miR-7a-5p Contributes to Suppressing NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Response to Streptococcus suis Type 2 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Cell Lines and Mice
2.2. J774A.1 Cells Infection Assay
2.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.4. Western Blotting (WB)
2.5. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.6. Staining of Tissue Sections
2.7. Cell Transfection
2.8. Mouse Transfection
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
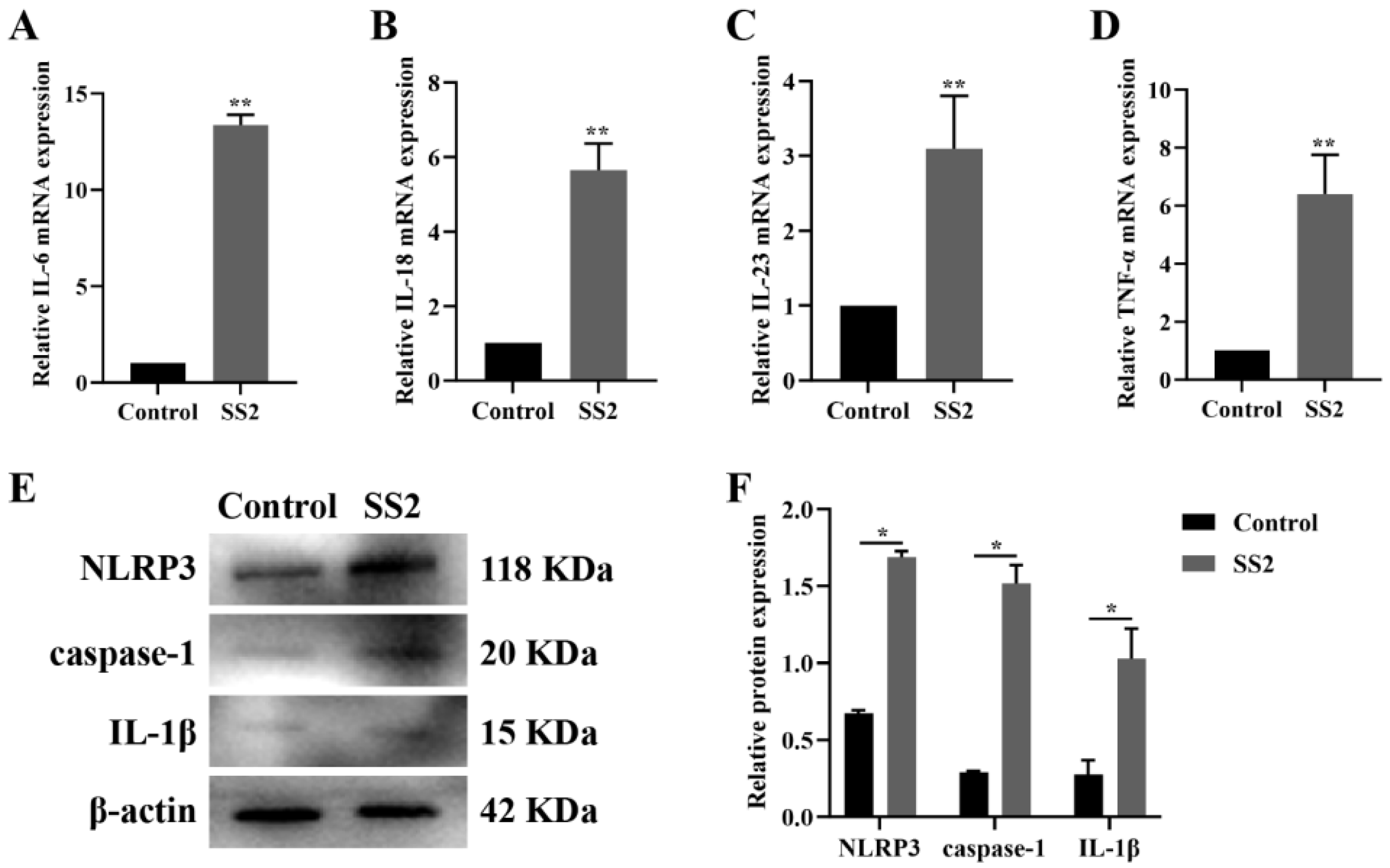
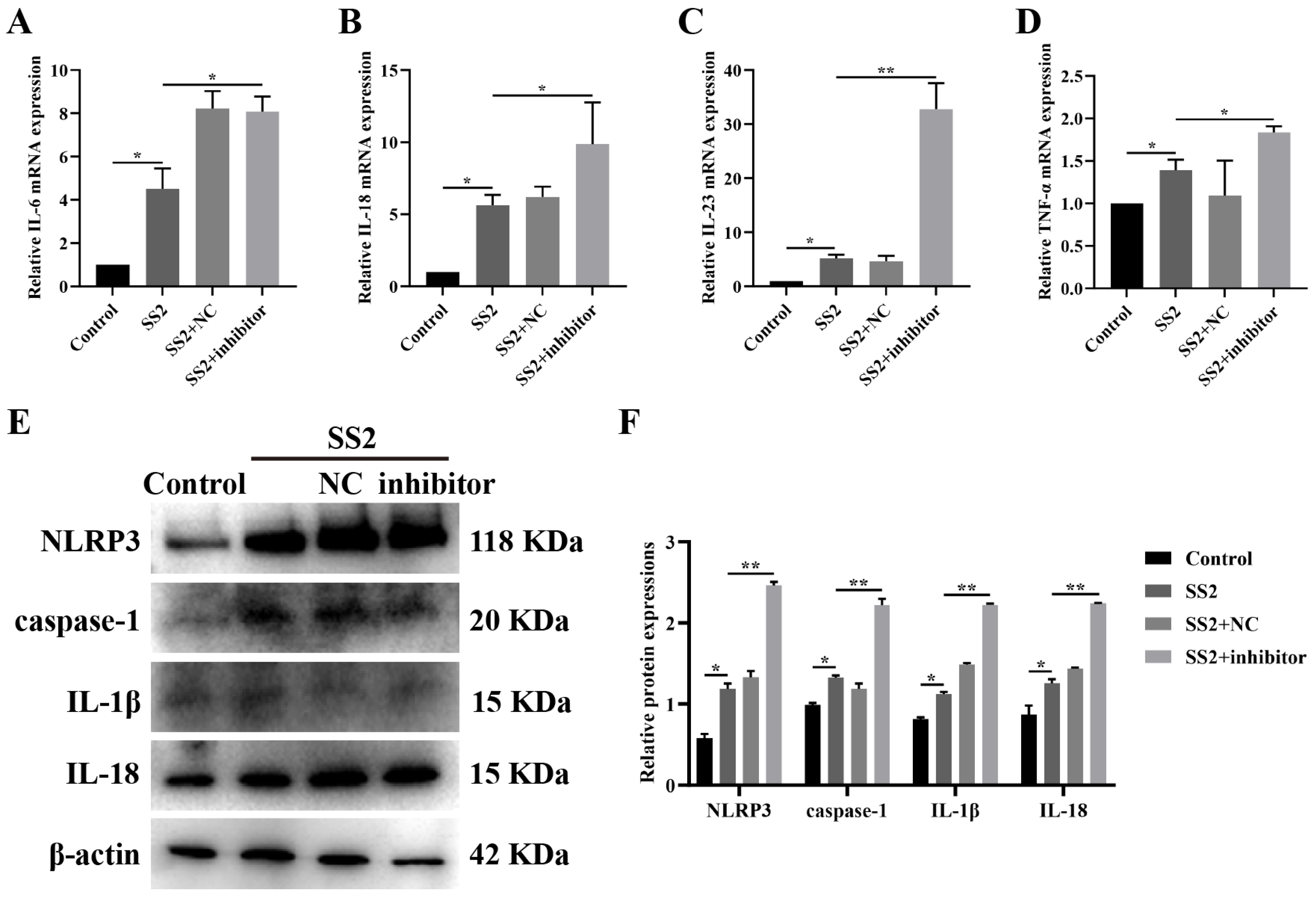
3.1. J774A.1 Cells Infected with SS2 Exhibited Up-Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Downstream Pathways
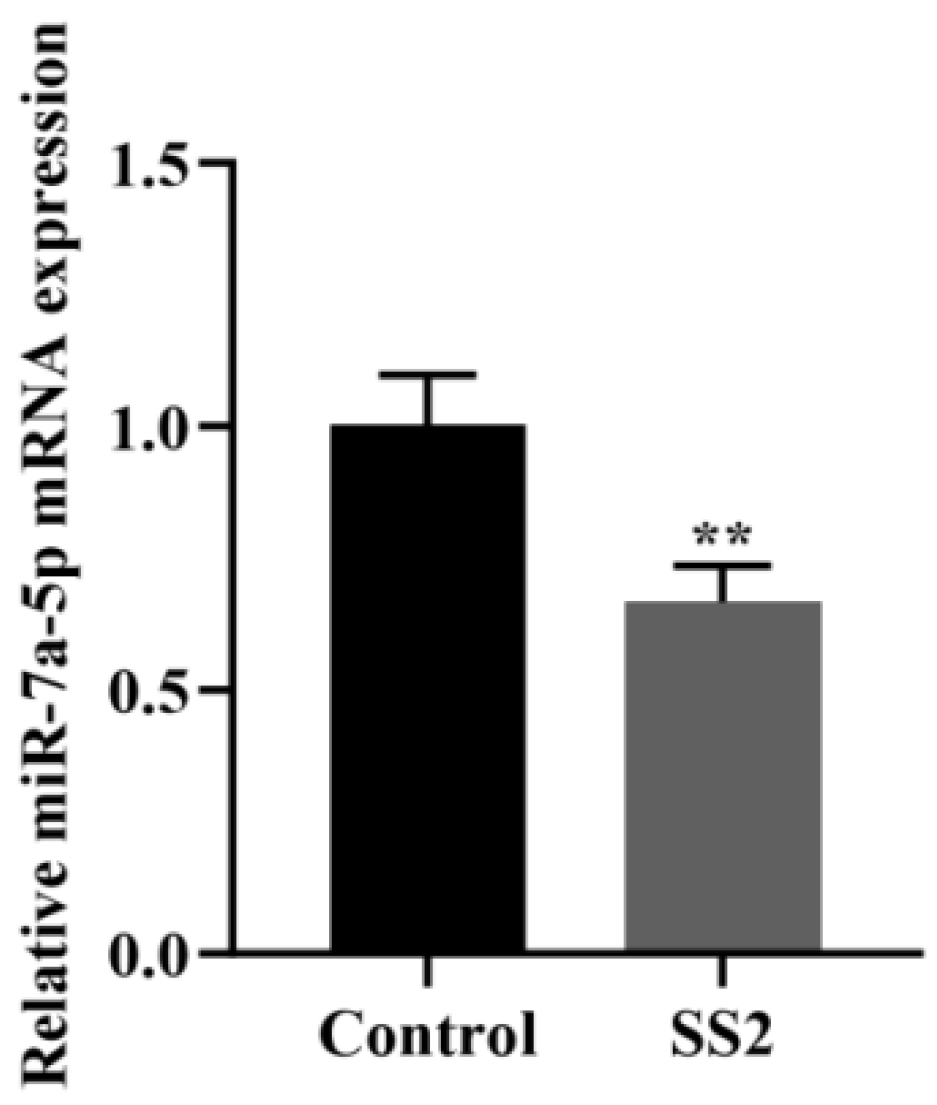
3.2. J774A.1 Cells Infected with SS2 Showed Down-Regulation of miR-7a-5p Expression
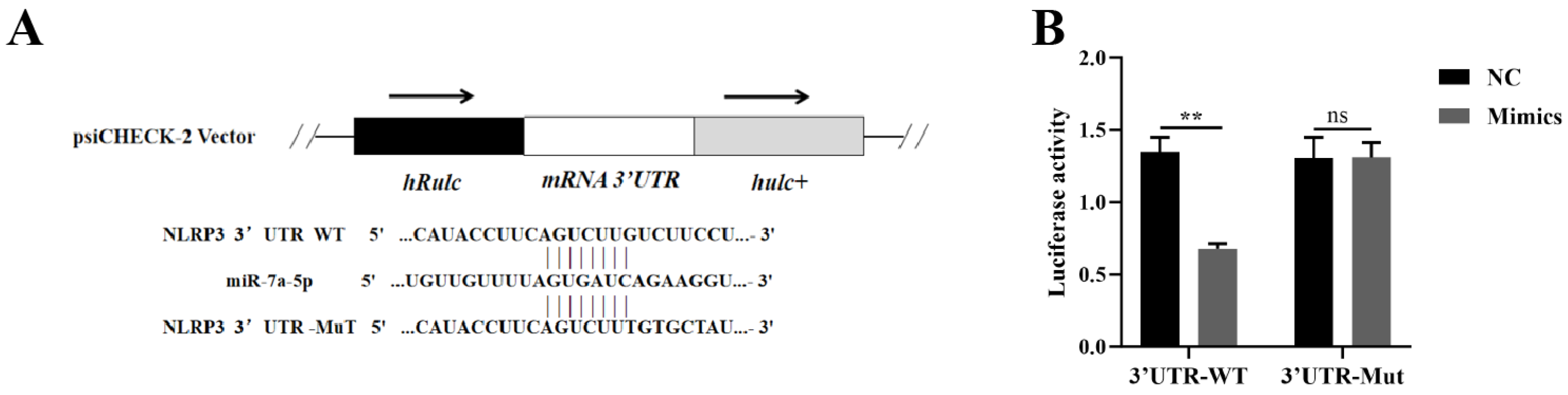
3.3. miR-7a-5p Interacted with the 3′UTR Region of NLRP3 mRNA
3.4. miR-7a-5p Overexpression Suppressed the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Downstream Pathways in Cells Infected with SS2
3.5. Blocking miR-7a-5p Boosted NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Downstream Pathways in SS2-Infected Conditions
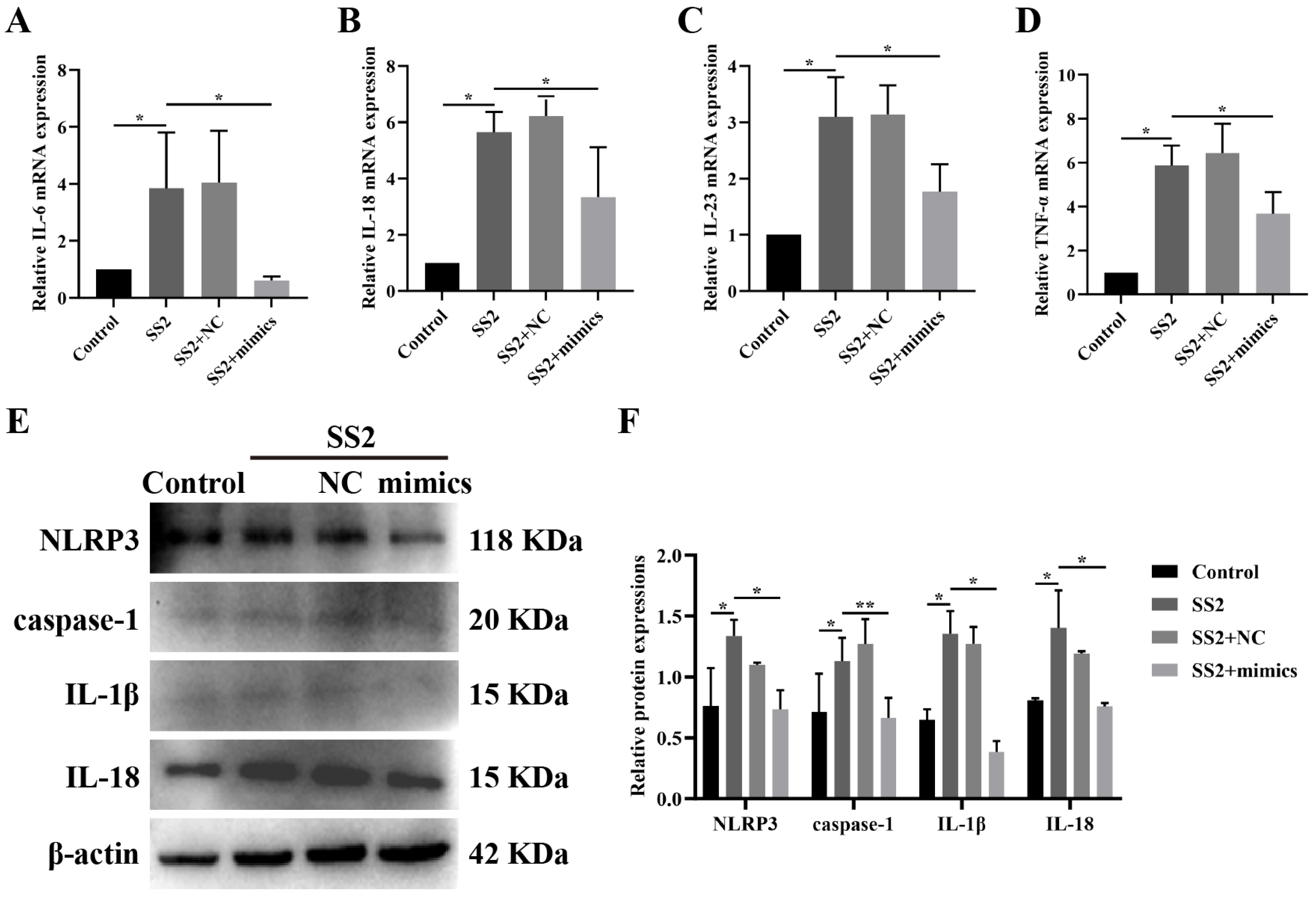
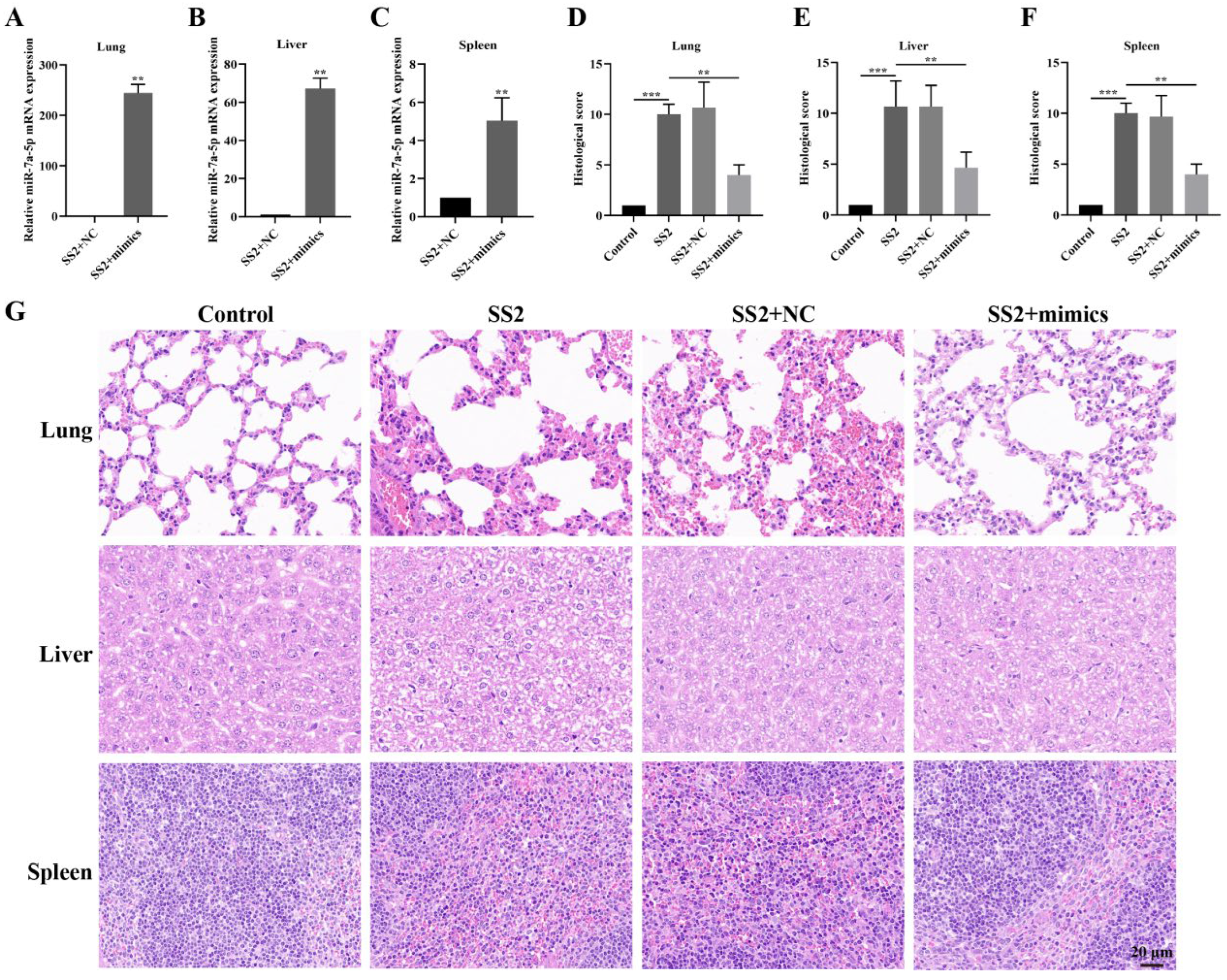
3.6. In Vivo Transfection with miR-7a-5p Mimics Alleviated Inflammation in Response to SS2
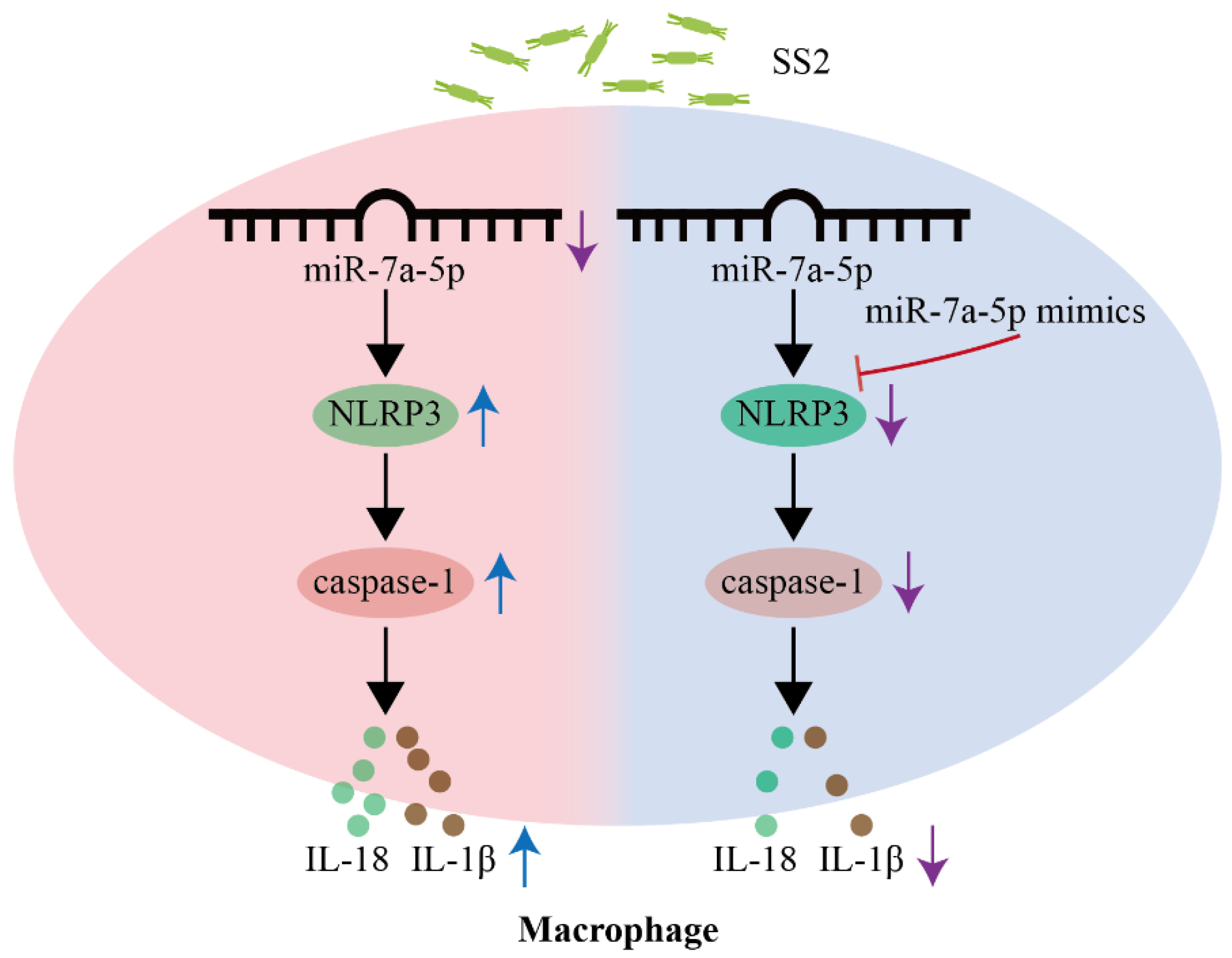
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SS2 | Streptococcus suis type 2 |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Tang, Y.-D.; Li, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.-B.; Gottschalk, M.; Cai, X. Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Infection Induces Splenomegaly with Splenocyte Apoptosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e03210–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; et al. Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria Mellonella Larvae Infection Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.-F.; Tan, J.; Zhang, F.-F.; Li, H.-Q.; Ji, H.-Y.; Fang, S.-P.; Wu, C.-C.; Rao, Y.-L.; Zeng, Y.-B.; Yang, Q. Exogenous Glycogen Utilization Effects the Transcriptome and Pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 938286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Li, M.; Yu, G.; Zhan, D.; Zeng, W.; Fu, N.; Jiang, X. Investigation of Choline-Binding Protein of CbpD in the Pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis Type 2. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1486347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucco, L.; Paniccià, M.; Massacci, F.R.; Morelli, A.; Ancora, M.; Mangone, I.; Di Pasquale, A.; Luppi, A.; Vio, D.; Cammà, C.; et al. New Sequence Types and Antimicrobial Drug–Resistant Strains of Streptococcus suis in Diseased Pigs, Italy, 2017–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Q.; Sun, L.; Yi, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. mRNA-Seq Reveals the Quorum Sensing System luxS Gene Contributes to the Environmental Fitness of Streptococcus suis Type 2. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An Overview of microRNAs: Biology, Functions, Therapeutics, and Analysis Methods. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilimova, M.; Pfeffer, S. Post-transcriptional Regulation of Polycistronic microRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2023, 14, e1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, I.; Patil, K.S.; Alves, G.; Larsen, J.P.; Møller, S.G. microRNAs as Neuroregulators, Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wu, M. MicroRNA-302b Augments Host Defense to Bacteria by Regulating Inflammatory Responses via Feedback to TLR/IRAK4 Circuits. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ruan, X.; Tian, T.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.; Sun, Y. miR-20b Attenuates Airway Inflammation by Regulating TXNIP and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthmatic Mice. J. Asthma 2023, 60, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, W. MiR-20b Inhibits Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Induced Inflammation in the Lung of Mice through Targeting NLRP3. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Du, S.; Lv, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F. Elevated microRNA-20b-3p and Reduced Thioredoxin-interacting Protein Ameliorate Diabetic Retinopathy Progression by Suppressing the NLRP3 Inflammasomes. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1433–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Xing, G.-L.; Chen, Z.; Tu, S.-H. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Knockdown Alleviates Gouty Arthritis through miR-20b Upregulation and NLRP3 Downregulation. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zong, X.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Deng, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, C.; Fu, Q. miR-223-3p Contributes to Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Streptococcus equi ssp. Zooepidemicus Infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 269, 109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.; Cossart, P.; Lebreton, A. Mammalian microRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in the Host-Bacterial Pathogen Crosstalk. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 65, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eledge, M.R.; Yeruva, L. Host and Pathogen Interface: MicroRNAs Are Modulators of Disease Outcome. Microbes Infect. 2018, 20, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, K.M.; Hoffmann, A. Functional Hallmarks of Healthy Macrophage Responses: Their Regulatory Basis and Disease Relevance. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebeler, R.; De Winther, M.P.J.; Hoeksema, M.A. The Regulatory Landscape of Macrophage Interferon Signaling in Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadole, I.; Blaha, D.; Personnic, N. The Macrophage–Bacterium Mismatch in Persister Formation. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, A.-E.; Li, L.; Westermann, A.J.; Appenzeller, S.; Stapels, D.A.C.; Schulte, L.N.; Helaine, S.; Vogel, J. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Ties Macrophage Polarization to Growth Rate of Intracellular Salmonella. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtale, G.; Rubino, M.; Locati, M. MicroRNAs as Molecular Switches in Macrophage Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, A.; Petrek, M. Roles of Macrophage Polarization and Macrophage-Derived miRNAs in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, G.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Giri, B.R.; Fu, Q. Deficiency of hasB Accelerated the Clearance of Streptococcus equi subsp. Zooepidemicus through Gasdermin d-Dependent Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, M.; Sun, Q.; Guo, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, Q. Magnolol Attenuates Macrophage Pyroptosis Triggered by Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielski, L.G.; Giustina, A.D.; Bonfante, S.; Barichello, T.; Petronilho, F. The NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Role in Sepsis Development. Inflammation 2020, 43, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.I.; Sutterwala, F.S. Initiation and Perpetuation of NLRP 3 Inflammasome Activation and Assembly. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, M.S.J.; Olhava, E.J.; Roush, W.R.; Seidel, H.M.; Glick, G.D.; Latz, E. Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shi, X. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Role in Autoimmune Diseases: A Promising Therapeutic Target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Ding, T.; Chen, Y.; Long, T.; Xu, Q.; Lian, W.; Liu, W. LncRNA-Meg3 Promotes Nlrp3-Mediated Microglial Inflammation by Targeting miR-7a-5p. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardo, D.; De Nardo, C.M.; Latz, E. New Insights into Mechanisms Controlling the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Role in Lung Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y. Cellular microRNAs and Picornaviral Infections. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Kothari, S.; Gohir, W.; Camargo, J.F.; Husain, S. MicroRNAs in Infectious Diseases: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e00015–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, R.; Zhao, M.; Garcia-Gomez, A.; Ballestar, E. miRNAs as Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Inazawa, J. Cancer-Associated miRNAs and Their Therapeutic Potential. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabortty, A.; Patton, D.J.; Smith, B.F.; Agarwal, P. miRNAs: Potential as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Cancer. Genes 2023, 14, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangmann, E.; Fröleke, H.; Kohse, K.P. Septic Shock Caused by Streptococcus suis: Case Report and Investigation of a Risk Group. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2002, 205, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| IL-6 | F: TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC R: TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| IL-18 | F: GTGAACCCCAGACCAGACTG R: CCTGGAACACGTTTCTGAAAGA |
| IL-23 | F: CCCGTATCCAGTGTGAAGATG R: GGCTCCCCTTTGAAGATGTC |
| TNF-α | F: CCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTAG R: GGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| GAPDH | F: TGACAACAGCCTCAAGATCG R: GTCTTCTGGGTGGCAGTGAT |
| U6 snRNA | F: CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| miR-7a-5p | F: GCGCGTGGAAGACTAGTGATTT |
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| miR-7a-5p mimics | F: UGGAAGACUAGUGAUUUUGUUGU R: ACAACAAAAUCACUAGUCUUCCA |
| miR-7a-5p mimics negative control, NC | F: UCGCGCGACACCGCUAGCUAG R: AGCUAGCGGUGUCGCGCGAUU |
| miR-7a-5p inhibitor | ACAACAAAAUCACUAGUCUUCCA |
| miR-7a-5p inhibitor negative control, inhibitor NC | CUAGCUAGCGGUGUCGCGCGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Sun, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Che, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liao, J.; Xie, H.; Zhan, X.; Sun, Q.; et al. miR-7a-5p Contributes to Suppressing NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Response to Streptococcus suis Type 2 Infection. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081924
Deng Z, Sun Q, Li S, Wang Y, Che Y, Huang Y, Liao J, Xie H, Zhan X, Sun Q, et al. miR-7a-5p Contributes to Suppressing NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Response to Streptococcus suis Type 2 Infection. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081924
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Ziteng, Qian Sun, Shun Li, Yibo Wang, Yuxin Che, Yunfei Huang, Jiedan Liao, Honglin Xie, Xiaoshu Zhan, Qinqin Sun, and et al. 2025. "miR-7a-5p Contributes to Suppressing NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Response to Streptococcus suis Type 2 Infection" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081924
APA StyleDeng, Z., Sun, Q., Li, S., Wang, Y., Che, Y., Huang, Y., Liao, J., Xie, H., Zhan, X., Sun, Q., & Fu, Q. (2025). miR-7a-5p Contributes to Suppressing NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Response to Streptococcus suis Type 2 Infection. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081924





