Ecological Health and Freshwater Pathogen Using eDNA Metabarcoding: A Preliminary Assessment for Environmental Surveillance Development in Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
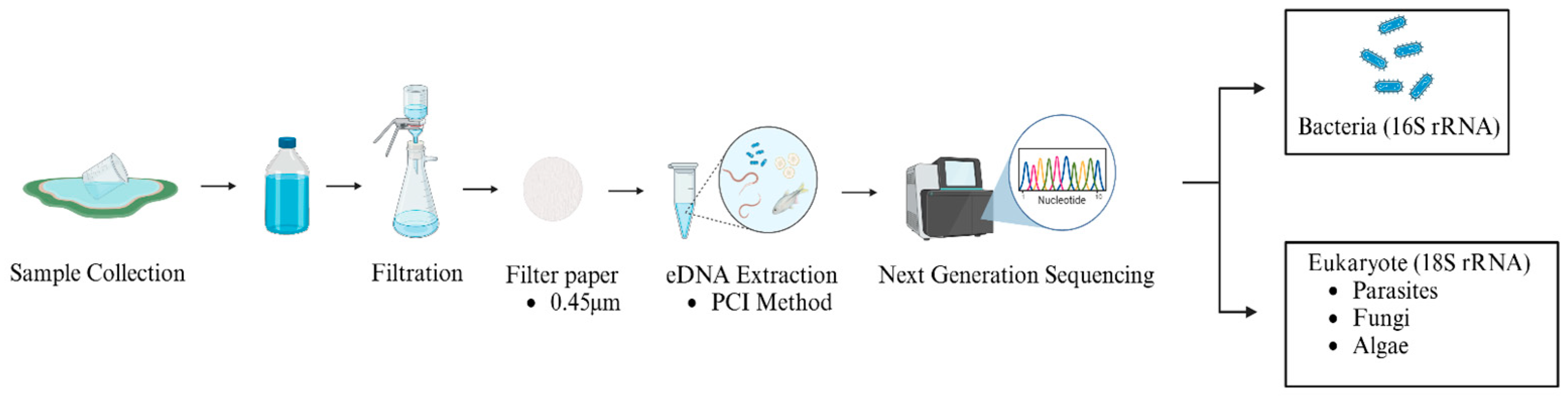
2.2. Extraction of eDNA
2.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
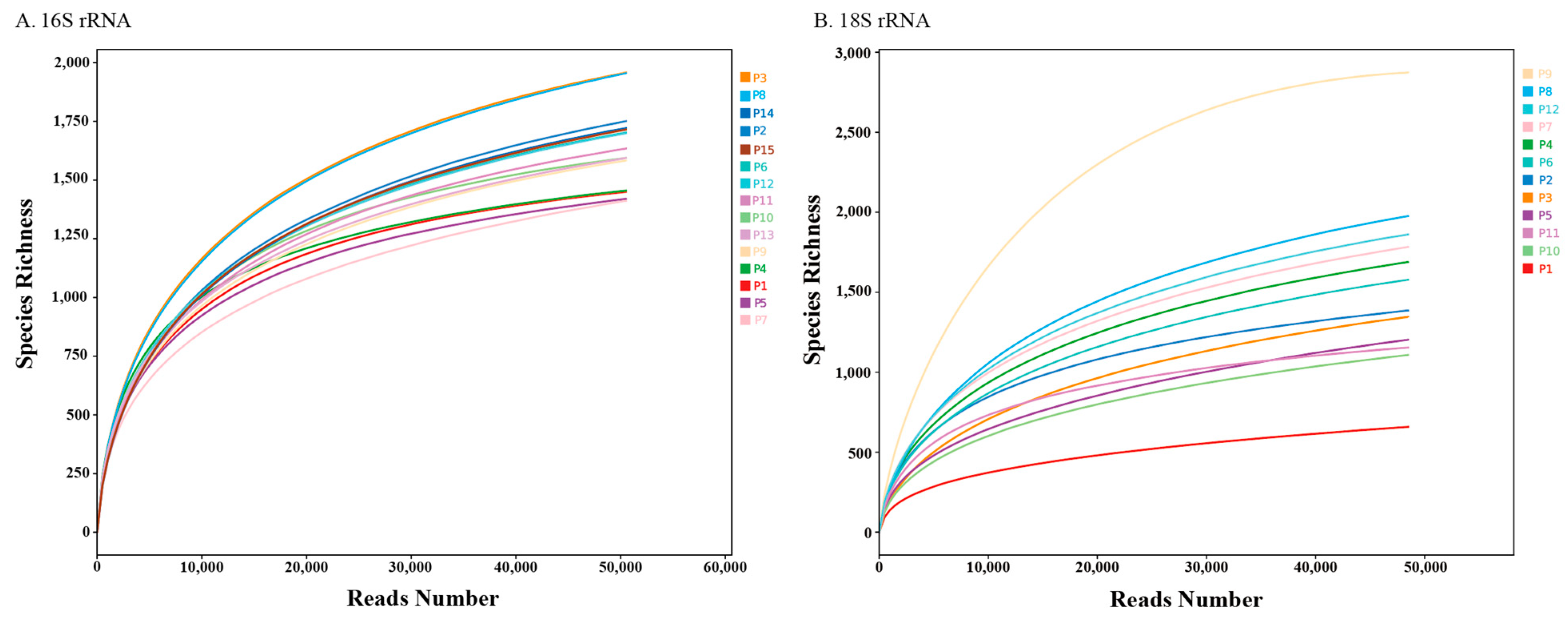
3.1. Illumina MiSeq Data Supports Sufficient Microbial Diversity Analysis
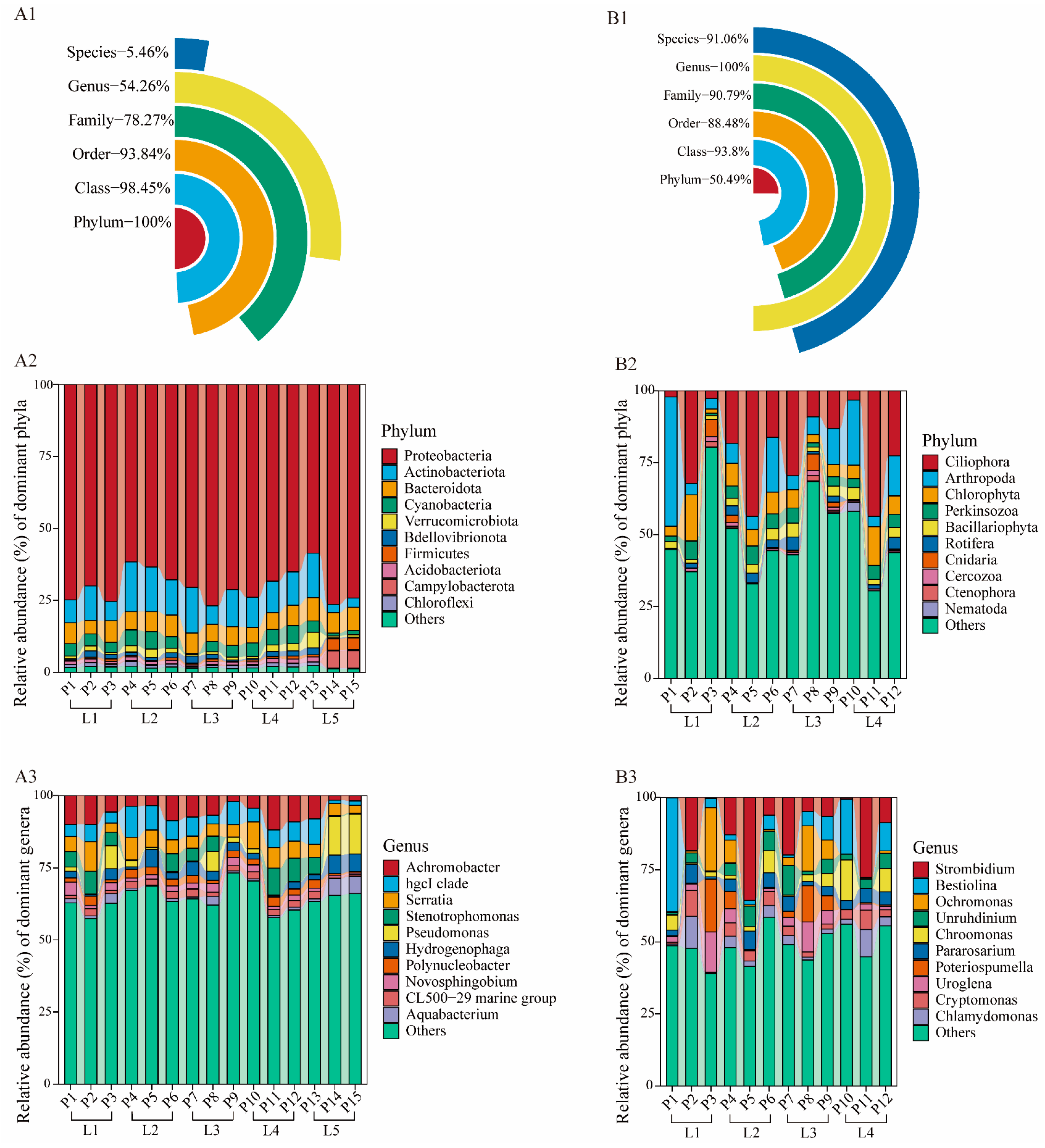
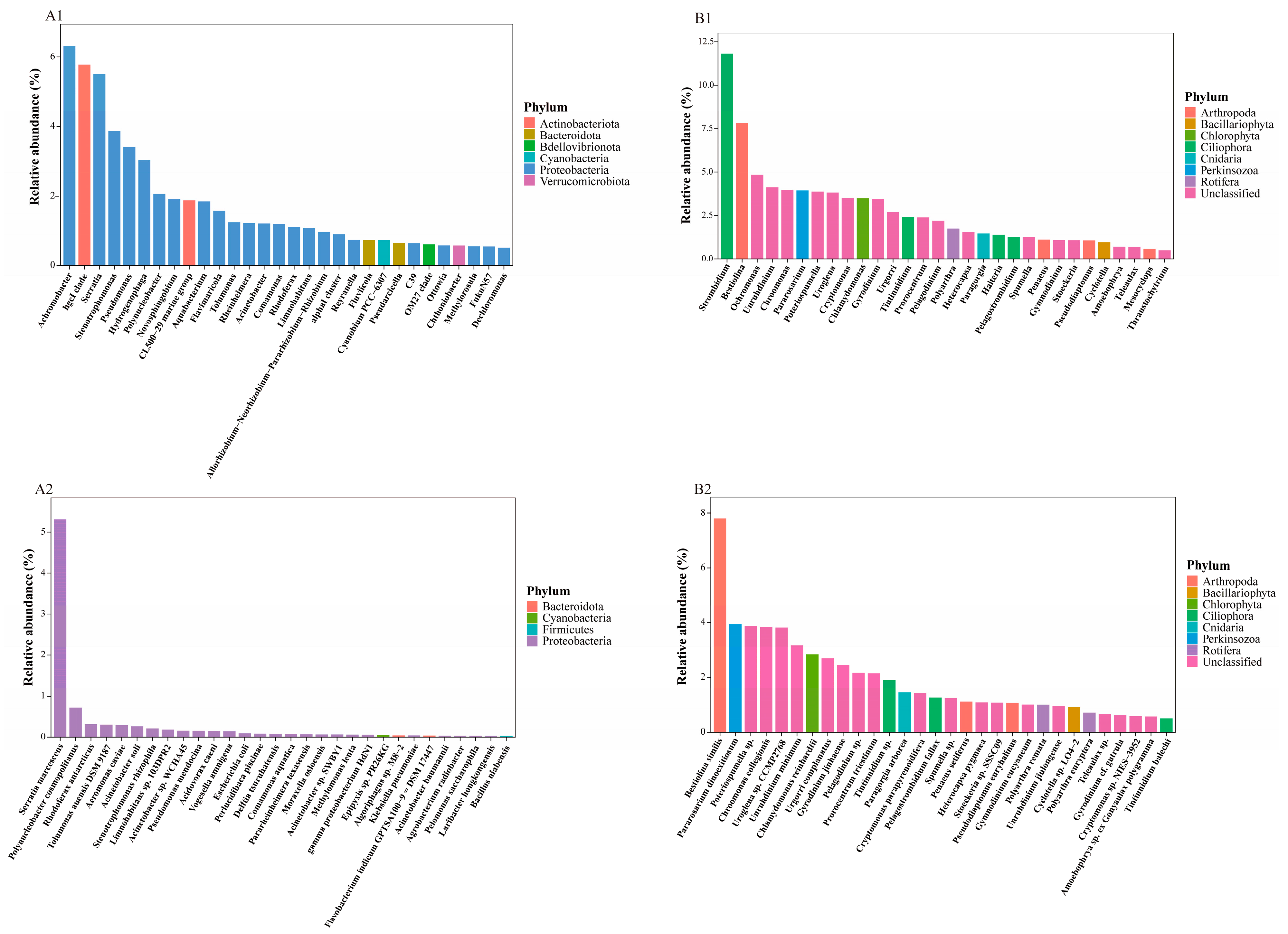
3.2. Taxonomic Composition of eDNA Metabarcoding Data
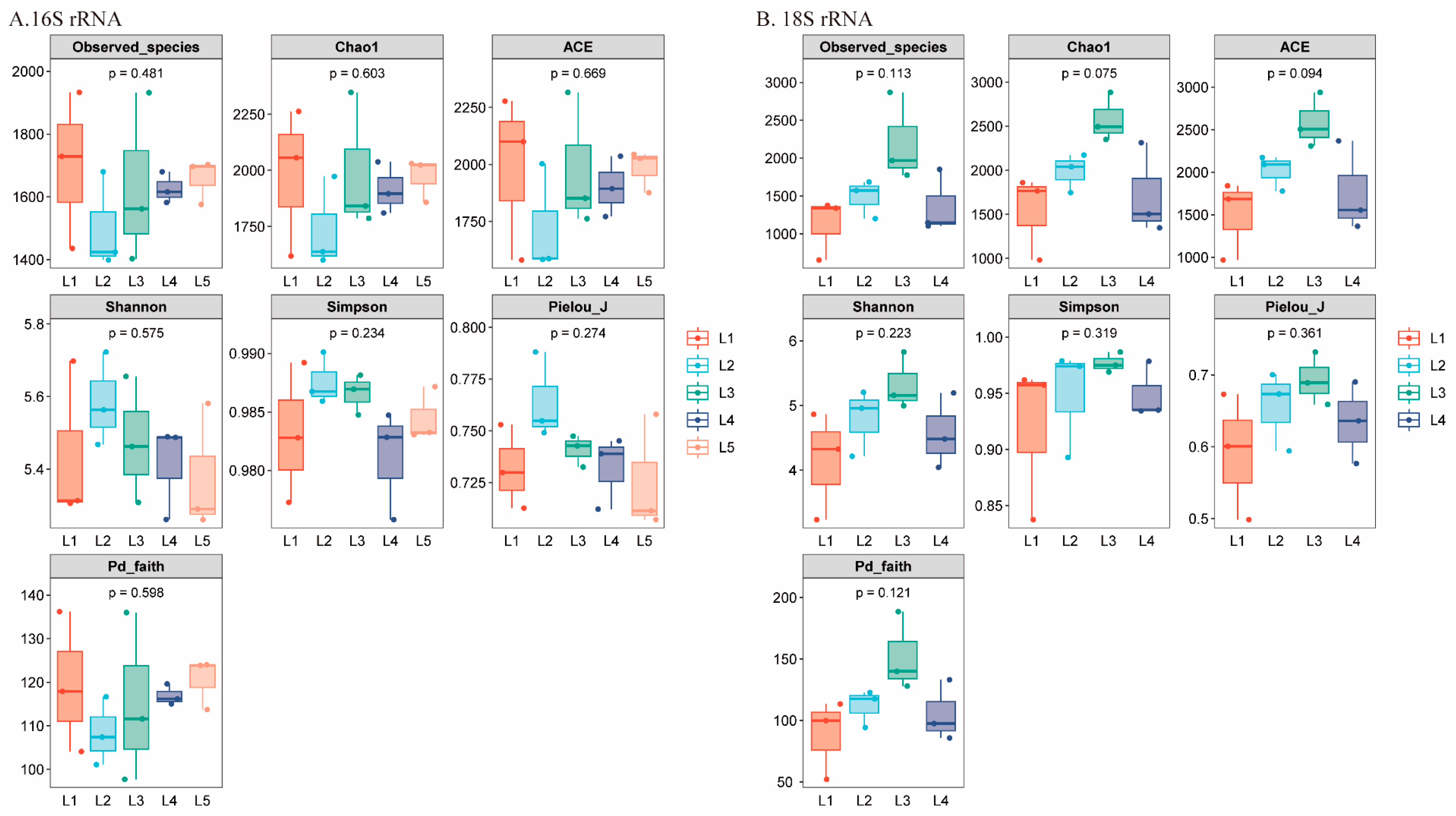
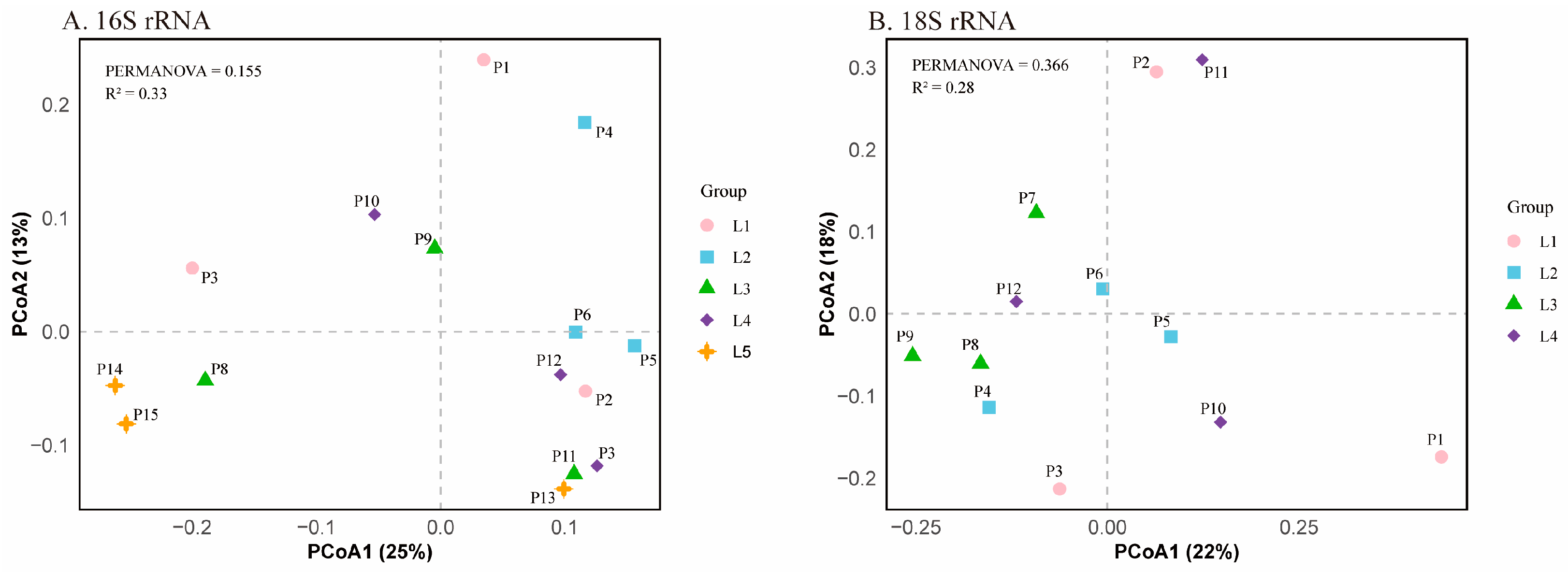
3.3. Comparison of Biodiversity Between River Samples
3.3.1. Alpha Diversity
3.3.2. Beta Diversity
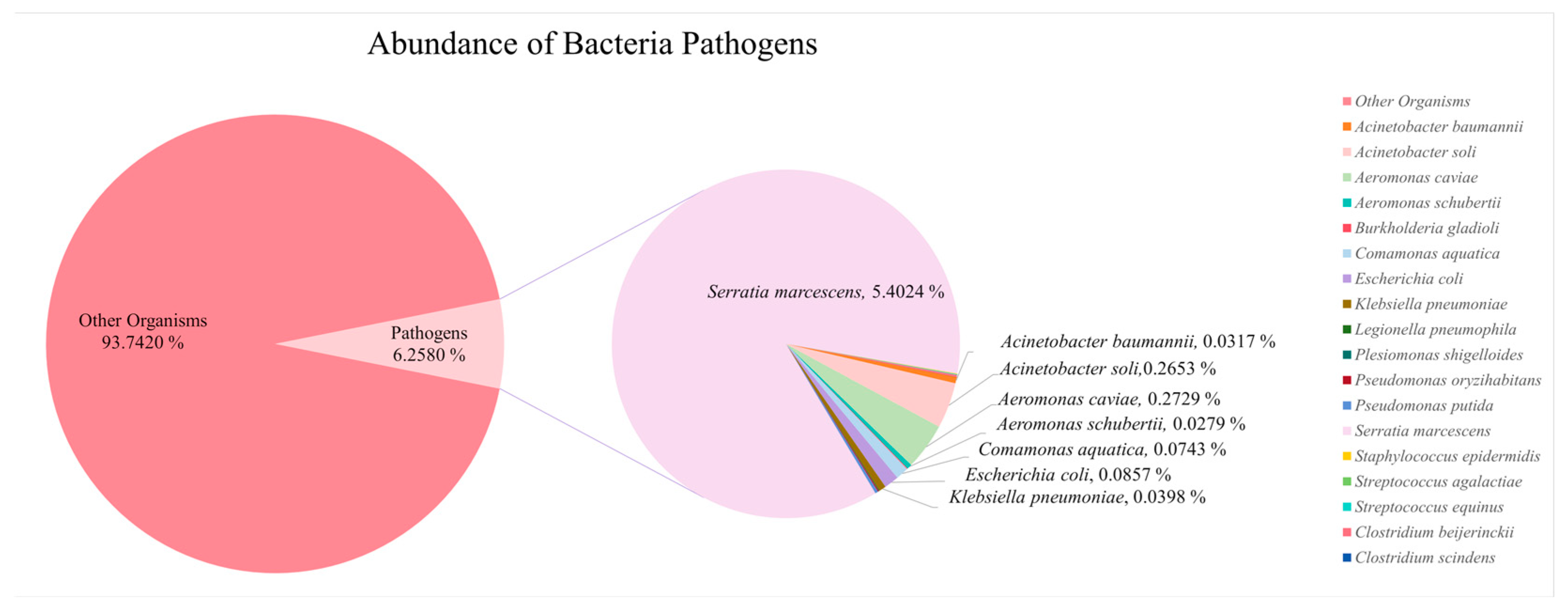
3.4. Diversity of Potential Pathogens in Perak River
| No. | Phylum | Organism | Abundance of Reads | Host | Diseases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pseudomonadota | Acinetobacter baumannii | 268 | Humans | Ventilator-associated pneumonia, blood stream infections, urinary tract infections and meningitis | [46,47,48] |
| 2 | Pseudomonadota | Acinetobacter soli | 2242 | Humans | Bacteremia | [49,50,51] |
| 3 | Pseudomonadota | Aeromonas caviae | 2306 | Aquatic animals such as Micropterus salmoides, Clarias gariepinus | Decaying and reddening of the body surface, mass deaths, visceral congestion and hepatocellular necrosis | [52,53] |
| Humans | Pneumonia, primary bacteremia and biliary tract infections | [54] | ||||
| 4 | Pseudomonadota | Aeromonas schubertii | 236 | Aquatic animals such as Channa striata, Oreochromis niloticus | Near-death state, hemorrhage, white nodules on the liver and inflammation in the organs | [55,56] |
| 5 | Pseudomonadota | Burkholderia gladioli | 38 | Plants | Plant tissue decay | [57] |
| Humans | Pulmonary infection and systemic abscesses (patient with Cystic Fibrosis) | [57,58] | ||||
| Animals | N/A | [57,59] | ||||
| 6 | Pseudomonadota | Comamonas aquatica | 628 | Humans | Bacteremia and septic shock | [60] |
| Labeo rohita | Tail and fin rot | [61] | ||||
| 7 | Pseudomonadota | Escherichia coli | 724 | Humans | Bacteremia, hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), watery and/or bloody diarrhea, and colitis | [62,63] |
| 8 | Pseudomonadota | Klebsiella pneumoniae | 336 | Humans | Urinary tract infections, liver abscesses, pneumonia, meningitis, and bacteremia | [64,65,66] |
| 9 | Pseudomonadota | Legionella pneumophila | 23 | Humans | Legionnaires’ disease (LD): pneumonia, fever, respiratory, gastrointestinal and neurological symptoms | [67,68] |
| 10 | Pseudomonadota | Plesiomonas shigelloides | 18 | Humans | Diarrhea, gastroenteritis, sepsis, central nervous system diseases, and eye infections, etc. | [69,70] |
| Freshwater fish such as Tilapia, Acipenser dabryanus | Reduced activity, pale body color, hemorrhages on the body surface, internal organ damage, and high mortality rate | [70,71] | ||||
| 11 | Pseudomonadota | Pseudomonas oryzihabitans | 53 | Cucumis melo L., rice | Browning and wilting of infected tissues | [72,73] |
| Humans | Skin abscess, bacteremia and yellow-green discoloration of the nails | [74,75,76] | ||||
| 12 | Pseudomonadota | Pseudomonas putida | 147 | Humans | Skin and soft tissue infections, bacteremia | [77] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | Skin ulcers, subcutaneous hemorrhages, mild internal organ swelling, and intestinal engorgement | [78] | ||||
| 13 | Pseudomonadota | Serratia marcescens | 45,649 | Humans | Urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, keratitis, conjunctivitis, surgical wound infections, bacteremia, sepsis, and meningitis | [79,80] |
| Animals and insects such as honey bees | N/A | [79,81,82] | ||||
| 14 | Bacillota | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 34 | Humans | Late-onset neonatal sepsis | [83] |
| 15 | Bacillota | Streptococcus agalactiae | 4 | Tilapia | Meningitis | [84] |
| Humans | Bacteremia, pneumonia and chorioamnionitis | [85,86] | ||||
| 16 | Bacillota | Streptococcus equinus | 36 | Humans | Infective endocarditis (IE), brain abscess | [87,88] |
| 19 | Bacillota | Enterococcus sp. | 35 | Humans | Endocarditis, sepsis, meningitis, bacteremia, urinary tract infections, | [89,90,91] |
| No. | Phylum | Organism | Abundance of Reads | Host | Diseases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ascomycota | Acremonium sp. 1 FW2SW3 | 2 | Humans | Infection peritonitis, fungal osteomyelitis | [92,93] |
| 2 | Ascomycota | Meyerozyma guilliermondii | 402 | Humans | Bloodstream infections and fever | [94,95,96] |
| 3 | Ascomycota | Pichia kudriavzevii | 11 | Humans | Late-onset sepsis, histopathologic changes in the intestine, mycosis peritonitis | [97,98,99] |
| 4 | Ascomycota | Wickerhamomyces anomalus | 2 | Humans | Keratitis, candidemia, meningitis, fungemia, ventriculitis, keratitis and endophthalmitis | [100,101,102] |
| 5 | Basidiomycota | Cryptococcus sp. SJ8L05 | 8 | Humans | Pneumonia, meningitis | [103,104,105] |
| 6 | Basidiomycota | Naganishia albida | 15 | Humans | Skin lesions, otomycosis | [106,107] |
| 7 | Basidiomycota | Rhodotorula mucilaginosa | 49 | Humans | Meningitis | [108,109,110] |
| No. | Phylum | Organism | Abundance of Reads | Host | Diseases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apicomplexa | Babesia sp. Kh-Hj540 | 3 | Brown bear | N/A | [111,112,113] |
| 2 | Apicomplexa | Blastocystis sp. | 3 | Humans | Diarrhea, dermatological symptoms | [114,115,116] |
| Animals | N/A | [114,117] | ||||
| 3 | Apicomplexa | Cryptosporidium serpentis | 21 | Reptiles | High mortality | [118,119] |
| 4 | Apicomplexa | Eimeria bukidnonensis | 768 | Cattle | Bovine eimeriosis (intestinal disease) | [120,121] |
| 5 | Apicomplexa | Eimeria sp. | 5 | Livestock | Diarrhea, anorexia and death | [122,123] |
| 6 | Apicomplexa | Theileria sp. | 7 | Livestock and wild animals | Fever, hemoglobinuria, anemia, and death | [124,125,126] |
| 7 | Myzozoa | Perkinsus olseni | 7 | Molluscs | Tissue inflammation, impaired reproduction, reduced growth and mass mortalities | [127,128,129] |
| 8 | Myzozoa | Perkinsus qugwadi | 50 | Molluscs | Mass mortalities | [130] |
| 9 | Oomycota | Pythium insidiosum | 25 | Animals | Pythiosis | [131,132] |
| Humans | Keratitis | [133] |
| Pathogens | Percentage (in All OTUs) | Organisms | Reads | Percentage (in All Pathogens) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungi | 0.0706% | Meyerozyma guilliermondii | 402 | 29.17% |
| Other fungal pathogens | 87 | 6.31% | ||
| Parasites | 0.1283% | Eimeria bukidnonensis | 768 | 55.73% |
| Other parasite pathogens | 121 | 8.78% |
4. Discussion
4.1. Biodiversity Helps Initial Assessment of Ecological Health
4.2. Influence of Sampling Limitations on Diversity Analysis
4.3. Bacterial Community Composition Indicative of Ecological Pollution
4.4. Eukaryotic Community Patterns Indicate Pollution
4.5. eDNA-NGS Significantly Improves Pathogen Surveillance Capabilities
4.6. Strengthening Environmental Policies and Public Health with eDNA Insights
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, S.-C. Vision 2020: Towards an environmentally sound and sustainable development of freshwater resources in Malaysia. GeoJournal 1996, 40, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Siwar, C.; Begum, R.A. Water resources in Malaysia: Issues and challenges. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2014, 12, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, M.; Kabir, M.; Yee, L.; Khan, M. Water quality assessment of perak river, Malaysia. Pollution 2019, 5, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Zeshan, M.T.; Mustafa, M.R.U.; Baig, M.F. Monitoring Land Use Changes and Their Future Prospects Using GIS and ANN-CA for Perak River Basin, Malaysia. Water 2021, 13, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, P.K.; Ganguly, S.; Wakchaure, R.; Para, P.A.; Mahajan, T.; Qadri, K.; Kamble, S.; Sharma, R.; Shekhar, S.; Dalai, N. Water-borne diseases and its effect on domestic animals and human health: A Review. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2016, 6, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich, E.E. Pathogenic agents in freshwater resources. Hydrol. Process. 1996, 10, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Suicide Worldwide in 2019: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Collier, S.A.; Deng, L.; Adam, E.A.; Benedict, K.M.; Beshearse, E.M.; Blackstock, A.J.; Bruce, B.B.; Derado, G.; Edens, C.; Fullerton, K.E.; et al. Estimate of Burden and Direct Healthcare Cost of Infectious Waterborne Disease in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Risks associated with the consumption of irrigation water contaminated produce: On the role of quantitative microbial risk assessment. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 41, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; da Silva, A.L.B.R.; Dunn, L.L. Factors Impacting the Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens in Agricultural Water Sources in the Southeastern United States. Water 2019, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungk, J.; Baumbach, J.; Landen, M.; Gaul, L.; Alaniz, L.; Dang, T.; Miller, E.; Weiss, K.; Hedican, E.; Smith, K. Outbreak of Salmonella serotype Saintpaul infections associated with multiple raw produce items—United States, 2008. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2008, 57, 929–934. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, R.H.; Thoms, M.C. What is river health? Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Defining and measuring river health. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Cooke, S.J.; Arthington, A.H.; Baigun, C.; Bossenbroek, L.; Dickens, C.; Harrison, I.; Kimirei, I.; Langhans, S.D.; Murchie, K.J.; et al. People need freshwater biodiversity. WIREs Water 2023, 10, e1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, G.A.; Khan, M.A.; Dar, M.A.; Shah, M.A.; Reshi, Z.A. Next Generation High Throughput Sequencing to Assess Microbial Communities: An Application Based on Water Quality. Bull. Env. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, J.X.; Chua, A.S.M.; Rabuni, M.F.; Tan, C.K.; Lai, S.H.; Takemura, Y.; Syutsubo, K. Water quality assessment and pollution threat to safe water supply for three river basins in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Maulud, K.N.; Fitri, A.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Wan Mohd Jaafar, W.S.; Zuhairi, N.Z.; Kamarudin, M.K.A. A study of spatial and water quality index during dry and rainy seasons at Kelantan River Basin, Peninsular Malaysia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Lei, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Yang, J. Culture-independent methods for studying environmental microorganisms: Methods, application, and perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.; Handelsman, J. Metagenomics for studying unculturable microorganisms: Cutting the Gordian knot. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: Opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlapati, D.; Charankumar, B.; Ramu, K.; Madeswaran, P.; Ramana Murthy, M.V. A review on the applications and recent advances in environmental DNA (eDNA) metagenomics. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2019, 18, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenekar, T. The current state of eDNA research in freshwater ecosystems: Are we shifting from the developmental phase to standard application in biomonitoring? Hydrobiologia 2022, 850, 1263–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernos, T.A.; Yates, M.C.; Docker, M.F.; Fitzgerald, A.; Hanner, R.; Heath, D.; Imrit, A.; Livernois, J.; Myler, E.; Patel, K.; et al. Environmental DNA (eDNA) applications in freshwater fisheries management and conservation in Canada: Overview of current challenges and opportunities. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 80, 1170–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Castillo, F.Y.; Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Garneau, P.; Avelar-Gonzalez, F.J.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. Waterborne pathogens: Detection methods and challenges. Pathogens 2015, 4, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, L.; Stauffer, J.B.; Altermatt, F. How to design optimal eDNA sampling strategies for biomonitoring in river networks. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkefli, N.S.; Kim, K.-H.; Hwang, S.-J. Effects of microbial activity and environmental parameters on the degradation of extracellular environmental DNA from a eutrophic lake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinlo, R.; Gleeson, D.; Lintermans, M.; Furlan, E. Methods to maximise recovery of environmental DNA from water samples. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.; Pace, B.; Olsen, G.; Stahl, D.; Sogin, M.; Pace, N. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6955–6959, Erratum in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P. Intragenomic heterogeneity between multiple 16S ribosomal RNA operons in sequenced bacterial genomes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 228, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillis, D.M.; Dixon, M.T. Ribosomal DNA: Molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q. Rev. Biol. 1991, 66, 411–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukin, Y.; Galachyants, Y.; Morozov, I.; Bukin, S.; Zakharenko, A.; Zemskaya, T. The effect of 16S rRNA region choice on bacterial community metabarcoding results. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 190007, Erratum in Sci. Data 2022, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; He, Z.; Wang, C.; Yan, Q.; Shu, L. Evaluation of different primers of the 18S rRNA gene to profile amoeba communities in environmental samples. Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egge, E.; Elferink, S.; Vaulot, D.; John, U.; Bratbak, G.; Larsen, A.; Edvardsen, B. An 18S V4 rRNA metabarcoding dataset of protist diversity in the Atlantic inflow to the Arctic Ocean, through the year and down to 1000 m depth. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4913–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, J.S. Comparative analyses of the V4 and V9 regions of 18S rDNA for the extant eukaryotic community using the Illumina platform. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Wan, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Zhu, W. Active bacterial communities of pig fecal microbiota transplantation suspension prepared and preserved under different conditions. AMB Express 2019, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritz, J.M.; Rogers, K.H.; Rock, T.M.; Liu, N.; Joseph, S.; Land, K.M.; Carlton, J.M. An 18S rRNA Workflow for Characterizing Protists in Sewage, with a Focus on Zoonotic Trichomonads. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janosik, A.M.; Whitaker, J.M.; VanTassel, N.M.; Rider, S.J. Improved environmental DNA sampling scheme for Alabama sturgeon provides new insight into a species once presumed extinct. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2021, 37, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellerberg, I.F.; Fedor, P.J. A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916–2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness, species diversity and the ‘Shannon–Wiener’ Index. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.K.; Caruso, T.; Buscot, F.; Fischer, M.; Hancock, C.; Maier, T.S.; Meiners, T.; Müller, C.; Obermaier, E.; Prati, D. Choosing and using diversity indices: Insights for ecological applications from the German Biodiversity Exploratories. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heip, C.H.; Herman, P.M.; Soetaert, K. Indices of diversity and evenness. Oceanis 1998, 24, 61–88. [Google Scholar]
- Scherson, R.; Faith, D. Phylogenetic Diversity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Borcard, D.; Peres-Neto, P. Analyzing Beta Diversity: Partitioning the Spatial Variation of Community Composition Data. Ecol. Monogr. 2005, 75, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.; Newton, J.C. Immunology and immunotherapy of the infections caused by Pythium insidiosum. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-López, R.; Solano-Gálvez, S.G.; Juárez Vignon-Whaley, J.J.; Abello Vaamonde, J.A.; Padró Alonzo, L.A.; Rivera Reséndiz, A.; Muleiro Álvarez, M.; Vega López, E.N.; Franyuti-Kelly, G.; Álvarez-Hernández, D.A. Acinetobacter baumannii resistance: A real challenge for clinicians. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarshar, M.; Behzadi, P.; Scribano, D.; Palamara, A.T.; Ambrosi, C. Acinetobacter baumannii: An ancient commensal with weapons of a pathogen. Pathogens 2021, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mea, H.J.; Yong, P.V.C.; Wong, E.H. An overview of Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenesis: Motility, adherence and biofilm formation. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 247, 126722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Yano, H.; Kanamori, H.; Inomata, S.; Aoyagi, T.; Hatta, M.; Gu, Y.; Tokuda, K.; Kitagawa, M.; Kaku, M. High frequency of Acinetobacter soli among Acinetobacter isolates causing bacteremia at a tertiary hospital in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, F.L.P.C.; Vieira, V.V.; Baio, P.V.P.; dos Santos, R.M.R.; dos Santos, A.L.A.; Santos, N.G.d.B.; Meohas, M.M.G.L.; Santos, R.T.; de Souza, T.C.; da Silva Dias, R.C. Acinetobacter soli as a cause of bloodstream infection in a neonatal intensive care unit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furugaito, M.; Anraku, M.; Kawahara, R.; Hisato, A.; Kamisako, T.; Yoshida, K. First report of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1-producing Acinetobacter soli in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2023, 29, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N.; Liu, W.; Meng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y. Isolation, identification and characteristics of Aeromonas caviae from diseased largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes 2022, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladele, O.; Ameji, N.; Gurumyen, G.; Adanu, W.; Kolade, T.; Agbato, O.; Lombin, L. Mortality of Clarias gariepinus caused by Aeromonas caviae and nitrite toxicity in a fish farm. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 19, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Su, S.-L.; Li, C.-W.; Tsai, C.-S.; Lo, C.-L.; Syue, L.-S.; Li, M.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Lee, N.-Y.; Ko, W.-C. Pancreaticobiliary cancers and Aeromonas isolates carrying type III secretion system genes ascF-ascG are associated with increased mortality: An analysis of 164 Aeromonas infection episodes in southern Taiwan. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 749269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Yuwono, C.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Wehrhahn, M.C.; Riordan, S.M.; Zhang, L. Analysis of global Aeromonas veronii genomes provides novel information on source of infection and virulence in human gastrointestinal diseases. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tian, L.; Liao, J.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W.; Zhou, Y. Antioxidant capacity, non-specific immunity, histopathological analysis and immune-related genes expression in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus infected with Aeromonas schubertii. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Webster, G.; Mullins, A.J.; Jenner, M.; Bull, M.J.; Dashti, Y.; Spilker, T.; Parkhill, J.; Connor, T.R.; LiPuma, J.J. Kill and cure: Genomic phylogeny and bioactivity of Burkholderia gladioli bacteria capable of pathogenic and beneficial lifestyles. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Stanbridge, T.; Isalska, B.; Dodd, M.; Webb, A. Burkholderia gladioli: Recurrent abscesses in a patient with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. 2001, 42, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Park, I.; Seo, Y.S. Differential regulation of toxoflavin production and its role in the enhanced virulence of Burkholderia gladioli. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeuffer, C.; Schramm, F.; Meyer, A.; Hansmann, Y.; Guffroy, A.; Argemi, X. First case of Comamonas aquatica bacteremia complicated by septic shock. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya Sanyal, K.; Mukherjee, D.; Guchhait, A.; Dash, G. Phenotypic and Molecular Identification of Bacterial Species in Indian Major Carps and Exotic Carps from South 24 Parganas, West Bengal, India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonten, M.; Johnson, J.R.; van den Biggelaar, A.H.; Georgalis, L.; Geurtsen, J.; de Palacios, P.I.; Gravenstein, S.; Verstraeten, T.; Hermans, P.; Poolman, J.T. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli bacteremia: A systematic literature review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurtsen, J.; de Been, M.; Weerdenburg, E.; Zomer, A.; McNally, A.; Poolman, J. Genomics and pathotypes of the many faces of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effah, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae: An increasing threat to public health. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.T.; Liebenthal, D.; Tran, T.K.; Ngoc Thi Vu, B.; Ngoc Thi Nguyen, D.; Thi Tran, H.K.; Thi Nguyen, C.K.; Thi Vu, H.L.; Fox, A.; Horby, P. Klebsiella pneumoniae oropharyngeal carriage in rural and urban Vietnam and the effect of alcohol consumption. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.-H.; Tee, W.Y.; Khan, T.M.; Ming, L.C.; Letchumanan, V. Legionella pneumophila—The causative agent of Legionnaires’ disease. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupia, T.; Corcione, S.; Shbaklo, N.; Rizzello, B.; De Benedetto, I.; Concialdi, E.; Navazio, A.S.; Penna, M.; Brusa, M.T.; De Rosa, F.G. Legionella pneumophila infections during a 7-year retrospective analysis (2016–2022): Epidemiological, clinical features and outcomes in patients with Legionnaires’ disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L.; McIver, C.J. Plesiomonas shigelloides revisited. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés-Sánchez, A.D.J.; Espinosa-Chaurand, L.D.; Díaz-Ramirez, M.; Torres-Ochoa, E. Plesiomonas: A Review on Food Safety, Fish-Borne Diseases, and Tilapia. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 3119958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.; Yan, L.H.; Yan, Q.G.; Wen, X.T.; Cao, S.J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.B.; Ma, X.P.; Han, X.F.; et al. Identification and pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides from Acipenser dabryanusin China. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, T.; Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Xu, L.; Ma, G. First report of Pseudomonas oryzihabitans causing stem and leaf rot on muskmelon in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Ding, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, S. First report of Pseudomonas oryzihabitans causing rice panicle blight and grain discoloration in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keikha, M.; Soori, T.; Azadi, D.; Karami-Zarandi, M.; Daneshpazhooh, M.; Ali Rahdar, H. The first report of Pseudomonas oryzihabitansin infection in a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.; Cho, S. Chloronychia caused by Pseudomonas oryzihabitans infection. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.; Siddiqui, T.; Kar, M.; Sahu, C.; Patel, S.S. Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Bacteremia from North India in a Terminally Ill Patient: A Rare Case Report. Innov. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Montano, A.; Bostick, A. Rapid severe sepsis from Pseudomonas fluorescens/putida bacteremia due to skin and soft tissue infection—A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 70, 102845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; El-Murr, A.; Abd Elhakim, Y.; Metwally, M.M.; Gharib, A.A.E.A.; Amer, S.A.; Younis, E.M.; Abdel-Warith, A.-W.A.; Davies, S.J.; Khalil, E.N. Comparative study on ginger powder and ginger extract nanoparticles: Effects on growth, immune–antioxidant status, tissue histoarchitecture, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila and Pseudomonas putida infection in Oreochromis niloticus. Fishes 2023, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlen, S.D. Serratia infections: From military experiments to current practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 755–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, M.L.; Sartini, M.; Spagnolo, A.M. Serratia marcescens infections in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimont, P.A.; Grimont, F. The genus serratia. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1978, 32, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymann, K.; Coon, K.L.; Shaffer, Z.; Salisbury, S.; Moran, N.A. Pathogenicity of Serratia marcescens strains in honey bees. MBio 2018, 9, 10–1128, Erratum in MBio 2019, 10, e02855-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, I.A.; Otto, M.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A.J. Look who’s talking: Host and pathogen drivers of Staphylococcus epidermidis virulence in neonatal sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Guo, F.; Gao, F.; Wang, M.; Yi, M.; Lu, M. Distribution and localization of Streptococcus agalactiae in different tissues of artificially infected tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.-Y.; Patras, K.A.; Seo, H.S.; Cavaco, C.K.; Rösler, B.; Neely, M.N.; Sullam, P.M.; Doran, K.S. Group B streptococcal serine-rich repeat proteins promote interaction with fibrinogen and vaginal colonization. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, N.; Kasahara, K.; Nakano, R.; Ogawa, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Hishiya, N.; Nakano, A.; Ichimura, S.; Yano, H. Clinical characteristics and molecular epidemiology of invasive Streptococcus agalactiae infections between 2007 and 2016 in Nara, Japan. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerty, D.; Yacoub, A.T.; Nguyen, T.-C.; Haynes, E.; Greene, J. First case of infective endocarditis with Streptococcus equinus in an immunocompetent patient in North America: A case report and review of literature. Cureus 2021, 13, e19473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiki, M.; Azar, M.H.; Hallit, S.; Maalouly, R.; Fahed, E.; Younes, P.; Slim, J.; Hallit, R. Concomitant Listeria monocytogenes and Streptococcus equinus brain abscess in an immunocompetent individual: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2024, 18, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccella, M.; Santella, B.; Pagliano, P.; De Filippis, A.; Casolaro, V.; Galdiero, M.; Borrelli, A.; Capunzo, M.; Boccia, G.; Franci, G. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Enterococcus species: A retrospective cohort study in Italy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, P.H.N.; Kline, K.A. Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hide: How Enterococcus faecalis subverts the host immune response to cause infection. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2932–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Wityk, P.; Gałęcka, M.; Michalik, M. The many faces of Enterococcus spp.—Commensal, probiotic and opportunistic pathogen. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Cao, M.; Xiao, N. Successful treatment of peritonitis caused by Acremonium species without catheter removal: Case report and literature review. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2023, 17, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, D.; Saini, M.K.; Elhence, P.; Elhence, A.; Jain, P. Calcaneal osteomyelitis caused by Acremonium sp. in an immunocompetent adult–A case report. Foot 2021, 47, 101781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, A.L.S.; Trilles, L.; Alves, G.M.; Figueiredo-Carvalho, M.H.G.; Brito-Santos, F.; Coelho, R.A.; Martins, I.S.; Almeida-Paes, R. A case-series of bloodstream infections caused by the Meyerozyma guilliermondii species complex at a reference center of oncology in Brazil. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tian, S.; Li, F.; Sun, G.; Yun, K.; Cheng, S.; Chu, Y. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of candidemia caused by Meyerozyma guilliermondii complex in cancer patients undergoing surgery. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, N.C.; Tosun, İ.; Aydin, F. The identification of Meyerozyma guilliermondii from blood cultures and surveillance samples in a university hospital in Northeast Turkey: A ten-year survey. J. Mycol. Med. 2017, 27, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarathnamma, T.; Chunchanur, S.K.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Vineetha, K.; Ramamurthy, K.; Joseph, J.; Ambica, R. Outbreak of Pichia kudriavzevii fungaemia in a neonatal intensive care unit. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopyev, V.; Kuklina, N.V.; Mazko, O.N.; Makarova, O.G. Oxidative stress induced by the human microbiota yeast component as a micromycetes pathogenicity factor. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. 2024, 14, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bshabshe, A.; Joseph, M.R.; Battayah, E.S.; Hamid, M.E. Fungal peritonitis caused by Pichia kudriavzevii following sleeve gastrectomy. Ann. Saudi Med. 2019, 39, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, M.; Arastehfar, A.; Ilkit, M.; Zou, J.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhao, J.; Fang, W. Investigation of the emerging nosocomial Wickerhamomyces anomalus infections at a Chinese tertiary teaching hospital and a systemic review: Clinical manifestations, risk factors, treatment, outcomes, and anti-fungal susceptibility. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 744502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, V.R.; Silva, L.F.; Oliveira, A.N.M.; Beirigo, E.F.; Arthur, V.M.; Bernardes da Silva, R.; Ferreira, T.B.; Andrade-Silva, L.; Silva, M.V.; Fonseca, F.M. Fatal case of fungemia by Wickerhamomyces anomalus in a pediatric patient diagnosed in a teaching hospital from Brazil. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Herai, Y.; Yahaba, M.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K.; Igari, H. Fungemia with Wickerhamomyces anomalus: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e53550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, F.N.; de Camargo Fenley, J.; Garcia, M.T.; Rossoni, R.D.; Junqueira, J.C.; de Barros, P.P.; Scorzoni, L. Cryptococcus spp. and Cryptococcosis: Focusing on the infection in Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pawar, S.; Dutta, O.; Wang, K.; Rivera, A.; Xue, C. Macrophage mediated immunomodulation during cryptococcus pulmonary infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 859049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.H.; Nyazika, T.K.; Ssebambulidde, K.; Lionakis, M.S.; Meya, D.B.; Drummond, R.A. Fungal CNS infections in Africa: The neuroimmunology of cryptococcal meningitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 804674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.F.d.; Funari, A.P.; Taborda, M.; Magri, A.S.G.K.; Levin, A.S.; Magri, M.M.C. Cutaneous Naganishia albida (Cryptococcus albidus) infection: A case report and literature review. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2023, 65, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboutalebian, S.; Mahmoudi, S.; Okhovat, A.; Khodavaisy, S.; Mirhendi, H. Otomycosis due to the rare fungi Talaromyces purpurogenus, Naganishia albida and Filobasidium magnum. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larone, D.H. Medically important fungi. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1994, 36, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wirth, F.; Goldani, L.Z. Epidemiology of Rhodotorula: An emerging pathogen. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2012, 2012, 465717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nor, F.; Tan, L.H.; Na, S.L.; Ng, K.P. Meningitis caused by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa in HIV-infected patient: A case report and review of the literature. Mycopathologia 2015, 180, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rar, V.; Epikhina, T.; Suntsova, O.; Kozlova, I.; Lisak, O.; Pukhovskaya, N.; Vysochina, N.; Ivanov, L.; Tikunova, N. Genetic variability of Babesia parasites in Haemaphysalis spp. and Ixodes persulcatus ticks in the Baikal region and Far East of Russia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, T.; Yeoh, B.; Manin, B.; Wong, S. First detection of Babesia sp. in bornean sun bear (Helarctos malayanus euryspilus horsfield) in Sabah, Malaysia. Tropical Biomedicine 2022, 39, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.I.; Chye, T.T.; Karmacharya, B.M.; Govind, S.K. Blastocystis sp.: Waterborne zoonotic organism, a possibility? Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, R.; Cuttell, L.; Stensvold, C.; Mills, P.C.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Traub, R.J. Blastocystis subtypes in symptomatic and asymptomatic family members and pets and response to therapy. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, D.M.A.; Hassanin, O.M.; Zuel-Fakkar, N.M. Association of Blastocystis hominis genetic subtypes with urticaria. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauff-Adedotun, A.A.; Mohd Zain, S.N.; Farah Haziqah, M.T. Current status of Blastocystis sp. in animals from Southeast Asia: A review. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Liu, H.; Deng, L.; Bi, B.; Yao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Fu, H.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Z. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium serpentis in captive snakes in China. J. Parasitol. 2021, 107, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogan, J.E., Jr.; Hoffman, M.; Mitchell, M.A.; Garner, M.M.; Childress, A.; Wellehan, J.F. Evaluation of the drug combination nitazoxanide, azithromycin, and rifabutin as a treatment for Cryptosporidium serpentis infection in eastern indigo snakes (Drymarchon couperi). J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2022, 32, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-C.; Choe, C.; Kim, S.; Chae, J.-S.; Yu, D.-H.; Park, J.; Park, B.-K.; Choi, K.-S. Epidemiological survey on Eimeria spp. associated with diarrhea in pre-weaned native Korean calves. Korean J. Parasitol. 2018, 56, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriao, M.M.; Lopes Bdo, B.; Berto, B.P.; Lopes, C.W. New approaches for morphological diagnosis of bovine Eimeria species: A study on a subtropical organic dairy farm in Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangoura, B.; Daugschies, A. Eimeria. In Parasitic Protozoa of Farm Animals and Pets; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 55–101. [Google Scholar]
- Utebaeva, G.; Berkinbay, O.; Tuganbay, A. Study of Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Eimeria sp., in Camelsin Turkestan Region. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1419. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, R.P.; Hemmink, J.; Morrison, W.; Weir, W.; Toye, P.G.; Sitt, T.; Spooner, P.; Musoke, A.; Skilton, R.A.; Odongo, D.O. The African buffalo parasite Theileria. sp.(buffalo) can infect and immortalize cattle leukocytes and encodes divergent orthologues of Theileria parva antigen genes. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2015, 4, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisi, M.E.; Sibeko, K.P.; Collins, N.E.; Potgieter, F.T.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Identification of Theileria parva and Theileria sp. (buffalo) 18S rRNA gene sequence variants in the African Buffalo (Syncerus caffer) in southern Africa. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kelly, P.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, C. Molecular detection of Theileria spp. in livestock on five Caribbean islands. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 624728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramilo, A.; Pintado, J.; Villalba, A.; Abollo, E. Perkinsus olseni and P. chesapeaki detected in a survey of perkinsosis of various clam species in Galicia (NW Spain) using PCR–DGGE as a screening tool. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 133, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretto, T.; Zambon, M.; Civettini, M.; Caburlotto, G.; Boffo, L.; Rossetti, E.; Arcangeli, G. Massive mortality in Manila clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) farmed in the lagoon of Venice, caused by Perkinsus olseni. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 2014, 34, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Sanil, N.; Vijayan, K.; Kripa, V.; Mohamed, K. Occurrence of the protozoan parasite, Perkinsus olseni in the wild and farmed Pearl Oyster, Pinctada fucata (Gould) from the Southeast coast of India. Aquaculture 2010, 299, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Meyer, G.R.; Tabata, A.; Lowe, G.; Abbott, C.L.; Johnson, S.C. Rediscovery of the Yesso scallop pathogen Perkinsus qugwadi in Canada, and development of PCR tests. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 104, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaastra, W.; Lipman, L.J.; De Cock, A.W.; Exel, T.K.; Pegge, R.B.; Scheurwater, J.; Vilela, R.; Mendoza, L. Pythium insidiosum: An overview. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 146, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, P.M.; Uzal, F.A.; Riet-Correa, F. Diseases caused by Pythium insidiosum in sheep and goats: A review. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurnani, B.; Kaur, K.; Venugopal, A.; Srinivasan, B.; Bagga, B.; Iyer, G.; Christy, J.; Prajna, L.; Vanathi, M.; Garg, P. Pythium insidiosum keratitis—A review. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, M.; Yadav, N.S. Assessment of river health of Chambal River based on biological communities, India. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 3045–3053. [Google Scholar]
- Matcher, G.; Froneman, P.; Dorrington, R. Aquatic Microbial Diversity: A Sensitive and Robust Tool for Assessing Ecosystem Health and Functioning; WRC Report No. 2038/1/14; Water Research Commission: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Hokajarvi, A.M.; Domingo, J.S.; Elk, M.; Jayaprakash, B.; Ryu, H.; Siponen, S.; Vepsalainen, A.; Kauppinen, A.; Puurunen, O.; et al. Bacterial diversity and predicted enzymatic function in a multipurpose surface water system—From wastewater effluent discharges to drinking water production. Env. Microbiome 2021, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogamba, E.N.; Charles, E.E.; Izah, S.C.; Vrinceanu, N. Phytoplankton Community of Taylor Creek in the Niger Delta Using Diversity Indices. J. Plant Anim. Ecol. 2019, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.A.; Pandit, A.K. Application of diversity indices to crustacean community of Wular Lake, Kashmir Himalaya. Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv. 2013, 5, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, K.; Odedra, K.N.; Jadeja, B.A. Unveiling the Ecological Tapestry: Alpha Diversity Patterns in the Banas River Corridor, Gujarat, India. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2023, 21, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.F.V.; Margis, R. The source of the river as a nursery for microbial diversity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhao, F.; Shang, G.; Wang, L.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Fang, X. Ammonia influences the zooplankton assemblage and beta diversity patterns in complicated urban river ecosystems. Water 2023, 15, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, T.K.; Grenouillet, G.; Villéger, S.; Ricciardi, A. Species contribute differently to the taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic alpha and beta diversity of freshwater fish communities. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Xiong, X.; Li, D. The relative role of spatial and environmental processes on seasonal variations of phytoplankton beta diversity along different anthropogenic disturbances of subtropical rivers in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, R.J.; Heino, J.; Chessman, B.C. Unravelling the joint effects of flow regime, climatic variability and dispersal mode on beta diversity of riverine communities. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 1350–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Kan, J.; Yang, M.; Yu, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, W. Assembly and network stability of planktonic microorganisms under the influence of salinity gradient: An Arctic case study from the Lena River estuary to the Laptev Sea. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02115–e02122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, J.; Grönroos, M.; Ilmonen, J.; Karhu, T.; Niva, M.; Paasivirta, L. Environmental heterogeneity and β diversity of stream macroinvertebrate communities at intermediate spatial scales. Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.; Almeida-Neto, M.; Arena, M. Amphibian Beta Diversity in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest: Contrasting the Roles of Historical Events and Contemporary Conditions at Different Spatial Scales. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Coz, M.; Chambord, S.; Meire, P.; Maris, T.; Azémar, F.; Ovaert, J.; Buffan-Dubau, E.; Kromkamp, J.; Sossou, A.; Prygiel, J. Test of some ecological concepts on the longitudinal distribution of zooplankton along a lowland water course. Hydrobiologia 2017, 802, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.d.A.; Ramos Okumura, A.T.; Silva, A.G.; Pereira, T.L.; Simões, N.R. Alpha and beta diversity of planktonic microcrustaceans are associated with environmental heterogeneity in the Frades River Basin, Brazil. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 2021, 58, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.; Olden, J.; Merritt, D.; Pepin, D.; Mooney, H. Homogenization of regional river dynamics by dams and global biodiversity implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5732–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strokal, M.; Lin; Bai, Z.; Luan, S.; Kroeze, C.; Oenema, O.; Velthof, G.; Zhang, F. Alarming nutrient pollution of Chinese rivers as a result of agricultural transitions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Sharma, S. Pollution shapes the bacterial community of a river: A case study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 2003–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ren, C.; Song, C.; Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhang, X. Using in situ bacterial communities to monitor contaminants in river sediments. Env. Pollut. 2016, 212, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, A. Environment-driven geographical distribution of bacterial communities and identification of indicator taxa in Songhua River. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagagnan, S.; Guerin-Rechdaoui, S.; Rocher, V.; Alphonse, V.; Moilleron, R.; Jusselme, M.D. Spatial and temporal characteristics of microbial communities in the Seine river in the greater Paris area under anthropogenic perturbation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghai, R.; Mizuno, C.M.; Picazo, A.; Camacho, A.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Key roles for freshwater A ctinobacteria revealed by deep metagenomic sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 6073–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohorquez-Herrera, J.; Abad Matias, I.D.; Gutierrez Castaneda, C.G. Impact of different environmental pollution processes on bacterial key-indicators in tropical rivers: Scoping review. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2023, 370, fnad098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Niu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C. Revealing the relationship between microbial community structure in natural biofilms and the pollution level in urban rivers: A case study in the Qinhuai River basin, Yangtze River Delta. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlejnková, H.; Sovová, K. Impact of pollution and seasonal changes on microbial community structure in surface water. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumampouw, O.J.; Risjani, Y. Bacteria as indicators of environmental pollution. Environment 2014, 51, 10–5923. [Google Scholar]
- Kumasi, T.C.; Obiri-Danso, K.; Ephraim, J.H. Microbial quality of water in Barekese reservoir and feeder streams in Ghana. Lakes Reserv. Sci. Policy Manag. Sustain. Use 2011, 16, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.; Fatoyinbo, O. Bacteriological Quality and Prevalence of Multidrug Resistant Gram-negative Bacteria from Surface and Underground Domestic Water Sources in Selected Locations in Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2016, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristani, M.; Naccari, C.; Nostro, A.; Pizzimenti, A.; Trombetta, D.; Pizzimenti, F. Possible use of Serratia marcescens in toxic metal biosorption (removal). Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giwa, O.; Arotupin, A.D.J.; Akinyosoye, A.F.A. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals from Crude Oil Polluted Soil Using Serratia marcescens and its Toxicology Assessment on Aquaculture. Br. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 2, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Żmijowska, A.; Wójcik, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Biodegradation and bioremediation potential of diazinon-degrading Serratia marcescens to remove other organophosphorus pesticides from soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, P.S.; Barboza, N.R.; Cordeiro, M.M.; Leão, V.A.; Guerra-Sá, R. Rich growth medium promotes an increased on Mn (II) removal and manganese oxide production by Serratia marcescens strains isolates from wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 140, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odonkor, S.T.; Ampofo, J.K. Escherichia coli as an indicator of bacteriological quality of water: An overview. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 4, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.M.; Arribas, R.M.; Pares, R. Distribution of Aeromonas species in waters with different levels of pollution. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1991, 71, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, K.; Lu, W. Bacterial community composition and indicators of water quality in Caizi Lake, a typical Yangtze-connected freshwater lake. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascault, N.; Roux, S.; Artigas, J.; Pesce, S.; Leloup, J.; Tadonleke, R.D.; Debroas, D.; Bouchez, A.; Humbert, J.-F. A high-throughput sequencing ecotoxicology study of freshwater bacterial communities and their responses to tebuconazole. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korajkic, A.; Parfrey, L.W.; McMinn, B.R.; Baeza, Y.V.; VanTeuren, W.; Knight, R.; Shanks, O.C. Changes in bacterial and eukaryotic communities during sewage decomposition in Mississippi river water. Water Res. 2015, 69, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Quan, Q.; Gan, Y.; Dong, J.; Fang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Effects of heavy metals on microbial communities in sediments and establishment of bioindicators based on microbial taxa and function for environmental monitoring and management. Sci. Total Env. 2020, 749, 141555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Pei, H. 18S rRNA gene sequencing reveals significant influence of anthropogenic effects on microeukaryote diversity and composition along a river-to-estuary gradient ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tohamy, W.S.; Taher, M.E.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Hopcroft, R.R. Protozoan communities serve as a strong indicator of water quality in the Nile River. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J. Ciliated Protozoa in marine pollution studies: A conspectus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1983, 7, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, T.d.S.; Silva-Neto, I.d. Ciliate protists from Cabiúnas Lagoon (Restinga de Jurubatiba, Macaé, Rio de Janeiro) with emphasis on water quality indicator species and description of Oxytricha marcili sp. n. Braz. J. Biol. 2004, 64, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debastiani, C.; Meira, B.; Lansac-Tôha, F.; Velho, L.; Lansac-Tôha, F. Protozoa ciliates community structure in urban streams and their environmental use as indicators. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barría de Cao, M.S.; Abbate, M.C.L.; Pettigrosso, R.E.; Hoffmeyer, M.S. The planktonic ciliate community and its relationship with the environmental conditions and water quality in two bays of the Beagle Channel, Argentina. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK. 2013, 93, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaš, A.; Gulin, V.; Matoničkin Kepčija, R.; Žutinić, P.; Sertić Perić, M.; Orlić, S.; Kajan, K.; Stoeck, T.; Lentendu, G.; Čanjevac, I.; et al. Ciliates (Alveolata, Ciliophora) as bioindicators of environmental pressure: A karstic river case. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.J.P.; de Souza, P.M.; Rossi, M.F.; Wieloch, A.H.; da Silva-Neto, I.D.; D’Agosto, M. Ciliates as bioindicators of water quality: A case study in the neotropical region and evidence of phylogenetic signals (18S-rDNA). Env. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sildever, S.; Laas, P.; Kolesova, N.; Lips, I.; Lips, U.; Nagai, S. Plankton biodiversity and species co-occurrence based on environmental DNA–a multiple marker study. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2021, 5, e72371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeyra Martin, J.; John, U.; Royer, C.; Gypens, N. Fantastic Beasts: Unfolding mixoplankton temporal variability in the Belgian coastal zone through DNA-metabarcoding. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 786787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Joo, G.-J.; Jeong, K.-S.; Gim, J.-S.; Lee, Y.; Hong, D.; Jo, H. Molecular Diet Analysis of Asian Clams for Supplementary Biodiversity Monitoring: A Case Study of Nakdong River Estuary. Biology 2023, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Xu, D.; Chen, X.; Warren, A.; Shin, M.K.; Song, W.; Li, L. Overview of the Diversity, Phylogeny and Biogeography of Strombidiid Oligotrich Ciliates (Protista, Ciliophora), With a Brief Revision and a Key to the Known Genera. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 700940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.C.; Fernandes, N.M. Exploring the impact of urban pollution on ciliate diversity along the Sapucai River (Minas Gerais, Brazil) via DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maselli, M.; Anestis, K.; Klemm, K.; Hansen, P.J.; John, U. Retention of Prey Genetic Material by the Kleptoplastidic Ciliate Strombidium cf. basimorphum. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 694508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welde, G.T.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Ayana, G.U.; Zhou, L.; Jia, R.; Zhu, J. Effect of Rice–Carp Coculture on Phytoplankton and Microzooplankton Community Composition in Paddy Water during Different Rice Growth Stages. Water 2024, 16, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zheng, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W. Distinct distribution patterns of planktonic ciliate communities along environmental gradients in a semi-enclosed bay. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuri, C.K.; Pazhaniyappan, E.; Munnooru, K.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Vinjamuri, R.R.; Karri, R.; Mallavarapu, R.V. Composition and distribution of planktonic ciliates with indications to water quality in a shallow hypersaline lagoon (Pulicat Lake, India). Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 18303–18316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, A.V.; Dias, C.O.; Bonecker, S.L.C. Differences in the structure of copepod assemblages in four tropical estuaries: Importance of pollution and the estuary hydrodynamics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, B.L.; Allen, A.E.; Carpenter, E.J.; Coles, V.J.; Crump, B.C.; Doherty, M.; Foster, R.A.; Goes, J.I.; Gomes, H.R.; Hood, R.R.; et al. Patterns of Transcript Abundance of Eukaryotic Biogeochemically-Relevant Genes in the Amazon River Plume. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.F.O.; Silva, H.D.; Souza, E.S., Jr.; Anunciação, C.E.; Silveira-Lacerda, E.P.; Vilanova-Costa, C.A.S.T.; Garcíazapata, M.T.A. Environmental Monitoring of Opportunistic Protozoa in Rivers and Lakes in the Neotropics Based on Yearly Monitoring. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2010, 2, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, R.L.; Ithoi, I.; Abd Majid, M.A.; Wan Sulaiman, W.Y.; Tan, T.C.; Nissapatorn, V.; Lim, Y.A.L. Monitoring of waterborne parasites in two drinking water treatment plants: A study in Sarawak, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, A.M.; Ithoi, I.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Ahmed, A.; Surin, J.; Mak, J.-W. Drinking water is a significant predictor of Blastocystis infection among rural Malaysian primary schoolchildren. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, N.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, T.; Ismail, S.; Ni, S.-Q. Insight into impact of sewage discharge on microbial dynamics and pathogenicity in river ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Aljaro, C.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Viñas-Balada, E.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Lucena, F.; Blanch, A.R. Mobilisation of microbial indicators, microbial source tracking markers and pathogens after rainfall events. Water Res. 2017, 112, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraay, A.N.; Man, O.; Levy, M.C.; Levy, K.; Ionides, E.; Eisenberg, J.N. Understanding the impact of rainfall on diarrhea: Testing the concentration-dilution hypothesis using a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 126001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, K.D.; Oliver, J.D. The ecology of Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio cholerae, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in North Carolina estuaries. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzulli, L.; Colwell, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Ocean warming and spread of pathogenic vibrios in the aquatic environment. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, M.; Reef, R. Potential Pollution Sources from Agricultural Activities on Tropical Forested Floodplain Wetlands Revealed by Soil eDNA. Forests 2020, 11, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminska, D.; Blankenberg, A.-G.B.; Nemes, A.; Bøe, F.; Skarbøvik, E. Retention of sediments and nutrients in buffer zones with different riparian vegetation. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2020, Online, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Song, C.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y. The Optimal Width and Mechanism of Riparian Buffers for Storm Water Nutrient Removal in the Chinese Eutrophic Lake Chaohu Watershed. Water 2018, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri, M.; Furukawa, T.; Nakajima, F.; Sei, K. Pathogens and disease vectors/hosts monitoring in aquatic environments: Potential of using eDNA/eRNA based approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huver, J.; Koprivnikar, J.; Johnson, P.; Whyard, S. Development and application of an eDNA method to detect and quantify a pathogenic parasite in aquatic ecosystems. Ecol. Appl. A Publ. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2015, 25, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, I.; Carvalho, G.; Walsh, K.; Seymour, M.; Hajibabaei, M.; Lallias, D.; Christmas, M.; Creer, S. Annual time-series analysis of aqueous eDNA reveals ecologically relevant dynamics of lake ecosystem biodiversity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, M.; Edwards, F.; Cosby, B.; Bista, I.; Scarlett, P.; Brailsford, F.; Glanville, H.; De Bruyn, M.; Carvalho, G.; Creer, S. Environmental DNA provides higher resolution assessment of riverine biodiversity and ecosystem function via spatio-temporal nestedness and turnover partitioning. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Dong, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Ali, I. Speciation Distribution of Heavy Metals in Uranium Mining Impacted Soils and Impact on Bacterial Community Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; McIlroy, S.; Archana, A.; Baker, D.; Panagiotou, G. A pollution gradient contributes to the taxonomic, functional, and resistome diversity of microbial communities in marine sediments. Microbiome 2019, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagova-Mareckova, M.; Boenigk, J.; Bouchez, A.; Cermakova, K.; Chonova, T.; Cordier, T.; Eisendle, U.; Eleršek, T.; Fazi, S.; Fleituch, T.; et al. Expanding ecological assessment by integrating microorganisms into routine freshwater biomonitoring. Water Res. 2020, 191, 116767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, S.; Segawa, T.; Okabe, S. Simultaneous Quantification of Multiple Food- and Waterborne Pathogens by Use of Microfluidic Quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
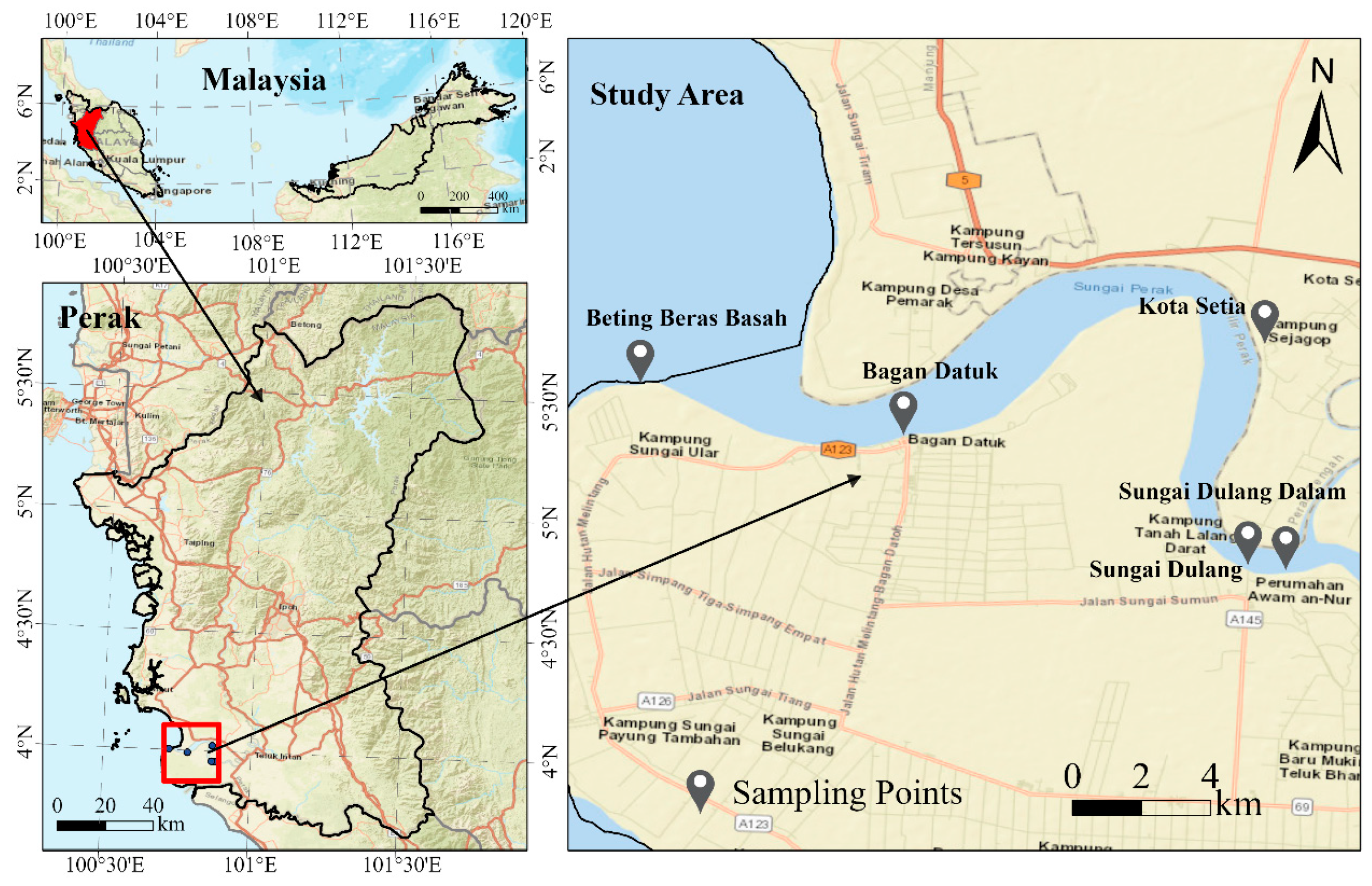
| Location ID | Name of Location | Coordinates | Sample ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Sungai Dulang Dalam | 3°57′29.2″ N 100°52′35.9″ E | P1, P2, P3 |
| L2 | Sungai Dulang | 3°57′32.8″ N 100°52′03.7″ E | P4, P5, P6 |
| L3 | Kota Setia | 4°01′25.0″ N 100°52′10.3″ E | P7, P8, P9 |
| L4 | Bagan Datuk | 3°59′33.7″ N 100°47′08.0″ E | P10, P11, P12 |
| L5 | Beting Beras Basah | 4°00′15.9″ N 100°43′23.7″ E | P13, P14, P15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Bhassu, S.; Ali, G.; Govindasamy, T.; Aziz, M.A.; Rajamanikam, A. Ecological Health and Freshwater Pathogen Using eDNA Metabarcoding: A Preliminary Assessment for Environmental Surveillance Development in Malaysia. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092055
Yang J, Bhassu S, Ali G, Govindasamy T, Aziz MA, Rajamanikam A. Ecological Health and Freshwater Pathogen Using eDNA Metabarcoding: A Preliminary Assessment for Environmental Surveillance Development in Malaysia. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092055
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiao, Subha Bhassu, Ghazanfer Ali, Thenmoli Govindasamy, Muhamad Afiq Aziz, and Arutchelvan Rajamanikam. 2025. "Ecological Health and Freshwater Pathogen Using eDNA Metabarcoding: A Preliminary Assessment for Environmental Surveillance Development in Malaysia" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092055
APA StyleYang, J., Bhassu, S., Ali, G., Govindasamy, T., Aziz, M. A., & Rajamanikam, A. (2025). Ecological Health and Freshwater Pathogen Using eDNA Metabarcoding: A Preliminary Assessment for Environmental Surveillance Development in Malaysia. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092055







