Gut Bacteria and their Metabolites: Which One Is the Defendant for Colorectal Cancer?
Abstract
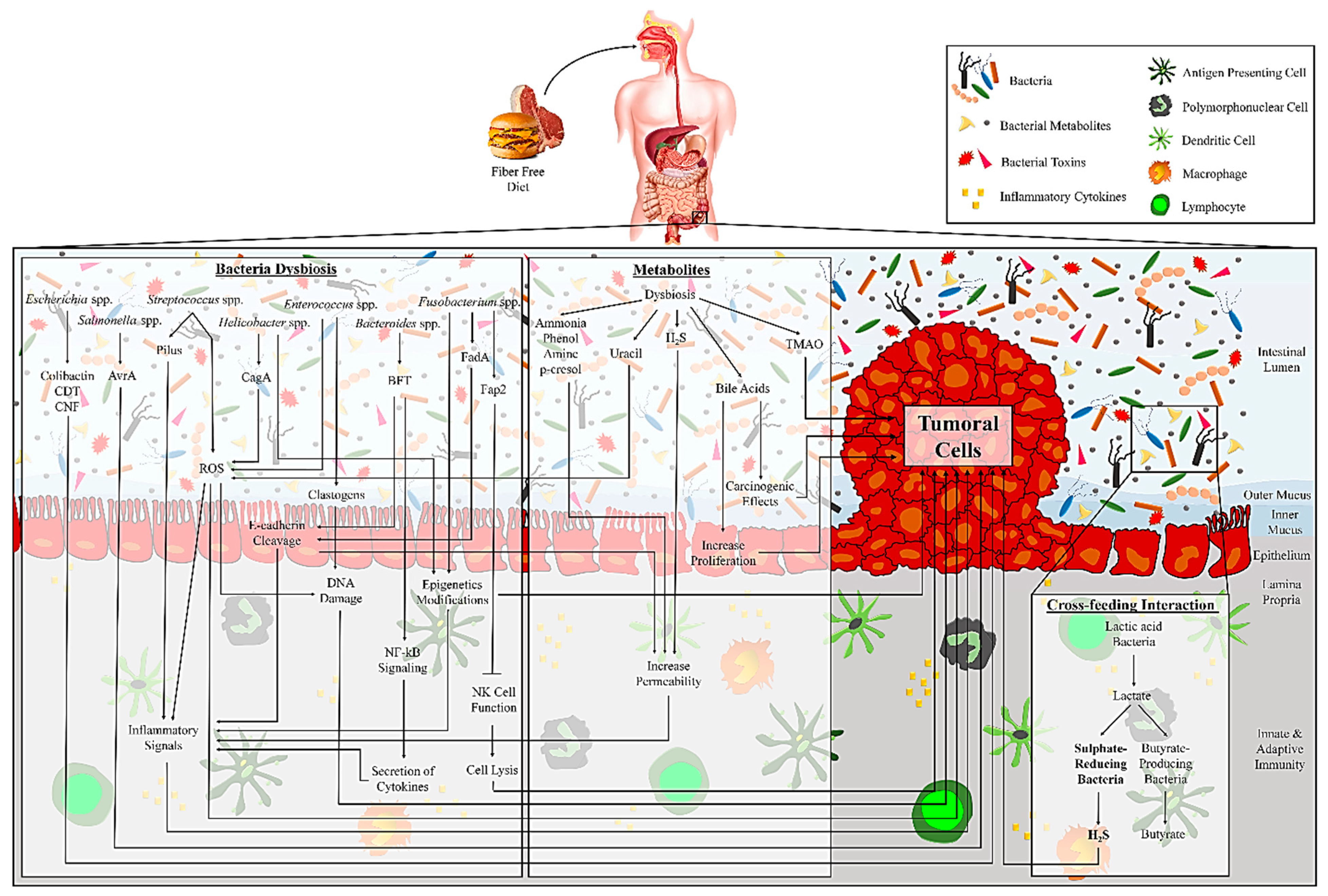
1. Introduction
2. The Intestinal Bacteria in Times of CRC:
3. The Importance of Gut Bacteria Detected in the Stool and Tissue in CRC:
4. Microbial-derived Metabolites and CRC:
5. The Role of Bacterial Metabolites in Epigenetic Modifications of CRC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azadeh, S.; Moghimi-Dehkordi, B.; Fatem, S.R.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Ghiasi, S.; Zali, M.R. Colorectal cancer in Iran: An epidemiological study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2008, 9, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stewart, B.; Wild, C.P. World Cancer Report 2014; World Cancer Report Publisher; International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Van, T.R.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Microbial Interactions and Interventions in Colorectal Cancer. Microbiology 2017, 47, 777–780. [Google Scholar]
- Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Zali, M.R. Colorectal cancer screening: Time for action in Iran. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 4, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuade, J.L.; Daniel, C.R.; Helmink, B.A.; Wargo, J.A. Modulating the microbiome to improve therapeutic response in cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e77–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, C.J.S. Precision medicine using microbiota. Science 2018, 359, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Owen, J.L.; Lightfoot, Y.L.; Kladde, M.P.; Mohamadzadeh, M.; Lightfooot, Y.L. Microbiota impact on the epigenetic regulation of colorectal cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi-Dehkordi, B.; Safaee, A.; Zali, M.R. Prognostic factors in 1,138 Iranian colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2008, 23, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C.; Round, J.L. Defining dysbiosis and its influence on host immunity and disease. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarashi, S.; Badi, S.A.; Moshiri, A.; Nasehi, M.; Fateh, A.; Vaziri, F.; Siadat, S.D. The human microbiota in pulmonary tuberculosis: Not so innocent bystanders. Tuberculosis 2018, 113, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Guidotti, M.; Fabbri, A.; Brigidi, P.; Franceschi, C.; Fiorentini, C. Human intestinal microbiota: Cross-talk with the host and its potential role in colorectal cancer. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vétizou, M.; Pitt, J.M.; Daillère, R.; Lepage, P.; Waldschmitt, N.; Flament, C.; Rusakiewicz, S.; Routy, B.; Roberti, M.P.; Duong, C.P.M.; et al. Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the gut microbiota. Science 2015, 350, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, K.; Tamada, K. Microbial biomarkers for immune checkpoint blockade therapy against cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, W.S. The gut microbiota and colon cancer. Science 2019, 364, 1133–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.G.; Rao, S.; Weir, T.L.; O’Malia, J.; Bazan, M.; Brown, R.J.; Ryan, E.P. Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Ahn, J.; Sampson, J.N.; Shi, J.; Yu, G.; Xiong, X.; Hayes, R.B.; Goedert, J.J. Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergiou, V.; Karatapanis, S.; Georgopoulos, S.D. Helicobacter pylori and colorectal neoplasia: Is there a causal link? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Gerner, R.R.; Moschen, A.R. The Intestinal Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Guinane, C.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D.; O’Toole, P.W. Beneficial modulation of the gut microbiota. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4120–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, S.; Martin, A. Insights into the role of the intestinal microbiota in colon cancer. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.; Narisawa, T.; Wright, P.; Vukusich, D.; Weisburger, J.H.; Wynder, E.L. Colon carcinogenesis with azoxymethane and dimethylhydrazine in germ-free rats. Cancer Res. 1975, 35, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Tjalsma, H.; Boleij, A.; Marchesi, J.R.; Dutilh, B.E. A bacterial driver–passenger model for colorectal cancer: Beyond the usual suspects. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 10, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.L.; Freeman, D.J.; Pleasance, S.; Watson, P.; Moore, R.A.; Cochrane, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Holt, R.A. Co-occurrence of anaerobic bacteria in colorectal carcinomas. Microbiome 2013, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarovitch, T.; Shango, M.; Levine, M.; Brusovansky, R.; Akins, R.; Hayakawa, K.; Lephart, P.; Sobel, J.; Kaye, K.; Marchaim, D. The relationship between the new taxonomy of Streptococcus bovis and its clonality to colon cancer, endocarditis, and biliary disease. Infection 2013, 41, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Dutilh, B.E.; Hall, N.; Peters, W.H.M.; Roelofs, R.; Boleij, A.; Tjalsma, H. Towards the Human Colorectal Cancer Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsu, G.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Sheng, J.; Wong, S.H.; Wu, W.K.K.; Ng, S.C.; Tsoi, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, N.; et al. Gut mucosal microbiome across stages of colorectal carcinogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, G.; Tap, J.; Voigt, A.Y.; Sunagawa, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Costea, P.I.; Amiot, A.; Böhm, J.; Brunetti, F.; Habermann, N.; et al. Potential of fecal microbiota for early-stage detection of colorectal cancer. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2014, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Ge, Q.X.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.J.; Du, Y.L.; Shen, B.; Wan, Y.J.Y.; Nie, Y.Q. Association of Fusobacterium nucleatum infection with colorectal cancer in Chinese patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3227–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangifesta, M.; Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Gaiani, F.; De’Angelis, N.; De’Angelis, G.L.; Van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M.; Turroni, F. Mucosal microbiota of intestinal polyps reveals putative biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Fan, H.; Tang, X.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, Z. Diversified pattern of the human colorectal cancer microbiome. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, H.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Nie, Y. Association of oncogenic bacteria with colorectal cancer in South China. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 80794–80802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Kong, C.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lan, P.; Wang, J.; Qin, H. Mucosa-associated microbiota signature in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.B.; Lynch, J.; Starr, T.K.; Knights, D.; Blekhman, R. Virulence genes are a signature of the microbiome in the colorectal tumor microenvironment. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Cao, S.; Liu, S.; Yao, Z.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Could gut microbiota serve as prognostic biomarker associated with colorectal cancer patients’ survival? A pilot study on relevant mechanism. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46158–46172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, I.; Boukhatem, N.; Bouguenouch, L.; Hardi, H.; Boudouaya, H.A.; Cadenas, M.B.; Ouldim, K.; Amzazi, S.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Ghazal, H. Gut microbiome of Moroccan colorectal cancer patients. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 207, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, J.L.; White, J.R.; Dejea, C.M.; Fathi, P.; Iyadorai, T.; Vadivelu, J.; Roslani, A.C.; Wick, E.C.; Mongodin, E.F.; Loke, M.F. High-resolution bacterial 16S rRNA gene profile meta-analysis and biofilm status reveal common colorectal cancer consortia. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2017, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, F.; Ilyas, S.; Damanik, H.A.; Fatchiyah, F. Microbiota Composition, HSP70 and Caspase-3 Expression as Marker for Colorectal Cancer Patients in Aceh, Indonesia. Acta Med. Indones. 2016, 48, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Balamurugan, R.; Rajendiran, E.; George, S.; Samuel, G.V.; Ramakrishna, B.S. Real-time polymerase chain reaction quantification of specific butyrate-producing bacteria, Desulfovibrio and Enterococcus faecalis in the feces of patients with colorectal cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’keefe, S.J. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Ascherio, A.; Willett, W.C. Intake of fat, meat, and fiber in relation to risk of colon cancer in men. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Sears, C.L.; Garrett, W.S. Microbes, Microbiota, and Colon Cancer. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mármol, I.; Sánchez-De-Diego, C.; Dieste, A.P.; Cerrada, E.; Yoldi, M.J.R. Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohoutova, D.; Smajs, D.; Moravkova, P.; Cyrany, J.; Moravkova, M.; Forstlova, M.; Cihak, M.; Rejchrt, S.; Bures, J. Escherichia coli strains of phylogenetic group B2 and D and bacteriocin production are associated with advanced colorectal neoplasia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, G.; Petit, C.R.; Marcq, I.; Boury, M.; Oswald, E.; Nougayrède, J.P. Escherichia coli induces DNA damage in vivo and triggers genomic instability in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11537–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buc, E.; Dubois, D.; Sauvanet, P.; Raisch, J.; Delmas, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Pezet, D.; Bonnet, R. High Prevalence of Mucosa-Associated E. coli Producing Cyclomodulin and Genotoxin in Colon Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compare, D.; Nardone, G. The bacteria-hypothesis of colorectal cancer: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. Transl. Gastrointest. Cancer 2013, 3, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.E.; Chiu, C.T.; Rayner, C.K.; Wu, K.L.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hu, M.L.; Chuah, S.K.; Tai, W.C.; Liang, C.M.; Wang, H.M. Associated factors in Streptococcus bovis bacteremia and colorectal cancer. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmerich, S.; Duranton, B.; Gosse, F.; Galluser, M.; Klein, J.P.; Raul, F.; Scholler, M. Promotion of intestinal carcinogenesis by Streptococcus bovis. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleij, A.; Tjalsma, H. The itinerary of Streptococcus gallolyticus infection in patients with colonic malignant disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleij, A.; Van Gelder, M.M.H.J.; Swinkels, D.W.; Tjalsma, H. Clinical Importance of Streptococcus gallolyticus Infection Among Colorectal Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulamir, A.S.; Hafidh, R.R.; Abu Bakar, F. Molecular detection, quantification, and isolation of Streptococcus gallolyticus bacteria colonizing colorectal tumors: Inflammation-driven potential of carcinogenesis via IL-1, COX-2, and IL-8. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleij, A.; Dutilh, B.E.; Kortman, G.A.M.; Roelofs, R.; Laarakkers, C.M.; Engelke, U.F.; Tjalsma, H. Bacterial Responses to a Simulated Colon Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleij, A.; Muytjens, C.M.J.; Bukhari, S.I.; Cayet, N.; Glaser, P.; Hermans, P.W.M.; Swinkels, D.W.; Bolhuis, A.; Tjalsma, H. Novel Clues on the Specific Association of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp gallolyticus With Colorectal Cancer. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, C.L.; Geis, A.L.; Housseau, F. Bacteroides fragilis subverts mucosal biology: From symbiont to colon carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4166–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, S.; Shariati, S.H.; Zali, M.R.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Asiabar, A.S.; Bokaie, S.; Nomanpour, B.; Sechi, L.A.; Feizabadi, M.M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, N.U.; Yagci, A.; Güllüoglu, B.M.; Akin, M.; Demirkalem, P.; Celenk, T.; Soyletir, G. A possible role of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, A.P.; Miller, R.; Laughlin, K.V.; Carp, N.Z.; Klurfeld, D.M.; Mullin, J.M. Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huycke, T.; Moore, D.R.; Lightfoot, S.A.; Huycke, M.M. Colon Macrophages Polarized by Commensal Bacteria Cause Colitis and Cancer through the Bystander Effect. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M.R.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Hao, Y.; Cai, G.; Han, Y.W. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by modulating E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling via its FadA adhesin. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Miskeen, A.Y.; Hazari, Y.M.; Asrafuzzaman, S.; Fazili, K.M. Fusobacterium nucleatum, inflammation, and immunity: The fire within human gut. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2805–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Schaefer, K.L.; Zhou, Z.; Bissonnette, M.; et al. Enteric bacterial protein AvrA promotes colonic tumorigenesis and activates colonic beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shmuely, H.; Passaro, D.; Figer, A.; Niv, Y.; Pitlik, S.; Samra, Z.; Koren, R.; Yahav, J. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori CagA status and colorectal cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 3406–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, O.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Helicobacter pylori: A ROS-inducing bacterial species in the stomach. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumkeller, N.; Brenner, H.; Zwahlen, M.; Rothenbacher, D. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Helicobacter 2006, 11, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.Y. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and colorectal neoplasm risk: A meta-analysis Based on East Asian population. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2014, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, N.N.; McCloud, J.M.; Cheetham, M.J. Clostridium septicum sepsis and colorectal cancer—A reminder. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dylewski, J.; Luterman, L. Septic arthritis and Clostridium septicum: A clue to colon cancer. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2010, 182, 1446–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D.; Milner, J.A. Gastrointestinal microflora, food components and colon cancer prevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.C.S.; Paulino, D.S.; Brambilla, S.R.; Camargo, J.A.; Persinoti, G.F.; Carvalheira, J.B.C. Microbiota modification by probiotic supplementation reduces colitis associated colon cancer in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.R.; Zaharuddin, L.; Chan, S.-N.; Wong, Z.; Ngiu, C.S.; Mokhtar, N.M. Sa1838—The Clinical and Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines Effects of Probiotic Containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Strains in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.J.M. Probiotics and Colon Cancer. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafter, J. Probiotics and colon cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, G.H.; Royle, P.J.; Playne, M.J. A Probiotic Strain of L. Acidophilus Reduces DMH-Induced Large Intestinal Tumors in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 35, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.R.; Bearne, C.A.; Fischer, R.; Pool-Zobel, B.L. The effect of lactulose on DNA damage induced by DMH in the colon of human flora-associated rats. Nutr. Cancer 1996, 26, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohwi, Y.; Imai, K.; Tamura, Z.; Hashimoto, Y. Antitumor effect of Bifidobacterium infantis in mice. Gan 1978, 69, 613–618. [Google Scholar]
- Lidbeck, A.; Övervik, E.; Rafter, J.; Nord, C.E.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus Supplements on Mutagen Excretion in Faeces and Urine in Humans. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1992, 5, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Akedo, I.; Otani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Takeyama, I.; Ishiguro, S.; Miyaoka, E.; Sobue, T.; Kakizoe, T. Randomized trial of dietary fiber andLactobacillus casei administration for prevention of colorectal tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafter, J.; Bennett, M.; Caderni, G.; Clune, Y.; Hughes, R.; Karlsson, P.C.; Klinder, A.; O’Riordan, M.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Pool-Zobel, B.; et al. Dietary synbiotics reduce cancer risk factors in polypectomized and colon cancer patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, K.; Rafter, J. The role of probiotic bacteria in cancer prevention. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.S.; Recco, R.A.; Catalano, M.T.; Edberg, S.C.; Casey, J.I.; Steigbigel, N.H. Association ofStreptococcus boviswith Carcinoma of the Colon. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargo, D.; Moskovitz, M.; Floch, M.H. Faecal bacterial flora in cancer of the colon. Gut 1980, 21, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Del Vecchio, F.; Mastroiaco, V.; Di Marco, A.; Compagnoni, C.; Capece, D.; Zazzeroni, F.; Capalbo, C.; Alesse, E.; Tessitore, A. Next-generation sequencing: Recent applications to the analysis of colorectal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, T.L.; Manter, D.K.; Sheflin, A.M.; Barnett, B.A.; Heuberger, A.L.; Ryan, E.P. Stool Microbiome and Metabolome Differences between Colorectal Cancer Patients and Healthy Adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanapareddy, N.; Legge, R.M.; Jovov, B.; McCoy, A.; Burcal, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Randall, T.A.; Galanko, J.; Benson, A.; Sandler, R.S.; et al. Increased rectal microbial richness is associated with the presence of colorectal adenomas in humans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.A.; Dominianni, C.; Shapiro, J.A.; Church, T.R.; Wu, J.; Miller, G.; Yuen, E.; Freiman, H.; Lustbader, I.; Salik, J.; et al. The gut microbiota in conventional and serrated precursors of colorectal cancer. Microbiome 2016, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, C.; Sugimoto, K.; Moritani, I.; Tanaka, J.; Oya, Y.; Inoue, H.; Tameda, M.; Shiraki, K.; Ito, M.; Takei, Y.; et al. Comparison of human gut microbiota in control subjects and patients with colorectal carcinoma in adenoma: Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism and next-generation sequencing analyses. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira-Pascual, L.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Ocon, S.; Costales, P.; Parra, A.; Suarez, A.; Moris, F.; Rodrigo, L.; Mira, A.; Collado, M.C. Microbial mucosal colonic shifts associated with the development of colorectal cancer reveal the presence of different bacterial and archaeal biomarkers. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Jia, H.; Stadlmayr, A.; Tang, L.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xia, H.; Xu, X.; Jie, Z.; et al. Gut microbiome development along the colorectal adenoma–carcinoma sequence. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, N.; Wang, Z.; et al. Dysbiosis Signature of Fecal Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogtmann, E.; Hua, X.; Zeller, G.; Sunagawa, S.; Voigt, A.Y.; Hercog, R.; Goedert, J.J.; Shi, J.; Bork, P.; Sinha, R. Colorectal Cancer and the Human Gut Microbiome: Reproducibility with Whole-Genome Shotgun Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Sinha, R.; Pei, Z.; Dominianni, C.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Goedert, J.J.; Hayes, R.B.; Yang, L. Human Gut Microbiome and Risk for Colorectal Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Ling, Z.; Tong, X.; Xiang, C. Human Intestinal Lumen and Mucosa-Associated Microbiota in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, I.; Tap, J.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Roperch, J.P.; Letulle, S.; Langella, P.; Corthier, G.; Van Nhieu, J.T.; Furet, J.P. Microbial Dysbiosis in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Jiang, B. Analysis of Mucosa-Associated Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 4422–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brim, H.; Yooseph, S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Lee, E.; Torralbo, M.; Laiyemo, A.O.; Shokrani, B.; Nelson, K.; Ashktorab, H. Microbiome Analysis of Stool Samples from African Americans with Colon Polyps. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemer, B.; Lynch, D.B.; Brown, J.M.; Jeffery, I.B.; Ryan, F.J.; Claesson, M.J.; O’riordain, M.; Shanahan, F.; O’toole, P.W. Tumour-associated and non-tumour-associated microbiota in colorectal cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cai, G.; Qiu, Y.; Fei, N.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Jia, W.; Cai, S.; Zhao, L. Structural segregation of gut microbiota between colorectal cancer patients and healthy volunteers. ISME J. 2012, 6, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, B.; Gao, R.; Zhu, Q.; Qin, H. Microbiota disbiosis is associated with colorectal cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chiu, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Higashimori, A.; Fang, J.; Brim, H.; Ashktorab, H.; Ng, S.C.; Ng, S.S.M. Fecal bacteria act as novel biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huipeng, W.; Lifeng, G.; Chuang, G.; Jiaying, Z.; Yuankun, C. The Differences in Colonic Mucosal Microbiota between Normal Individual and Colon Cancer Patients by Polymerase Chain Reaction-denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, J.L.; McCoy, A.N.; Addamo, C.J.; Jia, W.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Altered Tissue Metabolites Correlate with Microbial Dysbiosis in Colorectal Adenomas. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, V.L.; Chen, J.; Johnson, S.; Harrington, S.C.; Yab, T.C.; Smyrk, T.C.; Nelson, H.; Boardman, L.A.; Druliner, B.R.; Levin, T.R.; et al. Shifts in the Fecal Microbiota Associated with Adenomatous Polyps. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A.A.; Lyra, A.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Rolny, P.; Lindegren, H.; Cedgård, L.; Wettergren, Y. Intestinal microbiota is altered in patients with colon cancer and modified by probiotic intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, C.; Wolf, P.G.; Kim, H.; Cross, T.W.L.; Vermillion, K.; Carroll, T.; Augustus, G.J.; Mutlu, E.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Braunschweig, C.; et al. Race-dependent association of sulfidogenic bacteria with colorectal cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Tian, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Fang, J.Y. Systematic evaluation of supervised classifiers for fecal microbiota-based prediction of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9546–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejea, C.M.; Wick, E.C.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; White, J.R.; Welch, J.L.M.; Rossetti, B.J.; Peterson, S.N.; Snesrud, E.C.; Borisy, G.G.; Lazarev, M. Microbiota organization is a distinct feature of proximal colorectal cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18321–18326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yu, E.; Wang, N.; Cai, Q.; Shuai, Q.; Yan, F.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota and plasma inflammatory factors across the stages of colorectal tumorigenesis: A case-control study. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Shanahan, F.; Clune, Y.; Collins, J.K.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; O’Riordan, M.; Holmes, E.; Wang, Y.; Marchesi, J.R. Culture-independent analysis of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer and polyposis. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukugaiti, M.H.; Ignacio, A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Ribeiro, U.; Nakano, V.; Avila-Campos, M.J. High occurrence of Fusobacterium nucleatum and Clostridium difficile in the intestinal microbiota of colorectal carcinoma patients. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohigashi, S.; Sudo, K.; Kobayashi, D.; Takahashi, O.; Takahashi, T.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Onodera, H. Changes of the Intestinal Microbiota, Short Chain Fatty Acids, and Fecal pH in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; Gao, Q.Y.; Cai, G.X.; Sun, X.M.; Zou, T.H.; Chen, H.M.; Yu, S.Y.; Qiu, Y.W.; Gu, W.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; et al. Fecal Clostridium symbiosum for Noninvasive Detection of Early and Advanced Colorectal Cancer: Test and Validation Studies. EBioMedicine 2017, 25, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Rawls, J.F.; Randall, T.A.; Burcal, L.; Mpande, C.N.; Jenkins, N.; Jovov, B.; Abdo, Z.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Molecular characterization of mucosal adherent bacteria and associations with colorectal adenomas. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Yu, Y.N.; Wang, J.L.; Lin, Y.W.; Kong, X.; Yang, C.Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.J.; Yuan, Y.Z.; Liu, F.; et al. Decreased dietary fiber intake and structural alteration of gut microbiota in patients with advanced colorectal adenoma. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, G.; Rampelli, S.; Orena, B.S.; Rengucci, C.; De Maio, G.; Barbieri, G.; Passardi, A.; Gardini, A.C.; Frassineti, G.L.; Gaiarsa, S.; et al. Shifts of Faecal Microbiota During Sporadic Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, J.J.; Gong, Y.; Hua, X.; Zhong, H.; He, Y.; Peng, P.; Yu, G.; Wang, W.; Ravel, J.; Shi, J.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Characteristics of Patients with Colorectal Adenoma Detected by Screening: A Population-based Study. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, N.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, C.M.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Comparisons of Gut Microbiota Among Healthy Control, Patients with Conventional Adenoma, Sessile Serrated Adenoma, and Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 22, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.; Buc, E.; Sauvanet, P.; Darcha, C.; Dubois, D.; Pereira, B.; Déchelotte, P.; Bonnet, R.; Pezet, D.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A. Colonization of the human gut by E. coli and colorectal cancer risk. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swidsinski, A.; Khilkin, M.; Kerjaschki, D.; Schreiber, S.; Ortner, M.; Weber, J.; Lochs, H. Association between intraepithelial Escherichia coli and colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, M.A.; Baxter, N.T.; Ruffin, M.T.; Rogers, M.A.M.; Schloss, P.D. Normalization of the microbiota in patients after treatment for colonic lesions. Microbiome 2017, 5, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Feng, Q.; Wong, S.H.; Zhang, D.; Yi Liang, Q.; Qin, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhao, H.; Stenvang, J.; Li, Y. Metagenomic analysis of faecal microbiome as a tool towards targeted non-invasive biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Jin, X.; Lv, G. Comparison of microbiota in patients treated by surgery or chemotherapy by 16S rRNA sequencing reveals potential biomarkers for colorectal cancer therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Gevers, D.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Michaud, M.; Duke, F.; Earl, A.M.; Ojesina, A.I.; Jung, J.; Bass, A.J.; Tabernero, J. Genomic analysis identifies association of Fusobacterium with colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackular, J.P.; Rogers, M.A.M.; Ruffin, M.T.; Schloss, P.D. The Human Gut Microbiome as a Screening Tool for Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemer, B.; Warren, R.D.; Barrett, M.P.; Cisek, K.; Das, A.; Jeffery, I.B.; Hurley, E.; Micheal, O.R.; Shanahan, F.; Paul, W.T. The oral microbiota in colorectal cancer is distinctive and predictive. Gut 2018, 67, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, N.T.; Ruffin, M.T.; Rogers, M.A.M.; Schloss, P.D. Microbiota-based model improves the sensitivity of fecal immunochemical test for detecting colonic lesions. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitay, E.L.; Werner, S.; Vital, M.; Pieper, D.H.; Höfler, D.; Gierse, I.-J.; Butt, J.; Balavarca, Y.; Cuk, K.; Brenner, H. Fusobacterium and colorectal cancer: Causal factor or passenger? Results from a large colorectal cancer screening study. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Bacci, G.; Chiellini, C.; Fagorzi, C.; Niccolai, E.; Taddei, A.; Ricci, F.; Ringressi, M.N.; Borrelli, R.; Melli, F. Preliminary Comparison of Oral and Intestinal Human Microbiota in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Pilot Study. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.H.; Kwong, T.N.; Chow, T.-C.; Luk, A.K.; Dai, R.Z.; Nakatsu, G.; Lam, T.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.C.; Chan, F.K. Quantitation of faecal Fusobacterium improves faecal immunochemical test in detecting advanced colorectal neoplasia. Gut 2017, 66, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklöf, V.; Löfgren-Burström, A.; Zingmark, C.; Edin, S.; Larsson, P.; Karling, P.; Alexeyev, O.; Rutegård, J.; Wikberg, M.L.; Palmqvist, R. Cancer-associated fecal microbial markers in colorectal cancer detection. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, L.; Schmid, J.; Ebert, M.; Soucek, P.; Kunicka, T.; Liška, V.; Bruha, J.; Neary, P.; DeZeeuw, N.; Tommasino, M.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum associates with stages of colorectal neoplasia development, colorectal cancer and disease outcome. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repass, J.; Maherali, N.; Owen, K.; Reproducibility Project: Cancer, B.; Reproducibility Project Cancer, B. Registered report: Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. eLife 2016, 5, e10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellarin, M.; Warren, R.L.; Freeman, J.D.; Dreolini, L.; Krzywinski, M.; Strauss, J.; Barnes, R.; Watson, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Moore, R.A. Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, T.; Yamamoto, E.; Suzuki, H.; Maruyama, R.; Chung, W.; Garriga, J.; Jelinek, J.; Yamano, H.-O.; Sugai, T.; An, B.; et al. Fusobacterium in colonic flora and molecular features of colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Kanno, S.; Nosho, K.; Sukawa, Y.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Kurihara, H.; Igarashi, H.; Takahashi, T.; Tachibana, M.; Takahashi, H. Association of Fusobacterium nucleatum with clinical and molecular features in colorectal serrated pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.N.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Azcárate-Peril, A.; Yeh, J.J.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Fusobacterium Is Associated with Colorectal Adenomas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suehiro, Y.; Sakai, K.; Nishioka, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Takami, T.; Higaki, S.; Shindo, Y.; Hazama, S.; Oka, M.; Nagano, H.; et al. Highly sensitive stool DNA testing of Fusobacterium nucleatum as a marker for detection of colorectal tumours in a Japanese population. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2017, 54, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Lou, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y. Mucosal adherent bacterial dysbiosis in patients with colorectal adenomas. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Song, Q.; Tang, X.; Liang, X.; Fan, H.; Peng, H.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z. Co-occurrence of driver and passenger bacteria in human colorectal cancer. Gut Pathog. 2014, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.L.; Liguori, G.; Lamas, B.; Brandi, G.; da Costa, G.; Hoffmann, T.W.; Pierluigi Di Simone, M.; Calabrese, C.; Poggioli, G.; Langella, P.; et al. Mucosa-associated microbiota dysbiosis in colitis associated cancer. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Shanahan, F.; Marchesi, J.R. Culture-independent analysis of desulfovibrios in the human distal colon of healthy, colorectal cancer and polypectomized individuals. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Martinez-Medina, M.; Surís-Valls, R.; Aldeguer, X.; Sabat-Mir, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J.; Garcia-Gil, L.J. Changes in the Abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Phylogroups I and II in the Intestinal Mucosa of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Fermentation in the human large intestine: Its physiologic consequences and the potential contribution of prebiotics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, S120–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Haub, M.D. Effects of Dietary Fiber and Its Components on Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1266–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, P.; Giovannucci, E.; Michels, K.B.; Bergkvist, L.; Hansen, H.; Holmberg, L.; Wolk, A. Fruit, Vegetables, Dietary Fiber, and Risk of Colorectal Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishehsari, F.; Engen, P.A.; Preite, N.Z.; Tuncil, Y.E.; Naqib, A.; Shaikh, M.; Rossi, M.; Wilber, S.; Green, S.J.; Hamaker, B.R.; et al. Dietary Fiber Treatment Corrects the Composition of Gut Microbiota, Promotes SCFA Production, and Suppresses Colon Carcinogenesis. Genes 2018, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcheva, A.; Irrazabal, T.; Martin, A. Gut microbial metabolism and colon cancer: Can manipulations of the microbiota be useful in the management of gastrointestinal health? BioEssays 2015, 37, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Collins, L.B.; Wali, A.; Bigler, R.; Sun, W.; Bultman, S.J. The Warburg Effect Dictates the Mechanism of Butyrate Mediated Histone Acetylation and Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, F.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Tulipani, S.; Tinahones, F.J.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windey, K.; De Preter, V.; Verbeke, K. Relevance of protein fermentation to gut health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Adams, D.H.; Fava, F.; Hermes, G.D.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Hold, G.; Quraishi, M.N.; Kinross, J.; Smidt, H.; Tuohy, K.M. The gut microbiota and host health: A new clinical frontier. Gut 2016, 65, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquet, P.; Duncan, S.H.; Chassard, C.; Bernalier-Donadille, A.; Flint, H.J. Lactate has the potential to promote hydrogen sulphide formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 299, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonero, F.; Benefiel, A.C.; Gaskins, H.R. Contributions of the microbial hydrogen economy to colonic homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Lactate-Utilizing Bacteria, Isolated from Human Feces, That Produce Butyrate as a Major Fermentation Product. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5810–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, M.L.; Campilongo, R.; Casalino, M.; Micheli, G.; Colonna, B.; Prosseda, G. Polyamines: Emerging players in bacteria–host interactions. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S. Cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy: Dietary polyphenols and signalling pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.C.; Jobin, C. The struggle within: Microbial influences on colorectal cancer. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 17, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouli, I.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Prakash, S. Probiotics in colorectal cancer (CRC) with emphasis on mechanisms of action and current perspectives. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Delany, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Sharma, S.; O’Keefe, S.J.D. Association Between Low Colonic Short-Chain Fatty Acids and High Bile Acids in High Colon Cancer Risk Populations. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.A.; Kim, B.; Bhin, J.; Kim, D.H.; You, H.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, S.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Hwang, D.; Lee, W.J. Bacterial Uracil Modulates Drosophila DUOX-Dependent Gut Immunity via Hedgehog-Induced Signaling Endosomes. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. A genome-wide systems analysis reveals strong link between colorectal cancer and trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a gut microbial metabolite of dietary meat and fat. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homann, N. Alcohol and upper gastrointestinal tract cancer: The role of local acetaldehyde production. Addict. Biol. 2001, 6, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, J.R.; McInerney, M.J.; Gunsalus, R.P. Genomic Insights into Syntrophy: The Paradigm for Anaerobic Metabolic Cooperation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughn, A.D.; Malamy, M.H. The strict anaerobe Bacteroides fragilis grows in and benefits from nanomolar concentrations of oxygen. Nature 2004, 427, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Duncan, S.H.; Stams, A.J.M.; Van Dijl, J.M.; Flint, H.J.; Harmsen, H.J.M. The gut anaerobe Faecalibacterium prausnitzii uses an extracellular electron shuttle to grow at oxic–anoxic interphases. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, G.; Shitut, S.; Preussger, D.; Yousif, G.; Waschina, S.; Kost, C. Ecology and evolution of metabolic cross-feeding interactions in bacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 455–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, J.J.; Sampson, J.N.; Moore, S.C.; Xiao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J.; Shi, J.; Sinha, R. Fecal metabolomics: Assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Rao, B.; Deng, L. Gut flora profiling and fecal metabolite composition of colorectal cancer patients and healthy individuals. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2848–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, Z.; Wu, R. NMR-based fecal metabolomics fingerprinting as predictors of earlier diagnosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29454–29464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Xie, G.; Jia, W. Metabonomics of Human Colorectal Cancer: New Approaches for Early Diagnosis and Biomarker Discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3857–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monleon, D.; Morales, J.M.; Barrasa, A.; López, J.A.; Vázquez, C.; Celda, B. Metabolite profiling of fecal water extracts from human colorectal cancer. NMR BioMed 2009, 22, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Monerri, N.C.S.; Kim, K.J.T.A. Pathogens hijack the epigenome: A new twist on host-pathogen interactions. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullar, M.A.J.; Fu, B.C. Diet, the Gut Microbiome, and Epigenetics. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultman, S.J. Interplay between diet, gut microbiota, epigenetic events, and colorectal cancer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetro, J.; Allen-Vercoe, E. The Human Microbiome Handbook; DEStech Publications, Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, Y.L.; Yang, T.; Sahay, B.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Targeting aberrant colon cancer-specific DNA methylation with lipoteichoic acid-deficient Lactobacillus acidophilus. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demehri, F.R.; Frykman, P.K.; Cheng, Z.; Ruan, C.; Wester, T.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Kawaguchi, A.; Hui, T.T.; Granström, A.L.; Funari, V.J.J. Altered fecal short chain fatty acid composition in children with a history of Hirschsprung-associated enterocolitis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mima, K.; Nishihara, R.; Qian, Z.R.; Cao, Y.; Sukawa, Y.; Nowak, J.A.; Yang, J.; Dou, R.; Masugi, Y.; Song, M.J.G. Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal carcinoma tissue and patient prognosis. Gut 2016, 65, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.F.; Ballestar, E.; Villar-Garea, A.; Boix-Chornet, M.; Espada, J.; Schotta, G.; Bonaldi, T.; Haydon, C.; Ropero, S.; Petrie, K.; et al. Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar-Zaidi, B.; Cowper-Sal·lari, R.; Corradin, O.; Saiakhova, A.; Bartels, C.F.; Balasubramanian, D.; Myeroff, L.; Lutterbaugh, J.; Jarrar, A.; Kalady, M.F.; et al. Epigenomic enhancer profiling defines a signature of colon cancer. Science 2012, 336, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, A.; Goossens-Beumer, I.J.; Van Hoesel, A.Q.; De Graaf, W.; Horati, H.; Putter, H.; Zeestraten, E.C.; Van De Velde, C.J.; Kuppen, P.J. Histone trimethylation at H3K4, H3K9 and H4K20 correlates with patient survival and tumor recurrence in early-stage colon cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, R.; Bhattacharya, R.; Boulbes, D.R.; Fan, F.; Xia, L.; Adoni, H.; Ajami, N.J.; Wong, M.C.; Smith, D.P.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Subspecies Animalis Influences Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Monocyte Activation in Human Colorectal Tumors. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T.; Ma, D.; Han, J.; Qian, Y.; Kryczek, I.; Sun, D.; Nagarsheth, N.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell 2017, 170, 548–563.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchev, M.; Kahl, P.; Friedrichs, N.; Kotzev, I.; Buettner, R. DNA Methylation in Patients with Colorectal Cancer—Correlation with Some Clinical and Morphological Features and with Local Tumour Invasion. Folia Med. 2010, 52, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Y.; Hu, X.L.; Han, T.M.; Wang, N.N.; Zhu, Y.M.; Hu, W.; Ma, Z.H.; Zhang, C.J.; Xu, X.; Ye, Z.Y.; et al. Association between RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhana, L.; Banerjee, H.N.; Verma, M.; Majumdar, A.P.N. Role of Microbiome in Carcinogenesis Process and Epigenetic Regulation of Colorectal Cancer. In Advanced Structural Safety Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 1856, pp. 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Kelly, T.K.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.Z.; Akiyama, Y.; Pan, K.F.; Liu, Z.J.; Lu, Z.M.; Zhou, J.; Gu, L.K.; Dong, C.X.; Zhu, B.D.; Ji, J.F.; et al. Methylation of GATA-4 and GATA-5 and development of sporadic gastric carcinomas. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.J. TLRs as miRNA receptors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6333–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, T.; Ishigamori, R.J.I. Biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3209–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.W.; Ferland-McCollough, D.; Jackson, T.J.; Bushell, M.J. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e249–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Dong, Y.J.; Liang, Q.Y.; He, X.Q.; Ng, S.S.M.; Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-18a Attenuates DNA Damage Repair through Suppressing the Expression of Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Chang, E.B.; Wang, J.-Y.; Raufman, J.-P. Butyrate inhibits pro-proliferative miR-92a by diminishing c-Myc-induced miR-17-92a cluster transcription in human colon cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, K.; Liu, K. Epigenetics and Colorectal Cancer Pathogenesis. Cancers 2013, 5, 676–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Burns, M.B.; Subramanian, S.; Blekhman, R. Interaction between host MicroRNAs and the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer. MSystems 2018, 3, e00205-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gut bacteria | Author | Published Time | Enrolment Time | Country | Sample Type (S/Ta) | Cancer Type | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Gut Bacteria | |||||||
| Acidaminobacter | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Acidovorax | Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Actinomyces | Peters [87] | 2016 | 2012–2014 | USA | S | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Akkermansia | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Alistipes | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRAb/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Atopobium | Vogtmann [92] | 2016 | 1985–1987 | USA | S | CRC | Whole-genome Shotgun Sequencing |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Anaerococcus | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Anaerotruncus | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Aquabacterium | Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Bacteriodes | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Sobhani [95] | 2011 | 2004–2006 | France | S | CRC | Pyrosequencing/qPCR | |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS | |
| Brim [97] | 2013 | - | USA | S | Colon polyps | 16S rRNA Sequencing/HITChip/Pyrosequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Drewes [37] | 2017 | - | Malaysia | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Liang [101] | 2016 | - | China | S | CRC | duplex qPCR | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Huipeng [102] | 2014 | - | China | T | Colon cancer | PCR/DGGE | |
| Bifidobacterium | Nugent [103] | 2014 | - | USA | T | CRA | qPCR |
| Bilophila | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Yazici [106] | 2017 | 2011–2012 | USA | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Blautia | Ai [107] | 2017 | 2012 | China | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Butyrivibrio | Dejea [108] | 2014 | - | USA | T | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Campylobacter | Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP c | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Citrobacter | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Cloacibacterium | Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Clostridium | Dejea [108] | 2014 | - | USA | T | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Scanlan [110] | 2008 | - | Ireland | S | Colon cancer | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Allali [36] | 2018 | - | Morocco | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Fukugaiti [111] | 2015 | - | Brazil | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Xie [113] | 2017 | 2016 | China | S | CRA/CRC/A-CRC | PCR | |
| Liang [101] | 2016 | - | China | S | CRC | duplex qPCR | |
| Collinsella | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Desulfovibrio | Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Dialister | Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Dorea | Peters [87] | 2016 | 2012–2014 | USA | S | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | S | Colon cancer | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Eggerthella | Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Enterococcus | Chen [115] | 2013 | 2010–2011 | China | S | A-CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Balamurugan [39] | 2008 | - | India | S | CRC | Real-time PCR | |
| Escherichia | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS | |
| Mori [116] | 2018 | 2013–2015 | Italy | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Yoon [118] | 2017 | - | Korea | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Kohoutova [44] | 2014 | - | UK | T | CRC/CRA | PCR | |
| Bonnet [119] | 2013 | 2007–2010 | France | T | Colon cancer | PCR | |
| Swidsinski [120] | 1998 | - | Austria | T | CRC/CRA | PCR | |
| Eubacterium | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Faecalibacterium | Sze [121] | 2017 | - | USA | S | CRC/A-CRA/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Fastidiosipila | Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Fastidiosipila | Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Fusobacterium | Vogtmann [92] | 2016 | 1985–1987 | USA | S | CRC | Whole-genome Shotgun Sequencing |
| Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing | |
| Yu [122] | 2015 | - | China | S | CRC | Metagenomic Sequencing | |
| Dejea [108] | 2014 | - | USA | T | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing | |
| Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS | |
| Deng [123] | 2018 | - | China | S | CRC | NGS | |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/ NGS | |
| Kostic [124] | 2012 | - | Spain | T | CRC | WGS/16S rDNA Sequencing/qPCR/FISH | |
| Allali [36] | 2018 | - | Morocco | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zackular [125] | 2014 | - | Michigan | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | Washington | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Sinha [16] | 2016 | 1985–1987 | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [126] | 2017 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zeller [28] | 2014 | 2004–2006 | France/Germany | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Baxter [127] | 2016 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Drewes [37] | 2017 | - | Malaysia | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Yoon [118] | 2017 | - | Korea | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Amitay [128] | 2017 | 2005–2013 | Germany | S | CRC/A-CRA/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing/multiplex PCR | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Russo [129] | 2018 | 2015–2016 | Italy | S | CRC | qPCR/16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Liang [101] | 2016 | - | China | S | CRC | duplex qPCR | |
| Kostic [60] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Wong [130] | 2016 | - | China | S | CRC/A-CRA | qPCR | |
| Fukugaiti [111] | 2015 | - | Brazil | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Eklof [131] | 2017 | 2008–2013 | Sweden | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | S | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Yu [122] | 2015 | - | China | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Flanagan [132] | 2014 | 2008–2010 | Ireland | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Repass [133] | 2016 | - | USA | T | CRC | qPCR | |
| Castellarin [134] | 2012 | - | Canada | T | CRC | qPCR | |
| Tahara [135] | 2014 | - | Japan | T | CRC | qPCR | |
| Ito [136] | 2015 | 2001–2013 | Japan | T | CRC | qPCR | |
| McCoy [137] | 2013 | - | USA | T | CRA | qPCR | |
| Suehiro [138] | 2016 | - | Japan | S | CRC/CRA/A-CRA | PCR | |
| Gemella | Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014 - 2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Baxter [127] | 2016 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Granulicatella | Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR |
| Heamophilus | Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS |
| Helicobacter | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Klebsiella | Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Lactobacillus | Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS |
| Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Lactococcus | Lu [139] | 2016 | 2014 | China | T | CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Methanobrevibacter | Hibberd [105] Mira-Pascual [89] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| 2015 | - | Spain | S | qPCR | |||
| Methanosphaera | Ai [107] | 2017 | 2012 | China | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Mogibacterium | Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS |
| Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Morganella | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Odoribacter | Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Oscillibacter | Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Oscillospira | Deng [123] | 2018 | - | China | S | CRC | NGS |
| Pantoea | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Parabacteroides | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Parvimonas | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Yu [122] | 2015 | - | China | S | CRC | Metagenomic Sequencing | |
| Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Baxter [127] | 2016 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [126] | 2017 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Sze [121] | 2017 | - | USA | S | CRC/A-CRA/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Drewes [37] | 2017 | - | Malaysia | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing /qPCR | |
| Wong [130] | 2016 | - | China | S | CRC/A-CRA | qPCR | |
| Peptostreptococcus | Yu [122] | 2015 | - | China | S | CRC | Metagenomic Sequencing |
| Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Baxter [127] | 2016 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zeller [28] | 2014 | 2004–2006 | France/Germany | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [126] | 2017 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | S/T | Colon cancer | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Drewes [37] | 2017 | - | Malaysia | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Phascolarctobacterium | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Porphyromonas | Vogtmann [92] | 2016 | 1985–1987 | USA | S | CRC | Whole-genome Shotgun Sequencing |
| Sobhani [95] | 2011 | 2004–2006 | France | S | CRC | Pyrosequencing/qPCR | |
| Baxter [127] | 2016 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Allali [36] | 2018 | - | Morocco | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zackular [125] | 2014 | - | Michigan | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Sze [121] | 2017 | - | USA | S | CRC/A-CRA/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | Washington | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Sinha [16] | 2016 | 1985–1987 | USA | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zeller [28] | 2014 | 2004–2006 | France/Germany | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Geng [140] | 2014 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Prevotella | Deng [123] | 2018 | - | China | S | CRC | NGS |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Baxter [127] | 2016 | - | USA | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [126] | 2017 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR | |
| Paraprevotella | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Pseudomonas | Lu [139] | 2016 | 2014 | China | T | CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Zackular [125] | 2014 | - | Michigan | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Yoon [118] | 2017 | - | Korea | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Pyramidobacter | Yazici [106] | 2017 | 2011–2012 | USA | T | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Rhizobium | Yoon [118] | 2017 | - | Korea | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Roseburia | Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Liang [101] | 2016 | - | China | S | CRC | duplex qPCR | |
| Ruminococcus | Dejea [108] | 2014 | - | USA | T | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Allali [36] | 2018 | - | Morocco | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | 16S rRNA Sequencing | ||
| Salmonella | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Selenomonas | Allali [36] | 2018 | - | Morocco | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Serratia | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Slackia | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Sphingomonas | Richard [141] | 2018 | - | France | T | CACd/CRC | qPCR/16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Shigella | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Mori [116] | 2018 | 2013–2015 | Italy | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Solobacterium | Yu [122] | 2015 | - | China | S | CRC | Metagenomic Sequencing |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Streptococcus | Chen [115] | 2013 | 2010–2011 | China | S | A-CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Peters [87] | 2016 | 2012–2014 | USA | S | CRC/CRA | Pyrosequencing | |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Flemer [126] | 2017 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Geng [140] | 2014 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Richard [141] | 2018 | - | France | T | CAC/CRC | qPCR/16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Klein [82] | 1977 | - | Chicago | S | CRC | Culture | |
| Subdoligranulum | Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Sutterella | Mori [116] | 2018 | 2013–2015 | Italy | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Trabulsiella | Goedert [117] | 2015 | - | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Veillonella | Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS |
| Geng [140] | 2014 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Decreased Gut Bacteria | |||||||
| Acidovorax | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Acinetobacter | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Alistipes | Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Anaerostipes | Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Atopobium | Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR |
| Bacteriodes | Kostic [124] | 2012 | - | Spain | T | CRC | WGS |
| Zackular [125] | 2014 | - | Michigan | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Allali [36] | 2018 | - | Morocco | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Bacillus | Lu [139] | 2016 | 2014 | China | T | CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Bifidobacterium | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | S | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Yusuf [38] | 2016 | - | Indonesia | S | CRC | DGGE | |
| Blautia | Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Buttiauxella | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Caulobacter | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Collinsella | Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Clostridium | Chen [115] | 2013 | 2010–2011 | China | S | A-CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Zackular [125] | 2014 | - | Michigan | S | CRC/CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR | |
| Coprococcus | Vogtmann [92] | 2016 | 1985–1987 | USA | S | CRC | Whole-genome Shotgun Sequencing |
| Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Flemer [98] | 2015 | - | Ireland | S/T | CRC/Polyps | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Desulfovibrio | Scanlan [142] | 2009 | - | UK | S | CRC | qPCR |
| Dialister | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Dorea | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Enterococcus | Lu [139] | 2016 | 2014 | China | T | CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Epilithonimonas | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Eubacterium | Yu [122] | 2015 | - | China | S | CRC | Metagenomic Sequencing |
| Chen [115] | 2013 | 2010–2011 | China | S | A-CRA | Pyrosequencing | |
| Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS | |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Balamurugan [39] | 2008 | - | India | S | CRC | Real-time PCR | |
| Vargo [83] | 1980 | - | USA | S | Colon cancer | Culture | |
| Faecalibacterium | Xu [96] | 2017 | - | China | T | CRC/CRA | NGS |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Balamurugan [39] | 2008 | - | India | S | CRC | Real-time PCR | |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Lopez-Siles [143] | 2016 | - | Spain | T | CRC | qPCR | |
| Fusicatenibacter | Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Flavobacterium | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Fusobacterium | Shen [114] | 2010 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Richard [141] | 2018 | - | France | T | CAC/CRC | qPCR/16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Vargo [83] | 1980 | - | USA | S | Colon cancer | Culture | |
| Haemophilus | Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Janthinobacterium | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Lachnobacterium | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Lachnospira | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Lactobacillus | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Megamonas | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Megasphaera | Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | Washington | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Parasutterella | Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Pedobacter | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Propionibacterium | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Peptostreptococcus | Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | Washington | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Prevotella | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Pseudobutyrivibrio | Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Pseudomonas | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Psychrobacter | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Rahnella | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Roseburia | Chen [115] | 2013 | 2010–2011 | China | S | A-CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Wang [99] | 2012 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Wu [91] | 2013 | - | China | S | CRC | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | S | Colon cancer | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Chen [94] | 2012 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Ruminococcus | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | Washington | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Weir [85] | 2013 | - | USA | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Richard [141] | 2018 | - | France | T | CAC/CRC | qPCR/16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Selenomonas | Ahn [93] | 2013 | 1985–1989 | Washington | S | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Slackia | Kasai [88] | 2015 | 2012–2013 | Japan | S | CRC/CRA | T-RFLP/NGS |
| Solibacillus | Lu [139] | 2016 | 2014 | China | T | CRA | Pyrosequencing |
| Sphingobacterium | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Sphingomonas | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Staphylococcus | Ohigashi [112] | 2013 | 2009–2010 | Japan | S | CRC | qPCR |
| Mira-Pascual [89] | 2015 | - | Spain | T | CRC/CRA | qPCR | |
| Streptococcus | Feng [90] | 2015 | 2010–2012 | Austria | S | A-CRA/CRC | Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing |
| Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing | |
| Zhang [109] | 2018 | 2014–2015 | China | S | CRC/A-CRA/BP | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Hibberd [105] | 2017 | - | USA | T | Colon cancer | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Sanapareddy [86] | 2012 | - | USA | T | CRA | 16S rDNA Sequencing | |
| Stenotrophomonas | Gao [100] | 2015 | - | China | T | CRC | 16S rDNA Sequencing |
| Sutterella | Nakatsu [27] | 2015 | 2011–2014 | China | T | CRC/CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing/qPCR |
| Veillonella | Hale [104] | 2017 | 2001–2005 | USA | S | CRA | 16S rRNA Sequencing |
| Metabolite | Chemical Class | Bacterial Source | Bacterial Level in CRC a | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzoic Acid | Benzenoid (Benzene) | Serratia | + | [15,16,171] |
| Hippuric Acid(Benzamidoacetic Acid) | Benzenoid (Benzene) | Clostridium Eubacterium Ruminococcus Faecalibacterium | ± ± ± ± | [171] |
| Hydroxybenzoic Acid | Benzenoid (Benzene) | Arthrobacter Bifidobacterium Microbulbifer Escherichia Eubacterium Corynebacterium Clostridium | * ± * ± ± * ± | [16,171] |
| Syringic Acid | Benzenoid (Benzene) | Bifidobacterium | ± | [171] |
| 3-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid | Benzenoid (Phenol) | Klebsiella Clostridium | + ± | [15,171] |
| 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid | Benzenoid (Phenol) | Pseudomonas Klebsiella Acinetobacter Clostridium | ± + - ± | [15,16,171] |
| p-Cresol | Benzenoid (Phenol) | Bacteriodes Bifidobacterium Enterobacter Lactobacillus Clostridium | ± ± * ± ± | [15] |
| Allantoin | Organoheterocyclic Compound (Azole) | Bacillus Streptomyces | - * | [171] |
| N-Acetylputrescine | Organic Acid (Organic Carboximidic Acid) | Corynebacterium | * | [15,16,171] |
| 5-Aminopentanoic Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Carboximidic Acid) | Corynebacterium | * | [15,16,171] |
| Acetic Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Carboximidic Acid) | Acinetobacter Bacteriodes Bifidobacterium Enterobacter Prevotella Ruminococcus Streptococcus Staphylococcus Pseudomonas Proteus Klebsiella Escherichia Enterococcus Citrobacter Akkermansia | - ± ± * ± ± ± - ± * + ± ± + + | [85,172,173,174,175,176] |
| Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) | Organic Acid (Organic Carboximidic Acid) | Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus | ± ± | [15,16,171] |
| Glutaric Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Carboximidic Acid) | Escherichia | ± | [15,16,171] |
| Succinic Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Carboximidic Acid) | Acinetobacter Enterobacter Corynebacterium Basfia Pseudomonas Proteus Mannheimia Klebsiella Escherichia Enterococcus Citrobacter Anaerobiospirillum Actinobacillus | - * * * ± * * + ± ± + * * | [15,16,171,174] |
| 5-Keto-D-gluconate | Organic Acid (Organic Hydroxy Acid) | Gluconobacter | * | [15,171] |
| Hydroxypropionic Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Hydroxy Acid) | Escherichia Klebsiella | ± + | [15,16,171] |
| Lactic Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Hydroxy Acid) | Acinetobacter Enterobacter Corynebacterium Bacillus Streptococcus Staphylococcus Pseudomonas Proteus Klebsiella Escherichia Enterococcus Citrobacter | - * * - ± - ± * + ± ± + | [15,16,171,174,176] |
| Hydroxyacetic Acid(Glycolic Acid) | Organic Acid (Organic Hydroxy Acid) | Alcaligenes Acetobacter Rhodococcus Pseudomonas Leptospirillum Gluconobacter Escherichia Acidithiobacillus Corynebacterium | * * * ± * * ± * * | [15,16,171] |
| Pyruvic Acid | Organic Acid (Organic Keto Acid) | Corynebacterium Escherichia | * ± | [16,171] |
| Oxoglutaric Acid(Ketoglutaric Acid) | Organic Acid (Organic Keto Acid) | Corynebacterium | * | [15] |
| p-Cresol sulfate | Organic Acid (Organic Sulfuric Acid) | Clostridium Lactobacillus Enterobacter Bifidobacterium | ± ± * ± | [15,16,171] |
| Cadaverine | Organonitrogen Compound (Amine) | Corynebacterium | * | [15,16,171] |
| Putrescine | Organonitrogen Compound (Amine) | Enterobacter Cronobacter Citrobacter Corynebacterium | * * + * | [15,16,171] |
| 2,3-Butanediol | Organooxygen Compound (Alcohol) | Serratia Klebsiella Bacillus Enterobacter | + + - * | [15] |
| D-Arabinose | Organooxygen Compound (Carbohydrate) | Streptococcus Pediococcus Lactococcus Lactobacillus Geobacillus Escherichia Enterococcus Enterobacter Clostridium Alicyclobacillus Bifidobacterium | ± * + ± * ± ± * ± * ± | [15] |
| Mannitol | Organooxygen Compound (Carbohydrate) | Clostridium Streptococcus Leuconostoc Zymomonas Torulaspora Rhodobacter Pseudomonas Lactococcus Gluconobacter Lactobacillus | ± ± * * * * ± + * ± | [171] |
| Ribulose | Organooxygen Compound (Carbohydrate) | Acetobacter Gluconobacter | * * | [15] |
| Tartaric Acid | Organooxygen Compound (Carbohydrate) | Agrobacterium Nocardia Rhizobium | * * + | [171] |
| Indoleacetic Acid | Organoheterocyclic Compound (Indole) | Bradyrhizobium Rhizobium Pseudomonas Pantoea Enterobacter Clostridium Bacillus Agrobacterium Azospirillum | * + ± + * ± - * * | [15,16,171] |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine(Serotonin) | Indole | Enterococcus Streptococcus Escherichia | ± ± ± | [15] |
| Tryptamine | Indole | Ruminococcus Clostridium | ± ± | [15,171] |
| Ferulic Acid | Phenylpropanoid Polyketide (Phenylpropanoic Acid) | Pseudomonas | ± | [15,16,171] |
| Desaminotyrosine (4-Hydroxyphenylpropionic Acid) | Phenylpropanoid Polyketide (Phenylpropanoic Acid) | Klebsiella Staphylococcus Pseudomonas Lactobacillus Eubacterium Enterococcus Clostridium Bifidobacterium Acinetobacter Bacteriodes | + - ± ± ± ± ± ± - ± | [15,16,171] |
| Hydrocinnamic Acid | Phenylpropanoid Polyketide (Phenylpropanoic Acid) | Clostridium Eubacterium | ± ± | [15,16,171] |
| Hydroxyphenyllactic Acid | Phenylpropanoid Polyketide (Phenylpropanoic Acid) | Clostridium Bifidobacterium Staphylococcus Pseudomonas Lactobacillus Klebsiella Eubacterium Escherichia Enterococcus Acinetobacter Bacteriodes | ± ± - ± ± + ± ± ± - ± | [15,171] |
| Phenyllactic Acid | Phenylpropanoid Polyketide (Phenylpropanoic Acid) | Clostridium Klebsiella Staphylococcus Pseudomonas Lactobacillus Eubacterium Escherichia Enterococcus Bifidobacterium Acinetobacter Bacteriodes | ± + - ± ± ± ± ± ± - ± | [15] |
| 6-Hydroxynicotinic Acid | Organoheterocyclic Compound (Pyridine) | Serratia Achromobacter Pseudomonas | + * ± | [15,16,171] |
| Butyric Acid | Lipid (Fatty Acyl) | Anaerostipes Eubacterium Roseburia Faecalibacterium Coprococcus | - ± ± ± - | [85,174,176] |
| Coprosterol | Steroid (Cholesterol) | Lactobacillus | ± | [15] |
| Glycocholic Acid | Steroid (Bile Acid) | Bacteriodes Bifidobacterium Clostridium Lactobacillus | ± ± ± ± | [15,16,171] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarashi, S.; Siadat, S.D.; Ahmadi Badi, S.; Zali, M.; Biassoni, R.; Ponzoni, M.; Moshiri, A. Gut Bacteria and their Metabolites: Which One Is the Defendant for Colorectal Cancer? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110561
Tarashi S, Siadat SD, Ahmadi Badi S, Zali M, Biassoni R, Ponzoni M, Moshiri A. Gut Bacteria and their Metabolites: Which One Is the Defendant for Colorectal Cancer? Microorganisms. 2019; 7(11):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110561
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarashi, Samira, Seyed Davar Siadat, Sara Ahmadi Badi, Mohammadreza Zali, Roberto Biassoni, Mirco Ponzoni, and Arfa Moshiri. 2019. "Gut Bacteria and their Metabolites: Which One Is the Defendant for Colorectal Cancer?" Microorganisms 7, no. 11: 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110561
APA StyleTarashi, S., Siadat, S. D., Ahmadi Badi, S., Zali, M., Biassoni, R., Ponzoni, M., & Moshiri, A. (2019). Gut Bacteria and their Metabolites: Which One Is the Defendant for Colorectal Cancer? Microorganisms, 7(11), 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110561





