Stable Isotope and Metagenomic Profiling of a Methanogenic Naphthalene-Degrading Enrichment Culture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Establishment
2.2. Metabolite Analysis and 13C-bicarbonate Tracer Experiments
2.3. Microbial Community Analysis and Targeted Functional Gene Analysis
2.4. 13C-Naphthalene Stable Isotope Probing
2.5. Metagenomic Sequencing, Binning, and Genomic Annotation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analytical Evidence of Methanogenic Naphthalene Degradation
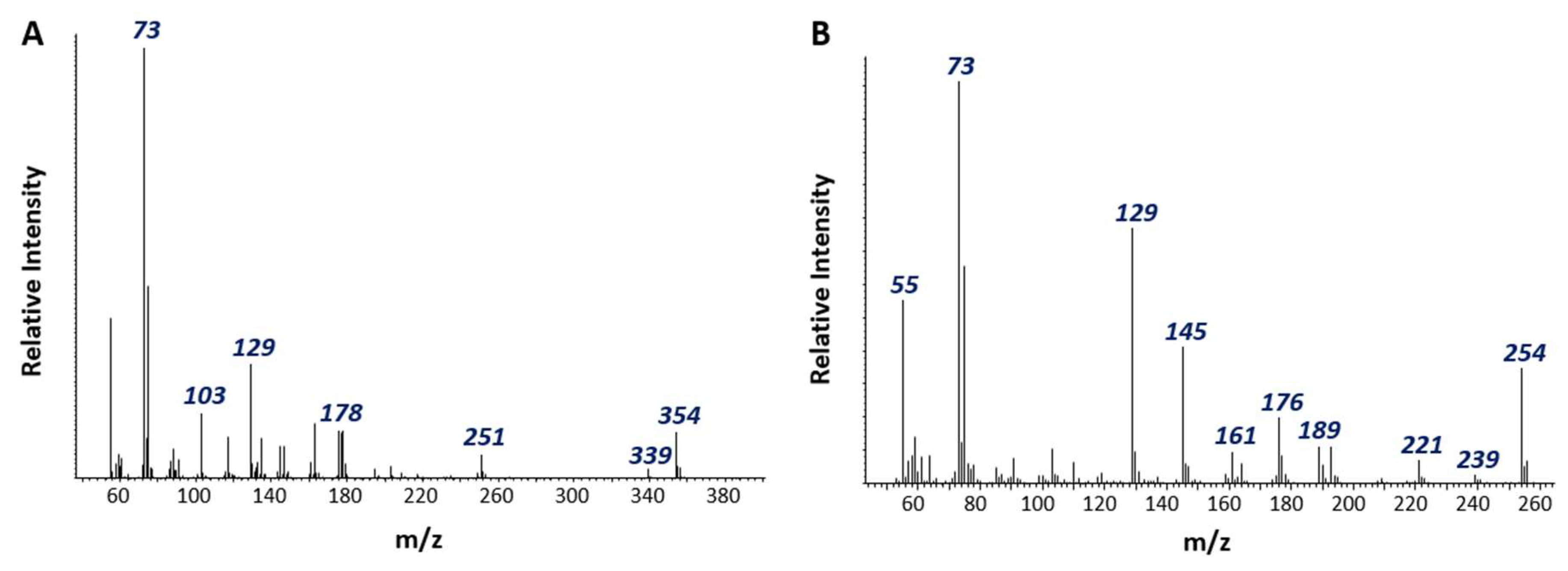
3.2. Detection of Putative Naphthalene Metabolites
3.3. Pinpointing Putative Naphthalene Degraders Using Pyrosequencing and DNA-SIP
3.4. Metagenomic Evidence Predicts Clostridiaceae to Be a Key Naphthalene Degrader in NDC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobelius, C.; Ruth, B.; Griebler, C.; Meckenstock, R.U.; Hollender, J.; Reineke, A.; Frimmel, F.H.; Zwiener, C. Metabolites indicate hot spots of biodegradation and biogeochemical gradients in a high-resolution monitoring well. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sverdrup, L.E.; Nielsen, T.; Henning Krogh, P. Soil ecotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to soil sorption, lipophilicity, and water solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Mouttaki, H. Anaerobic degradation of non-substituted aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Boll, M.; Mouttaki, H.; Koelschbach, J.S.; Cunha Tarouco, P.; Weyrauch, P.; Dong, X.; Himmelberg, A.M. Anaerobic degradation of benzene and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 92–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.V.; Shiung, L.C.; Yuan, S.Y. Anaerobic biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in soil. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safinowski, M.; Griebler, C.; Meckenstock, R.U. Anaerobic cometabolic transformation of polycyclic and heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Evidence from laboratory and field studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musat, F.; Galushko, A.; Jacob, J.; Widdel, F.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Wilkes, H.; Schink, B.; Rabus, R. Anaerobic degradation of naphthalene and 2-methylnaphthalene by strains of marine sulfate-reducing bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Annweiler, E.; Michaelis, W.; Richnow, H.H.; Schink, B. Anaerobic naphthalene degradation by a sulfate-reducing enrichment culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2743–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selesi, D.; Jehmlich, N.; von Bergen, M.; Schmidt, F.; Rattei, T.; Tischler, P.; Lueders, T.; Meckenstock, R.U. Combined genomic and proteomic approaches identify gene clusters involved in anaerobic 2-methylnaphthalene degradation in the sulfate-reducing enrichment culture N47. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galushko, A.; Minz, D.; Schink, B.; Widdel, F. Anaerobic degradation of naphthalene by a pure culture of a novel type of marine sulphate-reducing bacterium. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 1, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiDonato, R.J., Jr.; Young, N.D.; Butler, J.E.; Chin, K.J.; Hixson, K.K.; Mouser, P.; Lipton, M.S.; DeBoy, R.; Methe, B.A. Genome sequence of the Deltaproteobacterial strain NaphS2 and analysis of differential gene expression during anaerobic growth on naphthalene. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, F.; Selesi, D.; Weinmaier, T.; Tischler, P.; Rattei, T.; Meckenstock, R.U. Genomic insights into the metabolic potential of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading sulfate-reducing Deltaproteobacterium N47. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, F.D.; Selesi, D.; Meckenstock, R.U. Identification of new enzymes potentially involved in anaerobic naphthalene degradation by the sulfate-reducing enrichment culture N47. Arch. Microbiol. 2011, 193, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckel, W.; Kung, J.W.; Boll, M. The benzoyl-coenzyme A reductase and 2-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydratase radical enzyme family. Chembiochem 2014, 15, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouttaki, H.; Johannes, J.; Meckenstock, R.U. Identification of naphthalene carboxylase as a prototype for the anaerobic activation of non-substituted aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2770–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrauch, P.; Zaytsev, A.V.; Stephan, S.; Kocks, L.; Schmitz, O.J.; Golding, B.T.; Meckenstock, R.U. Conversion of cis-2-carboxycyclohexylacetyl-CoA in the downstream pathway of anaerobic naphthalene degradation. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberlein, C.; Estelmann, S.; Seifert, J.; von Bergen, M.; Muller, M.; Meckenstock, R.U.; Boll, M. Identification and characterization of 2-naphthoyl-coenzyme a reductase, the prototype of a novel class of dearomatizing reductases. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberlein, C.; Johannes, J.; Mouttaki, H.; Sadeghi, M.; Golding, B.T.; Boll, M.; Meckenstock, R.U. ATP-dependent/-independent enzymatic ring reductions involved in the anaerobic catabolism of naphthalene. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estelmann, S.; Blank, I.; Feldmann, A.; Boll, M. Two distinct old yellow enzymes are involved in naphthyl ring reduction during anaerobic naphthalene degradation. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 95, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieg, L.M.; Toth, C.R.A. Signature metabolite analysis to determine in situ anaerobic hydrocarbon biodegradation. In Anaerobic Utilization of Hydrocarbons, Oils, and Lipids; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Berdugo-Clavijo, C.; Dong, X.; Soh, J.; Sensen, C.W.; Gieg, L.M. Methanogenic biodegradation of two-ringed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 81, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdugo-Clavijo, C.; Gieg, L.M. Conversion of crude oil to methane by a microbial consortium enriched from oil reservoir production waters. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Um, Y.; Holoman, T.R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) degradation coupled to methanogenesis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, N.; Batstone, D.J.; He, Z.; Angelidaki, I.; Schmidt, J.E. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from sewage sludge by anaerobic degradation. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 9, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Um, Y.; Hoffman, B.; Pulliam Holoman, T.R. Molecular characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading methanogenic communities. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillacheruvu, K.Y.; Pathan, I.A. Biodegradation of naphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrene under anaerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2009, 44, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegert, M.; Cichocka, D.; Herrmann, S.; Grundger, F.; Feisthauer, S.; Richnow, H.H.; Springael, D.; Krüger, M. Accelerated methanogenesis from aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons under iron- and sulfate-reducing conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 315, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, R.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S. Microbial community changes in aquifer sediment microcosm for anaerobic anthracene biodegradation under methanogenic condition. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, S. Stable isotope probing identifies anthracene degraders under methanogenic conditions. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, Q.F.; Xie, S.G. Molecular characterization of phenanthrene-degrading methanogenic communities in leachate-contaminated aquifer sediment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolfing, J.; Xu, A.; Gray, N.D.; Larter, S.R.; Head, I.M. The thermodynamic landscape of methanogenic PAH degradation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marozava, S.; Mouttaki, H.; Muller, H.; Laban, N.A.; Probst, A.J.; Meckenstock, R.U. Anaerobic degradation of 1-methylnaphthalene by a member of the Thermoanaerobacteraceae contained in an iron-reducing enrichment culture. Biodegradation 2018, 29, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, J.D.; Dumont, M.G.; Vohra, J.; Murrell, J.C. Methodological considerations for the use of stable isotope probing in microbial ecology. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, C.; Lueders, T.; Richnow, H.H.; Krüger, M.; von Bergen, M.; Seifert, J. Stable isotope probing approaches to study anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation and degraders. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, G.T.; Prince, R.C.; Suflita, J.M. Anaerobic oxidation of crude oil hydrocarbons by the resident microorganisms of a contaminated anoxic aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieg, L.M.; Duncan, K.E.; Suflita, J.M. Bioenergy production via microbial conversion of residual oil to natural gas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3022–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdugo-Clavijo, C. Methanogenic Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morasch, B.; Annweiler, E.; Warthmann, R.J.; Meckenstock, R.U. The use of a solid adsorber resin for enrichment of bacteria with toxic substrates and to identify metabolites: Degradation of naphthalene, o-, and m-xylene by sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, J.D.; Vohra, J.; Dumont, M.G.; Lueders, T.; Manefield, M.; Friedrich, M.W.; Murrell, J.C. DNA stable-isotope probing. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Rui, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y. Enrichment and dynamics of novel syntrophs in a methanogenic hexadecane-degrading culture from a Chinese oilfield. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glockner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, C.R.A.; Gieg, L.M. Time course-dependent methanogenic crude oil biodegradation: Dynamics of fumarate addition metabolites, biodegradative genes, and microbial community composition. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.D.; Froula, J.; Egan, R.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT, an efficient tool for accurately reconstructing single genomes from complex microbial communities. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Netzer, F.; Pilloni, G.; Kleindienst, S.; Kruger, M.; Knittel, K.; Grundger, F.; Lueders, T. Enhanced gene detection assays for fumarate-adding enzymes allow uncovering of anaerobic hydrocarbon degraders in terrestrial and marine systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, S.J. Syntrophic Hydrocarbon Metabolism under Methanogenic Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, B.E.; Gissibl, A.; Kümmel, S.; Richnow, H.H.; Boll, M. A PCR-based assay for the detection of anaerobic naphthalene degradation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 354, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annweiler, E.; Michaelis, W.; Meckenstock, R.U. Identical ring cleavage products during anaerobic degradation of naphthalene, 2-methylnaphthalene, and tetralin indicate a new metabolic pathway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Laban, N.; Dao, A.; Foght, J. DNA stable-isotope probing of oil sands tailings pond enrichment cultures reveals different key players for toluene degradation under methanogenic and sulfidogenic conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, M.; Beckmann, S.; Engelen, B.; Thielemann, T.; Cramer, B.; Schippers, A.; Cypionka, H. Microbial methane formation from hard coal and timber in an abandoned coal mine. Geomicrobiol. J. 2008, 25, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, S.; Lueders, T.; Kruger, M.; von Netzer, F.; Engelen, B.; Cypionka, H. Acetogens and acetoclastic Methanosarcinales govern methane formation in abandoned coal mines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, P.A.; Wawrik, B.; Allen, T.D.; Johnson, C.N.; Marks, C.R.; Tanner, R.S.; Harriman, B.H.; Strapoc, D.; Callaghan, A.V. Youngiibacter fragilis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from natural gas production-water and reclassification of Acetivibrio multivorans as Youngiibacter multivorans comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrik, C.B.; Callaghan, A.V.; Stamps, B.W.; Wawrik, B. Genome sequence of Youngiibacter fragilis, the type strain of the genus Youngiibacter. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01183-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Nakamura, K.; Mikami, E. Fermentation of cinnamate by a mesophilic strict anaerobe, Acetivibrio multivorans sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 1991, 155, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, J. A new family of CoA-transferases. FEBS Lett. 2001, 509, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuthner, B.; Heider, J. Anaerobic toluene catabolism of Thauera aromatica: The bbs operon codes for enzymes of beta oxidation of the intermediate benzylsuccinate. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leutwein, C.; Heider, J. Succinyl-CoA:(R)-benzylsuccinate CoA-transferase: An enzyme of the anaerobic toluene catabolic pathway in denitrifying bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4288–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safinowski, M.; Meckenstock, R.U. Enzymatic reactions in anaerobic 2-methylnaphthalene degradation by the sulphate-reducing enrichment culture N47. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 240, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leutwein, C.; Heider, J. (R)-Benzylsuccinyl-CoA dehydrogenase of Thauera aromatica, an enzyme of the anaerobic toluene catabolic pathway. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 178, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Taxon | 13C Heavy | 12C Control | 13C Light |
|---|---|---|---|
| Archaea | |||
| Methanosaeta | 1.49 | 5.18 | 4.83 |
| Methanobacterium | 0.14 | 0.64 | 2.19 |
| Methanoculleus | 0.72 | 0.17 | 0.04 |
| Thermoplasmata WCHA-57 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.35 |
| Bacteroidetes | |||
| Proteiniphilum | 0.07 | 0.53 | 0.30 |
| Rikenellaceae vadinBC27 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.70 |
| Chloroflexi | |||
| Anaerolineaceae | 0.14 | 1.48 | 0.73 |
| Firmicutes | |||
| Clostridiaceae | 14.5 | 17.8 | 4.98 |
| Sedimentibacter | 0.07 | 1.59 | 0.47 |
| Clostridium | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| Peptococcaceae | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.01 |
| Proteobacteria | |||
| Desulfuromonadales | 68.5 | 61.6 | 81.0 |
| Geobacter | 1.88 | 1.70 | 2.06 |
| Desulfuromonas | 0.45 | 1.68 | 0.36 |
| Desulfobulbus | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.54 |
| Desulfovibrio | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.11 |
| Deltaproteobacteria | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.21 |
| Genome1 IMG ID | Genome1 Name | Genome Size, bp (Assembled) | Gene Count (Assembled) | Genome2 IMG ID | Genome2 Name | ANI 1→2 | ANI 2→1 | AF 1→2 | AF 2→1 | Total BBH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2724679725 | Anaerolinea sp. Bin 1 | 2333788 | 2249 | 649633005 | Anaerolinea thermophila UNI-1 | 67.6 | 67.6 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 221 |
| 2724679726 | Anaerolinea sp. Bin 2 | 2271625 | 2153 | 649633005 | Anaerolinea thermophila UNI-1 | 67.7 | 67.7 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 318 |
| 2724679696 | Unclassified Clostridiaceae sp. Bin 1 | 5438132 | 5424 | 2582580929 | Youngiibacter fragilis | 87.5 | 87.5 | 0.54 | 0.75 | 2904 |
| 2724679721 | Desulfovibrio sp. Bin 1 | 3088242 | 2959 | 2561511137 | Desulfovibrio alcoholivorans DSM 5433 | 72.6 | 72.7 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 1337 |
| 2724679697 | Unclassified Desulfuromonadales sp. Bin 1 | 4390079 | 4104 | 640427115 | Geobacter uraniireducens Rf4 | 72.4 | 72.4 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 1225 |
| 2724679723 | Unclassified Desulfuromonadales sp. Bin 2 | 3876684 | 3546 | 640427115 | Geobacter uraniireducens Rf4 | 72.2 | 72.2 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 1230 |
| 2724679724 | Unclassified Desulfuromonadales sp. Bin 3 | 2526538 | 2519 | 642555130 | Geobacter lovleyi SZ | 77.0 | 77.0 | 0.69 | 0.43 | 1737 |
| 2724679722 | Methanosaeta sp. Bin 1 | 2683322 | 2798 | 650716054 | Methanosaeta concilii GP-6 | 96.6 | 96.6 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 2209 |
| 2724679727 | Sphaerochaeta sp. Bin 1 | 1750954 | 1956 | 650377973 | Sphaerochaeta globosa Buddy | 80.5 | 80.5 | 0.70 | 0.37 | 1321 |
| 2724679720 | Unclassified Rhodospirillales Bin 1 | 3473168 | 3651 | 2651870079 | Unclassified Rhodospirillaceae Bin 35 | 69.5 | 69.5 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 546 |
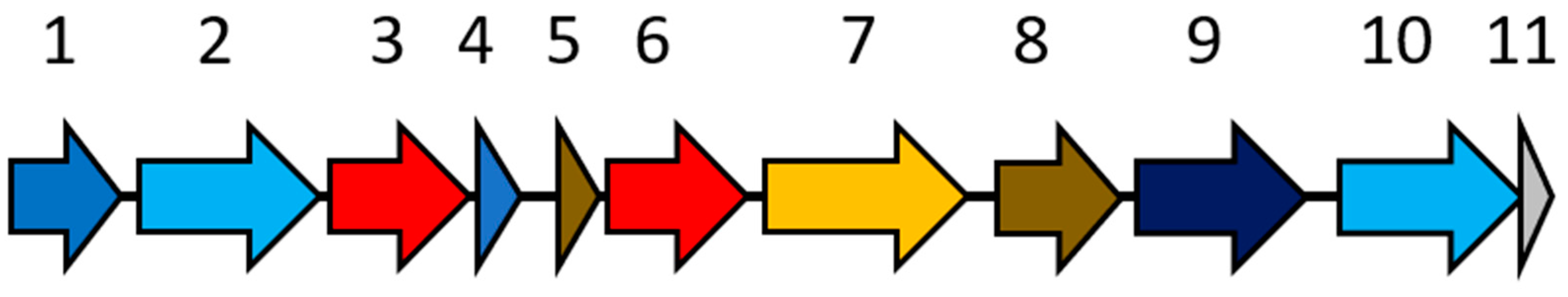
| Gene ID | IMG Predicted Protein Annotation | Length (aa) | NaphS2 Ortholog | Locus | % Identity (% Similarity) | Best BLASTP Ortholog | Accession No. | % Identity (% Similarity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2727804033 | Hypothetical protein | 60 | N/A | - | - | hypothetical protein [Clostridiales bacterium VE202-03] | WP_024723634 | 43 (71) |
| 2727804034 | Crotonobetainyl-CoA:carnitine CoA-transferase CaiB | 412 | CoA-transferase family III protein | NPH_4605 NPH_6726 NPH_5274 | 31 (50) 24 (46) 27 (44) | Formyl-coenzyme A transferase [uncultured Clostridium sp.] | SCJ80195 | 55 (74) |
| 2727804035 | acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase | 387 | Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase | NPH_3581 NPH_6994 NPH_6993 NPH_5273 | 43 (61) 43 (62) 38 (62) 38 (55) | MULTISPECIES: acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase [Geobacillus] | WP_074043744 | 51 (69) |
| 2727804036 | 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase | 288 | 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase | NPH_5812 NPH_5906 NPH_5896 NPH_7219 | 38 (58) 40 (56) 36 (53) 34 (53) | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase [Clostridiales bacterium PH28_bin88] | KKM10089 | 53 (71) |
| 2727804037 | H+/gluconate symporter | 444 | N/A | - | - | MULTISPECIES: hypothetical protein [Clostridiales] | WP_007862308 | 43 (65) |
| 2727804038 | enoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] reductase II | 315 | 2-nitropropane dioxygenase | NPH_5508 NPH_6957 | 35 (52) 33 (53) | 2-nitropropane dioxygenase [Anaerosporomusa subterranea] | WP_066237624 | 52 (70) |
| 2727804039 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase | 85 | 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase | NPH_5887 NPH_5907 | 47 (61) 40 (56) | MULTISPECIES: 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase [Clostridiales] | WP_007862300 | 52 (74) |
| 2727804040 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase | 78 | 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase | NPH_6695 NPH_5897 NPH_5898 | 39 (62) 38 (63) 45 (65) | enoyl-CoA hydratase [Desulfotomaculum thermosubterraneum] | WP_072869855 | 55 (77) |
| 2727804041 | 2-nitropropane dioxygenase precursor | 321 | 2-nitropropane dioxygenase | NPH_6957 NPH_5508 | 38 (60) 31 (48) | nitronate monooxygenase [Clostridium citroniae] | WP_083424018 | 71 (84) |
| 2727804042 | Crotonobetainyl-CoA:carnitine CoA-transferase CaiB | 409 | CoA-transferase family III protein | NPH_4605 NPH_1868 | 34 (52) 26 (44) | MULTISPECIES: CoA transferase [Clostridiales] | WP_007862305 | 48 (68) |
| 2727804043 | 2-(1,2-epoxy-1,2-dihydrophenyl)acetyl-CoA isomerase | 262 | putative enoyl-CoA hydratase | NPH_0885 NPH_5898 NPH_5897 | 31 (50) 32 (54) 32 (52) | enoyl-CoA hydratase [Enterococcus silesiacus] | WP_071879306 | 47 (71) |
| 2727804044 | Hypothetical protein | 25 | N/A | - | - | ATP-dependent endonuclease [Bacillus cereus] | OPA11549 | 72 (77) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toth, C.R.A.; Berdugo-Clavijo, C.; O’Farrell, C.M.; Jones, G.M.; Sheremet, A.; Dunfield, P.F.; Gieg, L.M. Stable Isotope and Metagenomic Profiling of a Methanogenic Naphthalene-Degrading Enrichment Culture. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030065
Toth CRA, Berdugo-Clavijo C, O’Farrell CM, Jones GM, Sheremet A, Dunfield PF, Gieg LM. Stable Isotope and Metagenomic Profiling of a Methanogenic Naphthalene-Degrading Enrichment Culture. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleToth, Courtney R. A., Carolina Berdugo-Clavijo, Corynne M. O’Farrell, Gareth M. Jones, Andriy Sheremet, Peter F. Dunfield, and Lisa M. Gieg. 2018. "Stable Isotope and Metagenomic Profiling of a Methanogenic Naphthalene-Degrading Enrichment Culture" Microorganisms 6, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030065
APA StyleToth, C. R. A., Berdugo-Clavijo, C., O’Farrell, C. M., Jones, G. M., Sheremet, A., Dunfield, P. F., & Gieg, L. M. (2018). Stable Isotope and Metagenomic Profiling of a Methanogenic Naphthalene-Degrading Enrichment Culture. Microorganisms, 6(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030065







