Antimicrobial Activities of Propolis Nanoparticles in Combination with Ampicillin Sodium Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Propolis Material and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Preparation of PNPs
2.3. Determination of the Characteristics of PNPs
2.4. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.5. Determination of Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Indices (FICIs)
2.6. Effect of PNPs in Combination with AS on MRSA Biofilm Formation
2.7. Effect of PNPs in Combination with AS on Mature MRSA Biofilm
2.8. Determination of Bacterial Adhesion
2.9. Extracellular Polysaccharide Production Analysis
2.10. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis to Determine Gene Expression Levels
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
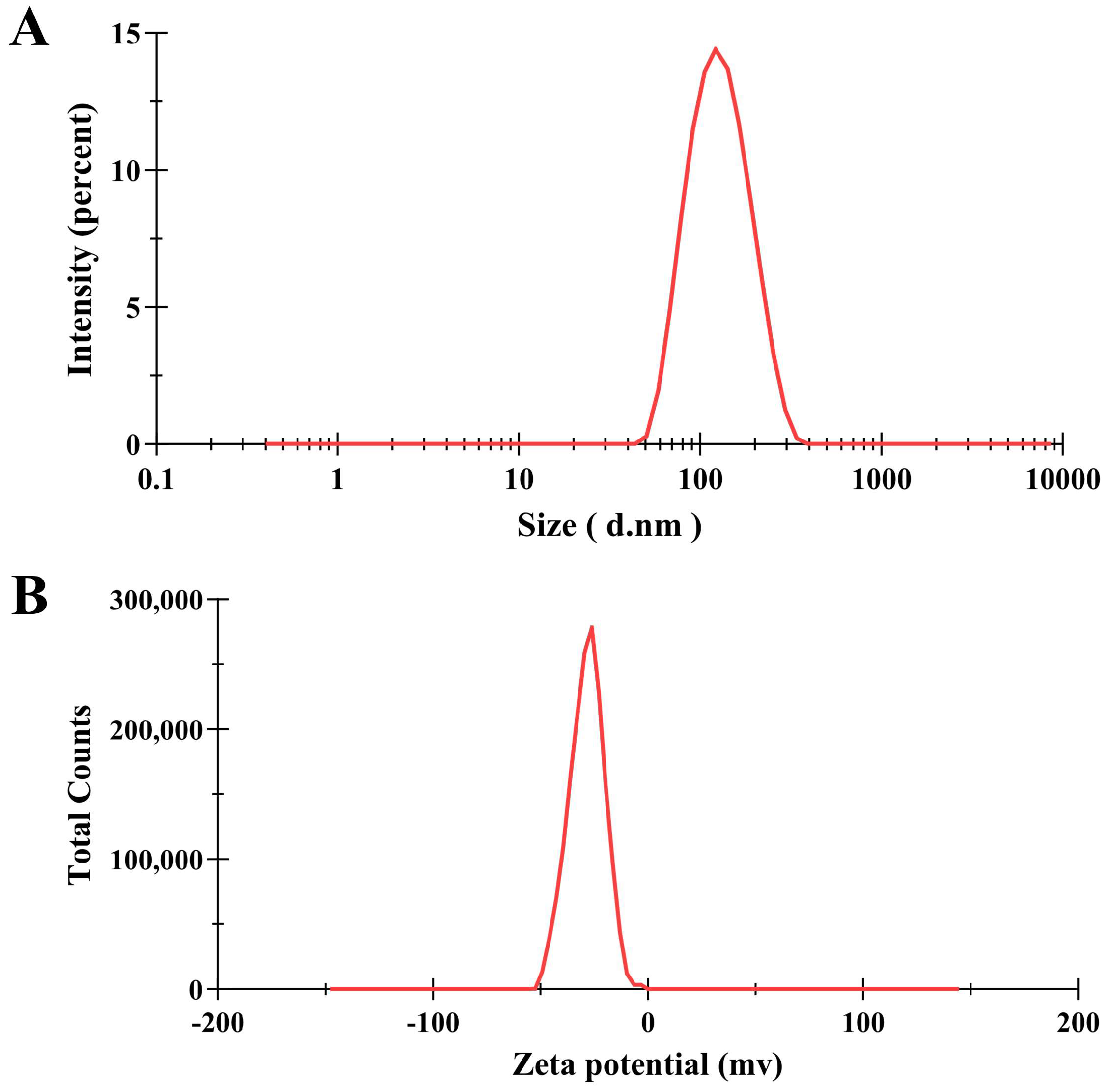
3.1. Characterization of PNPs
3.2. MIC of PNPs and AS
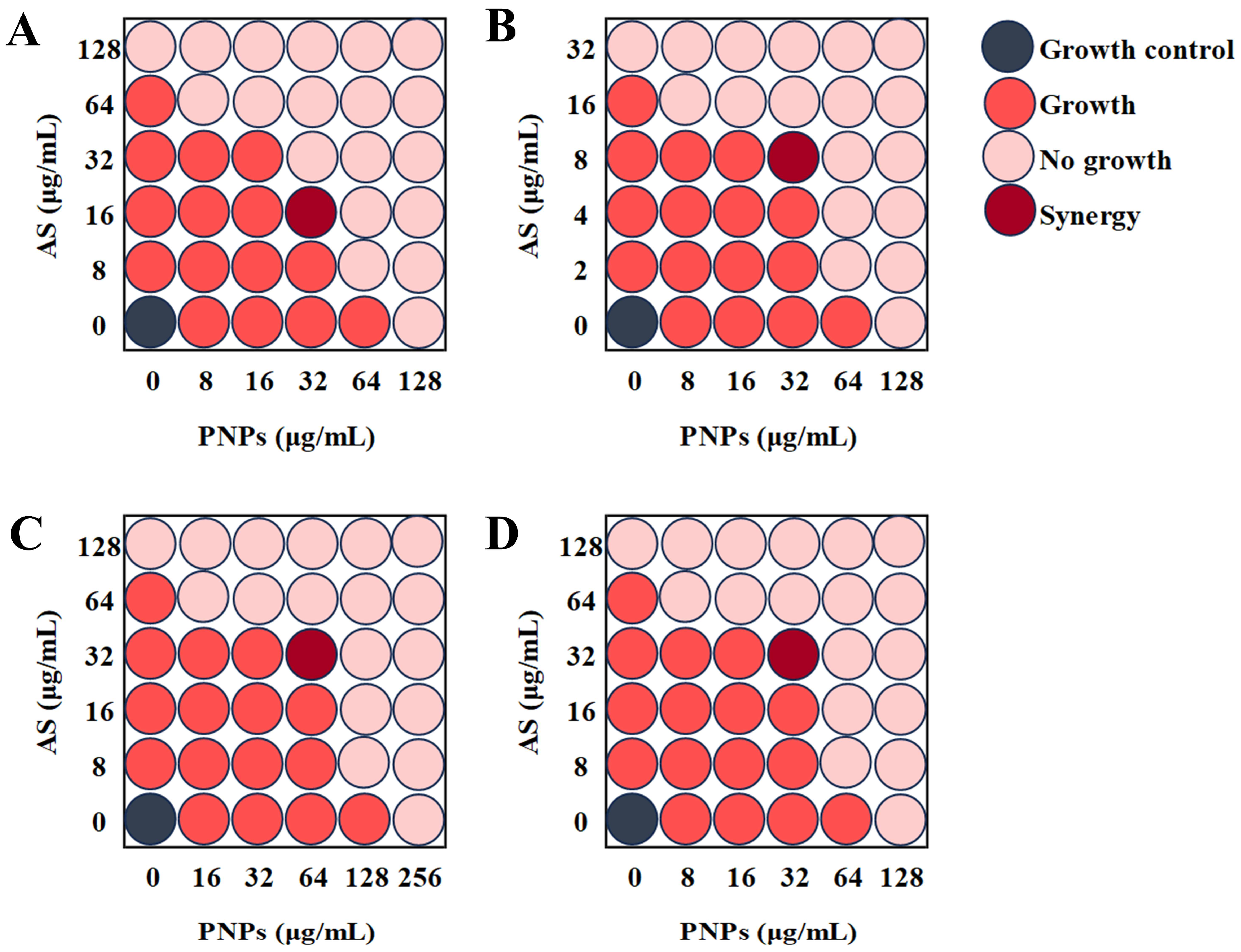
3.3. Synergistic Effect of PNPs with AS Against Planktonic MRSA
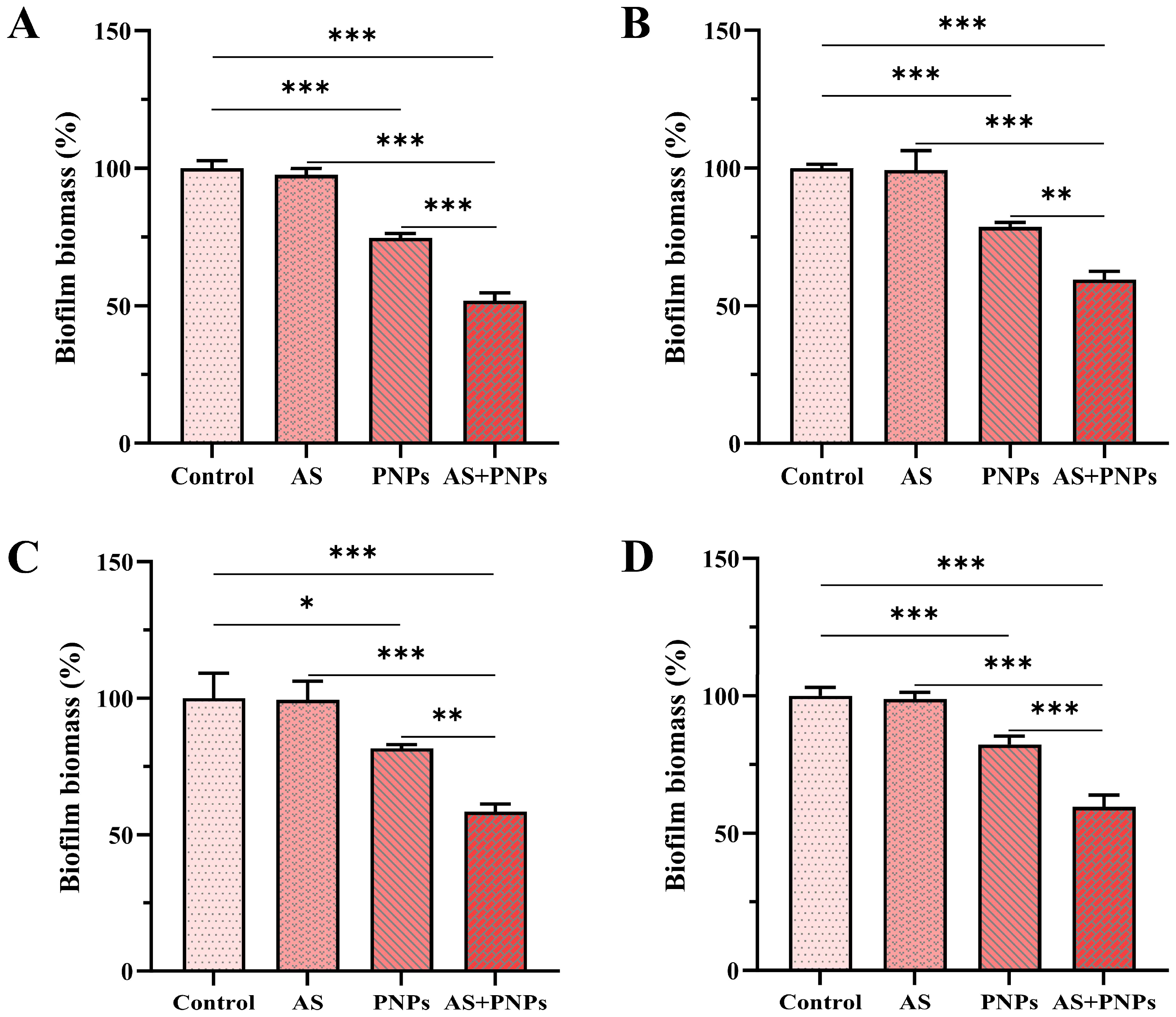
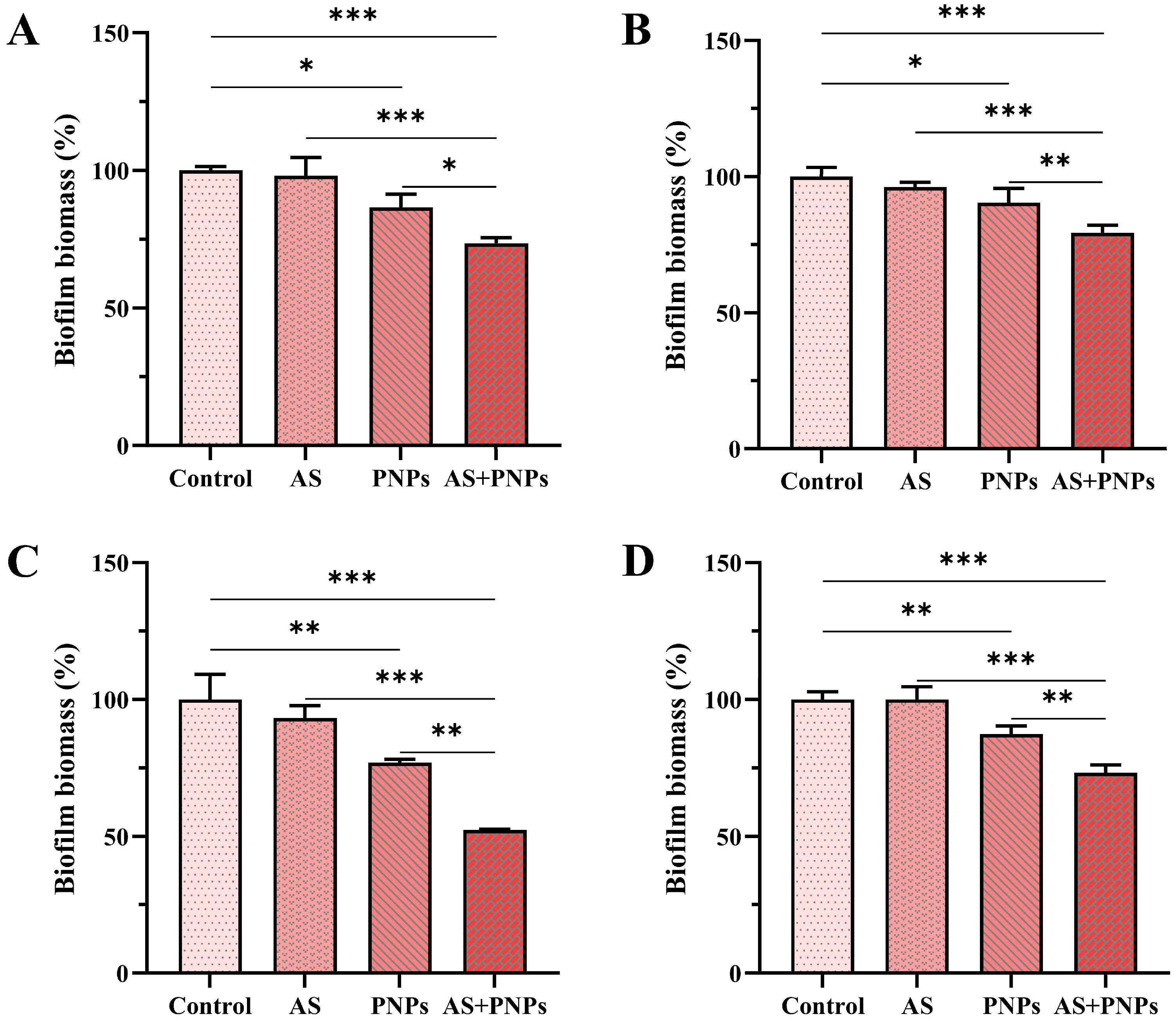
3.4. Synergistic Effect of PNPs with AS Against MRSA Biofilm
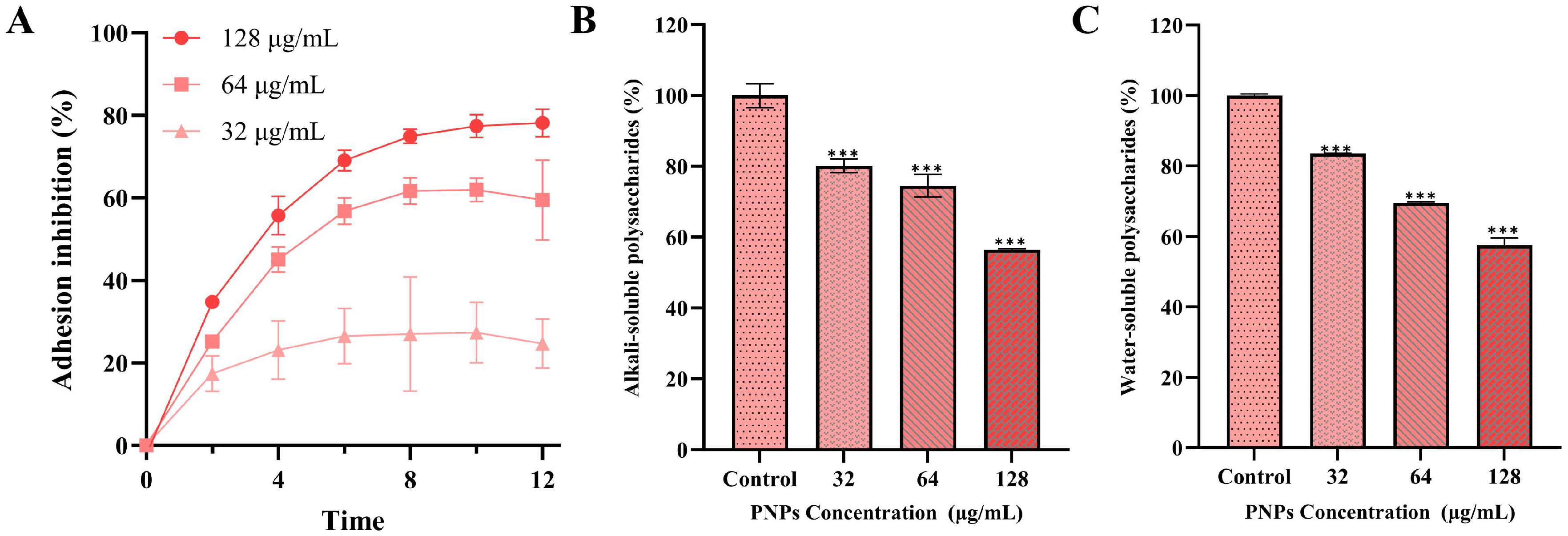
3.5. Effect of PNPs on Bacterial Adhesion
3.6. Effect of PNPs on Extracellular Polysaccharide Production
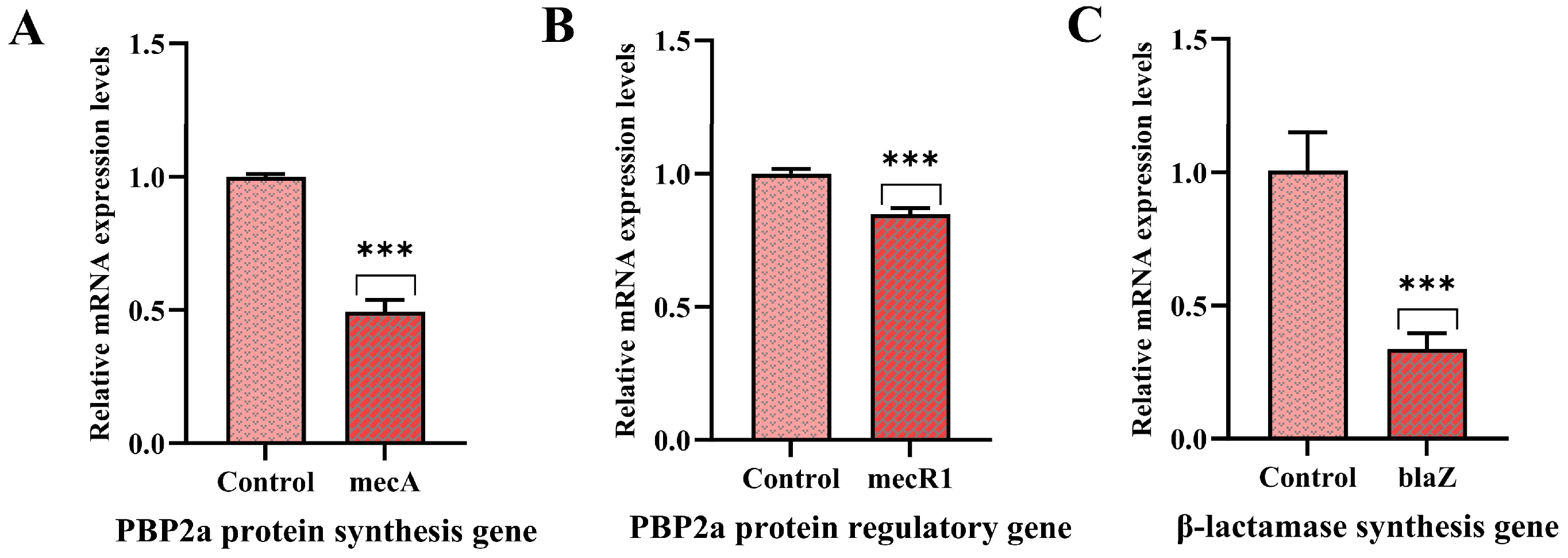
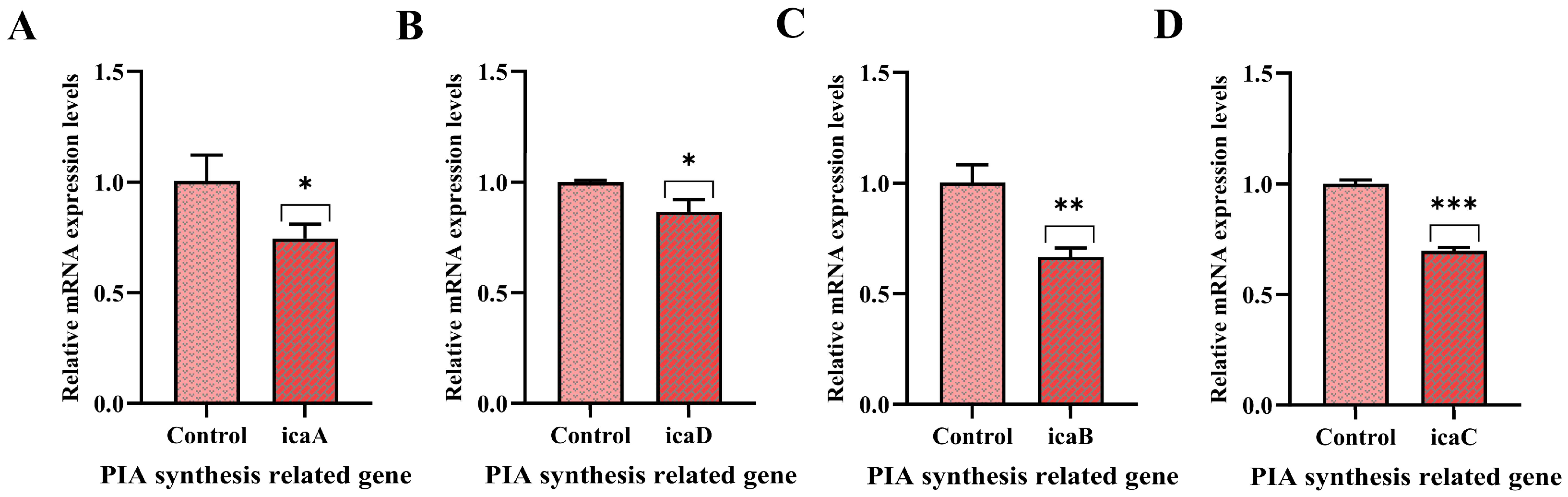
3.7. Effect of PNPs on Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PNPs | Propolis Nanoparticles |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| AS | Ampicillin Sodium |
| PBP2a | Penicillin-Binding Proteins 2a |
| PIA | Polysaccharide Intercellular Adhesin |
| TSB | Trypticase Soy Broth |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| MIC | Minimal Inhibitory Concentration |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Units |
| FICIs | Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Indices |
| CV | Crystal Violet |
References
- Freitas, A.S.; Cunha, A.; Oliveira, R.; Almeida-Aguiar, C. Propolis antibacterial and antioxidant synergisms with gentamicin and honey. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 2733–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripari, N.; Marques Pereira, A.F.; Fernandes Júnior, A.; Mores Rall, V.L.; Aldana-Mejía, J.A.; Kenupp Bastos, J.; Sforcin, J.M. Brazilian red propolis in combination with β-lactams exerts an efficient antibacterial action over methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisette, T.; Alosaimy, S.; Abdul-Mutakabbir, J.C.; Kebriaei, R.; Rybak, M.J. The evolving reduction of vancomycin and daptomycin susceptibility in MRSA-salvaging the gold standards with combination therapy. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, J. Distribution and resistance of pathogens in infected patients within 1 year after heart transplantation. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 103, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.T.; Fang, C.; Xu, B.J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xue, X.Y.; Liu, J.P.; Li, M.K.; Li, P.Y. Designing novel nucleoside inhibitors targeting the allosteric site of PBP2a: A strategic approach to overcome resistance in MRSA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2025, 122, 118133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beker, S.; Kahya Demirbilek, S. Optimizing detection methods for MRSA isolated from mastitis cases and assessing virulence genes. Res. Vet. Sci. 2025, 187, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalbert, J.R.; Varshney, K.; Tobin, R.; Pajaro, R. Clinical outcomes in patients co-infected with COVID-19 and Staphylococcus aureus: A scoping review. BMC. Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Jin, H.; Song, P.; Xu, W.; Wang, F. Gallic acid exerts antibiofilm activity by inhibiting methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm inhibition by high voltage prick electrostatic field (HVPEF) and the mechanism investigation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 362, 109499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Y.L.; Mahadi, A.M.; Wong, K.M.; Goh, J.K. Anti-methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) compounds from Bauhinia kockiana Korth and their mechanism of antibacterial activity. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Xiao, P.; Wang, Y.L.; Hao, Y. Mechanisms and control measures of mature biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents in the clinical context. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22684–22690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosswimmer, T.; Nick, S.E.; Bryers, J.D.; Daggett, V. Designed de novo α-sheet peptides destabilize bacterial biofilms and increase the susceptibility of E. coli and S. aureus to Antibiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Kest, H.; Sood, M.; Bryan, W.; Steussy, B.W.; Thieman, C.; Gupta, S. Biofilm Producing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in Humans: Clinical Implications and Management. Pathogens 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.; Mumtaz, S.; Singh, M.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Synergistic Potential of α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Based Analogues with Conventional Antibiotic against Planktonic, Biofilm-Embedded, and Systemic Infection Model of MRSA. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shiekh, R.A.; Radi, M.H.; Elshimy, R.; Abdel-Sattar, E.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Ali, M.E.; Hassanen, E.I. Friedelin: A natural compound exhibited potent antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and wound healing properties against MRSA-infected wounds. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhendri, F.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Kowacz, M.; Ravalia, M.; Kripal, K.; Fearnley, J.; Perera, C.O. Antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, and antiparasitic properties of propolis: A review. Foods 2021, 10, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendruscolo, I.; Berton, G.H.; Biffi, M.T.; Bressiani, P.A.; Oliveira, A.K.G.; Berti, A.P.; Concato-Lopes, V.M.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Simon, A.P.; Oldoni, T.L.C.; et al. Antiproliferative effect of hydroalcoholic brown propolis extract on tumor and non-tumor cells. Braz. J. Biol. 2025, 84, e287297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, S.; Pourhajibagher, M.; Chiniforush, N.; Bahador, A. Propolis nanoparticle enhances the potency of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy against Streptococcus mutans in a synergistic manner. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolia, A.; Kumar, H.; Ramamurthy, S.; Madheswaran, T.; Davamani, F.; Pichika, M.R.; Mak, K.K.; Fawzy, A.S.; Daood, U.; Pau, A. Effect of Propolis Nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm in the Root Canal. Molecules 2021, 26, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangboonruang, S.; Semakul, N.; Sookkree, S.; Kantapan, J.; Ngo-Giang-Huong, N.; Khamduang, W.; Kongyai, N.; Tragoolpua, K. Activity of propolis nanoparticles against hsv-2: Promising approach to inhibiting infection and replication. Molecules 2022, 27, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Divsalar, A.; Saboury, A.A.; Seyedarabia, A. Propolis nanoparticles prevent structural changes in human hemoglobin during glycation and fructation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Divsalar, A.; Saboury, A.A. Structural analysis of the interaction between free, glycated and fructated hemoglobin with propolis nanoparticles: A spectroscopic study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, X.R.; Xuan, H.Z. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Chinese propolis essential oil microemulsion against Streptococcus mutans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gezgin, Y.; Kazan, A.; Ulucana, F.; Yesil-Celiktas, O. Antimicrobial activity of propolis and gentamycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a 3D thermo-sensitive hydrogel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Pérez, M.L.; Vadillo-Rodríguez, V.; Fernández-Babiano, I.; Pérez-Giraldo, C.; Fernández-Calderón, M.C. Antimicrobial activity of a novel Spanish propolis against planktonic and sessile oral Streptococcus spp. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23860. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wei, F.Y.; Song, C.X.; Jiang, B.; Tian, S.Y.; Yi, J.W.; Yu, C.L.; Song, Z.B.; Sun, L.G.; Bao, Y.L.; et al. Dodartia orientalis L. essential oil exerts antibacterial activity by mechanisms of disrupting cell structure and resisting biofilm. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhao, H.Z.; Lu, Y.J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Z.X. Surfactin effectively inhibits Staphylococcus aureus adhesion and biofilm formation on surfaces. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4565–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Xiao, J. Determination of tea polysaccharides in camellia sinensis by a modified phenol-sulfuric acid method. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2010, 62, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Margarita, G.E.; Wu, D.; Yuan, W.Q.; Yan, S.; Qi, S.Z.; Xue, X.F.; Wang, K.; Wu, L.M. Antibacterial activity of Chinese red propolis against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA. Molecules 2022, 27, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, B.; Sytykiewicz, H.; Sprawka, I. Expression of the biofilm-associated genes in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in biofilm and planktonic conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijo, P.; Abuamara, T.M.M.; Lashin, S.A.; Kamar, S.A.; Isca, V.M.S.; Mohammed, T.S.; Abdrabo, M.S.M.; Amin, M.A.; El Maksoud, A.I.A.; Hassan, A. Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanoparticles Subside the Activity of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Suppressing PBP2a. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, H.; Burandt, E.C.; Siemssen, N.; Frommelt, L.; Burdelski, C.; Wurster, S.; Scherpe, S.; Davies, A.P.; Harris, L.G.; Horstkotte, M.A.; et al. Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin or protein factors in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from prosthetic hip and knee joint infections. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masimen, M.A.A.; Harun, N.A.; Maulidiani, M.; Wan, W.I. Overcoming methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using antimicrobial peptides-silver nanoparticles. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, F.Y.; Xuan, H.Z. Antibacterial activity of Chinese propolis and its synergy with β-lactams against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Xuan, H.Z. Australian propolis ethanol extract exerts antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by mechanisms of disrupting cell structure, reversing resistance, and resisting biofilm. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1651–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, S.; Saraee, A.; Salamy, S.; Tahmourespour, A.; Shahbazi, S. Antimicrobial and gene expression modulation effects of ethanolic extract of propolis on Streptococcus mutans Adherence and biofilm formation. Ind. Biotechnol. 2025, 21, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slickers, P.; O’Connell, B.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Coleman, D.C.; Brennan, G.; Shore, A.C.; Deasy, E.C. Detection of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec Type XI Carrying Highly Divergent mecA, mecI, mecR1, blaZ, and ccr Genes in Human Clinical Isolates of Clonal Complex 130 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.; Flint, S.; Brooks, J. Bacterial cell attachment, the beginning of a biofilm. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 34, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Memarzadeh, K.; Chang, B.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ma, Z.; Allaker, R.P.; Ren, L.; Yang, K. Antibacterial effect of copperbearing titanium alloy (Ti-Cu) against Streptococcus mutans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29985. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, J.L.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Ravaioli, S.; Montanaro, L. Polysaccharide in-tercellular adhesin in biofilm: Structural and regulatory aspects. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| mecA | F: TCCAGGAATGCAGAAAGACC | [29] |
| R: TTGGAACGATGCCTATCTCA | ||
| mecR1 | F: GTGCTCGTCTCCACGTTAATTCCA | [31] |
| R: GACTAACCGAAGAAGTCGTGTCAG | ||
| blaZ | F: GCTTTAAAAGAACTTATTGAGGCTTC | [31] |
| R: CCACCGATYTCKTTTATAATTT | ||
| icaA | F: CTTGCTGGCGCAGTCAATAC | [29] |
| R: GTAGCCAACGTCGACAACTG | ||
| icaD | F: TGGGCATTTTCGCGATTATCA | [29] |
| R: ACGATTCTCTTCCTTTCTGCCA | ||
| icaB | F: CCTGTAAGCACACTGGATGG | [29] |
| R: TCGCTTTTCTTACACGGTGA | ||
| icaC | F: TGCGTTAGCAAATGGAGACT | [29] |
| R: TGCGTGCAAATACCCAAGAT | ||
| 16S rRNA | F: CGCAATGGGCGAAAGC | [29] |
| R: TACGATCCGAAGACCTTCATCA |
| PNPs | |
|---|---|
| Size (nm) | 118.0 ± 0.40 |
| PDI | 0.129 ± 0.01 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −28.2 ± 0.26 |
| Bacteria | Combinations | MIC (μg/mL) a | MIC (μg/mL) b | FICI | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA ATCC 43300 | PNPs | 128 | 32 | 0.375 | Synergy |
| AS | 128 | 16 | |||
| MRSA ATCC 33591 | PNPs | 128 | 32 | 0.5 | Synergy |
| AS | 32 | 8 | |||
| MRSA CI2 | PNPs | 256 | 64 | 0.5 | Synergy |
| AS | 128 | 32 | |||
| MRSA CI3 | PNPs | 128 | 32 | 0.5 | Synergy |
| AS | 128 | 32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, K.; Sang, H.; Jin, H.; Song, P.; Xu, W.; Xuan, H.; Wang, F. Antimicrobial Activities of Propolis Nanoparticles in Combination with Ampicillin Sodium Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081844
Feng K, Sang H, Jin H, Song P, Xu W, Xuan H, Wang F. Antimicrobial Activities of Propolis Nanoparticles in Combination with Ampicillin Sodium Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081844
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Kaiyue, He Sang, Han Jin, Peng Song, Wei Xu, Hongzhuan Xuan, and Fei Wang. 2025. "Antimicrobial Activities of Propolis Nanoparticles in Combination with Ampicillin Sodium Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081844
APA StyleFeng, K., Sang, H., Jin, H., Song, P., Xu, W., Xuan, H., & Wang, F. (2025). Antimicrobial Activities of Propolis Nanoparticles in Combination with Ampicillin Sodium Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081844




