Isolation and Characterization of the Trimethylamine (TMA)-Degrading Microbacterium lacticum Strain PM-1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Media
2.2. Enrichment, Isolation, Purification, and Identification of TMA-Degrading Bacterial Strains
2.3. Quantitative Correlation Between OD600 and Colony Forming Units (CFU)
2.4. Batch Experiments Under Different Temperatures, Salinities, and TMA Contents
2.5. Bacterial Growth and TMA Conversion in Different Media
2.6. TMA Evaporation Verification
2.7. TMA Analysis with GC
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
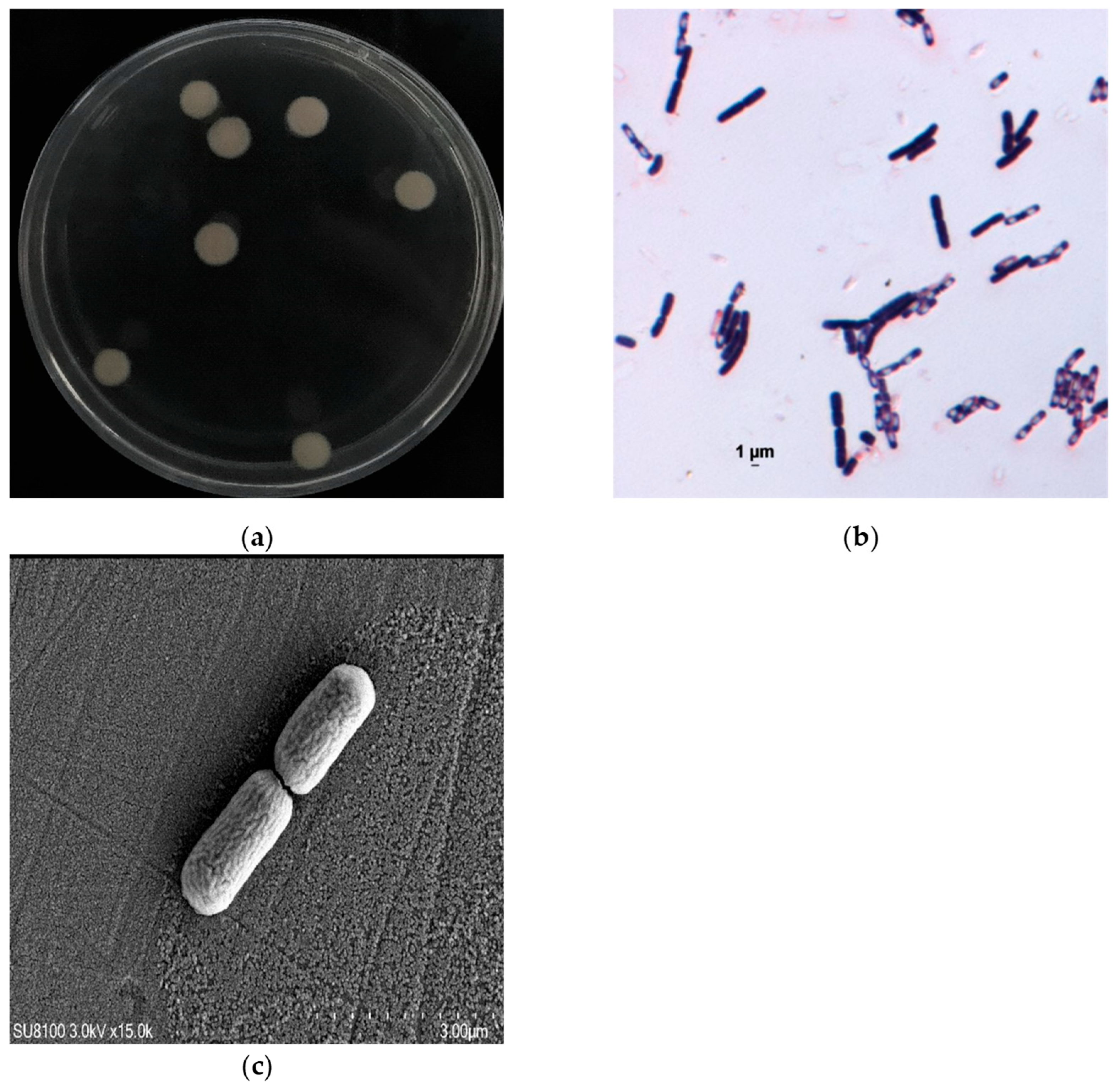
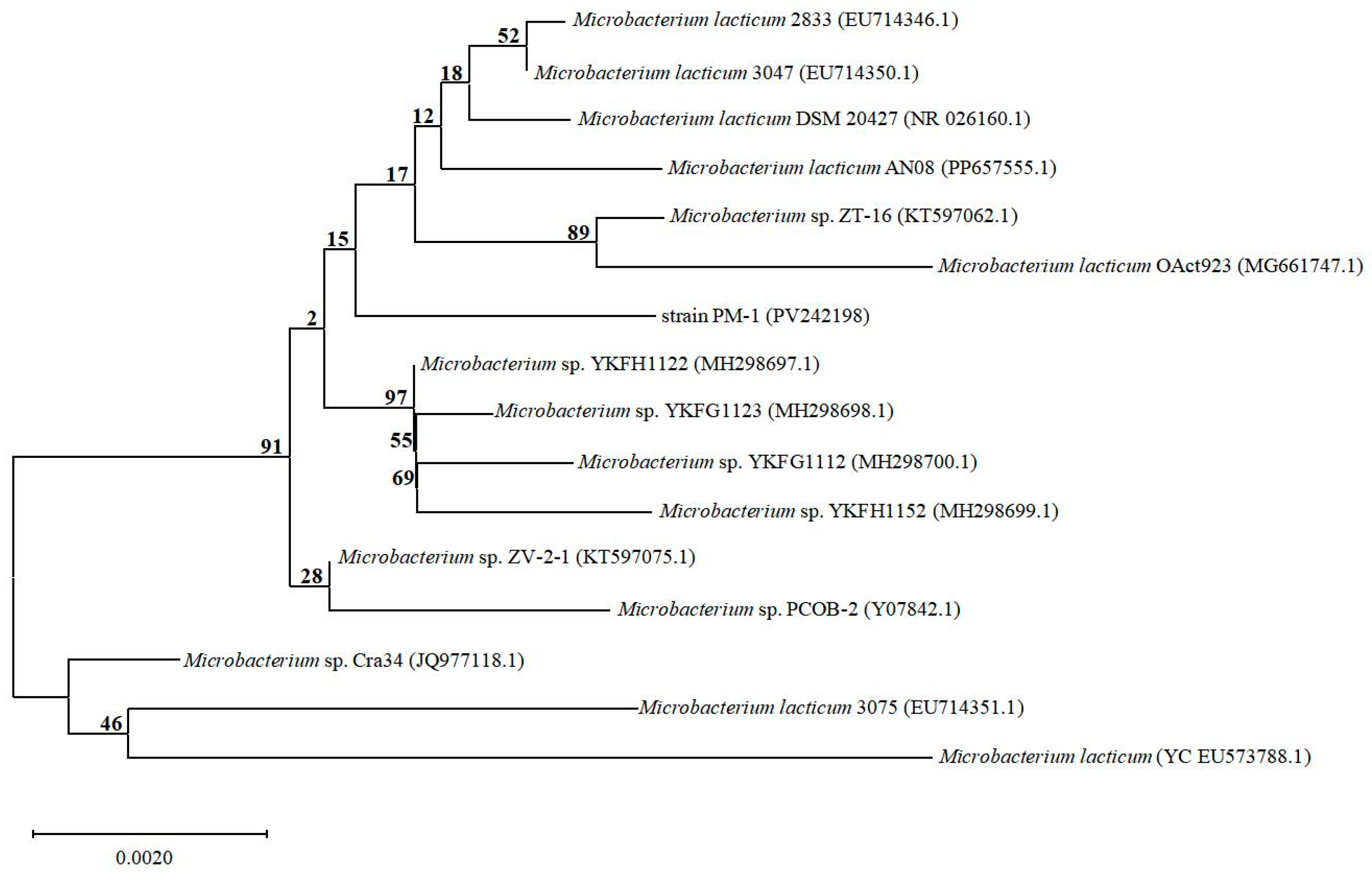
3.1. Isolation and Identification of the TMA-Degrading Strain
3.2. TMA Evaporation
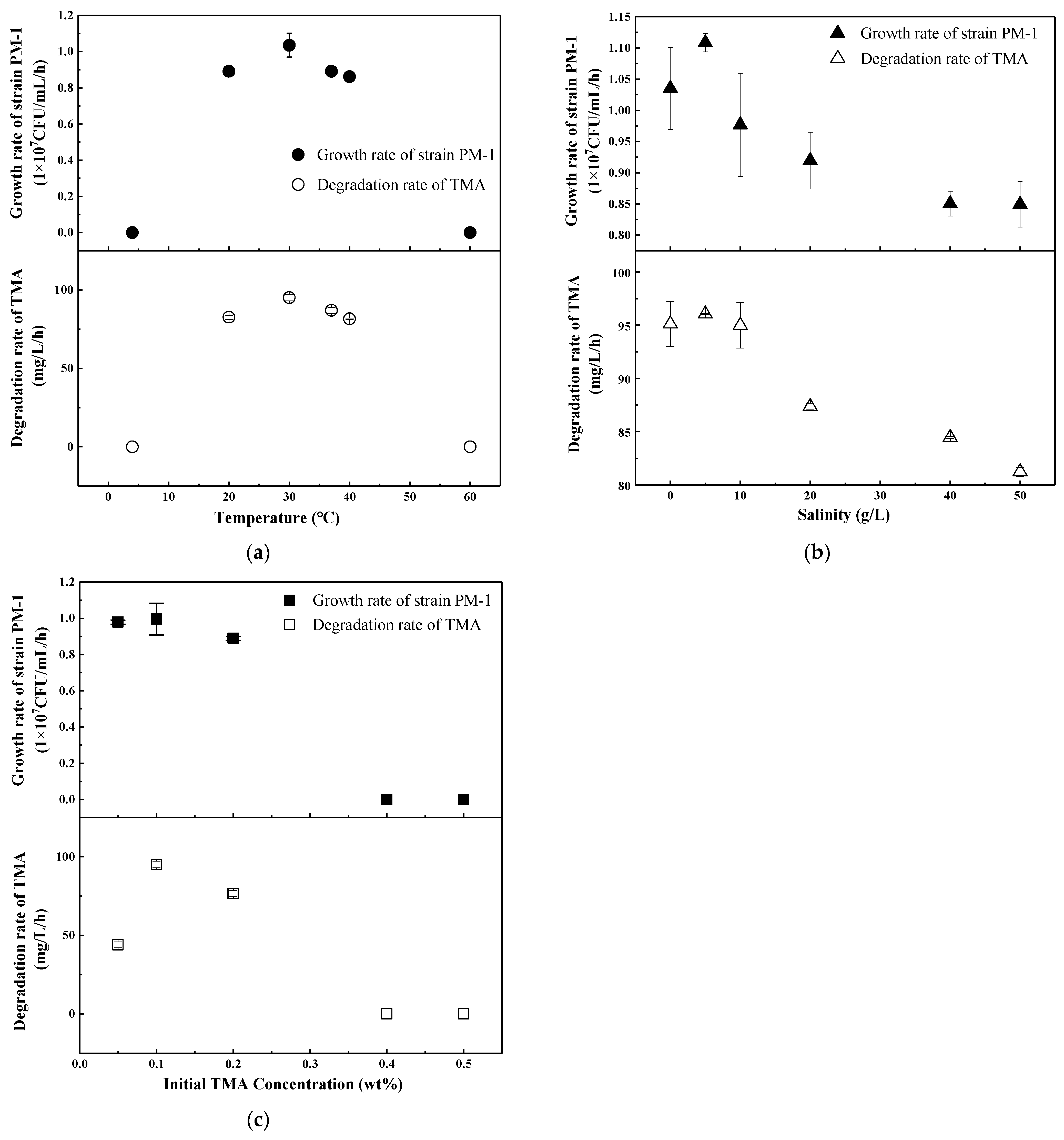
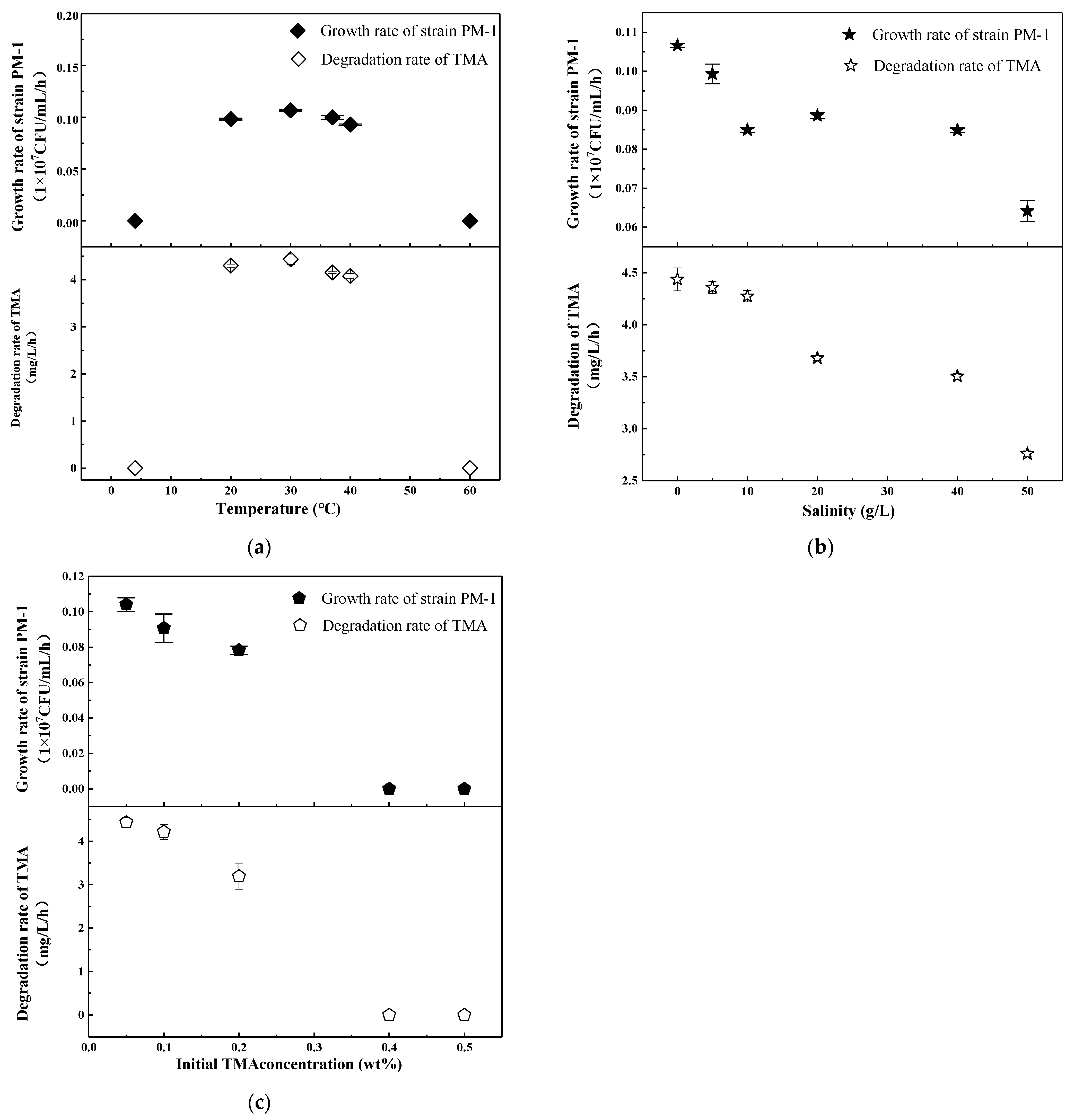
3.3. Temperature, Salinity, and TMA Content Ranges for Strain PM-1
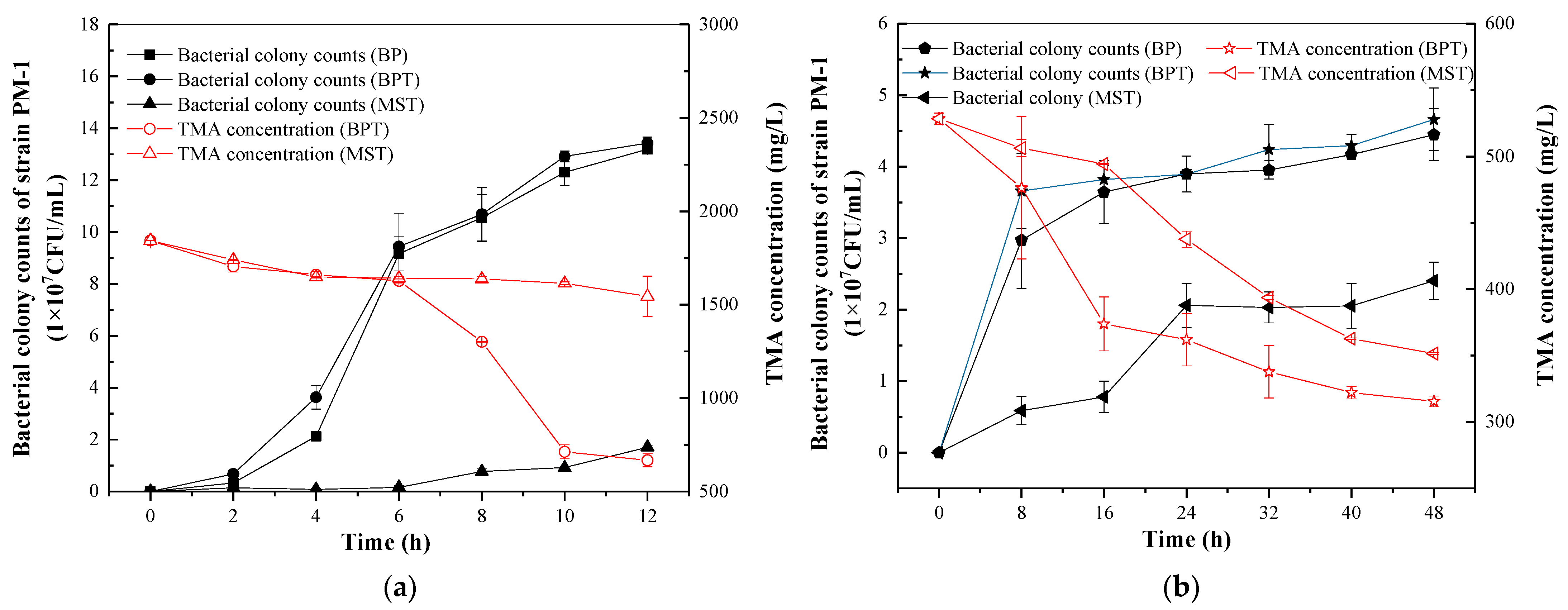
3.4. TMA Degradation with Different Media
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TMA | Trimethylamine |
| DMA | Dimethylamine |
| MA | Methylamine |
| BP | Beef extract peptone medium |
| BPT | Beef extract peptone with trimethylamine |
| MST | The mineral salt medium with trimethylamine |
References
- Fazzalari, F.A. (Ed.) Compilation of Odor and Taste Threshold Values Data; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.G.; Bae, H.S.; Lee, S.T. A novel denitrifying bacterial isolate that degrades trimethylamine both aerobically and anaerobically via two different pathways. Arch. Microbiol. 2001, 176, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.A.M.; Eltayeb, M.E.; Mori, N.; Arima, J.; Tanaka, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Yamanaka, N. Proteomic analysis of homocholine catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strain A9. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, J.M.; Kraakman, N.J.R.B.; Muñoz, R.; Lebrero, R. A comparative analysis of odour treatment technologies in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Lv, Z.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Nitrogen removal through different pathways in an aged refuse bioreactor treating mature landfill leachate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9225–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groenestijn, J.W.; Kraakman, N.J.R. Recent developments in biological waste gas purification in Europe. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 113, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Mausz, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Giovannoni, S.J. Microbial trimethylamine metabolism in marine environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyarzun, P.; Alarcón, L.; Calabriano, G.; Bejarano, J.; Nuñez, D.; Ruiz-Tagle, N.; Urrutia, H. Trickling filter technology for biotreatment of nitrogenous compounds emitted in exhaust gases from fishmeal plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 14554-1993; Emission Standard for Odor Pollutants. Beijing Standards Press: Beijing, China, 1993. (In Chinese)
- Wang, Y.C.; Han, M.F.; Jia, T.P.; Hu, X.R.; Zhu, H.Q.; Tong, Z.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Liu, D.Z.; Peng, Y.Z.; et al. Emissions, measurement, and control of odor in livestock farms: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, M. Fabrication of ZnO/Ag photocatalyst and its photocatalytic degradation properties on trimethylamine. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2024, 21, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Duan, Z.; He, F.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Ag/AgBr-oxygen enriched g-C3N4 for efficient photocatalytic degradation of trimethylamine. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 14068–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, L.; Lu, X. Sustainable and continuous removal of trimethylamine in a bio-photoelectrochemical reactor using g-C3N4/TiO2 photocathode with power generation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Volatile organic compound removal via biofiltration: Influences, challenges, and strategies. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.; Bernal, P.; Maureira, D.; Ramos, N.; Vásquez, J.; Urrutia, H.; Gentina, J.C.; Aroca, G. Biofiltration of trimethylamine in biotrickling filter inoculated with Aminobacter aminovorans. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 33, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liffourrena, A.S.; Salvano, M.A.; Lucchesi, G.I. Pseudomonas putida A ATCC 12633 oxidizes trimethylamine aerobically via two different pathways. Arch. Microbiol. 2010, 192, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Basran, J.; Scrutton, N.S.; Hille, R. The reaction of trimethylamine dehydrogenase with trimethylamine. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13147–13154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiberg, J.B.M.; Harderm, W. Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of trimethylamine, dimethylamine and methylamine in Hyphomicrobium X. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1978, 106, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, I.; Gupta, A.; Pandharipande, S.L.; Bansiwal, A.; Vaidya, A.N. A high performance biological degradation of trimethylamine: Experimental study and mathematical modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yang, M.; Li, J.X.; Yao, L.; Hu, H.R. Biolog microbial identiffcation system-study on the operating regulation of bacteria identification. Food Ferment. Ind. 2006, 32, 50–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mokashi, S.A.; Paknikar, K.M. Arsenic (III) oxidizing Microbacterium lacticum and its use in the treatment of arsenic contaminated groundwater. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.Q.; Na, J.R.; Bang, M.H.; Kim, M.K.; Yang, D.C. Conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 by Microbacterium sp. GS514. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.; Qin, W.; Yuan, J.; Ding, A.; Xie, E.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Growth kinetics of Microbacterium lacticum and nitrate-dependent degradation of ethylbenzene under anaerobic conditions. Bioremediat. J. 2014, 18, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzina, N.E.; Machulin, A.V.; Sorokin, V.V.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Esikova, T.Z.; Shorokhova, A.P.; Delegan, Y.A.; Abashina, T.N. Capture of essential trace elements and phosphate accumulation as a basis for the antimicrobial activity of a new ultramicrobacterium Microbacterium lacticum Str. F2E. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.T.; Martinko, J.M.; Stahl, D.A.; Clark, D.P. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 12th ed.; Pearson Benjamin Cummings: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 151–159. ISBN 0132324601. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, C.K.; Maurya, S.; Ramanathan, G. Insight into the metabolic pathways of Paracoccus sp. strain DMF: A non-marine halotolerant methylotroph capable of degrading aliphatic amines/amides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 125947–125964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, M.; Mondal, P.; Ghosh, D.; Biswas, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K. Metabolomic and genomic insights into TMA degradation by a novel halotolerant strain-Paracoccus sp. PS1. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Bae, H.S.; Oh, H.M.; Lee, S.T. Isolation and characterization of novel halotolerant and/or halophilic denitrifying bacteria with versatile metabolic pathways for the degradation of trimethylamine. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 225, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of Carbon Source | Results | Type of Carbon Source | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates (27 types) | Citric Acid | w | |
| N-Acety-D-glucosamine | + | α-Keto-Glutaric Acid | + |
| Dextrin | + | D-Malic Acid | − |
| D-Maltose | + | L-Lactic Acid | + |
| D-Cellobiose | w | L-Malic Acid | + |
| Trehalose | + | Bromo-Succinic Acid | w |
| Sucrose | + | γ-Amino-Butryric Acid | − |
| D-Turanose | − | α-Hydroxy-Butyric Acid | − |
| D-Fructose | + | Hydroxy-D,L-Buytric Acid | w |
| D-Galactose | − | α-Keto-Butyric Acid | − |
| Gentiobiose | − | Acetoacetic Acid | + |
| D-Lactose | − | Propionic Acid | − |
| D-Melibiose | − | Polymers (3 types) | |
| D-Raffinose | − | Gelatin | + |
| Stachyose | − | Pectin | w |
| β-Methyl-D-Glucosamine | + | Tween 40 | − |
| N-Acetyl-D-Mannosamine | w | Amide compounds (1 type) | |
| N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamine | w | Glucuronamide | w |
| D-Glucose | + | Polyols (5 types) | |
| D-Mannose | + | D-Mannitol | − |
| 3-Methyl Glucose | − | D-Sorbitol | − |
| D-Fucose | − | D-Arabitol | − |
| L-Fucose | − | myo-Inositol | − |
| L-Rhamnose | − | Glycerol | + |
| D-Galaturonic Acid | w | Antibiotics (6 types) | |
| L-Galactonic Acid Lactone | w | Troleandomycin | − |
| Mucic Acid | − | Rifamycin SV | + |
| Amino acids (10 types) | Minocycline | + | |
| D-Serine | + | Lincomycin | − |
| D-Aspartic Acid | − | Vancomycin | − |
| Glycol-L-proline | w | Aztreonam | + |
| L-Alanine | w | Miscellaneous (17 types) | |
| L-Arginine | w | D-Salicin | + |
| L-Aspartic Acid | w | Inosine | + |
| L-Glutamic Acid | + | D-Glucose-6-PO4 | + |
| L-Histidine | + | D-Fructose-6-PO4 | + |
| L-Pyroglutamic Acid | w | Guanidine HCl | + |
| L-Serine | + | Niaproof 4 | − |
| Carboxylic acids(25 types) | Tetrazolium Violet | − | |
| N-Acetyl Neuraminic Acid | − | Tetrazolium Blue | − |
| 1% Sodium Lactate | + | D-Lactic Acid Methyl Ester | w |
| Fusidic Acid | − | Nalidixic Acid | − |
| D-Glucuronic Acid | − | Lithium Chloride | + |
| D-Gluconic Acid | w | Potassium Tellurite | + |
| Quinic Acid | − | 10 g/L NaCl | + |
| p-Hydroxy-Phenylacetic Acid | − | 40 g/L NaCl | + |
| D-Saccharic | w | 80 g/L NaCl | + |
| Methyl Pyruvate | + | pH 6 | + |
| Acetic Acid | + | pH 5 | w |
| Formic Acid | + | ||
| Sodium Butyrate | + |
| Strain Name | Characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colony Color | Morphology | Gram Strain | pH | Temperature (°C) | Metabolism Diversity | References | |
| Microbacterium lacticum PM-1 | yellowish | Rod | + | 7.0 | 30 | Degrading TMA | This study |
| Microbacterium lacticum sp. | - | - | + | 7.5 | 30 | Oxidizing Arsenic (III) | [21] |
| Microbacterium lacticum strain GS514 | - | Rod | + | 7.0 | 28 | Converting Ginsenoside | [22] |
| Microbacterium lacticum strain DJ-1 | yellowish | Rod | + | - | - | Degrading Ethylbenzene | [23] |
| Microbacterium lacticum strain F2E | yellowish | Rod | + | 7.0 | 28–30 | Antimicrobial activity | [24] |
| Total TMA Reduction (mg/L) | Biodegraded TMA (mg/L) | Evaporated TMA (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) 1 | 4 | 155.19 | 0 | 155.19 |
| 20 | 1178.61 | 991.29 | 187.32 | |
| 30 | 1340.25 | 1141.39 | 198.86 | |
| 37 | 1247.82 | 1044.03 | 203.79 | |
| 40 | 1221.93 | 979.38 | 242.55 | |
| 60 | 501.11 | 0 | 501.11 | |
| Salinity (g/L) 2 | 0 | 1340.25 | 1141.39 | 198.86 |
| 5 | 1358.15 | 1152.79 | 205.36 | |
| 10 | 1387.49 | 1139.89 | 247.60 | |
| 20 | 1322.14 | 1048.29 | 273.85 | |
| 40 | 1338.71 | 1013.39 | 325.32 | |
| 50 | 1351.52 | 974.66 | 376.86 | |
| Initial TMA concentration (wt%) 3 | 0.05 4 | 687.99 | 527.15 | 160.84 |
| 0.1 4 | 1340.25 | 1141.39 | 198.86 | |
| 0.2 4 | 1288.51 | 920.13 | 368.38 | |
| 0.4 4 | 514.72 | 0 | 514.72 | |
| 0.5 4 | 580.97 | 0 | 580.97 | |
| Total TMA Reduction (mg/L) | Biodegraded TMA (mg/L) | Evaporated TMA (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) 1 | 4 | 46.53 | 0 | 46.53 |
| 20 | 259.34 | 206.46 | 52.88 | |
| 30 | 269.18 | 212.92 | 56.26 | |
| 37 | 259.76 | 199.31 | 60.45 | |
| 40 | 337.84 | 195.82 | 142.02 | |
| 60 | 239.70 | 0 | 239.70 | |
| Salinity (g/L) 2 | 0 | 269.18 | 212.92 | 56.26 |
| 5 | 283.25 | 209.22 | 74.03 | |
| 10 | 284.42 | 205.17 | 79.25 | |
| 20 | 260.01 | 176.53 | 83.48 | |
| 40 | 261.31 | 168.13 | 93.18 | |
| 50 | 235.76 | 132.42 | 103.34 | |
| Initial TMA concentration (wt%) 3 | 0.05 4 | 291.21 | 212.92 | 78.29 |
| 0.1 4 | 274.75 | 202.52 | 72.23 | |
| 0.2 4 | 296.37 | 153.21 | 143.16 | |
| 0.4 4 | 183.04 | 0 | 183.04 | |
| 0.5 4 | 187.08 | 0 | 187.08 | |
| Microbes | Oxygen | Media | TMA Degradation Rate (mg/L/h) | Optimal Environmental Conditions | TMA Concentration (wt%) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | Salinity (gNaCl/L) | pH | ||||||
| Paracoccus sp. T231 | Aerobic | Mineral salts medium 1 and TMA | 29.89 | 30 | - | - | - | [2] |
| Anaerobic | Mineral salts medium 1, TMA and nitrate | 26.86 | ||||||
| PH32, PH34, GRP21 | Anaerobic | Mineral salts medium 1, TMA, nitrate and NaCl | 3.48 | - | 14.61–29.22 | 6.5–8.0 | - | [28] |
| Pseudomonas putida A ATCC 12633 | Aerobic | Basal salt medium 2 and TMA | 25.79 | 30 | - | - | - | [16] |
| Paracoccus sp. strain DMF | Aerobic | Mineral medium 3 and N,N-Dimethylformamide | 16.67–41.67 | 37 | 5.84–35.06 | - | - | [26] |
| Paracoccus sp. PS1 | Aerobic | Modified Davis Minimal broth medium and TMA 4 | 0.19 | 30 | 0–17.53 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 12.66 wt% | [27] |
| Microbacterium lacticum PM-1 | Aerobic | MST medium BPT medium | 24.93 5 98.02 6 | 30 | 0–10 | 7.0 | 0.1 wt% | This study |
| Anaerobic | 3.68 5 4.44 6 | 0.05 wt% | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J. Isolation and Characterization of the Trimethylamine (TMA)-Degrading Microbacterium lacticum Strain PM-1. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081944
Feng P, Zhang L, Wu Y, Hu Y, Chen W, Liu Y, Yang J. Isolation and Characterization of the Trimethylamine (TMA)-Degrading Microbacterium lacticum Strain PM-1. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081944
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Pai, Lei Zhang, Yihao Wu, Yuxuan Hu, Wenda Chen, Yuan Liu, and Jiayuan Yang. 2025. "Isolation and Characterization of the Trimethylamine (TMA)-Degrading Microbacterium lacticum Strain PM-1" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081944
APA StyleFeng, P., Zhang, L., Wu, Y., Hu, Y., Chen, W., Liu, Y., & Yang, J. (2025). Isolation and Characterization of the Trimethylamine (TMA)-Degrading Microbacterium lacticum Strain PM-1. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081944







