Dynamics of a Perturbed Microbial Community during Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Chemically Defined Soluble Organic Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
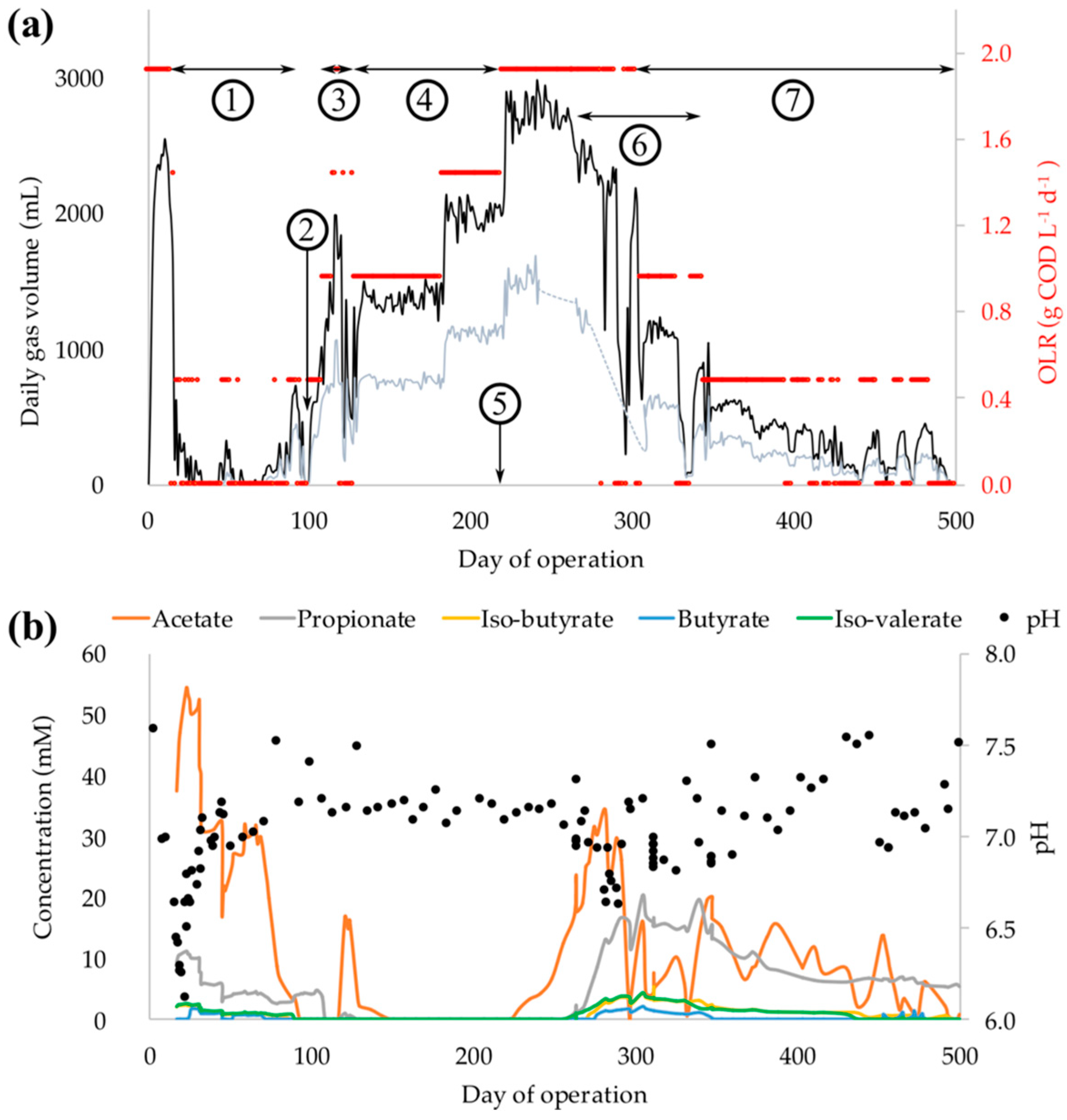
3.1. Process Startup, Recovery, and Failure
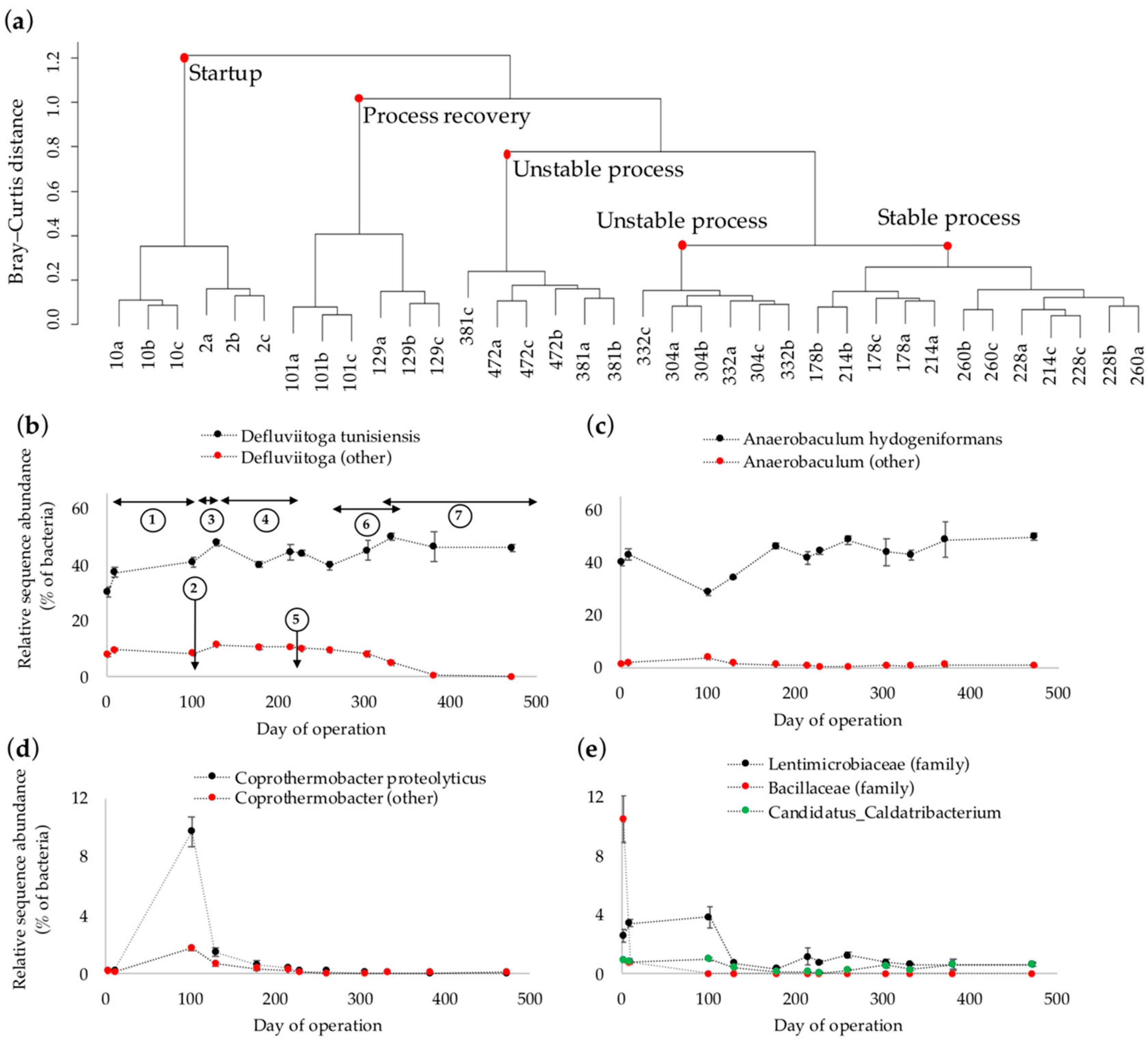
3.2. Dynamics of the Bacterial Community Composition
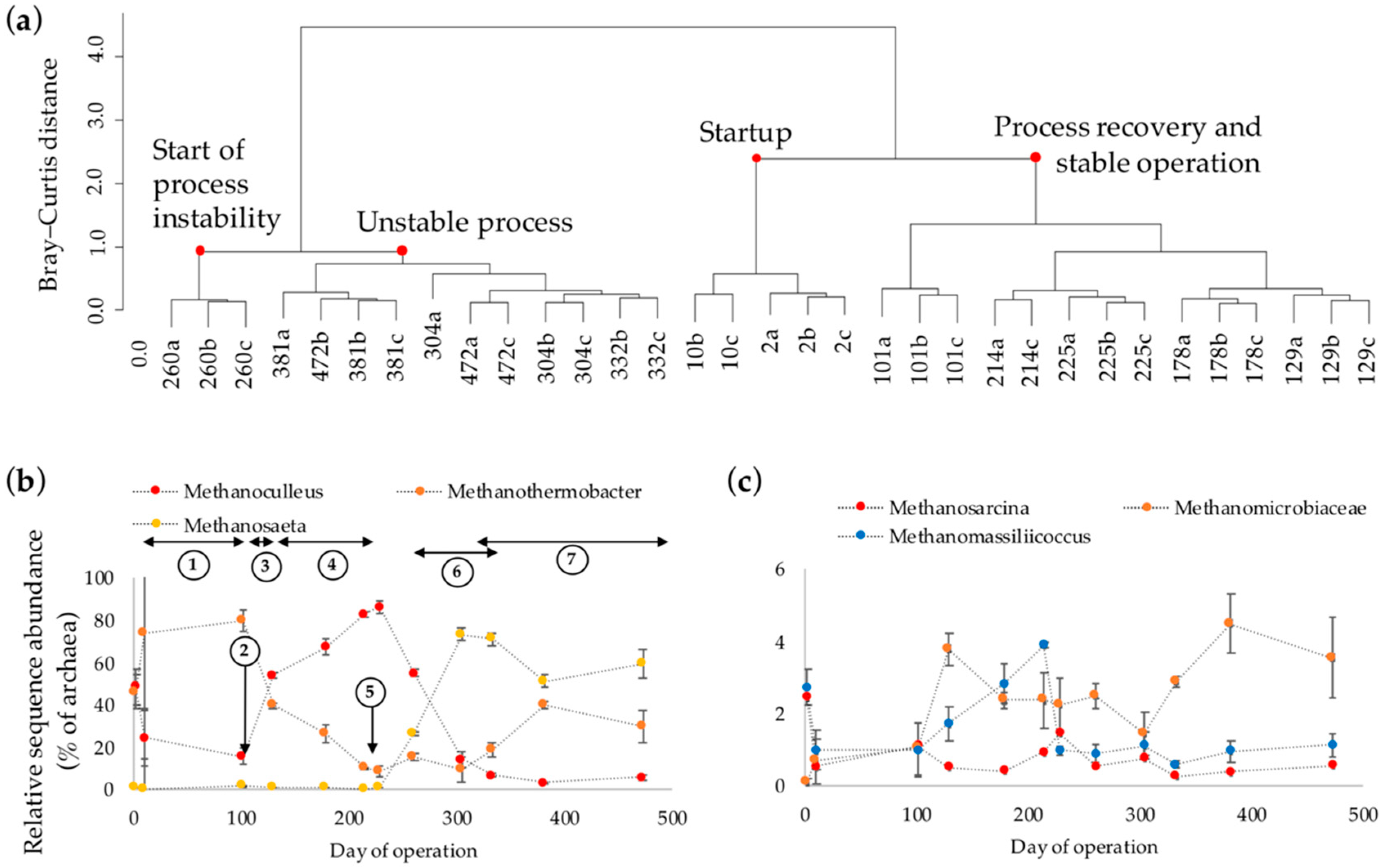
3.3. Dynamics of the Archaeal Community Composition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schnürer, A. Biogas production: Microbiology and technology. Adv. Biot. 2016, 156, 195–234. [Google Scholar]
- Fagbohungbe, M.O.; Herbert, B.M.J.; Hurst, L.; Ibeto, C.N.; Li, H.; Usmani, S.Q.; Semple, K.T. The challenges of anaerobic digestion and the role of biochar in optimizing anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, P.L. One hundred years of anaerobic treatment. Anaerobic Digestion 1981, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Amha, Y.M.; Anwar, M.Z.; Brower, A.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Stadler, L.B.; Webster, T.M.; Smith, A.L. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion processes: Applications of molecular tools. Bioresource Technol. 2018, 247, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Khan, A.; Xiong, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X. A critical review on the interaction of substrate nutrient balance and microbial community structure and function in anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziels, R.M.; Svensson, B.H.; Sundberg, C.; Larsson, M.; Karlsson, A.; Shakeri Yekta, S. Microbial rRNA gene expression and co-occurrence profiles associate with biokinetics and elemental composition in full-scale anaerobic digesters. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervin, H.M.; Dennis, P.G.; Lim, H.J.; Tyson, G.W.; Batstone, D.J.; Bond, P.L. Drivers of microbial community composition in mesophilic and thermophilic temperature-phased anaerobic digestion pre-treatment reactors. Water Res. 2013, 47, 7098–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levén, L.; Eriksson, A.R.B.; Schnürer, A. Effect of process temperature on bacterial and archaeal communities in two methanogenic bioreactors treating organic household waste. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke-Whittle, I.H.; Walter, A.; Ebner, C.; Insam, H. Investigation into the effect of high concentrations of volatile fatty acids in anaerobic digestion on methanogenic communities. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreeyessus, G.; Jenicek, P. Thermophilic versus mesophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: A comparative review. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speda, J.; Johansson, M.A.; Jonsson, B.H.; Karlsson, M. Applying theories of microbial metabolism for induction of targeted enzyme activity in a methanogenic microbial community at a metabolic steady state. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 7989–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M. Metaproteogenomics-Guided Enzyme Discovery: Targeted Identification of Novel Proteases in Microbial Communities. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Westerholm, M.; Moestedt, J.; Schnürer, A. Biogas production through syntrophic acetate oxidation and deliberate operating strategies for improved digester performance. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G. Effect of ammonia on methane production, methanogenesis pathway, microbial community and reactor performance under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, S.; Boren, H. Analysis of mono- and diesters of o-phthalic acid by solid-phase extractions with polystyrene-divinylbenzene-based polymers. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 963, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, H.; Pesaro, M.; Widmer, F.; Zeyer, J. A strategy for optimizing quality and quantity of DNA extracted from soil. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2001, 45, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugerth, L.W.; Wefer, H.A.; Lundin, S.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Lindberg, M.; Rodin, S.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. Degeprime, a program for degenerate primer design for broad-taxonomic-range pcr in microbial ecology studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, K.; Horikoshi, K. Rapid detection and quantification of members of the archaeal community by quantitative PCR using fluorogenic probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5066–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Sun, L.; Müller, B.; Schnürer, A. Importance of inoculum source and initial community structure for biogas production from agricultural substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerholm, M.; Müller, B.; Singh, A.; Karlsson Lindsjö, O.; Schnürer, A. Detection of novel syntrophic acetate-oxidizing bacteria from biogas processes by continuous acetate enrichment approaches. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 11, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Updating the 97% identity threshold for 16s ribosomal RNA OTUs. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The silva ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, L. Entropy and diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.; Groeneveld, J.; Harms, H.; Johst, K.; Frank, K.; Kleinsteuber, S. A critical evaluation of ecological indices for the comparative analysis of microbial communities based on molecular datasets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2017.
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R package version 2.5-2. 2018.
- Schnürer, A. Biogas production: Microbiology and technology. In Advances in Biochemicl Engineering/Biotechnology; Hatti-Kaul, R., Mamo, G., Mattiasson, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 195–234. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ortiz, R.; Steele, T.; Stuckey, D. Toxicants inhibiting anaerobic digestion: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Heaven, S. Trace element requirements for stable food waste digestion at elevated ammonia concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, A.T.W.M.; van Lier, J.B.; de Kreuk, M.K. Growth media in anaerobic fermentative processes: The underestimated potential of thermophilic fermentation and anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, P.; Fermoso, F.G.; Stams, A.J.M.; Lens, P.N.L.; Plugge, C.M. Transcription of fdh and hyd in Syntrophobacter spp. And Methanospirillum spp. As a diagnostic tool for monitoring anaerobic sludge deprived of molybdenum, tungsten and selenium. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, R. Molybdenum and tungsten in biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Norli, I.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Yhaya, M.F. Impacts of trace element supplementation on the performance of anaerobic digestion process: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, J.B.; Orphan, V.J. Trace metal requirements for microbial enzymes involved in the production and consumption of methane and nitrous oxide. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hania, W.B.; Godbane, R.; Postec, A.; Hamdi, M.; Ollivier, B.; Fardeau, M.L. Defluviitoga tunisiensis gen. Nov., sp. Nov., a thermophilic bacterium isolated from a mesothermic and anaerobic whey digester. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, I.; Bremges, A.; Stolze, Y.; Hahnke, S.; Cibis, K.G.; Koeck, D.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Kreubel, J.; Hassa, J.; Wibberg, D.; et al. Genomics and prevalence of bacterial and archaeal isolates from biogas-producing microbiomes. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, I.; Koeck, D.E.; Cibis, K.G.; Hahnke, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Langer, T.; Kreubel, J.; Erhard, M.; Bremges, A.; Off, S.; et al. Unraveling the microbiome of a thermophilic biogas plant by metagenome and metatranscriptome analysis complemented by characterization of bacterial and archaeal isolates. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maune, M.W.; Tanner, R.S. Description of Anaerobaculum hydrogeniformans sp. Nov., an anaerobe that produces hydrogen from glucose, and emended description of the genus Anaerobaculum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollivier, B.M.; Mah, R.A.; Ferguson, T.J. Emendation of the genus Thermobacteroides: Thermobacteroides proteolyticus sp. Nov., a proteolytic acetogen from a methanogenic enrichment. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1985, 35, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, L.H.; Frank, J.A.; Zamanzadeh, M.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Pope, P.B.; Horn, S.J.; Arntzen, M.ï. Quantitative metaproteomics highlight the metabolic contributions of uncultured phylotypes in a thermophilic anaerobic digester. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Vazquez, I.; Torres-Aguirre, G.J.; Molina, C.; Ruiz-Aguilar, G.M.L. Characterization of a lignocellulolytic consortium and methane production from untreated wheat straw: Dependence on nitrogen and phosphorous content. BioResources 2016, 11, 4237–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Vazquez, I.; Morales, A.L.; Escalante, A.E. History of adaptation determines short-term shifts in performance and community structure of hydrogen-producing microbial communities degrading wheat straw. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserfallen, A.; Nölling, J.; Pfister, P.; Reeve, J.; De Macario, E.C. Phylogenetic analysis of 18 thermophilic Methanobacterium isolates supports the proposals to create a new genus, Methanothermobacter gen. Nov., and to reclassify several isolates in three species, Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus comb. Nov., Methanothermobacter wolfeii comb. Nov., and Methanothermobacter marburgensis sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maestrojuan, G.M.; Boone, D.R.; Xun, L.; Mah, R.A.; Zhang, L. Transfer of Methanogenium bourgense, Methanogenium marisnigri, Methanogenium olentangyi, and Methanogenium thermophilicum to the genus Methanoculleus gen. Nov., emendation of Methanoculleus marisnigri and Methanogenium, and description of new strains of Methanoculleus bourgense and Methanoculleus marisnigri. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1990, 40, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Barret, M.; Gagnon, N.; Kalmokoff, M.L.; Topp, E.; Verastegui, Y.; Brooks, S.P.J.; Matias, F.; Neufeld, J.D.; Talbot, G. Identification of Methanoculleus spp. as active methanogens during anoxic incubations of swine manure storage tank samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, I.; Kim, Y.S.; Wibberg, D.; Stolze, Y.; Off, S.; Antonczyk, S.; Pühler, A.; Scherer, P.; Schlüter, A. Biphasic study to characterize agricultural biogas plants by high-throughput 16s rRNA gene amplicon sequencing and microscopic analysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, S.; Schnürer, A.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E.; Müller, B. Complete genome sequence of Methanoculleus bourgensis strain mab1, the syntrophic partner of mesophilic acetate-oxidising bacteria (saob). Standards Genom. Sci. 2016, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ran, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, X. Instability diagnosis and syntrophic acetate oxidation during thermophilic digestion of vegetable waste. Water Res. 2018, 139, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, S. Syntrophic acetate-oxidizing microbes in methanogenic environments. Microbes Environ. 2008, 23, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, E.; Xie, G.; Barabote, R.D.; Saunders, E.; Han, C.S.; Detter, J.C.; Richardson, P.; Brettin, T.S.; Das, A.; Ljungdahl, L.G.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Moorella thermoacetica (f. Clostridium thermoaceticum). Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2550–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Ren, Q.; Scott Durkin, A.; Daugherty, S.C.; Brinkac, L.M.; Dodson, R.J.; Madupu, R.; Sullivan, S.A.; Kolonay, J.F.; Nelson, W.C.; et al. Life in hot carbon monoxide: The complete genome sequence of Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans z-2901. PLoS Genet. 2005, 1, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliano, M.C.; Braguglia, C.M.; Petruccioli, M.; Rossetti, S. Ecology and biotechnological potential of the thermophilic fermentative Coprothermobacter spp. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, F.; Bize, A.; Guillot, A.; Monnet, V.; Madigou, C.; Chapleur, O.; Mazéas, L.; He, P.; Bouchez, T. Metaproteomics of cellulose methanisation under thermophilic conditions reveals a surprisingly high proteolytic activity. ISME J. 2014, 8, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.; Jensen, P.; Batstone, D. Effects of temperature and hydraulic retention time on acetotrophic pathways and performance in high-rate sludge digestion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6468–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Methanogenesis from acetate: A comparison of the acetate metabolism in Methanothrix soehngenii and Methanosarcina spp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 88, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri Yekta, S.; Ziels, R.M.; Björn, A.; Skyllberg, U.; Ejlertsson, J.; Karlsson, A.; Svedlund, M.; Willén, M.; Svensson, B.H. Importance of sulfide interaction with iron as regulator of the microbial community in biogas reactors and its effect on methanogenesis, volatile fatty acids turnover, and syntrophic long-chain fatty acids degradation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrieze, J.; Hennebel, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Methanosarcina: The rediscovered methanogen for heavy duty biomethanation. Bioresource Technol. 2012, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Hazen, T.C.; Huang, V.; He, Q. Unexpected competitiveness of Methanosaeta populations at elevated acetate concentrations in methanogenic treatment of animal wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinder, S.H.; Anguish, T. Carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and formate metabolism during methanogenesis from acetate by thermophilic cultures of Methanosarcina and Methanothrix strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3323–3329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šafarič, L.; Shakeri Yekta, S.; Liu, T.; Svensson, B.H.; Schnürer, A.; Bastviken, D.; Björn, A. Dynamics of a Perturbed Microbial Community during Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Chemically Defined Soluble Organic Compounds. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6040105
Šafarič L, Shakeri Yekta S, Liu T, Svensson BH, Schnürer A, Bastviken D, Björn A. Dynamics of a Perturbed Microbial Community during Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Chemically Defined Soluble Organic Compounds. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(4):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6040105
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠafarič, Luka, Sepehr Shakeri Yekta, Tong Liu, Bo H. Svensson, Anna Schnürer, David Bastviken, and Annika Björn. 2018. "Dynamics of a Perturbed Microbial Community during Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Chemically Defined Soluble Organic Compounds" Microorganisms 6, no. 4: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6040105
APA StyleŠafarič, L., Shakeri Yekta, S., Liu, T., Svensson, B. H., Schnürer, A., Bastviken, D., & Björn, A. (2018). Dynamics of a Perturbed Microbial Community during Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Chemically Defined Soluble Organic Compounds. Microorganisms, 6(4), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6040105





