Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila by Basic and Fluorescent MIRA Assays
Abstract
1. Introduction
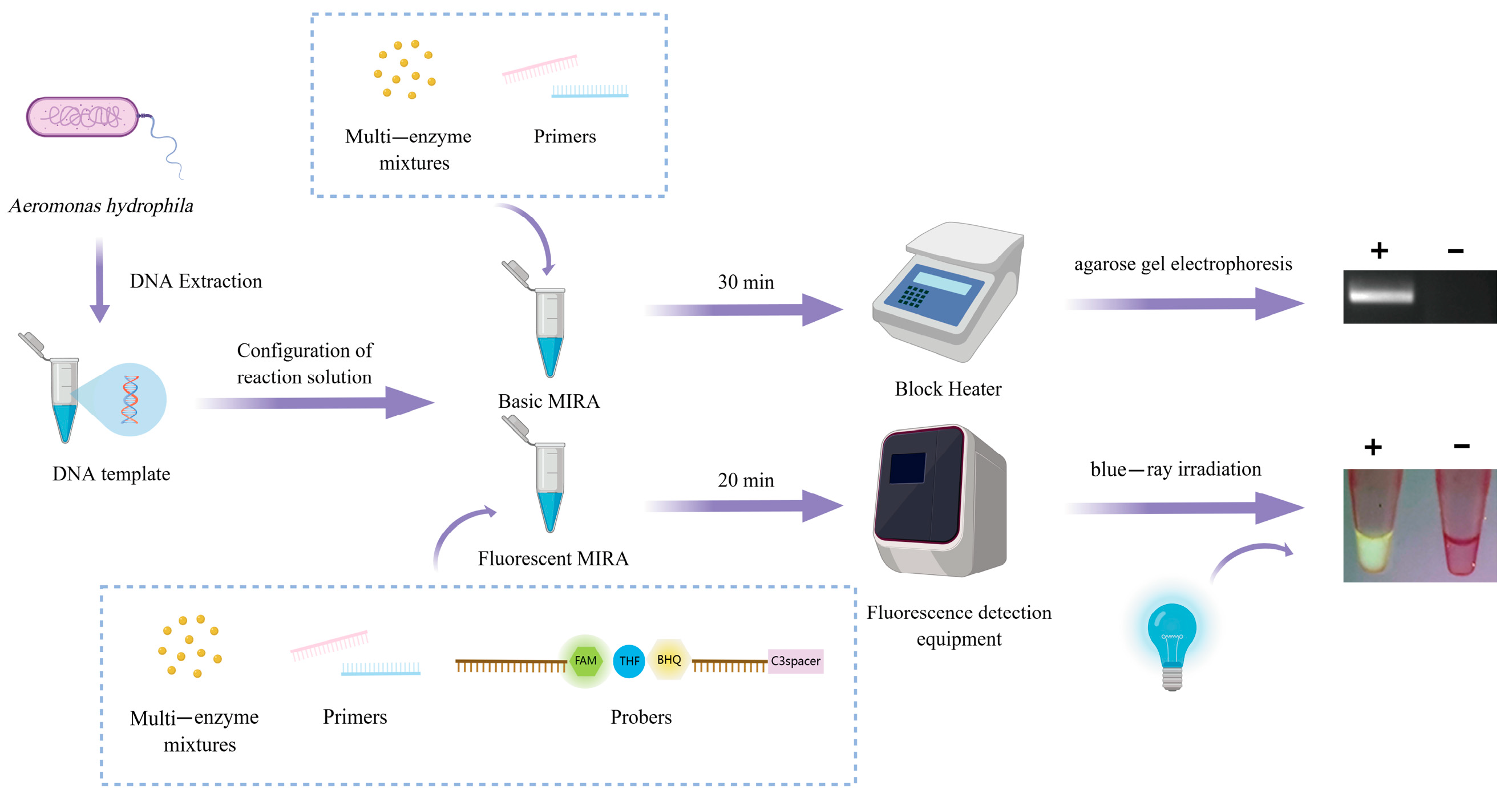
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Genomic DNA Extraction
2.2. MIRA Probe and Primers
2.3. Construction of Recombinant Plasmid
2.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.5. Basic Multienzyme Isothermal Rapid Amplification
2.5.1. Primer Screening for the Basic MIRA Assay
2.5.2. Specificity of the Basic MIRA Assay
2.5.3. Sensitivity of the Basic MIRA Assay
2.6. Fluorescent Multienzyme Isothermal Rapid Amplification
2.6.1. Primer Screening for the Fluorescent MIRA Assay
2.6.2. Specificity of the Fluorescent MIRA Assay
2.6.3. Sensitivity of the Fluorescent MIRA Assay
3. Results
3.1. Basic MIRA Assay
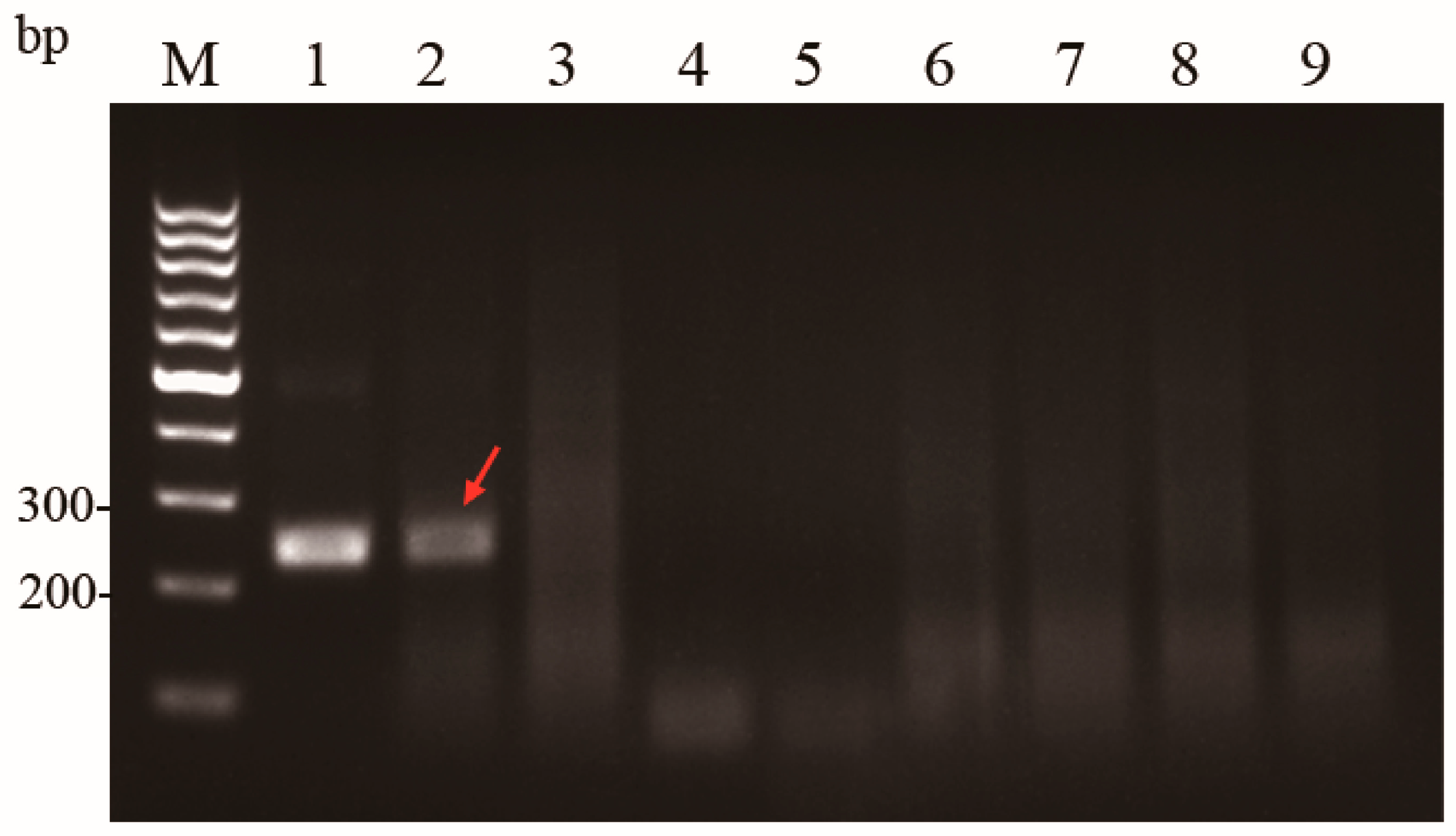
3.1.1. Optimal Primer Set for the Basic MIRA Assay
3.1.2. The Basic MIRA Assay with High Specificity
3.1.3. The Basic MIRA Assay with High Sensitivity
3.2. Fluorescent MIRA Assay
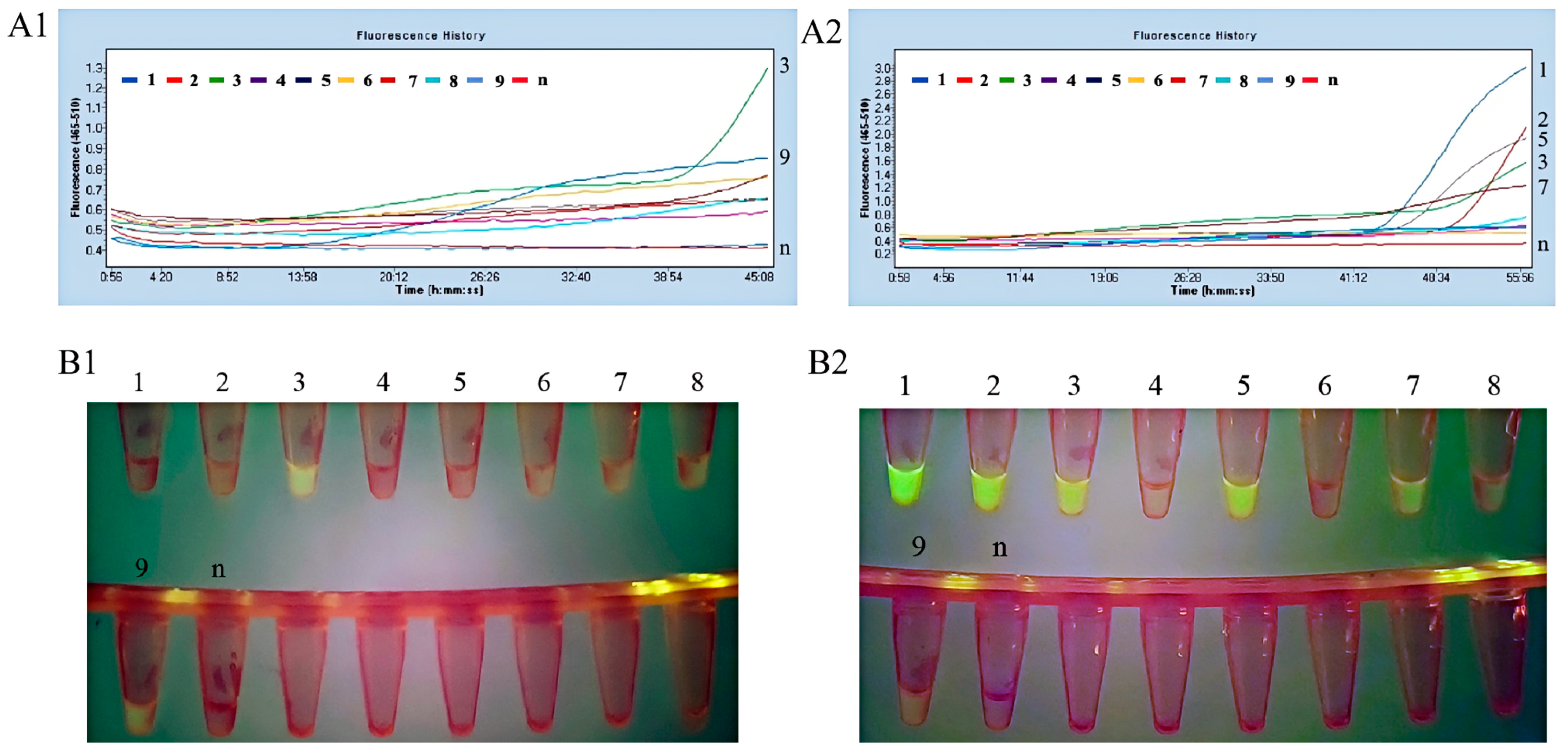
3.2.1. Optimal Primer Set for the Fluorescent MIRA Assay
3.2.2. The Fluorescent MIRA Assay with High Specificity
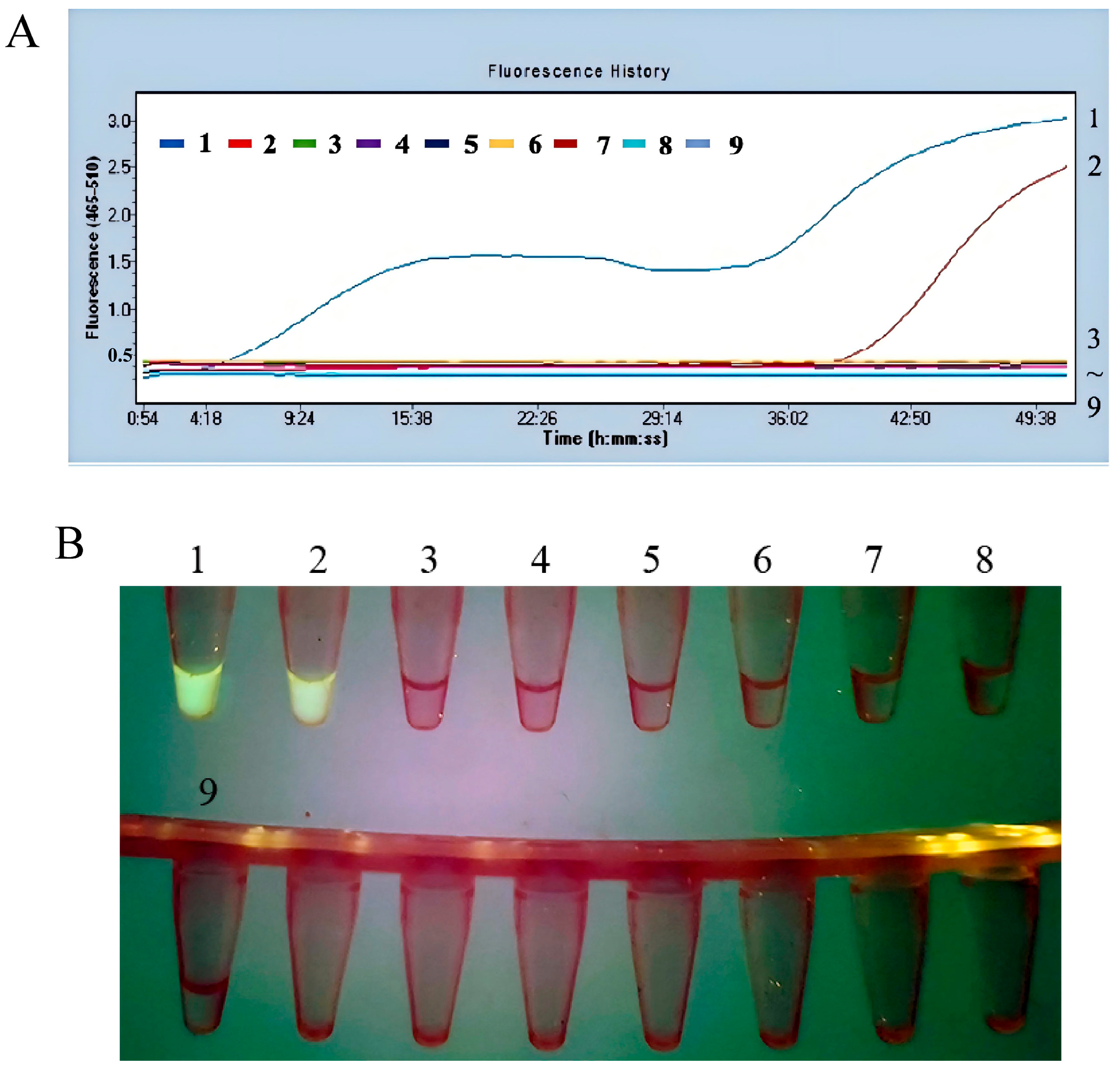
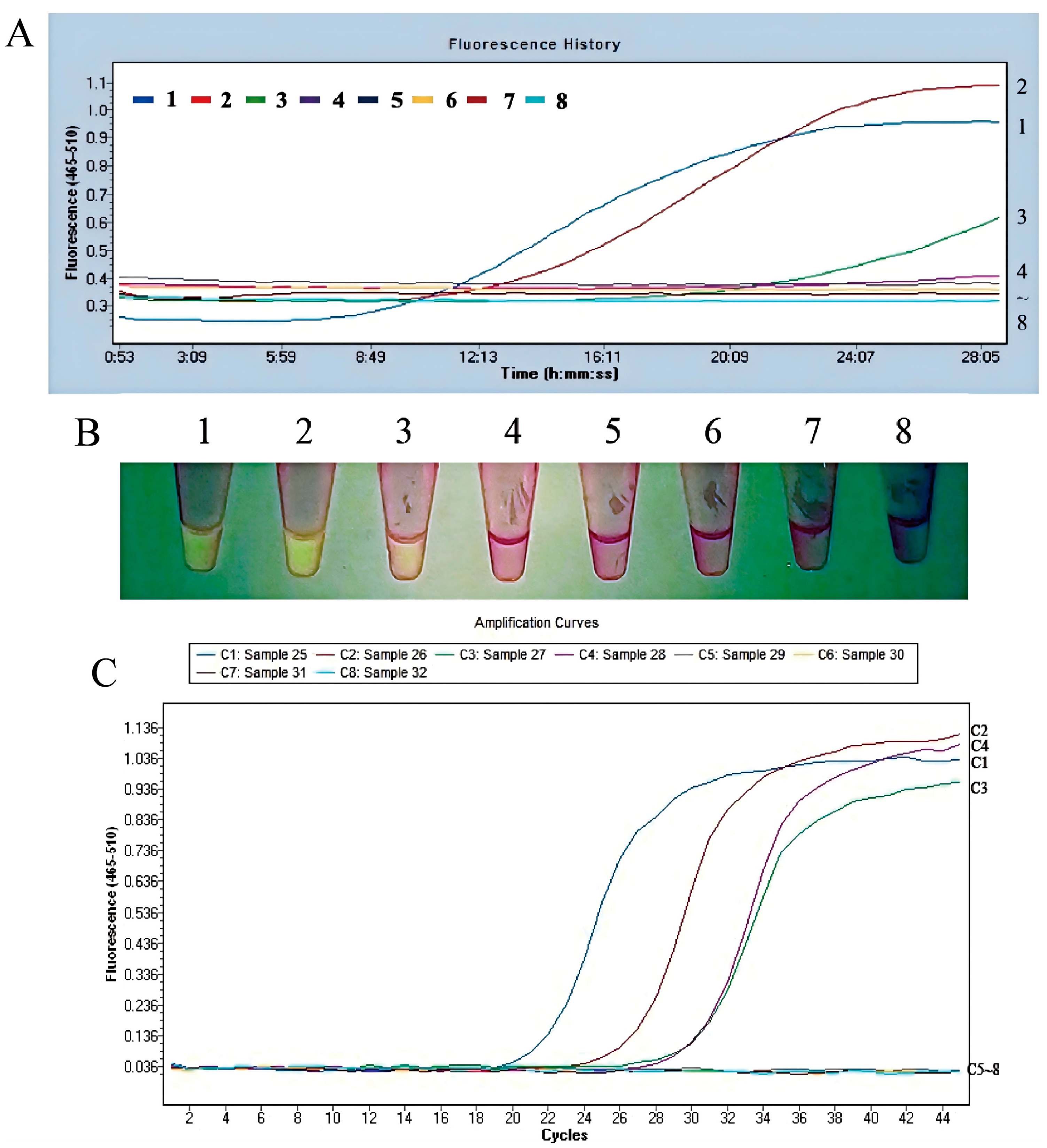
3.2.3. The Fluorescent MIRA Assay with High Sensitivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. State of the World’s Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorella, K.J.; Okronipa, H.; Baker, K.; Heilpern, S. Contemporary aquaculture: Implications for human nutrition. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. State of the World’s Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, A.; Thompson, K.D. Development of diagnostics for aquaculture: Challenges and opportunities. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A. Progress, challenges and opportunities in fish vaccine development. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękala-Safińska, A. Contemporary threats of bacterial infections in freshwater fish. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, A.; Beck, B.H.; Richardson, B.M.; Bader, T.J.; Peatman, E.; Liles, M.R.; Barger, P.C.; Shoemaker, C.A. Efficacy of orally-delivered virulent Aeromonas hydrophila bacterin vaccines in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2025, 611, 743066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lau, Y.L.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M.; Howard, S.P.; Leung, K.Y. Identification and characterization of putative virulence genes in Aeromonas hydrophila PPD134/91. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4469–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: In the wake of reclassification. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, H.W.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.D.; Zeng, L.B.; Qu, C.J.; Meng, Y. Isolation, identification and virulence gene analysis of an Aeromonas hydrophila from diseased Pelodiscus sinensis. Chin Agric. Sci. Bull. 2021, 37, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Xiong, C.; Lu, J.; Long, R.; Jiao, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, Y.; Ye, H.; Lin, L.; et al. flgL mutation reduces pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila by negatively regulating swimming ability, biofilm forming ability, adherence and virulence gene expression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kari, Z.A.; Wee, W.; Sukri, S.A.M.; Harun, H.C.; Reduan, M.F.H.; Khoo, M.I.; Van Doan, H.; Goh, K.W.; Wei, L.S. Role of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on aquatic animals: A mini-review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1023784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citterio, B.; Biavasco, F. Aeromonas hydrophila virulence. Virulence 2015, 6, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Bu, X.; Xiao, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L. Effect of single and combined immunostimulants on growth, anti-oxidation activity, non-specific immunity and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, Q.; Dai, H. Identification of differentially expressed immune-relevant genes in Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Trionyx sinensis) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 125, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, X.D.; Liu, Y.J.; Lu, C.P. Detection of three virulence genes alt, ahp and aerA in Aeromonas hydrophila and their relationship with actual virulence to zebrafish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarroux, J.; Morillon, A.; Pinskaya, M. History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1008, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, N.S. The polymerase chain reaction. History, methods, and applications. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 1992, 1, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, C.A.; Stevens, J.; Livak, K.J.; Williams, P.M. Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.F.; Bi, K.; Wu, T.; Gu, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.X. A simple PCR method for the detection of pathogenic spiroplasmas in crustaceans and environmental samples. Aquaculture 2007, 265, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Xie, L.; Huang, J.; Zeng, T.; Wang, S.; Luo, S.; Li, M. A multiplex fluorescence-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for identifying chicken parvovirus, chicken infectious anaemia virus, and fowl aviadenovirus serotype 4. Avian Pathol. 2023, 52, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Honda, E.; Ogura, A.; Nomoto, A.; Hanaki, K. Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. Biotechniques 2009, 46, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M.; Shih, S.H. An integrated microfluidic loop-mediated isothermal amplification platform for koi herpesvirus detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, L.; Dong, M.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Lu, Y.; You, J.; Feng, X. Development of two novel on-site detection visualization methods for murine hepatitis virus based on the multienzyme isothermal rapid amplification. Microb. Pathogen. 2024, 193, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, K.; Li, Z.; Shang, W.; Song, X.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K.; Tu, J. Rapid detection of porcine circovirus type 4 via multienzyme isothermal rapid amplification. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 949172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, S.; Pang, X.; Michael, G.M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L. Development of a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assay for rapid detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Anal. Biochem. 2023, 670, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Duan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, W.; Li, J. Development and evaluation of a real-time multienzyme isothermal rapid amplification assay for rapid detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.L.; Lai, H.Y.; Chong, N.Y.; Liu, D.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Pang, B.; Yao, J. Simple and feasible detection of Hepatitis B virus via combination of multienzyme isothermal rapid amplification and lateral flow dipstick strip. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 763079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.T.; Verma, C.S.; Lane, D.P.; Gan, S.K. A comparison and optimization of methods and factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33, e00086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikri, F.; Wardhana, D.K.; Purnomo, A.; Khairani, S.; Chhetri, S.; Purnama, M.T.E. Aerolysin gene characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from milkfish (Chanos chanos) in Gresik, Indonesia. Vet. World 2022, 15, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Ding, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xu, N.; Yang, Y.; Ai, X. Magnolol protects channel catfish from Aeromonas hydrophila infection via inhibiting the expression of aerolysin. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 211, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Huhle, B.; Hof, H.; Bergbauer, H.; Goebel, W. Marker exchange mutagenesis of the aerolysin determinant in Aeromonas hydrophila demonstrates the role of aerolysin in A. hydrophila-associated systemic infections. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Rathore, G.; Kapoor, D.; Mishra, B.N.; Lakra, W.S. Detection of aerolysin gene in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from fish and pond water. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichoniuk, M.; Gwiazdowska, D.; Ligaj, M.; Filipiak, M. Electrochemical detection of foodborne pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila by DNA hybridization biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panangala, V.S.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Van Santen, V.L.; Dybvig, K.; Klesius, P.H. Multiplex-PCR for simultaneous detection of 3 bacterial fish pathogens, Flavobacterium columnare, Edwardsiella ictaluri, and Aeromonas hydrophila. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 74, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Yang, X.L.; Tong, G.X.; Wu, X.Q.; Xie, Z.S.; Huang, G.Q.; Liao, Y.Z.; Ye, X.Y.; Li, X.Z. Detection of pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila by quadruple PCR. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2013, 29, 587–593. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Z.F.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhao, B.B.; Xu, X. Establishment on real-time PCR method for detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Mod. Preven. Med. 2012, 39, 3339–3341. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.L.; Ji, X.; Guo, X.J.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.W.; Zhou, W.; Feng, S.Z.; Sun, Y. Establishment and application of a duplex real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR assay for detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2016, 32, 1126–1130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kuang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Cao, J. Establishment of a rapid LAMP assay for Aeromonas hydrophila and comparison with the application of qPCR. Metabolites 2023, 13, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yin, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, W. Development of a real-time recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degiacomi, M.T.; Iacovache, I.; Pernot, L. Molecular assembly of the aerolysin pore reveals a swirling membrane-insertion mechanism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biscardi, D.; Castaldo, A.; Gualillo, O.; de Fusco, R. The occurrence of cytotoxic Aeromonas hydrophila strains in Italian mineral and thermal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 292, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Prime | Sequence (from 5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| AH-aerA-F1 | TGCGGCCAACCAGTCATGGGCATCCCAGAACG |
| AH-aerA-F2 | TACCACCACCTCCCTGTCGCAATCCGTGCGG |
| AH-aerA-F3 | TGTCGCAATCCGTGCGGCCGACGGTGCCGG |
| AH-aerA-R1 | CAACGCAGGAAGCCACTCAGGGTCAGGTCA |
| AH-aerA-R2 | TTGTCCTTGTACGGCCCGATGACGAAGGTG |
| AH-aerA-R3 | GGGCGATTGTCCGGATGGGTATACCAGGCAT |
| AH-aerA-F | GAGAAGGTGACCACCAAGAACA |
| AH-aerA-R | AACTGACATCGGCCTTGAACTC |
| AH-aerA-P | 5′-CGGTGAAGATCGAGCTCTACAAGGCTGATA[FAM-dT][THF][BHQ-dT]CCTATCCCTATGAGT-3′C3spacer |
| Detection Methods | Target Gene for Detection | Reaction Time | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCR [37] | aerA | 1 h | Genomic DNA concentration 100 fg/μL |
| Multiplex-PCR [38] | aerA | 1.5 h | Genomic DNA concentration 8 × 102 fg/μL |
| Quadruple PCR [39] | ahpA; aerA; hlyA; 16S rRNA | 2.3 h | Genomic DNA content 100 fg |
| Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR [40] | hlyA | 30 min | Bacterial quantification linear range 5.4 × 103~5.4 × 108 CFU/mL |
| Dual fluorescence quantitative PCR [41] | 16S rDNA; aerA | 1.2 h | Plasmid 10 copies/reaction |
| Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) [42] | aerA | 40 min | Genomic DNA concentration 0.559 ng/μL |
| Real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (real-time RPA) [43] | haemolysin | 20 min | 102 copies of the A. hydrophila per reaction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Dai, F.; Su, L.; Zhang, M.; Miao, X.; Ding, Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, J. Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila by Basic and Fluorescent MIRA Assays. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092191
Huang Q, Dai F, Su L, Zhang M, Miao X, Ding Y, Xu C, Xu J. Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila by Basic and Fluorescent MIRA Assays. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092191
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qiuya, Fa Dai, Lujia Su, Miaomiao Zhang, Xinjie Miao, Yujie Ding, Cheng Xu, and Jiehao Xu. 2025. "Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila by Basic and Fluorescent MIRA Assays" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092191
APA StyleHuang, Q., Dai, F., Su, L., Zhang, M., Miao, X., Ding, Y., Xu, C., & Xu, J. (2025). Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila by Basic and Fluorescent MIRA Assays. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092191







