Abstract
The Helicobacter pylori vapD gene is transcribed and expressed when the bacteria are within the gastric cell. In this current study, we investigated how vapD knockout affects the survival of H. pylori inside human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. We constructed an H. pylori 26695 vapD (Hp ΔvapD) mutant strain. H. pylori 26695 wt and Hp ΔvapD strains were grown in synthetic media and were co-cultured with AGS cells. From the start, the growth curve, total protein concentration and colony-forming units (CFUs) of each strain were measured. From each co-culture, CFUs and total RNA were obtained, and transcript levels of GAPDH, vapD, vacA, ureA, and 16s Hp were measured by qRT-PCR. Hp ΔvapD did not affect the growth rate of the strain in synthetic media, showing that the vapD gene is not necessary when the bacteria grow outside eukaryote cells. However, in the intracellular environment, the number of CFUs recovered from the Hp ΔvapD strain from AGS cells decreased after 36 h. Transcription levels of the vacA gene from the Hp ΔvapD strain were 10,000-fold lower than those of H. pylori wt, to the point of being undetectable. The results suggest that the vapD gene contributed to maintaining H. pylori inside gastric cells.
1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori is a Gram-negative bacterium that colonizes the human gastric mucosa. There are different H. pylori genotypes, which have important genetic differences and clinical implications, with some being more prevalent in specific geographic regions [1]. H. pylori is responsible for producing atrophic gastritis and peptic ulcers, and it is an important contributing factor to the development of gastric cancer [2]. For practical purposes, the strains of H. pylori can be divided into two main genotypes: genotype I and genotype II [3]. While H. pylori genotype II stains lack virulence genes and colonize the epithelial cells of the stomach of asymptomatic patients who can carry the bacterium for decades without any clinic outcome, H. pylori genotype I strains are associated with the development of various severe gastric pathologies, since these strains possess genes that encode for the virulence factor, such as the vacA gene that encodes for vacuolating cytotoxin A; the cag pathogenicity island [cag-PAI (cytotoxin-associated genes pathogenicity island)], which encodes a type IV secretion system (T4SS); the cagA gene that encodes for the CagA oncoprotein, which is translocated within the epithelial cell through T4SS, altering intracellular signal transduction pathways and probably contributing to oncogenesis [2]; and different adhesins.
Recently, our research group studied the vapD (virulence-associated protein) gene of H. pylori (strain 26695) in co-cultures with human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cells using RT-PCR, and we found that the vapD gene was transcribed at high levels when the bacteria interact with the eukaryote cell. In this same study, we showed that vapD was transcribed in gastric biopsy samples (antrum and corpus) from patients with severe gastric diseases such as atrophic chronic gastritis, follicular gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer [4]. Another recent study demonstrated that the vapD gene is not only transcribed but the VapD protein is also expressed in the intracellular environment of AGS cells, maintaining its expression (manuscript in preparation) over an indefinite time. The VapD protein mechanism of action is not known; however, it has been attributed to endoribonuclease activity [5].
The vapD gene has been described in other microorganisms, such as Rhodococcus equi, a Gram-positive pathogen associated with life-threatening bronchopneumonia in foals; Haemophilus influenzae, a Gram-negative microorganism associated with otitis media and respiratory disease in humans; Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a Gram-negative bacterium associated with gonorrhea in humans; and Dichelobacter nodosus, a Gram-negative bacterium responsible of ovine foot rot, all of which are facultative intracellular microorganisms that have developed strategies to remain inside eukaryotic cells [6,7,8,9]. In different microorganisms, the vapD gene is located on the chromosome as a single gene or as part of a toxin–antitoxin (TA) system or on a plasmid as part of a group of genes of the vap family (vapA-VapH). For example, in H. influenzae, the vapD gene is part of the vapXD (TA) system, which is involved in the stress-induced post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression via the mechanism of mRNA cleavage to maintain the survival and virulence of NTHi under stress conditions such as starvation, as well as heat, osmotic and free radical-induced stress. In R. equi, the VapA and VapD proteins are encoded by the vapA and vapD genes present in a virulence plasmid that are overexpressed under acidic conditions. The presence of other Vap proteins that participate in the virulence of the microorganism has been documented, such as VapK and B (produced by plasmids often found in porcine species) or VapN (produced by plasmids often isolated in bovine and human samples), all of them key for the intracellular survival of R. equi in the host macrophages [10]. The virulence or intracellular capacity of these microorganisms is due to the presence of the vapD gene, since when it is mutated in R. equi and H. influenzae, the microorganisms cannot survive in macrophages [6,8] or in respiratory epithelial cells, respectively. It should be noted that in some strains of N. gonorrhoeae, vapD is present in a cryptic plasmid (pCryp) that is part of the putative vapDX system and in the chromosome, located within a putative VirB T4SS locus, although N. gonorrhoeae usually has two vapD genes, one of them in a pConj and the other associated with a pCrip; in both cases, the vapD genes have homology with the CRISPR/Cas-associated Cas2 protein, which forms a complex with Cas1, which provides immunity against invading mobile genetic elements [11]. In the case of D. nodosus and Riemerella anatipestifer, the vapD gene is present in a plasmid, and when these microorganisms are released from the plasmid, they lose their virulence [9,12] and are unable to cause disease. In this current study, we wanted to know if the survival or persistence of H. pylori (strain 26695) within the AGS cells is affected by knocking out the vapD gene. Our results show that the vapD gene mutant of H. pylori prevented the survival of H. pylori within the cell, concluding that vapD is playing an important role in maintaining the bacterium in the intracellular environment and that it probably contributes to the chronicity of the infection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial and Cell Culture
H. pylori 26695 (ATCC 700392) was grown in Brucella agar plates with 5% sheep blood and 5% fetal bovine serum (Biowest) under humidified and microaerophilic conditions (5% O2, 8% CO2 and 85% N2) at 37 °C for 48 h.
AGS cells (ATCC 1739) were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Biowest) and incubated under humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37 °C.
2.2. Molecular Cloning of vapD and Chloramphenicol Resistance Cassette
2.2.1. Molecular Cloning of vapD (HP0315) Gene
H. pylori 26695 chromosomal DNA was used for the amplification of the vapD (HP0315) gene by PCR using Platinum HF DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with primers 1F and 1R [13] (Table 1). The 285 bp amplified product was cloned into the pCR 2.1 vector (Invitrogen) to generate the pvapD plasmid, where the vapD gene was flanked by EcoRI sites (Figure S1A). The construct was transformed into E. coli DH5α competent cells, and the correct insertion of the vapD gene locus was confirmed by PCR analysis.

Table 1.
Primers used in the construction of vapD knockouts and in the detection of different transcription levels of genes by RT-PCR.
2.2.2. Molecular Cloning of Chloramphenicol Resistance Cassette (Cmr)
The chloramphenicol resistance cassette (Cmr) was obtained from a chloramphenicol-resistant strain of E. coli O42 by PCR using the primer sets catSpeIF and catSpeIR (Table 1) and Platinum HF DNA polymerase (Invitrogen). The PCR product (900 bp) with its SpeI flanking sequence was cloned into pCR 2.1 vector (Invitrogen); the resulting pcatSpe plasmid was transformed into E. coli DH5α competent cells (Figure S1B). The correct sequence of Cmr cassette was confirmed by sequencing using universal primers M13F and M13R.
2.3. Construction of vapD (HP0315) Knockout Mutant
2.3.1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis in vapD Gene
To generate the vapD gene disruption mutant, the pvapD plasmid was subjected to site-directed mutagenesis to create a unique SpeI restriction site (position 117 bp of vapD) using the primer sets vapDSpeF and vapDSpeR (Table 1). To determine if the SpeI restriction site was created, the resulting pPCvapSpe plasmid was transformed into E. coli DH5α. The correct sequence and direction were confirmed by sequencing using the universal primers M13F and M13R.
The pvapSpe plasmid was then digested with EcoRI, and the DNA fragment containing the unique restriction site SpeI was subcloned into the pK18mobsacB vector (ATCC 87097) to obtain the pk18-vapSpe plasmid. The chloramphenicol resistance cassette (Cmr) obtained from the pcatSpe plasmid was then inserted into the SpeI site of the pk18-vapSpe plasmid.
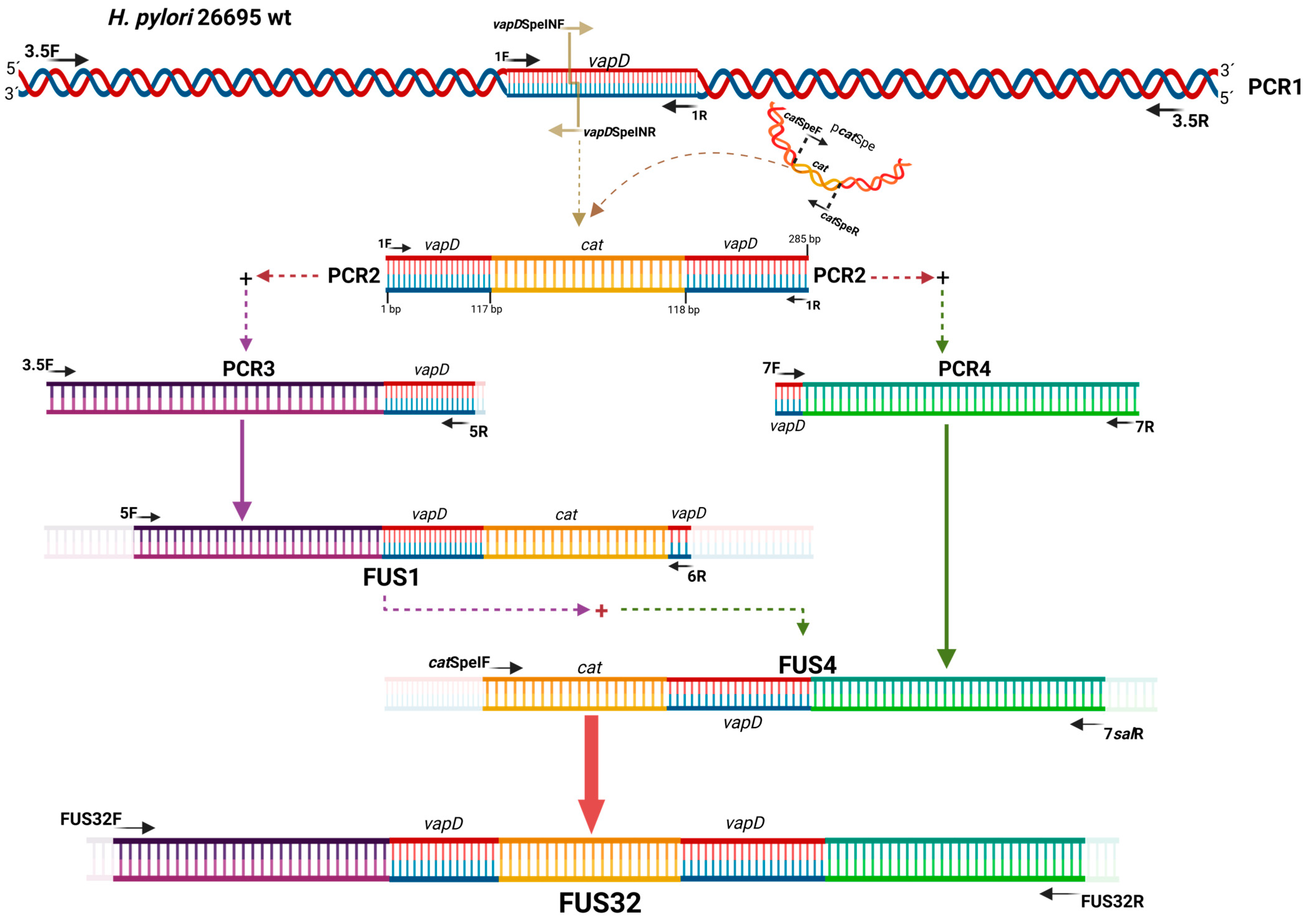
To disrupt the vapD gene and create the vapD knockout construction, a chloramphenicol resistance cassette (Cmr) was inserted into the unique SpeI site of the pk18-vapSpe plasmid, giving rise to the pk18-vapD::Cmr plasmid. This plasmid was transformed into E. coli DH5α. The successful insertion of the resistance cassette was confirmed by PCR, and the resistant colonies were selected on Brucella agar plates of sheep blood containing 30 µg/mL of chloramphenicol (Figure 1).
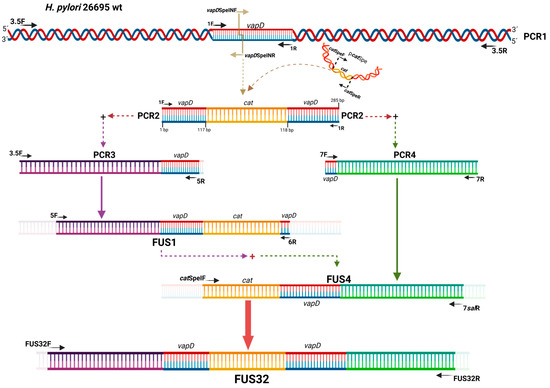
Figure 1.
vapD gene knockout construction. The vapD gene knockout construction was performed by cat cassette insertion between nucleotides 117 and 118 of vapD ORF (HP315) of the H. pylori 26695 strain.
2.3.2. Introduction of Homologous Flanking Regions by Overlap Extension PCR
To increase the probability that homologous recombination would take place between the knockout construction and the H. pylori 26695 wt strain, we introduced the 5′and 3′ flanking regions of vapD wt into the knockout vapD::Cmr construction, with approximately 1000 bp in each region.
To obtain the specific homologous flanking regions of the wild-type vapD gene, the chromosomal DNA from H. pylori 26695 wild-type was amplified by PCR using primers 3.5F and 3.5R (Table 1) to obtain a sequence of 3.5 Kb (PCR1). Six chimeric primers were designed with additional 5′ sequences to introduce homologous ends into the fragments to be fused (Table 1). The Lasergene 7 software was used to construct the primer sequences. Six PCR products with distinct overlapping ends were achieved (Figure 1). Additionally, the vapD::Cmr construction was amplified with 1F and 1R primers [13] (Table 1). The amplifications were carried out using Accuprime Pfx DNA polymerase (Invitrogen). The conditions for the reactions are shown in Table S1. All PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and purified by Nucleospin gel and a PCR clean-up kit (Macherey–Nagel).
To ligate PCR products of the homologous DNA fragments upstream (PCR3) and downstream (PCR4) of the vapD wt gene to the vapD::Cmr construct (PCR2), we used an overlap extension PCR method (Table S1). In this method, 1 μL of PCR3 upstream DNA fragment and 1 μL of PCR2 (vapD::Cmr) were mixed along with Accuprime Pfx DNA polymerase and cycled without primers. This was followed by the fused DNA amplification phase for which a new PCR reaction was carried out with appropriate primer sets (5F and 6R), 2 μL of the overlap extension product (acted as template) and Accuprime Taq DNA polymerase High Fidelity (Invitrogen). The final PCR product of ~2.9 Kb (FUS1) was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, cloned into a pCR 2.1 vector (Invitrogen) and transformed into E. coli DH5α.
Subsequently, the PCR4 fragment was joined downstream to the 3′ region of the vapD::Cmr construction (PCR2) as previously described. Table 1 shows the primer set 7F/7R used to amplify PCR4, as well as the primers catSpeIF/7salR used in the fused DNA amplification phase. The PCR product obtained from DNA fusion (FUS4) was of 2.6 Kb and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, purified by Nucleospin gel and a PCR clean-up kit (Macherey–Nagel), cloned into pCR 2.1 vector (Invitrogen) and transformed into E. coli DH5α.
Finally, the DNA FUS1 and FUS4 fragments were combined. As mentioned above, 1 μL of FUS1 and 1 μL of FUS4 were mixed with Accuprime Pfx DNA polymerase (Invitrogen) and cycled without primers (Table S1). To recover the product from this final fusion, 1.5 μL of the overlap extension product (template) was amplified by PCR using the FUS32F/ FUS32R primer sets and Accuprime Taq DNA polymerase High Fidelity (Invitrogen) Table S1. The final PCR product of ~3.6 Kb (FUS32) was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, purified by Nucleospin gel and a PCR clean-up kit (Macherey–Nagel), cloned into pCR 2.1 (Invitrogen) and pK18-mobsacB (ATCC 87097) vectors, and transformed into E. coli DH5α. The correct sequence and direction of the pCRFUS32 plasmid were confirmed by sequencing, using the universal primers M13F/M13R and the specific primer sets FUS32 R5′F/FUS32 R5′R, FUS 32 RMF/FUS32 RMR and FUS32 R3′F/FUS32 R3′R (Table 1, Figure S2).
2.4. Electrotransformation and Homologous Recombination
2.4.1. Preparation of Recipient H. pylori Cells
H. pylori 26695 wt strain was inoculated into ten Brucella agar plates with 5% sheep blood and supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum. The plates were incubated under humidified and micro-aerophilic conditions (5% O2, 8% CO2 and 85% N2) at 37 °C for 36 h. After incubation, cells were harvested and suspended in 10 mL sterile water. The cell suspension was transferred to 50 mL conic tube and cold sterile water was added until a volume of 40 mL was achieved. The tube was then centrifugated at 3500 rpm at 4 °C for 10 min. The pellet was resuspended in 20 mL of cold 10% glycerol before being centrifugated as before, and resuspended in 14 mL of cold electroporation buffer (15% glycerol and 10% sucrose). Then the cells were centrifuged at 3500 rpm at 4 °C for 10 min, before removing the supernatant and resuspending it in 1 mL of cold electroporation buffer. The cells were aliquoted at 200 μL vol and prepared for electroporation. For long-term storage, competent cells were frozen in dry ice and stored at −80 °C until needed.
2.4.2. Transformation and Recombination
To perform the transformation, 1 mL of the FUS32 construct was amplified by PCR. The PCR reaction was carried out using the specific primer set FUS32 F/R, the Accuprime Taq DNA polymerase High Fidelity (Invitrogen) and the pCRFUS32 plasmid as a template. The PCR product (1 mL) was purified with Nucleospin gel and a PCR clean-up kit (Macherey–Nagel), and the sample was eluted with 500 μL of ultrapure water.
A tube with frozen competent H. pylori 26695 cells was thawed on ice for 15 min. The 500 μL of purified FUS32 product was added and mixed with 200 μL of the competent cells’ suspension. The sample was chilled on ice for 5 min. Then, the bacterial suspension and FUS32 mixture was added very slowly to the bottom of a prechilled (0.2 cm gap) electroporation cuvette. The electroporation was performed with the Bio-Rad gene pulser, and it was set up at 2.5 kV, 25 μF capacitor and a resistance of 600 Ω in parallel, and the sample was subjected to single-pulse electroporation using a time constant of 12.5 ms.
After the pulse, aliquots of 225 μL of the sample were transferred onto three cold Brucella agar plates with 5% sheep blood and 5% fetal bovine serum and then incubated for 12 h at 37 °C under a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. After incubation, the cells were inoculated and streaked onto three cold Brucella agar plates with 5% sheep blood, 5% fetal bovine serum and 8 μg/mL of chloramphenicol (selective antibiotic). The plates were incubated for five days under microaerobic conditions as described above.
At the end of the five-day incubation, all colonies that grew on the selective medium were harvested and propagated individually on a fresh cold Brucella agar plate with 5% sheep blood, 5% fetal bovine serum and 8 μg/mL of chloramphenicol and then incubated for 48 h at 37 °C under the microaerobic conditions as described above.
Finally, to confirm that homologous recombination was carried out, the DNA of all those H. pylori 26695 clones that grew in the selective medium was purified and sequenced with the primer sets FUS32 R5′F/FUS32 R5′R, FUS32 RMF/FUS32 RMR and FUS32 R3′F/FUS32 3′R (Table 1, Figure S2).
All recombinant H. pylori 26695 mutant (HpΔvapD) strains were stored in Brucella broth with 15% glycerol cryotubes at −80 °C.
2.5. Bacterial Growth Curves Comparison
To determine whether the vapD gene mutation in the H. pylori 26695 wt strain triggered any alteration in the behavior or growth rate of the strain, parallel growth curves were performed for both H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD strains.
2.5.1. Bacterial Culture and Inoculation of Growth Curve
H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD were cultured in Brucella agar plates with 5% sheep blood and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C under microaerobic conditions. A small sample was taken from each culture to adjust 10 mL of Brucella broth (BB) to a density equivalent to a McFarland tube 1 (3 × 108 CFU/mL). From these stock suspensions, 1 mL was inoculated into flasks with 9 mL BB with 5% SFB (by duplication) at a final concentration of 3 × 107 CFU/mL per flask. The samples were incubated for five days at 37 °C under microaerobic conditions. The time interval between each sample collection was 24 h.
Growth curves of H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD were evaluated under the conditions outlined above. A non-inoculated flask was also included as a control sample and was used as a negative control for growth and blank for the OD 620 nm measurements.
At each time point [12 h (t1), 24 h (t2), 36 h (t3), 48 h (t4), 60 h (t5), 72 h (t6), 84 h (t7), 96 h (t8) and 108 h (t9)] of the curve, two aliquots of each sample were taken to perform three different measurements. An aliquot of 1 mL was used to determine total proteins. The viability of H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD was determined by counting Colony Forming Units (CFUs). The average colony count for each strain was determined based on three different assays: by inoculate, 100 μL of diluted aliquots (1:10; 1:100) on Brucella agar plates supplemented with 5% sheep blood and 5% fetal bovine serum. A non-inoculated flask was also plated as a negative control. The plates were incubated for five days at 37 °C under a humidified atmosphere of 8% CO2, and then the colonies were counted. The results for each interval were estimated as the average of three independent repetitions, including three replicates per independent assessment. Finally, in parallel to previously depicted assays, the growth of each sample was measured by means of the absorbance (OD) of the culture at 620 nm in a visible light spectrophotometer (Tecan Instruments, Männedorf, Switzerland).
2.5.2. Total Protein Extraction
The pellet (H. pylori-AGS) was resuspended in 500 µL of RIPA buffer (NaCl 150 mM, Tris-HCl 50 mM pH 7.4, EDTA 2 mM, Nonidet-40 1% v/v, sodium deoxycholate 0.5% w/v, SDS 0.05% w/v) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail, EDTA-free and PMSF 0.2 mM, and incubated for 30 min on ice with gentle agitation using an end-over-end rotator. The lysate was centrifuged at 15,000× g for 20 min at 4 °C, before recovering the supernatant. The protein was quantified by the Bradford method at 595 nm.
2.6. H. pylori 26695 wt-AGS Cell and H. pylori 26695 ΔvapD-AGS Cell Co-Cultures
AGS cells (ATCC® CRL-1739) were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM, Life Technologies®, Woodland, CA, USA), supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Corning Costar, Manassas, VA, USA) and antibiotics. The AGS cells were incubated in 5% CO2 atmosphere until 80% confluency was reached and then distributed into 12-well plates. H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD strains were grown in blood agar plates (BAPs) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum for 48 h in microaerobic conditions. AGS cells (3.2 × 105) with fresh DMEM were inoculated separately with H. pylori 26695 wt strain and HpΔvapD strain to a 3.2 × 107 CFU/mL inoculum. All the resulting co-cultures were incubated, cultivated and worked as previously mentioned by Morales-Espinosa et al. [4] (Table 1).
Detection of transcription levels of vacA, vapD, ureA and 16s Hp genes from H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD strains in the intracellular environment. Total RNA was isolated from the cellular package (intracellular H. pylori-AGS cells) at different time points using Hybrid-RTM (GeneAll Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Song-gu, Seoul, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Total RNA (1 µg) was reverse transcribed using a QuantiTect® Reverse Transcription Kit (QIAGEN®, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. vacA, vapD, 16s Hp, ureA and GAPDH (life Technologies) mRNA levels were determined using real-time PCR and a step one plus Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems®, Singapore) as Morales-Espinosa et al. mentioned previously [4].
3. Results
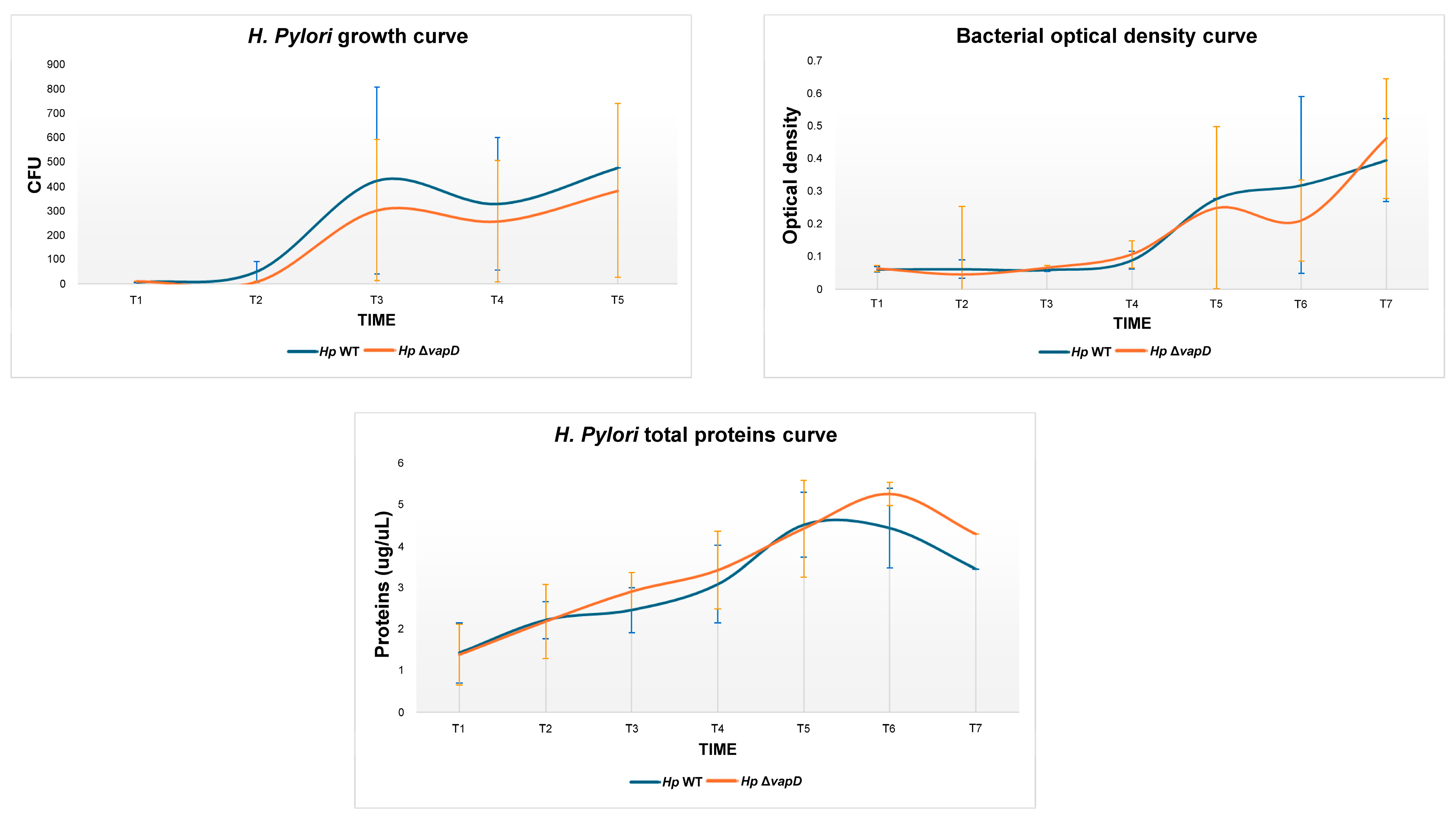
We determined the growth behavior of the H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD strains, which were grown in vitro (synthetic media) in the laboratory at different time points (from 0 to 96 h). An aliquot of 1 mL was used to obtain CFU count, optical density (O.D) and total proteins. We observed that both strains of H. pylori 26695 (wt and HpΔvapD) showed the same behavior, suggesting that HpΔvapD did not affect the growth rate of H. pylori in synthetic media. This suggests that the vapD gene is not necessary when the bacterium is growing outside of the eukaryote cells (Figure 2).
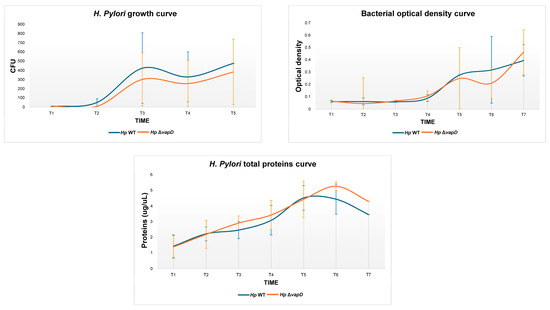
Figure 2.
Growth behavior of H. pylori 26695 wild-type (wt) strain and H. pylori 26695 ΔvapD strain under in vitro conditions (synthetic media) at different time points. The figure depicts the growth curve of the H. pylori wt strain (blue line) and H. pylori 26695ΔvapD strain (red line) obtained by CFU count, optical density, and total protein curve.
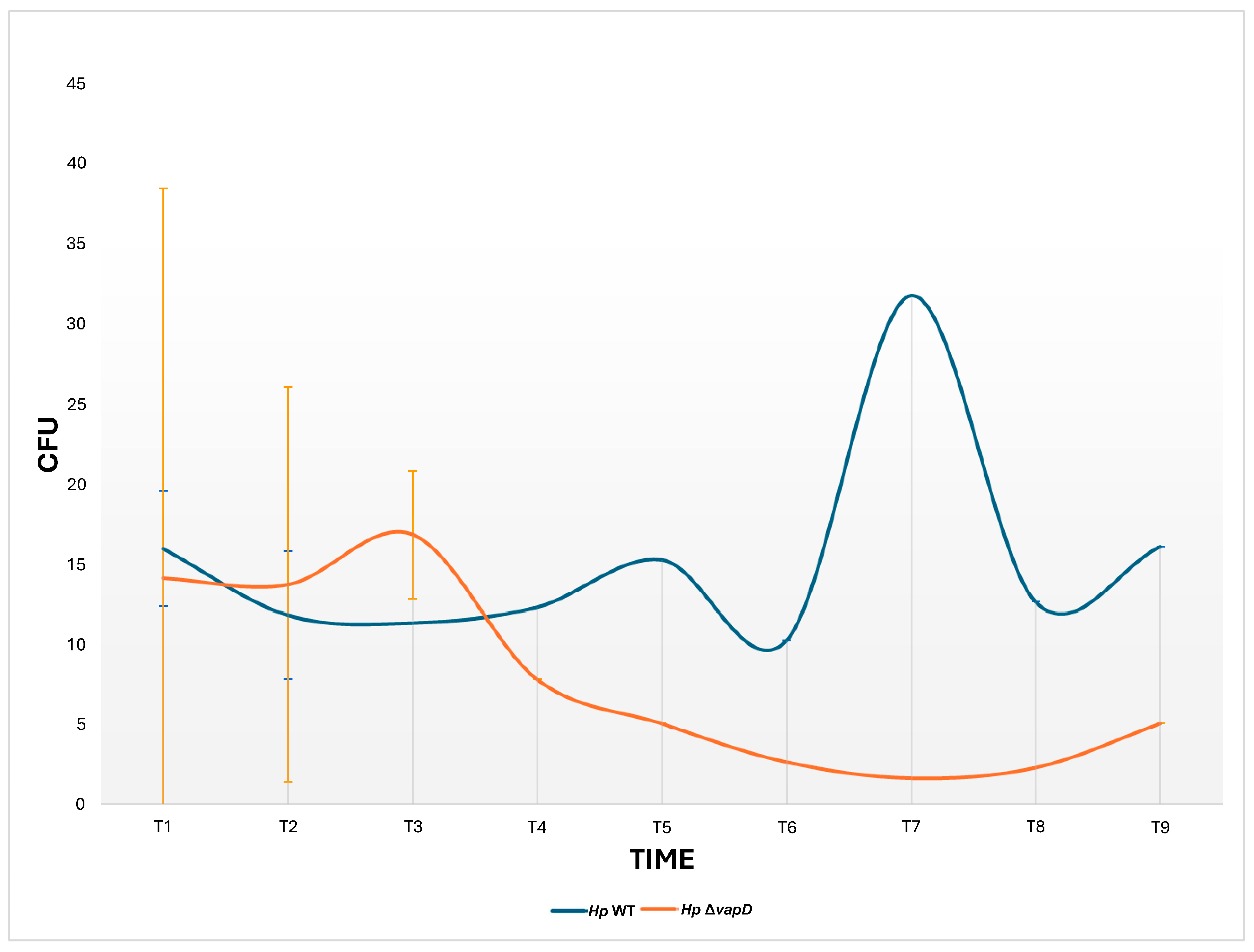
We also wanted to know if the vapD gene mutation would affect the survival of H. pylori inside gastric cells, so we performed parallel assays of both H. pylori 26695 strains (wt and HpΔvapD) in co-culture with AGS cells, which were maintained up to 108 h (t9). A CFU count from each co-culture was determined from the intracellular niche.
In terms of growth rate, our results showed a significant difference (p = 0.002) between the two strains. While the number of CFUs from the H. pylori 26695 wt strain was maintained throughout the assay (12–108 h), the number of HpΔvapD strain colonies identified from co-culture with AGS cells decreased significantly after 36 h until it disappeared completely (Figure 3).
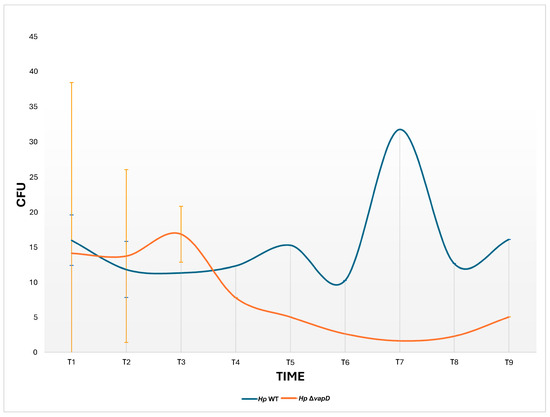
Figure 3.
Growth curves of the H. pylori 26695 wild-type (wt) strain and H. pylori 26695ΔvapD strain from the intracellular environment at different time points. This shows the growth curve of the H. pylori wt strain (blue line) and H. pylori 26695 ΔvapD mutant strain (red line) in co-culture with AGS cells, which was determined by CFU count obtained from the intracellular environment. The results show a significant difference (p = 0.002) between the two strains.
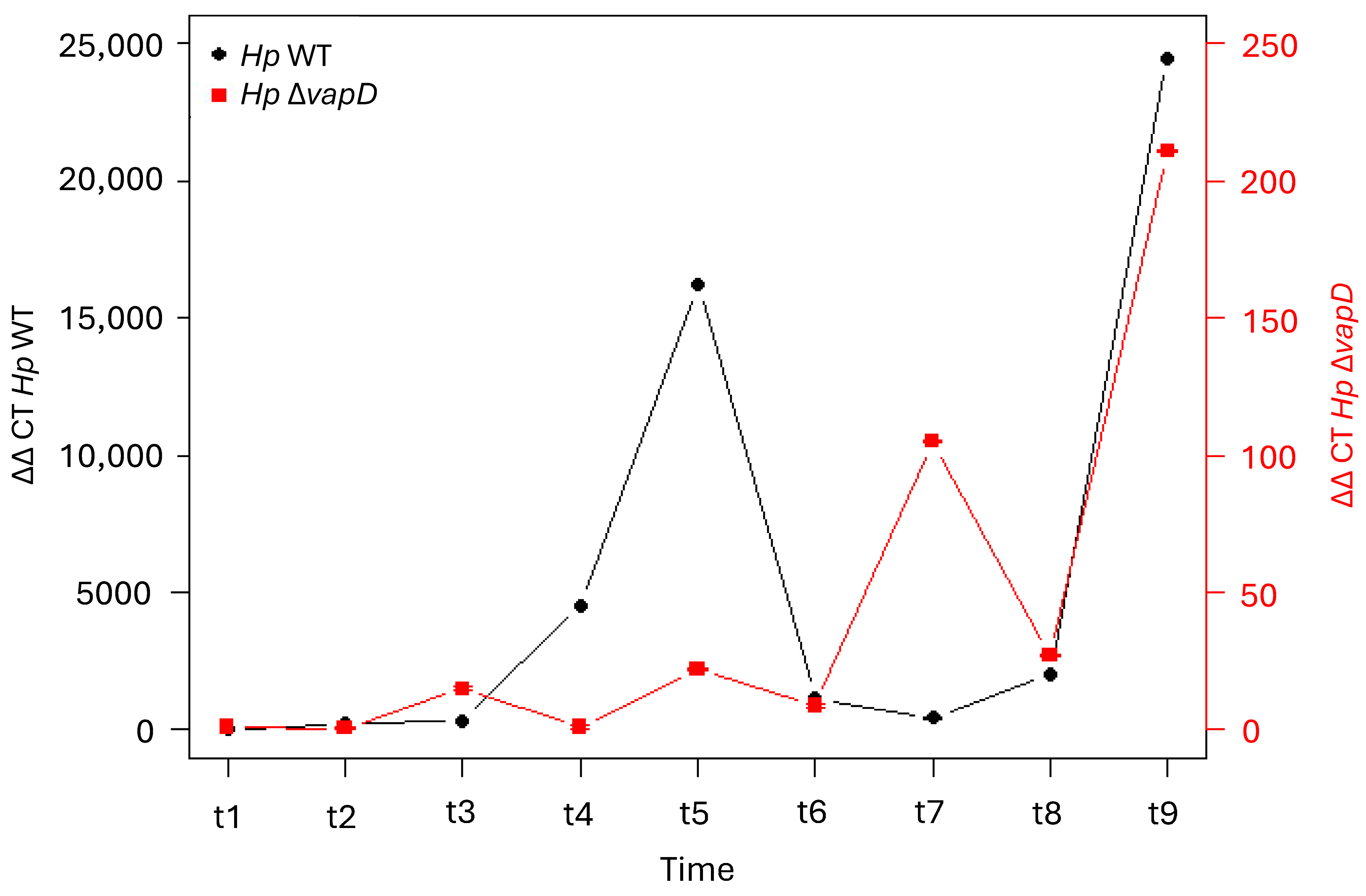
However, when the intracellular transcription levels of the vacA gene from H. pylori 26695 wt was compared with the HpΔvapD strain (taking the transcription level of the endogenous bacterial gene 16s as a reference value), we observed that the vacA gene from H. pylori 26695 wt had very high transcription levels in comparison to vacA from the HpΔvapD strain (Figure 4, Table S2). In the H. pylori wt strain, vacA was transcribed up to 10,000-fold higher than vacA from the HpΔvapD strain, with a significant difference of p = 0.005 (Figure 4, Table S3). This suggests metabolic impairment of vapD-mutated H. pylori within the intracellular environment.
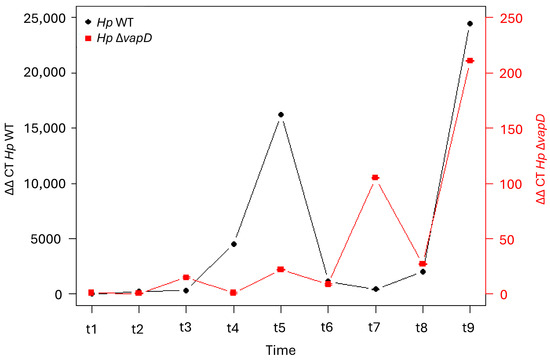
Figure 4.
Relation of transcription level of vacA with the 16s endogenous control gene of H. pylori 26695 wild-type strain and H. pylori 26695 ΔvapD strain. H. pylori wt strain (black line) and H. pylori 26695 ΔvapD mutant strain (red line). A significant difference in the vacA transcription levels can be observed between both strains (p = 0.005).
With regard to the ureA gene, we could not determine transcription levels of this gene in both H. pylori 26695 (wt and ΔvapD mutant) strains in the intracellular environment.
4. Discussion
In a previous study, we showed that vapD is a strain-specific gene, and approximately 38% of the Mexican strains of H. pylori present this gene [14], although its frequency varies depending on the geographic region and the population type [13]. Initially, this gene was described by Cao et al. in a hypervariable chromosomal region of the H. pylori 60190 strain and in other microorganisms, such as Rhodococcus equi, non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae, Dichelobacter nodosus, Neisseriae gonorrhoea and other microorganisms of different phyla and genera, where it was shown that the vapD gene had been acquired by horizontal gene transfer [15]. However, in H. pylori, vapD became fixed in its chromosome once it was acquired. In Rhodococcus equi, the vapD gene is highly inducible inside macrophages and participates in preventing the fusion of the phagolysosome [7]. In non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi), the vapD gene forms part of the toxin–antitoxin module (vapXD), which is involved in metabolic regulation of bacteria by enabling a switch to a dormant state under stress conditions. Ren et al. (2012) concluded that the vapXD TA locus enhances NTHi survival and virulence during infection in vitro and in vivo using a mechanism of mRNA cleavage [8]. Mutations of the vapD gene have shown reduced NTHi persistence in the chinchilla model of otitis media, leading to the belief that vapD is involved in the persistence of NTHi within otic epithelial cells [8].
In H. pylori, the role of vapD is unknown, although a relationship between the Cas2 family of ribonuclease associated with the CRISPR system of microbial immunity and VapD has been suggested [5]. Contrary to what was reported by Chakraborty and Chatterjee [16], the vapD gene of the HP0315 locus in the H. pylori 26695 strain is not a component of the TA system, and no genes associated with it as antitoxins are found, as corroborated by Gilep [17] and Kwon [5], which suggests that it may be an evolutionary intermediate that does not belong to either the Cas2 family or the TA system. There have been very few studies carried out on the vapD gene and its protein. In previous studies carried out by our group, we tested the vapD-positive H. pylori 26695 strain in co-culture with AGS cells, where H. pylori remained metabolically active inside AGS cells up to 108 h (time chosen by our experiment). In that study, the vapD transcription levels were measured by RT-PCR, and the assay showed high transcription levels of the vapD gene, reaching a maximum level of transcription after 96 h of being inside the AGS cells [4]. In this same study, it was also demonstrated that the transcription of the vapD gene occurred in gastric biopsies (in vivo) from patients with severe gastric pathologies, such as chronic atrophy gastritis, follicular gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric metaplasia and gastric cancer, and the results showed high levels of vapD transcription from the gastric antrum and corpus in all patients, indicating that vapD-positive H. pylori strains were colonizing both anatomic sites at the same time that the vapD gene was being transcribed in vivo [4]. In another study, our group produced polyclonal antibodies against the recombinant VapD protein of H. pylori [18], and they were used in immunofluorescence assays to visualize the VapD protein of H. pylori in the cytoplasm of AGS cells in co-cultures at different times (manuscript in preparation). It is well known that different proteins or virulence factors of H. pylori are expressed into gastric cells and under different environmental conditions [4,19,20,21].
The relevance and importance of the invasiveness of any microorganism could be an advantage in its pathogenicity, favoring its permanence, multiplication and dissemination into other cells, since within the cells it is protective against both innate and acquired immune systems and antibiotics, as well as having an important source of nutrients [22]. However, the microorganisms need strategies that allow survival within eukaryotic cells, such as taking refuge within a vesicular structure, avoiding intracellular antimicrobial defenses, inhibiting the fusion of phagolysosomes or preventing apoptosis, ensuring, in turn, that the cell maintains its division cycle [23,24]. Actually, it is well documented that there are invasive strains of H. pylori [25,26,27] that enter gastric cells via a zipper-like phagocytic mechanism that depends on protein kinase C and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase [28]. Once inside, they find refuge within large vacuolar compartments in which H. pylori can persist for a long time [25,26,27]. The VacA protein is an important virulence factor and has been identified as being responsible for the formation of vacuoles mediated by late endosomal compartments that depend on vacuolar ATPase, the small GTPase Rab7, dynamin and syntaxin 7 [29]. The vacuolar phenotype of the strains results in the formation and maintenance of an intracellular niche for H. pylori [29], which may contribute to the protection of bacteria inside AGS cells. However, this does not provide a satisfactory explanation of the molecular mechanism responsible for the intracellular survival of H. pylori inside gastric epithelial cells.
In the current study, we wanted to determine if the mutation of the vapD gene in the H. pylori 26695 strain could affect its persistence and survival within the gastric epithelial cell. With this in mind, we performed parallel assays of co-cultures of AGS cells with H. pylori 26695 wt and HpΔvapD strains. Our results show that the H. pylori 26695 wt strain behaved within AGS cells in a similar way to that previously reported, in which H. pylori invades AGS cells in the first 6 h of co-culture: the VapD expression increased while it remained for a longer time in the intracellular niche [4], and CFUs were recovered in sufficient amounts at different time points. Meanwhile, co-infection of AGS cells by the HpΔvapD strain also maintained its ability to invade AGS cells in the first 6 h, but after that, its growth curve was significantly affected, which was reflected in the gradual decrease in the number of CFUs in AGS cells at different times points until none were found. These results were corroborated by the significant decrease (p = 0.0005) in the expression levels of VacA of this HpΔvapD strain (in relation to the H. pylori 26695 wt strain), until they became imperceptible, probably due to an important decrease in the number of H. pylori within the cell or due to the death of the bacteria in the intracellular environment, suggesting that the vapD gene is somehow involved in the survival of H. pylori within gastric cells.
Contrary to what was observed in the intracellular environment, the growth of both strains in vitro (synthetic medium) shows no difference between the development (bacterial optical density curve, bacterial growth curve and protein concentration) of both strains, indicating that the vapD gene is silenced and that it is not necessary when the bacterium is growing outside eukaryote cells. Our results suggest that the VapD protein is participating in the persistence of H. pylori within gastric cells.
Further studies will have to be carried out to detail the mechanism of action of vapD and its participation in the survival of the bacteria within gastric cells.
5. Conclusions
The results obtained in the current study suggest that vapD plays a role in the survival and persistence of H. pylori in the intracellular environment, and this needs further study to determine its precise role.
Our results suggest that this intracellular characteristic of some H. pylori strains increases the risk of developing chronic infection, contributes to treatment failure and helps the chronic inflammatory process that promotes the development of gastric cancer.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13081952/s1, Figure S1: Construction of the pvapD and pcatSpe plasmids; Figure S2: Complete nucleotides sequence of the recombinant region (FUS32) of vapD knockout (Hp26695ΔvapD.seq).F32R5’corresponds to the nucleotide sequences (1 bp-708 bp) amplified by PCR with FUS32R5’F/R primers.F32RM corresponds to the nucleotide sequences (394 bp-1102 bp) amplified by PCR with FUS32RM’F/R primers.F32R3’ corresponds to the nucleotide sequences (1085 bp-1793 bp) amplified by PCR with FUS32R3’F/R primers. The color of the nucleotide sequences was preserved in relation to those used in the Figure 1; Table S1: Protocol conditions used of each PCR for the construction of knockout vapD::Cmr; Table S2: Transcriptional values of vacA and 16sHp genes of intracellular Helicobacter pylori 26695 wild type strain; Table S3: Transcriptional values of vacA and 16sHp genes of intracellular Helicobacter pylori 26695 wild type strain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, visualization, funding acquisition and writing-original Draft Preparation, R.M.-E.; Investigation, methodology and validation G.D. and A.F.-A.; Methodology and validation, C.A.S., R.D.-M. and J.L.M.; Formal analysis, A.G.-P.; Supervision, writing—review and editing A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, DGAPA-PAPIIT grant IN213921; Mexican government, CONAHCYT grant CF-2023-G-919.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocol was approved by the ethics commission from the Faculty of Medicine with the number 055/2014 at the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Francisca Trujillo for help with the laboratory techniques.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kersulyte, D.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Velapatiño, B.; Su, W.; Pan, Z.; Garcia, C.; Hernandez, V.; Valdez, Y.; Mistry, R.S.; Gilman, R.H.; et al. Differences in Genotypes of Helicobacter pylori from Different Human Populations. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3210–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.L.; Yeh, Y.C.; Sheu, B.S. The Impacts of H. pylori Virulence Factors on the Development of Gastroduodenal Diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J.; Atherton, J.C. Helicobacter pylori Persistence: Biology and Disease. J. Clin. Invest 2004, 113, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Espinosa, R.; Delgado, G.; Serrano, L.R.; Castillo, E.; Santiago, C.A.; Hernández-Castro, R.; Gonzalez-Pedraza, A.; Mendez, J.L.; Mundo-Gallardo, L.F.; Manzo-Merino, J.; et al. High Expression of Helicobacter pylori VapD in Both the Intracellular Environment and Biopsies from Gastric Patients with Severity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Min, Y.H.; Im, H.; Lee, I.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, B.J. Structural and Biochemical Characterization of HP0315 from Helicobacter pylori as a VapD Protein with an Endoribonuclease Activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4216–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.; Benachour, A.; Taouji, S.; Auffray, Y.; Hartke, A. Induction of vap Genes Encoded by the Virulence Plasmid of Rhodococcus equi during Acid Tolerance Response. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.; Benachour, A.; Taouji, S.; Auffray, Y.; Hartke, A. H2O2, Which Causes Macrophage-Related Stress, Triggers Induction of Expression of Virulence-Associated Plasmid Determinants in Rhodococcus equi. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3768–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Walker, A.N.; Daines, D.A. Toxin-Antitoxin Loci vapBC-1 and vapXD Contribute to Survival and Virulence in Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.E.; Strugnell, R.A.; Rood, J.I. Molecular Characterization of a Genomic Region Associated with Virulence in Dichelobacter nodosus. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 4586–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganderton, T.R.; Ghete, D.; Hogg, K.; Park, G.J.; Baumann, C.G.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Pryor, P.R. Commonality of Virulence-Promoting Function in Rhodococcus equi Virulence Associated Proteins (Vaps). Cell. Microbiol. 2023, 2023, 9141112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cehovin, A.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Harrison, O.B.; Tang, C.M. Association of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Plasmids with Distinct Lineages and the Economic Status of Their Country of Origin. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.C.; Lin, W.H.; Chang, Y.F.; Chang, C.F. Identification of a Virulence-Associated Protein Homolog Gene and ISRa1 in a Plasmid of Riemerella anatipestifer. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 179, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Cover, T.L. High-Level Genetic Diversity in the VapD Chromosomal Region of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 2852–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-espinosa, R.; González-valencia, G.; Delgado, G.; Luis, J.; Torres, J.; Cravioto, A. Frequency and Characterization of vapD Gene in Helicobacter pylori Strains of Different vacA and cag-PAI Genotype. Bioquimia 2008, 33, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Sapién, G.; Cerritos-Flores, R.; Flores-Alanis, A.; Méndez, J.L.; Cravioto, A.; Morales-Espinosa, R. Evolutionary Dynamics of vapD Gene in Helicobacter pylori and Its Wide Distribution among Bacterial Phyla. SOJ Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Chatterjee, R. Comparative Genomics Analysis of Statistically Significant Genomic Islands of Helicobacter pylori Strains for Better Understanding the Disease Prognosis. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20212084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilep, K.; Bikmetov, D.; Popov, A.; Rusanova, A.; Tagami, S.; Dubiley, S.; Severinov, K. Novel Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems with VapD-like Proteins. MBio 2025, 16, e00003-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Alanis, A.; Delgado, G.; Santiago-Olivares, C.; Luna-Pineda, V.M.; Cruz-Rangel, A.; Guerrero-Mejía, D.; Escobar-Sánchez, M.L.; Torres-Ramírez, N.; Morales-Espinosa, R. Effective Polyclonal Antibodies against the Virulence-Associated Protein D (VapD) of Helicobater pylori, Obtained from Recombinant VapD. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.E.; Peek, R.M.; Krishna, U.; Cover, T.L. Global Analysis of Helicobacter pylori Gene Expression in Human Gastric Mucosa. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semino-Mora, C.; Doi, S.Q.; Marty, A.; Simko, V.; Carlstedt, I.; Dubois, A. Intracellular and Interstitial Expression of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Genes in Gastric Precancerous Intestinal Metaplasia and Adenocarcinoma. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, M.A.; Ares, M.A.; Bargen, K.V.; Panunzi, L.G.; Martínez-Cruz, J.; Valdez-Salazar, H.A.; Jiménez-Galicia, C.; Torres, J. Gene Expression Profiling of Transcription Factors of Helicobacter pylori under Different Environmental Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotade Titilayo, O.; Roy, C.R. Manipulation of Host Cell Organelles by Intracellular Pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faherty, C.S.; Maurelli, A.T. Staying Alive: Bacterial Inhibition of Apoptosis during Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, A.P.; Guttman, J.A.; Finlay, B.B. Manipulation of Host-Cell Pathways by Bacterial Pathogens. Nature 2007, 449, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Borén, T. Helicobacter pylori Is Invasive and It May Be a Facultative Intracellular Organism. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Xu, W.; Lu, N. Adhesion and Invasion of Gastric Mucosa Epithelial Cells by Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.H.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.K.; Youn, H.S.; Baik, S.C.; Cho, M.; Lee, W.K.; Rhee, K.H. Invasiveness of Helicobacter pylori into Human Gastric Mucosa. Helicobacter 1999, 4, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, T.; Backert, S.; Schwarz, H.; Berger, J.; Meyer, T.F. Specific Entry of Helicobacter pylori into Cultured Gastric Epithelial Cells via a Zipper-like Mechanism. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2108–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terebiznik, M.R.; Vazquez, C.L.; Torbicki, K.; Banks, D.; Wang, T.; Hong, W.; Blanke, S.R.; Colombo, M.I.; Jones, N.L. Helicobacter pylori VacA Toxin Promotes Bacterial Intracellular Survival in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6599–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).