The Influence of Moderate Electroporation on E. coli Membrane Permeability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Conditions
2.2. Characterization of the PEF Treatment
2.3. Examination of the Bacterial Membrane Permeability and Cell Size
2.4. Examination of the Membrane Permeability to Different Molecule Sizes
2.5. Viable Count Assay
2.6. The Conductivity of the Buffer in the Bacterial Suspension
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
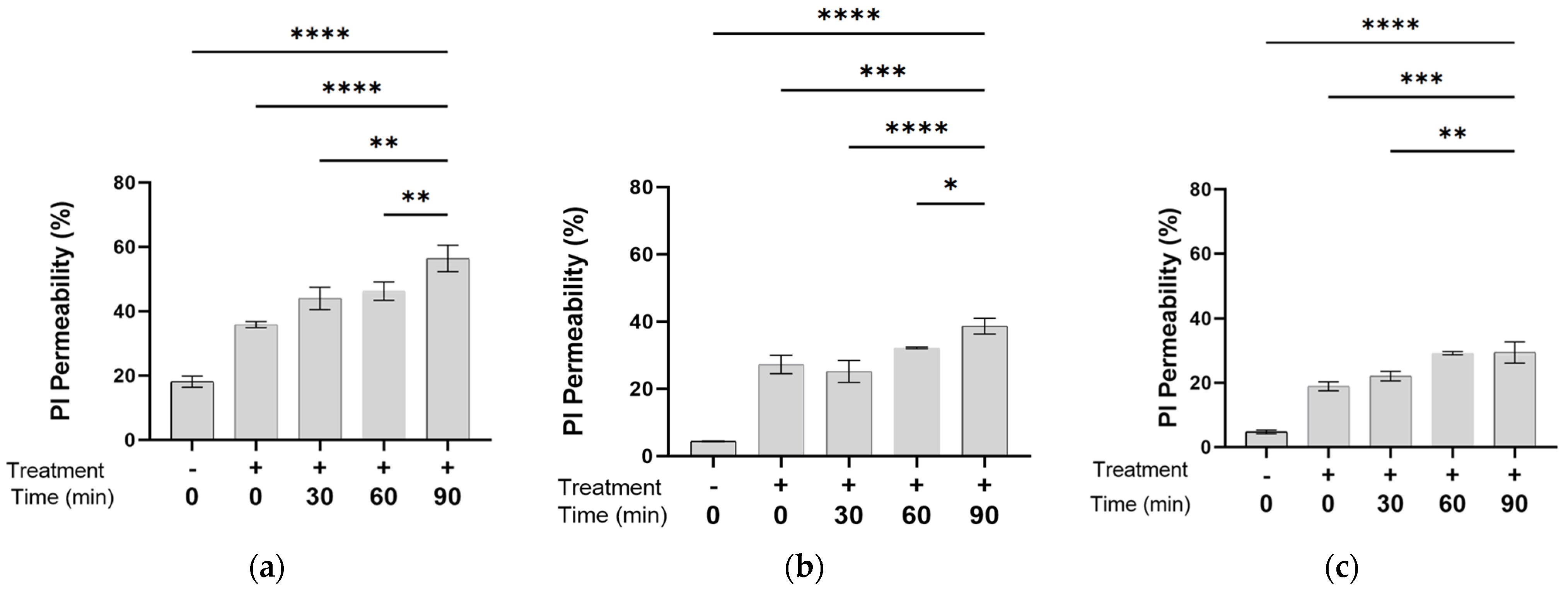
3.1. Membrane Permeability at a Bacterial Density of 0.05–0.5 OD, as a Function of the Time After PEF Exposure
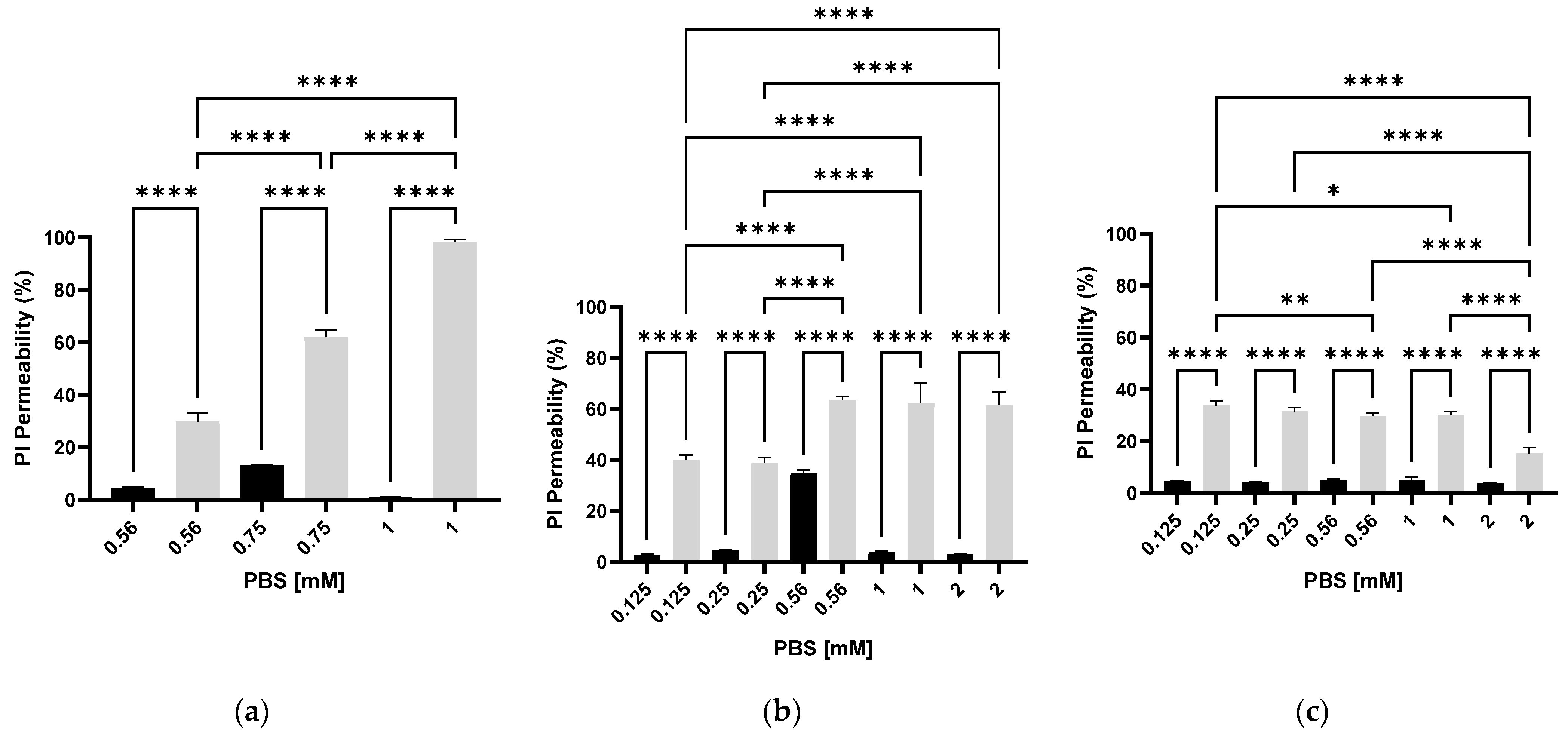
3.2. The Effect of PEF on Membrane Permeability as a Function of Different PBS Concentrations
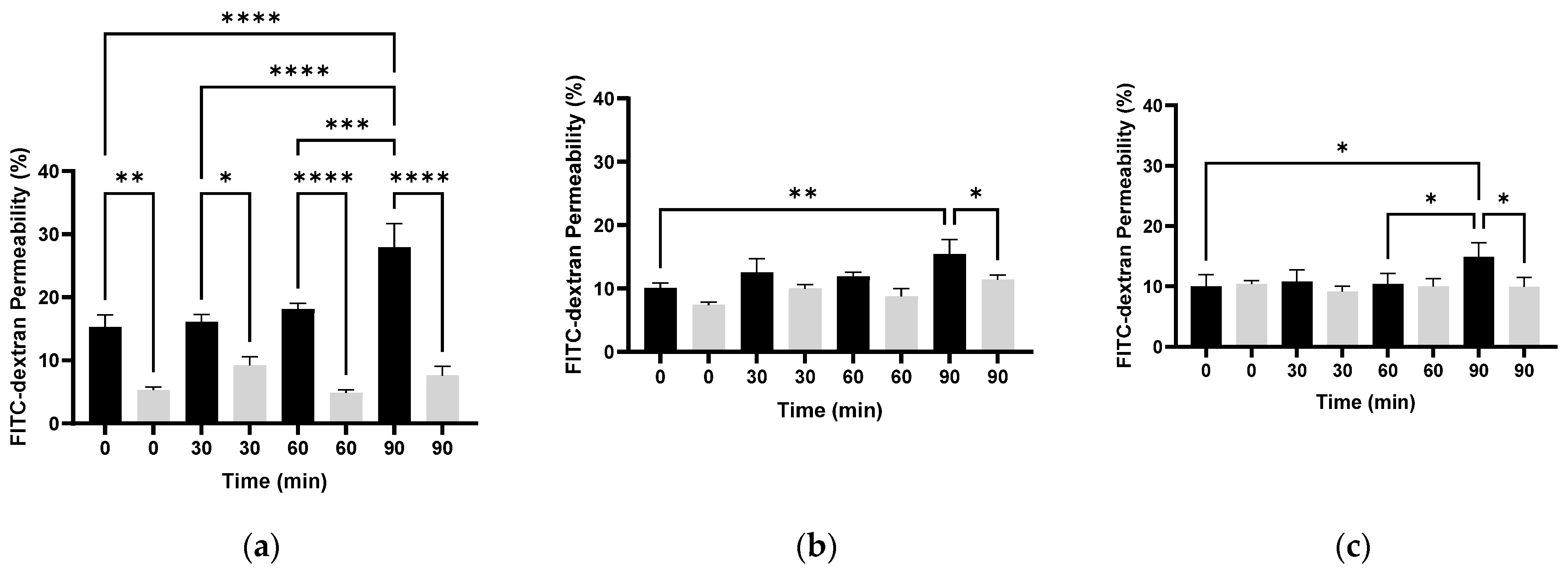
3.3. Examination of Bacterial Membrane Permeability with Different Molecular Weights of FITC-Dextran
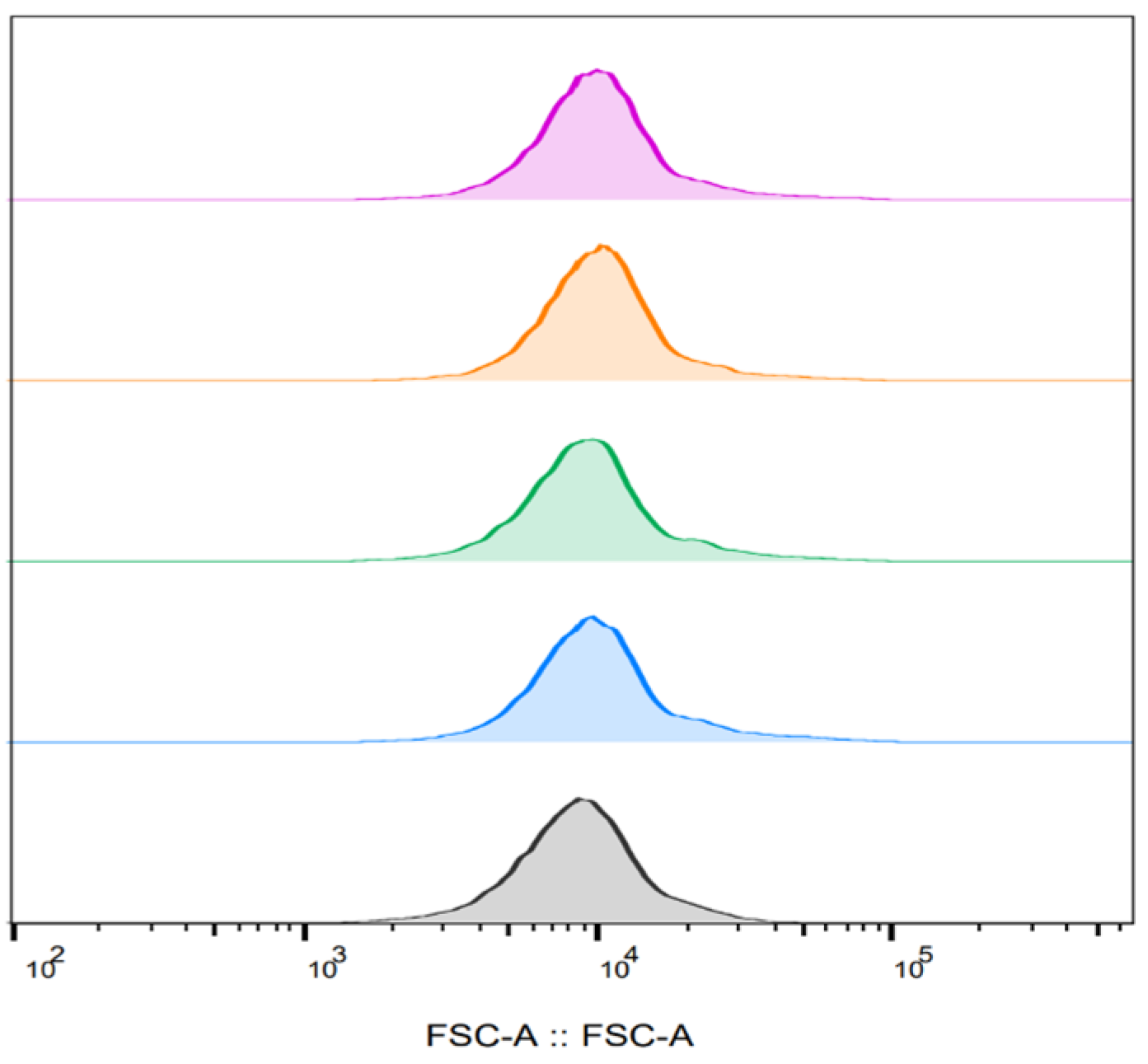
3.4. The Effect of PEF on Bacterial Cell Size as a Function of Time After PEF Exposure
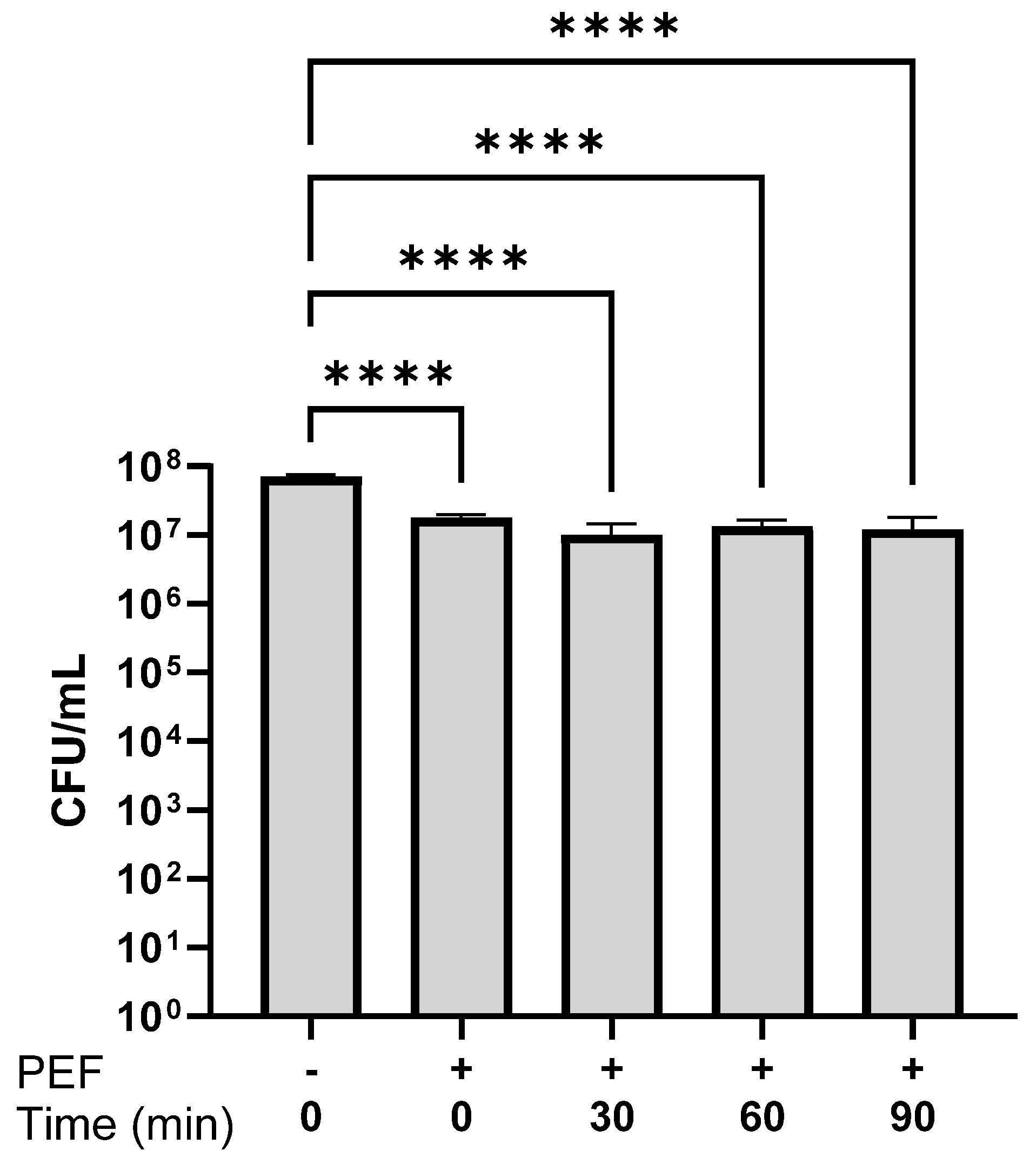
3.5. Bacterial Viability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotnik, T.; Kramar, P.; Pucihar, G.; Miklavčič, D.; Tarek, M. Cell Membrane Electroporation—Part 1: The Phenomenon. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2012, 28, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teissie, J.; Tsong, T.Y. Electric Field Induced Transient Pores in Phospholipid Bilayer Vesicles. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.; Schaefer-Ridder, M.; Wang, Y.; Hofschneider, P.H. Gene Transfer into Mouse Lyoma Cells by Electroporation in High Electric Fields. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, H.; Schulz, M.; Lu, P.; Knorr, D. Adjustment of Milling, Mash Electroporation and Pressing for the Development of a PEF Assisted Juice Production in Industrial Scale. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 14, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Abida, A.; Chacha, J.S.; Athar, A.; Madni, G.M.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Rusu, A.V.; Zeng, X.A.; Aadil, R.M.; Trif, M. Applications of Innovative Non-Thermal Pulsed Electric Field Technology in Developing Safer and Healthier Fruit Juices. Molecules 2022, 27, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, L.G.; Daud, A.; Lancellotti, F.; Arroyo, J.P.; Davalos, R.V.; Di Prata, C.; Gehl, J. Pulsed Electric Fields in Oncology: A Snapshot of Current Clinical Practices and Research Directions from the 4th World Congress of Electroporation. Cancers 2023, 15, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionet, A.; David, F.; Zaepffel, C.; Coustets, M.; Helmi, K.; Cheype, C.; Packan, D.; Garnier, J.P.; Blanckaert, V.; Teissi??, J.E. Coli Electroeradication on a Closed Loop Circuit by Using Milli-, Micro- and Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields: Comparison between Energy Costs. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 103, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sale, A.J.H.; Hamilton, W.A. Effects of High Electric Fields on Microorganisms: I. Killing of Bacteria and Yeasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1967, 148, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coustets, M.; Ganeva, V.; Galutzov, B.; Teissie, J. Millisecond Duration Pulses for Flow-through Electro-Induced Protein Extraction from E. coli and Associated Eradication. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 103, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, S.; Castle, G.S.P.; Margaritis, A. The Effects of High Field DC Pulse and Liquid Medium Conductivity on Survivability of Lactobacillus brevis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 40, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Evrendilek, G.A.; Zhang, H.Q. Pulsed Electric Fields: Processing System, Microbial and Enzyme Inhibition, and Shelf Life Extension of Foods. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2007, 35, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.Z.; Guo, M.; Zhang, H.Q. Upscaling from Benchtop Processing to Industrial Scale Production: More Factors to Be Considered for Pulsed Electric Field Food Processing. J. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, E.; Dubrovin, I.; Pogreb, R.; Pinhasi, G.A.; Cahan, R. Resuscitation of Pulsed Electric Field-Treated Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas putida in a Rich Nutrient Medium. Foods 2021, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambach, B.C.; Michels, A.; Franzke, J.; Kettler, R. Current Density and Conductivity Dependent Electroporation of Escherichia coli C600. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2013, 111, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Wang, L.H.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Yang, J.; Hou, Z.P.; Wang, Y.Z.; Dai, Q.Z.; Zeng, X.A. A Review of Sublethal Effects of Pulsed Electric Field on Cells in Food Processing. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, B. Pulsed Electric Field Promotes the Growth Metabolism of Aerobic Denitrifying Bacteria Pseudomonas putida W207-14 by Improving Cell Membrane Permeability. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.C.W.; Su, C.A.; Chen, Y.L.; Ng, H.S. Application of AC-Impedance in Microbial Cultivation System for in-Situ Biomass Measurements. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 136, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucihar, G.; Kotnik, T.; Kandušer, M.; Miklavčič, D. The Influence of Medium Conductivity on Electropermeabilization and Survival of Cells in Vitro. Bioelectrochemistry 2001, 54, 107–115, Erratum in Bioelectrochemistry 2002, 58, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, E.; Potier, E.; Logeart-Avramoglou, D.; Salomskaite-Davalgiene, S.; Mir, L.M.; Petite, H. Optimization of a Gene Electrotransfer Method for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transfection. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, E.; Dubrovin, I.; Hanya, E.; Pinhasi, G.A.; Pogreb, R.; Cahan, R. Eradication of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Pulsed Electric Field Treatments. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivorra, A.; Villemejane, J.; Mir, L.M. Electrical Modeling of the Influence of Medium Conductivity on Electroporation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 10055–10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, R.N.; Balthazar, C.F.; Margalho, L.P.; Freitas, M.Q.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Cruz, A.G. Pulsed Electric Field-Based Technology for Microbial Inactivation in Milk and Dairy Products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 54, 101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, Z.; Wei, J.; Du, J.; Li, Z. Effects of PEF on Cell and Transcriptomic of Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Pyatkovskyy, T.; Yousef, A.; Zeng, X.A.; Sastry, S.K. Mechanism of Bacillus Subtilis Spore Inactivation Induced by Moderate Electric Fields. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghavi, L.; Sastry, S.K.; Yousef, A.E. Effect of Moderate Electric Field Frequency and Growth Stage on the Cell Membrane Permeability of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongkong, S.; Klangpetch, W.; Unban, K.; Tangjaidee, P.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Schönlechner, R.; Thipchai, P.; Phongthai, S. Impacts of Electroextraction Using the Pulsed Electric Field on Properties of Rice Bran Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, R.L.; Rutherford, S.T.; Silhavy, T.J. Border Control: Regulating LPS Biogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, E.; Roman, P.; Cahan, R. Influence of the Current Density in Moderate Pulsed Electric Fields on P. putida F1 Eradication. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 126, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Okamura, T.; Tajima, M.; Kawano, R.; Yamaji, M.; Ohsaki, S.; Watano, S. Enhancement of Cell Membrane Permeability by Using Charged Nanoparticles and a Weak External Electric Field. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 32356–32363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, D.; Gómez, N.; Mañas, P.; Raso, J.; Pagán, R. Pulsed Electric Fields Cause Bacterial Envelopes Permeabilization Depending on the Treatment Intensity, the Treatment Medium PH and the Microorganism Investigated. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfona, T.; Bustard, M.T. Impact of Pulsed Electric Fields on Corynebacterium Glutamicum Cell Membrane Permeabilization. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 105, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirke, A.; Celiesiute-Germaniene, R.; Zimkus, A.; Zurauskiene, N.; Simonis, P.; Dervinis, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Balevicius, S. The Link between Yeast Cell Wall Porosity and Plasma Membrane Permeability after PEF Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gančytė, G.; Šimonis, P.; Stirkė, A. Investigation of Osmotic Shock Effect on Pulsed Electric Field Treated S. cerevisiae Yeast Cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlacchio, R.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Mattei, N.; Lévêque, P.; Rols, M.P.; Arnaud-Cormos, D.; Golzio, M. Effects of Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Field (NsPEF) on a Multicellular Spheroid Tumor Model: Influence of Pulse Duration, Pulse Repetition Rate, Absorbed Energy, and Temperature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesin, O.M.; Pakhomova, O.N.; Xiao, S.; Pakhomov, A.G. Manipulation of Cell Volume and Membrane Pore Comparison Following Single Cell Permeabilization with 60- and 600-Ns Electric Pulses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensalem, S.; Pareau, D.; Cinquin, B.; Français, O.; Le Pioufle, B.; Lopes, F. Impact of Pulsed Electric Fields and Mechanical Compressions on the Permeability and Structure of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, R.; Northrop, N.; Yamamoto, B. Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)-Dextran Extravasation as a Measure of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2017, 2017, 9.58.1–9.58.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. A Comparative Study of Molecular Structures, Solution Properties and Food Applications for Three Branched Polysaccharides: Amylopectin, Glycogen, and Dextran. Curr. Trends Polym. Sci. 2012, 16, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.C.; Son, R.S.; Gowrishankar, T.R.; Weaver, J.C. Emergence of a Large Pore Subpopulation during Electroporating Pulses. Bioelectrochemistry 2014, 100, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvier, T.; Troussellier, M.; Anzil, A.; Courties, C.; Servais, P. Using Light Scatter Signal to Estimate Bacterial Biovolume by Flow Cytometry. Cytometry 2001, 44, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaessen, E.M.J.; Timmermans, R.A.H.; Tempelaars, M.H.; Schutyser, M.A.I.; den Besten, H.M.W. Reversibility of Membrane Permeabilization upon Pulsed Electric Field Treatment in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, X.A.; Ngadi, M.; Han, Z. Effect of Cell Membrane Fatty Acid Composition of Escherichia Coli on the Resistance to Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) Treatment. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gędas, A.; Levante, A.; Cattani, L.; Bottari, B.; Weiss, A. Impact of Thermal Treatment, Pulsed Electric Fields, and High-Pressure Processing on the Transcriptome of Escherichia coli ATCC 8739. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 104, 104077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, A.; Chopra, R.; Singh, R.; Saxena, V.; GV, P.K. Effect of Pulsed Electric Field Parameters on the Alkaline Extraction of Valuable Compounds from Perilla Seed Meal and Optimization by Central Composite Design Approach. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanzadeh, M.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Gullon, P.; Hesari, J.; Gullón, B.; Alirezalu, K.; Lorenzo, J. Quality Aspects and Safety of Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) Processing on Dairy Products: A Comprehensive Review. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbruch, E.; Wise, J.; Levkov, K.; Chemodanov, A.; Israel, Á.; Livney, Y.D.; Golberg, A. Enzymatic Cell Wall Degradation Combined with Pulsed Electric Fields Increases Yields of Water-Soluble-Protein Extraction from the Green Marine Macroalga Ulva Sp. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 84, 103231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punthi, F.; Yudhistira, B.; Gavahian, M.; Chang, C.K.; Cheng, K.C.; Hou, C.Y.; Hsieh, C.W. Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Drying: A Review of Its Underlying Mechanisms, Applications, and Role in Fresh Produce Plant-Based Food Preservation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 5109–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Berrada, H.; Zhu, Z.; Grimi, N.; Barba, F.J. Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF), Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) and Combined PEF + PLE Process Evaluation: Effects on Spirulina Microstructure, Biomolecules Recovery and Triple TOF-LC-MS-MS Polyphenol Composition. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 77, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0 | OD 600 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G (µS/cm) | PBS (mM) | |||
| 285 ± 0.1 | 278 ± 0.03 | 457.33 ± 2.5 | 445.33 ± 0.57 | 0.125 |
| 534 ± 0.04 | 524 ± 0.02 | 576.67 ± 3.51 | 647.67 ± 0.57 | 0.25 |
| 1061.5 ± 0.85 | 1104.5 ± 0.19 | 911.33 ± 17.78 | 1168 ± 3.6 | 0.5 |
| 1881 ± 0.61 | 1887.5 ± 0.29 | 1944 ± 8.89 | 1956 ± 7 | 1 |
| 3430 ± 0.42 | 3750 ± 0.14 | 3943.33 ± 15.27 | 3956.67 ± 5.78 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bar-Hanun, E.; Hanya, E.; Chiliveru, A.; Cahan, R. The Influence of Moderate Electroporation on E. coli Membrane Permeability. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081925
Bar-Hanun E, Hanya E, Chiliveru A, Cahan R. The Influence of Moderate Electroporation on E. coli Membrane Permeability. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081925
Chicago/Turabian StyleBar-Hanun, Ester, Ester Hanya, Abhishiktha Chiliveru, and Rivka Cahan. 2025. "The Influence of Moderate Electroporation on E. coli Membrane Permeability" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081925
APA StyleBar-Hanun, E., Hanya, E., Chiliveru, A., & Cahan, R. (2025). The Influence of Moderate Electroporation on E. coli Membrane Permeability. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081925






