Shrub Expansion Impacts on Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles and Microorganism Communities in Wetlands in Northeastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Determination of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.5. DNA Extraction, Metagenome Sequencing, and Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Shrub Expansion on the Physicochemical Properties of Soils
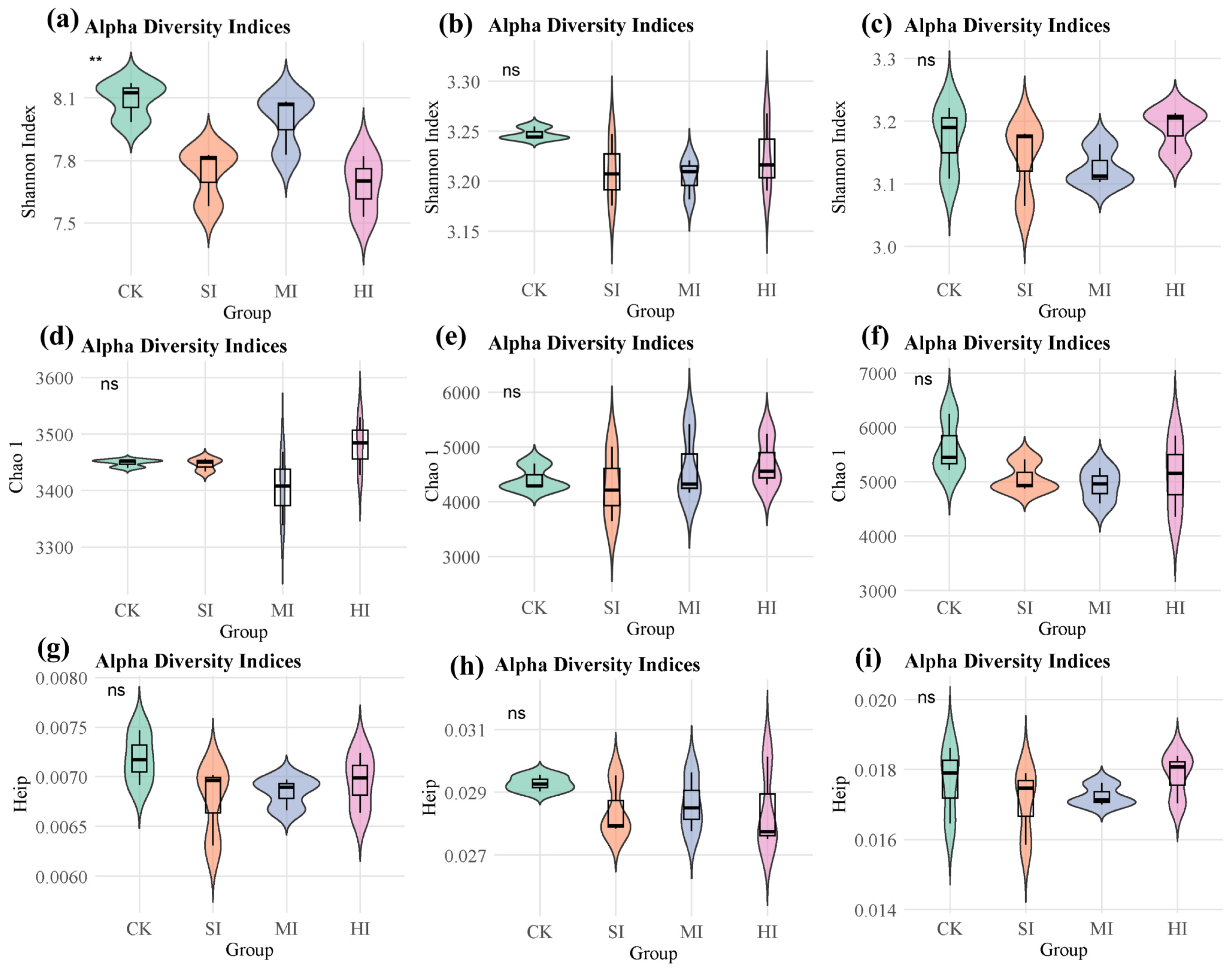
3.2. Changes in Microbial Diversity Related to Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles
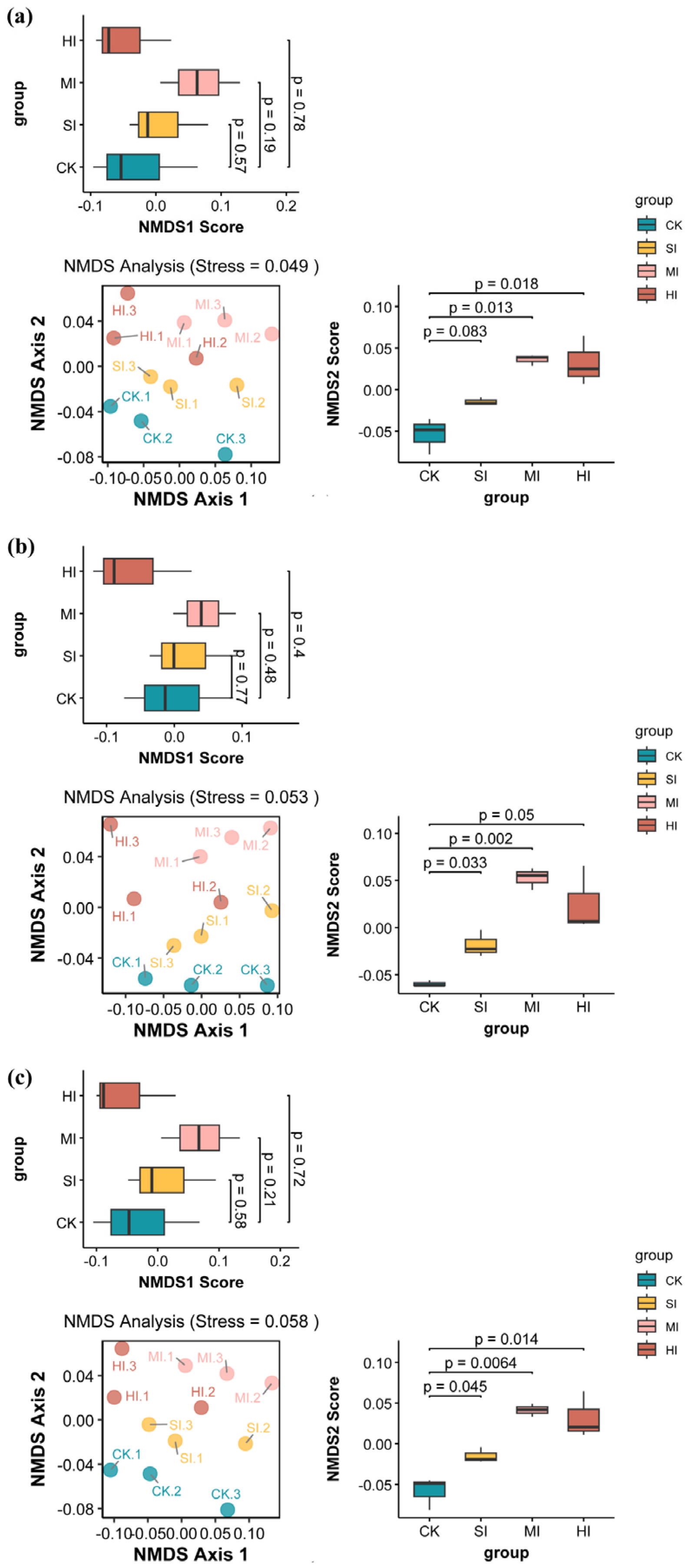
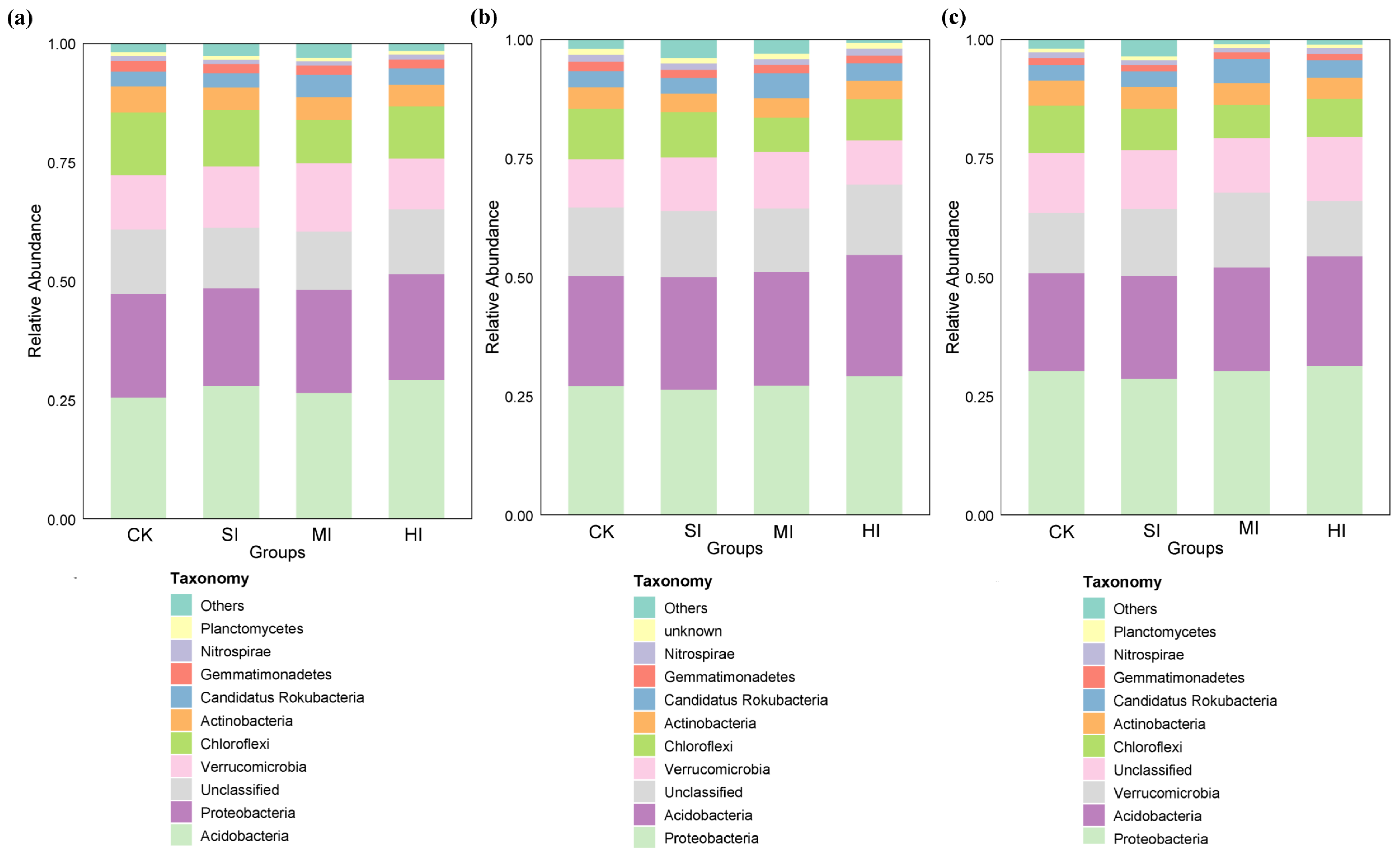
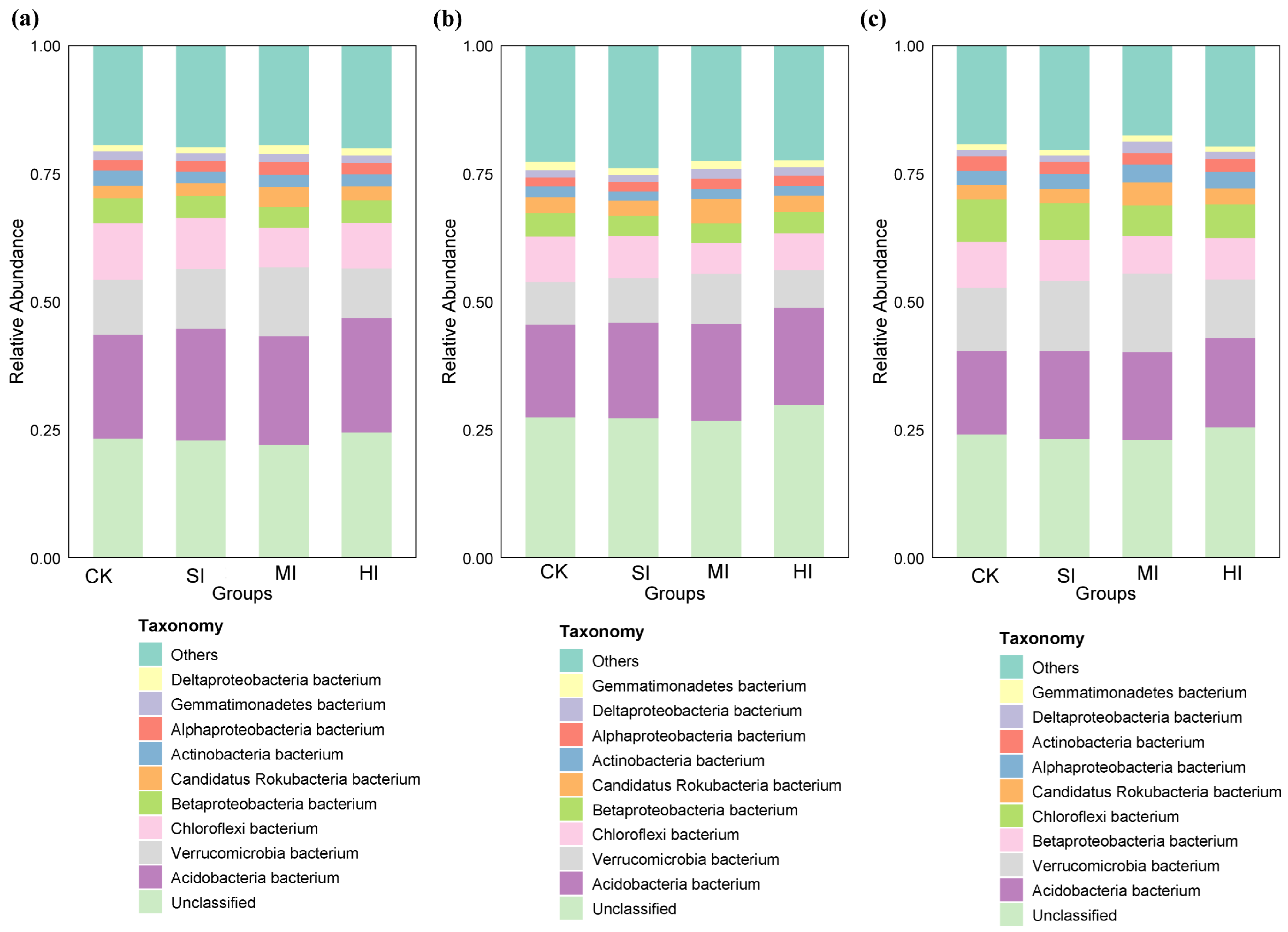
3.3. Shrub Expansion Effects on Microbial Community Composition
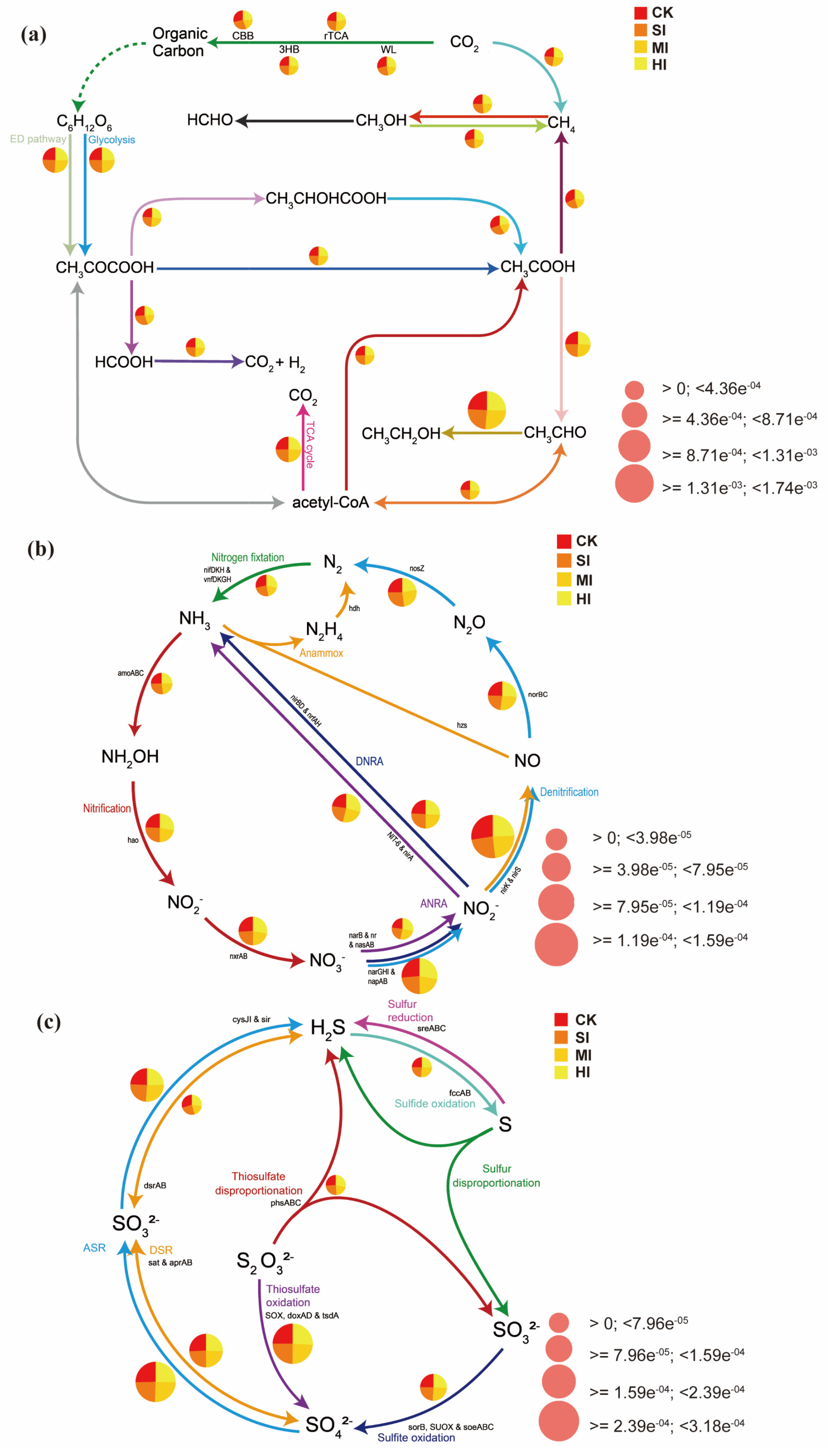
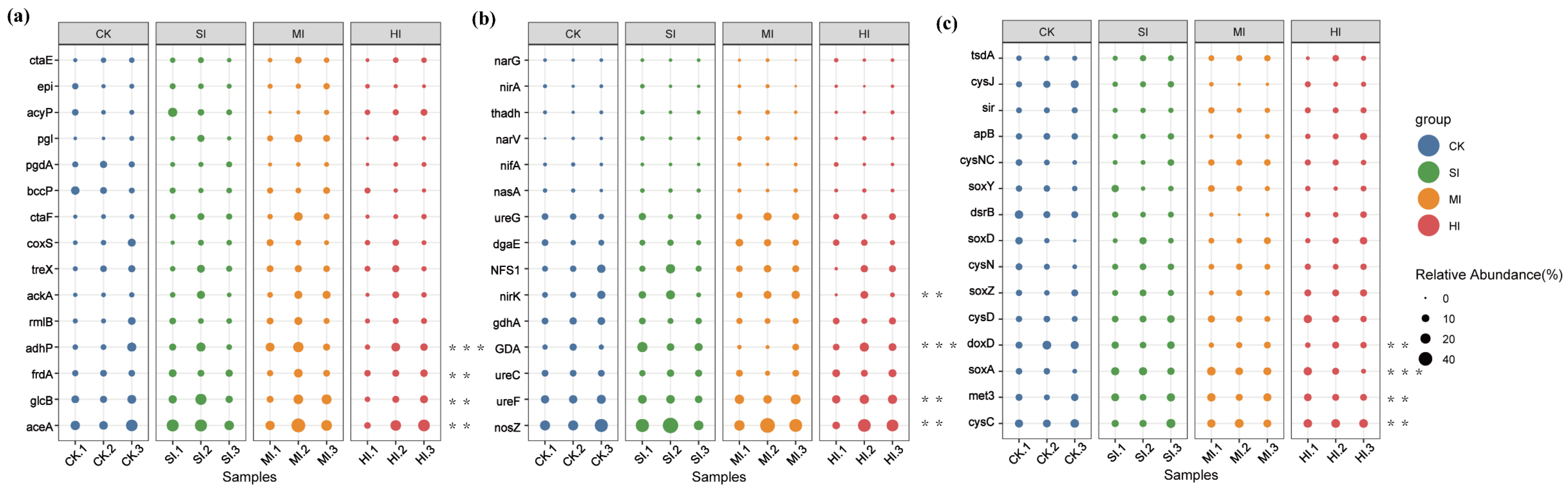
3.4. Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Metabolism: Metabolic Pathways and Genetic Changes
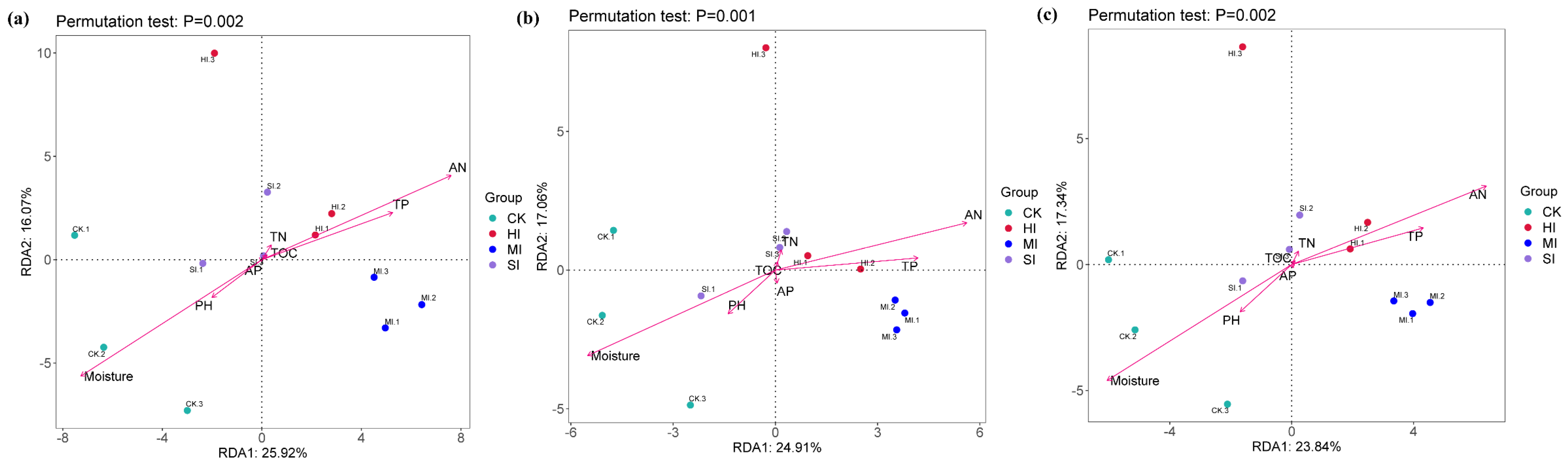
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Shrub Expansion Significantly Altered Soil Properties
4.2. Shrub Expansion Impacts on Microbial Community Diversity
4.3. Shrub Expansion Impacts on Microbial Community Composition
4.4. Effects of Shrub Expansion on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles
4.5. Correlation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Song, C.; Xin, S. Effects of Long-Term (17 Years) Nitrogen Input on Soil Bacterial Community in Sanjiang Plain: The Largest Marsh Wetland in China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Lu, C.; Yuan, F.; Fan, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Qiu, P.; Feng, Z.; Wang, C.; Zou, X. Soil carbon-fixing bacterial communities respond to plant community change in coastal salt marsh wetlands. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunois, M.; Stavert, A.R.; Poulter, B.; Bousquet, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Raymond, P.A.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Houweling, S.; Patra, P.K.; et al. The Global Methane Budget 2000–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 12, 1561–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulter, B.; Bousquet, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Peregon, A.; Saunois, M.; Arora, V.K.; Beerling, D.J.; Brovkin, V.; Jones, C.D.; et al. Global wetland contribution to 2000–2012 atmospheric methane growth rate dynamics. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 094013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Y.; Su, Y.; Song, C. Marshland conversion to cropland in northeast China from 1950 to 2000 reduced the greenhouse effect. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, D.W.; Song, K.S.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Duan, H. Changes of land use and of ecosystem service values in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 112, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X. Marshland loss warms local land surface temperature in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Li, L.; Jia, M.; Dong, Z.; Miao, Z.; Ren, C.; Song, C. Quantifying changes in multiple ecosystem services during 1992–2012 in the Sanjiang Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.Q.; Zhang, S.W. Ecosystem service decline in response to wetland loss in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.A.; Wurzburger, N. Elevated rates of heterotrophic respiration in shrub-conditioned arctic tundra soils. Pedobiologia 2019, 72, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent Arthur, A.D.; Michael, B.; Pritchard William, J.; Newbold Lindsay, K.; Tim, G.; Andrew, G.; Snell Helen, S.K.; Irene, C.; Antonios, M.; Grant Helen, K.; et al. Shrub expansion modulates belowground impacts of changing snow conditions in alpine grasslands. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 25, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oriol, G.; Karita, S.; Ninot Josep, M.; József, G.; Annamari, M.; Ahonen Saija, H.K.; Josep, P. Encroachment of shrubs into subalpine grasslands in the Pyrenees modifies the structure of soil fungal communities and soil properties. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, B.; Carnol, M.; Dharmarajah, A.; Brunner, I.; Schleppi, P. Only minor changes in the soil microbiome of a sub-alpine forest after 20 years of moderately increased nitrogen loads. Front. For. Glob. Change 2020, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, G.; Chhabra, S.; Prasad, R. Role of soil microbes in biogeochemical cycle for enhancing soil fertility. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, G.; Okafor, B.N.; Visconti, D. Soil microarthropods and nutrient cycling. In Environment, Climate, Plant and Vegetation Growth; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J. Effects of plants and soil microorganisms on organic carbon and the relationship between carbon and nitrogen in constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 62249–62261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Qin, S.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Yan, R.; Fa, K. Effects of xeric shrubs on soil microbial communities in a desert in northern China. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Tian, Y.; Bai, S.; Zuoma, D.; Zhang, D.; Ma, X.; Mu, X. The mitigation of microbial carbon and nitrogen limitations by shrub encroachment: Extracellular enzyme stoichiometry of the alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biogeochemistry 2023, 165, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazza, L.; Bardgett, R.D.; Mitchell, E.A.D.; Buttler, A. Linking soil microbial communities to vascular plant abundance along a climate gradient. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, X.C.; Yu, K.; Wei, J.Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Hu, X.; D’Odorico, P. Does phenology play a role in the feedbacks underlying shrub encroachment? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, M.D.; Collins, S.L.; Swann, A.M.; Ford, P.L.; Litvak, M. Grassland to shrubland state transitions enhance carbon sequestration in the northern Chihuahuan Desert. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, W.; Ji-Shi, A.; Ma, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, R.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.-F.; Leite, P.A.; Ding, L.; et al. Shrub encroachment increases soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in alpine grassland ecosystems of the central Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauclet, E.; Agnan, Y.; Hirst, C.; Monhonval, A.; Pereira, B.; Vandeuren, A.; Villani, M.; Ledman, J.; Taylor, M.; Jasinski, B.L.; et al. Changing sub-Arctic tundra vegetation upon permafrost degradation: Impact on foliar mineral element cycling. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2022, 19, 2333–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, T.; Bao, D.; Ji, W.; Su, J. Shrub encroachment in alpine meadows facilitates soil carbon and nitrogen storage by redistributing soil water. Catena 2025, 256, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.C. Collaborative Research: Shrub Impacts on Nitrogen Inputs and Turnover in the Arctic, and the Potential Feedbacks to Vegetation and Climate Change. In NSF Award Number 1556496; Directorate for Biological Sciences: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2016; Volume 15, p. 56496. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, X.H.; Sui, X.; Li, M.S.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhang, R.T.; Yang, L.B. Effects of Simulated Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial CarbonC Metabolism in Calamagrostis angustifolia Wetland in Sanjiang Plain. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2022, 43, 4674–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Fu, X.; Zhong, H.; Sui, X.; Liu, Y. Changes in Soil Bacterial Community and Function in Winter Following Long-Term Nitrogen (N) Deposition in Wetland Soil in Sanjiang Plain, China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.T.; Wang, S.Z.; Zhong, H.X.; Sui, X.; Liu, Y.-N. Seasonal variations in the soil microbiota of a temperate wetland in Northeast China in response to nitrogen deposition. Catena 2025, 250, 108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.S.; Han, Y.J.; Chen, L.X.; Liu, J.; Hu, M.; Li, S.-J.; Kuang, J.-L.; Chain, P.S.G.; Huang, L.-N.; Shu, W.-S. Ecological roles of dominant and rare prokaryotes in acid mine drainage revealed by metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1280–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sena Brandine, G.; Smith, A.D. Falco: High-speed FastQC emulation for quality control of sequencing data. F1000Research 2021, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y.L. IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for singlecell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. readxl: Read Excel Files (Version 1.4.3) [R Package]. Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=readxl (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Hester, J. glue: Interpreted String Literals (Version 1.6.2) [R Package]. Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=glue (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Cui, Z.; Wu, G.L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y. Fine roots determine soil infiltration potential than soil water content in semi-arid grassland soils. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.H.; Caldwell, M.M. Hydraulic lift: Substantial nocturnal water transport between soil layers by Artemisia tridentata roots. Oecologia 1987, 73, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Raikes, J.A.; Hartley, A.E.; Cross, A.F. On the spatial pattern of soil nutrients in desert ecosystems. Ecology 1996, 77, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, D.J.; Bowker, M.A.; Maestre, F.T.; Roger, E.; Reynolds, J.F.; Whitford, W.G. Impacts of shrub encroachment on ecosystem structure and functioning: Towards a global synthesis. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Okin, G.S.; Bestelmeyer, B.T. A synthetic review of feedbacks and drivers of shrub encroachment in arid grasslands. Ecohydrology 2012, 5, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zheng, H.; Penuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Deng, D.; Cai, X.; Gao, D.; Nie, S.; He, Y.; Lü, X.; et al. Shrub encroachment leads to accumulation of C, N, and P in grassland soils and alters C: N: P stoichiometry: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Zuo, X.A.; Zhao, X.Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Zhou, X.; Lv, P.; Luo, Y.-Q.; Yun, J.-Y. Responses of soil fungal community to the sandy grassland restoration in Horqin Sandy Land, northern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuoma, D.; Ma, W.; Wang, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, D. Effect of shrub encroachment on alpine grass soil microbial community assembly. Front. Soil Sci. 2022, 2, 829575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Leff, J.W.; Adams, B.J.; Nielsen, U.N.; Bates, S.T.; Lauber, C.L.; Owens, S.; Gilbert, J.A.; Wall, D.H.; Caporaso, J.G. Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21390–21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, R.; Herbert, R.A.; Jaffe, A.L.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Power, M.E.; Koskella, B. Priority effects in microbiome assembly. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnolucci, M.; Battini, F.; Cristani, C.; Giovannetti, M. Diverse bacterial communities are recruited on spores of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T. Historical contingency in community assembly: Integrating niches, species pools, and priority effects. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.L.; Hättenschwiler, S.; Yang, J.J.; Sistla, S.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.; Cui, S.; Lü, X.; et al. Increasing rates of long-term nitrogen deposition consistently increased litter decomposition in a semi-arid grassland. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, K.; Xu, Q.; Hu, K.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B. Metagenomic insights into the effects of desiccation on functions associated with biogeochemical cycles and resistome of microbial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 212, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathour, R.; Gupta, J.; Mishra, A.; Rajeev, A.C.; Dupont, C.L.; Thakur, I.S. A comparative metagenomic study reveals microbial diversity and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of Pangong lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Bernhardt, E.S. Biogeochemistry: An Analysis of Global Change, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, E.; Yang, X.; Yang, J. Shifts in Microbial Community Structure and Co-occurrence Network along a Wide Soil Salinity Gradient. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.D.; Martiny, J.B.H. Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105 (Suppl. S1), 11512–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, J.; Dai, H.; Chen, Y. Phosphorus availability regulates nitrogen fixation rate through a key diazotrophic assembly: Evidence from a subtropical Moso bamboo forest subjected to nitrogen application. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alber, B.E.; Fuchs, G. Propionyl-coenzyme A synthase from Chloroflexus aurantiacus, a key enzyme of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle for autotrophic CO2 fixation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 12137–12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, S.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ma, Q.; Cai, Y.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Long-term nitrogen addition increases denitrification potential and functional gene abundance and changes denitrifying communities in acidic tea plantation soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinder, S.H.; Brock, T.D. Dimethyl sulfoxide as an electron acceptor for anaerobic growth. Arch. Microbiol. 1978, 116, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, F.; Fang, W.; Yang, T.; Chen, G.-H.; He, Z.; Wang, S. Microbial sulfur metabolism and environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

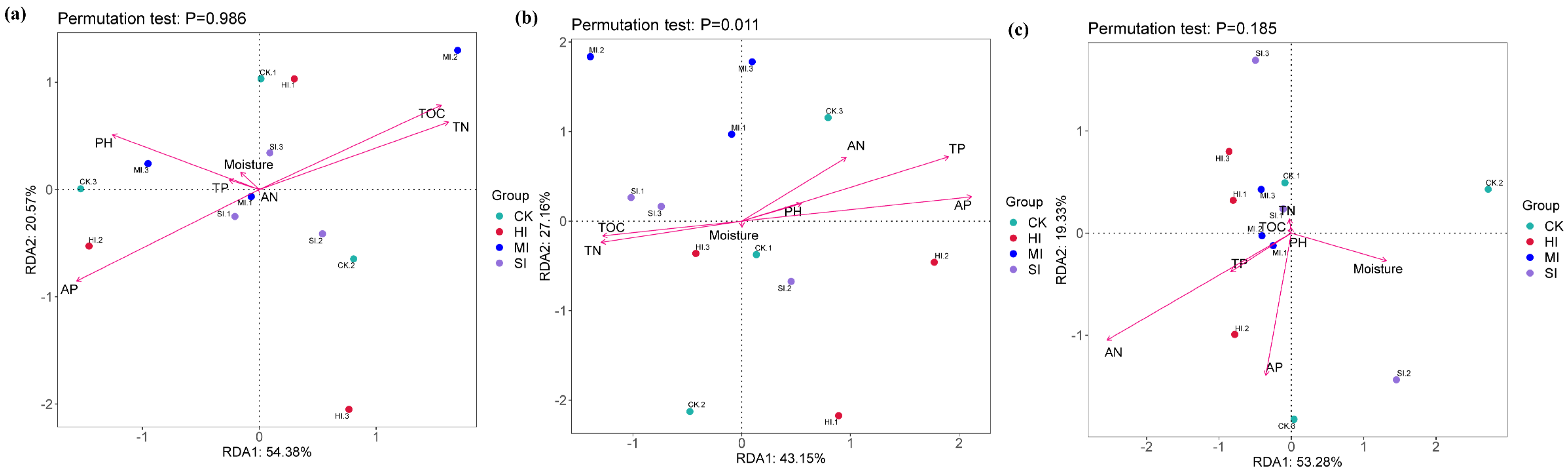
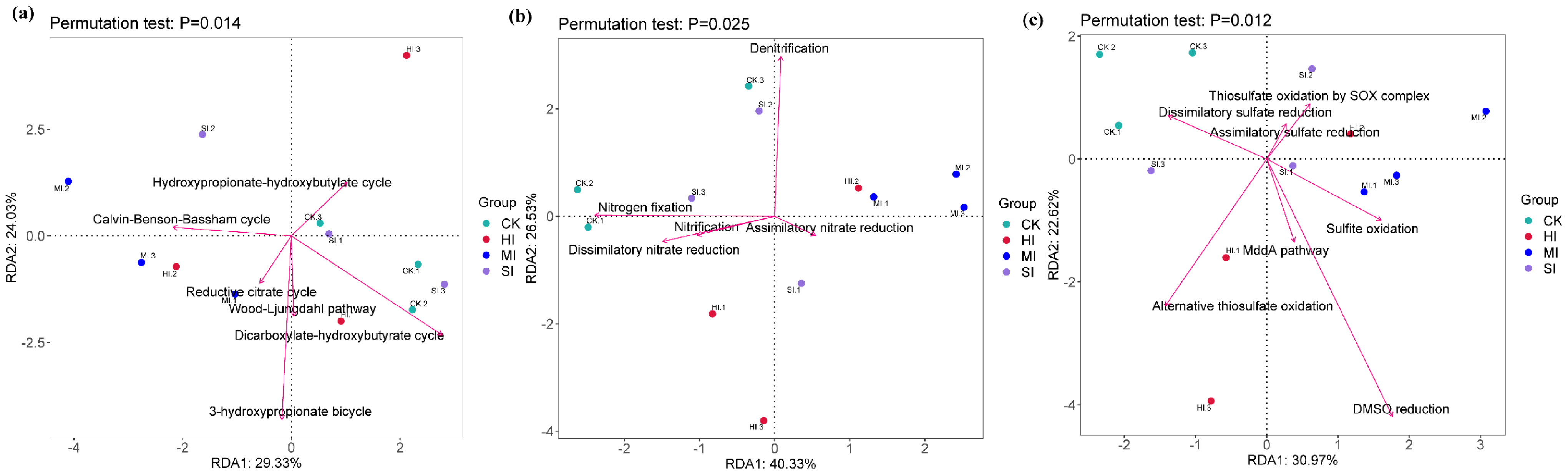
| Plot | PH | TN (g/kg) | TOC (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | Moisture (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.35 ± 0.12 a | 3.00 ± 0.24 a | 33.48 ± 3.87 a | 0.84 ± 0.07 a | 8.75 ± 1.62 a | 0.24 ± 0.03 b | 81.54 ± 0.98 a |
| SI | 5.22 ± 0.12 a | 3.75 ± 0.84 a | 39.85 ± 8.91 a | 1.03 ± 0.15 a | 8.26 ± 4.14 a | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 71.20 ± 0.13 b |
| MI | 5.26 ± 0.14 a | 3.27 ± 1.65 a | 35.42 ± 19.41 a | 1.07 ± 0.17 a | 8.17 ± 2.92 a | 0.32 ± 0.02 a | 70.67 ± 0.46 b |
| HI | 5.20 ± 0.12 a | 3.31 ± 1.20 a | 34.44 ± 13.59 a | 1.09 ± 0.10 a | 10.17 ± 3.88 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 a | 68.88 ± 0.59 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, R.; Sui, X. Shrub Expansion Impacts on Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles and Microorganism Communities in Wetlands in Northeastern China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092014
Wang S, Li L, Fu X, Zhong H, Zhang R, Sui X. Shrub Expansion Impacts on Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles and Microorganism Communities in Wetlands in Northeastern China. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092014
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shenzheng, Lin Li, Xiaoyu Fu, Haixiu Zhong, Rongtao Zhang, and Xin Sui. 2025. "Shrub Expansion Impacts on Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles and Microorganism Communities in Wetlands in Northeastern China" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092014
APA StyleWang, S., Li, L., Fu, X., Zhong, H., Zhang, R., & Sui, X. (2025). Shrub Expansion Impacts on Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Cycles and Microorganism Communities in Wetlands in Northeastern China. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092014







