Dissolved Oxygen Decline in Northern Beibu Gulf Summer Bottom Waters: Reserve Management Insights from Microbiome Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
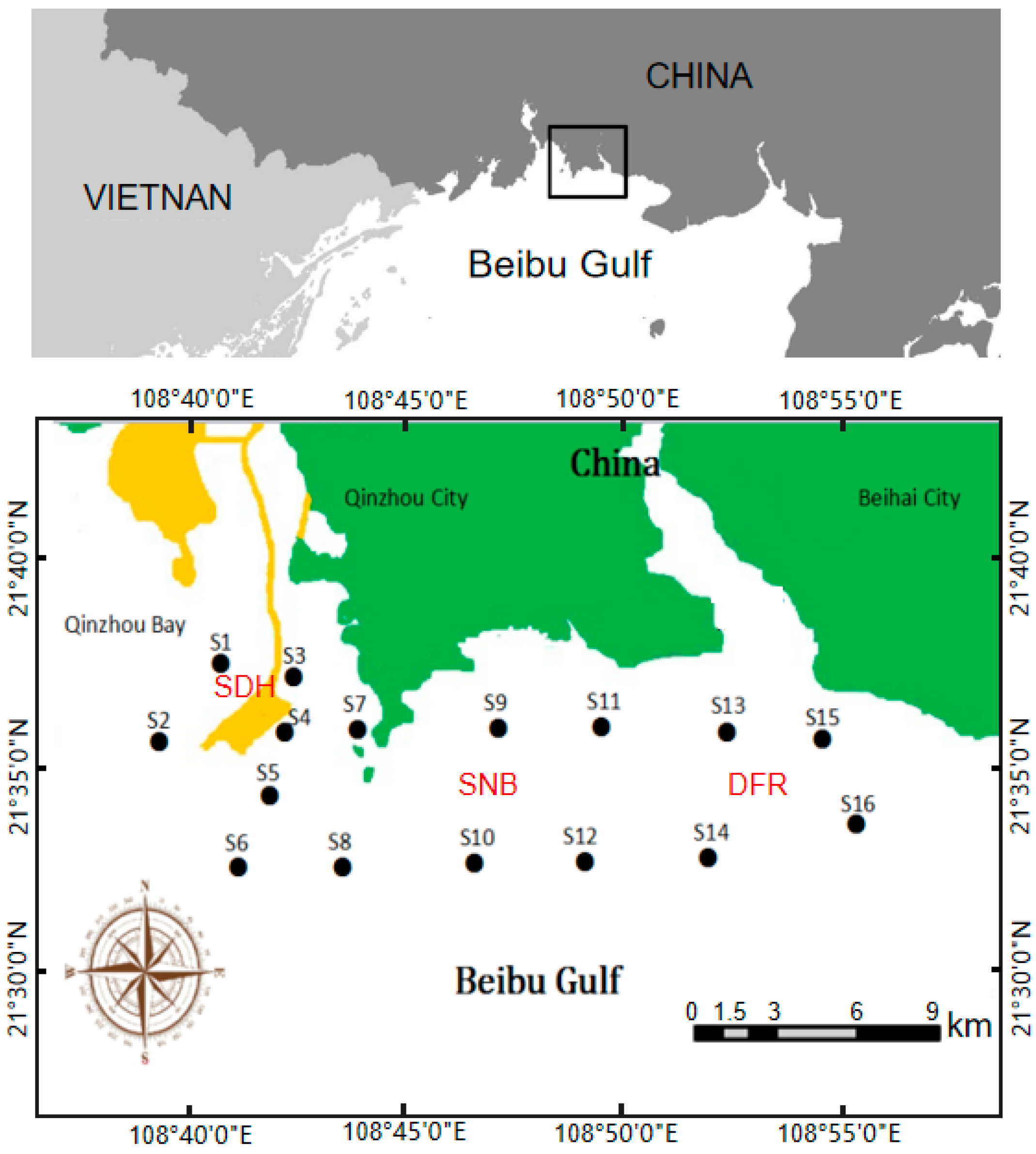
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Amplicon Sequencing 16S rRNA Gene
2.4. The qPCR Analysis of Sulfate-Reducing Genes dsrA and dsrB
2.5. Bioinformatics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
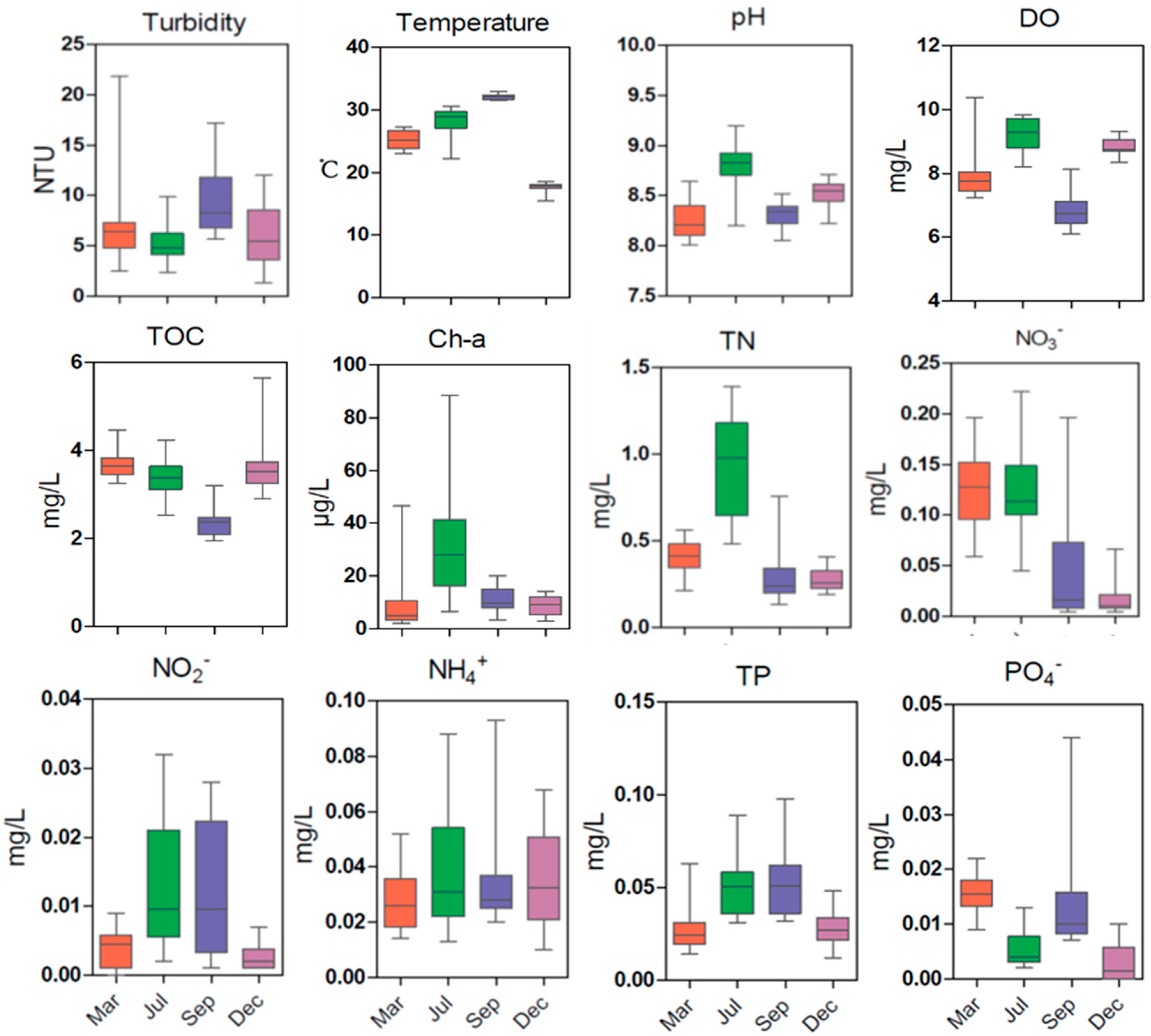
3.1. Seasonal Variation of Environmental Variables
3.2. Spatial Variation in Oceanographic Characteristics, Nutrients, and Chl-a
3.3. Seasonal Variation in Dissolved Oxygen (DO) in the SNB and DFR Regions
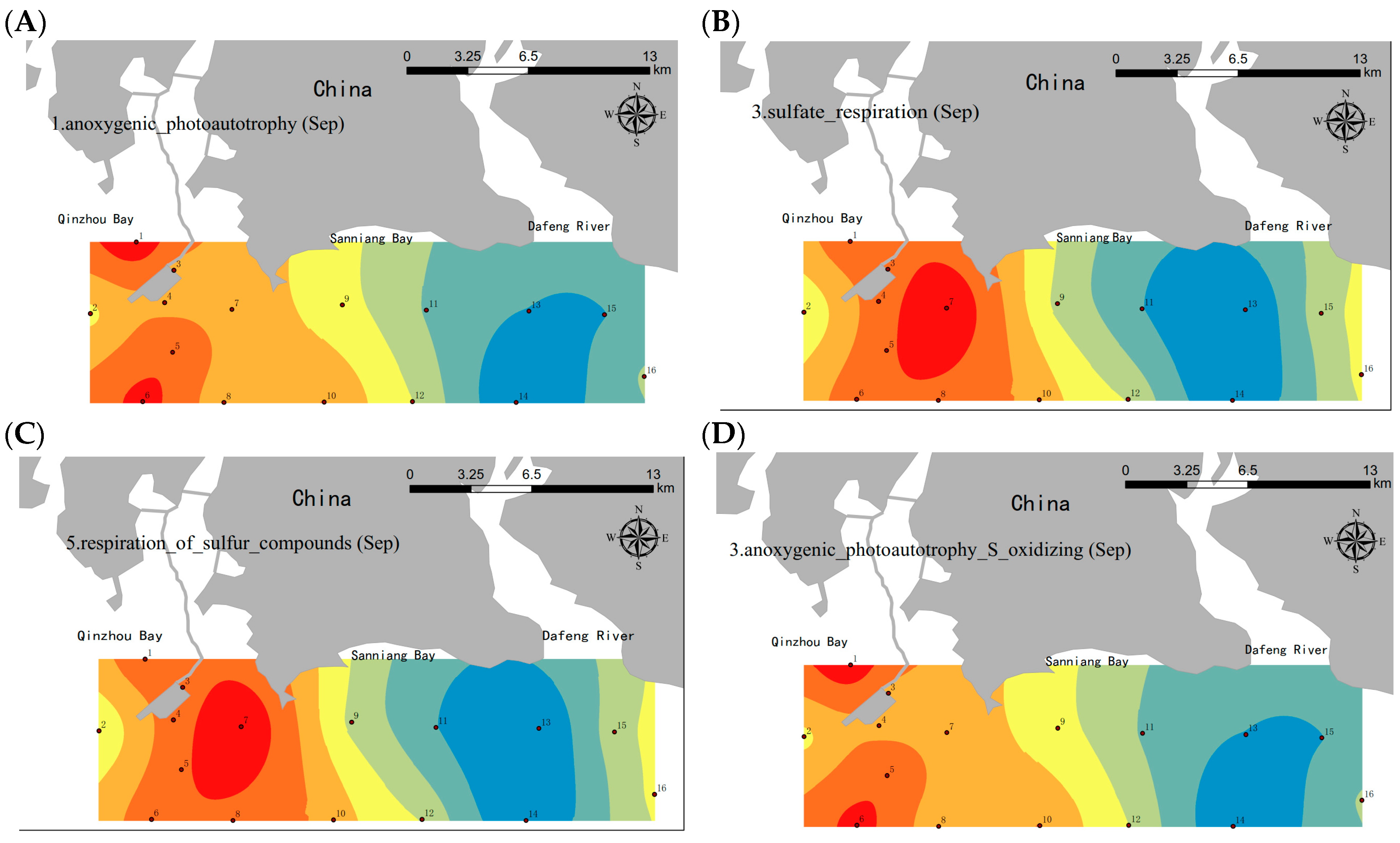
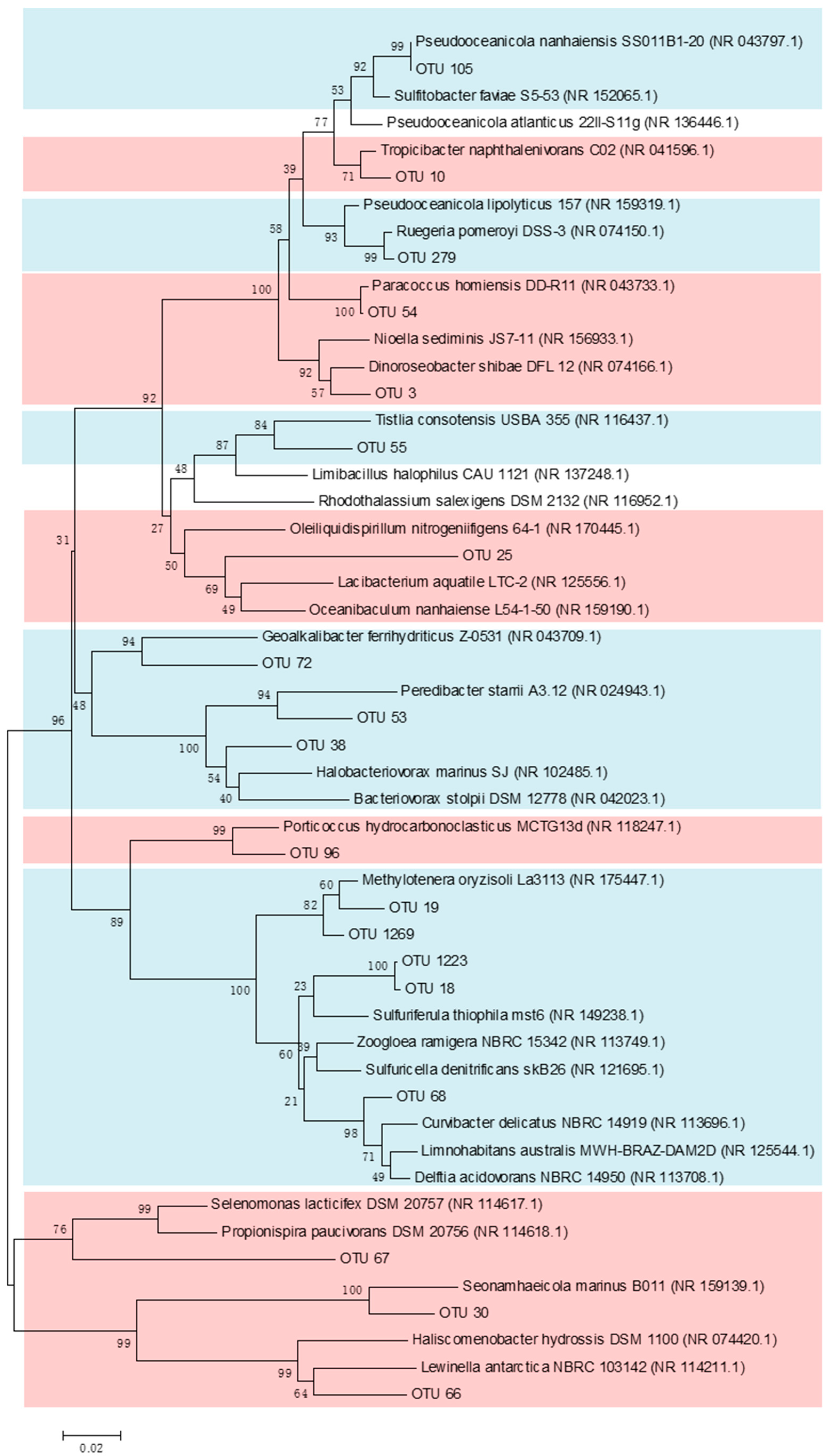
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Functional Bacterial Groups in September When Seawater Stratification and a DO Decrease Occurred in the SNB Region
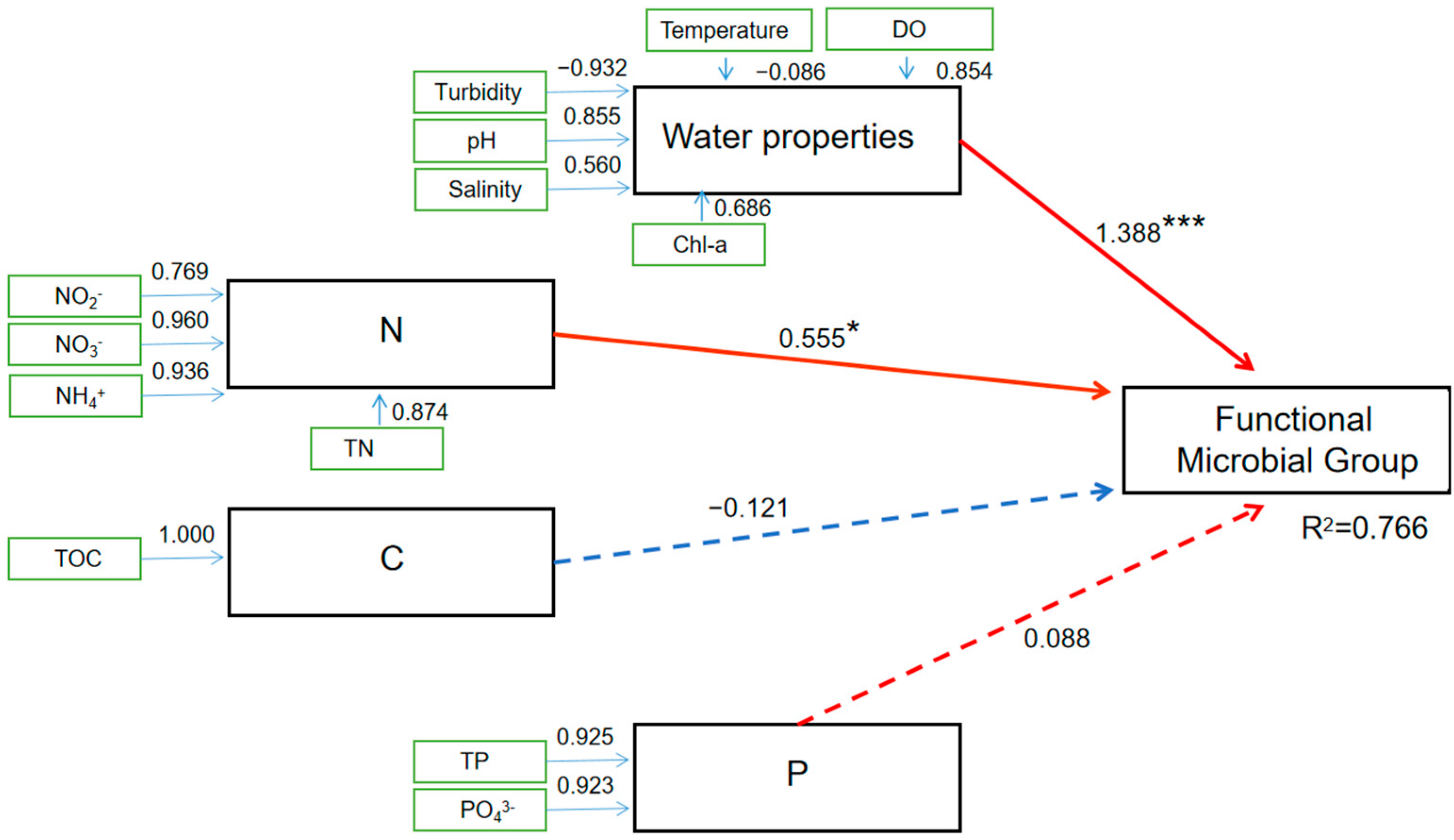
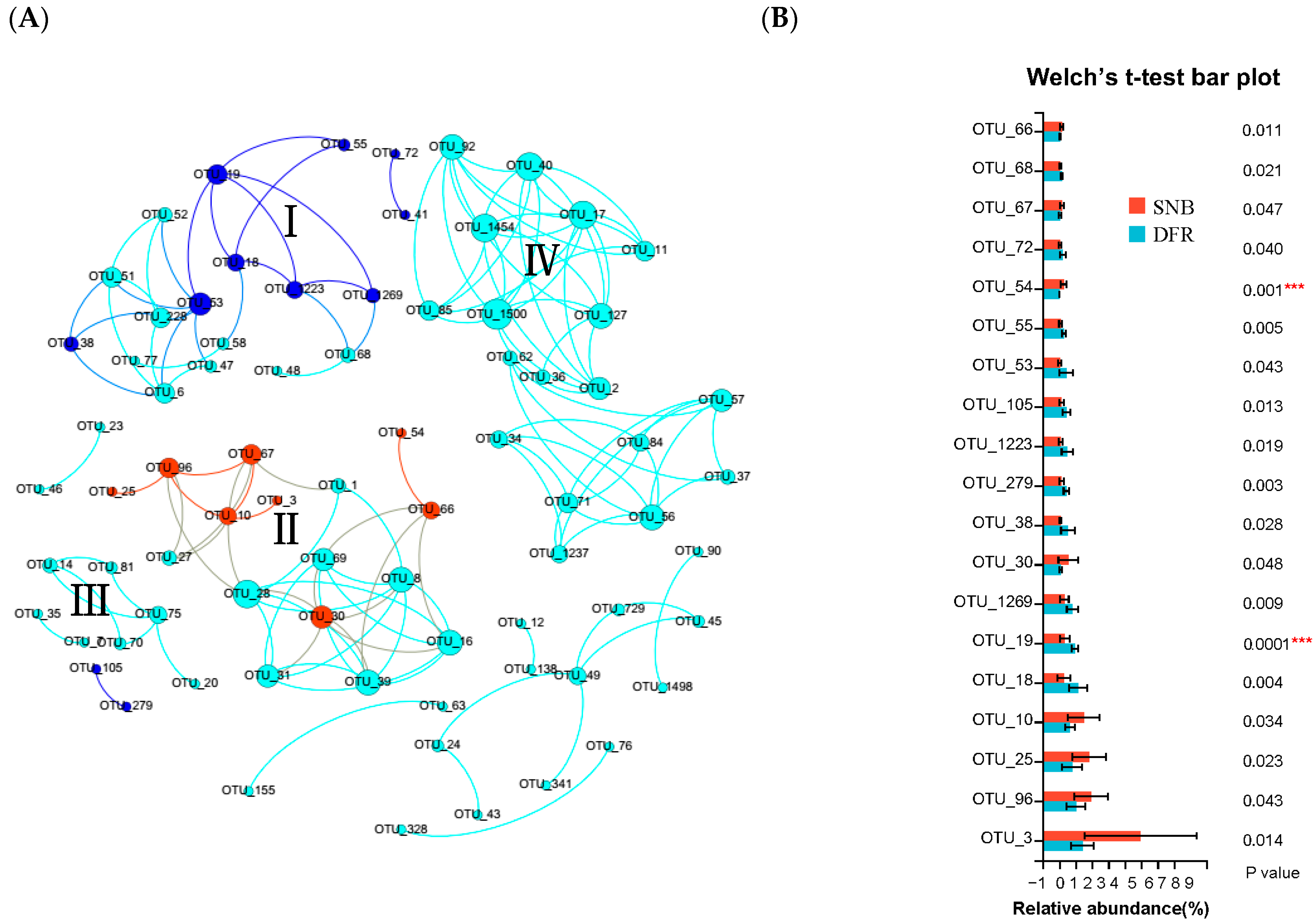
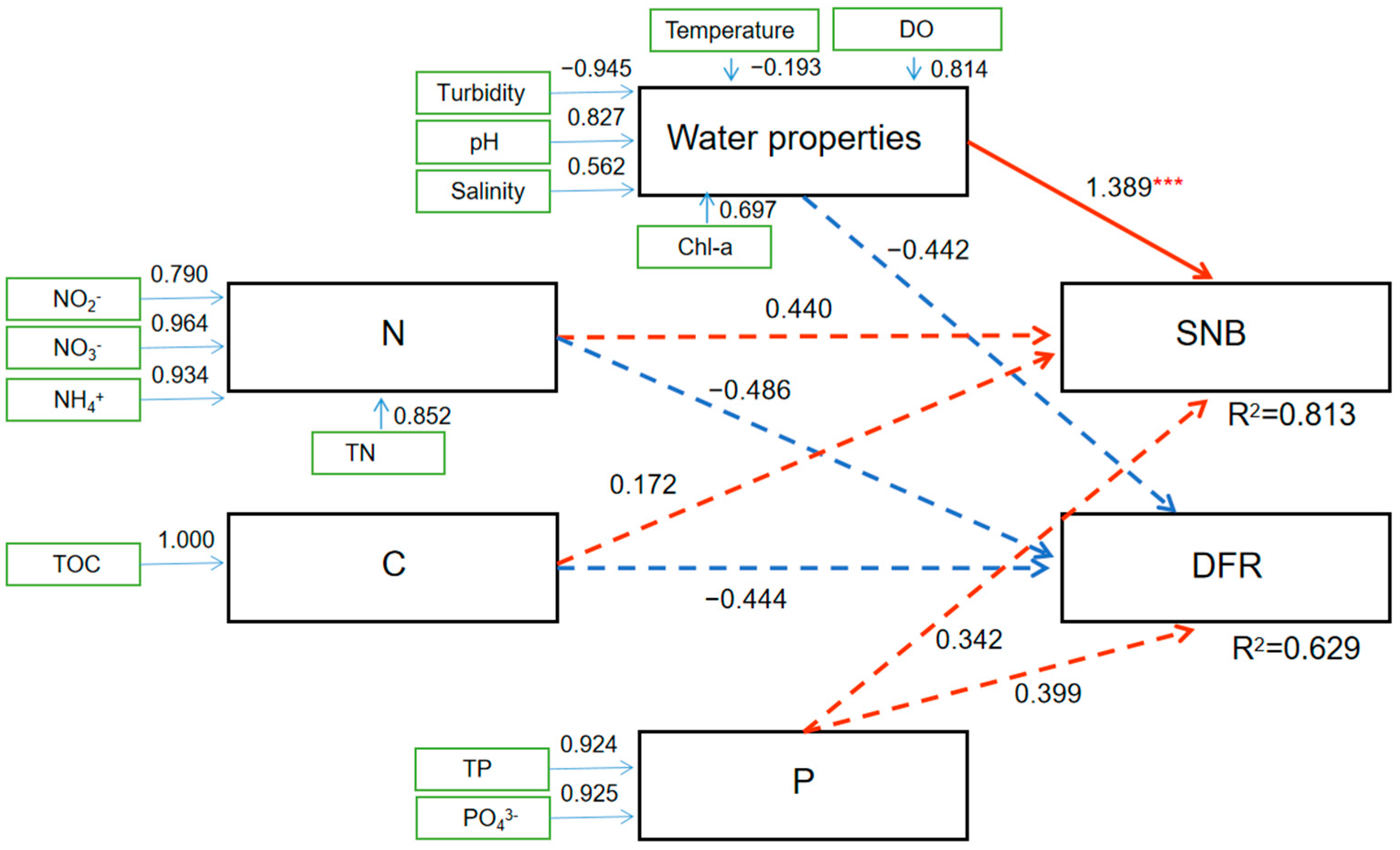
3.5. Effect of Environmental Characteristics on the Co-Occurrence Network in September When Seawater Stratification and a DO Decrease Occurred in the SNB Region
4. Discussion
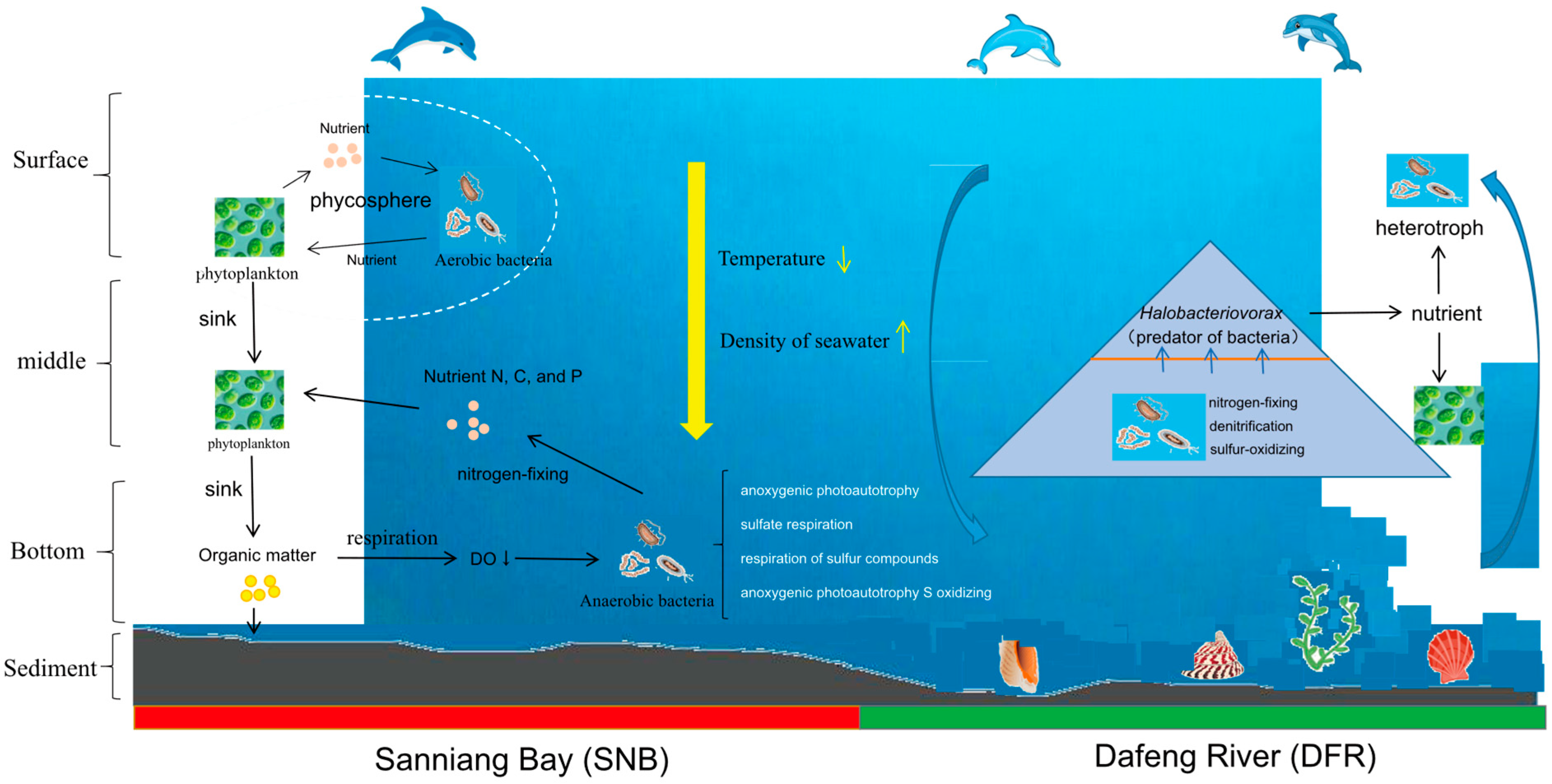
4.1. Lower Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Profile in the Bottom Seawater of the Sanniang Bay (SNB) Region
4.2. Vertical Seawater Stratification May Result in Lower DO and Higher Concentrations of Chl-a in SNB
4.3. Lower DO in Bottom Seawater Significantly Alters Functional Bacterial Groups
4.4. Environmental Factors Significantly Shape the Microbiota in the Co-Occurrence Network
4.5. Ecological Implications of Lower DO for Benthic Fauna and Fisheries
4.6. Lower DO and Its Ecological Implications for Humpback Dolphins
4.7. Evidence-Based Adaptive Management Strategies
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Anaerobic dominance: SRB (dsrA/dsrB abundance: SNB > DFR, p < 0.01) and anoxygenic phototrophs increased in SNB, confirming hypoxia adaptation.
- (2)
- Hierarchical drivers: PLS-PM quantified seawater properties as the primary direct driver of anaerobic taxa, with nitrogen loading exerting secondary effects via phytoplankton blooms.
- (3)
- Network divergence: SNB’s co-occurrence network centered on phytoplankton-associated denitrifiers (e.g., Dinoroseobacter), while DFR harbored sulfur oxidizers and nitrogen fixers, indicating distinct biogeochemical pathways.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Gu, Y.; Sun, L.; Hu, L.; Wu, W. Physical controls of summer variations in bottom layer oxygen concentrations in the coastal hypoxic region off the northeastern Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E. Gulf of Mexico hypoxia: Past, present, and future. Limnol. Oceanogr. Bull. 2019, 28, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, B.; Yao, Q.; Xue, L.; Sun, J.; Xin, M.; Yu, Z. Spatiotemporal variations in the summer hypoxia in the Bohai Sea (China) and controlling mechanisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralj, M.; Lipizer, M.; Čermelj, B.; Celio, M.; Fabbro, C.; Brunetti, F.; Giani, M. Hypoxia and dissolved oxygen trends in the northeastern Adriatic Sea (Gulf of Trieste). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 164, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Summer hypoxia adjacent to the Changjiang Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 67, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, J.; Kudoh, T.; Takatsuji, H.; Kawaguchi, O.; Kasai, A. Distribution of moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita in relation to summer hypoxia in Hiroshima Bay, Seto Inland Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Horiguchi, T. Effects of hypoxia on benthic organisms in Tokyo Bay, Japan: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N.; Justić, D. Predicting summer hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico: Redux. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagens, M.; Slomp, C.P.; Meysman, F.J.R.; Seitaj, D.; Harlay, J.; Borges, A.V.; Middelburg, J.J. Biogeochemical processes and buffering capacity concurrently affect acidification in a seasonally hypoxic coastal marine basin. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1561–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Peng, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Jefferson, T.A.; Xu, Y.; Wu, H. Habitat configuration for an obligate shallow-water delphinid: The Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin, Sousa chinensis, in the Beibu Gulf (Gulf of Tonkin). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, C.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H. Morphological changes in the Qinzhou Bay, Southwest China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, G. Sedimentological Analysis of Regional Differentiation and Sediment Provenance in the Lu’erhuan River Sea Area of Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi Province. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yan, M.; Long, L.; Ma, J.; Ji, D.; Liu, D.; Yang, Z. Modeling the effects of hydrodynamics on thermal stratification and algal blooms in the Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 8, 610622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Huang, H.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, H. The microbiomic and environmental analysis of sediments in the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis) habitat in the Northern Beibu Gulf, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6957–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikan, C.; Herbold, C.W.; Hausmann, B.; Müller, A.L.; Pester, M.; Loy, A. Diversity analysis of sulfite-and sulfate-reducing microorganisms by multiplex dsrA and dsrB amplicon sequencing using new primers and mock community-optimized bioinformatics. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Jefferson, T.A.; Peng, C.; Liao, Y.; Huang, H.; Lin, M.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; et al. Distribution and habitat characteristics of the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis) in the northern Beibu Gulf, China. Aquat. Mamm. 2017, 43, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Jefferson, T.A.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, S.L. Abundance and residency dynamics of the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin, Sousa chinensis, in the Dafengjiang River Estuary, China. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2020, 36, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; He, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, H. Advances in the Technologies for Marine Salinity Measurement. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry-Shields, J.; Wang, A.; Cory, R.M.; Stewart, J.R. Determination of specific types and relative levels of QPCR inhibitors in environmental water samples using excitation–emission matrix spectroscopy and PARAFAC. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3467–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Iguchi, A.; Inoue, M.; Mori, C.; Sakai, K.; Suzuki, A.; Nakamura, T. Microscopic observation of symbiotic and aposymbiotic juvenile corals in nutrient-enriched seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, I.; Jalukse, L.; Leito, I. A highly accurate method for determination of dissolved oxygen: Gravimetric Winkler method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 741, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, M.; Abtahi, B.; Gholamipour, S. Spatial distribution of nutrients and chlorophyll a across the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 201, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Murayama, M.; Yamamoto, K. Efficient optimization design method using kriging model. J. Aircr. 2005, 42, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduano, S.; Valeriani, F.; Romano-Spica, V.; Bargellini, A.; Borella, P.; Marchesi, I. Microbial biodiversity of thermal water and mud in an Italian spa by metagenomics: A pilot study. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2018, 18, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.C.; Morrison, H.G.; Benjamino, J.; Grim, S.L.; Graf, J. Analysis, optimization and verification of Illumina-generated 16S rRNA gene amplicon surveys. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashram, S.; Suo, X. Exploring the microbial community (microflora) associated with ovine Haemonchus contortus (macroflora) field strains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 70, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holm, J.B.; Humphrys, M.S.; Robinson, C.K.; Settles, M.L.; Ott, S.; Fu, L.; Ravel, J. Ultrahigh-throughput multiplexing and sequencing of> 500-base-pair amplicon regions on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform. mSystems 2019, 4, e00029-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, C.; Cao, H.; Song, J.; Gong, B.; Li, L.; Lu, L. Microbial functional assemblages predicted by the FAPROTAX analysis are impacted by physicochemical properties, but C, N and S cycling genes are not in mangrove soil in the Beibu Gulf, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dov, E.; Brenner, A.; Kushmaro, A. Quantification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in industrial wastewater, by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using dsrA and apsA genes. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, A.; Park, J.; Chen, Y.A.; Kawashima, H.; Mizuguchi, K. Impact of quality trimming on the efficiency of reads joining and diversity analysis of Illumina paired-end reads in the context of QIIME1 and QIIME2 microbiome analysis frameworks. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kassian Kobert, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.S.; Yilmaz, L.S.; Noguera, D.R. DECIPHER, a search-based approach to chimera identification for 16S rRNA sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. SINTAX: A simple non-Bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16S and ITS sequences. bioRxiv 2016. bioRxiv:074161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansupa, C.; Wahdan, S.F.M.; Hossen, S.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Wubet, T.; Purahong, W. Can we use functional annotation of prokaryotic taxa (FAPROTAX) to assign the ecological functions of soil bacteria? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Xia, P.; Song, X.; Lin, T.; Cao, H. Community structure and functional diversity of epiphytic bacteria and planktonic bacteria on submerged macrophytes in Caohai Lake, southwest of China. Ann. Microb. 2019, 69, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J. On the convergence of the partial least squares path modeling algorithm. Comput. Stat. 2010, 25, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, Y.; Sukigara, C.; Ishizaka, J. Enhanced oxygen consumption results in summertime hypoxia in Mikawa Bay, Japan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 26120–26136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melrose, D.C.; Oviatt, C.A.; Berman, M.S. Hypoxic events in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, during the summer of 2001. Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Denderen, P.D.; Törnroos, A.; Sciberras, M.; Hinz, H.; Friedland, R.; Lasota, R.; Hiddink, J.G. Effects of bottom trawling and hypoxia on benthic invertebrate communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 694, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, J.M.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Li, M.; Brady, D.C.; Di Toro, D.M.; Fitzpatrick, J.J. Quantifying the effects of nutrient loading on dissolved O2 cycling and hypoxia in Chesapeake Bay using a coupled hydrodynamic–biogeochemical model. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 139, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogakker, B.A.; Lu, Z.; Umling, N.; Jones, L.; Zhou, X.; Rickaby, R.E.; Galbraith, E. Glacial expansion of oxygen-depleted seawater in the eastern tropical Pacific. Nature 2018, 562, 410–413, Erratum in Nature 2019, 568, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, M.S.; Jarvis, B.M.; Wan, Y. Impacts of climate change on estuarine stratification and implications for hypoxia within a shallow subtropical system. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 279, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahardja, B.; Bashevkin, S.M.; Pien, C.; Nelson, M.; Davis, B.E.; Hartman, R. Escape from the heat: Thermal stratification in a well-mixed estuary and implications for fish species facing a changing climate. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 2895–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockenreiter, M.; Isanta Navarro, J.; Buchberger, F.; Stibor, H. Community shifts from eukaryote to cyanobacteria dominated phytoplankton: The role of mixing depth and light quality. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, D.; Vogt, M.; Gruber, N.; Psomas, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Global pattern of phytoplankton diversity driven by temperature and environmental variability. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, S.A.; Seppälä, J.; Karjalainen, J.S.; Kuha, J.; Vähätalo, A.V. Increasing air temperature relative to water temperature makes the mixed layer shallower, reducing phytoplankton biomass in a stratified lake. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora-Williams, K.; Holder, C.; Secor, M.; Ellis, H.; Xia, M.; Gnanadesikan, A.; Preheim, S.P. Abundant and persistent sulfur-oxidizing microbial populations are responsive to hypoxia in the Chesapeake Bay. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 42, 2315–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, B.; Webster, G.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y. Abundance and diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in high arsenic shallow aquifers. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pjevac, P.; Dyksma, S.; Goldhammer, T.; Mujakić, I.; Koblížek, M.; Mußmann, M.; Orlić, S. In situ abundance and carbon fixation activity of distinct anoxygenic phototrophs in the stratified seawater lake Rogoznica. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3896–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komova, A.V.; Bakhmutova, E.D.; Izotova, A.O.; Kochetova, E.S.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Namsaraev, Z.B.; Korzhenkov, A.A. Nitrogen fixation activity and genome analysis of a moderately haloalkaliphilic anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium Rhodovulum tesquicola. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.P.; Capone, D.G. Changing perspectives in marine nitrogen fixation. Science 2020, 368, eaay9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Q.; Liu, G.; Shen, Y.; Su, Q.; Lei, X. Biogeochemical processes and eutrophication status of nutrients in the northern Beibu Gulf, South China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 130, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Dai, M.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Sun, J. Seasonal variation in the phytoplankton community of a continental-shelf sea: The East China Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 516, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Cárdenas, C.; Patel, B.K.C.; Baena, S. Tistlia consotensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic, chemoheterotrophic, free-living, nitrogen-fixing alphaproteobacterium, isolated from a Colombian saline spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustakhimov, I.; Kalyuzhnaya, M.G.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. Insights into denitrification in Methylotenera mobilis from denitrification pathway and methanol metabolism mutants. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.S.; Roepke, E.W.; Hua, A.A.; Flood, B.E.; Bailey, J.V. Complete genome sequence of Sulfuriferula sp. strain AH1, a sulfur-oxidizing autotroph isolated from weathered mine tailings from the Duluth Complex in Minnesota. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00673-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Lyu, J. Mechanism of carbonate mineralization induced by microbes: Taking Curvibacter lanceolatus strain HJ-1 as an example. Micron 2021, 140, 102980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Laws, E.A.; Martin, J.L.; Berhane, T.K.; Gulig, P.A.; Williams, H.N. Relative contributions of Halobacteriovorax and bacteriophage to bacterial cell death under various environmental conditions. mBio 2018, 9, e01202-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.N.; Lymperopoulou, D.S.; Athar, R.; Chauhan, A.; Dickerson, T.L.; Chen, H.; Noble, R.T. Halobacteriovorax, an underestimated predator on bacteria: Potential impact relative to viruses on bacterial mortality. ISME J. 2016, 10, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biebl, H.; Allgaier, M.; Tindall, B.J.; Koblizek, M.; Lünsdorf, H.; Pukall, R.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Dinoroseobacter shibae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new aerobic phototrophic bacterium isolated from dinoflagellates. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Döbler, I.; Ballhausen, B.; Berger, M.; Brinkhoff, T.; Buchholz, I.; Bunk, B.; Simon, M. The complete genome sequence of the algal symbiont Dinoroseobacter shibae: A hitchhiker’s guide to life in the sea. ISME J. 2010, 4, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.B.; Han, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Du, Z.J. Seonamhaeicola marinus sp. nov., isolated from marine algae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4857–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Du, Z.J.; Chen, G.J. Seonamhaeicola algicola sp. nov., a complex-polysaccharide-degrading bacterium isolated from Gracilaria blodgettii, and emended description of the genus Seonamhaeicola. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y. Nitrogen transfer and cross-feeding between Azotobacter chroococcum and Paracoccus aminovorans promotes pyrene degradation. ISME J. 2023, 17, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.L.; Garbayo, I.; Cuaresma, M.; Montero, Z.; González-del-Valle, M.; Vílchez, C. Impact of microalgae-bacteria interactions on the production of algal biomass and associated compounds. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakata, Y.; Hatamoto, M.; Oshiki, M.; Watari, T.; Kuroda, K.; Araki, N.; Yamaguchi, T. Temporal variation of eukaryotic community structures in UASB reactor treating domestic sewage as revealed by 18S rRNA gene sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Byeon, E.; Kim, D.H.; Maszczyk, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, R.S.S.; Lee, J.S. Hypoxia in aquatic invertebrates: Occurrence and phenotypic and molecular responses. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 263, 106685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adámek, Z.; Maršálek, B. Bioturbation of sediments by benthic macroinvertebrates and fish and its implication for pond ecosystems: A review. Aquac. Int. 2013, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.; Orvain, F.; Morelle, J.; Romero-Ramirez, A.; Bernard, G.; Paulin-Henricksson, S.; Maire, O. Impact of sediment bioturbation on microphytobenthic primary producers: Importance of macrobenthic functional traits. Ecosystems 2023, 26, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Grégoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Zhang, J. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Baustian, M.M. Historical shifts in benthic infaunal diversity in the northern Gulf of Mexico since the appearance of seasonally severe hypoxia. Diversity 2020, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeagu, E.I.; Obeagu, G.U. Maternal Hypoxia: Impact on Immune System Development in Offspring. Elite J. Health Sci. 2024, 2, 45–57. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Sun, D.; Jia, J.; Xie, Z.; Gong, B. Dissolved Oxygen Decline in Northern Beibu Gulf Summer Bottom Waters: Reserve Management Insights from Microbiome Analysis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081945
Peng C, Liu Y, Qin Y, Sun D, Jia J, Xie Z, Gong B. Dissolved Oxygen Decline in Northern Beibu Gulf Summer Bottom Waters: Reserve Management Insights from Microbiome Analysis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081945
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Chunyan, Ying Liu, Yuyue Qin, Dan Sun, Jixin Jia, Zongsheng Xie, and Bin Gong. 2025. "Dissolved Oxygen Decline in Northern Beibu Gulf Summer Bottom Waters: Reserve Management Insights from Microbiome Analysis" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081945
APA StylePeng, C., Liu, Y., Qin, Y., Sun, D., Jia, J., Xie, Z., & Gong, B. (2025). Dissolved Oxygen Decline in Northern Beibu Gulf Summer Bottom Waters: Reserve Management Insights from Microbiome Analysis. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081945





