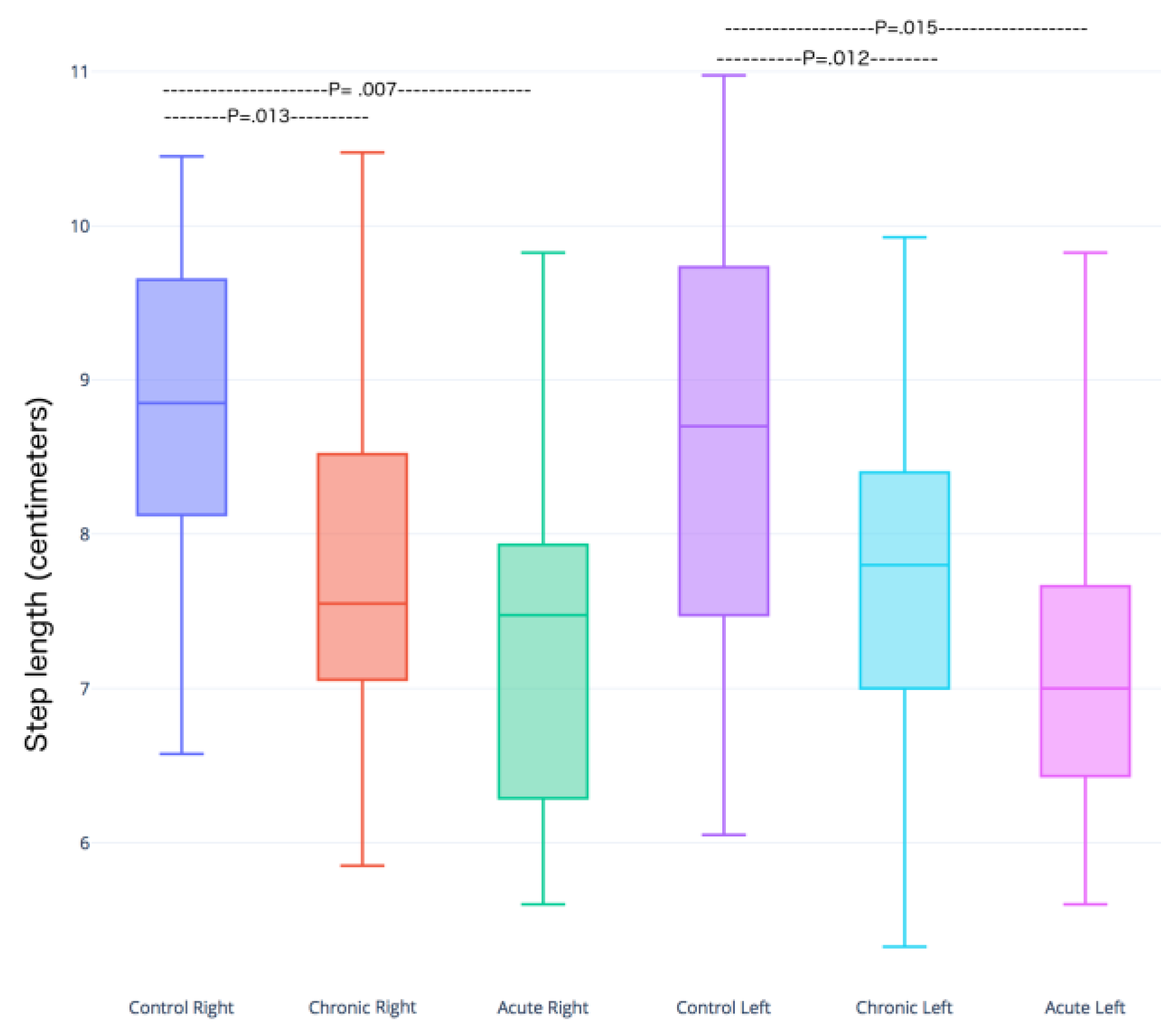
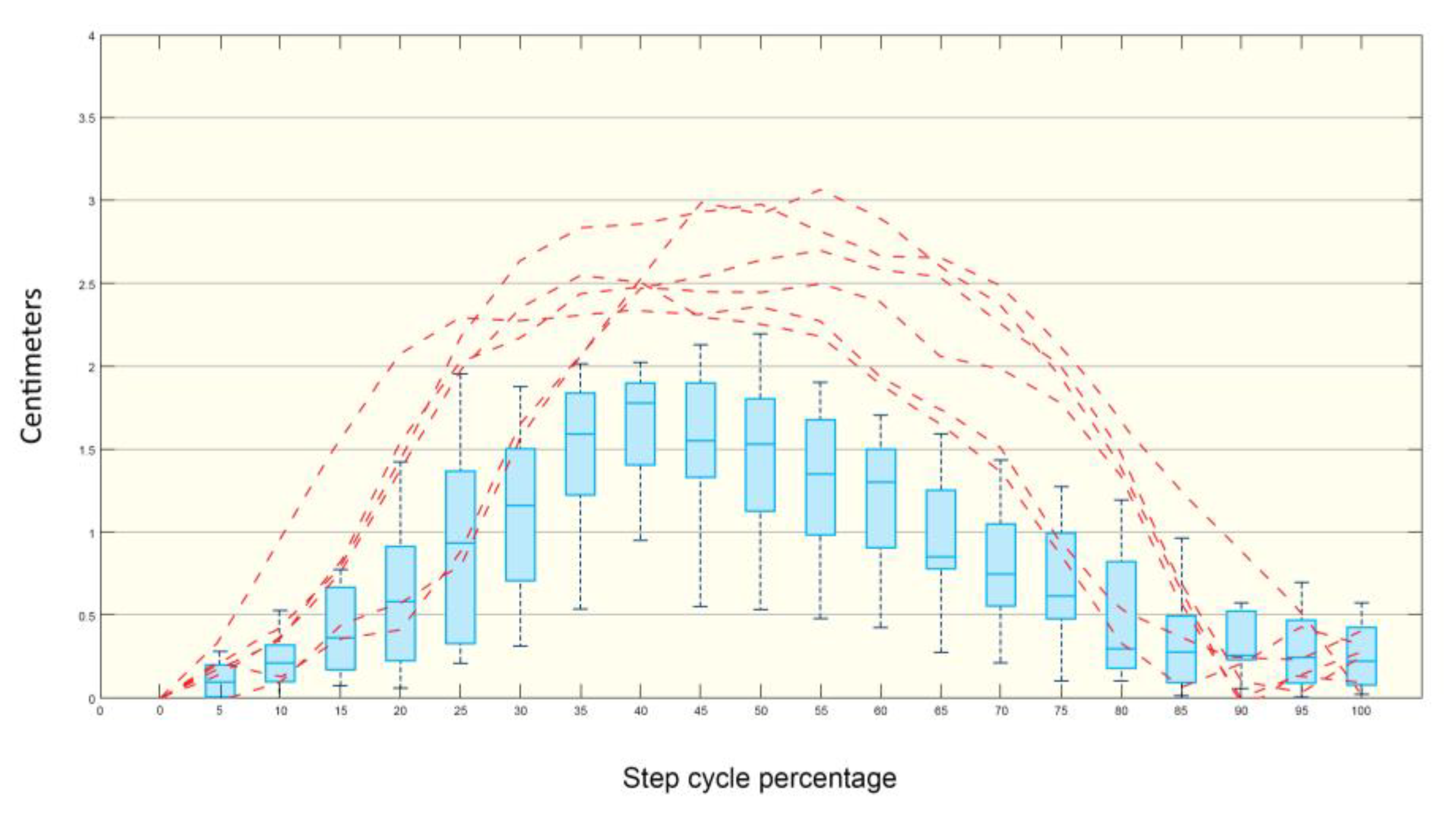
3.1. Step and Displacement Analysis
3.2. Brain Toxoplasma Cyst Distribution
3.3. Cysts in Acute Mice
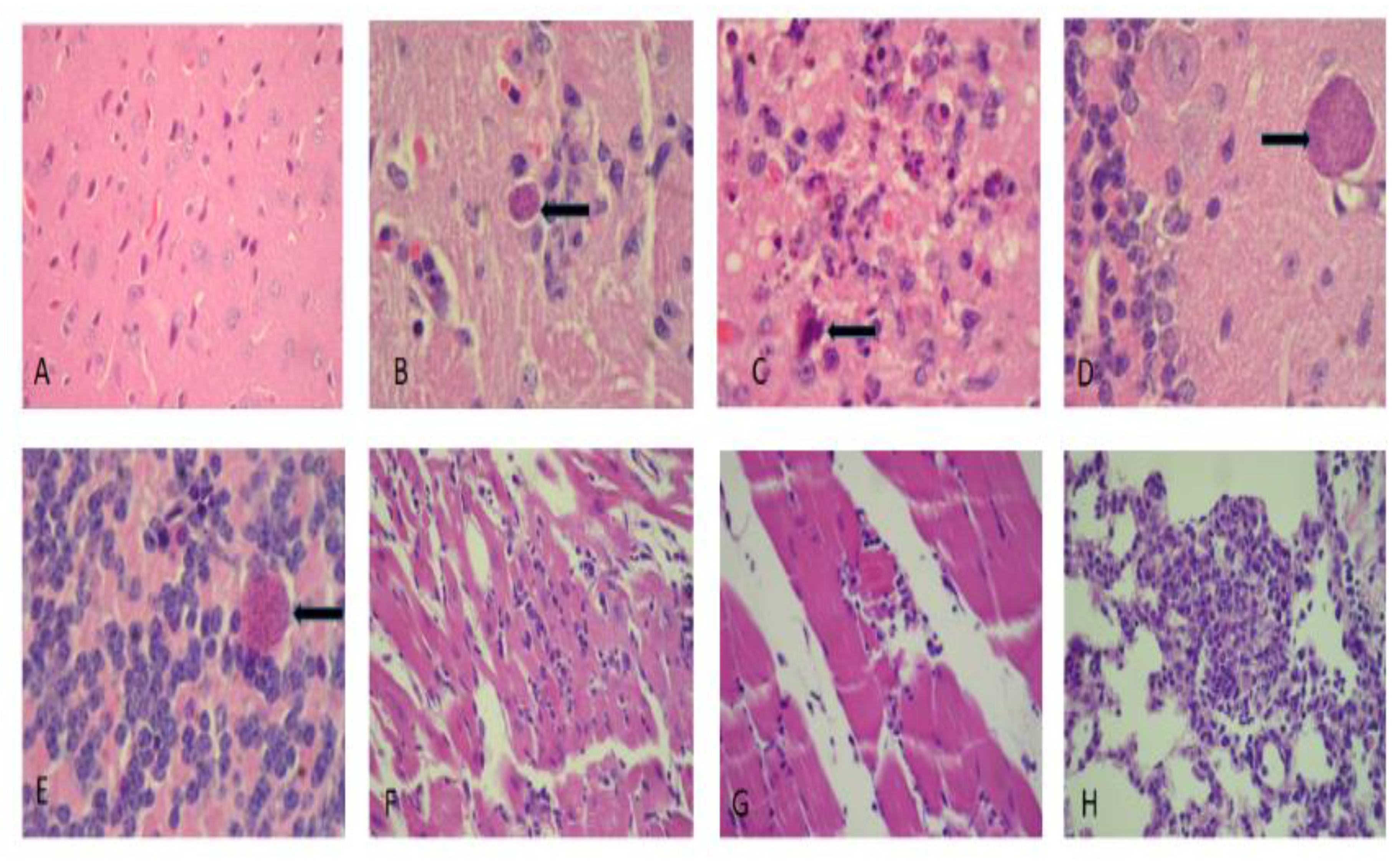
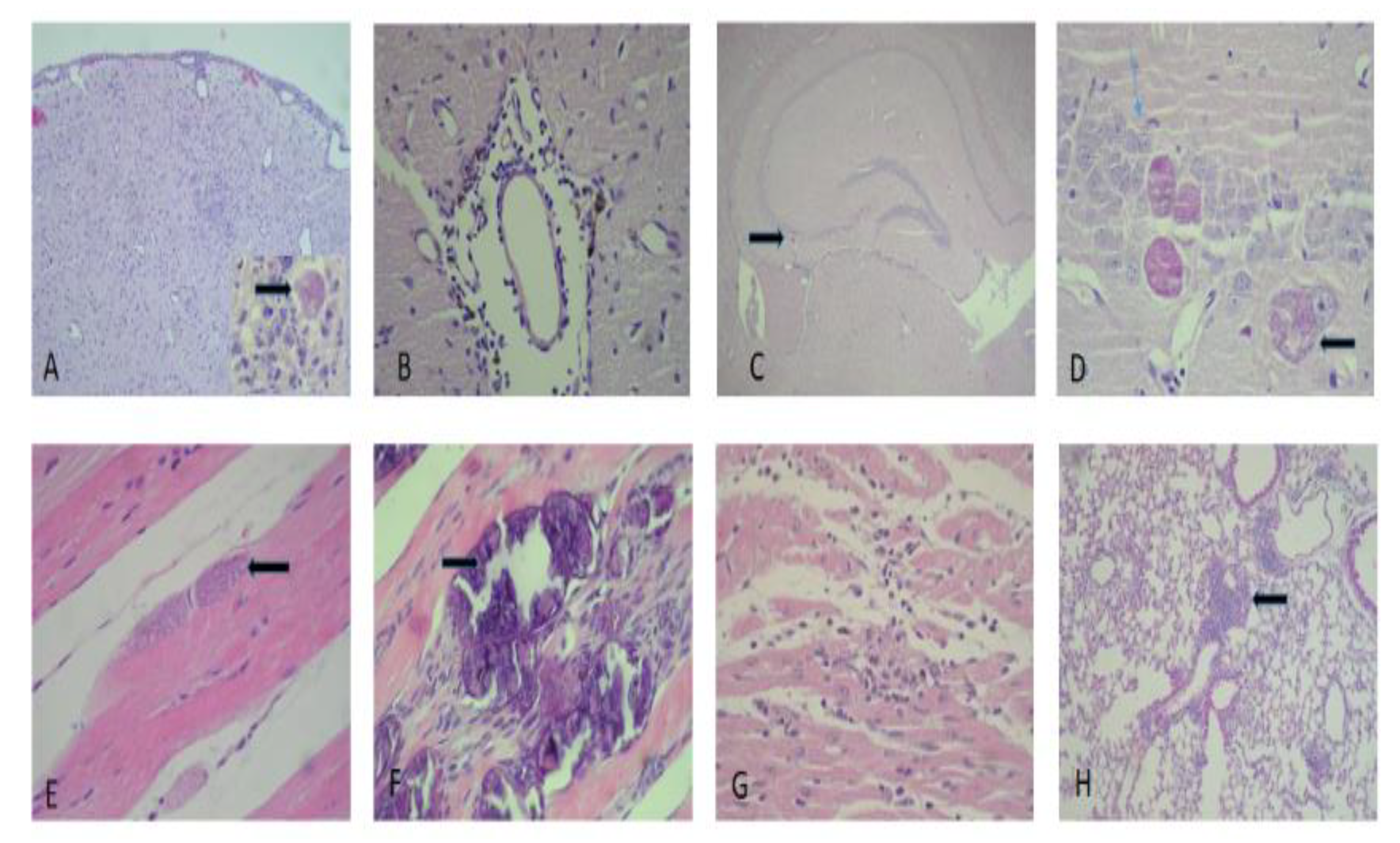
3.4. Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galván-Ramirez, M.; Monragón-Flores, R. Toxoplasmosis Humana, 1st ed.; Ecorfan: Mexico City, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, J.P. Rats, cats, people and parasites: The impact of latent toxoplasmosis on behaviour. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.P. The effect of Toxoplasma gondii on animal behavior: Playing cat and mouse. Schizophr. Bull. 2007, 33, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegr, J. Influence of latent toxoplasmosis on the phenotype of intermediate hosts. Folia Parasitol. 2010, 57, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, A.; Sapolsky, R. Manipulation of host behaviour by Toxoplasma gondii: What is the minimum a proposed proximate mechanism should explain? Folia Parasitol. 2010, 57, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenreiterová, M.; Flegr, J.; Kuběna, A.A.; Němec, P. The Distribution of Toxoplasma gondii Cysts in the Brain of a Mouse with Latent Toxoplasmosis: Implications for the Behavioral Manipulation Hypothesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskell, E.A.; Smith, J.E.; Pinney, J.W.; Westhead, D.R.; McConkey, G.A. A unique dual activity amino acid hydroxylase in Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulinello, M.; Acquarone, M.; Kim, J.H.; Spray, D.C.; Barbosa, H.S.; Sellers, R.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Weiss, L.M. Acquired infection with Toxoplasma gondii in adult mice results in sensorimotor deficits but normal cognitive behavior despite widespread brain pathology. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.; Paixão, V.B.; Costa, R.M. Chronic Toxoplasma Infection Modifies the Structure and the Risk of Host Behavior. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Castro, B.E.; Reyes-García, J.G.; Valenzuela-Vargas, M.T.; Martínez-Gómez, F. Histopathology of murine toxoplasmosis under treatment with dialyzable leukocyte extract. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhle, L.; Parlog, A.; Pahnke, J.; Dunay, I.R. Spinal cord pathology in chronic experimental Toxoplasma gondii infection. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 4, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierzy, I.J.; Muhammad, M.; Kroll, J.; Abelmann, A.; Tenter, A.M.; Lüder, C.G.K. Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells: A critical interplay for food-borne parasite transmission. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfert, E.A.; Blader, I.J.; Wilson, E.H. Brains and Brawn: Toxoplasma Infections of the Central Nervous System and Skeletal Muscle. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Estrada, R.; Bañuelos-Pineda, J.; Osuna Carrasco, L.P.; Jiménez-Vallejo, S.; Jiménez-Estrada, I.; Rivas-Celis, E.; Dueñas-Jiménez, J.M.; Dueñas-Jiménez, S.H. Aberrant gastrocnemius muscle innervation by tibial nerve afferents after implantation of chitosan tubes impregnated with progesterone favored locomotion recovery in rats with transected sciatic nerve. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asencio Pina, C.R.; Pérez-Cisneros, M.; Dueñas-Jimenez, S.; Mendizabal-Ruíz, G.A. System for High-Speed Synchronized Acquisition of Video Recording of Rodents During Locomotion. In VIII Latin American Conference on Biomedical Engineering and XLII National Conference on Biomedical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez Pena, S.I.; González-Sandoval, J.; Dueñas-Jimenez, S.H.; Mendizabal-Ruíz, G. Modeling hind-limb kinematics using a bio-inspired algorithm with a local search. BioMedical Eng. OnLine 2018, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuna-Carrasco, L.P.; López-Ruiz, J.R.; Mendizabal-Ruiz, E.G.; De la Torre-Valdovinos, B.; Bañuelos-Pineda, J.; Jiménez-Estrada, I.; Dueñas-Jiménez, S.H. Quantitative analysis of hindlimbs locomotion kinematics in spinalized rats treated with Tamoxifen plus treadmill exercise. Neuroscience 2016, 1, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Access Online via Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- López Ruiz, J.R.; Osuna Carrasco, L.P.; López Valenzuela, C.L.; Franco Rodríguez, N.E.; de la Torre Valdovinos, B.; Jiménez Estrada, I.; Dueñas Jiménez, J.M.; Dueñas Jiménez, S.H. The hippocampus participates in the control of locomotion speed. Neuroscience 2015, 17, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon-Moreno, L.; Castañeda-Arellano, R.; Rivas-Carrillo Mendizabal-Ruiz, G.; Dueñas-Jiménez, S. Analysis of hindlimbs locomotion kinematics in a mouse model of penetrating brain injury. In Proceedings of the Society for Nuerociense L Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 19–23 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aronov, B.; Har-Peled, S.; Knauer, C.; Wang, Y.; Wenk, C. Fréchet Distance for Curves, Revisited. In Algorithms—ESA. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Azar, Y., Erlebach, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; p. 4168. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.J.; Hutchison, W.M. The host-parasite relationship of Toxoplasma gondii in the brains of chronically infected mice. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1987, 411, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, F.; Händel, U.; Angenstein, F.; Goldschmidt, J.; Kreutzmann, P.; Lison, H.; Fischer, K.D.; Scheich, H.; Wetzel, W.; Schlüter, D.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii actively inhibits neuronal function in chronically infected mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragan, A.; Brossier, F.; Sibley, L.D. Transepithelial migration of Toxoplasma gondii involves an interaction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) with the parasite adhesin MIC2. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.M.; Blair, S.J.; Warunek, J.; Heffner, R.R.; Blader, I.J.; Wohlfert, E.A. Regulatory T Cells Promote Myositis and Muscle Damage in Toxoplasma gondii Infection. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
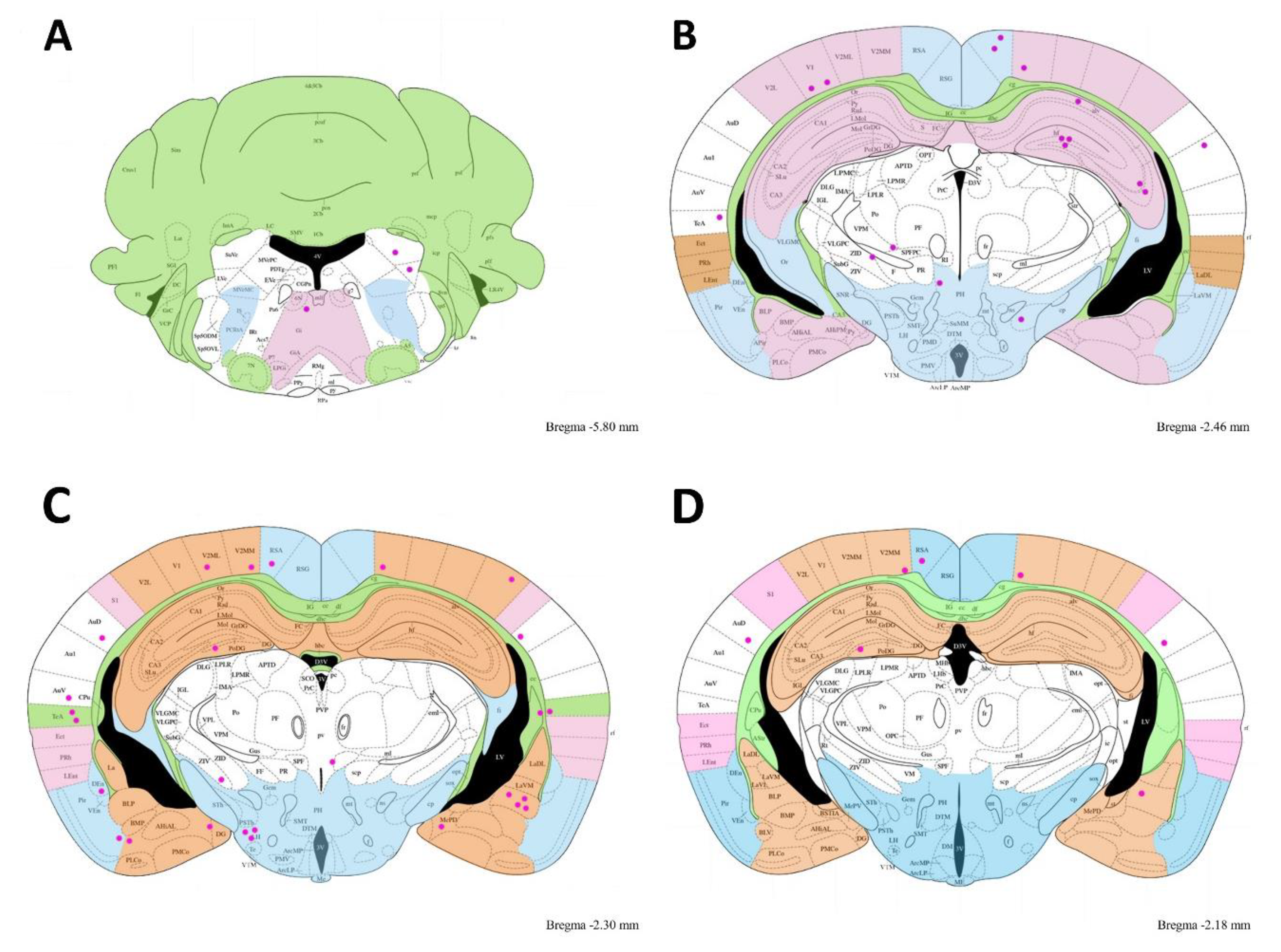
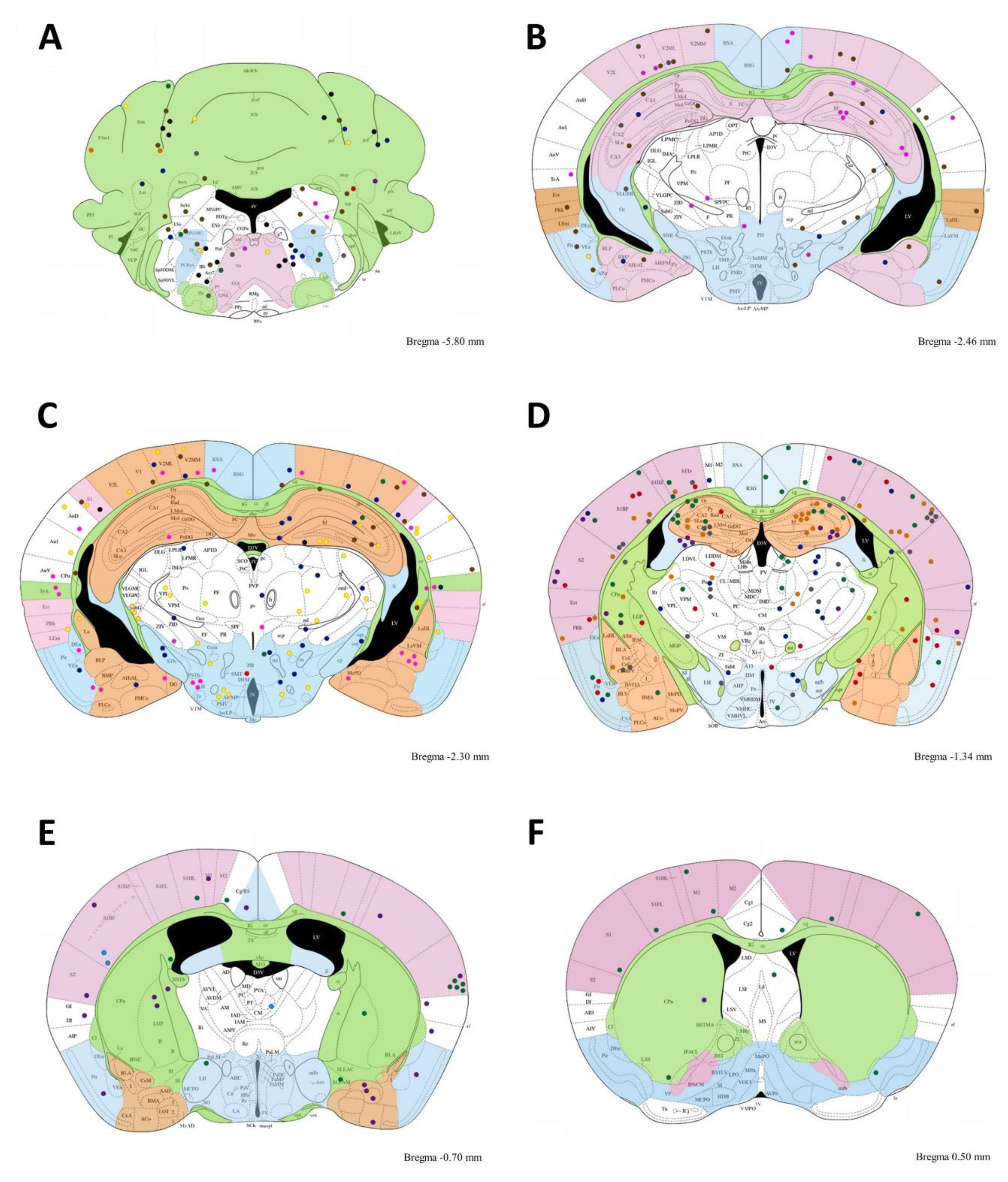
| Abbreviation Name | Left | Right | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3V 3rd ventricle | 1 | 1 | |
| AAD anterior amygdaloid area, dorsal part | 3 | 3 | |
| ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| AHiAL amygdalohippocampal area, anterolateral part | 3 | 3 | |
| AIP agranular insular cortex | 1 | 1 | |
| alv alveus of the hippocampus | 2 | 2 | |
| APTD anterior pretectal nucleus, dorsal part | 1 | 1 | |
| ArcLP arcuate hypothalamic nucleus, lateroposterior part | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Au1 primary auditory cortex | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| BLP basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part | 1 | 1 | |
| BMA basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| BMP basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part | 1 | 1 | |
| cc corpus callosum | 3 | 3 | |
| CA1 field CA1 of hippocampus | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| CA3 field CA3 of hippocampus | 5 | 5 | |
| cg cingulum | 1 | 1 | |
| Cg/RS cingulate/retrosplenial cortex | 2 | 2 | |
| Cg2 cingulate cortex, area 2 | 6 | 6 | |
| Cl claustrum | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| CM central medial thalamic nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| cp cerebral peduncle, basal part | 2 | 6 | 8 |
| CPu caudate putamen | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| DEn dorsal endopiriform nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| df dorsal fornix | |||
| DG dentate gyrus | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| ec external capsule | 1 | 1 | |
| FC fasciola cinereum | 2 | 2 | |
| fi fimbria of the hippocampus | 4 | 4 | |
| fr fasciculus retroflexus | 2 | 2 | |
| Gem gemini hypothalamic nucleus | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Gi gigantocellular reticular nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| GI granular insular ex | 1 | 1 | |
| hf hippocampal fissure | 10 | 7 | 17 |
| ic internal capsule | 1 | 1 | |
| IPAC interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure | 1 | 1 | |
| LA lateroanterior hypothalamic nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| Ld lambdoid septal zone | 1 | 1 | |
| IODM inferior olive, dorsomedial cell group | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| LEnt lateral entorhinal cortex | 1 | 1 | |
| LH lateral hypothalamic area | 11 | 7 | 18 |
| LPLR lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, laterorostral part | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| LVe latral vestibular nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| mcPV med amyg, postvent | 1 | 1 | |
| MCPC magnocellular nucleus of posterior commissure | 2 | 2 | |
| ml medial lemniscus | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| mt mammillothalamic tract | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Or oriens layer of the hippocampus | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| PF parafascicular thalamic nucleus | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| PH posterior hypothalamic area | 6 | 6 | |
| Po posterior thalamic nuclear group | 5 | 3 | 8 |
| PoDG polymorph layer of the dentate gyrus | 15 | 12 | 27 |
| PR prerubral field | 1 | 1 | |
| PRh perirhinal cortex | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| Rad stratum radiatum of the hippocampus | 1 | 1 | |
| RMg raphe magnus nu | 2 | 2 | |
| RSA retrosplenial agranular cortex | 7 | 4 | 11 |
| RSG retrosplenial granular cortex | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Rt reticular thalamic nucleus | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| S1 primary somatosensory cortex | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| SolIM solitary nu interm | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| S1BF primary somatosensory cortex, barrel field | 17 | 12 | 29 |
| S1Tr primary somatosensory cortex, trunk region | 4 | 5 | 9 |
| S2 secondary somatosensory cortex | 8 | 5 | 13 |
| SLu stratum lucidum, hippocampus | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| SPF subparafascicular thalamic nucleus | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| st stria terminalis | 1 | 1 | |
| STh subthalamic nucleus | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| Sub submedius thalamic nucleus | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| SubG subgeniculate nucleus | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| SubI subincertal nucleus | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| TeA temporal association cortex | 7 | 3 | 10 |
| V1 primary visual cortex | 6 | 5 | 11 |
| V2L secondary visual cortex, lateral area | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| V2ML secondary visual cortex, mediolateral area | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| V2MM secondary visual cortex, mediomedial area | 5 | 4 | 9 |
| VEn ventral endopiriform nucleus | 1 | 1 | |
| VL ventral thalm nu | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| VLGMC ventral lateral geniculate nucleus, magnocellular part | 1 | 1 | |
| VLGPC ventral lateral geniculate nucleus, parvicellular part | 1 | 1 | |
| VPL ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus | 5 | 2 | 7 |
| VPM ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| VRe ventral reuniens thalamic nucleus | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| TC tuber cinereum area | 2 | 2 | |
| ZID zona incerta, dorsal part | 5 | 6 | 11 |
| Total | 213 | 173 | 386 |
| Pathological Damage | Acute Group | Chronic Group |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive gliosis | +++ | ++ |
| Glionecrosis | +++ | + |
| Meningoencephalitis | + | +++ |
| Vasculitis | + | − |
| Cerebral hypoxia | ++ | + |
| Cysts in hippocampal cortical region | + | +++ |
| Cysts in the cerebellar region | ++ | + |
| Peribronchial inflammation | ++ | +++ |
| Acute pneumonitis | ++ | + |
| Myocarditis | + | ++ |
| Myositis | + | +++ |
| Dystrophic calcification of sarcoplasm | − | ++ |
| Cysts in sarcoplasm | − | + |
| Reactive hepatitis | ++ | + |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galván-Ramírez, M.d.l.L.; Salas-Lais, A.G.; Dueñas-Jiménez, S.H.; Mendizabal-Ruiz, G.; Franco Topete, R.; Berumen-Solís, S.C.; Rodríguez Pérez, L.R.; Franco Topete, K. Kinematic Locomotion Changes in C57BL/6 Mice Infected with Toxoplasma Strain ME49. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110573
Galván-Ramírez MdlL, Salas-Lais AG, Dueñas-Jiménez SH, Mendizabal-Ruiz G, Franco Topete R, Berumen-Solís SC, Rodríguez Pérez LR, Franco Topete K. Kinematic Locomotion Changes in C57BL/6 Mice Infected with Toxoplasma Strain ME49. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(11):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110573
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalván-Ramírez, María de la Luz, Angel Gustavo Salas-Lais, Sergio Horacio Dueñas-Jiménez, Gerardo Mendizabal-Ruiz, Ramón Franco Topete, Sofía Citlalli Berumen-Solís, Laura Roció Rodríguez Pérez, and Karina Franco Topete. 2019. "Kinematic Locomotion Changes in C57BL/6 Mice Infected with Toxoplasma Strain ME49" Microorganisms 7, no. 11: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110573
APA StyleGalván-Ramírez, M. d. l. L., Salas-Lais, A. G., Dueñas-Jiménez, S. H., Mendizabal-Ruiz, G., Franco Topete, R., Berumen-Solís, S. C., Rodríguez Pérez, L. R., & Franco Topete, K. (2019). Kinematic Locomotion Changes in C57BL/6 Mice Infected with Toxoplasma Strain ME49. Microorganisms, 7(11), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110573





