Challenges and Potential of Remote Sensing for Assessing Salmonella Risk in Water Sources: Evidence from Chile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Source of Data on Salmonella Occurrence
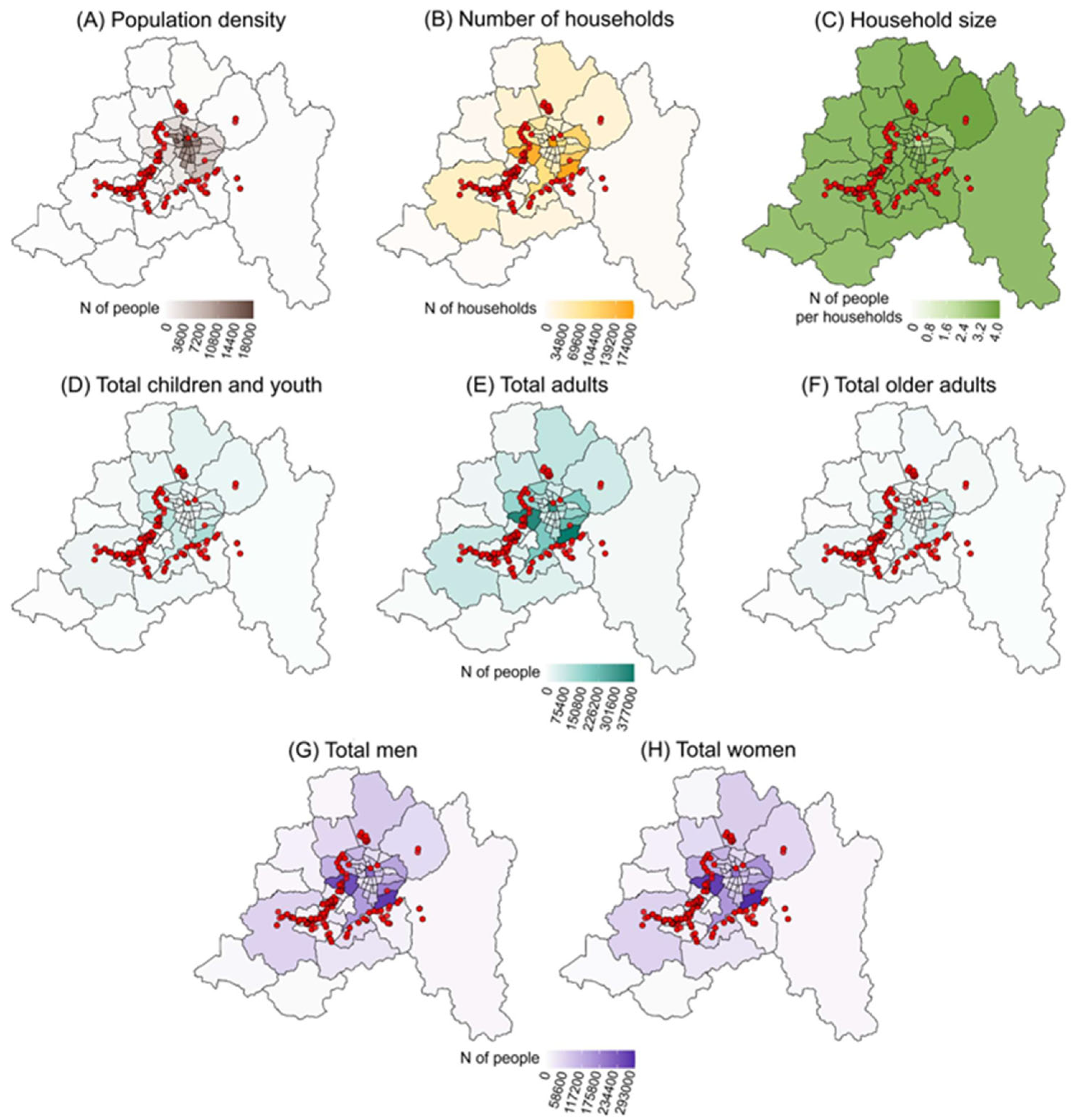
2.3. Sociodemographic Data: Who Are the Affected?
2.4. Environmental and Land Use Data Processing
2.5. Remote Sensing-Based Environmental Variables
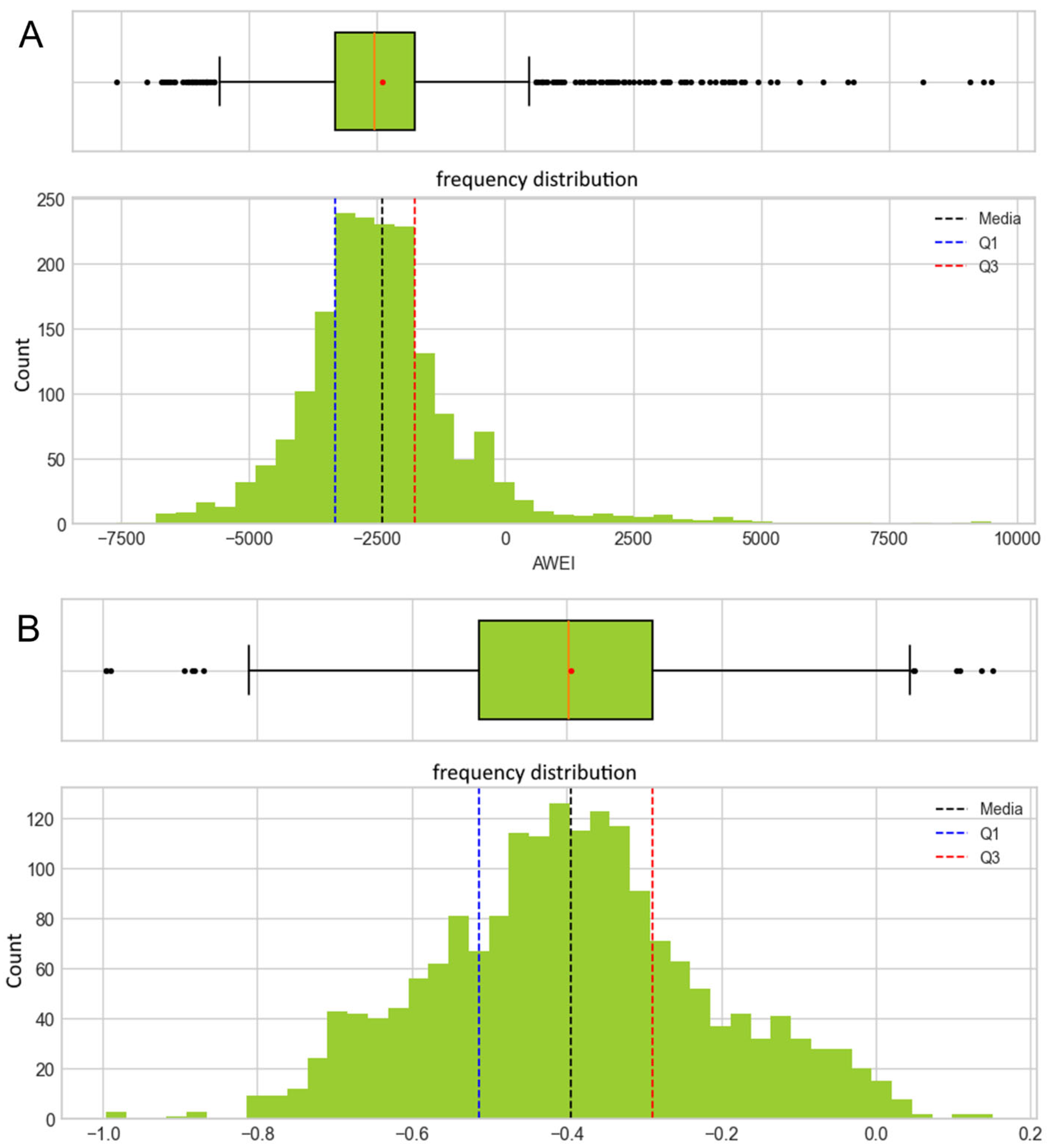
2.5.1. Analysis of Derived Spectral Indices
Vegetation-Related Indices
Water-Related Indices
Urban Development-Related Indices
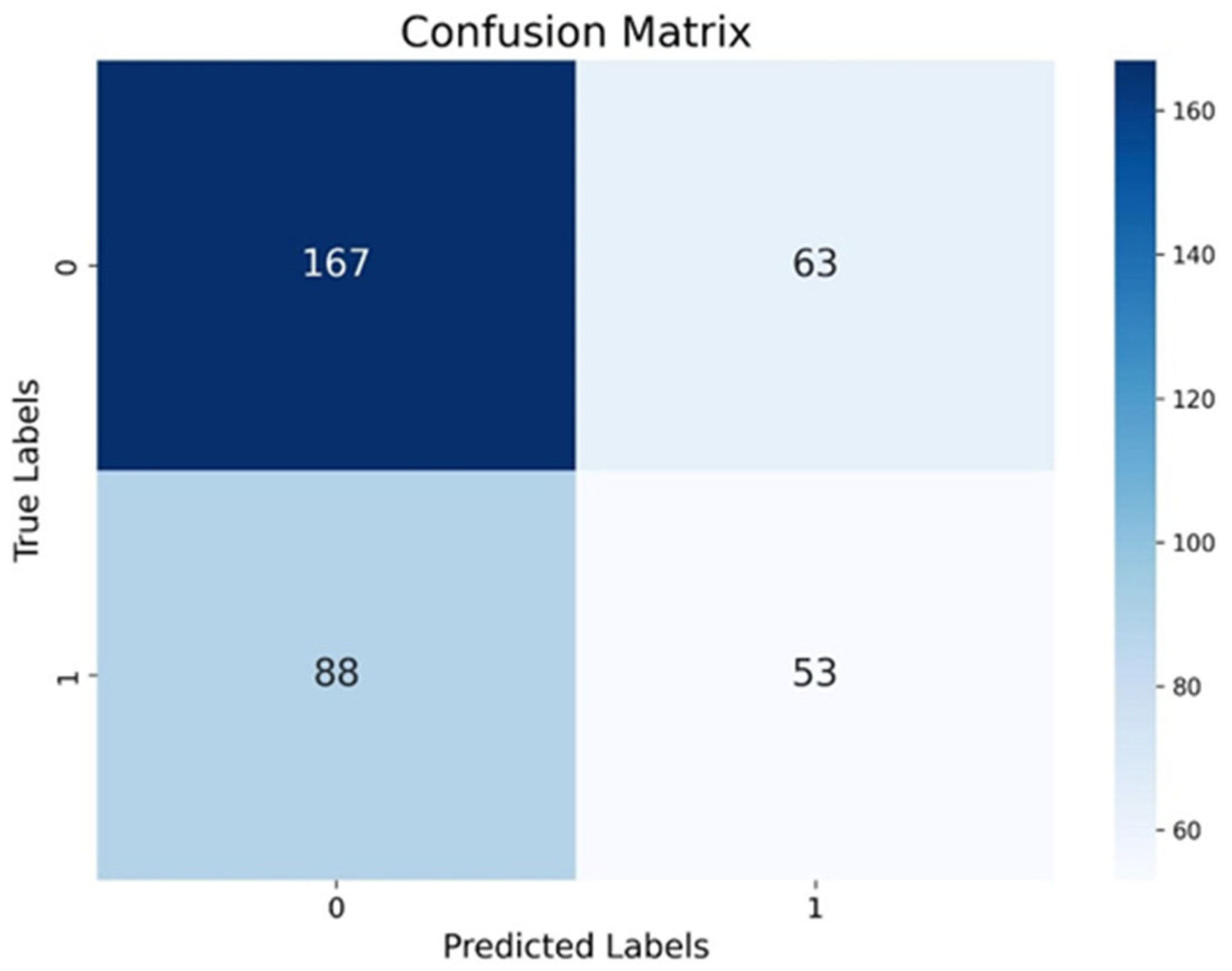
2.6. Detection of Salmonella Based Index Derived Remote Sensing
2.7. Salmonella Prevalence
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Demographic Analysis and Its Association with the Presence of Salmonella
3.2. Assessing the Role of Erosion and WWTP Proximity in Salmonella Detection
3.3. Remote Sensing
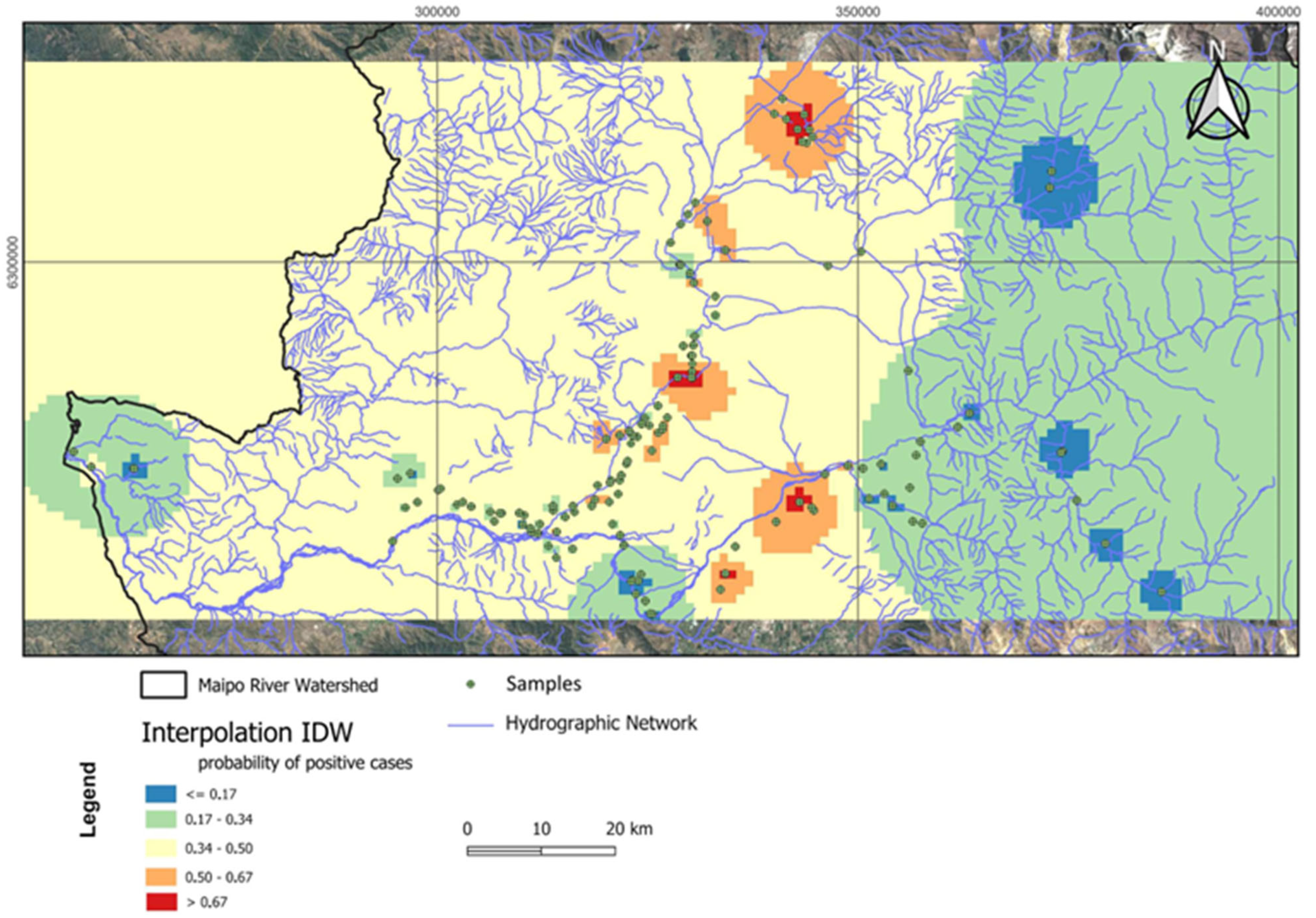
3.4. Spatial Analysis of Salmonella Prevalence
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carbas, B.; Cardoso, L.; Coelho, A.C. Investigation on the Knowledge Associated with Foodborne Diseases in Consumers of Northeastern Portugal. Food Control 2013, 30, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, L. The Genus Salmonella. In The Prokaryotes: An Evolving Electronic Resource for the Microbiological Community; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Uyttendaele, M.; Jaykus, L.-A.; Amoah, P.; Chiodini, A.; Cunliffe, D.; Jacxsens, L.; Holvoet, K.; Korsten, L.; Lau, M.; McClure, P.; et al. Microbial Hazards in Irrigation Water: Standards, Norms, and Testing to Manage Use of Water in Fresh Produce Primary Production. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 336–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, J.L.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Microbiological Reduction Strategies of Irrigation Water for Fresh Produce. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.Y.; Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Garneau, P.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. Waterborne Pathogens: Detection Methods and Challenges. Pathogens 2015, 4, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.S.G.; Palharini, R.S.A.; Monteiro, F.F.; Ayala, S.; Undurraga, E.A. Prevalence and Distribution of Salmonella in Water Bodies in South America: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.; da Silva, A.L.B.R.; Dunn, L.L. Factors Impacting the Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens in Agricultural Water Sources in the Southeastern United States. Water 2019, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ispch.cl/sites/default/files/BoletínSalmonella-12052020A.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- INE—Instituto Nacional de Estadisticas de Chile: Resultados.del censo 2024. Resultados. Available online: https://censo2024.ine.gob.cl/resultados/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Biblioteca del Congreso Nacional. SIIT Hidrografía Región Metropolitana de Santiago. Available online: https://www.bcn.cl/siit/nuestropais/region13/hidrografia.htm (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Ingenheros integrales LTDA. “INFORME AMBIENTAL Modificación PRC de San Antonio Sector Portuario Sur” (2012). Available online: https://eae.mma.gob.cl/storage/documents/01_Ingreso_PRC_San_Antonio-Portuario_Sur.pdf.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Álvarez-Garretón, C.; Marinao y Juan Pablo Boisier, R. La Crítica Situación del Agua Potable en la Región Metropolitana. Available online: https://www.cr2.cl/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Infografia_UsoAgua_062022.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Toro, M.; Weller, D.; Ramos, R.; Diaz, L.; Alvarez, F.P.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Meng, J.; Adell, A.D. Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors Associated with the Likelihood of Detecting Salmonella in Agricultural Watersheds. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Wolfram, A.; Desin, T.S. Advancements in Detection Methods for Salmonella in Food: A Comprehensive Review. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Yalcinkaya, F.; Altıok, E.; Pietrelli, A.; Nastro, R.A.; Lovecchio, N.; Ieropoulos, I.A.; Tsipa, A. The Role of Remote Sensing in the Evolution of Water Pollution Detection and Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review. Phys. Chem. Earth 2024, 136, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.J.; Ford, T.E.; Colwell, R.R.; Baker-Austin, C.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Subramaniam, A.; Capone, D.G. Viewing Marine Bacteria, Their Activity and Response to Environmental Drivers from Orbit: Satellite Remote Sensing of Bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racault, M.-F.; Abdulaziz, A.; George, G.; Menon, N.; C, J.; Punathil, M.; McConville, K.; Loveday, B.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; et al. Environmental Reservoirs of Vibrio Cholerae: Challenges and Opportunities for Ocean-Color Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Z.-Q.; Rusch, K.A.; Wing, M.G.; Chenier, K. Remote Sensing Algorithms for Estimating Enterococcus Concentration in Coastal Louisiana Beaches. In Proceedings of the The Ninth International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Houston, TX, USA, 25–29 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Overview of the Application of Remote Sensing in Effective Monitoring of Water Quality Parameters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.T.; Can, L.D.; Nhan, N.T.; Schmalz, B.; Luu, T.L. Influences of Key Factors on River Water Quality in Urban and Rural Areas: A Review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Wang, J.; McCarthy, A.J.; Sekar, R. Industrial and Agricultural Land Uses Affected the Water Quality and Shaped the Bacterial Communities in the Inflow Rivers of Taihu Lake. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, L.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Sridhar, G.; Legesse, G. Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Soil Erosion in Yezat Watershed, North Western Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censos de Población y Vivienda. Available online: https://www.ine.gob.cl/estadisticas/sociales/censos-de-poblacion-y-vivienda#:~:text=El%20censo%20permite%20contar%20con,total%20de%2017.574.003%20personas (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Quiénes Somos. Available online: https://www.conaf.cl/quienes-somos/#:~:text=Monitorear%2C%20a%20distintas%20escalas%2C%20el,en%20el%20enfoque%20de%20g%C3%A9nero (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Saha, D.; Sanyal, A.K. Vulnerability of f(Q) Gravity Theory and a Possible Resolution. Acad. Quantum 2025, 2, 7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TECHO Chile, Aumentan a Cerca de 114 Mil las Familias que Viven en Campamentos; TECHO Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2023; p. 1.
- Web Diseminación Censo 2017. Available online: http://resultados.censo2017.cl/Region?R=R13 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Chen, Z.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Delgado Suarez, E.; Adell, A.D.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Bonelli, R.R.; Huang, X.; Brown, E.; Allard, M.; et al. A Multicenter Genomic Epidemiological Investigation in Brazil, Chile, and Mexico Reveals the Diversity and Persistence of Salmonella Populations in Surface Waters. mBio 2024, 15, e0077724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web Diseminación Censo 2017. Available online: http://resultados.censo2017.cl/Home/Concepto (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Superintendencia de Servicios Sanitarios. Available online: https://www.siss.gob.cl/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Geoportal de Chile. Available online: https://www.geoportal.cl/catalog (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Planificación Catastral. Available online: https://ide.minagri.gob.cl/geoweb/2019/11/22/planificacion-catastral (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Garcez Utsumi, A.; Martins de Almeida Oliveira, N.; Guimarães Sousa, N. Análise de Imagens Sentinel-2 No Mapeamento de Formações Florestais No Município de Uberaba-MG. Sci. Plena 2024, 19, 129901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Jimmy, A.N.; Alam, M.S.; Khan, N.A. The Use of Multi-Temporal Landsat Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Data for Assessing Forest Cover Change of Lawarchara National Park. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 17702–17722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Huete, A.R.; Nagler, P.L.; Nelson, S.G. Relationship between Remotely-Sensed Vegetation Indices, Canopy Attributes and Plant Physiological Processes: What Vegetation Indices Can and Cannot Tell Us about the Landscape. Sensors 2008, 8, 2136–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Chen, S.; Yin, T.; Chavanon, E.; Lauret, N.; Guilleux, J.; Henke, M.; Qin, W.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; et al. Using the Negative Soil Adjustment Factor of Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI) to Resist Saturation Effects and Estimate Leaf Area Index (LAI) in Dense Vegetation Areas. Sensors 2021, 21, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhong, R.; Yan, K.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Pu, J.; Gao, S.; Qi, J.; Yin, G.; Myneni, R.B. Evaluating the Saturation Effect of Vegetation Indices in Forests Using 3D Radiative Transfer Simulations and Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, B.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Onda, Y.; Qiu, G. Sensitivity of the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to Topographic Effects: A Case Study in High-Density Cypress Forest. Sensors 2007, 7, 2636–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, R.; Li, D.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Jia, K.; Hicks, B.J. Remote Sensing Big Data for Water Environment Monitoring: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Earths Future 2022, 10, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Mouazen, A.M. A Novel Spectral Index for Estimation of Relative Chlorophyll Content of Sugar Beet. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 184, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Tang, W.; Gao, D.; Zhao, R.; An, L.; Li, M.; Sun, H.; Song, D. UAV-Based Chlorophyll Content Estimation by Evaluating Vegetation Index Responses under Different Crop Coverages. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, Z.; Varco, J.J.; Dhillon, J.S.; Fox, A.A.A.; Czarnecki, J.; Henry, W.B. Ground versus Aerial Canopy Reflectance of Corn: Red-edge and Non-red Edge Vegetation Indices. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 2782–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hunt, E.R., Jr.; Qu, J.J.; Hao, X.; Daughtry, C.S.T. Towards Estimation of Canopy Foliar Biomass with Spectral Reflectance Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Duan, H.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, C. Assessing Habitat Suitability for Wintering Geese by Using Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in a Large Floodplain Wetland, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deoli, V.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, M.; Kuriqi, A.; Elbeltagi, A. Water Spread Mapping of Multiple Lakes Using Remote Sensing and Satellite Data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.L.K.; Rao, C.V.; Kumar, P.R.; Anjaneyulu, R.V.G.; Krishna, B.G. A Novel Method for Water and Water Canal Extraction from Landsat-8 Oli Imagery. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-5, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, R. Semi-Automated Extraction of Surface Water Based on ZhuHai-1 Hyperspectral Satellite Images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 12, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhaimin, M.; Fitriani, D.; Adyatma, S.; Arisanty, D. Mapping Build-up Area Density Using Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI) and Urban Index (UI) Wetland in the City Banjarmasin. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1089, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Irmak, S.; Kilic, A.; Sharma, V.; Gilley, J.; Meyer, G.; Knezevic, Z.; Marx, S. Quantification and Mapping of Surface Residue Cover for Maize and Soybean Fields South Central Nebraska. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 925–939. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.; Chong, K. Modified Inverse Distance Weighting Interpolation for Particulate Matter Estimation and Mapping. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmanov, R.; Miftakhov, I.; Ishbulatov, M.; Galeev, E.; Shafeeva, E. Comparison of the Effectiveness of GIS-Based Interpolation Methods for Estimating the Spatial Distribution of Agrochemical Soil Properties. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, C.; Yamada, K. Impact of Population Growth on the Water Quality of Natural Water Bodies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catastro de Campamentos. Available online: https://www.minvu.gob.cl/catastro-de-campamentos/ (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Vergara-Perucich, J.F.; Aguirre-Nuñez, C.; Gil, D.; Domínguez, P.; Undurraga, E.A.; Valenzuela, E. Housing Prices in Unregulated Markets: Study on Verticalised Dwellings in Santiago de Chile. J. Urban Health 2019, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, B.; Prieto Suárez, I.; Sabatini Downey, J.J. Vivir en Campamentos: ¿Camino Hacia la Vivienda Formal o Estrategia de Localización para Enfrentar la Vulnerabilidad? EURE 2010, 36, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milad, A. The Reproduction of Informal Settlements in Santiago: Housing Policy, Cycles of Repopulation and the “politics of Poverty” as a Regime of Government. Urban Stud. 2024, 61, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: A One Health Perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Li, B. Presence and Persistence of Salmonella in Water: The Impact on Microbial Quality of Water and Food Safety. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, K.; Walker, D.I.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; McDonald, J.E.; Hillary, L.S.; Malham, S.K.; Jones, D.L. Viral Indicators for Tracking Domestic Wastewater Contamination in the Aquatic Environment. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apau, J.; Osei-Owusu, J.; Yeboah, A.; Gyamfi, O.; Darko, G.; Akoto, O.; Dodd, M. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Sediments, Physicochemical and Microbial Parameters of Water from River Subin of Kumasi Metropolis in Ghana. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantesi, C.; Bonadonna, L.; Briancesco, R.; Grohmann, E.; Toze, S.; Tandoi, V. Salmonella in Surface and Drinking Water: Occurrence and Water-Mediated Transmission. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, C.; Xu, H.; Gamarra, C.; Villanueva, C.; Siguayro, H. Clasificación de La Vegetación Acuática En El Lago Titicaca a Partir de índices Del Satélite Sentinel-2. Bol. Inst. Mar Perú 2022, 37, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikechukwu, M.N.; Ebinne, E.; Idorenyin, U.; Raphael, N.I. Accuracy Assessment and Comparative Analysis of IDW, Spline and Kriging in Spatial Interpolation of Landform (topography): An Experimental Study. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2017, 09, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Mattevada, S.; O’Bryant, S.E. Comparison of the Accuracy of Kriging and IDW Interpolations in Estimating Groundwater Arsenic Concentrations in Texas. Environ. Res. 2014, 130, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




   |
| Presence Salmonella | Precision | Recall | f1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 230 |
| 1 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 141 |
| Accuracy | 0.59 | 371 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palharini, R.S.A.; Reyes, M.S.G.; Monteiro, F.F.; Villavicencio, L.M.M.; Adell, A.D.; Toro, M.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Undurraga, E.A. Challenges and Potential of Remote Sensing for Assessing Salmonella Risk in Water Sources: Evidence from Chile. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071539
Palharini RSA, Reyes MSG, Monteiro FF, Villavicencio LMM, Adell AD, Toro M, Moreno-Switt AI, Undurraga EA. Challenges and Potential of Remote Sensing for Assessing Salmonella Risk in Water Sources: Evidence from Chile. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071539
Chicago/Turabian StylePalharini, Rayana Santos Araujo, Makarena Sofia Gonzalez Reyes, Felipe Ferreira Monteiro, Lourdes Milagros Mendoza Villavicencio, Aiko D. Adell, Magaly Toro, Andrea I. Moreno-Switt, and Eduardo A. Undurraga. 2025. "Challenges and Potential of Remote Sensing for Assessing Salmonella Risk in Water Sources: Evidence from Chile" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071539
APA StylePalharini, R. S. A., Reyes, M. S. G., Monteiro, F. F., Villavicencio, L. M. M., Adell, A. D., Toro, M., Moreno-Switt, A. I., & Undurraga, E. A. (2025). Challenges and Potential of Remote Sensing for Assessing Salmonella Risk in Water Sources: Evidence from Chile. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071539








