Gut Microbiome Alterations in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Findings from the ALBION Greek Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population Sample
2.2. Clinical Assessment
2.3. APOEε4 Status
2.4. Fecal Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Pre-Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
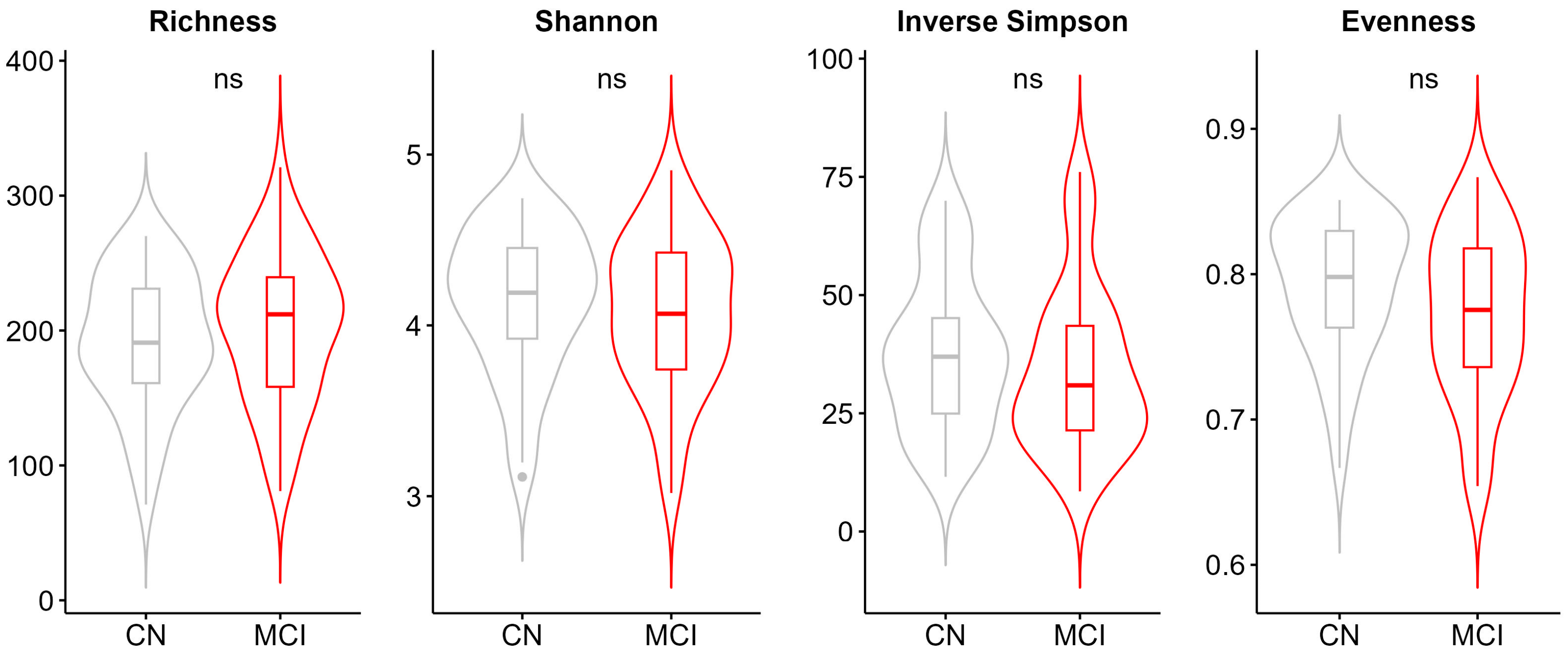
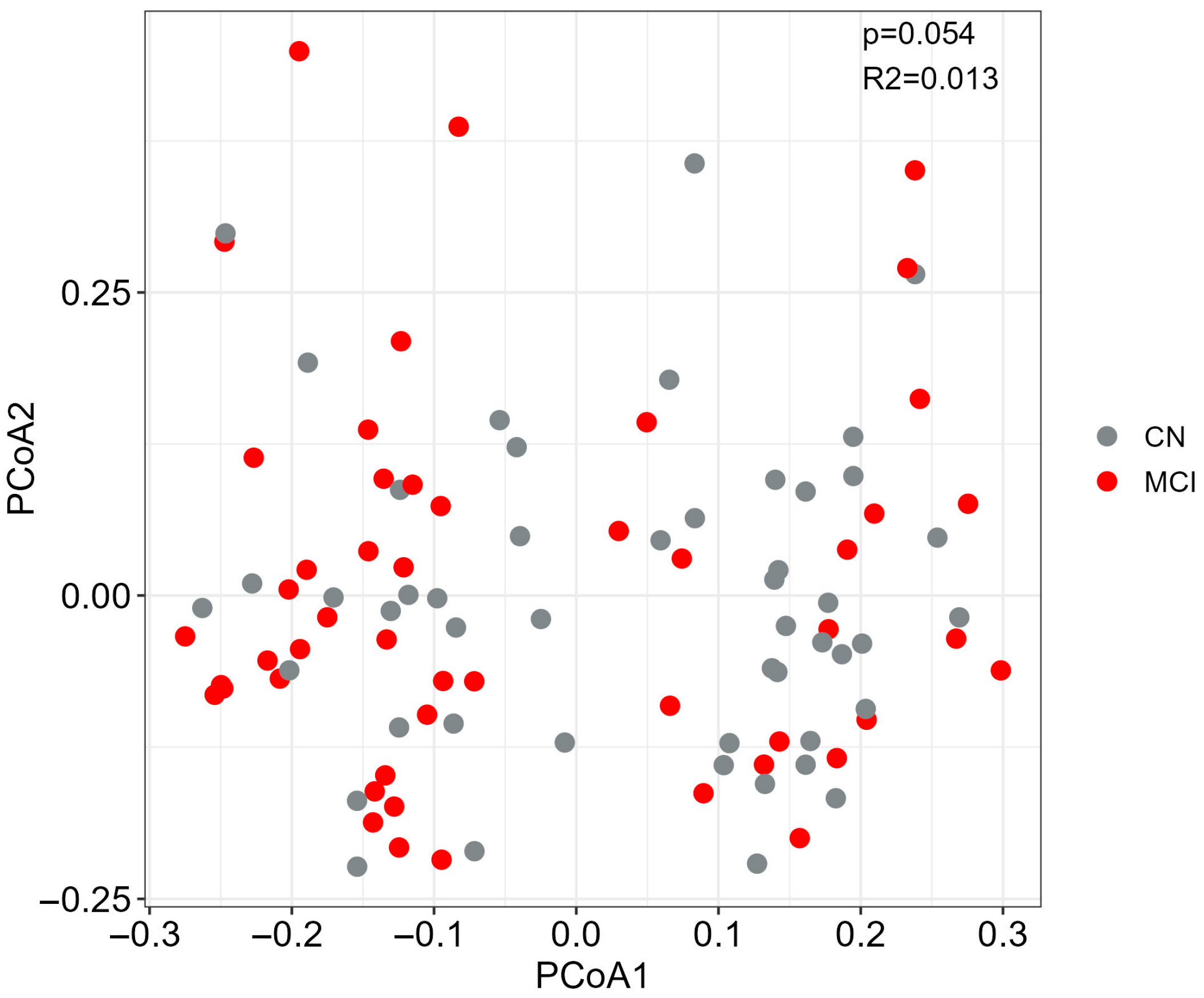
2.6. Alpha and Beta Diversity
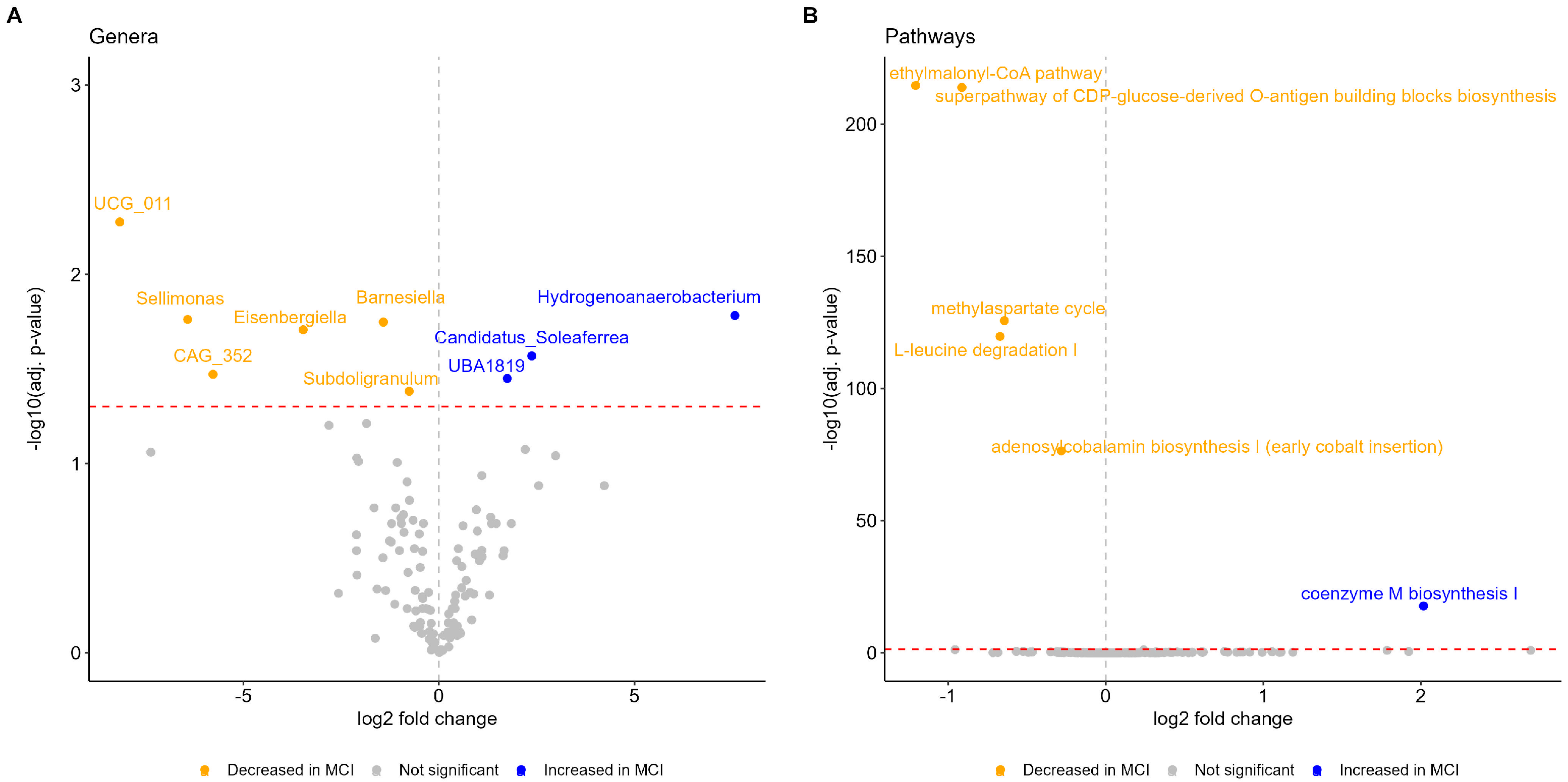
2.7. Differential Abundance Analysis of Genera and of Pathways
2.8. Correlation Between Bacterial Abundance and Covariates
2.9. Discriminatory Capacity of Genera
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics and Global Differences in the Gut Microbiome
3.2. Microbial Alterations in MCI
3.3. Functional Profiles Associated with MCI
3.4. Correlation of Microbiota with Clinical and Demographic Factors
3.5. Discriminative Capacity of Microbiota for MCI Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| CN | Cognitively normal |
| BMI | Body mass index |
References
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chetelat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Fu, S.; Hummel, N.; Qi, L.; Chandak, A.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q. Estimating Transition Probabilities Across the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum Using a Nationally Representative Real-World Database in the United States. Neurol. Ther. 2023, 12, 1235–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, W.K.; Holtzman, D.M. Emerging diagnostics and therapeutics for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2187–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insel, P.S.; Weiner, M.; Mackin, R.S.; Mormino, E.; Lim, Y.Y.; Stomrud, E.; Palmqvist, S.; Masters, C.L.; Maruff, P.T.; Hansson, O.; et al. Determining clinically meaningful decline in preclinical Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2019, 93, e322–e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Q. A Conceptual Framework for Research on Cognitive Impairment with No Dementia in Memory Clinic. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2020, 17, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; Touchon, J.; Vellas, B. Mild cognitive impairment: A nosological entity? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2003, 16 (Suppl. S2), S43–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.D.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment [RETIRED]: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepsell, T.D.; Monsell, S.E. Reversion from mild cognitive impairment to normal or near-normal cognition: Risk factors and prognosis. Neurology 2012, 79, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Villarraso, J.; Galvan, A.; Escribano, B.M.; Tunez, I. Interrelationships Among Gut Microbiota and Host: Paradigms, Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Future Prospects. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 945–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Sisodia, S.S.; Vassar, R.J. The gut microbiome in Alzheimer’s disease: What we know and what remains to be explored. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Ke, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, F.; et al. Metagenomic analysis characterizes stage-specific gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, 30, 3951–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; Khatib, L.A.; Heston, M.B.; Dilmore, A.H.; Labus, J.S.; Deming, Y.; Schimmel, L.; Blach, C.; McDonald, D.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Gut microbiome compositional and functional features associate with Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 21, e70417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L., IV; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Hendriksen, H.M.A.; de Leeuw, F.A.; Doorduijn, A.S.; van Leeuwenstijn, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Kraaij, R.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to AD Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 794519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Y. Multi-omics analyses identify gut microbiota-fecal metabolites-brain-cognition pathways in the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabrucker, S.; Marizzoni, M.; Silajdžić, E.; Lopizzo, N.; Mombelli, E.; Nicolas, S.; Dohm-Hansen, S.; Scassellati, C.; Moretti, D.V.; Rosa, M.; et al. Microbiota from Alzheimer’s patients induce deficits in cognition and hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain 2023, 146, 4916–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Martone, A.M.; Liperoti, R.; Cipriani, M.C.; Ibba, F.; Camilli, S.; Rognoni, F.M.; Landi, F.; Montalto, M. Mild cognitive impairment and microbiota: What is known and future perspectives. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1410246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chiu, Y.L.; Koh, S.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Chuang, Y.F. Compositional and functional gut microbiota alterations in mild cognitive impairment: Links to Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Wang, J.; Darzi, Y.; Faust, K.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Vandeputte, D.; et al. Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation. Science 2016, 352, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschasaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Attaye, I.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J.; et al. Depicting the composition of gut microbiota in a population with varied ethnic origins but shared geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdill, R.J.; Graham, S.P.; Rubinetti, V.; Ahmadian, M.; Hicks, P.; Chetty, A.; McDonald, D.; Ferretti, P.; Gibbons, E.; Rossi, M.; et al. Integration of 168,000 samples reveals global patterns of the human gut microbiome. Cell 2025, 188, 1100–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.C.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chao, Y.P.; Lai, Y.J.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chuang, Y.F. Altered gut microbiota in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A case-control study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1162057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, G.; Byun, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, D.; Park, H.; Lee, D.Y.; Group, K.R. Gut microbiome alterations in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exarchos, T.P.; Skolariki, K.; Mahairaki, V.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Vlamos, P.; Scarmeas, N.; Dardiotis, E.; On Behalf of The Hellenic Initiative Against Alzheimer’s Disease. Geographic Distribution and Future Projections of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Greece: Analysis from 1991 to 2050. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavandegar, A.; Heidarzadeh, A.; Angoorani, P.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Larijani, B.; Qorbani, M. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet can beneficially affect the gut microbiota composition: A systematic review. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalligerou, F.; Ntanasi, E.; Voskou, P.; Velonakis, G.; Karavasilis, E.; Mamalaki, E.; Kyrozis, A.; Sigala, E.; Economou, N.T.; Patas, K.; et al. Aiginition Longitudinal Biomarker Investigation Of Neurodegeneration (ALBION): Study design, cohort description, and preliminary data. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Daskalaki, A.; Kalligerou, F.; Ntanasi, E.; Mamalaki, E.; Gargalionis, A.N.; Patas, K.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Yannakoulia, M.; Constantinides, V.C. Initial Data and a Clinical Diagnosis Transition for the Aiginition Longitudinal Biomarker Investigation of Neurodegeneration (ALBION) Study. Medicina 2022, 58, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H., Jr.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Smailagic, N.; Roque-Figuls, M.; Ciapponi, A.; Sanchez-Perez, E.; Giannakou, A.; Pedraza, O.L.; Bonfill Cosp, X.; Cullum, S. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the early detection of dementia in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 7, CD010783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mioshi, E.; Dawson, K.; Mitchell, J.; Arnold, R.; Hodges, J.R. The Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised (ACE-R): A brief cognitive test battery for dementia screening. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, C.A.; Yannakoulia, M.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Sakka, P.; Arampatzi, X.; Bougea, A.; Labropoulos, I.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean diet and cognitive health: Initial results from the Hellenic Longitudinal Investigation of Ageing and Diet. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Doody, R.; Kurz, A.; Mohs, R.C.; Morris, J.C.; Rabins, P.V.; Ritchie, K.; Rossor, M.; Thal, L.; Winblad, B. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampatakakis, S.N.; Mamalaki, E.; Ntanasi, E.; Kalligerou, F.; Liampas, I.; Yannakoulia, M.; Gargalionis, A.N.; Scarmeas, N. Objective Physical Function in the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum: Association with Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in the ALBION Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data [Online]. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Kaller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo Lahti Shetty, S. Tools for Microbiome Analysis in R. 2017. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/microbiome.html (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Oksanen, J.S.G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.S.M.; Szoecs, E.; Wagner, H.; Barbour, M.; et al. Community Ecology Package R Package Version 2.6-4. 2022. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Lotfi, F.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Heidarian, P.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Fazeli, J.; Najafi, H.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in geriatric population with emphasis on influential factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, C.E. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1978, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.; Pun, M.D.; Wise, C.E.; Streit, B.R.; Mus, F.; Berim, A.; Kincannon, W.M.; Islam, A.; Partovi, S.E.; Gang, D.R.; et al. The pathway for coenzyme M biosynthesis in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207190119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, A.I.; Zhu, F.; Knox, N.; Forbes, J.D.; Van Domselaar, G.; Bernstein, C.N.; Graham, M.; Marrie, R.A.; Hart, J.; Yeh, E.A.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of the Pediatric-Onset Multiple Sclerosis Gut Microbiome. Neurology 2022, 98, e1050–e1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, A.A.; Grimm, H.S.; Apel, B.; Golobrodska, N.; Kruse, L.; Ratanski, E.; Schulten, N.; Schwarze, L.; Slawik, T.; Sperlich, S.; et al. Mechanistic Link Between Vitamin B12 and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Peng, J.; Huang, X.; Xiao, L.; Huang, F.; Zuo, Z. Gut Microbiome Features of Chinese Patients Newly Diagnosed with Alzheimer’s Disease or Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 80, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, P.; Du, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Tang, H.; Chen, S. Mild cognitive impairment has similar alterations as Alzheimer’s disease in gut microbiota. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Dong, X. Hydrogenoanaerobacterium saccharovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from H2-producing UASB granules. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59 Pt 2, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.J.; Lee, J.; Shin, N.R.; Kim, M.S.; Hyun, D.W.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, P.S.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Chronic Repression of mTOR Complex 2 Induces Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Sui, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J. Alteration of the fecal microbiota in North-Eastern Han Chinese population with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 707, 134297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Nie, K. Gut Microbiota Altered in Mild Cognitive Impairment Compared with Normal Cognition in Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Huang, X. The causal relationship between gut microbiota and type 2 diabetes: A two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1255059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Roh, H.W.; Ly, M.; Kolobaric, A.; Aizenstein, H.; Andreescu, C.; Jasarevic, E.; Pascoal, T.A.; Ferreira, P.C.L.; et al. Brain age mediates gut microbiome dysbiosis-related cognition in older adults. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachamo, S.; Gaultier, A. The emerging role of microbiota derived SCFAs in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2025, 46, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.O.; O’Donnell, D.; Jain, N.; Ulrich, J.D.; Herz, J.; Li, Y.; Lemieux, M.; Cheng, J.; Hu, H.; Serrano, J.R.; et al. ApoE isoform- and microbiota-dependent progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Science 2023, 379, eadd1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.H.; Xie, R.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Chen, S.D.; Tang, H.D. Mechanisms of Short-Chain Fatty Acids Derived from Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.X.; Jiao, B.; Liao, X.X.; Guo, L.N.; Yuan, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tang, B.S.; Shen, L. Analysis of Salivary Microbiome in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, D.; Engen, P.A.; Villanueva, M.; Raeisi, S.; Ramirez, V.; Naqib, A.; Green, S.J.; Bishehsari, F.; Barnes, L.L.; Keshavarzian, A.; et al. Oral microbiome brain axis and cognitive performance in older adults. npj Dement. 2025, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, F.; Yildirim, S.; Arikan, M.; Garcia-Guevara, F.; Hanoglu, L.; Yilmaz, N.H.; Sen, A.; Celik, H.K.; Neslihan, A.A.; Demir, T.K.; et al. Microbiome signatures of virulence in the oral-gut-brain axis influence Parkinson’s disease and cognitive decline pathophysiology. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2506843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Meslier, V.; Bidkhori, G.; Garcia-Guevara, F.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Clasen, F.; Park, J.; Plaza Onate, F.; Cai, H.; Le Chatelier, E.; et al. Transient colonizing microbes promote gut dysbiosis and functional impairment. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, S.; Boman, M. Predictive models for clinical decision making: Deep dives in practical machine learning. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, A.L.; Choi, J.; Ryou, J.; Newcomer, E.P.; Thompson, R.; Bollinger, R.M.; Hall-Moore, C.; Ndao, I.M.; Sax, L.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; et al. Gut microbiome composition may be an indicator of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabo2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CN | MCI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (% of total) | 49 (49.5) | 50 (50.5) | |
| Female (%) | 34 (69.4) | 31 (62) | 0.4390 |
| Age (yrs) | 62.7 (8.6); [42; 84] | 68 (9.8); [41; 81] | 0.0007 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.9 (4); [19.8; 37.9] | 27.6 (4.9); [14.9; 45.5] | 0.3272 |
| ApoEε4 carriers (%) | 13 of 38 genotyped (34.2) | 8 of 31 genotyped (25.8) | 0.45045 |
| Smokers (%) | 16 (32.7) | 23 (46) | 0.1742 |
| Alcohol consumption (%) | 1 (2) | 3 (6) | 0.3172 |
| Medical history of diabetes (%) | 3 (6.1) | 8 (16) | 0.1179 |
| Medical history of hypertension (%) | 11 (22.4) | 27 (54) | 0.0012 |
| Medical history of dyslipidemia (%) | 17 (34.7) | 23 (46) | 0.2518 |
| Sequencing platform, MiSeq (%) | 30 (61.2) | 20 (40) | 0.0347 |
| Cognitive assessment | |||
| MMSE score | 29 (1.5); [22; 30] | 27.3 (2); [23; 30] | <0.0001 |
| ACE score | 94.9 (3.2); [88; 100] | 86.3 (7.67); [61; 99] | <0.0001 |
| Composite Z score | 0.2 (0.4); [−0.9; 0.9) | −0.8 (0.9); [−3.8; 0.6) | <0.0001 |
| Z-memory | 0.2 (0.6); [−1.3; 1.1] | −1.2 (1.2); [−4.1; 1.2] | <0.0001 |
| Z-attention | 0.2 (0.8); [−2.1; 2] | −0.9 (1.3); [−5.8; 1.1] | <0.0001 |
| Z-executive | 0.2 (0.6); [−1.6; 1.5] | −0.7 (0.8); [−3.5; 0.5] | <0.0001 |
| Z-language | 0.2 (0.5); [−1.1; 1.1] | −0.7 (1.3); [−7.2; 0.5] | <0.0001 |
| Z-visuospatial | 0.2 (0.5); [−0.9; 0.7] | −0.5 (2.2); [−12.7; 0.7] | 0.0516 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rouskas, K.; Mamalaki, E.; Ntanasi, E.; Pantoura, M.; Anezaki, M.; Emmanouil, C.; Novau-Ferré, N.; Bulló, M.; Dimas, A.S.; Papandreou, C.; et al. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Findings from the ALBION Greek Cohort. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092112
Rouskas K, Mamalaki E, Ntanasi E, Pantoura M, Anezaki M, Emmanouil C, Novau-Ferré N, Bulló M, Dimas AS, Papandreou C, et al. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Findings from the ALBION Greek Cohort. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092112
Chicago/Turabian StyleRouskas, Konstantinos, Eirini Mamalaki, Eva Ntanasi, Marianna Pantoura, Maria Anezaki, Christina Emmanouil, Nil Novau-Ferré, Mònica Bulló, Antigone S. Dimas, Christopher Papandreou, and et al. 2025. "Gut Microbiome Alterations in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Findings from the ALBION Greek Cohort" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092112
APA StyleRouskas, K., Mamalaki, E., Ntanasi, E., Pantoura, M., Anezaki, M., Emmanouil, C., Novau-Ferré, N., Bulló, M., Dimas, A. S., Papandreou, C., Yannakoulia, M., Argiriou, A., & Scarmeas, N. (2025). Gut Microbiome Alterations in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Findings from the ALBION Greek Cohort. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092112


_Di_Marco.png)





