Periorbital and Central Nervous System Infection Due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
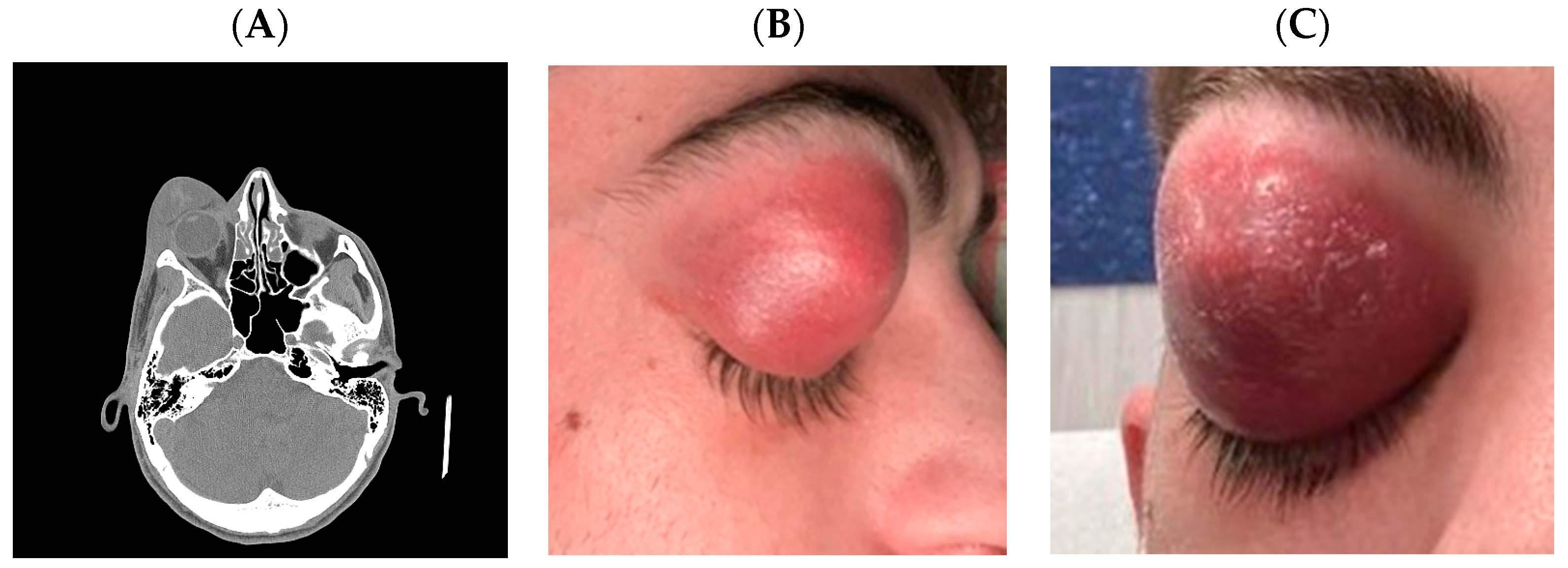
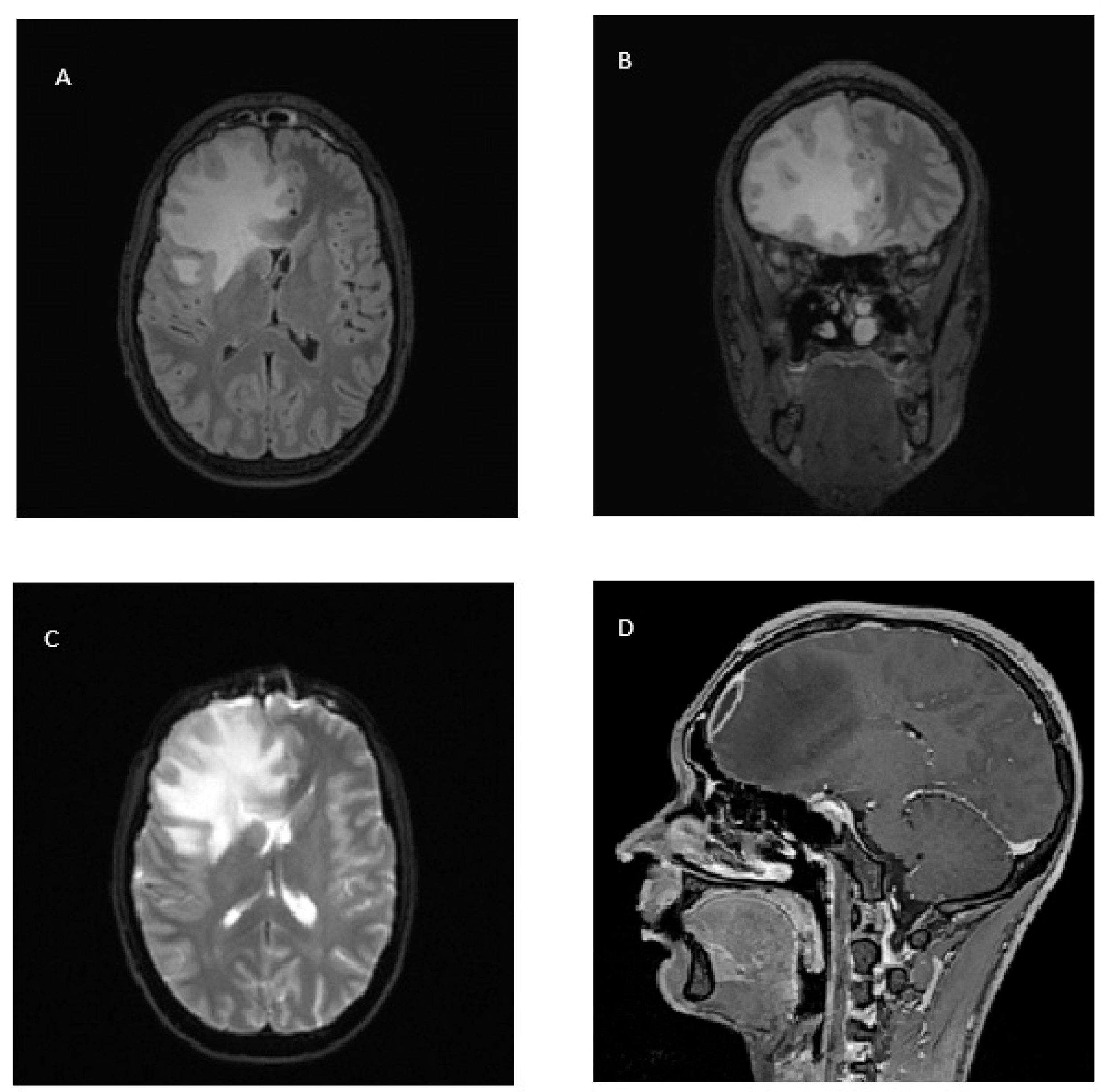
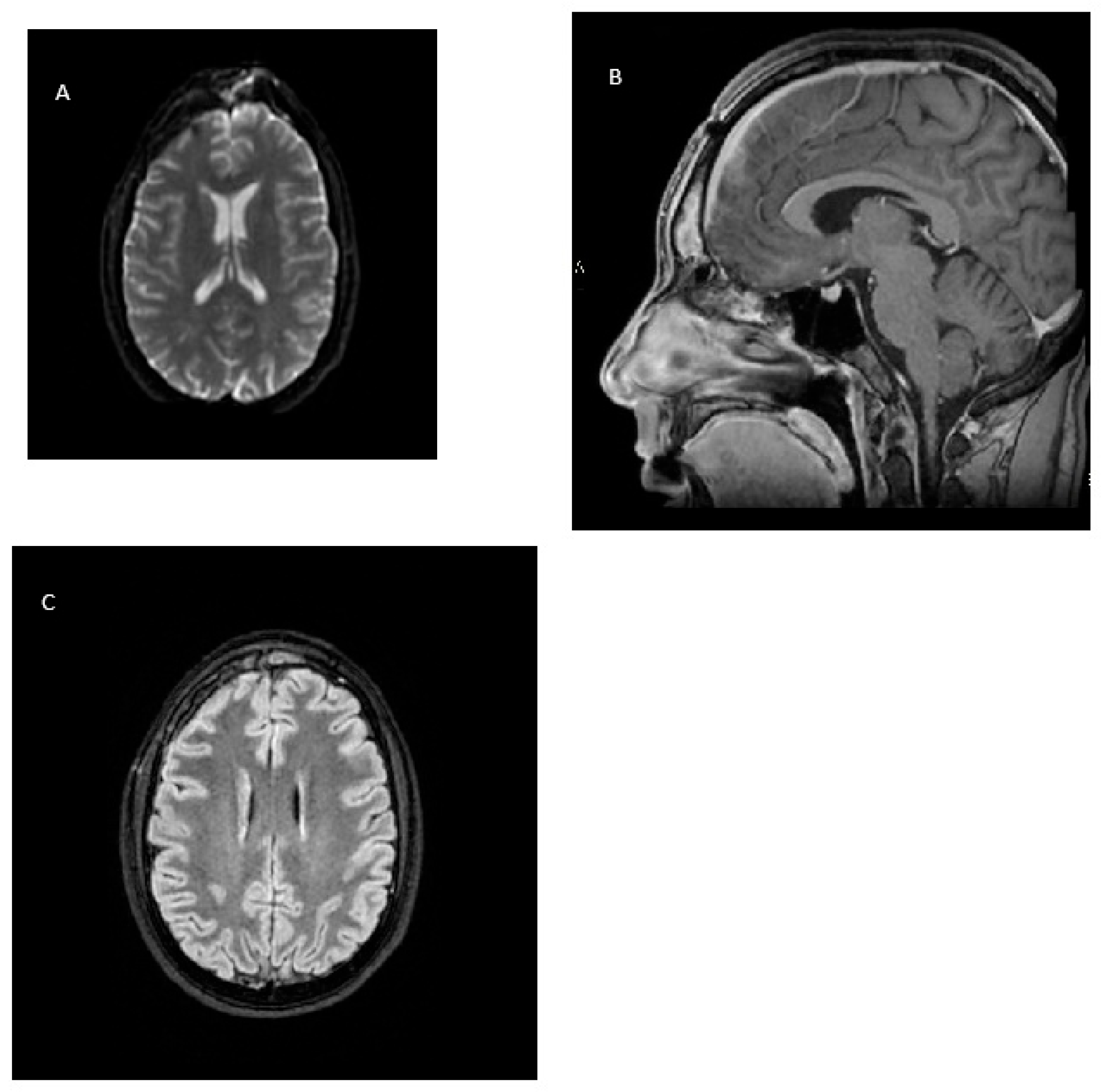
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortés-Penfield, N.; Kohli, A.; Weatherhead, J.; El Sahly, H. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum CNS abscess and bacteremia following head trauma: A case report and literature review. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2017, 25, e9–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahhar, H.S.; Rubin, E.; Rishmawi, S.E.; Logan, M. Invasive Sinusitis with Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Fusobacterium necrophorum Complicated by Subdural Empyema in an Immunocompetent Adolescent Patient. Cureus 2023, 15, e44517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K.F.; Renton, N.E.; Lee, P.Y.; James, D.H. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum wound infection. J. Infect. 1992, 24, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, A.; Bradlow, A. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Mycoplasma pneumoniae co-infection. J. Infect. 1999, 38, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Lennard, K.; Rao, A.; Elliott, M.; Dharan, N.; Wong, J. Polymicrobial Arcanobacterium haemolyticum intracerebral abscess: A case report and review of the literature. IDCases 2024, 36, e01960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclean, P.D.; Liebow, A.A.; Rosenberg, A.A. A hemolytic corynebacterium resembling Corynebacterium ovis and Corynebacterium pyogenes in man. J. Infect. Dis. 1946, 79, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.D.; Jones, D.; Schofield, G.M. Reclassification of ‘Corynebacterium haemolyticum’ (MacLean, Liebow & Rosenberg) in the genus Arcanobacterium gen. nov. as Arcanobacterium haemolyticum nom. rev., comb. nov. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1982, 128, 1279–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzewuska, M.; Kwiecień, E.; Chrobak-Chmiel, D.; Kizerwetter-Świda, M.; Stefańska, I.; Gieryńska, M. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Trueperella pyogenes: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.L.D.; Rajnik, M. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560927/ (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Vila, J.; Juiz, P.; Salas, C.; Almela, M.; de la Fuente, C.G.; Zboromyrska, Y.; Navas, J.; Bosch, J.; Agüero, J.; de la Bellacasa, J.P.; et al. Identification of clinically relevant Corynebacterium spp., Arcanobacterium haemolyticum, and Rhodococcus equi by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1745–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazin, M.; Hassan, A.A.; Alber, J.; Lämmler, C.; Timke, M.; Kostrzewa, M.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Zschöck, M. Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for species identification of bacteria of genera Arcanobacterium and Trueperella. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammra, O.; Friis-Møller, A.; Balbutskaya, A.; Hijazin, M.; Nagib, S.; Alber, J.; Lämmler, C.; Abdulmawjood, A.; Timke, M.; Kostrzewa, M.; et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum isolated from clinical samples in a Danish hospital. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2014, 59, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). MicrobeNet: A CDC Virtual Reference Laboratory. Available online: https://microbenet.cdc.gov/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Wragg, P.N.; Strugnell, B.W.; Whatmore, A.M.; Foster, G. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in a badger (Meles meles). J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2011, 23, 1234–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.; Turmezei, T.; Cartmill, M.; Soo, S. Infective endocarditis caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: A case report. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2011, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayad, E.; Zeid, C.A.; Hajjar, R.E.; Cabrera, N.L.; Radi Abou Jaoudeh, R.A.; Malek, A.E. The burden of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum pharyngitis: A systematic review and management algorithm. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 146, 110759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.; Snitchler, C.; Kong, M.; Ikeda, D.; Skinner, A.; Rodriguezbarrantes, J.; Leverette, R.; Bell, R. When upper respiratory tract infections go rogue: A case report of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Cerebral Abscess. IDCases 2020, 23, e01014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.; Hernandez, M.; Silvestri, C.; Jiménez, O.; Guevara, N.; Carballo, M.; Rojas, N.; Riera, J.; Alayo, E.; Fernández, M.; et al. Brain abscess due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum after dental extraction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1810–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplin, V.; McKinsey, D.S. Arcanobacterium Brain Abscesses, Subdural Empyema, and Bacteremia Complicating Epstein-Barr Virus Mononucleosis. Kans. J. Med. 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Skov, R.L.; Sanden, A.K.; Danchell, V.H.; Robertsen, K.; Ejlertsen, T. Systemic and deep-seated infections caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1998, 17, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minárik, T.; Sufliarsky, J.; Trupl, J.; Krcméry, V., Jr. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum invasive infections, including meningitis in cancer patients. J. Infect. 1997, 34, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, P.H.; Molinari, J.A. Corynebacterium hemolyticum bacteremia with fatal neurologic complication in an intravenous drug addict. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, I.F.; Cabral, D.A.; Reed, W.D.; Bond, R.J.; Henderson, A. Intracranial complications of sphenoidal sinus inflammation. Med. J. Aust. 1981, 1, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhang, W.H.; Ayyagari, A.; Sharma, B.S.; Kak, V.K. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum brain abscess in a child (a case report). Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 1991, 34, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, J.A.; Martin, W.J.; Spiekerman, R.E. Brain abscess with Corynebacterium hemolyticum: Report of a case. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1971, 56, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, G.; Bogokovsky, B. Brain abscess due to Corynebacterium haemolyticum. Lancet 1973, 1, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yaacob, D.; Waron, M.; Boldur, I.; Gil, I.; Sompolinsky, D. Septicemia due to Corynebacterium haemolyticum. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1984, 20, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.J.; Horton, D. Double whammy: Delayed cerebral ischemia of a 19-year-old secondary to sinogenic complications from an uncommon bacterial sinusitis, Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Radiol. Case Rep. 2024, 19, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouriemchi, W.; Jeddi, D.; Ziane, Y.; El Quessar, A.; Benouda, A. Abcès cérébral à Arcanobacterium haemolyticum mimant une tumeur cérébrale [Arcanobacterium haemolyticum brain abscess mimicking a brain tumor]. Med. Mal. Infect. 2011, 41, 397–399. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, M.; Tarasawa, K.; Hidaka, H.; Yun, Y.; Fujimori, K.; Fushimi, K.; Hamada, S.; Asako, M.; Kawachi, R.; Yagi, M.; et al. Risk factors in patients treated with surgical drainage for rhinogenic intracranial complications: A nationwide study. Rhinology 2025, 63, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrwashdeh, A.M.; Saluja, P.; Hasan, L.; Kocurek, E.; Dare, R.K. Arcanobacterium haemolyticum bacteremia presenting as severe sepsis: A case report and review of the literature. IDCases 2022, 31, e01645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampejo, T.; Alsheikh, F.; Crilly, D.; Brown, M. Lemierre’s syndrome: Varying pathogens, clinical presentations and complications. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 108, 116123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, F.; Chua, A.; Tortora, G.; Jimenez, V.E. Lemierre’s disease caused by co-infection of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Fusobacterium necrophorum: A case report. J. Infect. 2002, 45, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblom, K.; Jung, K.; Kalin, M. Lemierre syndrome caused by co-infection by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Fusobacterium necrophorum. Infect. 2010, 38, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, P.; Korpela, J.; Walder, M.; Nyman, M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and biotypes of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum blood isolates. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999, 18, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, P.; Kontiainen, S.; Renkonen, O.V. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, M.; Banck, G.; Thore, M. Penicillin tolerance in Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banck, G.; Nyman, M. Tonsillitis and rash associated with Corynebacterium haemolyticum. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 154, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterlund, A. Are penicillin treatment failures in Arcanobacterium haemolyticum pharyngotonsillitis caused by intracellularly residing bacteria? Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 27, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, CLSI Supplement M100, 35th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clinical Breakpoints v.15.0. 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Veerman, K.; Goosen, J.; Spijkers, K.; Jager, N.; Heesterbeek, P.; Telgt, D. Prolonged use of linezolid in bone and joint infections: A retrospective analysis of adverse effects. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojutti, P.G.; Merelli, M.; Bassetti, M.; Pea, F. Proactive therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) may be helpful in managing long-term treatment with linezolid safely: Findings from a monocentric, prospective, open-label, interventional study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Numata, R.; Machino-Ohtsuka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ishizu, T. Successful Management of Infective Endocarditis utilizing Rapid High-performance Liquid Chromatography-based Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: Balancing Linezolid Efficacy and Thrombocytopenia Risk. Intern. Med. 2025. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gender & Age | Organisms | Focus of Infection | Intracranial Complication | Antibiotic Treatment | Duration of Treatment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F 16 | A.haemolyticum, Bacteroides sp., Anaerococcus tetradius, Dialister micraerophilus, Erysipelotrichaceae sp., Propionibacterium acnes | Sinusitis, head trauma | Subdural empyema, cerebral abscess | Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, metronidazole, amoxicillin/clavulanate | 6 weeks | [1] |
| M 17 | A.haemolyticum, Fusobacterium necrophorum | Sinusitis | Meningitis, subdural empyema, cerebral edema | Vancomycin, cefepime, metronidazole | 3 days (terminated due to fatal cerebral edema) | [2] |
| M 21 | A.haemolyticum, F. necrophorum, Streptococcus anginosus | Pharyngitis and sinusitis | Subdural empyema, meningitis, cerebritis, cerebral abscess | Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, metronidazole, azithromycin, oral amoxicillin | 6 weeks IV followed by 3 months oral | [5] |
| F 21 | A.haemolyticum | Endocarditis | Cerebral abscess, intracerebral hemorrhage | Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, metronidazole, gentamicin | 6 weeks | [15] |
| M 24 | A.haemolyticum, Propionibacterium avidum | Pharyngitis, Sinusitis | Cerebral abscess | Ceftriaxone, metronidazole | 7 weeks | [17] |
| M 18 | A.haemolyticum | Dental extraction | Cerebral abscess | Ceftriaxone, penicillin G | 4 weeks | [18] |
| M 20 | A.haemolyticum, EBV | Sinusitis | Cerebral abscesses, subdural empyema, meningitis | Ceftriaxone, metronidazole | 9 weeks | [19] |
| M 15 | A.haemolyticum, F. necrophorum | Tonsillitis, sinusitis | Meningitis, abducent palsy | Cefotaxime, metronidazole | Not reported | [20] |
| M 58 | A.haemolyticum | Not reported, immunocompromised | Meningitis | Teicoplanin, penicillin G, ceftazidime | 16 days (discharge a.m.a.) | [21] |
| M 50 | A.haemolyticum | Infective endocarditis | Cerebritis, cerebral abscess, intracerebral haemmorrhage | Penicillin G | 7 days (fatal intracerebral hemorrhage) | [22] |
| M 24 | A.haemolyticum | Sinusitis | Meningitis, abducent palsy | Gentamicin, ampicillin, metronidazole, probenecid | Not reported | [23] |
| M 11 | A.haemolyticum, bacteroides melanogenicus | Not reported | Cerebral abscess | Penicillin G, metronidazole | Not reported | [24] |
| M 17 | A.haemolyticum, F. necrophorum | Not reported | Meningitis, cerebral abscess, abducent palsy | Cephalothin, gentamicin, chloramphenicol | 2 days (fatal cerebral abscess) | [25] |
| M 16 | A.haemolyticum | Not reported | Cerebral abscess | Penicillin G | Not reported | [26] |
| M 65 | A.haemolyticum, B. fragilis | Not reported | Meningitis, encephalitis | Penicillin, cloxacillin | Not reported | [27] |
| M 19 | A.haemolyticum | Sinusitis, orbital cellulitis | Meningitis, cerebritis, intracranial collection, delayed cerebral ischemia | Not reported | 40 days IV | [28] |
| M 54 | A.haemolyticum | Poor dental conditions | Cerebral abscess | Amoxicillin, metronidazole | 10 days IV + 3 weeks oral | [29] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chinello, P.; Capone, A.; Al Moghazi, S.; Cirillo, P.; Fontana, C.; Cicalini, S. Periorbital and Central Nervous System Infection Due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092208
Chinello P, Capone A, Al Moghazi S, Cirillo P, Fontana C, Cicalini S. Periorbital and Central Nervous System Infection Due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092208
Chicago/Turabian StyleChinello, Pierangelo, Alessandro Capone, Samir Al Moghazi, Paolo Cirillo, Carla Fontana, and Stefania Cicalini. 2025. "Periorbital and Central Nervous System Infection Due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: Case Report and Review of the Literature" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092208
APA StyleChinello, P., Capone, A., Al Moghazi, S., Cirillo, P., Fontana, C., & Cicalini, S. (2025). Periorbital and Central Nervous System Infection Due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2208. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092208






