Modulation of Gut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota in Fibromyalgia Patients Following a Carb-Free Oloproteic Diet: Evidence for Candida Suppression and Symptom Improvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Dietary Intervention
2.3. Fecal Sample Collection and Storage
2.4. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
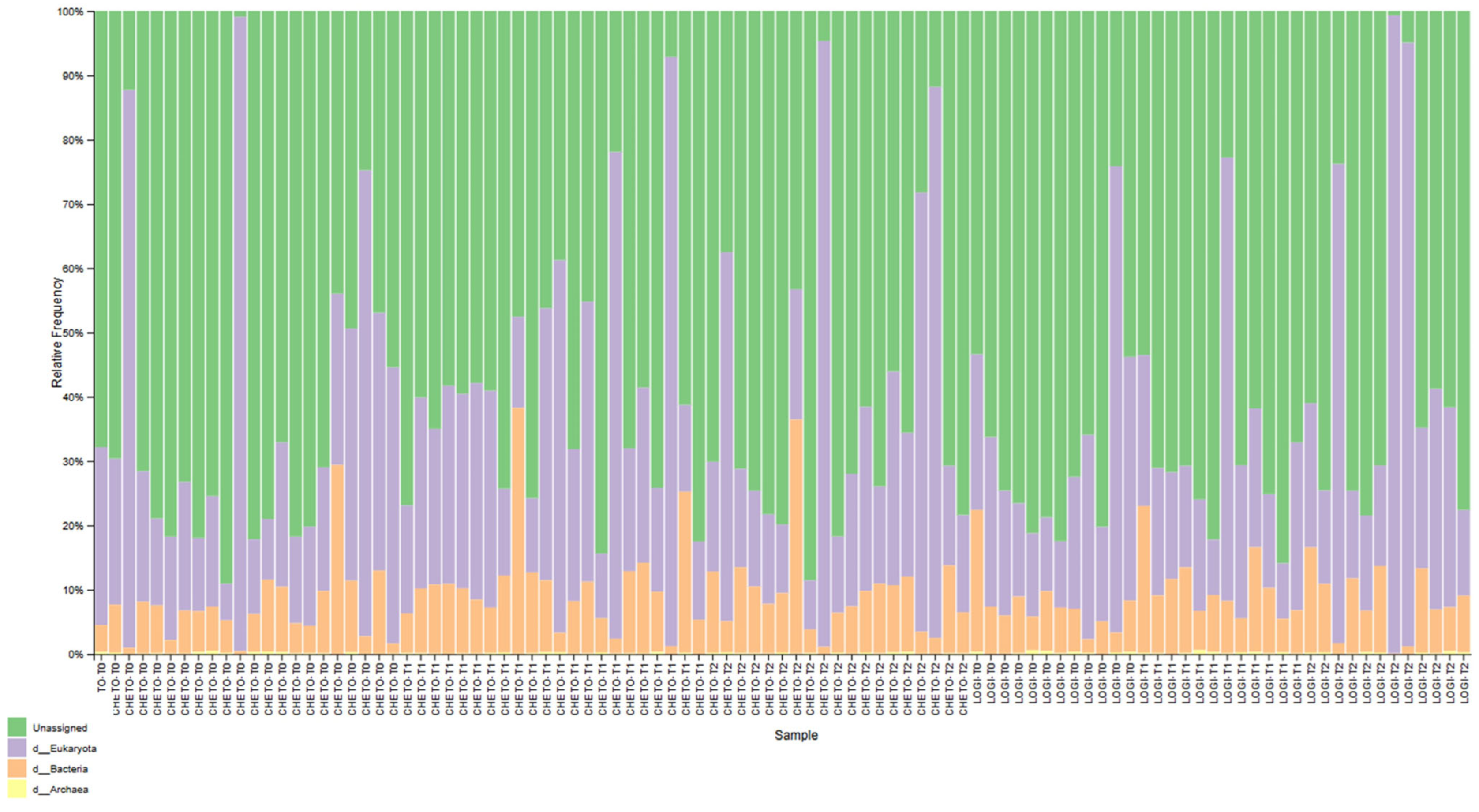
3.1. Gut Microbiota Dynamics Across Dietary Interventions
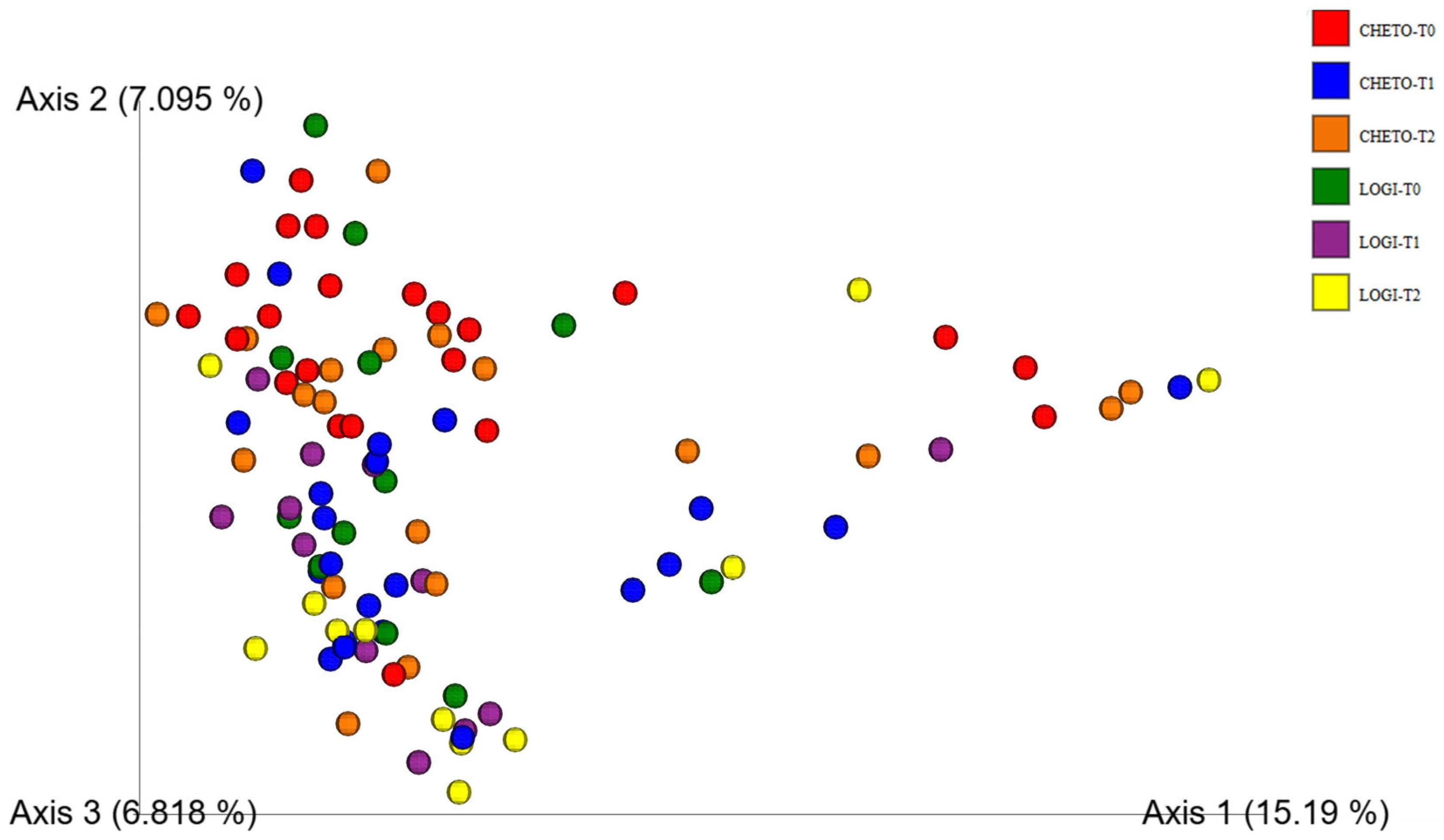
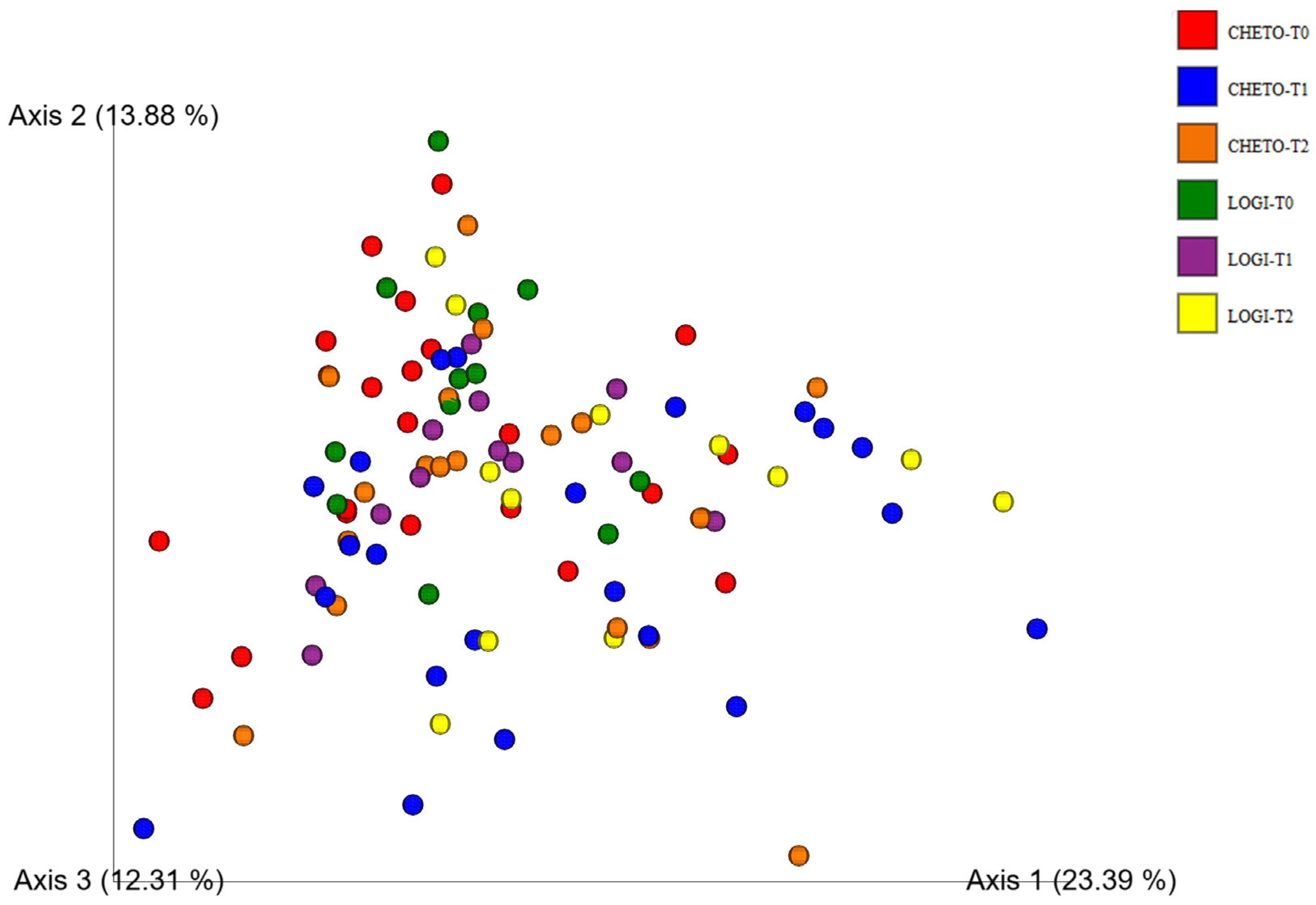
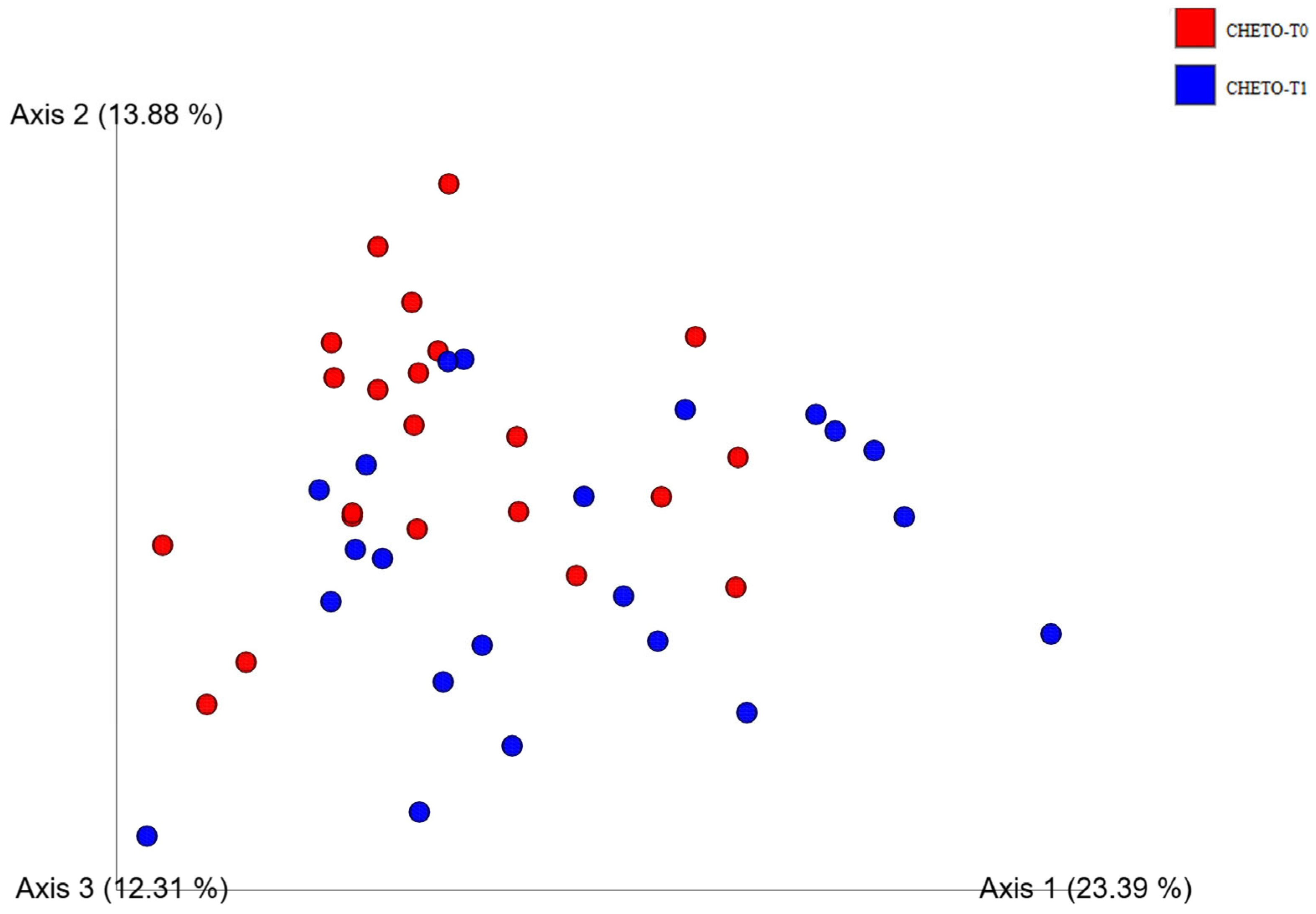
3.2. Beta-Diversity and Community Structure Shifts
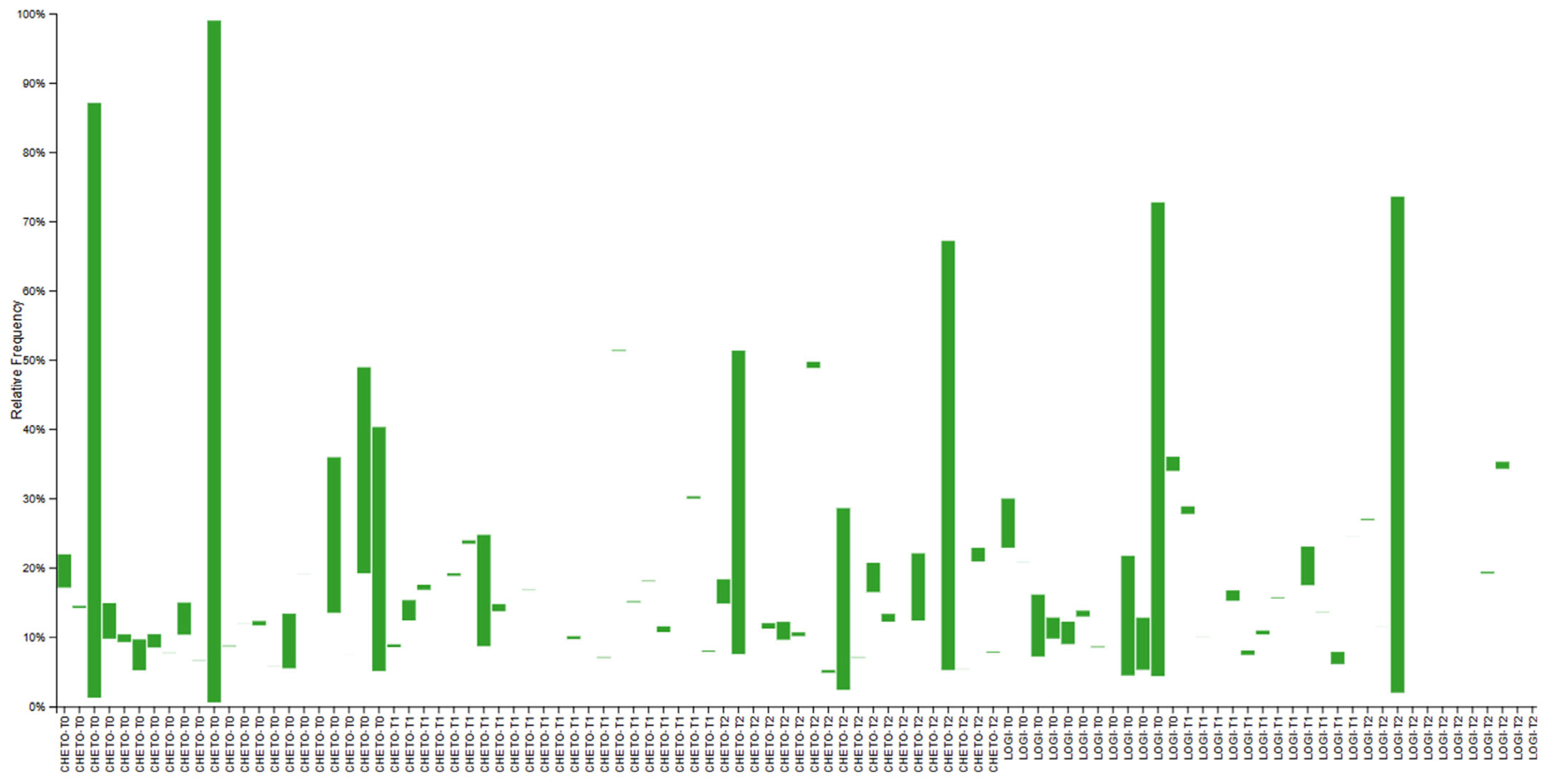
3.3. Eukaryotic Microbiome Complexity
3.4. Enhanced Beta-Diversity Resolution with Updated Analysis
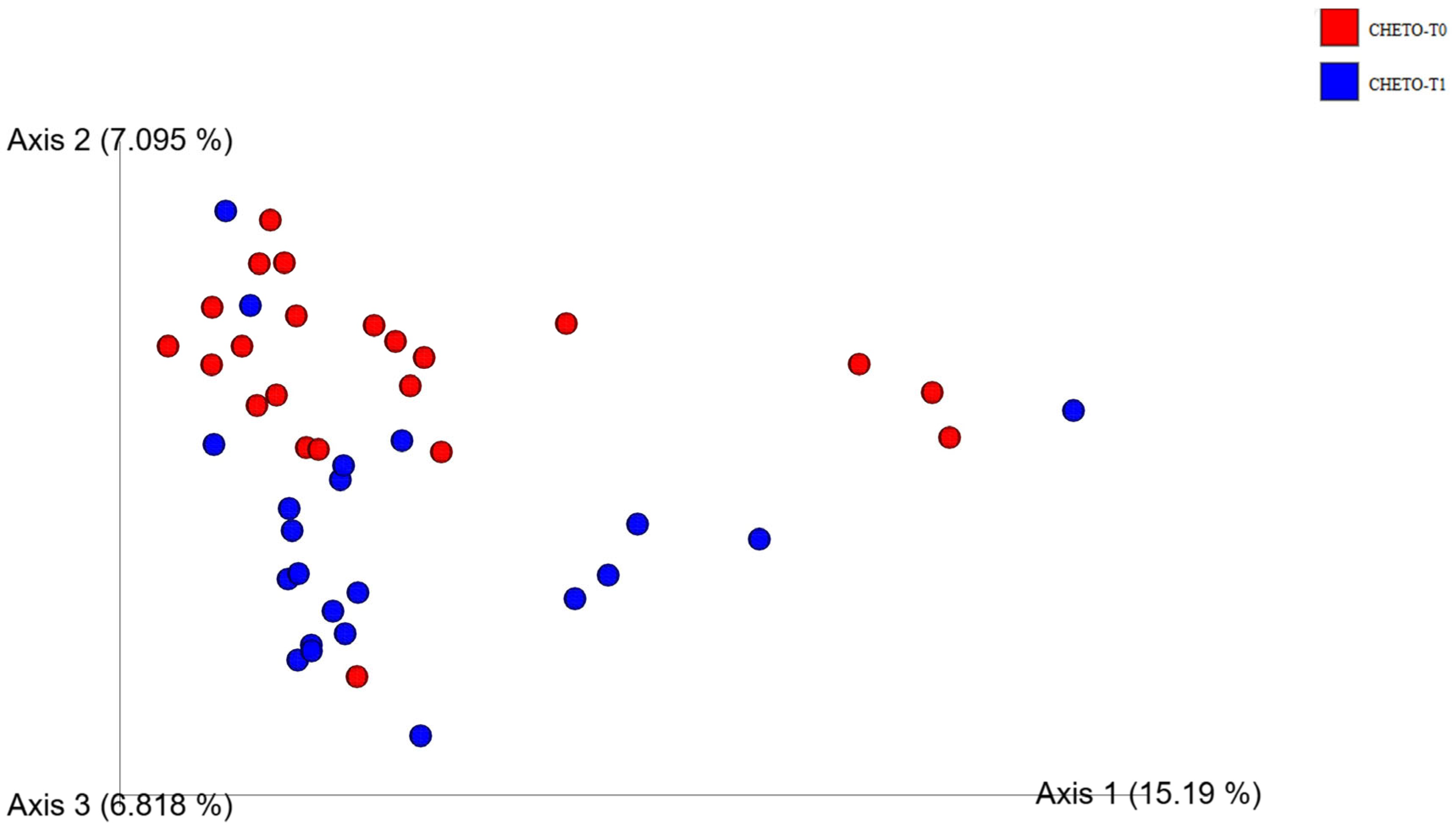
3.5. Distinct Clustering Following Oloproteic Diet in FM1
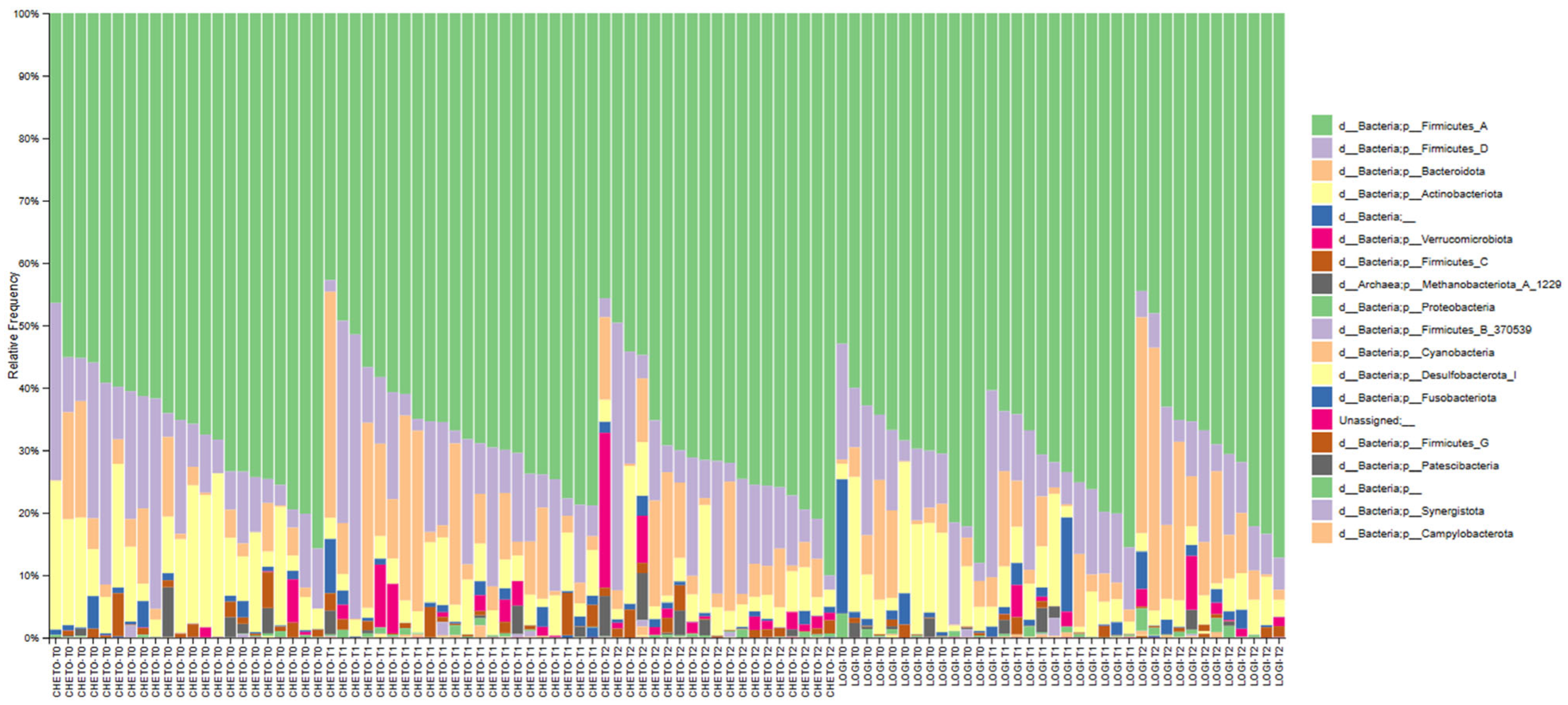
3.6. Phylum-Level Compositional Changes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freidin, M.B.; Stalteri, M.A.; Wells, P.M.; Lachance, G.; Baleanu, A.-F.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Zhernakova, A.; Steves, C.J.; Williams, F.M.K. An Association between Chronic Widespread Pain and the Gut Microbiome. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3727–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.H.S. The Role of Sleep in Pain and Fibromyalgia. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; Paola, R.D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Impellizzeri, D. Fibromyalgia: Pathogenesis, Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Priego, L.N.; Cueto-Ureña, C.; Ramírez-Expósito, M.J.; Martínez-Martos, J.M. Fibromyalgia: A Review of the Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Multidisciplinary Treatment Strategies. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imane, E.B.; Salma, B.; Samira, R.; Hajar, E.A.; Salma, Z.; Bouchra, A.; Rachid, B. Insights into Diagnosis and Treatment of Fibromyalgia among Moroccan Rheumatologists: A Cross Sectional Online Survey. Reumatologia 2025, 63, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; El-Mowafy, M.; Elgaml, A.; Ahmed, T.A.E.; Hassan, H.; Mottawea, W. Metabolic Influences of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 715506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunrinola, G.A.; Oyewale, J.O.; Oshamika, O.O.; Olasehinde, G.I. The Human Microbiome and Its Impacts on Health. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8045646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minerbi, A.; Khoutorsky, A.; Shir, Y. Decoding the Connection: Unraveling the Role of Gut Microbiome in Fibromyalgia. Pain Rep. 2025, 10, e1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdrich, S.; Hawrelak, J.A.; Myers, S.P.; Vuyisich, M.; Harnett, J.E. Investigating the Association between the Symptoms of Women with Fibromyalgia, Digestive Function, and Markers of the Microbiota of the Gastrointestinal Tract (The FIDGIT Study): Study Protocol. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudes, M.; Geisler, C.; Rohmann, N.; Bouwman, J.; Pischon, T.; Schlicht, K. Microbiota in Health and Disease—Potential Clinical Applications. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Schwerk, C.; Schroten, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Schubert, R.; Lehrnbecher, T.; Rudolph, H. Hyphal Penetration Is the Major Pathway of Translocation of Candida Albicans across the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 2025, 22, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Queiroz, K. Breaking Barriers: Candidalysin Disrupts Epithelial Integrity and Induces Inflammation in a Gut-on-Chip Model. Toxins 2025, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumwenda, P.; Cottier, F.; Hendry, A.C.; Kneafsey, D.; Keevan, B.; Gallagher, H.; Tsai, H.-J.; Hall, R.A. Estrogen Promotes Innate Immune Evasion of Candida Albicans through Inactivation of the Alternative Complement System. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, D.; Klose, P.; Lauche, R.; Dobos, G.; Langhorst, J.; Cramer, H. Low Fermentable, Oligo-, Di-, Mono-Saccharides and Polyol Diet in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrition 2018, 45, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, S.; Putignani, L.; Del Chierico, F. The Impact of Low-FODMAPs, Gluten-Free, and Ketogenic Diets on Gut Microbiota Modulation in Pathological Conditions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, G.; Muscaritoli, M. Clinical Perspective of Low Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diets: A Narrative Review Samir. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 642628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, J.; Peacock, C.A.; Ellerbroek, A.; Fromhoff, B.; Silver, T. The effects of consuming a high protein diet (4.4 g/kg/d) on body composition in resistance-trained individuals. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, M.-P.; Bosarge, A. Weight-Loss Diet That Includes Consumption of Medium-Chain Triacylglycerol Oil Leads to a Greater Rate of Weight and Fat Mass Loss than Does Olive Oil. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerford, K.B.; Drewnowski, A.; Papanikolaou, Y.; Jones, J.M.; Slavin, J.; Angadi, S.S.; Rodriguez, J. Application of a New Carbohydrate Food Quality Scoring System: An Expert Panel Report. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, S.L.D.; Vilhena Da Silva, R.D.C.; Macarini, A.F.; Cechinel Filho, V.; De Souza, P. Prolonged Diuretic, Natriuretic, and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Rats. Plants 2025, 14, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, C.T.; Denniston, K.; Chopra, D. Therapeutic Uses of Triphala in Ayurvedic Medicine. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2017, 23, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, G.; Marino, C.; D’Elia, M.; Grimaldi, M.; Napolitano, E.; D’Ursi, A.M.; Rastrelli, L. The Effectiveness of the Low-Glycemic and Insulinemic (LOGI) Regimen in Maintaining the Benefits of the VLCKD in Fibromyalgia Patients. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Jia, Q.; Ding, G.; Wu, X.; Yang, M. Low-Glycemic Index Diets as an Intervention in Metabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerontiti, E.; Shalit, A.; Stefanaki, K.; Kazakou, P.; Karagiannakis, D.S.; Peppa, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Paschou, S.A. The Role of Low Glycemic Index and Load Diets in Medical Nutrition Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes: An Update. Hormones 2024, 23, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacciani-Mori, L.; Giometto, A.; Suweis, S.; Maritan, A. Dynamic Metabolic Adaptation Can Promote Species Coexistence in Competitive Microbial Communities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, W.; Lorenzo, M.B.; Cintoni, M.; Porcari, S.; Rinninella, E.; Kaitsas, F.; Lener, E.; Mele, M.C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty-Acid-Producing Bacteria: Key Components of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability, and Systemic Inflammation: A Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rew, L.; Harris, M.D.; Goldie, J. The Ketogenic Diet: Its Impact on Human Gut Microbiota and Potential Consequent Health Outcomes: A Systematic Literature Review. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2022, 15, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gong, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X. Ketogenic Diet and Gut Microbiota: Exploring New Perspectives on Cognition and Mood. Foods 2025, 14, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, B.F.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.S.A.; Zeydabadinejad, S.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Yeoh, B.S.; Saha, P. Gut Feelings: How Microbes, Diet, and Host Immunity Shape Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milajerdi, A.; Saneei, P.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. The Effect of Dietary Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load on Inflammatory Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapko, J.; Juzbašić, M.; Matijević, T.; Pustijanac, E.; Bekić, S.; Kotris, I.; Škrlec, I. Candida Albicans-The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Pacheco, J.; Alves, R.; Costa-Barbosa, A.; Cerqueira-Rodrigues, B.; Pereira-Silva, P.; Paiva, S.; Silva, S.; Henriques, M.; Pais, C.; Sampaio, P. The Role of Candida Albicans Transcription Factor RLM1 in Response to Carbon Adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttar, J.; Kon, E.; Lee, A.; Kaur, G.; Lunken, G. Effect of Diet on the Gut Mycobiome and Potential Implications in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2399360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliev, I.D.; Leonardi, I. Fungal Dysbiosis: Immunity and Interactions at Mucosal Barriers. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dujaili, E.A.S.; Ashmore, S.; Tsang, C. A Short Study Exploring the Effect of the Glycaemic Index of the Diet on Energy Intake and Salivary Steroid Hormones. Nutrients 2019, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xie, L.; Chen, W.; Qin, J.; Zhang, J.; Lei, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Xue, S.; Liang, X.; et al. Dynamics of the Gut Bacteria and Fungi Accompanying Low-Carbohydrate Diet-Induced Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Adults. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 846378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Wu, A.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; et al. The Nutritional Significance of Intestinal Fungi: Alteration of Dietary Carbohydrate Composition Triggers Colonic Fungal Community Shifts in a Pig Model. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00038-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, A.C.; Katzman, M.A.; Balanzá-Martínez, V. Natural Environments, Ancestral Diets, and Microbial Ecology: Is There a Modern “Paleo-Deficit Disorder”? Part II. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2015, 34, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijašić, M.; Meštrović, T.; Paljetak, H.Č.; Perić, M.; Barešić, A.; Verbanac, D. Gut Microbiota beyond Bacteria-Mycobiome, Virome, Archaeome, and Eukaryotic Parasites in IBD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Sarkar, A.; McSkimming, D.I. Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytriv, T.R.; Storey, K.B.; Lushchak, V.I. Intestinal Barrier Permeability: The Influence of Gut Microbiota, Nutrition, and Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1380713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castaldo, G.; D’Elia, M.; De Prisco, M.; Folliero, V.; Marino, C.; D’Ursi, A.; Franci, G.; Rastrelli, L. Modulation of Gut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota in Fibromyalgia Patients Following a Carb-Free Oloproteic Diet: Evidence for Candida Suppression and Symptom Improvement. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092069
Castaldo G, D’Elia M, De Prisco M, Folliero V, Marino C, D’Ursi A, Franci G, Rastrelli L. Modulation of Gut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota in Fibromyalgia Patients Following a Carb-Free Oloproteic Diet: Evidence for Candida Suppression and Symptom Improvement. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092069
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastaldo, Giuseppe, Maria D’Elia, Mariagrazia De Prisco, Veronica Folliero, Carmen Marino, Annamaria D’Ursi, Gianluigi Franci, and Luca Rastrelli. 2025. "Modulation of Gut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota in Fibromyalgia Patients Following a Carb-Free Oloproteic Diet: Evidence for Candida Suppression and Symptom Improvement" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092069
APA StyleCastaldo, G., D’Elia, M., De Prisco, M., Folliero, V., Marino, C., D’Ursi, A., Franci, G., & Rastrelli, L. (2025). Modulation of Gut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota in Fibromyalgia Patients Following a Carb-Free Oloproteic Diet: Evidence for Candida Suppression and Symptom Improvement. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092069









