Halogenation and Dehalogenation Potential of Microorganisms in Yangtze River Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Metagenomic Data Acquisition
2.2. Metagenomic Data Analysis
2.2.1. Assembly
2.2.2. Functional Annotation, Halogenase and Dehalogenase Genes Identification and Calculation of Their Relative Abundance
2.2.3. Genome Binning and Dereplication
2.2.4. Identification, Relative Abundance Calculation and Metabolic Pathway of Halogenated and Dehalogenated MAGs
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
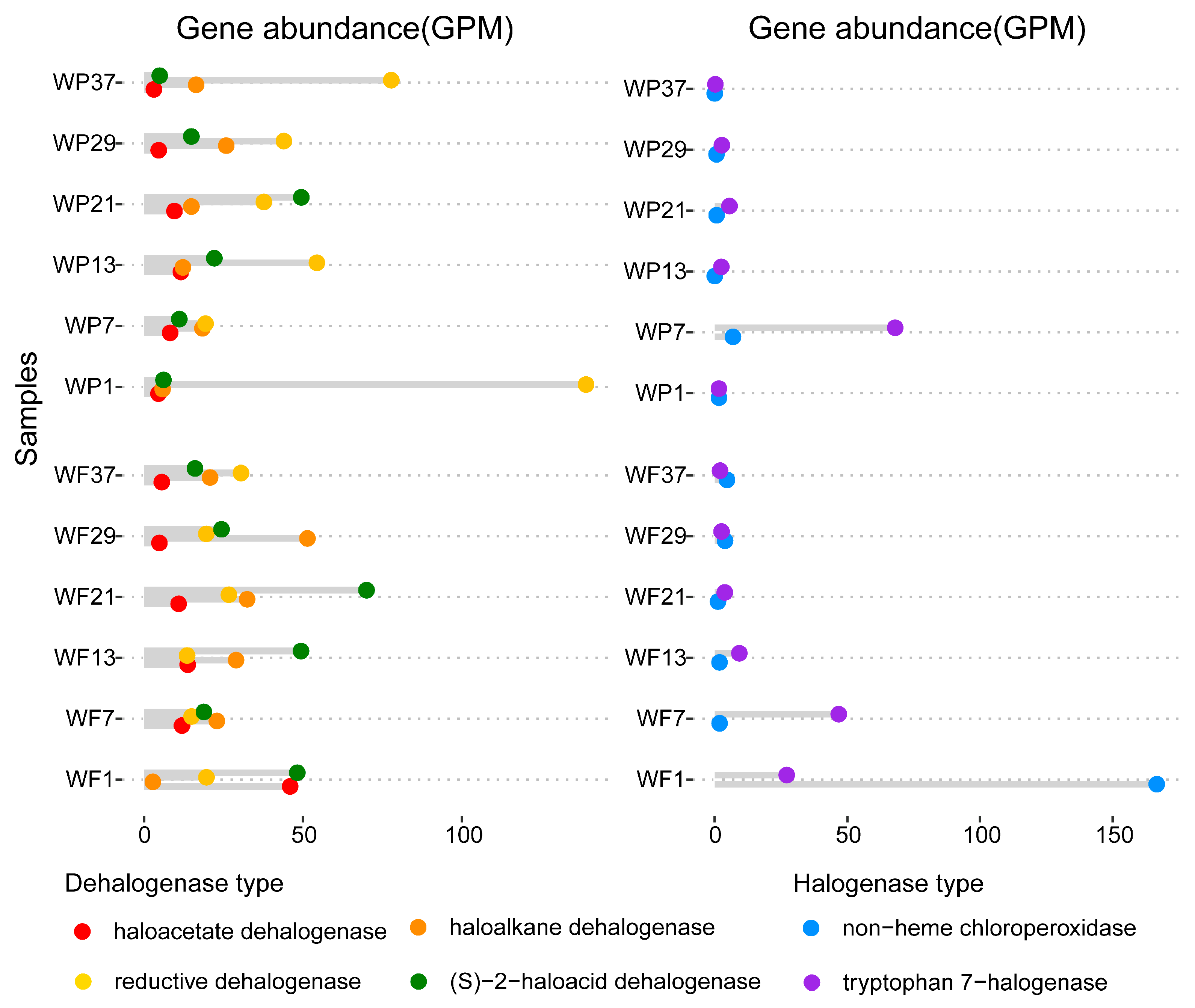
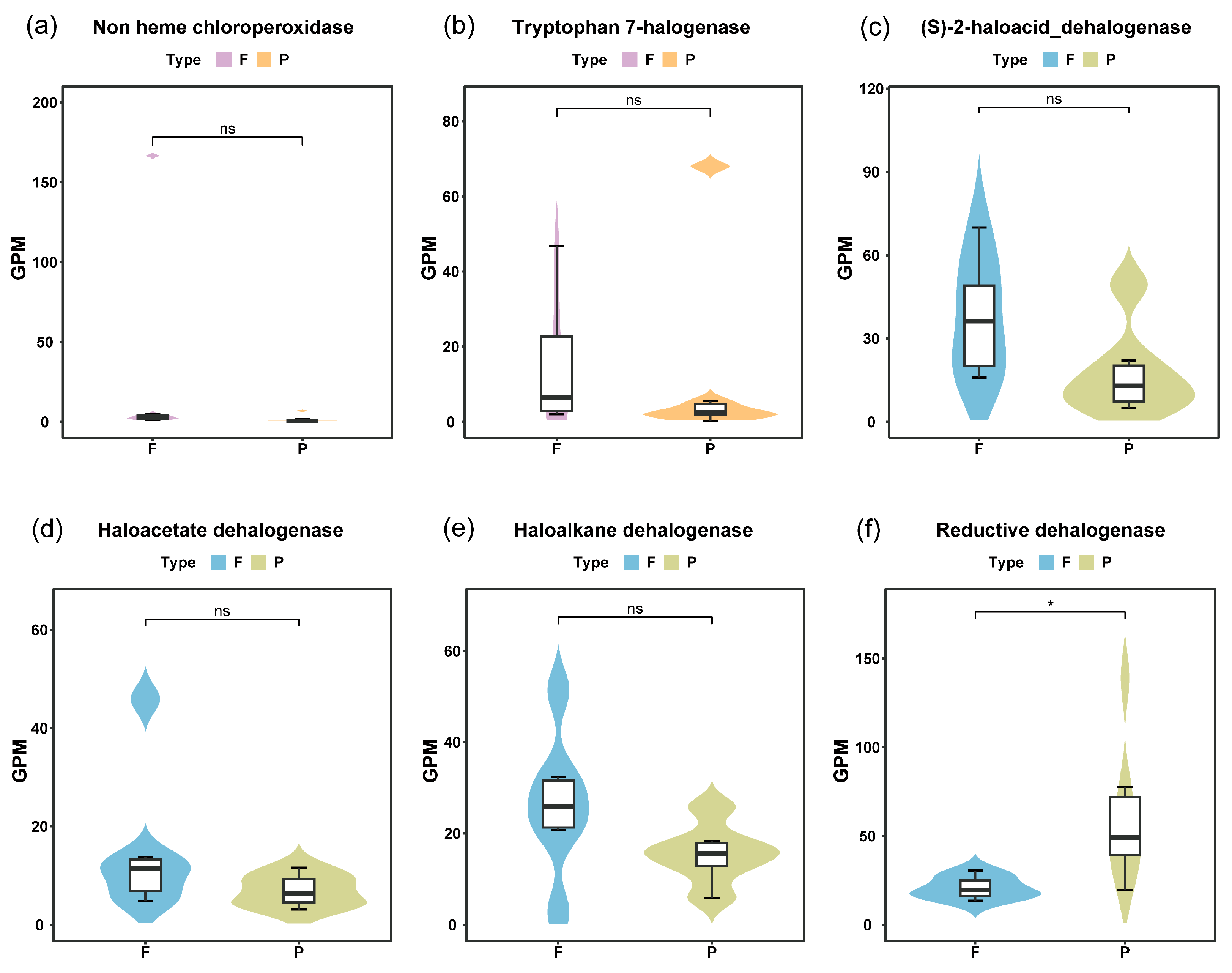
3.1. Relative Abundance of Genes for Dehalogenases and Halogenases in Yangtze River Waters
3.2. MAG Reconstruction and Phylogenomic Analysis of MAGs with Halogenation and Dehalogenation Potential
3.3. Relative Abundance of Halogenating and Dehalogenating Microorganisms
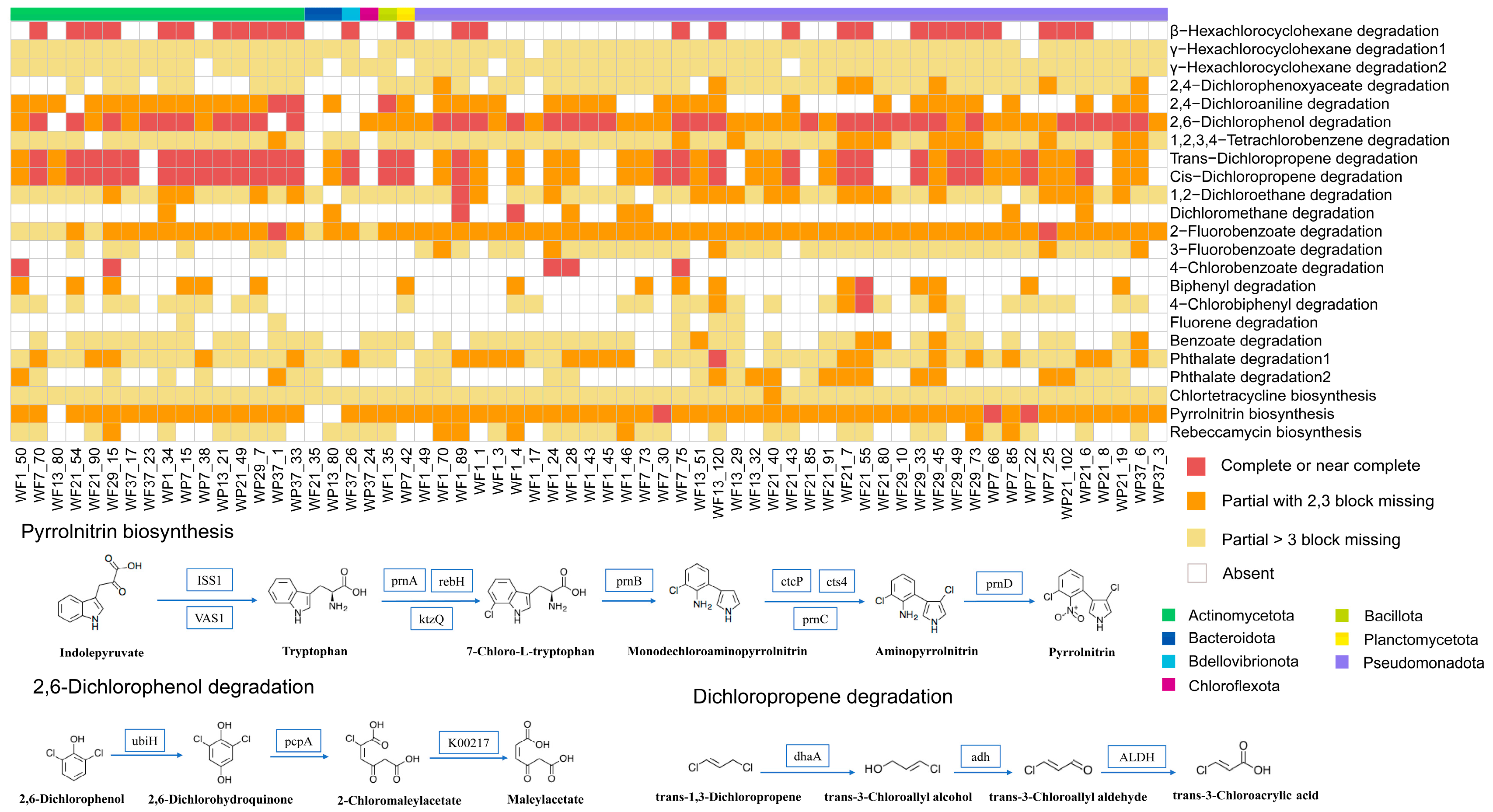
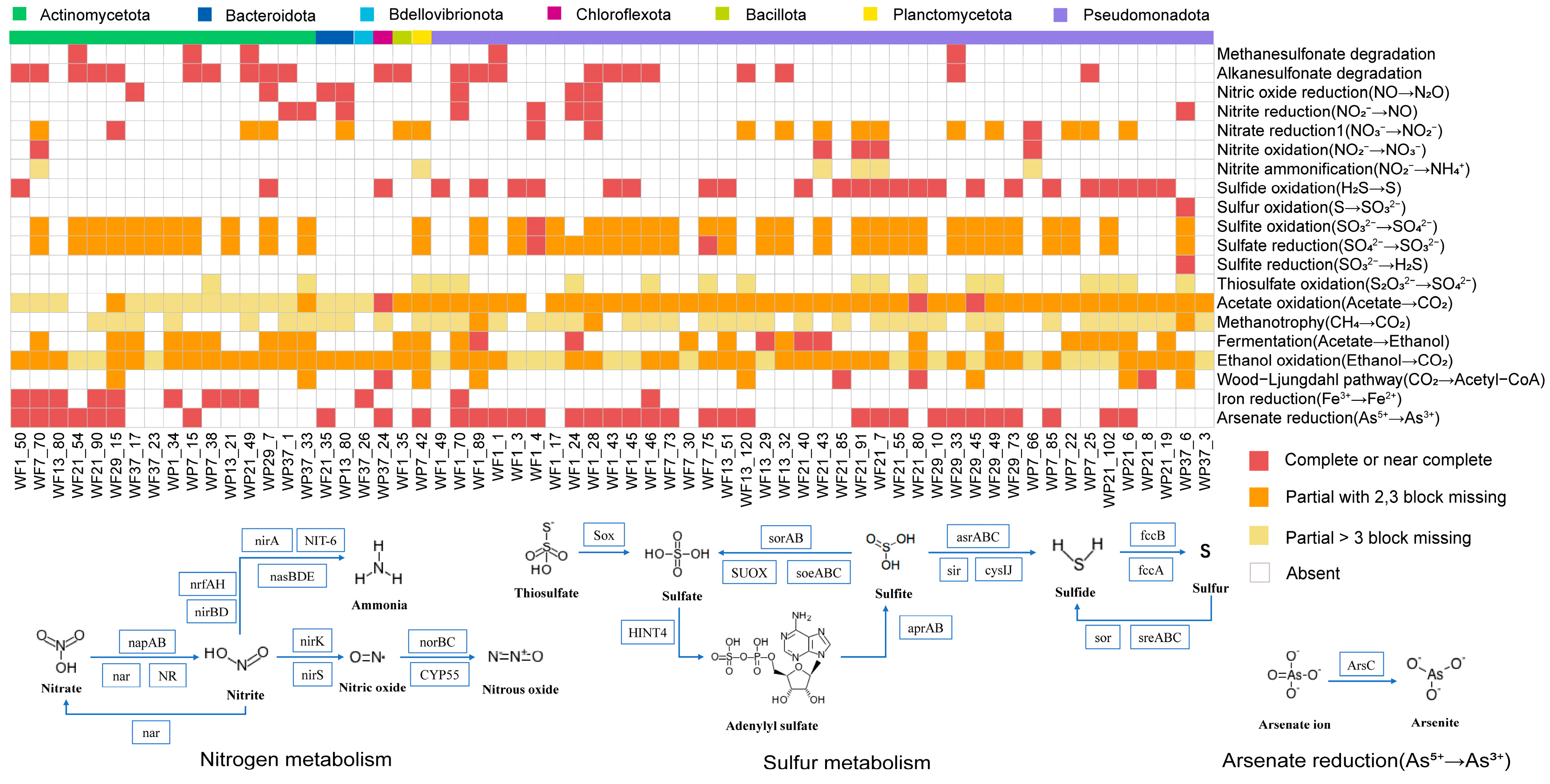
3.4. Metabolic Pathway of Halogenated and Dehalogenated Microorganisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.-Z.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Liang, B.; Li, G.-L.; Chen, T.-H. Halogenated organic contaminants (HOCs) in sediment from a highly eutrophicated lake, China: Occurrence, distribution and mass inventories. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufhold, T.; Schmidt, M.; Cichocka, D.; Nikolausz, M.; Nijenhuis, I. Dehalogenation of diverse halogenated substrates by a highly enriched Dehalococcoides-containing culture derived from the contaminated mega-site in Bitterfeld. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 83, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, E.M.M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Bartrons, M.; Lòpez, J.F.; Camarero, L.; Catalan, J.; Stuchlik, E.; Battarbee, R. Altitudinal Gradients of PBDEs and PCBs in Fish from European High Mountain Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomar, B. Sources of adsorbable organic halogens (AOX) in sludge of Gaza. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssebugere, P.; Sillanpää, M.; Matovu, H.; Mubiru, E. Human and environmental exposure to PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in Africa: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, G.W. A Survey of Recently Discovered Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 1285–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.A. Natural Production of Organohalide Compounds in the Environment. In Organohalide-Respiring Bacteria; Adrian, L., Löffler, F.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 7–29. [Google Scholar]
- Atashgahi, S.; Liebensteiner, M.G.; Janssen, D.B.; Smidt, H.; Stams, A.J.M.; Sipkema, D. Microbial Synthesis and Transformation of Inorganic and Organic Chlorine Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T.; Yoneyama, Y.; Taniai, G.; Kurihara, M.; Tamegai, H.; Hashimoto, S. Methyl halide production by cultures of marine proteobacteria Erythrobacter and Pseudomonas and isolated bacteria from brackish water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, T.P.; Coates, J.D. The biogeochemical cycling of chlorine. Geobiology 2022, 20, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Häggblom, M.M. Genome-Guided Identification of Organohalide-Respiring Deltaproteobacteria from the Marine Environment. mBio 2018, 9, e02471-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wei, X.; Song, W.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Wu, J.; Thomas, T.; Jin, T.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W.; et al. Novel Chloroflexi genomes from the deepest ocean reveal metabolic strategies for the adaptation to deep-sea habitats. Microbiome 2022, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, B.; Berg, M.; Yao, Z.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Ding, W.; Pfluger, A. How polluted is the Yangtze river? Water quality downstream from the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.-C.; Zhang, L.; Ni, J.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Lang, X.-P.; He, Z.; Yang, G.-P. Occurrence of halogenated organic contaminants in surface sediments of the Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent marine area. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Martens, D.; Schramm, K.W.; Kettrup, A.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.S. Polychlorinated organic compounds (PCOCs) in waters, suspended solids and sediments of the Yangtse River. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Yin, J.; Du, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.-Y. Significance of the great protection of the Yangtze River: Riverine input contributes primarily to the presence of PAHs and HMs in its estuary and the adjacent sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzioch, I.; Stoll, C.; Holbach, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, B.; Norra, S.; Bi, Y.; Schramm, K.W.; Tiehm, A. Dechlorination and organohalide-respiring bacteria dynamics in sediment samples of the Yangtze Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7046–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, D.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y. Rare resistome rather than core resistome exhibited higher diversity and risk along the Yangtze River. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A new versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.R.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Niu, B.; Gao, Y.; Fu, L.C.; Li, W. CD-HIT Suite: A web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Ahmad, S.; Alpi, E.; Bowler-Barnett, E.; Britto, R.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; Cukura, A. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.S.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenda, O.; Jácome, L.A.P.; Cao, X.; Nesbø, C.; Tang, S.W.; Morson, N.; Patron, J.; Lomheim, L.; Wishart, D.S.; Edwards, E.A. Insights into origins and function of the unexplored majority of the reductive dehalogenase gene family as a result of genome assembly and ortholog group classification. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham-Quoc, C.; Kieu-Do, B.; Thinh, T.N. An FPGA-Based Seed Extension IP Core for BWA-MEM DNA Alignment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications (ACOMP), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 27–29 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.M.; McCarthy, S.; Davies, R.M. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Zhong, W. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alneberg, J.; Bjarnason, B.S.; Bruijn, I.d.; Schirmer, M.; Quick, J.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Loman, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Quince, C. CONCOCT: Clustering cONtigs on COverage and ComposiTion. arXiv 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, C.M.K.; Probst, A.J.; Sharrar, A.; Thomas, B.C.; Hess, M.; Tringe, S.G.; Banfield, J.F. Recovery of genomes from metagenomes via a dereplication, aggregation and scoring strategy. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olm, M.R.; Brown, C.T.; Brooks, B.; Banfield, J.F. dRep: A tool for fast and accurate genomic comparisons that enables improved genome recovery from metagenomes through de-replication. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing Large Minimum Evolution Trees with Profiles instead of a Distance Matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumeil, P.-A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, C.M.; Petriglieri, F.; Kristensen, J.M.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Michaelsen, T.Y.; Andersen, M.H.; Kondrotaite, Z.; Karst, S.M.; Dueholm, M.S.; Nielsen, P.H. Connecting structure to function with the recovery of over 1000 high-quality metagenome-assembled genomes from activated sludge using long-read sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial Surface Colonization and Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.-F.; Maiangwa, J.; Salleh, A.B.; Normi, Y.M.; Leow, A.T.C. Dehalogenases: From Improved Performance to Potential Microbial Dehalogenation Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, A.; Wahab, R.A.; Aliyu, F.; Aminu, A.H.; Hamza, M.M.; Huyop, F. Haloacid dehalogenases of Rhizobium sp. and related enzymes: Catalytic properties and mechanistic analysis. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashgahi, S.; Häggblom, M.M.; Smidt, H. Organohalide respiration in pristine environments: Implications for the natural halogen cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 20, 934–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Fang, M.; Ma, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. Substantial halogenated organic chemicals stored in permafrost soils on the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.L.; Brooks, M.D.; Boothe, M.A.; Krzmarzick, M.J. Novel bacterial diversity is enriched with chloroperoxidase-reacted organic matter under anaerobic conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floehr, T.; Xiao, H.; Scholz-Starke, B.; Wu, L.; Hou, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, X.; Ji, R.; Yuan, X.; Schäffer, A. Solution by dilution?—A review on the pollution status of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6934–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Luo, C.; Zhang, D.; Cai, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, G. Autochthonous Bioaugmentation-Modified Bacterial Diversity of Phenanthrene Degraders in PAH-Contaminated Wastewater as Revealed by DNA-Stable Isotope Probing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Yan, P.-F.; Mezzari, M.P.; Abriola, L.M.; Pennell, K.D.; Cápiro, N.L. Using Network Analysis and Predictive Functional Analysis to Explore the Fluorotelomer Biotransformation Potential of Soil Microbial Communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 7480–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, T.C.; Gomes, T.S.; Fernandes, C.D.; Barros, F.D.; Oliveira, K.V.; Bilal, M.; Bharagava, R.N.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Hollanda, L.M. Antitumor Microbial Products by Actinomycetes Isolated from Different Environments. In Microbial Technology for Health and Environment; Arora, P.K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 113–160. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.; Das, S. Potential and prospects of Actinobacteria in the bioremediation of environmental pollutants: Cellular mechanisms and genetic regulations. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 273, 127399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, D.C.O.; Dias, G.M.; Castro, M.R.; Tschoeke, D.A.; de Oliveira, F.J.S.; Sérvulo, E.F.C.; Neves, B.C. Exploring the diversity and functional profile of microbial communities of Brazilian soils with high salinity and oil contamination. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, H.; Kaur, J.; Thakur, V.; Dhingra, G.G.; Lal, R. Comprehensive review on Haloalkane dehalogenase (LinB): A β-hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) degrading enzyme. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirner, S.; Hammer, P.E.; Hill, D.S.; Altmann, A.; Fischer, I.; Weislo, L.J.; Lanahan, M.; Pée, K.H.v.; Ligón, J.M. Functions Encoded by Pyrrolnitrin Biosynthetic Genes from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Nan, Z.; Deng, X.; Ma, F.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y. Study of the sorption/desorption behavior of chlortetracycline on sediments in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommerehne, K.; Walisko, J.; Ebersbach, A.; Krull, R. The antitumor antibiotic rebeccamycin—Challenges and advanced approaches in production processes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3627–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.-S.; Wang, G. Genomic Evidence Reveals the Extreme Diversity and Wide Distribution of the Arsenic-Related Genes in Burkholderiales. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fike, D.A.; Bradley, A.S.; Rose, C. Rethinking the Ancient Sulfur Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 43, 593–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Nelson, D.C. Sulfide oxidation in marine sediments: Geochemistry meets microbiology. In Sulfur Biogeochemistry—Past and Present; Amend, J.P., Edwards, K.J., Lyons, T.W., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Aarhus, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Weigold, P.; El-Hadidi, M.; Ruecker, A.; Huson, D.H.; Scholten, T.; Jochmann, M.A.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. A metagenomic-based survey of microbial (de)halogenation potential in a German forest soil. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rua, C.P.J.; de Oliveira, L.S.; Froes, A.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Soares, A.C.; Leomil, L.; Gregoracci, G.B.; Coutinho, R.; Hajdu, E.; Thompson, C.C.; et al. Microbial and Functional Biodiversity Patterns in Sponges that Accumulate Bromopyrrole Alkaloids Suggest Horizontal Gene Transfer of Halogenase Genes. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regeard, C.; Maillard, J.; Dufraigne, C.; Deschavanne, P.; Holliger, C. Indications for Acquisition of Reductive Dehalogenase Genes through Horizontal Gene Transfer by Dehalococcoides ethenogenes Strain 195. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphosa, F.; Lieten, S.H.; Dinkla, I.; Stams, A.J.; Smidt, H.; Fennell, D.E. Ecogenomics of microbial communities in bioremediation of chlorinated contaminated sites. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, R. Halogenation and Dehalogenation Potential of Microorganisms in Yangtze River Waters. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092133
Wang Z, Hu L, Wang L, Liu R. Halogenation and Dehalogenation Potential of Microorganisms in Yangtze River Waters. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092133
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhixuan, Lin Hu, Li Wang, and Rulong Liu. 2025. "Halogenation and Dehalogenation Potential of Microorganisms in Yangtze River Waters" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092133
APA StyleWang, Z., Hu, L., Wang, L., & Liu, R. (2025). Halogenation and Dehalogenation Potential of Microorganisms in Yangtze River Waters. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092133




