Dams Determine the Composition and Activity of Microbial Communities in Semiclosed Marine Basins of the White and Barents Seas, Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Investigation Objects
2.2. Main Idea and Scheme of Research
2.3. Sampling and Sample Processing
2.4. Rates of Microbial Processes
2.5. Isolation of Metagenomic DNA, PCR Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Gene Fragments
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the Samples
3.2. Rates of Microbial Processes in the Upper Sediment Layers
3.3. Total Microbial Abundance
3.4. Results of High-Throughput Sequencing
3.5. Taxonomic Composition of the Sediment Microbial Communities at the Phylum Level
3.6. Taxonomic Composition of the Sediment Microbial Communities at the Family Level
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ignatov, E.; Kalynychenko, O.; Pantiulin, A. The White Sea as an estuarine system. In The Diversity of Russian Estuaries and Lagoons Exposed to Human Influence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 223–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Yeoh, D.E.; Krispyn, K.N.; Greenwell, C.N.; Cronin-O’Reilly, S.; Chabanne, D.B.; Hyndes, G.A.; Johnston, D.; Fairclough, D.V.; Wellington, C.; et al. Ecological resources of a heavily modified and utilised temperate coastal embayment: Cockburn Sound. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1563654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, M.; Qi, F.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J. The influence of thermal discharge from power plants on the biogeochemical environment of Daya Bay during high primary productivity seasons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 211, 117408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pjevac, P.; Korlević, M.; Berg, J.S.; Bura-Nakić, E.; Ciglenečki, I.; Amann, R.; Orlić, S. Community shift from phototrophic to chemotrophic sulfide oxidation following anoxic holomixis in a stratified seawater lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassi, F.; Fazi, S.; Rossetti, S.; Pratesi, P.; Ceccotti, M.; Cabassi, J.; Capecchiacci, F.; Venturi, S.; Vaselli, O. The biogeochemical vertical structure renders a meromictic volcanic lake a trap for geogenic CO2 (Lake Averno, Italy). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storesund, J.E.; Lanzèn, A.; Nordmann, E.-L.; Armo, H.R.; Lage, O.M.; Øvreås, L. Planctomycetes as a Vital Constituent of the Microbial Communities Inhabiting Different Layers of the Meromictic Lake Sælenvannet (Norway). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvichev, A.S.; Demidenko, N.A.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Belenkova, V.V.; Rusanov, I.I.; Gorlenko, V.M. Microbial Community Composition as an Indicator of the State of Basins Located at the Sea Coast (Exemplified by the Kanda Bay, Kandalaksha Gulf, White Sea). Microbiology 2023, 92, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlenko, V.M.; Vainstein, M.V.; Chebotarev, E.N. Bacteria of sulfur and iron cycles in the low-sulfate meromictic lake Kuznechikha. Microbiology 1980, 49, 653–659. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gemerden, H.; Mas, J. Ecology of phototrophic sulfur bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 49–85. [Google Scholar]
- Overmann, J. Mahoney Lake: A Case Study of the Ecological Significance of Phototrophic Sulfur Bacteria. Adv. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 15, 251–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozin, D.Y.; Zykov, V.V.; Chernetsky, M.Y.; Degermendzhy, A.G.; Gulati, R.D. Effect of winter conditions on distributions of anoxic phototrophic bacteria in two meromictic lakes in Siberia, Russia. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, G.; Zubkov, M.V.; Yakushev, E.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K. High abundance and dark CO2 fixation of chemolithoautotrophic bacteria in anoxic waters of the Baltic Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.D.; Zadereev, T.S.; Degermendzhi, A.G. Ecology of Meromictic Lakes; Springer Cham International Publish: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfenin, N.N.; Malutin, O.I.; Pantiulin, A.N.; Pertzova, N.M.; Usachev, I.N. The Impact of Tidal Power Plants on the Environment; Lomonosov Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 1995. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Savvichev, A.S.; Demidenko, N.A.; Krasnova, E.D.; Kalmatskaya, O.V.; Kharcheva, A.N.; Ivanov, M.V. Microbial processes in the Kanda Bay, a meromictic water body artificially separated from the White Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2017, 474, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velinsky, D.J.; Fogel, M.L. Cycling of dissolved and particulate nitrogen and carbon in the Framvaren Fjord, Norway: Stable isotopic variations. Mar. Chem. 1999, 67, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gilbert, D.; Gooday, A.J.; Levin, L.; Naqvi, S.W.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; Scranton, M.; Ekau, W.; Pena, A.; Dewitte, B.; et al. Natural and human-induced hypoxia and consequences for coastal areas: Synthesis and future development. Biogeosciences Eur. Geosci. Union 2010, 7, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, E.D. Ecology of Meromictic Lakes of Russia. 1. Coastal Marine Waterbodies. Water Resour. 2021, 48, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvichev, A.S.; Babenko, V.V.; Lunina, O.N.; Letarova, M.A.; Boldyreva, D.I.; Veslopolova, E.F.; Demidenko, N.A.; Kokryatskaya, N.M.; Krasnova, E.D.; Gaisin, V.A.; et al. Sharp water column stratification with an extremely dense microbial population in a small meromictic lake, Trekhtzvetnoe. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3784–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenov, N.V.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. In situ activity studies in thermal environments. Methods Microbiol. 2006, 35, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvichev, A.S.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Rusanov, I.I.; Beletsky, A.V.; Krasnova, E.D.; Voronov, D.A.; Kallistova, A.Y.; Veslopolova, E.F.; Zakharova, E.E.; Kokryatskaya, N.M.; et al. Microbial Processes of the Carbon and Sulfur Cycles and the Relevant Microorganisms in the Water Column of the Meromictic Lake Bol’shie Khruslomeny Lake at the White Sea Coast. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.; Rime, T.; Phillips, M.; Stierli, B.; Hajdas, I.; Widmer, F.; Hartmann, M. Microbial diversity in European alpine permafrost and active layers. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könneke, M.; Bernhard, A.E.; de La Torre, J.R.; Walker, C.B.; Waterbury, J.B.; Stahl, D.A. Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 2005, 437, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, J.G.; Jung, M.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Cha, I.T.; Ghai, R.; Martín-Cuadrado, A.B.; Rodríguez-Valera, F.; Rhee, S.K. Draft genome sequence of an ammonia-oxidizing archaeon, “Candidatus Nitrosopumilus sediminis” AR2, from Svalbard in the arctic circle. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6946–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Heal, K.R.; Ramdasi, R.; Kobelt, J.N.; Martens-Habbena, W.; Bertagnolli, A.D.; Amin, S.A.; Walker, C.B.; Urakawa, H.; Konneke, M.; et al. Nitrosopumilus maritimus gen. nov., sp. nov., Nitrosopumilus cobalaminigenes sp. nov., Nitrosopumilus oxyclinae sp. nov., and Nitrosopumilus ureiphilus sp. nov., four marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea of the phylum Thaumarchaeota. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 5067–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, K.I.; Garcia, R.O.; Gerth, K.; Irschik, H.; Müller, R. Sandaracinus amylolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a starch-degrading soil myxobacterium, and description of Sandaracinaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, B.A.; Portillo, E.R.; Rogel, J.A.; Giménez-Casalduero, F.; Otero, X.L.; Belando, M.D.; Bernardeau-Esteller, J.; García-Muñoz, R.; Forcada, A.; Ruiz, J.M.; et al. Factors structuring microbial communities in highly impacted coastal marine sediments (Mar Menor lagoon, SE Spain). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 937683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhao, J.X.; Chen, G.J. Woeseia oceani gen. nov., sp. nov., a chemoheterotrophic member of the order Chromatiales, and proposal of Woeseiaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Bienhold, C.; Buttigieg, P.L.; Knittel, K.; Laso-Pérez, R.; Rapp, J.Z.; Boetius, A.; Offre, P. Diversity and metabolism of Woeseiales bacteria, global members of marine sediment communities. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, I.; Cho, J. Metabolic Versatility of the Family Halieaceae Revealed by the Genomics of Novel Cultured Isolates. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03879-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Xu, X.W. The Family Hyphomicrobiaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.I.; Head, I.M.; Stein, L.Y. The Family Nitrosomonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, S.L.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Ward, R.J.; Yavitt, J.B.; Zinder, S.H. Methanoregula boonei gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidiphilic methanogen isolated from an acidic peat bog. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hanada, S. Sulfurovum denitrificans sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing epsilonproteobacterium isolated from a hydrothermal field. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2183–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; McIlroy, S.J.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Karst, S.M.; Fernando, W.E.Y.; Aslan, H.; Meyer, R.L.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Dueholm, M.S. Novel prosthecate bacteria from the candidate phylum Acetothermia. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2225–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, M.E.; Wood, W.A.; Key, R.; Nakamura, K.; Stahl, D. Isolation of three species of Geotoga and Petrotoga: Two new genera, representing a new lineage in the bacterial line of descent distantly related to the “Thermotogales”. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1993, 16, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Castelle, C.J.; Probst, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Banfield, J.F.; Gu, J.D. Insights into the ecology, evolution, and metabolism of the widespread Woesearchaeotal lineages. Microbiome 2018, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Perner, M. The globally widespread genus Sulfurimonas: Versatile energy metabolisms and adaptations to redox clines. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.X.; Cao, L.; Du, Z.F.; Sun, Y.Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Li, C.L.; Sun, L. High-throughput sequencing reveals a potentially novel Sulfurovum species dominating the microbial communities of the seawater–sediment interface of a deep-sea cold seep in South China sea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narihiro, T.; Terada, T.; Ohashi, A.; Kamagata, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Sekiguchi, Y. Quantitative detection of previously characterized syntrophic bacteria in anaerobic wastewater treatment systems by sequence-specific rRNA cleavage method. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, S.; Ramette, A.; Amann, R.; Knittel, K. Distribution and in situ abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria in diverse marine hydrocarbon seep sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2689–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.L.; Biggerstaff, J.; Eichhorn, A.; Ewing, E.; Shahan, R.; Soriano, D.; Stewart, S.; VanMol, K.; Walker, R.; Walters, P.; et al. Genomic characterization of three novel Desulfobacterota classes expand the metabolic and phylogenetic diversity of the phylum. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4326–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhnaya, M.G.; Bowerman, S.; Lara, J.C.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. Methylotenera mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately methylamine-utilizing bacterium within the family Methylophilaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56 Pt 12, 2819–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekeman, B.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Cremers, G.; Vos, P.; Vandamme, P.; Boon, N.; Camp, H.J.M.; Heylen, K. New Methyloceanibacter diversity from North Sea sediments includes methanotroph containing solely the soluble methane monooxygenase. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4523–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, K.; Graf, J.S.; Littmann, S.; Tienken, D.; Brand, A.; Wehrli, B.; Albertsen, M.; Daims, H.; Wagner, M.; Kuypers, M.M.; et al. Crenothrix are major methane consumers in stratified lakes. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2124–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, H. Ten Years of Experience at the “La Rance” Tidal Power Plant. Ocean Manag. 1978, 4, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroy, N.; Retière, C. Long-term changes in muddy fine sand community of the Rance Basin: Role of recruitment. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2001, 81, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang-Soon, C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.S.; Heo, W.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, H.J. Eutrophication in the Upper Regions of Brackish Lake Sihwa with a Limited Water Exchange. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 41, 216–227. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Vicente, E.; Camacho, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Vila, X.; Cristina, X.P.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, J. Vertical distribution of photosynthetic sulphur bacteria linked to saline gradients in Lake ‘El Tobar’ (Cuenca, Spain). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A.; Erez, J.; Chicote, A.; Florin, M.; Squires, M.M.; Lehmann, C.; Bahofen, R. Microbial microstratification, inorganic carbon photoassimilation and dark carbon fixation at the chemocline of the meromictic Lake Cadagno (Switzerland) and its relevance to the food web. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 63, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlenko, W.M.; Kuznezov, S.I. Über die photosynthesierenden Bakterien des Kononjer-Sees. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1972, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Kuenen, J.G.; Cohen, Y. Microbial transformations of sulfur-compounds in a stratified lake (Solar Lake, Sinai). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1979, 24, 799–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrssen, D.W.; Hall, P.O.J.; Haraldsson, C.; Chierici, M.; Skei, J.M.; Göteöstlund, H. Time dependence of organic matter decay and mixing processes in Framvaren, a permanently anoxic fjord in South Norway. Aquat. Geochem. 1996, 2, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.V.; Rusanov, I.I.; Pimenov, N.V.; Bairamov, I.T.; Yusupov, S.K.; Savvichev, A.S.; Lein AYu Sapozhnikov, V.V. Microbial Processes of the Carbon and Sulfur Cycles in Lake Mogilnoe. Microbiology 2001, 70, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelkov, P.; Shunatova, N.; Fokin, M.; Usov, N.; Fedyuk, M.; Malavenda, S.; Lubina, O.; Poloskin, A.; Korsun, S. Marine Lake Mogilnoe (Kildin Island, the Barents Sea): One hundred years of solitude. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.V.; Savvichev, A.S.; Klyuvitkin, A.A.; Chul’tsova, A.L.; Zakharova, E.E.; Rusanov, I.I.; Lein, A.Y.; Lisitsyn, A.P. Resumption of hydrogen sulfide contamination of the water column of deep basins in the Caspian Sea. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2013, 453, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, E.D.; Pantyulin, A.N.; Belevich, T.A.; Voronov, D.A.; Demidenko, N.A.; Zhitina, L.S.; Ilyash, L.V.; Kokryatskaya, N.M.; Lunina, O.N.; Mardashova, M.V.; et al. Multidisciplinary Studies of the Separating Lakes at Different Stage of Isolation from the White Sea Performed in March 2012. Oceanology 2013, 53, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losyuk, G.; Kokryatskaya, N.; Krasnova, E. Formation of hydrogen sulfide in isolated basins at the Karelian of the White Sea coast. EARSeL eProc. 2015, 14, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
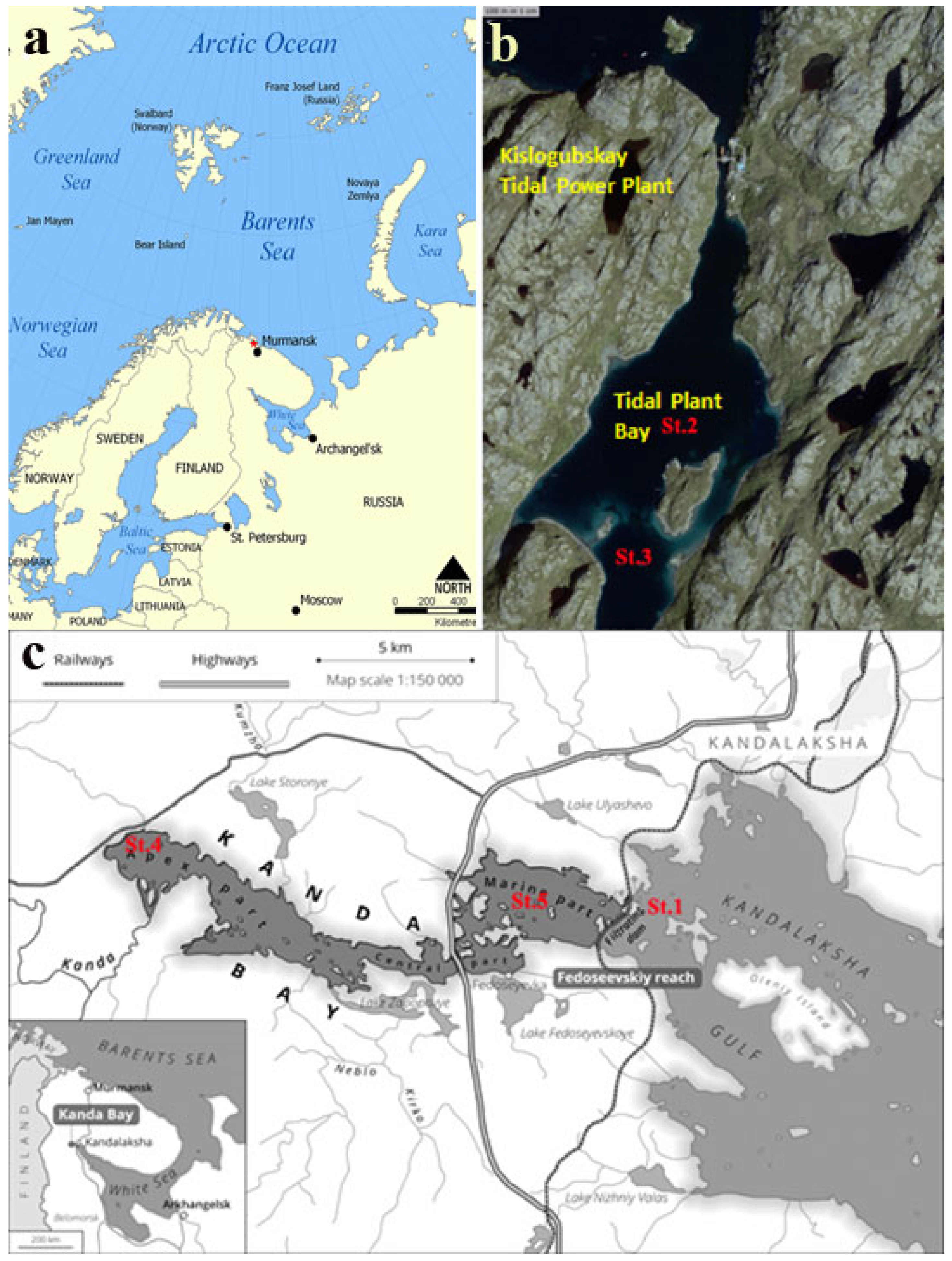

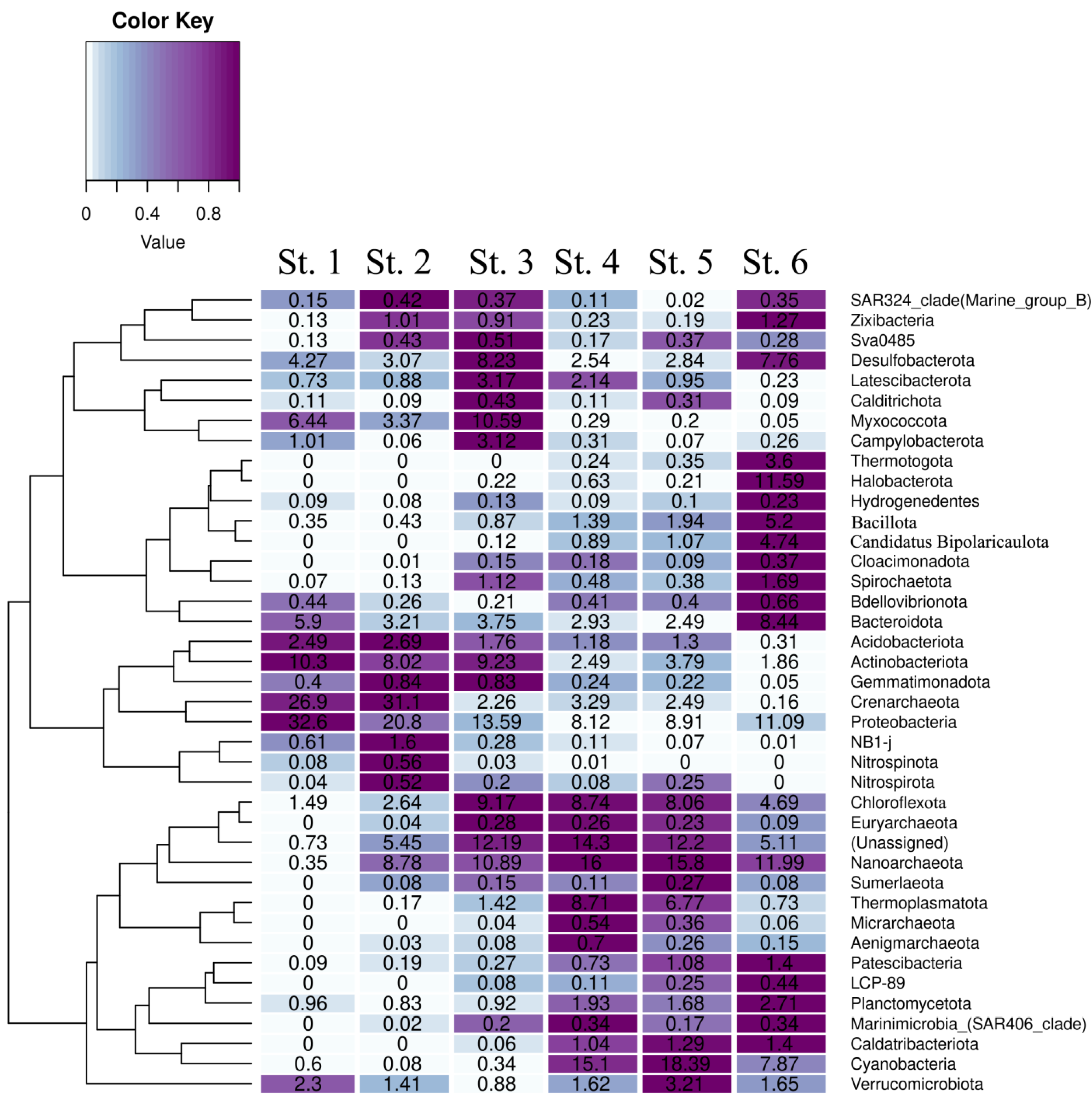
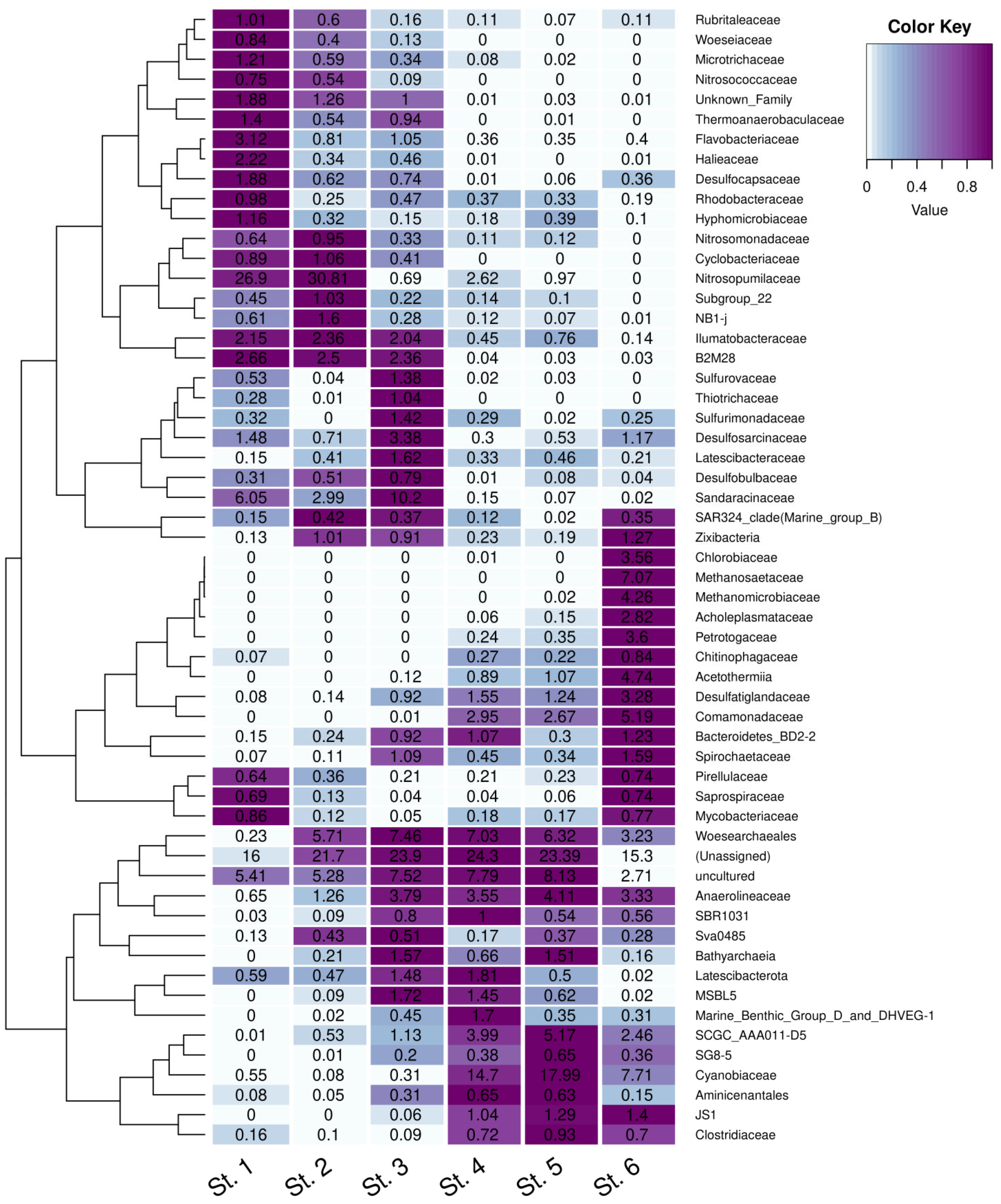
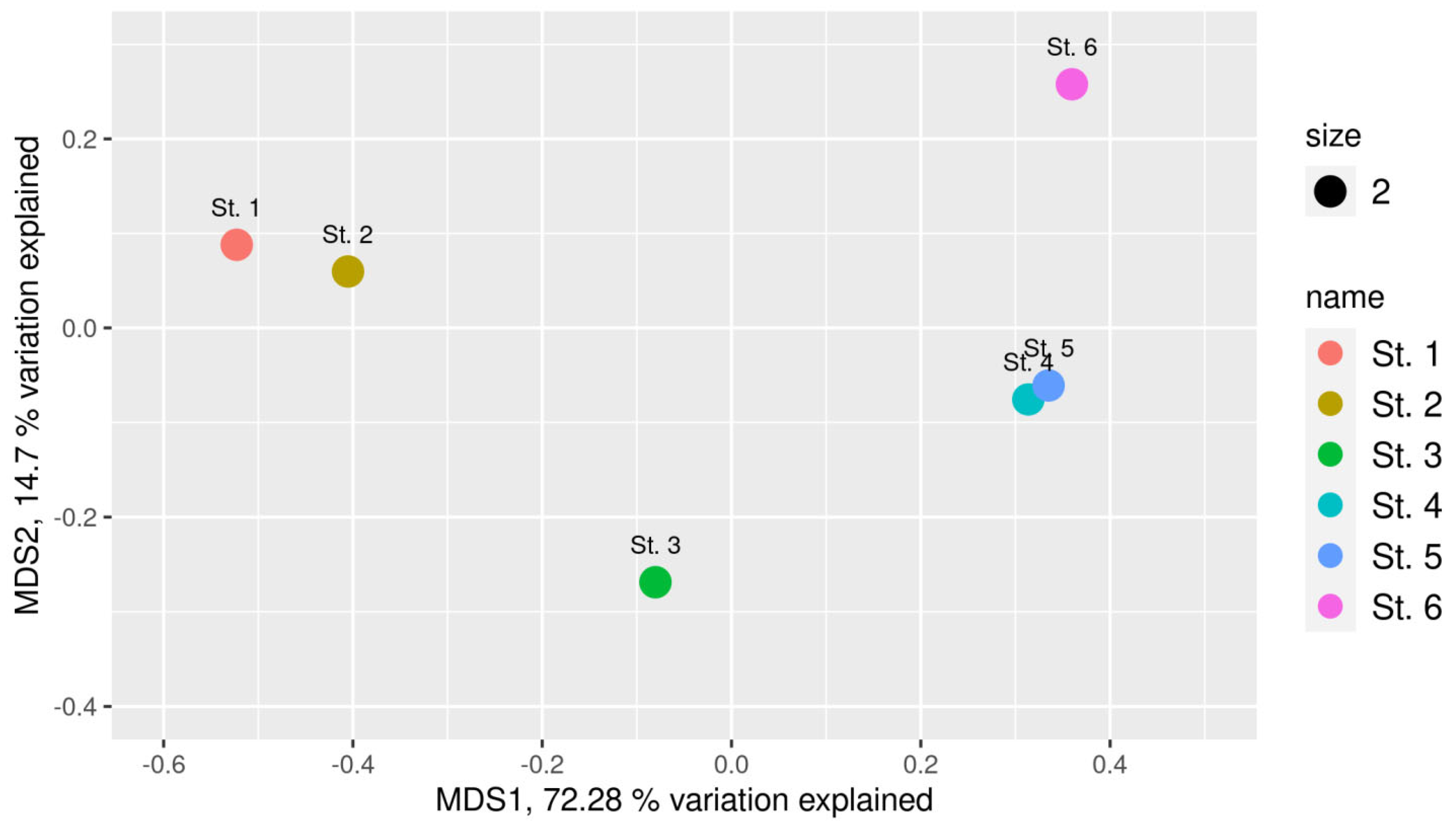
| Station | St. 1. “Marine,” Marine Sediment, White Sea Gulf | St. 2. Kislaya Guba, Tidal Power Station Bay | St. 3. Kislaya Guba, Tidal Power Station Bay | St. 4. Kanda Guba, Apex Reach | St. 5. Kanda Guba, Marine Reach | St. 6. “Anoxic,” Meromictic Lake Trekhtzvetnoe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordinates | 67°07′25″ N 32°15′42″ E | 69°21′90″ N 33°04′12″ E | 69°21′58″ N 33°03′98″ E | 67°08′23″ N 31°53′20″ E | 67°08′88″ N 32°10′70″ E | 66°43′01″ N, 32°51′28″ E |
| Depth, m | 28 | 34 | 35 | 18 | 21.5 | 7.0 |
| Sediment layer | 0–2 cm | 0–2 cm | 2–7 cm | 0–2 cm | 0–2 cm | 0–2 cm |
| Sediment appearance | Liquid, with gray sand and aleurite | Brown, loose, flaky | Black, pelitic, homogeneous | Liquid, black, sulfide-containing | Liquid, black, sulfide-containing | Liquid, black, sulfide-containing |
| Tbottom, °C | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 5.1 |
| Salinity, ‰ | 24 | 33.2 | 33.2 | 13.5 | 22.0 | 21.9 |
| Eh, mV | 220 | 20 | +40 − 30 | −390 | −340 | −420 |
| O2, * mmol L−1 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H2S mmol dm−3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.46 | 0.85 | up to 13.25 |
| CH4 mmol dm−3 | 0.64 | 12.4–15.8 | 12–28 | 45–80 | 124–158 | up to 2220 |
| MGh, µmol dm−3 day−1 | ˂2.0 × 10−3 | 3–6 × 10−3 | 8–10 × 10−3 | 12–40 × 10−3 | 8–24 × 10−3 | 90–130 × 10−3 |
| DCA, µmol dm−3 day−1 | 0.9–1.1 | 1.4–4.0 | 1.2–3.8 | 3–5 | 5–7 | 48–122 |
| SR µmol S dm−3 day−1 | 0.05–0.15 | 0.5–1.2 | 0.3– 0.9 | 8–14 | 12–20 | 68 |
| MO, µmol dm−3 day−1 | 0.05–0.09 | 0.25–0.31 | 0.1–0.17 | 0.17–0.41 | 0.08–0.19 | 1.8 |
| MA, 106 cells mL−1/B, µg L−1 | 0.20/78 | 0.48/182 | 0.48/182 | 0.52 195 | 0.42/170 | 12/4800 |
| Sediment Sample | Archaea OTU % | Bacteria OTU % | Chao1 | Shannon H’ (Log with Base e) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| St. 1. Marine sediment | 27.98 | 71.40 | 789.5 | 4.63 |
| St. 2. Kislaya Guba, tidal power station bay, 0–2 cm | 39.80 | 54.6 | 1425.9 | 5.08 |
| St. 3. Kislaya Guba, tidal power station bay, 2–7 cm | 13.80 | 74.02 | 1606.2 | 5.98 |
| St. 4. Kanda Guba, apex part | 20.30 | 65.40 | 1471.1 | 5.68 |
| St. 5. Kanda Guba, Fedoseevskiy reach | 18.83 | 68.83 | 1568.3 | 5.68 |
| St. 6. Meromictic Lake Trekhcvetnoe | 23.85 | 71.04 | 873.5 | 5.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savvichev, A.S.; Demidenko, N.A.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Beletsky, A.V.; Belenkova, V.V.; Rusanov, I.I.; Sigalevich, P.A.; Ivanova, D.A. Dams Determine the Composition and Activity of Microbial Communities in Semiclosed Marine Basins of the White and Barents Seas, Russia. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092143
Savvichev AS, Demidenko NA, Kadnikov VV, Beletsky AV, Belenkova VV, Rusanov II, Sigalevich PA, Ivanova DA. Dams Determine the Composition and Activity of Microbial Communities in Semiclosed Marine Basins of the White and Barents Seas, Russia. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092143
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavvichev, Alexander S., Nikolay A. Demidenko, Vitaly V. Kadnikov, Alexey V. Beletsky, Valeria V. Belenkova, Igor I. Rusanov, Pavel A. Sigalevich, and Daria A. Ivanova. 2025. "Dams Determine the Composition and Activity of Microbial Communities in Semiclosed Marine Basins of the White and Barents Seas, Russia" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092143
APA StyleSavvichev, A. S., Demidenko, N. A., Kadnikov, V. V., Beletsky, A. V., Belenkova, V. V., Rusanov, I. I., Sigalevich, P. A., & Ivanova, D. A. (2025). Dams Determine the Composition and Activity of Microbial Communities in Semiclosed Marine Basins of the White and Barents Seas, Russia. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092143








