Microbial and Geochemical Diversity of Laguna Timone, an Extreme Hypersaline Crater Lake in Patagonia (52° S)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Climate Conditions
4. Methods
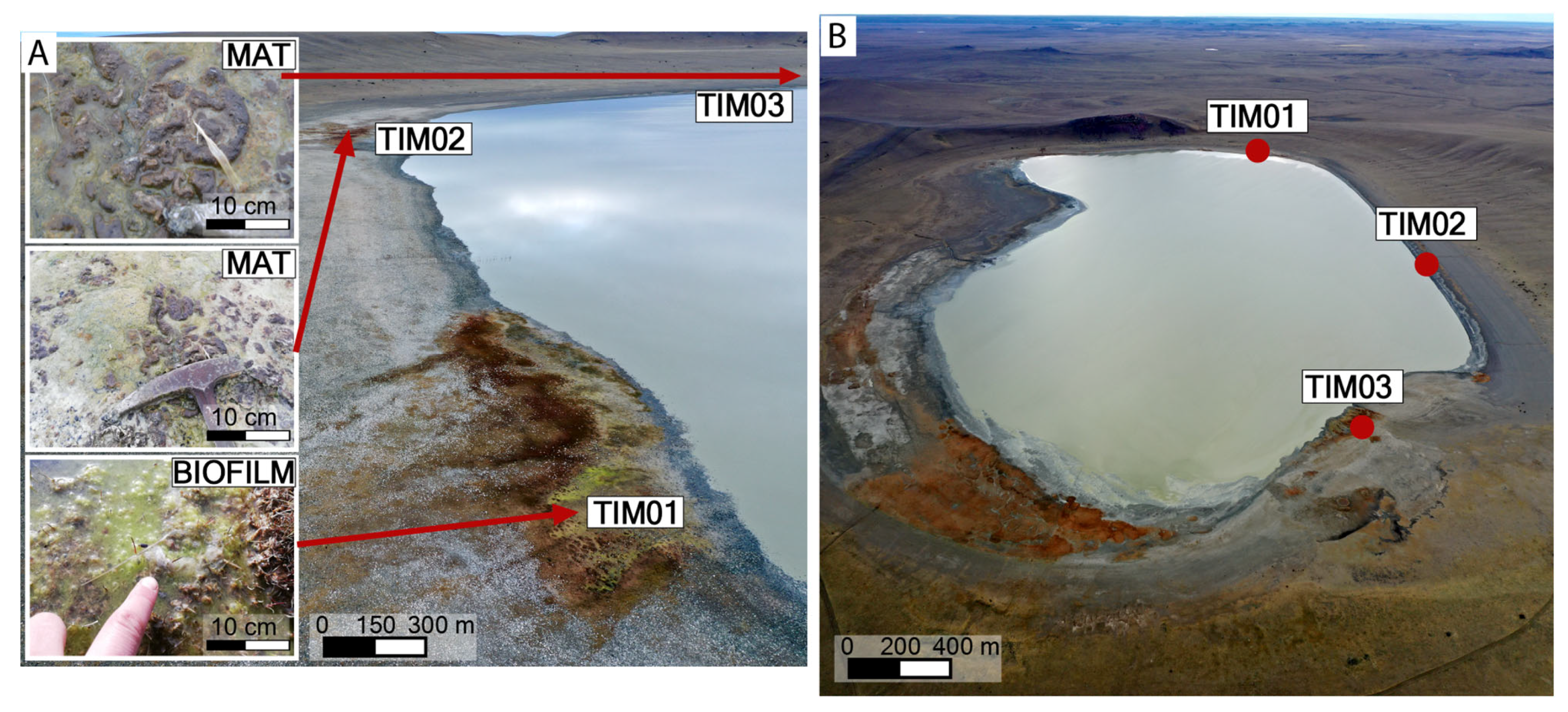
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Microbial Mats and Biofilm Microscopy Characterization
4.3. Analysis of Microbial Communities
4.4. Water Chemistry and 13CDIC Composition
4.5. Chemical and Mineralogical Analyses of Sediment and Carbonate
4.6. Isotope Composition (δ13C and δ18O)
5. Results
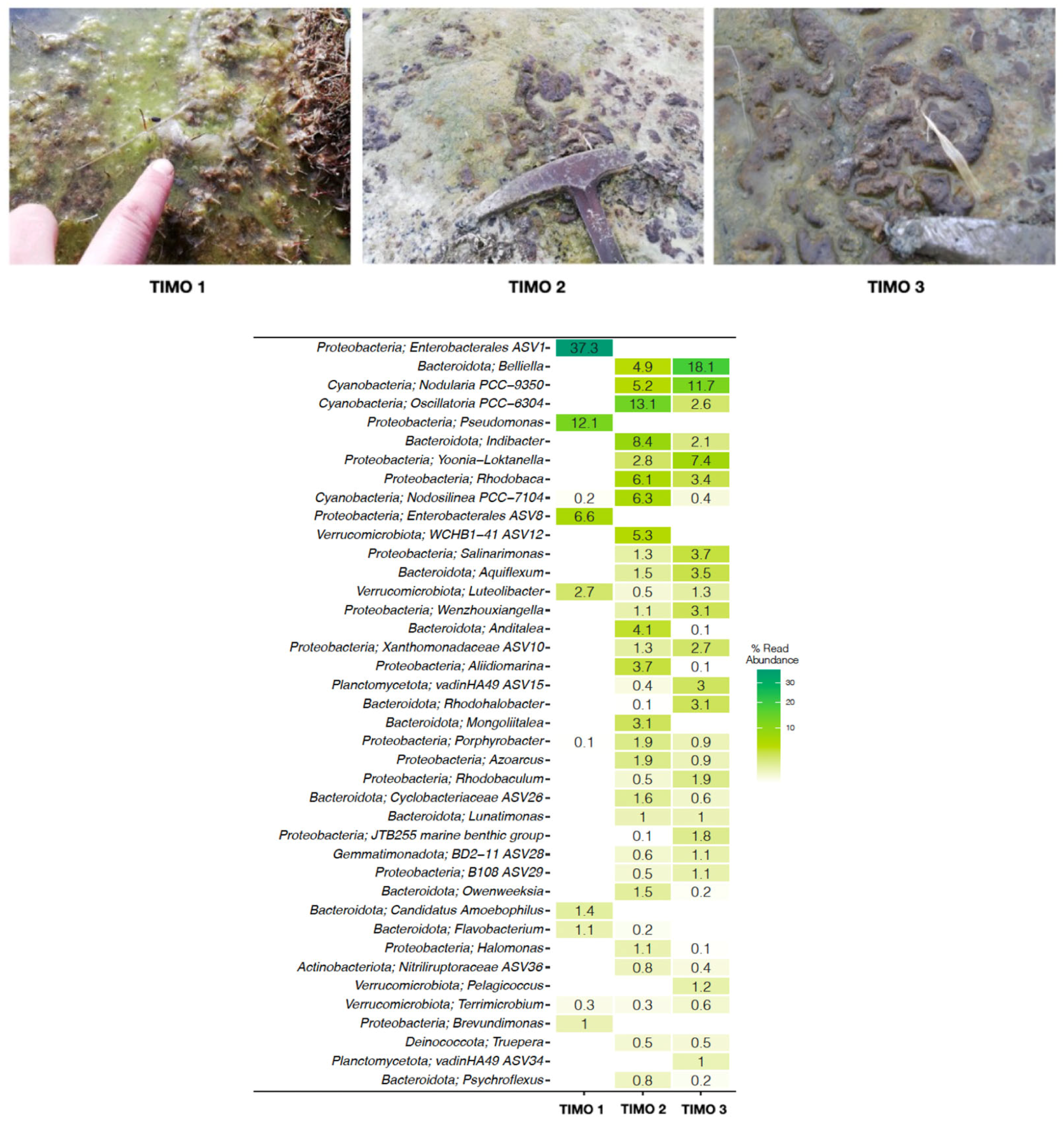
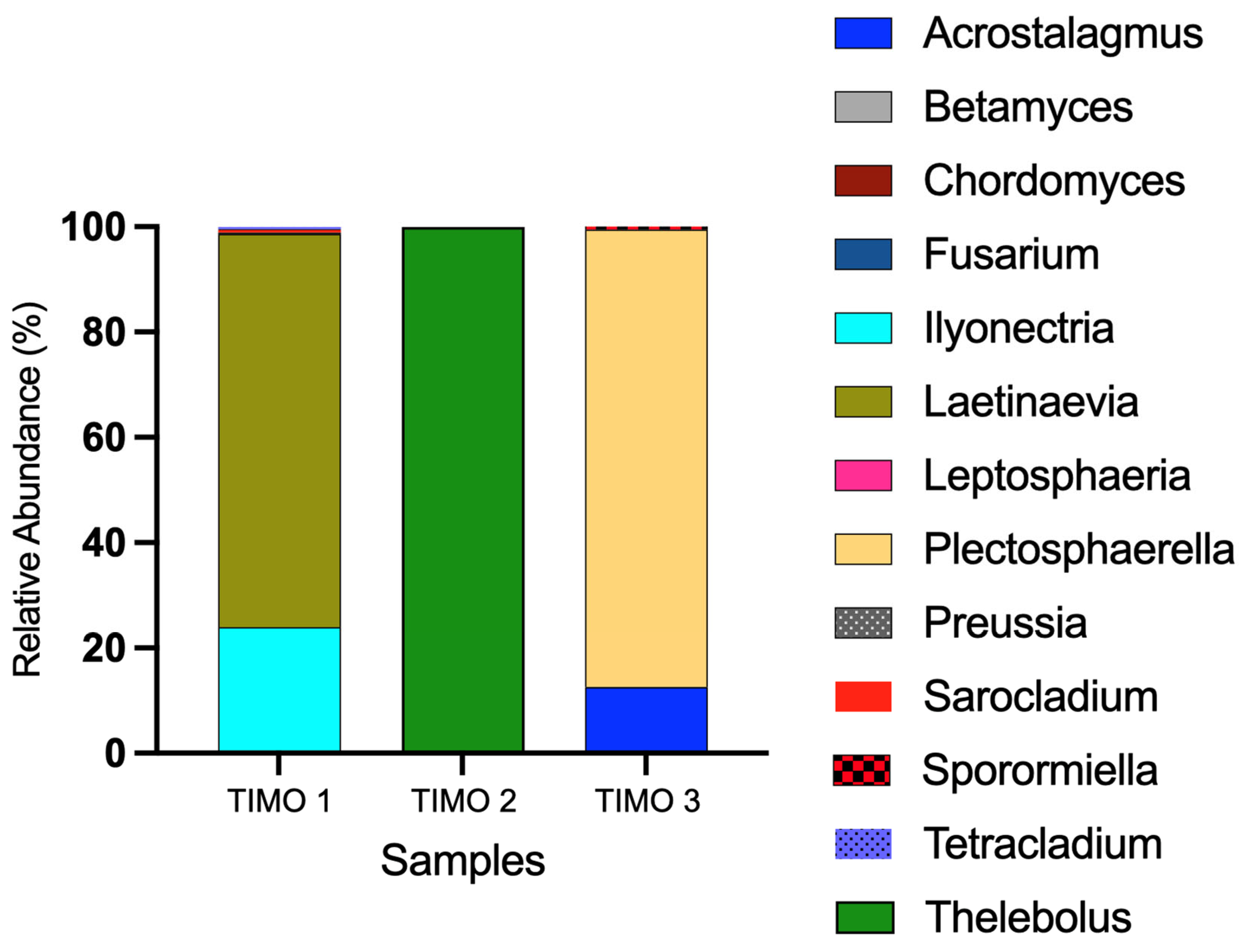
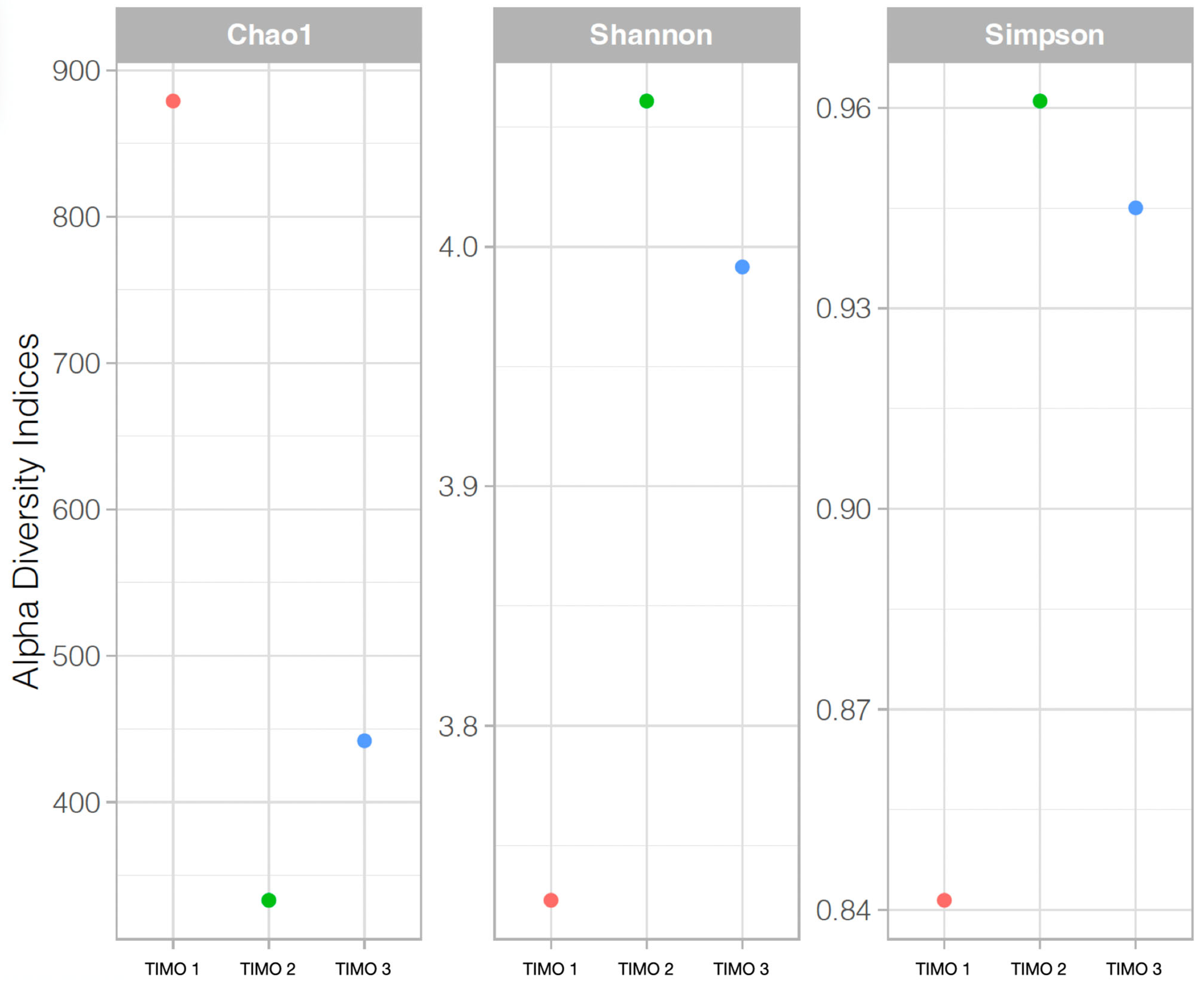
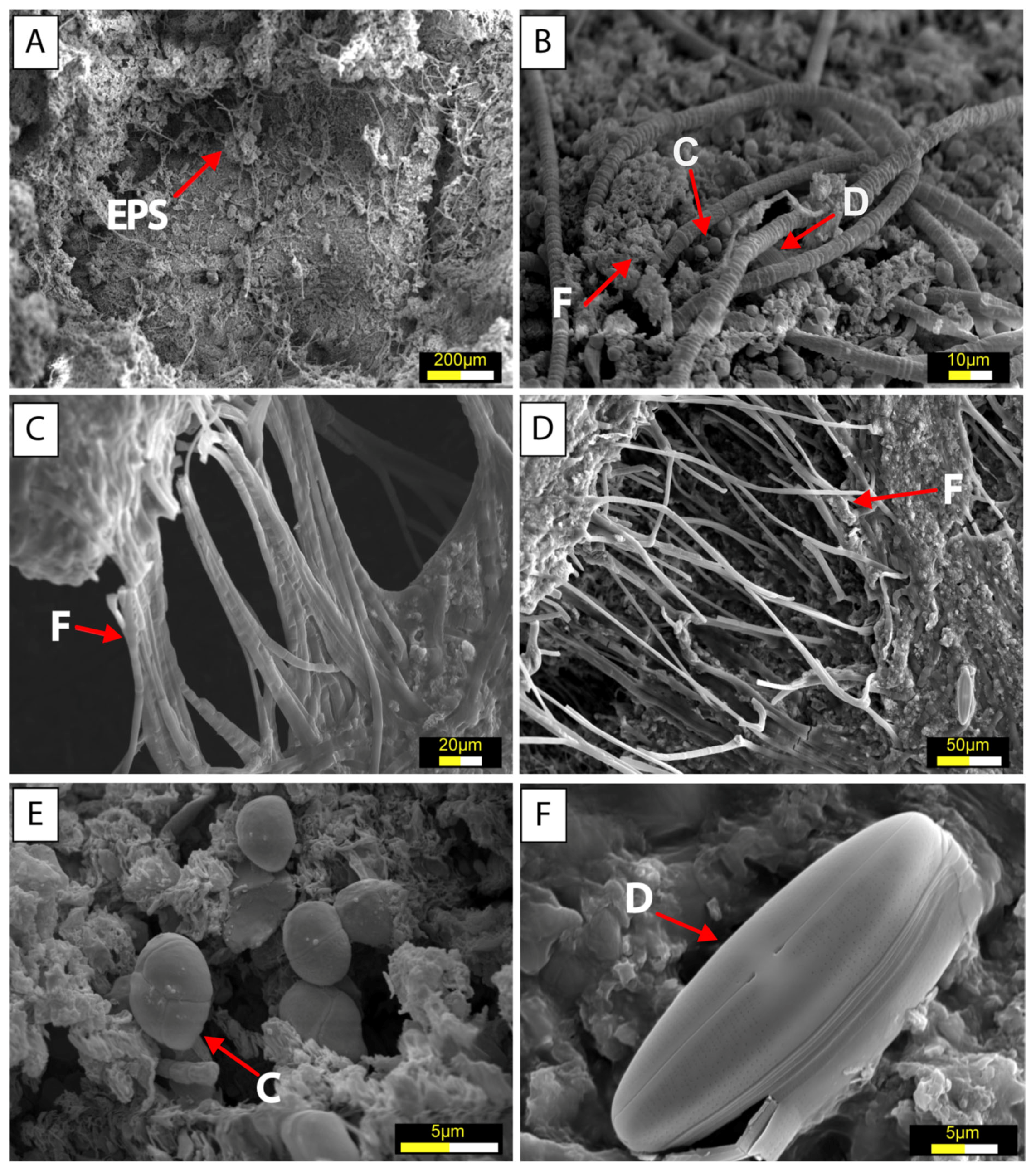
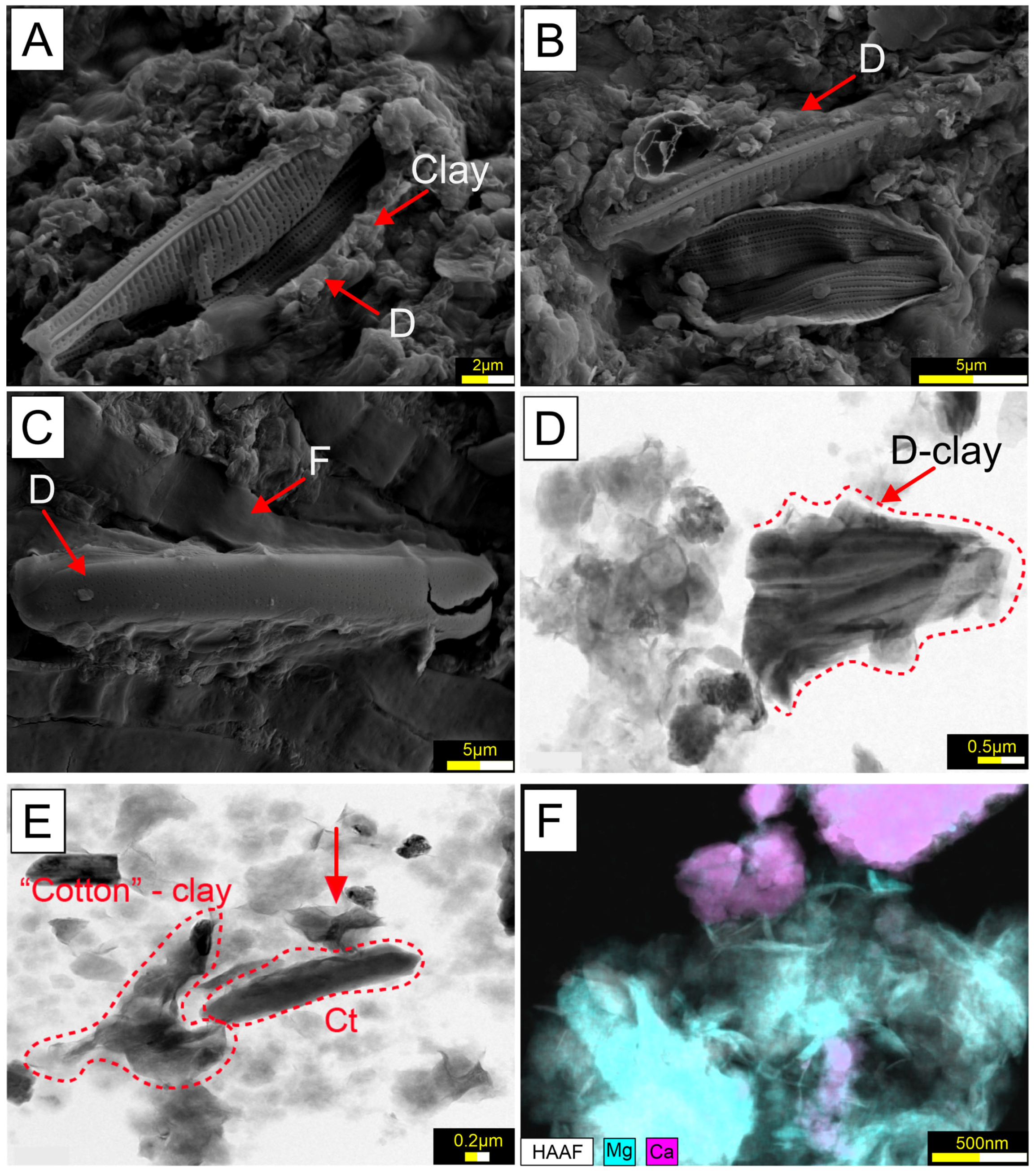
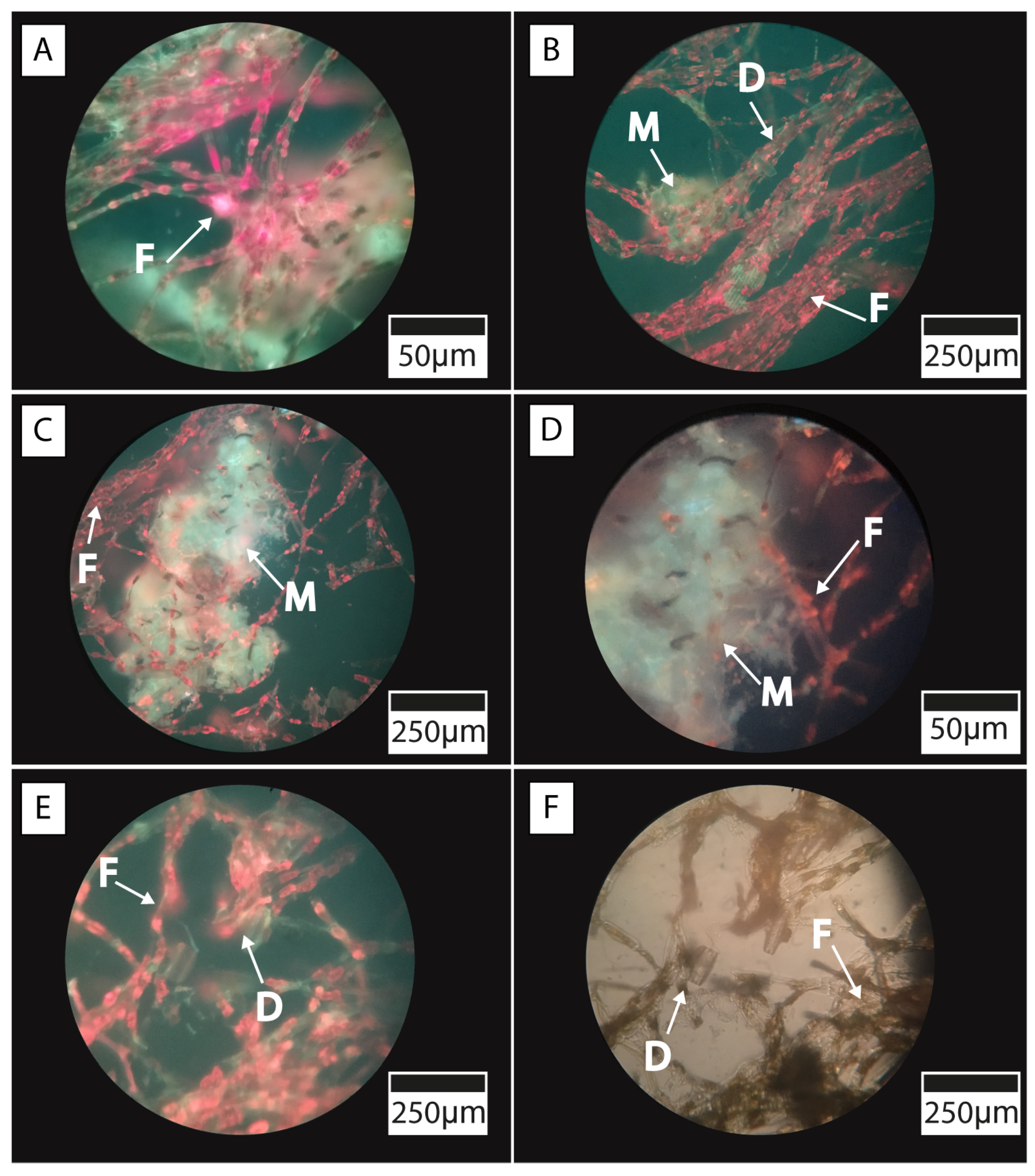
5.1. Microbial Mats and Biofilm Communities in Laguna Timone
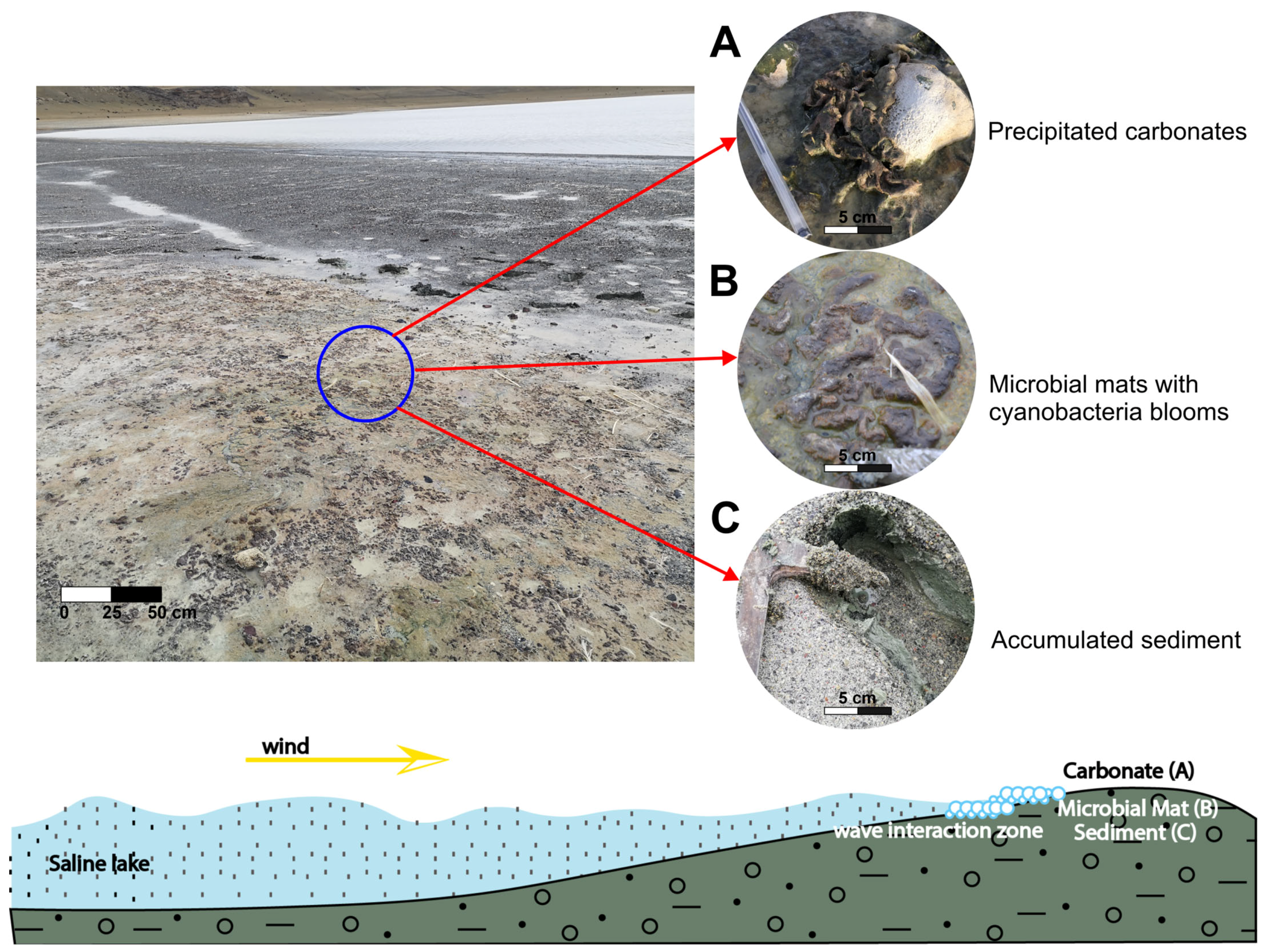
5.2. Characterization of Microbial Mats
5.3. Chemical Composition of Water, Sediments, and Carbonates
5.4. Isotopic Compositions of Water, Microbial Mats and Carbonates
6. Discussion
6.1. Microbial Diversity of the Microbial Mats and Biofilm of Laguna Timone
6.2. Environmental and Geo-Microbiological Context
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beraldi-Campesi, H. Early life on land and the first terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Process. 2013, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.W.; Tino, C.J.; Fournier, G.P.; Anderson, R.E.; Leavitt, W.D.; Konhauser, K.O.; Stüeken, E.E. Co-evolution of early Earth environments and microbial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundas, I. Was the environment for primordial life hypersaline? Extremophiles 1998, 2, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasSarma, S.; DasSarma, P. Halophiles. In eLS; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: Environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.S.; Burne, R.V. The modern thrombolites of Lake Clifton, Western Australia. In Phanerozoic Stromatolites II; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, C.J.; Nelson, W.M. Microbialitic structures in Storr’s Lake, San Salvador Island, Bahamas. Palaios 1989, 4, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, R.P.; Macintyre, I.G.; Steneck, R.S. A microbialite/algal ridge fringing reef complex, Highborne Cay, Bahamas. In Atoll Research Bulletin; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V.G.; Wronkiewicz, D.J.; Mormile, M.R.; Foster, J.S. Mineralogy and microbial diversity of microbialites in hypersaline Storr’s Lake, Bahamas. Astrobiology 2016, 16, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, B.K.; Zalar, P. The extremophiles of Great Salt Lake. In Model Ecosystems in Extreme Environments; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 57–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, A.B.; Rasuk, M.C.; Visscher, P.T.; Contreras, M.; Novoa, F.; Poire, D.G.; Patterson, M.M.; Ventosa, A.; Farias, M.E. Microbial diversity in sediment ecosystems of hypersaline Laguna Tebenquiche, Salar de Atacama, Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.J.; Kah, L.C.; Bartley, J.K.; Astini, R.A. Microbialites in a high-altitude Andean lake: Multiple controls on carbonate precipitation. Palaios 2014, 29, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlewski, E.C.; Pisapia, C.; Gomez, F.; Lecourt, L.; Soto Rueda, E.; Benzerara, K.; Ménez, B.; Borensztajn, S.; Jamme, F.; Ménez, M.; et al. Characterization of pustular mats and rivularia-rich laminations in oncoids from Laguna Negra. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boidi, F.J.; Mlewski, E.C.; Fernández, G.C.; Flores, M.R.; Gérard, E.; Farías, M.E.; Gomez, F.J. Community vertical composition of the Laguna Negra hypersaline microbial mat. Biology 2022, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencina, A.I.; Soria, M.N.; Gomez, F.J.; Gérard, E.; Farias, M.E. Composite microbialites in Pozo Bravo lake, Argentinean Andes. J. Sediment. Res. 2021, 91, 1305–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.A.; Surakasi, V.P.; Siddharth, J.; Raghavan, R.G.; Patole, M.S.; Ranade, D.; Shouche, Y.S. Microbial diversity in Lonar soda lake, India. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, C.P.; Kumaresan, D.; Hunger, S.; Drake, H.L.; Murrell, J.C.; Shouche, Y.S. Microbiology of Lonar Lake and other soda lakes. ISME J. 2013, 7, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Abbas, B.; Geleijnse, M.; Pimenov, N.V.; Sukhacheva, M.V.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Methanogenesis at extremely haloalkaline conditions in soda lakes of Kulunda Steppe. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henríquez, C.; Calderón, M.; Cury, L.F.; Athayde, G.; Carvajal, S.; Oyarzún, P.; Bahniuk, A. Carbonate precipitation in the Laguna Timone maar, Patagonia. Sediment. Geol. 2022, 439, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabassa, J.; Coronato, A.; Martinez, O. Late Cenozoic glaciations in Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 103, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, M.; Agostini, S.; Mazzarini, F.; Innocenti, F.; Manetti, P.; Haller, M.J.; Lahsen, A. Slab-window magmatism in Pali Aike Volcanic Field. Tectonophysics 2000, 321, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, W.R. Cenozoic plate tectonic setting of the Cordilleran region. In Cenozoic Tectonics and Regional Geophysics of the Western Cordillera; Burke, R.M., Drake, C.L., Eds.; Geological Society of America Memoir 152; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1979; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, M.; Agostini, S.; Innocenti, F.; Haller, M.J.; Manetti, P.; Mazzarini, F. Slab window-related volcanism in Estancia Glencross, South America. Lithos 2001, 57, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skewes, M.A.; Stern, C.R. Petrology of basalts from the Pali-Aike volcanic field. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1979, 6, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natland, M.L. A System of Stages for Magallanes Basin Sediments; Geological Society of America Memoirs: Boulder, CO, USA, 1974; Volume 139. [Google Scholar]
- Fosdick, J.C.; VanderLeest, R.A.; Bostelmann, J.E.; Leonard, J.S.; Ugalde, R.; Oyarzún, J.L.; Griffin, M. Revised timing of Atlantic incursions in southern Patagonia. Lithosphere 2020, 2020, 8883099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolitschka, B.; Schäbitz, F.; Lücke, A.; Corbella, H.; Ercolano, B.; Fey, M.; Haberzettl, T.; Janssen, S.; Maidana, N.; Mayr, C.; et al. Crater lakes of Pali Aike for paleoenvironmental reconstructions. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2006, 21, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarini, F.; D’Orazio, M. Cone distribution in Pali Aike Volcanic Field. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2003, 125, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronato, A.; Rabassa, J. Pleistocene glaciations in southern Patagonia. In Quaternary Glaciations—Extent and Chronology; Part IV; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 15, pp. 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbella, H. El campo volcano-tectónico de Pali Aike. In Geología y Recursos Naturales de Santa Cruz. Relatorio del XV° Congreso Geológico Argentino; Haller, M.J., Ed.; Asociación Geológica Argentina: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2002; pp. 287–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, P.S.; Delpit, S.; Haller, M.J.; Németh, K.; Corbella, H. Influence of the substrate on maar–diatreme volcanoes—An example of a mixed setting from the Pali Aike volcanic field, Argentina. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2011, 201, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.M.; Borrero, L.A. Climate change, availability of territory, and Late Pleistocene human exploration of Ultima Esperanza, South Chile. Quat. Int. 2017, 428, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weischet, W. Regionale Klimatologie Teil 1; Schweizerbart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Paruelo, J.M.; Beltrán, A.; Jobbágy, E.; Sala, O.E.; Golluscio, R.A. The climate of Patagonia: General patterns. Ecol. Austral 1998, 8, 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, V.R.; Scian, B.; Mattio, F.F. Campos de precipitación de Chubut. Geoacta 1979, 10, 175–192. [Google Scholar]
- Garreaud, R.; López, P.; Minvielle, M.; Rojas, M. Large-scale climate controls in Patagonia. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME for microbial sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owners, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput analysis on MiSeq and HiSeq. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE database for fungal identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Xu, H.; Konishi, H.; Roden, E.E. Dolomite solid-solution series analysis. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Microorganisms 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, R.; Hood, R.D.; Savage, D.F. Live-cell imaging of cyanobacteria. Photosynth. Res. 2015, 126, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, M. Desiccation tolerance of prokaryotes. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 755–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Yu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, C.L. Microbial response to salinity change in Lake Chaka. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2603–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Harris, J.K.; Wilcox, J.; Spear, J.R.; Miller, S.R.; Bebout, B.M.; Maresca, J.A.; Bryant, D.A.; Sogin, M.L.; Pace, N.R. Unexpected diversity and complexity of the Guerrero Negro hypersaline microbial mat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. J. 2006, 72, 3685–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, D.; Mathes, F.; Farrell, M.; Leopold, M. Environmental drivers of soil microbial community structure and function at the Avon River Critical Zone Observatory. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boquet, E.; Boronat, A.; Ramos-Cormenzana, A. Production of calcite (calcium carbonate) crystals by soil bacteria is a general phenomenon. Nature 1973, 246, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendrich, C. Halovibrio variabilis gen. nov. sp. nov., Pseudomonas halophila sp. nov. and a new halophilic aerobic coccoid Eubacterium from Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1988, 11, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Stabnikov, V.; Ivanov, V. Microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation on surface or in the bulk of soil. Geomicrobiol. J. 2012, 29, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edbeib, M.F.; Wahab, R.A.; Kaya, Y.; Huyop, F. In silico characterization of a novel dehalogenase (DehHX) from the halophile Pseudomonas halophila HX isolated from Tuz Gölü Lake, Turkey: Insights into a hypersaline-adapted dehalo-genase. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete-Morales, M.; Carvajal, D.; Almasia, R.; Michea, S.; Cantillana, C.; Levican, A.; Silva-Moreno, E. Pseudomonas atacamensis sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of desert bloom plant in the region of Atacama, Chile. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangari, H.; Forouhandeh, H.; Ebrahimi, T.; Ebrahimi, V.; Montazersaheb, S.; Tarhriz, V. Pseudomonas sp. a Domi-nant Population of Bacteria in the Cold Water of Mount Sabalan Crater Lake. Curr. Biotechnol. 2021, 10, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Pak, S.; Rim, S.; Ren, L.; Jiang, F.; Chang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, C.; Zheng, C.; et al. Luteolibacter arcticus sp. nov., isolated from high Arctic tundra soil, and emended description of the genus Luteolibacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.K.; Si, J.; Wu, G.J.; Tian, L.D.; Xiang, S.R. Changes of the bacterial abundance and communities in shallow ice cores from Dunde and Muztagata glaciers, western China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Tang, Y. Planktonic and sedimentary bacterial diversity of Lake Sayram in summer. Microbiol. Open 2015, 4, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, B.; Wang, R.; Su, Y.; Han, S.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, G.; Sun, C.; Wu, M. Luteolibacter flavescens sp. nov., isolated from deep seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, S.; Kannan, V.M.; Saritha, V.N.; Loganathachetti, D.S.; Mohan, M.; Krishnan, K.P. Bacterial diversity and community structure along the glacier foreland of Midtre Lovénbreen, Svalbard, Arctic. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmin, M.; Azzaro, M.; Buzzini, P.; Battistel, D.; Roman, M.; Ponti, S.; Turchetti, B.; Sannino, C.; Borruso, L.; Papale, M.; et al. A possible unique ecosystem in the endoglacial hypersaline brines in Antarctica. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, X.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Huang, T. Experimental and visual research on the microbial induced carbonate precipitation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. AMB Express 2017, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, D.J. Butane metabolism by butane-grown Pseudomonas butanovora. Microbiology 1999, 145, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demergasso, C.; Casamayor, E.O.; Chong, G.; Galleguillos, P.; Escudero, L.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Distribution of prokaryotic genetic diversity in athalassohaline lakes of the Atacama Desert, Northern Chile. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorador, C.; Meneses, D.; Urtuvia, V.; Demergasso, C.; Vila, I.; Witzel, K.P.; Imhoff, J.F. Diversity of Bacteroidetes in high-altitude saline evaporitic basins in northern Chile. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristyanto, S.; Nguyen, T.M.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, J. Characterization of Flavobacterium aquimarinum sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from seawater. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, T.-L.; Howard-Williams, C.; Castenholz, R.W. Effects of solar UV and visible irradiance on photosynthesis and vertical migration of Oscillatoria sp. (Cyanobacteria) in an Antarctic microbial mat. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demergasso, C.; Chong, G.; Galleguillos, P.; Escudero, L.; Martinez-Alonso, M.; Esteve, I. Microbial mats from the Llamará salt flat, northern Chile. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2003, 76, 485–499. [Google Scholar]
- Brigmon, R.L.; Smith, G.W.; Morris, P.A.; Byrne, M.; McKay, D.S. Microbial ecology in modern stromatolites from San Salvador, Bahamas. In Proceedings of the 12th Symposium on the Geology of the Bahamas and Other Carbonate Regions, Bahamian Field Station, San Salvador, Bahamas, 2006; pp. 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Valadez, F.; Rosiles-González, G.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Merino-Ibarra, M. Planktonic Cyanobacteria of the tropical karstic lake Lagartos from the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Rev. De Biol. Trop. 2013, 61, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreote, A.P.D.; Vaz, M.G.M.V.; Genuário, D.B.; Barbiero, L.; Rezende-Filho, A.T.; Fiore, M.F. Nonheterocytous cyanobacteria from Brazilian saline-alkaline lakes. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzi, R.; Muangmai, N.; Broady, P.; Wan Omar, W.M.; Lavoue, S.; Convey, P.; Merican, F. Nodosilinea signiensis sp. nov. (Leptolyngbyaceae, Synechococcales), a new terrestrial cyanobacterium isolated from mats collected on Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwuanyi, I.; Fogel, M.L.; Steele, A.; Glamoclija, M. Microbial Ecology of Jotun Spring, an Artic Geothermal Spring, Svalbard, Norway and Its Astrobiological Relevance. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union (AGU): New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022; Abstract B12I-1155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhilina, T.N.; Sorokin, D.Y.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Kublanov, I.V.; Zavarzina, D.G. Natronogracilivirga saccharolytica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Cyclonatronum proteinivorum gen. nov., sp. nov., haloalkaliphilic organotrophic bacteroidetes from hypersaline soda lakes forming a new family Cyclonatronaceae fam. nov. in the order Balneolales. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 46, 126403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, A.B.; Young, C.C.; Chen, W.M.; Hung, M.H.; Lai, W.A.; Chou, J.H.; Rekha, P.D.; Shen, F.-T.; Su, S.P. Belliella pelovolcani sp. nov., isolated from a mud-volcano in Taiwan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2534–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.P.; Liu, Y.; Hou, T.T.; Zhou, Y.G.; Liu, H.C.; Liu, Z.P. Belliella aquatica sp. nov., isolated from a saline lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyreva, L.; Egorova, D.; Anan’ina, L.; Plotnikova, E.; Ariskina, E.; Prisyazhnaya, N.; Radnaeva, L.; Namsaraev, B. Belliella buryatensis sp. nov., isolated from alkaline lake water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzaro, M.; Papale, M.; Rizzo, C.; Forte, E.; Lenaz, D.; Guglielmin, M.; Lo Giudice, A. Antarctic salt-cones: An oasis of microbial life? The example of Boulder Clay Glacier (Northern Victoria Land). Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Hawes, I.; Mountfort, D.; Hitzfeld, B.; Dietrich, D.R.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Diversity within cyanobacterial mat communities in variable salinity meltwater ponds of McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roney, H.C.; Booth, G.M.; Cox, P.A. Competitive exclusion of cyanobacterial species in the Great Salt Lake. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, E.D.; Prufert-Bebout, L. Characterization of cyanobacterial communities from high-elevation lakes in the Bolivian Andes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2010, 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítek, P.; Jehlička, J.; Ascaso, C.; Mašek, V.; Gómez-Silva, B.; Olivares, H.; Wierzchos, J. Distribution of scytonemin in endolithic microbial communities from halite crusts in the hyperarid zone of the Atacama Desert, Chile. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Genuário, D.B.; Fiore, M.F.; Elster, J. Heterocytous cyanobacteria of the ulu peninsula, James Ross Island, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguila, B.; Alcantara-Hernandez, R.J.; Montejano, G.; Lopez-Martinez, R.; Falcón, L.I.; Becerra-Absalon, I. Cyanobacteria in microbialites of Alchichica Crater Lake: A polyphasic characterization. Eur. J. Phycol. 2021, 56, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, L.; Redman, R.; Craig, S.; Rodriguez, R. Distribution and abundance of fungi in the soils of Taylor Valley, Antarctica. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenz, B.; Blanchette, R. Distribution and abundance of soil fungi in Antarctica at sites on the Peninsula, Ross Sea Region and McMurdo Dry Valleys. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoog, G.S.; Nishikaku, A.S.; Fernandez-Zeppenfeldt, G.; Padín-González, C.; Burger, E.; Badali, H.; Richard-Yegres, N.; van den Ende, A.H.G. Molecular analysis and pathogenicity of the Cladophialophora carrionii complex, with the description of a novel species. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 58, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anupama, A.; Jayaraman, G. Detergent stable, halotolerant α-amylase from Bacillus aquimaris vitp4 exhibits reversible unfolding. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. Technol. 2011, 2, 366–376. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Roy, U.; Tsuji, M. Characterization of yeast and filamentous fungi from Brøggerbreen glaciers, Svalbard. Polar Rec. 2016, 52, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, N.; Kalpana, D.; Han, J.H.; Cha, H.J.; Soo Lee, Y. A novel low temperature chitinase from the marine fungus Plectosphaerella sp. strain MF-1. Bot. Mar. 2011, 54, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, M.; Carlucci, A. Characterization and pathogenicity of Plectosphaerella spp. collected from basil and parsley in Italy. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2018, 57, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Zou, X.; Han, Y.F.; Huang, J.Z.; Liang, Z.Q.; Deshmukh, S.K. Phylogeny and taxonomy of two new Plectosphaerella (Plectosphaerellaceae, Glomerellales) species from China. MycoKeys 2019, 57, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Rego, C.; Oliveira, H.; Crous, P.W. Cylindrocarpon root rot: Multi-gene analysis re-veals novel species within the Ilyonectria radicicola species complex. Mycol. Prog. 2012, 11, 655–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, D.; Tanabe, Y.; Uchida, M.; Kudoh, S.; Osono, T. Microfungi associated with withering willow wood in ground contact near Syowa Station, East Antarctica for 40 years. Polar Biol. 2013, 36, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyers, H.S.; Suberkropp, K. Fungal and bacterial production during the breakdown of yellow poplar leaves in 2 streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1996, 15, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, L.M.; Willey, J.M.; Sherwood, L.M.; Woolverton, C.J. Prescott, Harley and Klein’s Microbiology, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druschel, G.K.; Kappler, A. Geomicrobiology and microbial geochemistry. Elements 2015, 11, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, D.; Chao, L.; Qu, H.; Wang, B.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Differences in microbial communities from Quaternary volcanic soils at different stages of development: Evidence from Late Pleistocene and Holocene volcanoes. Catena 2021, 201, 105211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, P.; McQueen, N.; Wilcox, J.; Renforth, P.; Dipple, G.; Vankeuren, A. Engineered carbon mineralization in ultramafic rocks for CO2 removal from air: Review and new insights. Chem. Geol. 2020, 550, 119628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, K.; Sirantoine, E.; Wilson, M.E.; George, A.D.; Mendes Monteiro, J.; Saunders, M. Spherulitic microbialites from modern hypersaline lakes, Rottnest Island, Western Australia. Geobiology 2020, 18, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burne, R.V.; Moore, L.S.; Christy, A.G.; Troitzsch, U.; King, P.L.; Carnerup, A.M.; Hamilton, P.J. Stevensite in the modern thrombolites of Lake Clifton, Western Australia: A missing link in microbialite mineralization? Geology 2014, 42, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontognali, T.R.; McKenzie, J.A.; Warthmann, R.J.; Vasconcelos, C. Microbially influenced formation of Mg-calcite and Ca-dolomite in the presence of exopolymeric substances produced by sulphate-reducing bacteria. Terra Nova 2014, 26, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, V.P.; Barnett, A.J. An Abiotic Model for the Development of Textures in Some South Atlantic Early Cretaceous Lacustrine Carbonates; Geological Society: London, UK, 2015; Volume 418, pp. 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E. The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 71, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E.; Solomon, D.K.; Quade, J.A.Y.; Bowman, J.R. On the isotopic composition of carbon in soil carbon dioxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3403–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Physicochemical Analysis of Water | |
|---|---|
| Physical Parameters | |
| Total dissolved solids (mg/L) | 147,396 |
| pH | 9.7 |
| Electric conductivity (uScm−1) | 120,400 |
| Temperature (°C) | 4 |
| Chemistry (mg/L) | |
| Calcium (Ca) | 141.3 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 448 |
| Sodium (Na) | 81,000 |
| Potassium (K) | 3500 |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.42 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.25 |
| Chloride (Cl) | 41,000 |
| Fluoride (F) | 12.5 |
| Sulfates (SO42−) | 727.1 |
| Phosphorus (PO3) | 110 |
| Nitrates (NH3) | 618 |
| Nitrites (NO2) | 0.272 |
| Carbonates (CO3) | 54,844 |
| Silica (SiO2) | 2 |
| Alkalinity Total | 65,854 |
| Samples | δ13C (‰VPDB) | δ18O (‰VPDB) | d(A°) Carbonates (DRX) | Mineral Classification (Zhang et al., 2010 [41]) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIMO 2 | −2.8 | −4.4 | 3.031 | Calcite |
| TIMO 3 | 0.8 | −6.5 | 3.031 | Calcite |
| Calcite aggregates (TIMO 2) | −2.5 | −7.8 | 3.031 | Calcite |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henríquez, C.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M.; Bruna, N.; Calderón, M.; Cury, L.F.; Quezada, P.; Athayde, G.; Oyarzún, P.; Bahniuk, A. Microbial and Geochemical Diversity of Laguna Timone, an Extreme Hypersaline Crater Lake in Patagonia (52° S). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081957
Henríquez C, Pérez-Donoso JM, Bruna N, Calderón M, Cury LF, Quezada P, Athayde G, Oyarzún P, Bahniuk A. Microbial and Geochemical Diversity of Laguna Timone, an Extreme Hypersaline Crater Lake in Patagonia (52° S). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081957
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenríquez, Carolina, José M. Pérez-Donoso, Nicolás Bruna, Mauricio Calderón, Leonardo Fadel Cury, Paulo Quezada, Gustavo Athayde, Poldie Oyarzún, and Anelize Bahniuk. 2025. "Microbial and Geochemical Diversity of Laguna Timone, an Extreme Hypersaline Crater Lake in Patagonia (52° S)" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081957
APA StyleHenríquez, C., Pérez-Donoso, J. M., Bruna, N., Calderón, M., Cury, L. F., Quezada, P., Athayde, G., Oyarzún, P., & Bahniuk, A. (2025). Microbial and Geochemical Diversity of Laguna Timone, an Extreme Hypersaline Crater Lake in Patagonia (52° S). Microorganisms, 13(8), 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081957







