Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella via Immunomagnetic Separation and Nanoparticle-Enhanced SPR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Cultural Conditions
2.2. Binding and Characterization of IMBs
2.3. Separation of Bacterial Samples
2.4. Synthesis of AuNPs
2.5. Preparation of the AuNP-Ab Conjugate
2.6. Fabrication of the Immunosensor and SPR Detection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
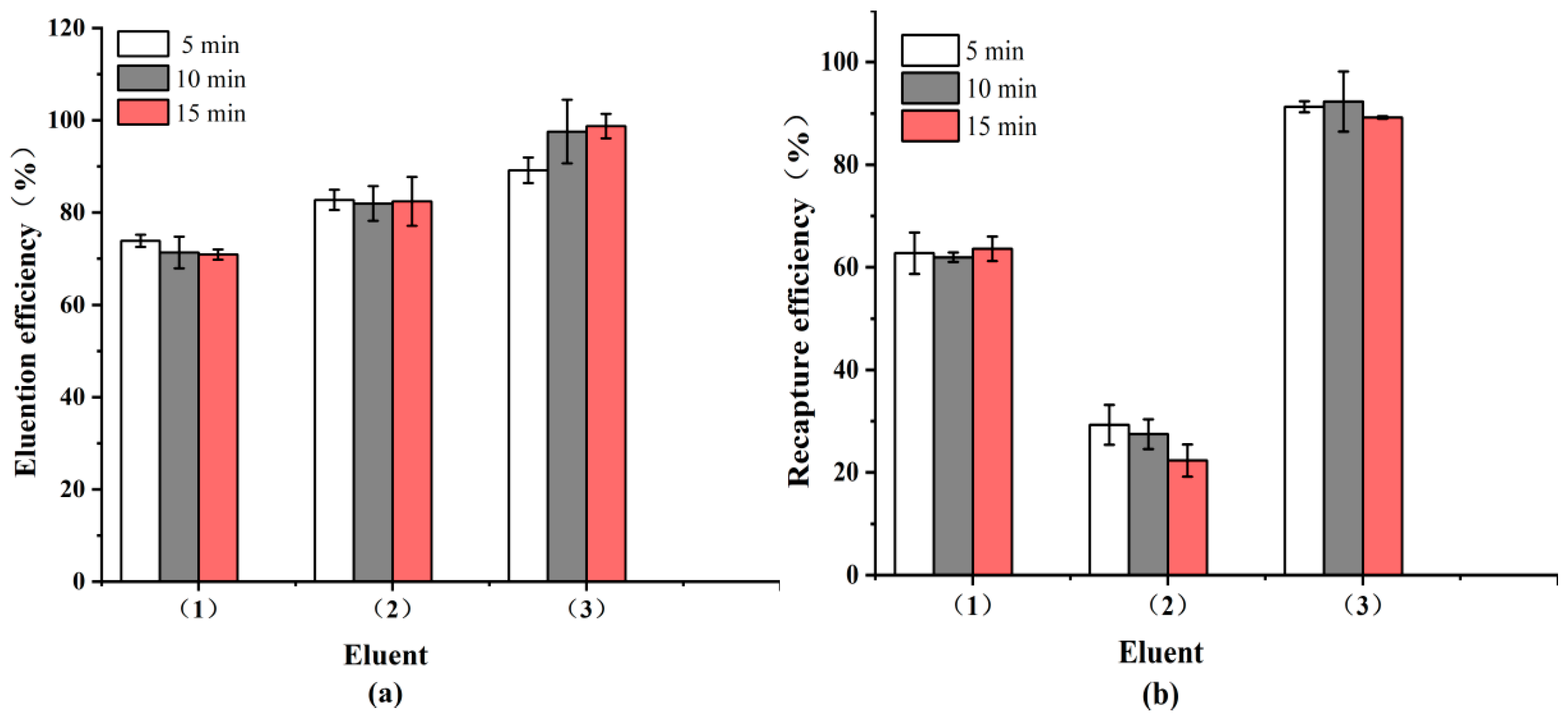
3.1. Capture Efficiency of Bacterial Samples
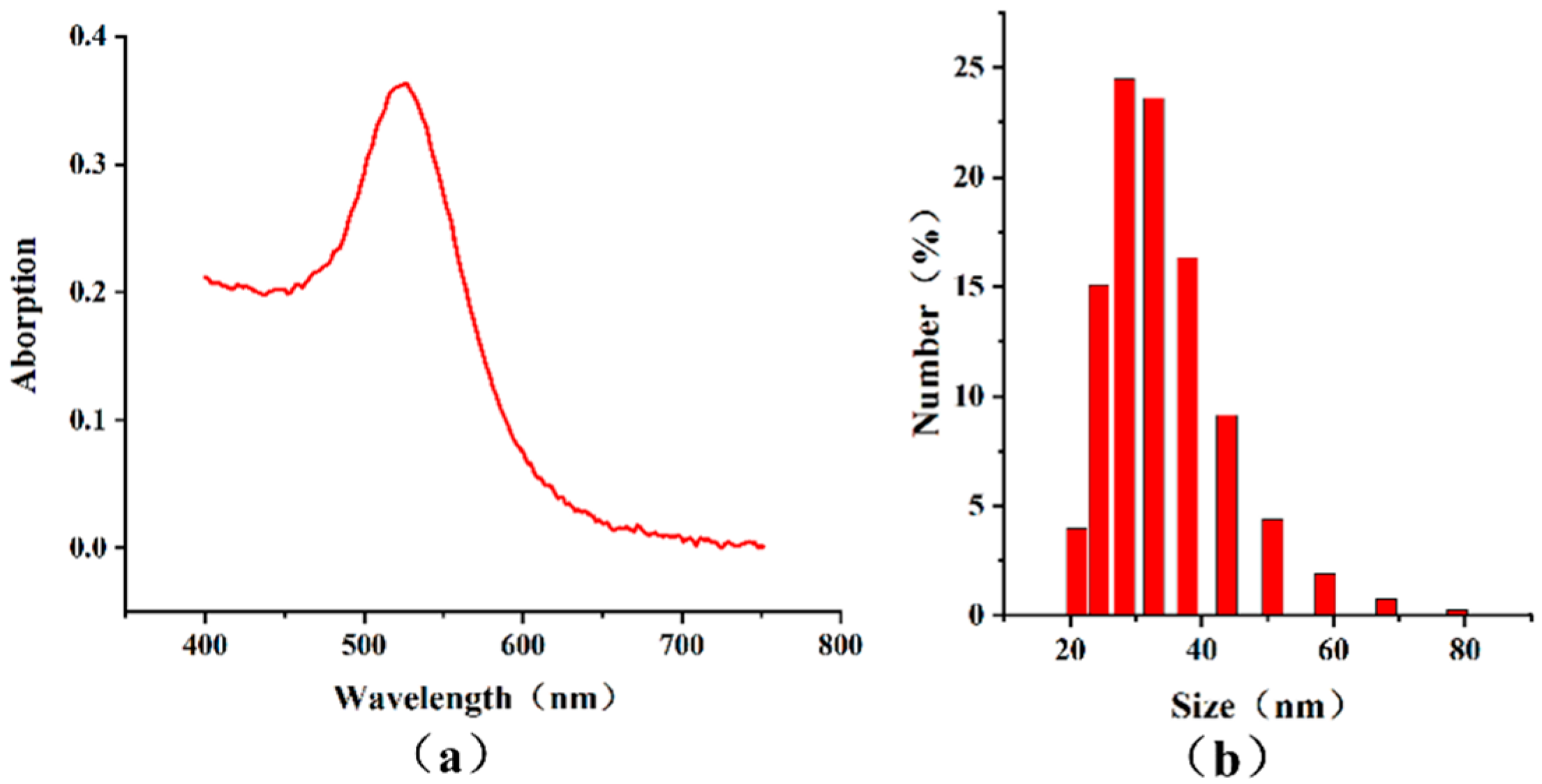
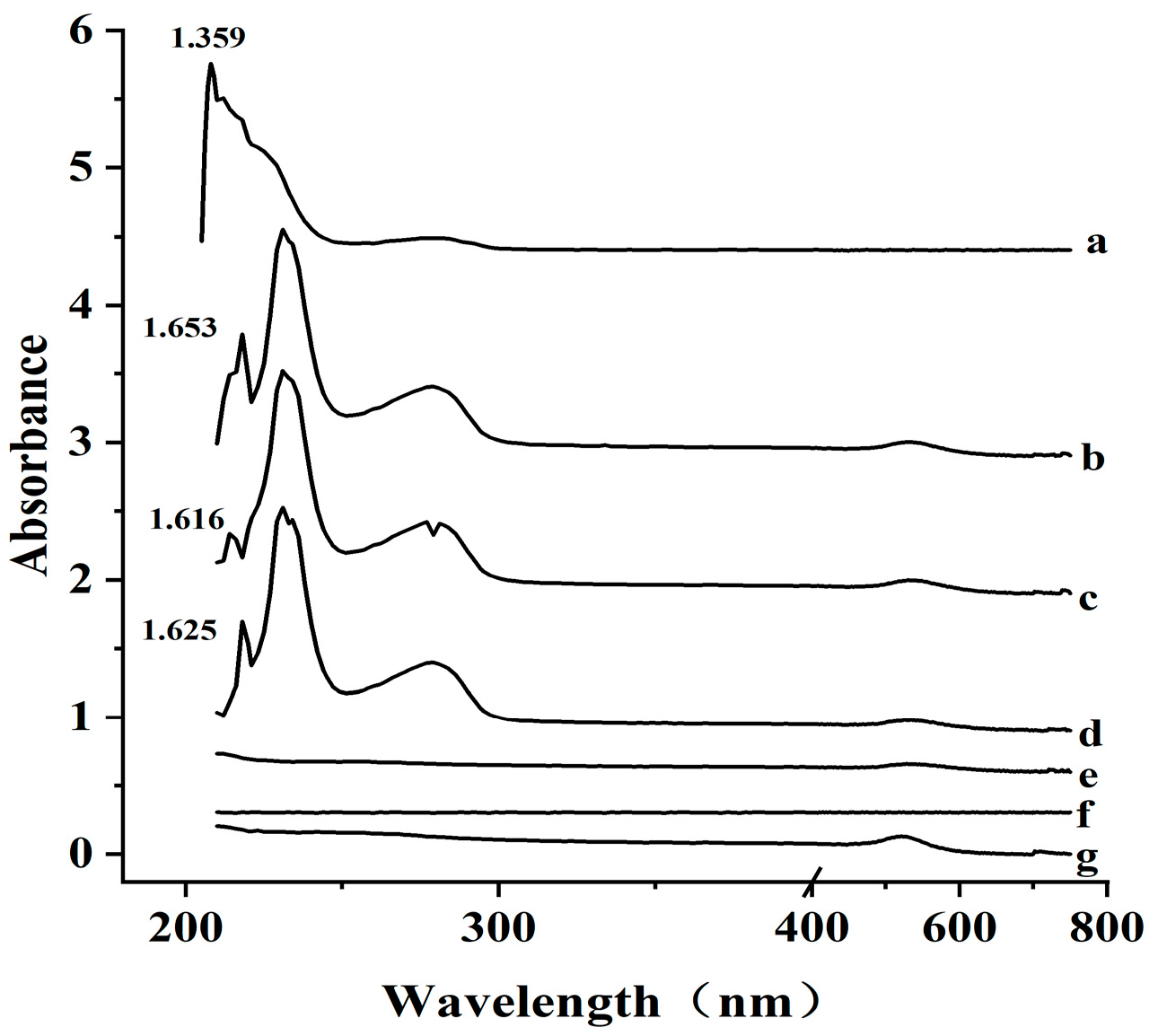
3.2. Characterization of AuNP-Ab Conjugate
3.3. Direct and Sandwich Strategies for SPR Detection of S. Typhimurium
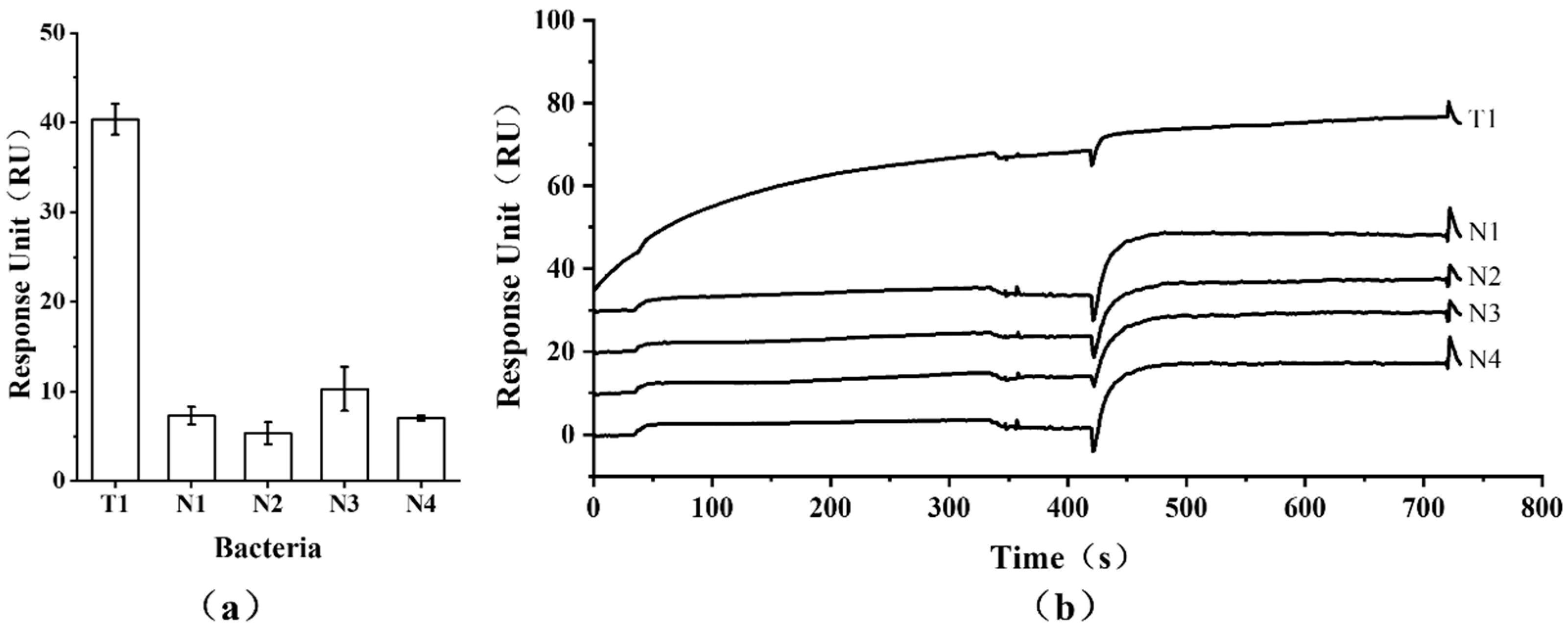
3.4. Specificity of Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balasubramanian, R.; Im, J.; Lee, J.S.; Jeon, H.J.; Mogeni, O.D.; Kim, J.H.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Baker, S.; Marks, F. The global burden and epidemiology of invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella infections. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 15, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.G.; Rosario, D.K.; Cunha-Neto, A.; Mano, S.B.; Figueiredo, E.E.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Worldwide epidemiology of Salmonella serovars in animal-based foods: A meta-analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Li, F.; Dong, N.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Xie, J.; et al. Investigation of a salmonellosis outbreak caused by multidrug resistant Salmonella Typhimurium in China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.M.J.; Hill Cawthorne, G.A.; Ward, M.P.; Mor, S.M. Diversity of Salmonella serotypes from humans, food, domestic animals and wild life in New South Wales, Australia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, L.; Wu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Kan, B.; Klena, J.D.; Wong, D.M.A.L.F.; Angulo, F.J.; et al. Laboratory-based surveillance of nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, C.; Alali, W.Q.; Cui, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Yang, B. Distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of foodborne Salmonella serovars in eight provinces in China from 2007 to 2012 (Except 2009). Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. Detection of Salmonella enterica in food using targeted mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 141985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, Y.; Kavvas, E.; Lachance, J.C.; Yurkovich, J.T.; Nuccio, S.P.; Fang, X.; Catoiu, E.; Raffatellu, M.; Palsson, B.O.; Monk, J.M. Genome-scale metabolic reconstructions of multiple Salmonella strains reveal serovar-specific metabolic traits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical biosensors for Salmonella: State of the art and challenges in food safety assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.F.; Zheng, K.C.; Nambiar, R.B.; Xu, X.B.; Weng, S.T.; Yue, M. Global genomic characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Telelkebir. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 704152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, M.S.; Bustami, Y.; Hamzah, H.H.; Zambry, N.S.; Najib, M.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Aziah, I.; Manaf, A.A. Advancement in Salmonella detection methods: From conventional to electrochemical-based sensing detection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Makino, H.; Katto, M.; Oishi, K.; Hori, T.; Kurakawa, T. Immunomagnetic separation for isolation and enrichment of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strain Shirota from human feces. Microbe 2023, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Yonogi, S.; Yamaguchi, N. Rapid quantification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium in lettuce using immunomagnetic separation and a microfluidic system. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 47, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.K.; Zhang, T.T.; Bi, Y.; Shu, M.; Zhong, C.; Tang, K.-J.; Wu, G.-P. A novel real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with immunomagnetic bead separation and ethidium bromide monoazide treatment for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, K.; Cheng, X.; Wan, Y.; Wu, X. Effective pre-treatment technique based on immune-magnetic separation for rapid detection of trace levels of Salmonella in milk. Food Control 2018, 91, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Wan, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, E.; Cheng, X.; Du, M. Rapid detection of trace Salmonella in milk and chicken by immunomagnetic separation in combination with a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6067–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.J.B.; Leon-Velarde, C.G.; McEwen, S.; Odumeru, J.A. Evaluation of an automated immunomagnetic separation method for the rapid detection of Salmonella species in poultry environmental samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 58, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Fang, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q. Colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strips for broad-spectrum detection of Salmonella. Food Control 2021, 126, 108052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, F.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; He, X. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by a fluorescent microsphere-based immunochromatographic assay and immunomagnetic separation. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 564, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K. Comparison of gold biosensor combined with light microscope imaging system with ELISA for detecting Salmonella in chicken after exposure to simulated chilling condition. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, L.; Varda, E.; Apostolou, T.; Loizou, K.; Dougiakis, L.; Inglezakis, A.; Hadjilouka, A. A novel application of B.EL.DTM technology: Biosensor-based detection of Salmonella spp. in food. Biosensors 2024, 14, 582. [Google Scholar]
- Almalaysha, M.; Singh, A.; Muhsin, S.A.; Carlson, A.V.; Trout, K.E.; Morey, A.; Zhang, S.; Channaiah, L.H.; Almasri, M. A highly sensitive microfluidic biosensor for rapid and accurate detection of Salmonella in raw chicken products. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2025, 9, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, X.; Mou, H.; Ke, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; et al. A microfluidic biosensor for quantitative detection of Salmonella in traditional Chinese medicine. Biosensors 2025, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Hirst, N.A.; Millner, P.A. Biosensors for whole-cell bacterial detection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical biosensors: An exhaustive and comprehensive review. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for fast, highly sensitive, and in situ detection of the magnetic nanoparticle-enriched Salmonella enteritidis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skottrup, P.D.; Nicolaisen, M.; Justesen, A.F. Towards on-site pathogen detection using antibody-based sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlen, B.; Mazumdar, S.D.; Lezrich, O.; Kämpfer, P.; Keusgen, M. Detection of Salmonella by surface plasmon resonance. Sensors 2007, 7, 1427–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukose, J.; Shetty, V.; Ballal, M.; Chidangil, S.; Sinha, R.K. Real-time and rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using an inexpensive lab-built surface plasmon resonance setup. Laser Phys. Lett. 2018, 15, 075701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.-C.; Bridgman, R.C. Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in romaine lettuce using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.-C.; Bridgman, R.C. Magnetic nanoparticles enhanced surface plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in romaine lettuce. Sensors 2022, 22, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Heo, N.S.; Shukla, S.; Cho, H.J.; Vilian, A.E.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Han, Y.-K.; Yoo, S.M.; Huh, Y.S. Development of gold nanoparticle-aptamer-based LSPR sensing chips for the rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in pork meat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Mao, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Hu, Y. SPR quantitative analysis of direct detection of atrazine traces on Au-nanoparticles: Nanoparticles size effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zou, F.; Hu, X.; Zhu, H.; Koh, K.; Chen, H. Analyte induced AuNPs aggregation enhanced surface plasmon resonance for sensitive detection of paraquat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Huh, Y.-M.; Yoon, D.S.; Yang, J. Nanobiosensors based on localized surface plasmon resonance for biomarker detection. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 759830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Han, X.; Pan, S.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Jin, H. Gold nanomaterials and bone/cartilage tissue engineering: Biomedical applications and molecular mechanisms. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 724188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereli, N.; Bakhshpour, M.; Topçu, A.A.; Denizli, A. Surface plasmon resonance-based immunosensor for Igm detection with gold nanoparticles. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, J.; Han, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Guo, T. Gold nanoparticle-functionalized surface plasmon resonance optical fiber biosensor: In situ detection of thrombin with 1 nM detection limit. J. Light Technol. 2019, 37, 2748–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghubi, F.; Zeinoddini, M.; Saeedinia, A.R.; Azizi, A.; Nemati, A.S. Design of localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) biosensor for immunodiagnosis of E. coli O157:H7 using gold nanoparticles conjugated to chicken antibody. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, Z.G.K. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yoo, J.G.; Ham, J.S.; Oh, M.H. Direct detection of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella spp. in animal-derived foods using a magnetic bead-based immunoassay. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 727–736. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, S.; Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xiong, Y. Large-volume immunomagnetic separation combined with multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria ivanovii in lettuce. Food Control 2016, 59, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripabelli, G.; Sammarco, M.L.; Grasso, G.M. Evaluation of immunomagnetic separation and plating media for recovery of Salmonella from meat. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskila, S.; Tuomola, M.; Ojamo, H. Enrichment cultivation in detection of food-borne Salmonella. Food Control 2012, 26, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Ming, T.; Li, Y.; Su, X. Immunomagnetic separation-based nanogold enhanced surface plasmon resonance and colloidal gold test strips for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soelberg, S.D.; Stevens, R.C.; Limaye, A.P.; Furlong, C.E. Surface plasmon resonance detection using antibody-linked magnetic nanoparticles for analyte capture, purification, concentration, and signal amplification. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Charlermroj, R.; Morton, M.J.; Oplatowska-Stachowiak, M.; Grant, I.R.; Elliott, C.T. Development of a M13 bacteriophage-based SPR detection using Salmonella as a case study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguelia, S.; Roupioz, Y.; Slimani, S.; Mondani, L.; Casabona, M.G.; Durmort, C.; Vernet, T.; Calemczuk, R.; Livache, T. On-chip microbial culture for the specific detection of very low levels of bacteria. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; Quinn, J.; O’Kennedy, R. A generic approach for the detection of whole Listeria monocytogenes cells in contaminated samples using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratamico, P.M.; Strobaugh, T.P.; Medina, M.B.; Gehring, A.G. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. BioTechniques 1998, 12, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, S.; Park, T.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, Y.J. Directed self-assembly of gold binding polypeptide-protein A fusion proteins for development of gold nanoparticle-based SPR immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2592–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisocherová-Lísalová, H.; Víšová, I.; Ermini, M.L.; Špringer, T.; Song, X.C.; Mrázek, J.; Lamačová, J.; Lynn, N.S.; Šedivák, P.; Homola, J. Low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor for multi-step detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens in complex food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, N.F.; Tai, M.J.; Wu, H.P.; Lin, T.-L.; Chen, C.-Y. Development of a bioaffinity SPR immunosensor based on functionalized graphene oxide for the detection of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A2 in human plasma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6735–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, L.A.; Musick, M.D.; Smith, P.C.; Reiss, B.D.; Peña, D.J.; Natan, M.J. Surface plasmon resonance of colloidal Au-modified gold films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yu, X.; Lawd, W.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, R.; Dinh, X.-Q.; Ho, H.-P.; Yong, K.-T. Size dependence of Au NP-enhanced surface plasmon resonance based on differential phase measurement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella via Immunomagnetic Separation and Nanoparticle-Enhanced SPR. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081914
Liang F, Li Y, Cui Y, Zhang J. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella via Immunomagnetic Separation and Nanoparticle-Enhanced SPR. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081914
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Fengzhu, Yuzhen Li, Yan Cui, and Jianhua Zhang. 2025. "Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella via Immunomagnetic Separation and Nanoparticle-Enhanced SPR" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081914
APA StyleLiang, F., Li, Y., Cui, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella via Immunomagnetic Separation and Nanoparticle-Enhanced SPR. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081914






