Abstract
In recent years, the incidence of severe Streptococcus pyogenes (group A Streptococcus, GAS) infections has been increasing worldwide, similar to trends observed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, alongside a rise in antibiotic resistance. In the present study, we identified the circulating 12 emm types and 8 clusters of 70 GAS isolates among inpatients, investigated their association with antibiotic susceptibility, and compared these findings with earlier research conducted in our country. The predominant emm types and clusters were emm1, emm3, and emm4, and A-C3, E4, and, A-C5, respectively. emm1 was the most common among patients with skin and soft tissue infections or pneumonia, while emm3 was detected in patients with peritonsillar abscesses. All isolates demonstrated susceptibility to penicillin and linezolid, whereas the prevalence of resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and tetracyclines was found to be 14.3%, 14.3%, and 18.6%, respectively. A notable change in the distribution of emm-types/clusters has been observed, with emm1/A-C3 now identified as the most prevalent, differing from our previous study conducted in the pre-COVID-19 period. Additionally, we noted a decrease in resistance to macrolides attributed to a lower prevalence of emm28 clone. The current research is important for monitoring isolates responsible for severe infections, which is crucial for GAS surveillance.
Keywords:
Streptococcus pyogenes; GAS; emm types; emm clusters; antimicrobial resistance; inpatients 1. Introduction
Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A Streptococcus (GAS), is a microbial species known for its high virulence, leading to infections that often spread on an epidemic scale and result in significant morbidity worldwide [1,2]. The severity of the clinical manifestations of this pathogen exhibits a broad spectrum: ranging from tonsillopharyngitis to purulent skin infections, as well as infections with a systemic course (scarlet fever), and life-threatening (toxic shock syndrome, cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis) [3,4,5]. Occasionally, streptococcal infections may initially present to be benign; however, an inaccurate diagnosis, improper treatment, or a recurrence of the infection, can result in complications that may lead to disability and a significantly elevated mortality rate. Complications caused by GAS can be divided into two categories: the most common being peritonsillar or other abscesses, which arise from the invasive characteristics of the streptococcal infection. Less frequently, there are non-invasive, non-purulent complications that are challenging to diagnose and treat, specifically post-streptococcal autoimmune complications such as acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever [6,7,8,9]. In the past twenty years, there has been an increase in both non-suppurative and suppurative complications resulting from GAS infections. This growing impact of diseases can be associated with various factors, such as changes in virulence, the development of antibiotic resistance, and confirmed by the documented increase in GAS infections throughout European countries and other regions [1,5,10,11,12,13].
The ability of GAS to cause disease is associated with various virulence factors, many of which are unique to this species. They can be classified into two categories: cell-wall associated factors and secreted extracellular factors. Each category has distinct effects on tissues, cells, and components of the immune response, as well as impacting biofilm formation [14]. The M protein serves as a crucial virulence factor; therefore, several vaccine candidates are based on it. It is a surface adhesin encoded by the emm gene and it is involved in various stages of GAS infections pathogenesis, including adhesion, immune modulation, and tissue invasion [15,16]. According to studies, horizontal gene transfer has been identified as a significant mechanism for generating emm gene diversity through recombination, and it contributes to the spread of antibiotic resistance, as certain emm variants are associated with specific mobile genetic elements and exhibit high frequency of resistance [1,17,18]. Penicillin continues to be the drug of choice for the empirical treatment of GAS infection, as these bacteria have consistently demonstrated susceptibility to β-lactam antibiotics [19]. Macrolides and lincosamides (ML) are regarded as crucial alternative treatments, particularly for patients who are allergic to β-lactams. Moreover, in cases of severe and extended infections, the standard recommendation is to use lincosamide in combination with penicillin, since clindamycin inhibits the synthesis of GAS exotoxins and the expression of M protein. However, it is important to note that varying levels of resistance to these antibiotics can be observed among different regions [17,19,20].
One of the most commonly used techniques for the epidemiological characterization of GAS is the emm typing, based on the sequencing of 180 bp region from the 5′ end of the emm gene according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) protocols [21]. At present, the GAS is classified into more than 275 emm types, which are grouped into 48 different emm clusters [22]. The monitoring of circulating emm types and clusters provides substantial epidemiological insights and contributes to understanding the connection between emm types and the manifestation of the disease, along with the dissemination of resistant clones. This information will support the future development of a vaccine for GAS [23,24]. The epidemiological investigation of invasive isolates obtained from hospitalized patients suffering from severe infections offers essential insights into population dynamics and strain characteristics linked to emerging lineages, the spread of resistance, and vaccine targets across different geographic regions [8,25,26].
The aim of the study is to identify the circulating emm types and clusters of GAS isolates, investigate their association with antibiotic susceptibility, and compare these findings with earlier research conducted on hospitalized patients in our country. This will help in monitoring the evolution of GAS responsible for severe infections, which could be employed in GAS surveillance and future vaccine development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
Between January 2023 to December 2024, a total of 70 GAS samples were collected from two University hospitals located in Sofia (University Hospital ‘Acibadem City Clinic Tokuda’) (72.9%) and Pleven (University Hospital) (27.1%), Bulgaria. The samples were transported and maintained at a temperature of 4 °C. Upon their arrival at the laboratory, microbiological analyzes were conducted systematically. The age range of inpatients was between 3 and 86 years. The majority of the isolates were collected from patients who had been previously diagnosed with infections of the skin and soft tissue (SSTI) (n = 40, 57.1%). These isolates were obtained from purulent wound secretions (62.5%), soft tissue aspirates (25.0%), and erosive skin lesions (12.5%). The distribution of patients’ diagnoses was erysipelas (47.5%), deep soft tissue abscess (25.0%), cellulitis (12.5%), surgical wound infections (10.0%), and necrotising fasciitis (5.0%). The second most common type of sample was obtained from patients who were diagnosed with pneumonia (n = 15, 21.4%). The analysis of pleural fluid (26.7%) and sputum (73.3%) was performed. The remaining isolates were from peritonsillar abscess (n = 12, 17.1%) and perianal abscess (n = 3, 4.3%).
2.2. Cultivation and Identification of GAS
All strains were grown in Columbia agar with 5% sheep blood (BD BBL, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) at 35 °C in the presence of 5% CO2 for 24–48 h. Isolates were confirmed as GAS by routine identification—colony morphology, beta-hemolysis on blood agar plates, Gram staining, positive PYR (Pyrrolidonyl-β-naphthylamide) test, and positive Lancefield group A antigen test (PathoDxtra Strep Grouping Kit, Oxoid™, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). GAS isolates were kept frozen at −70 °C in skim milk. Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 21547 was used as a control strain.
2.3. DNA Extraction
The isolation DNA was achieved by automated DNA extraction using the MagCore® Genomic DNA Bacterial kit, which is compatible with the MagCore® automated extraction instrument that utilizes magnetic-particle technology (RBC Bioscience Corp., New Taipei City, Taiwan).
2.4. Determination of Antibiotic Susceptibility
The Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method was used to test the susceptibility of all isolates, in accordance with the 2024 EUCAST recommendations (EUCAST, 2024) [27]. This method was performed on Mueller-Hinton agar with 5% defibrinated horse blood and 20 mg/L beta-NAD as antimicrobial agents. The following antimicrobial disks were used: benzilpenicillin G (1 unit), erythromycin (15 μg), clindamycin (2 μg), tetracycline (30 μg), and linezolid (10 μg) (HiMedia, Mumbai, India). The prevalence of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLSB) phenotypes was determined by the double-disk method, whereby erythromycin and clindamycin disks were placed 12–16 mm apart (edge to edge). The plates were then subjected to an incubation process at a temperature of 36 °C for a period of 18 ± 2 h. After incubation, the inhibition zones were measured to determine results based on EUCAST breakpoint rules (EUCAST, 2024) [27].
2.5. Molecular Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
All stains were screened by PCR for the presence of major genes responsible for resistance to macrolides (mefA, ermA, and ermB) and tetracycline (tetM and tetO) in GAS. The primer sequences and amplicon sizes have been previously described by Malhotra-Kumar et al. [28]. The following procedure was used to amplify DNA: 30 cycles of initial denaturation at 95 °C for 4 min, annealing at 60 °C for 40 s, extension at 72 °C for 90 s, and final elongation at 72 °C for 7 min.
2.6. emm Typing
The entire collection of GAS isolates was analyzed with emm typing. The sequencing was performed in accordance with the protocol established by the CDC (https://www.cdc.gov/strep-lab/php/group-a-strep/emm-typing.html, accessed on 10 April 2025). The DNA fragments were subjected to sequencing using the emmseq2 primer (5′-TAATCGCTTAGAAAATTAAAAACAGG-3′). Homology was analyzed using a BLAST search, version BLAST+ 2.15.0 (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 14 April 2025). To extend the research, the data was analyzed using the emm cluster typing method. The recognized emm types were categorized into related emm clusters (https://www.cdc.gov/strep-lab/media/distribution-emm-types.pdf, accessed on 18 April 2025).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows v19.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Fisher’s exact test was used. A p-value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Emm Typing
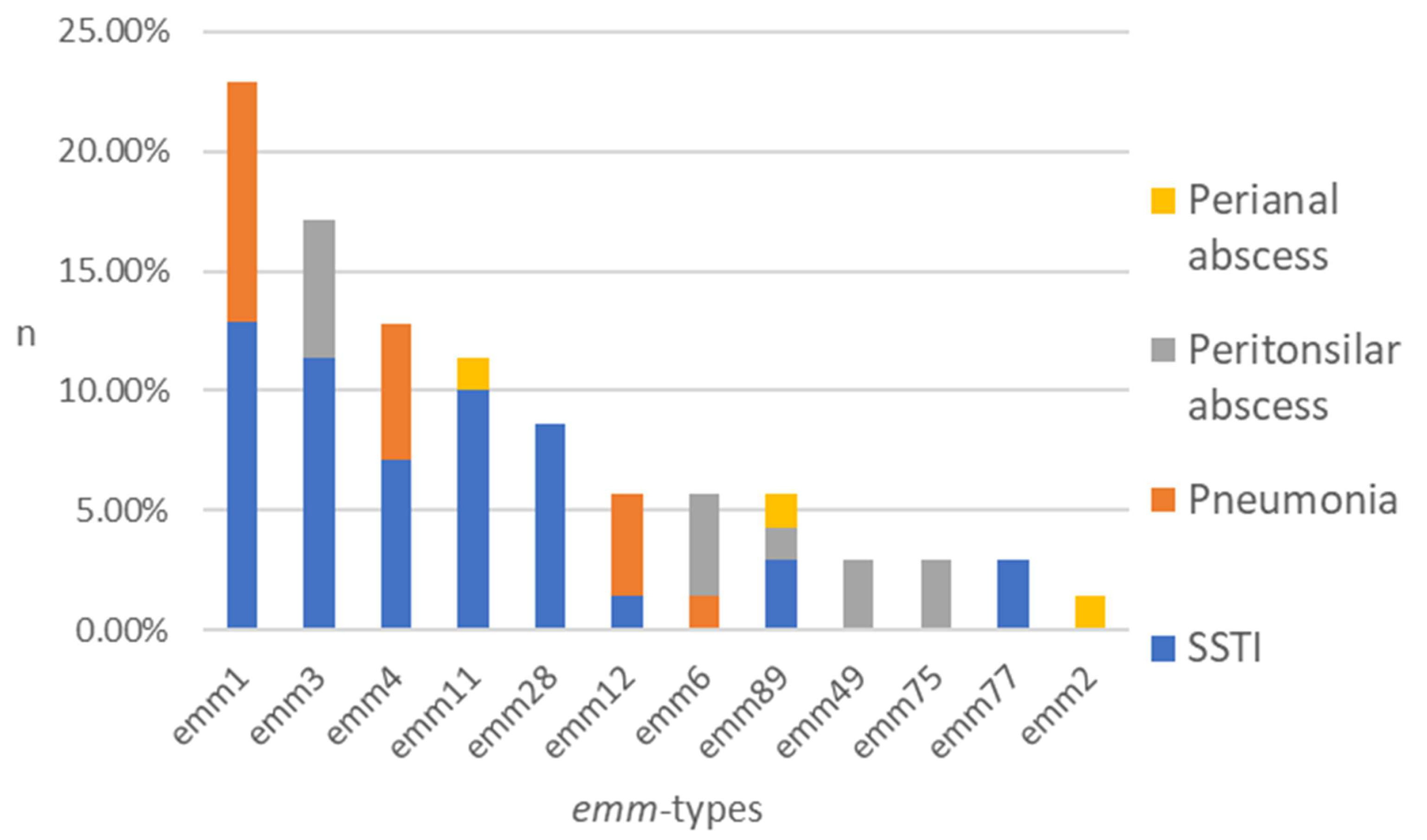
The typing process, including all isolates (n = 70), resulted in the identification of 12 different emm types among eight clusters (Figure 1). The five most common types of emm were identified as follows: emm1 (22.9%), emm3 (17.1%), emm4 (12.9%), emm11 (11.4%), and emm28 (8.6%). The following were present in smaller percentages: emm12 (5.7%), emm6 (5.7%), emm89 (5.7%), emm49 (2.9%), emm75 (2.9%), emm77 (2.9%), and emm2 (1.4%) (Figure 1).
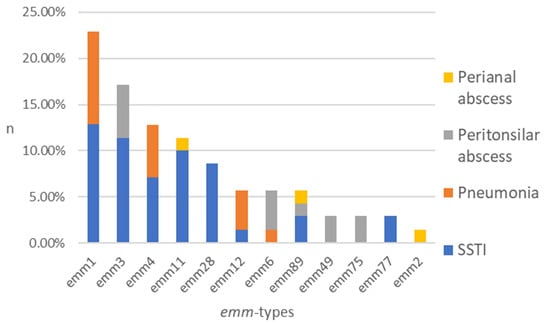
Figure 1.
Distribution of emm types among the GAS isolates obtained from patient groups represented by stacked columns. n—number of strains in %.
A total of 40 isolates from SSTI were tested, and the results demonstrated notable heterogeneity, with the following emm types identified: emm1 (22.5%), emm3 (20.0%), emm11 (17.5%), emm28 (15.0%), emm4 (12.5%), emm89 (5.0%), emm77 (5.0%), and emm12 (2.5%). The subsequent emm types have been detected in pneumonia samples (n = 15): emm1 (46.7%), emm4 (26.7%), emm12 (20.0%), and emm6 (6.7%). A total of 12 isolates from peritonsillar abscesses were examined. The results were as follows: emm3 (33.3%), emm6 (25.0%), emm49 (16.7%), emm75 (16.7%), and emm89 (8.3%). Three distinct emm types were identified from isolates obtained from perianal abscesses (n = 3): emm11, emm89, and emm2 (Figure 1).
3.2. Emm-Typing Cluster System
The twelve recognized emm-types within the studied population were clearly categorized into eight distinct emm-clusters. The distribution of emm clusters were: A-C3 (22.9%), E4 (18.6%), A-C5 (17.1%), E6 (14.3%), E1 (12.9%), A-C4 (n = 7, 10.0%), clade_Y_M6 (5.7%) and E3 (2.9%).
Table 1 demonstrates the prevalence of emm clusters regarding clinical manifestations, comparing it with our previous study among hospitalized patients conducted between 2014 and 2018 [29]. Regarding the distribution of all strains in both studies, statistical significance was observed for the A-C5 cluster, which was prevalent in 2014–2018 (p < 0.05). In the current study, the most common emm cluster found in SSTI isolates was E4 (25.0%), followed by A-C3 (22.5%), A-C5 (20.0%), and E6 (17.5%). In samples collected from patients with pneumonia, A-C3 (46.7%) was found to be the most common cluster. In peritonsillar abscess group, A-C5 (33.3%) was the most common, whereas perianal abscess was represented by E4 и E6. Compared to the previous study (2014–2018), statistical significance was found only in the distribution of A-C5 in SSTI group (p < 0.05), while there was no significance established for the remaining clinical diagnoses (Table 1). One limitation of comparing the studies is that the earlier study included additional materials from inpatients (n = 34), such as those with meningitis, sepsis, otitis, and TSS (toxic shock syndrome) whereas the current study does not encompass such clinical manifestations.

Table 1.
Evolution of emm clusters prevalence among the GAS isolates regarding clinical manifestations in strains from 2023 to 2024 compared to strains from 2014 to 2018. Clusters are ordered according to their frequency in the current study.
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
All 70 GAS isolates examined demonstrated susceptibility to both penicillin G and linezolid. The prevalence of resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and tetracyclines was found to be 14.3%, 14.3%, and 18.6%, respectively. No resistance isolates were identified among the isolates from pneumonia and peritonsillar abscess. In the current study, 90.0% of the strains resistant to macrolides and lincosamides, along with 85.6% of the strains resistant to tetracycline, were isolated from SSTI. There was a statistically significant difference in the distribution of macrolide, lincosamide, and tetracycline resistance among strains isolated from SSTI when compared to other clinical manifestations (p < 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Distribution of antibiotic resistance according to the disease entities.
Regarding the genes that determine resistance to ML, we found that ermB was present in all resistant strains (n = 10), leading to constitutive MLSB phenotype in each of the isolates. In addition, two isolates were identified to possess both ermB and mefA gene, while the ermA gene was not detected. Concerning the association between emm-types/clusters and antibiotic resistance, we observed that the most common among erythromycin-resistant isolates (n = 10) was emm28/E4, identified in five strains, followed by emm11/E6 in two strains, and emm3/A-C5, emm1/A-C5, and emm12/A-C4 in one strain each. The mefA gene was identified in emm3 and emm12, when all resistant isolates contained ermB as mentioned above.
The isolates demonstrating resistance to tetracycline were found to be positive for the tetM and tetO genes at rates of 76.9% and 23.1%, respectively. The distribution of emm-types/clusters among tetracycline-resistant isolates was: emm1/A-C3 (4), emm11/E6 (3), emm28/E4 (3), emm3/A-C5 (2), and emm49/E3 (1). The tetM gene was identified in all listed emm-types, whereas tetO gene was present in emm1, emm11 and emm28. Two isolates from emm28 and emm11 demonstrated resistance to ML and tetracyclines.
4. Discussion
Infections caused by GAS can range from mild to severe, potentially resulting in immune-mediated complications, and pose a significant public health challenge, despite the advancements achieved in healthcare. Individuals in hospitals and facilities that host large groups of people encounter an increased risk of developing infections and complications due to factors such as immunocompromising conditions, overcrowding, and elevated levels of social interaction [4,5,30]. The dissemination of highly virulent and resistant strains in these institutions highlights the need to improve surveillance strategies designed to prevent and manage human GAS infections [14]. The most common method for epidemiological surveillance and identifying shifts in the geographical distribution of disease patterns is the emm-typing and clustering [31]. Notable variations in the prevalence of emm types have been observed in different regions and counties. The worldwide disparities in emm types suggest that vaccine targeting particular genotypes may need to be tailored to align with the distribution of local strains [32,33]. A shift in GAS variants or the appearance of new clones may lead to alterations in the incidence and severity of disease within the community [34]. In Europe, between 2000 and 2017 the predominant emm types were consistent across all countries, with emm1 being the most prevalent, except in Scandinavian countries where emm28 and emm89 were frequently observed. Similar results were reported in North and South America, where emm1 was identified as the most prevalent [31,35]. Before the COVID pandemic in China, Taiwan, and Hong Kong, the most common genotypes were emm12, emm1, and emm4 [36,37]. In the post-COVID period, the predominant emm-type in Europe remains emm1, followed by emm3, emm12, emm28, and emm89 [38,39]. Recent reports indicate that in Asia, as well as North and South America, the distribution has remained similar to the pre-COVID period; however, there appears to be an increase in the frequency of emm1 [40,41,42,43]. In comparison to our previous study conducted in 2014–2018, when analyzing the group of inpatients, in which emm3/A-C5 was the predominant type, emm1/A-C3 has now emerged as the most prevalent [29]. This indicated a notable change in the distribution of emm-types/clusters, which is crucial for GAS monitoring in our region. Additionally, the prevalence of emm1 is concerning due to its increased virulence and its association with more serious infections [39].
Globally, the prevalence of SSTIs has been reported to be as high as 32.0% of all infections, with GAS being one of the causative agents that result in challenging infections due to its potential for rapid progression and development of complications [44,45]. In the present work, the majority of the isolates (57.1%) were obtained from patients diagnosed with SSTI. In addition to deep soft tissue abscess, cellulitis, surgical wound infections, and necrotising fasciitis, we included 19 strains from patients who were diagnosed with erysipelas. Despite being a superficial infection that affects the outer layers of the skin, numerous studies indicate that erysipelas is a subtype or variant of cellulitis due to its significant involvement and spread through lymphatic vessels, which may result in severe or even life-threatening complications [46,47,48,49,50]. Certain emm-types are associated with the expression of various virulence factors, which affect the severity of the diseases they cause. The emm1 and emm3 GAS strains have been consistently linked to an increased risk of invasive complications, while emm4 are generally less correlated with severe disease [51]. The occurrence of rare emm-types has been identified as prevalent in SSTI in earlier studies [52,53]. In our research, emm1 and emm3 together accounted for 42.5%, while in the previous study, they constituted 76.2% [29]. This indicates a reduction in these virulent emm-types; however, the rise in less prevalent emm types indicates diversity, contributes to understanding epidemic patterns, and is essential for the advancement of vaccines development.
In recent studies, it was proposed that GAS is one of the most common causes of bacterial pneumonia, following S. pneumoniae in particular geographic regions, and that leads to more severe disease progression, thereby requiring prolonged hospitalizations [54]. In our study regarding the isolates obtained from inpatients with pneumonia, emm1 was found to be the most common, which is consistent with results from other post-COVID-19 research [55,56]. Additionally, our study included 15 isolates obtained from peritonsillar and perianal abscesses. Previous studies have established that GAS is the main causative agent associated with the development of abscesses, with possible significant additional sequelae [57,58]. In both our previous and current studies, emm-types showed diversity among strains isolated from abscesses [29]. Isolates from perianal abscesses were in limited number in the present study and showed affiliation to different emm-types, which does not confirm their association with a specific emm-type. In support of these results, other studies on the same specimens have indicated a heterogeneous structure of emm-types, such as emm3, emm89, and emm1, without significant distribution [59,60].
In contrast to other streptococci, GAS has consistently shown universal susceptibility to penicillin and subsequent generations of β-lactam antibiotics, due to its lack of ability to produce β-lactamase enzymes [61,62]. GAS is generally highly susceptible to linezolid, as data indicates a 100% susceptibility rate in numerous clinical isolates from different countries [63,64]. Although it may exhibit bacteriostatic properties against certain bacteria, linezolid is generally bactericidal for GAS strains. Furthermore, it exhibits antitoxin properties as a protein synthesis inhibitor, decreasing the production of toxins and virulence factors, thereby establishing this antibiotic as a viable alternative to other antimicrobial agents, including clindamycin, for managing severe infections [65,66,67]. As expected, all tested isolates in the current study demonstrated susceptibility to both penicillin and linezolid. This supports that penicillin serves as an effective empirical treatment antibiotic for GAS infections. However, patients with penicillin allergies are managed with alternative antibiotics, such as macrolides and lincosamides [68].
There are significant differences in the prevalence of macrolide resistance in GAS worldwide, with rates as low as 5.0% in Europe and as high as 90.0% in China [69]. In the pre-COVID-19 period the incidence of macrolide and lincosamide increased significantly reaching levels of 20.0–40.0% and 19.0%, respectively, across several European countries including Bulgaria as highlighted in our previous report from the years 2013–2016 [8,70]. In recent years, a similar trend of increase was observed in other continents, with Asia exhibiting the highest levels of resistance; however, some reports from Western Europe and South Asia indicated a decrease in resistance rates. The changes in the resistance rate have frequently been associated with the shift in the predominant resistant clones. This correlation is noted between certain emm types and macrolide resistance phenotypes and/or genotypes, including a demonstrated connection between ermB and emm28 [8,69]. In Asia, the rise in ML resistance has been linked to erm12 (Taiwan), emm12 and emm1 (China), as well as emm12 and emm28. Furthermore, four emm clusters (A-C4, E1, E6, E2) have been associated with resistance, along with increased invasive potential. As a result, monitoring particular clones could be beneficial in addressing the spread of antibiotic resistance [69,71,72,73]. For this purpose, in the current research, we investigated the genes responsible for the primary mechanisms of resistance to macrolides and clindamycin—the erm genes, whose products induce a modification in the binding site on ribosomes, and the mef genes that encode efflux pumps, leading to bacterial resistance specifically against macrolides [9,74]. In a previous study among 102 investigated strains, certain emm types were associated with ML resistance—emm28, emm12, and emm4 accounted for 57.0% of the isolates examined. emm1 and emm3 were the most prevalent among mef positive isolates, while emm77 and emm12 were found in ermA, and emm28 was predominant (88.0%) in ermB positive isolates [75]. This indicated that the circulation of emm28 contributes to the rise in the ML resistance rate and explained the decrease in resistance with more than 25.0% observed in the current study, where this clone is demonstrated in only six strains.
The prevalence of tetracycline resistance observed in this study was lower compared to both the findings from our earlier research and those reported by other studies in the region [8,75,76]. This observation could be associated with the low resistance of ML, since the resistance genes for both groups of antibiotics in GAS are frequently located on conjugative elements, facilitating the horizontal transfer of these gene determinants together [1,5]. The tetracycline-resistant isolates that were analyzed harbored either the tet(M) or the tet(O) gene determinant, and the corresponding emm-types were distributed heterogeneously without any particular clonal spread.
Limitation statement: The study included data collected from two university hospitals situated in two cities within a relatively short period due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Some of the collected specimens (perianal abscesses) were in limited numbers, but the results disclose the emm-types associated with them and allow comparison with data from other studies. Other limitations are the absence of isolates from blood culture and the fact that we do not specifically investigate the presence of M1 UK genetic variant.
The strengths of the study: Despite these limitations, the application of modern techniques and the evaluation of antibiotic susceptibility in isolates derived from hospitalized patients have enhanced our comprehension of the current situation regarding severe GAS infections, which are relatively rare. Furthermore, we compared the obtained data with previous study to monitor the prevalence of emm types and clusters, which is crucial for GAS surveillance.
5. Conclusions
The present study investigated the emm-types and clusters, as well as antibiotic resistance in hospitalized patients suffering from severe GAS infections, representing the first such analysis conducted in western and northern Bulgaria following the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. We analyzed the data obtained in comparison with the research conducted in 2014–2018 to highlight the differences in the distribution of emm-types and clusters between the two periods, thus directing efforts to develop future vaccines against this pathogen in the region. A notable change in the distribution of emm-types/clusters has been observed, as emm1/A-C3 has now emerged as the most prevalent among inpatients when compared to our previous study conducted in the pre-COVID-19 period. Additionally, we noted a decrease in resistance to ML attributed to a lower prevalence of the emm28 clone, which is typically associated with the ermB gene.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.A., A.A.M., R.T.G. and V.S.B.; Data curation, A.A.M., A.S.A. and V.S.B.; Formal analysis, A.A.M., V.S.B. and A.S.A.; Funding acquisition, A.A.M. and R.T.G.; Investigation, A.A.M., A.S.A. and V.S.B.; Methodology, A.A.M., V.S.B., A.S.A. and R.T.G.; Project administration, A.A.M. and R.T.G.; Resources, A.A.M. and R.T.G.; Software, A.S.A., A.A.M. and V.S.B.; Supervision, A.S.A. and R.T.G.; Validation, A.S.A., A.A.M., V.S.B. and R.T.G.; Visualization, A.A.M., A.S.A. and V.S.B.; Writing—original draft, A.A.M.; Writing—review and editing V.S.B., A.S.A. and R.T.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Grant No.157/4.06.2025 of Medical University-Sofia, Bulgaria.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the Laboratory of the Department of Microbiology and Virology, Medical University—Pleven and Acibadem City Clinic Tokuda Hospital for their efforts in collecting the samples for the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wong, S.S.; Yuen, K.Y. Streptococcus pyogenes and re-emergence of scarlet fever as a public health problem. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2012, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.J.; Barnett, T.C.; McArthur, J.D.; Cole, J.N.; Gillen, C.M.; Henningham, A.; Nizet, V. Disease manifestations and pathogenic mechanisms of group A Streptococcus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 264–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, J.; Eisen, J.A.; Jospin, G.; Coil, D.A.; Khazen, G.; Tokajian, S. Genome analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes associated with pharyngitis and skin infections. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avire, N.J.; Whiley, H.; Ross, K. A Review of Streptococcus pyogenes: Public Health Risk Factors, Prevention and Control. Pathogens 2021, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacharodi, A.; Hassan, S.; Vithlani, A.; Ahmed, T.; Kavish, S.; Geli Blacknell, N.M.; Alqahtani, A.; Pugazhendhi, A. The burden of group A Streptococcus (GAS) infections: The challenge continues in the twenty-first century. iScience 2024, 28, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imöhl, M.; Reinert, R.R.; Ocklenburg, C.; van der Linden, M. Epidemiology of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes disease in Germany during 2003-2007. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 58, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergova, R.; Boyanov, V.; Muhtarova, A.; Alexandrova, A. A review of the impact of streptococcal infections and antimicrobial resistance on human health. Antibiot 2024, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girlando, V.; De Angelis, L.; D’Egidio, G.; Di Ludovico, A.; Breda, L. From infection to autoimmunity: S. pyogenes as a model pathogen. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo, Y.N.; Oliver, J.; McMinn, A.; Osowicki, J.; Baker, C.; Clark, J.E.; Steer, A.C. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal disease among Australian children coinciding with northern hemisphere surges. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023, 41, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gier, B.; Marchal, N.; de Beer-Schuurman, I.; Te Wierik, M.; Hooiveld, M.; de Melker, H.E.; GAS Study Group. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal (Streptococcus pyogenes) infections (iGAS) in young children in the Netherlands, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.; Henderson, K.L.; Coelho, J.; Hughes, H.; Mason, E.L.; Gerver, S.M.; Lamagni, T. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infection notifications, England, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca, B.V.; Cyr, P.R.; Bentdal, Y.E.; Watle, S.V.; Wester, A.L.; Strand, Å.M.W.; Bøås, H. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infections (iGAS) in children and older adults, Norway, 2022 to 2024. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 2400242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, S.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Curren, B.F.; Harbison-Price, N.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Jespersen, M.G.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of Group A Streptococcus infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.M.A.; Anwar, S.; Pirzada, Z.A. Streptococcus pyogenes strains associated with invasive and non-invasive infections present possible links with emm types and superantigens. Iran J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.; Handique, S.; Rajkhowa, S.; Das, A.; Panda, D.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Zaki, M.E.A. Targeting Streptococcus pyogenes atpF protein for multi-epitope vaccine development: A genomics-driven immunoinformatics strategy. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2025, 23, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friães, A.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M. Portuguese Group for the Study of Streptococcal Infections. Changes in emm types and superantigen gene content of Streptococcus pyogenes causing invasive infections in Portugal. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanson, M.A.; Macias, O.R.; Shah, B.J.; Hanson, B.; Vega, L.A.; Alamarat, Z.; Flores, A.R. Unexpected relationships between frequency of antimicrobial resistance, disease phenotype and emm type in group A Streptococcus. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.F.; LaRock, C.N. Antibiotic treatment, mechanisms for failure, and adjunctive therapies for infections by Group A Streptococcus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 760255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelli, M.; Malangoni, M.A.; May, A.K.; Viale, P.; Kao, L.S.; Catena, F.; Yuan, K.C. World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) guidelines for management of skin and soft tissue infections. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2014, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapatai, G.; Coelho, J.; Platt, S.; Chalker, V.J. Whole genome sequencing of group A Streptococcus: Development and evaluation of an automated pipeline for emmgene typing. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeesters, P.R.; Botteaux, A. The emm-cluster typing system. In Group A Streptococcus: Methods and Protocols; Proft, T., Loh, J., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2136, pp. 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jespersen, M.G.; Lacey, J.A.; Tong, S.Y.C.; Davies, M.R. Global genomic epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 86, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, C.; Mannino, E.; Bongiorno, D.; Vocale, C.; Amicucci, A.; Bivona, D.; Guariglia, D.; Nicitra, E.; Privitera, G.F.; Sangiorgio, G.; et al. Molecular and clinical characterization of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes isolates: Insights from two Northern-Italy centers. Pathogens 2025, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rivers, J.; Mathis, S.; Li, Z.; Velusamy, S.; Nanduri, S.A.; Van Beneden, C.A.; Snippes-Vagnone, P.; McGee, L.; Chochua, s.; et al. Genomic surveillance of Streptococcus pyogenes strains causing invasive disease, United States, 2016-2017. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beres, S.B.; Zhu, L.; Pruitt, L.; Olsen, R.J.; Faili, A.; Kayal, S.; Musser, J.M. Integrative reverse genetic analysis identifies polymorphisms contributing to decreased antimicrobial agent susceptibility in Streptococcus pyogenes. mBio 2022, 13, e0361821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and Zone di-370 Ameters. Version 14.0. 2024. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Lammens, C.; Piessens, J.; Goossens, H. Multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of macrolide and tetracycline resistance determinants in streptococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4798–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergova, R.; Muhtarova, A.; Mitov, I.; Setchanova, L.; Mihova, K.; Kaneva, R.; Markovska, R. Relation between emm types and virulence gene profiles among Bulgarian Streptococcus pyogenes clinical isolates. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, C.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Wu, H.; Dong, W.; Wei, L. Streptococcus pyogenes: Pathogenesis and the current status of vaccines. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, G.; Vitali, L.A.; Creti, R. Prevalent emm Types among invasive GAS in Europe and North America since year 2000. Front. Public Health. 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.B.; Penfound, T.A.; Chiang, E.Y.; Walton, W.J. New 30-valent M protein-based vaccine evokes cross-opsonic antibodies against non-vaccine serotypes of group A streptococci. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8175–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.B.; Walker, M.J. Update on group A streptococcal vaccine development. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, R.; Itzek, A.; Marr, L.; Manzke, J.; Voigt, S.; Chapot, V.; Steinmann, J. Divergent effects of emm types 1 and 12 on invasive group A streptococcal infections—Results of a retrospective cohort study, Germany 2023. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e00637-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amicis, K.M.; de Barros, F.S.; Alencar, R.E.; Postól, E.; Martins Cde, O.; Arcuri, H.A.; Goulart, C.; Kalil, J.; Guilherme, L. Analysis of the coverage capacity of the StreptInCor candidate vaccine against Streptococcus pyogenes. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4104–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang-Ni, C.; Zheng, P.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsai, P.J.; Chuang, W.J.; Lin, Y.S.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, J.J. Epidemiology analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes in a hospital in southern Taiwan by use of the updated emm cluster typing system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F.; You, Y. emm type distribution of group A Streptococcus in China during 1990 and 2020: A systematic review and implications for vaccine coverage. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1157289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg-Bockhorn, E.; Hagemann, B.; Furitsch, M.; Hoffmann, T.K. Invasive group A streptococcal infections in Europe after the COVID-19 pandemic. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2024, 121, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo-Vázquez, E.; Aguilera-Alonso, D.; Grandioso-Vas, D.; Gamell, A.; Rello-Saltor, V.; Oltra-Benavent, M.; Cervantes, E.; Sanz-Santaeufemia, F.; Carrasco-Colom, J.; Manzanares-Casteleiro, Á.; et al. Sharp increase in the incidence and severity of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes infections in children after the COVID-19 pandemic (2019–2023): A nationwide multicenter study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 159, 107982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Hussain, M.; Qasim, M.; Fozia, F.; Naveed, H.; Rehman, A.; Ahmad, I.; Mohany, M.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Djurasevic, S. Prevalence and emm typing of multi-drugresistant Streptococcus pyogenes in tertiary care health settings. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapati, E.; Tsantes, A.G.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Boutsikou, T.; Paliatsiou, S.; Domouchtsidou, A.; Ioannou, P.; Petrakis, V.; Iacovidou, N.; Sokou, R. Group A Streptococcus infections in children: Epidemiological insights before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Zeng, M. Ongoing epidemic of scarlet fever in Shanghai and the emergence of M1UK lineage group A Streptococcus: A 14-year surveillance study across the COVID-19 pandemic period. Lancet. Reg. Health West Pac. 2025, 58, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, L.; Gianecini, A.; Poklepovich, T.; Etcheverry, P.; Rocca, F.; Prieto, M. Genomic epidemiology of invasive group A Streptococcus infections in Argentina, 2023: High prevalence of emm1-global and detection of emm1 hypervirulent lineages. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0131024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Larosa, B.; Lamarina, A.; Vena, A.; Brucci, G. The reemergence of Streptococcus pyogenes in skin and soft tissue infections: A review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management strategies. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2025, 38, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.; Chitrapady, S.K.; Haritha, K.; Tejashree, M.U.; Balakrishnan, J.M.; Thunga, G. Bacterial pathogens causing skin and soft tissue infections and antibiotic susceptibility in South Asia: A scoping review protocol. Syst. Rev. 2025, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titou, H.; Ebongo, C.; Bouati, E.; Boui, M. Risk factors associated with local complications of erysipelas: A retrospective study of 152 cases. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2017, 26, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendoubi, F.; Rohde, M.; Prinz, J.C. Intracellular streptococcal uptake and persistence: A potential cause of erysipelas recurrence. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettler, M.A.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Chung, C.G. Cellulitis: A review of current practice guidelines and differentiation from pseudocellulitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabanova, M. Erysipelas. In European Handbook of Dermatological Treatments, 4th ed.; Katsambas, A.D., Lotti, T.M., Dessinioti, C., D’Erme, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 283–286. ISBN 978-3-031-15130-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Khulbe, P.; Ahire, E.D.; Gupta, M.; Chauhan, N.; Keservani, R.K. Skin and soft tissue diseases and their treatment in society. Community Acquir. Infect. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Masetti, M.; Calanca, C.; Canducci, N.; Rasmi, S.; Fradusco, A.; Principi, N. Recent changes in the epidemiology of group A Streptococcus infections: Observations and implications. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pato, C.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M.; Friaes, A. Portuguese Group for the Study of Streptococcal Infections. Streptococcus pyogenes causing skin and soft tissue infections are enriched in the recently emerged emm 89 clade 3 and are not associated with abrogation of CovRS. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2372. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chang, L.; Lai, C.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y. Clinical and molecular characteristics of invasive and noninvasive skin and soft tissue infections caused by group A Streptococcus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3632–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, S.; Ficari, A.; Romani, L.; De Luca, M.; Tripiciano, C.; Chiurchiù, S.; Calo Carducci, F.I.; Cursi, L.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Krzysztofiak, A.; et al. The Thousand faces of invasive group A streptococcal infections: Update on epidemiology, symptoms, and therapy. Children 2024, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellés-Bellés, A.; Prim, N.; Mormeneo-Bayo, S.; Villalón-Panzano, P.; Valiente-Novillo, M.; Jover-Sáenz, A.; Aixalà, N.; Bernet, A.; López-González, É.; Prats, I.; et al. Changes in Group A Streptococcus emm types associated with invasive infections in adults, Spain, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2390–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroidi, A.; Katsiaflaka, A.; Petinaki, E.; Froukala, E.; Papadopoulos, D.; Vrioni, G.; Tsakris, A. M1UK Streptococcus pyogenes causing community-acquired pneumonia, pleural empyema and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 37, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, T.E.; Greve, T.; Hentze, M. Complications of peritonsillar abscess. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slouka, D.; Hanakova, J.; Kostlivy, T.; Skopek, P.; Kubec, V.; Babuska, V.; Kucera, R. Epidemiological and microbiological aspects of the peritonsillar abscess. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzi, F.; Tsakris, A.; Chatzichristou, P.; Koutouzis, E.; Daikos, G.L.; Kirikou, E.; Petropoulou, N.; Syriopoulou, V.; Michos, A. Streptococcus pyogenes emm types and clusters during a 7-Year Period (2007 to 2013) in pharyngeal and nonpharyngeal pediatric isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, S.; Das, S.; Hayes, A.J.; Bertolla, O.M.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J.; Whiley, D.M.; Irwin, A.D.; Tickner, J.A. A rapid molecular detection tool for toxigenic M1UK Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 231, e375–e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imöhl, M.; van der Linden, M. Antimicrobial susceptibility of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes isolates in Germany during 2003-2013. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kebede, D.; Admas, A.; Mekonnen, D. Prevalence and antibiotics susceptibility profiles of Streptococcus pyogenes among pediatric patients with acute pharyngitis at Felege Hiwot Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lagace-Wiens, P.; Adam, H.; Pieroni, P.; Zhanel, G.; Karlowsky, J.; Walkty, A. P-1493. In vitro activity of clindamycin in comparison with linezolid versus Streptococcus pyogenes clinical isolates recovered from patients in Manitoba, Canada. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2025, 12, ofae631.1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünübol, N.; Caglayan, N.; Cebeci, S.; Beşli, Y.; Sancak, B.; Uyar, N.Y.; Ahrabi, S.S.; Alebouyeh, M.; Kocagöz, T. Antimicrobial resistance and epidemiological patterns of Streptococcus pyogenes in Türkiye. J. Infect. Public Health 2025, 18, 102633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, B.A.; Equils, O.; Huang, D.B.; Gladue, R. Linezolid effects on bacterial toxin production and host immune response: Review of the evidence. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2012, 73, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.B.; Albrecht, B.; Chapin, R.; Walters, J. Toxin inhibition: Examining tetracyclines, clindamycin, and linezolid. Am. J. Health. Syst. Pharm. 2025, 82, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiker, A.; Warner, S.; Li, X.; Chishti, E.A.; Saad, E.; Swihart, B.J.; Dekker, J.P.; Walker, M.; Lawandi, A.; Kadri, S.S.; et al. Adjunctive linezolid versus clindamycin for toxin inhibition in β-lactam-treated patients with invasive group A streptococcal infections in 195 US hospitals from 2016 to 2021: A retrospective cohort study with target trial emulation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, A.B.; Fenta, D.A.; Negash, A.A.; Hayile, B.J. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility pattern and associated factors of Streptococcus pyogenes among pediatric patients with acute pharyngitis in Sidama, Southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Microbiol. 2024, 2024, 9282571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei, R.; Al Iaali, R.; Osman, M.; Dabboussi, F.; Hamze, M. A global snapshot on the prevalent macrolide-resistant emm types of Group A Streptococcus worldwide, their phenotypes and their resistance marker genotypes during the last two decades: A systematic review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 99, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhtarova, A.A.; Gergova, R.T.; Mitov, I.G. Distribution of macrolide resistance mechanisms in Bulgarian clinical isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes during the years of 2013–2016. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Fang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; et al. High prevalence of macrolide-resistance and molecular characterization of Streptococcus pyogenes isolates circulating in China from 2009 to 2016. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Xu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Shen, A.; Wang, B. A multicomponent vaccine provides immunity against local and systemic infections by Group A Streptococcus across serotypes. mBio 2019, 10, e02600-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbel, D.; González-Díaz, A.; López de Egea, G.; Càmara, J.; Ardanuy, C. An Overview of macrolide resistance in streptococci: Prevalence, mobile elements and dynamics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyanov, V.S.; Alexandrova, A.S.; Hristova, P.M.; Hitkova, H.Y.; Gergova, R.T. Antibiotic resistance and serotypes sistribution in Streptococcus agalactiae Bulgarian clinical isolates during the years of 2021-2024. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2024, 73, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhtarova, A.; Mihova, K.; Markovska, R.; Mitov, I.; Kaneva, R.; Gergova, R. Molecular emm typing of Bulgarian macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes isolates. Acta Microbiol. Hung. 2020, 67, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G.; Ketikidis, A.L.; Floropoulou, N.; Tychala, A.; Kagkalou, G.; Vasilaki, O.; Protonotariou, E. Antimicrobial resistance rates of Streptococcus pyogenes in a Greek tertiary care hospital: 6-year data and. New Microbiol. 2023, 46, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).