Analysis of Genomic and Characterization Features of Microbulbifer weihaiensis sp. nov., Isolated from Coastal Sediment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Cultivation
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Genomic and Phylogenomic Analyses
2.4. Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Microbulbifer
2.5. Morphology, Physiology, and Biochemistry
2.6. Chemotaxonomy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phenotypic Properties
3.2. Chemotaxonomic Characteristics
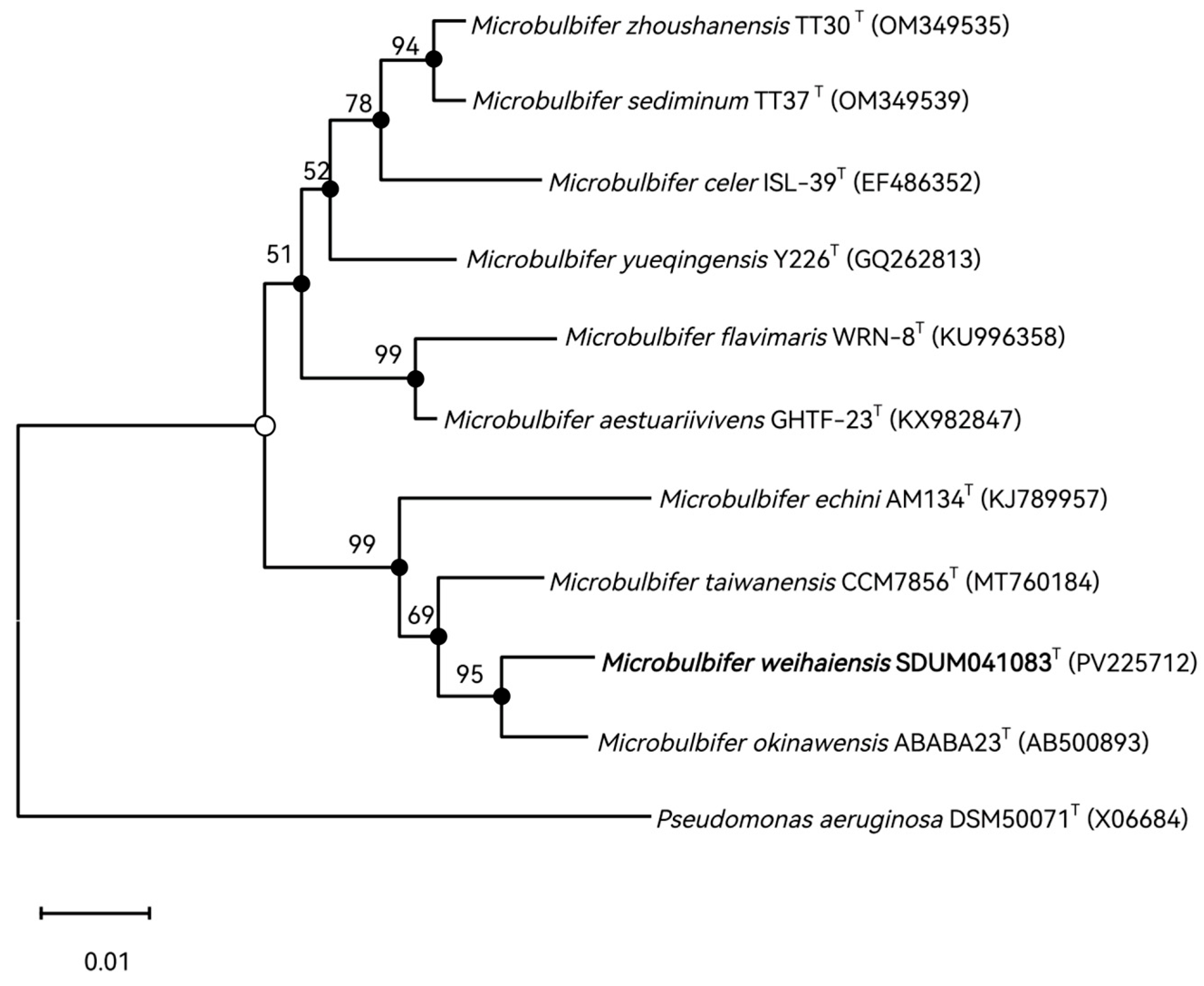
3.3. The 16S rRNA Gene Sequence and Phylogenetics
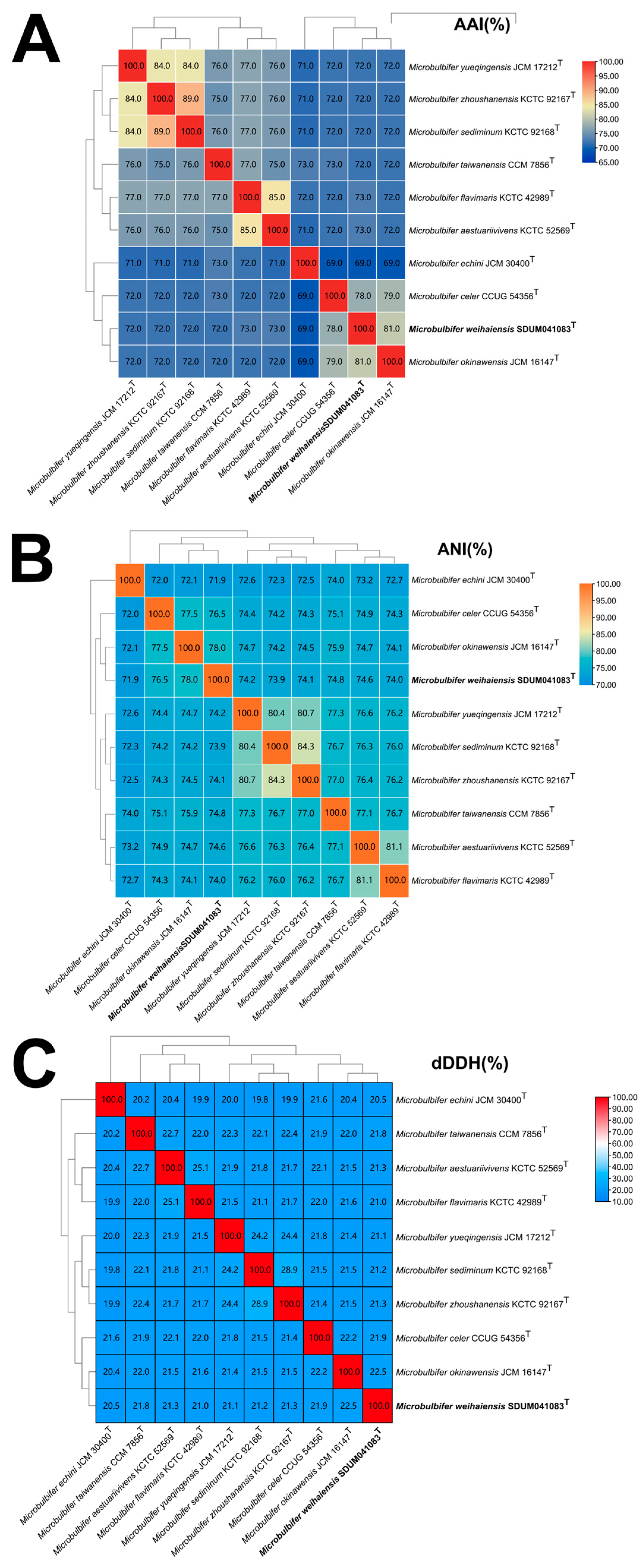
3.4. Genomic Features and Phylogenomics
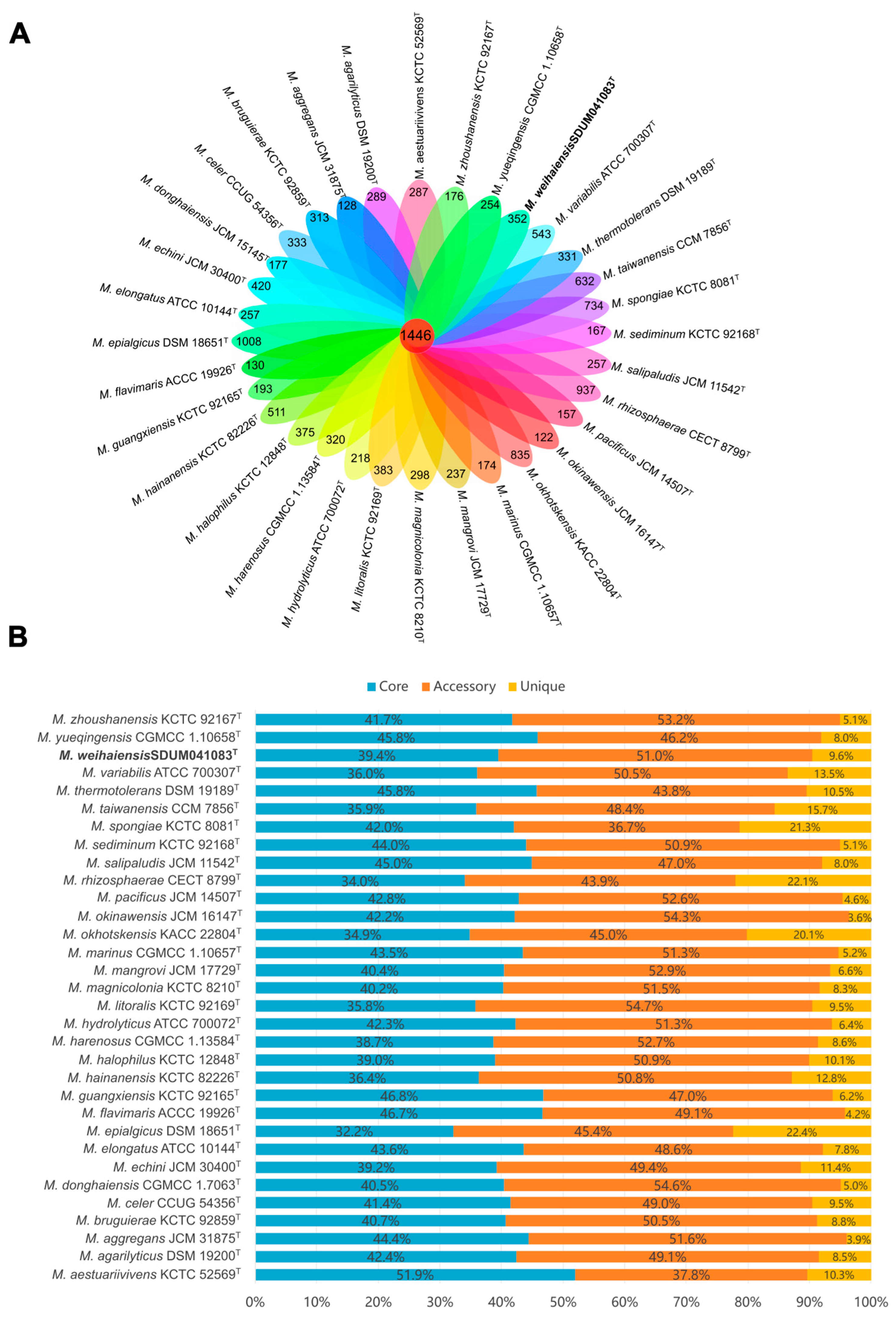
3.5. Comparative Genomic Analysis and Pan-Genome Analysis of the Genus Microbulbifer
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes of the Genus Microbulbifer
3.7. Global Biogeographic Distribution of Microbulbifer Based on MAPseq Meta-Analysis
3.8. Description of Microbulbifer weihaiensis sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González, J.M.; Mayer, F.; Moran, M.A.; Hodson, R.E.; Whitman, W.B. Microbulbifer hydrolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., and Marinobacterium georgiense gen. nov., sp. nov., two marine bacteria from a lignin-rich pulp mill waste enrichment community. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Lou, K.; Mao, P.H.; Jin, X.; Jiang, C.L.; Xu, L.H.; Li, W.J. Microbulbifer halophilus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from north-west China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2036–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Camacho, M.; Del Carmen Montero-Calasanz, M.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.; Schumann, P.; Klenk, H.P. Microbulbifer rhizosphaerae sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of the halophyte Arthrocnemum macrostachyum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Yoon, S.Y.; Ha, M.J.; Yoon, J.H. Microbulbifer aestuariivivens sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Nogi, Y.; Ohta, Y.; Hatada, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ito, S.; Horikoshi, K. Microbulbifer agarilyticus sp. nov. and Microbulbifer thermotolerans sp. nov., agar-degrading bacteria isolated from deep-sea sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, I.G.; Oh, T.K.; Park, Y.H. Microbulbifer maritimus sp. nov., isolated from an intertidal sediment from the Yellow Sea, Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moh, T.H.; Furusawa, G.; Amirul, A.A. Microbulbifer aggregans sp. nov., isolated from estuarine sediment from a mangrove forest. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Oh, T.K. Microbulbifer celer sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, M.; Takadera, T.; Imamura, N.; Kasai, H.; An, K.D.; Adachi, K.; Nagao, T.; Sano, H.; Yamasato, K. Microbulbifer variabilis sp. nov. and Microbulbifer epialgicus sp. nov., isolated from Pacific marine algae, possess a rod-coccus cell cycle in association with the growth phase. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Yang, S.H.; Jin, H.M.; Kim, J.M.; Kwon, K.K.; Jeon, C.O. Microbulbifer gwangyangensis sp. nov. and Microbulbifer pacificus sp. nov., isolated from marine environments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Nagahama, T.; Nogi, Y. Microbulbifer chitinilyticus sp. nov. and Microbulbifer okinawensis sp. nov., chitin-degrading bacteria isolated from mangrove forests. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, P.; Nogi, Y.; Ghadi, S.C.; Verma, P.; Shouche, Y.S. Microbulbifer mangrovi sp. nov., a polysaccharide-degrading bacterium isolated from an Indian mangrove. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, S.; Guo, C.; Xie, F.; Jung, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; He, S. Microbulbifer hainanensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from mangrove sediment. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kang, K.H.; Oh, T.K.; Park, Y.H. Transfer of Pseudomonas elongata Humm 1946 to the genus Microbulbifer as Microbulbifer elongatus comb. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Agarwal, V. Polymer degrading marine Microbulbifer bacteria: An un(der)utilized source of chemical and biocatalytic novelty. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1635–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Hong, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ni, H.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a thermostable and halotolerant endo-β-1,4-glucanase from Microbulbifer sp. ALW1. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Gui, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, A.; Fu, L.; Cao, Z.; Li, J. Identification and characterization of ι-carrageenase from macroalgae-associated bacterium Microbulbifer sp. YNDZ01. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2023, 103, 6095–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.L.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Bhatia, S.K.; Gurav, R.; Park, S.H.; Park, K.; Yang, Y.H. Isolation of Microbulbifer sp. SOL66 with high polyhydroxyalkanoate-degrading activity from the marine environment. Polymers 2021, 13, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.L.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Suh, M.J.; Ham, S.; Bhatia, S.K.; Gurav, R.; Park, S.H.; et al. Novel polyhydroxybutyrate-degrading activity of the Microbulbifer genus as confirmed by Microbulbifer sp. SOL03 from the marine environment. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wei, R.; Gao, M.; Ren, Y.; Yu, B.; Nie, K.; Xu, H.; Liu, L. Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by Microbulbifer hydrolyticus IRE-31. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 263, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Adachi, K.; Chen, C.; Kasai, H.; Kanoh, K.; Shizuri, Y.; Misawa, N. Discovery of a marine bacterium producing 4-hydroxybenzoate and its alkyl esters, parabens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5556–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.U.; Harunari, E.; Oku, N.; Akasaka, K.; Igarashi, Y. Bulbimidazoles A-C, antimicrobial and Cytotoxic alkanoyl imidazoles from a marine Gammaproteobacterium Microbulbifer Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Chen, D.K.; Fan, H.M.; Tang, S.S.; Gan, Z.; Xia, H.L.; Lu, Y.S. Microbulbifer bruguierae sp. nov., isolated from sediment of mangrove plant Bruguiera sexangula, and comparative genomic analyses of the genus Microbulbifer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 006209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KleinJan, H.; Jeanthon, C.; Boyen, C.; Dittami, S.M. Exploring the cultivable Ectocarpus microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, T.S.; Shang, D.D.; Du, Z.J. Salibaculum halophilum gen. nov., sp. nov. and Salibaculum griseiflavum sp. nov., in the family Rhodobacteraceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciufo, S.; Kannan, S.; Sharma, S.; Badretdin, A.; Clark, K.; Turner, S.; Brover, S.; Schoch, C.L.; Kimchi, A.; DiCuccio, M. Using average nucleotide identity to improve taxonomic assignments in prokaryotic genomes at the NCBI. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, L.; Wheeler, W.C. Maximum parsimony on phylogenetic networks. Algorithms. Mol. Biol. 2012, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.X.; Du, Z.J.; Mu, D.S. Aequorivita vitellina sp. nov. and Aequorivita xiaoshiensis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 005801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; De Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. antiSMASH: Rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Glöckner, F.O.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acid Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk2: Memory friendly classification with the genome taxonomy database. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 5315–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG tools for functional characterization of genome and metagenome sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Dutta, C. BPGA—An ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drula, E.; Garron, M.L.; Dogan, S.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Terrapon, N. The Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme Database: Functions and literature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D571–D577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias Rodrigues, J.F.; Schmidt, T.S.; Tackmann, J.; von Mering, C. MAPseq: Highly efficient k-mer search with confidence estimates, for rRNA sequence analysis. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3808–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, J.P. Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhao, J.X.; Chen, G.J. Woeseia oceani gen. nov., sp. nov., a chemoheterotrophic member of the order Chromatiales, and proposal of Woeseiaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Li, C.M.; Li, Y.X.; Du, Z.J. Aquimarina celericrescens sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.Y.; Xu, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.J.; Du, Z.J. Salegentibacter sediminis sp. nov., a marine bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from coastal sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, A.; Ueda, Y.; Ishihara, J.; Mori, T. Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 42, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J. A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1990, 13, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Ye, Y.Q.; Tan, X.Y.; Du, Z.J.; Ye, M.Q. Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov. Isolated from coastal sediment, and comparative genomic analysis and biogeographic distribution of the genus Aequorivita. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.S.; Huo, Y.Y.; Xu, X.W.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, C.S.; Xu, X.F.; Wu, M. Microbulbifer marinus sp. nov. and Microbulbifer yueqingensis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, P.S.; Hyun, D.W.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, N.R.; Jung, M.J.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Microbulbifer echini sp. nov., isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of a purple sea urchin, Heliocidaris crassispina. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P.; Arun, A.B.; Young, C.C.; Rekha, P.D.; Martin, K.; Busse, H.J.; Chen, W.M. Microbulbifer taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from coastal soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2485–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.C.; Gulvik, C.A.; Whitney, A.M.; Humrighouse, B.W.; Bell, M.E.; Holmes, B.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Villarma, A.; Sheth, M.; Batra, D.; et al. Division of the genus Chryseobacterium: Observation of discontinuities in amino acid identity values, a possible consequence of major extinction events, guides transfer of nine species to the genus Epilithonimonas, eleven species to the genus Kaistella, and three species to the genus Halpernia gen. Nov., with description of Kaistella daneshvariae sp. nov. and Epilithonimonas vandammei sp. nov. derived from clinical specimens. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 4432–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Klappenbach, J.A.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innamorati, K.A.; Earl, J.P.; Aggarwal, S.D.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Hiller, N.L. The bacterial guide to designing a diversified gene portfolio. In The Pangenome: Diversity, Dynamics and Evolution of Genomes.; Tettelin, H., Medini, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 51–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, T.; von Blohn, C.; Stanek, A.; Moses, S.; Barzantny, H.; Bremer, E. Synthesis, release, and recapture of compatible solute proline by osmotically stressed Bacillus subtilis cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5753–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, J.W.; Liu, L.M.; Chen, J. Arginine: A novel compatible solute to protect Candida glabrata against hyperosmotic stress. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C.M.; Santos, H.; Galinski, E.A. An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes in bacteria and archaea. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 1998, 61, 117–153. [Google Scholar]
- Roesser, M.; Muller, V. Osmoadaptation in bacteria and archaea: Common principles and differences. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.M.; Bremer, E.; Csonka, L.N.; Kraemer, R.; Poolman, B.; van der Heide, T. Osmosensing and osmoregulatory compatible solute accumulation by bacteria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 130, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomposiello, P.J.; Demple, B. Global adjustment of microbial physiology during free radical stress. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2002, 46, 319–341. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q.; Wang, D.; Dong, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; et al. Microbulbifer flavimaris sp. nov., a halophilic Gammaproteobacteria isolated from marine sediment of the Yellow Sea, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanenko, L.; Kurilenko, V.; Otstavnykh, N.; Velansky, P.; Isaeva, M.; Mikhailov, V. Microbulbifer okhotskensis sp. nov., isolated from a deep bottom sediment of the Okhotsk Sea. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramin, K.I.; Allison, S.D. Bacterial tradeoffs in growth rate and extracellular enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Bertilsson, S. Bacterial chitin degradation—Mechanisms and ecophysiological strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Shao, S.J.; Li, L.L.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, L.; Gao, P.J.; Wang, L.S. Substrate-binding specificity of chitinase and chitosanase as revealed by active-site architecture analysis. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 418, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristic | 1 | 2 | 3 a | 4 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sampling environment | Intertidal sediments | mud samples from mangrove forests | the gastrointestinal tract of a purple sea urchin | sediment |
| Motility/flagella | +/− | −/− | −/− | −/− |
| Temperature range (optimum) (°C) | 20–40 (35) | 10–45 (37) | 10–36 (30) | 15–45 (30–37) |
| NaCl range (optimum) (g/L) | 5–110 (35) | 5–150 (30) | 10–80 (20) | 0–100 (20–30) |
| pH range (optimum) | 5.5–9.5 (7.0) | 5.5–9.5 (7.0–7.5) | 6.2–9.0 (7.0) | 5.0–10.0 (7.0–8.0) |
| DNA G+C content (mol%) | 57.5 | 57.8 | 56.1 | 56.7 |
| Polar lipids | PG, PE, AL | PG, PE | PE, PS | PE, PG |
| Oxidase | − | + | + | + |
| Hydrolysis of: | ||||
| Tween-20 | + | + | − | − |
| Tween-40 | + | + | + | − |
| Casein | + | + | + | + |
| Starch | − | + | + | − |
| Gelatin | + | + | + | − |
| API ZYM tests: | ||||
| Cystine arylamines | + | + | − | − |
| chymotrypsin | + | − | − | − |
| N-acetyl-glucosaminidase | + | + | − | − |
| Trypsin | − | − | − | + |
| lipase (C14) | (+) | + | + | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-X.; Liu, A.-Q. Analysis of Genomic and Characterization Features of Microbulbifer weihaiensis sp. nov., Isolated from Coastal Sediment. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092005
Zhang Y-X, Liu A-Q. Analysis of Genomic and Characterization Features of Microbulbifer weihaiensis sp. nov., Isolated from Coastal Sediment. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092005
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu-Xuan, and Ai-Qiu Liu. 2025. "Analysis of Genomic and Characterization Features of Microbulbifer weihaiensis sp. nov., Isolated from Coastal Sediment" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092005
APA StyleZhang, Y.-X., & Liu, A.-Q. (2025). Analysis of Genomic and Characterization Features of Microbulbifer weihaiensis sp. nov., Isolated from Coastal Sediment. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092005





