Proteus sp. Strain JHY1 Synergizes with Exogenous Dopamine to Enhance Rice Growth Performance Under Salt Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
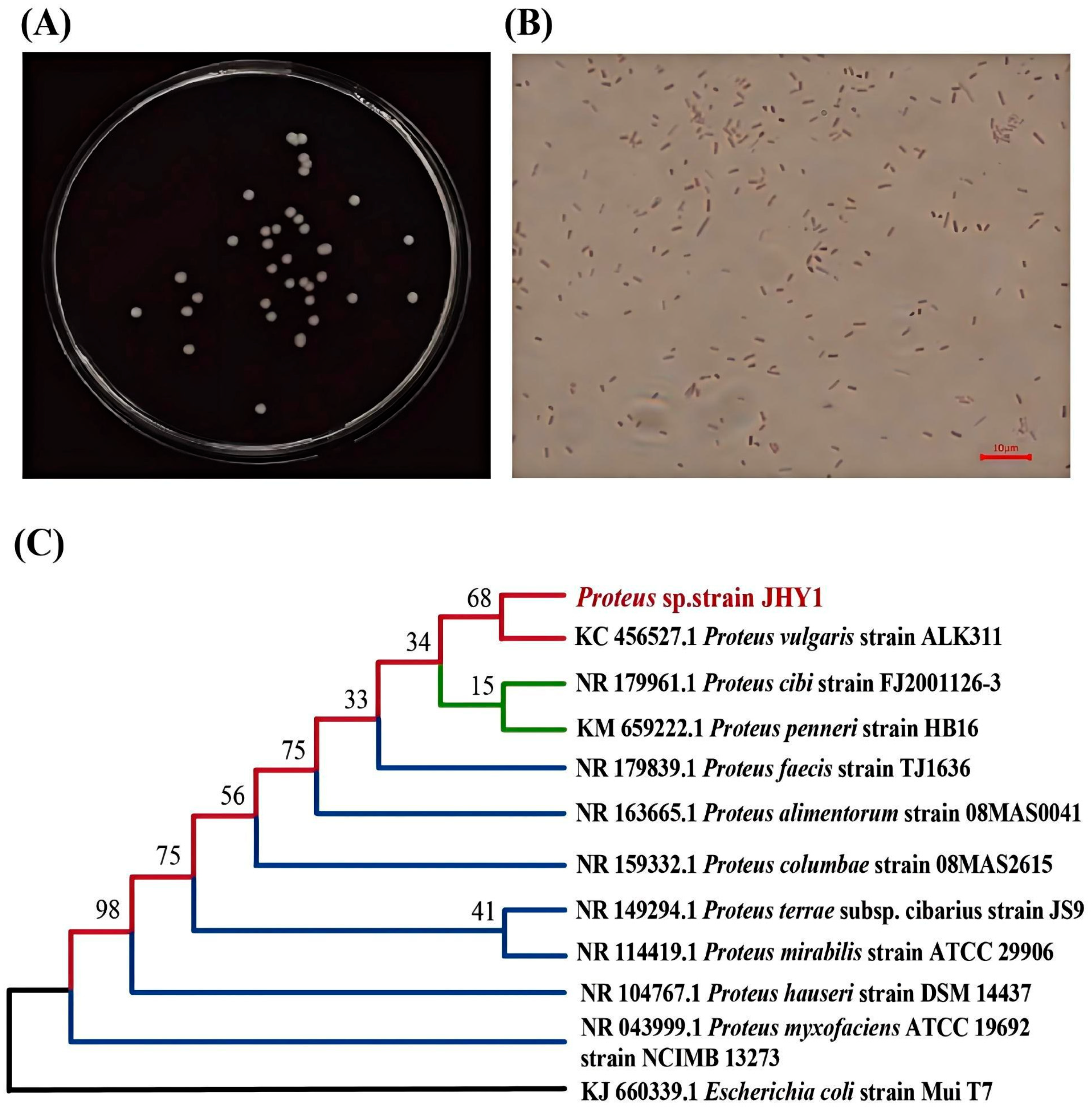
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Salt-Tolerant PGPR
2.2. Growth Performance and PGP Traits of Strain JHY1
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Growth Performance of Strain JHY1
2.2.3. Determination of PGP Traits of Strain JHY1
Nitrogen Fixation Capacity
IAA Production Capacity
ACC Deaminase Activity
Siderophore Production Capacity
Phosphate-Solubilizing Capacity
Ammonia (NH3) Production Capacity
Biofilm Formation Production Capacity
EPS Production Capacity
2.3. Pot Experiment
2.3.1. Plant Materials and Treatment Groups
2.3.2. Measurement of Rice Growth Parameters
2.3.3. Measurement of Chlorophyll Content and Photosynthetic Rate
2.3.4. Measurement of Antioxidase and Osmotic Substances
2.3.5. Assessment of Soil Fertility Levels
2.3.6. Determining Na+ and K+ Concentrations in Plants and Soil
2.3.7. Analysis of Rhizosphere Microbial Community
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of PGPR Under Salt Stress
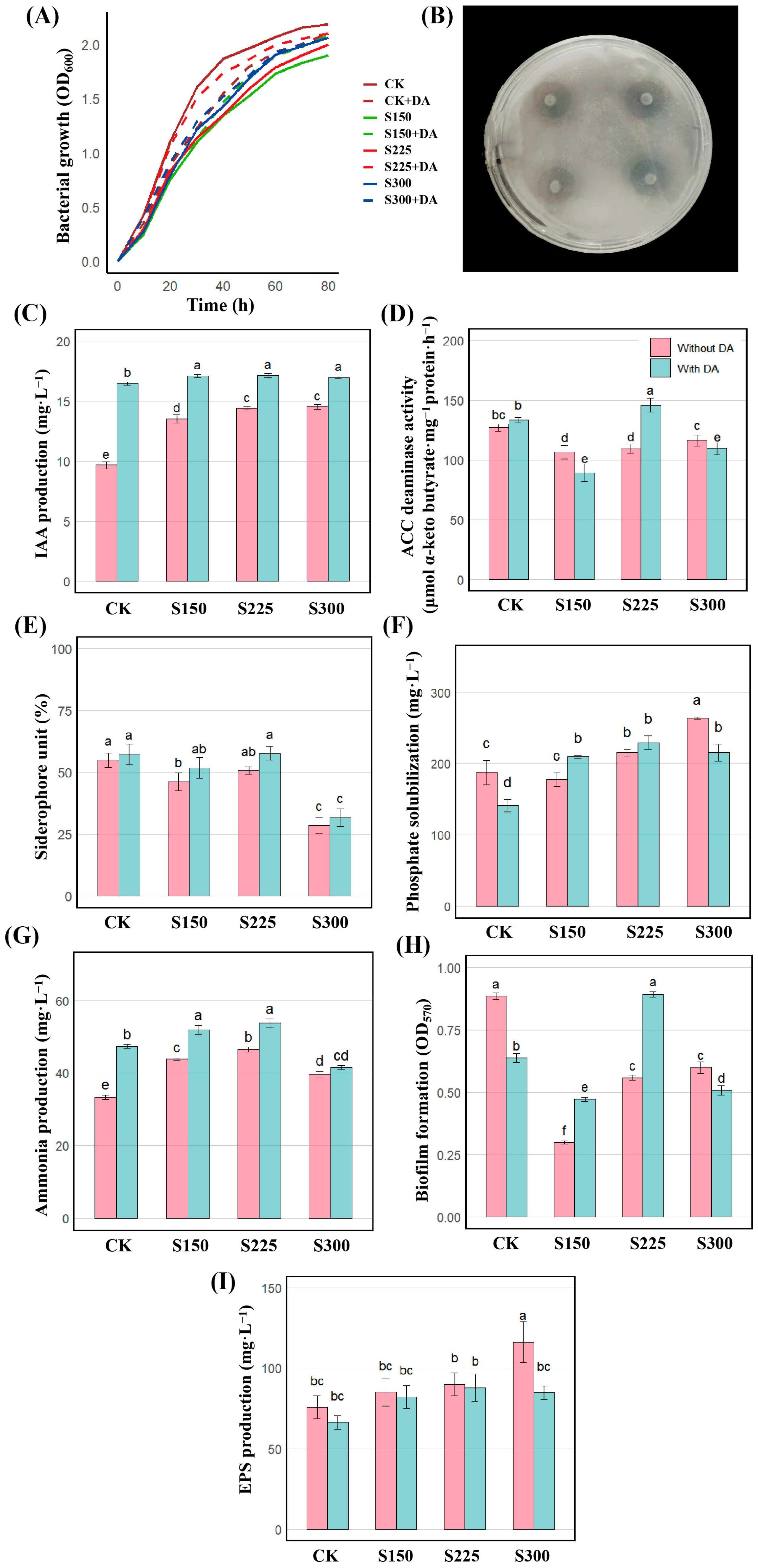
3.2. Determination of Growth Curve and Growth-Promoting Indicators of Strain JHY1
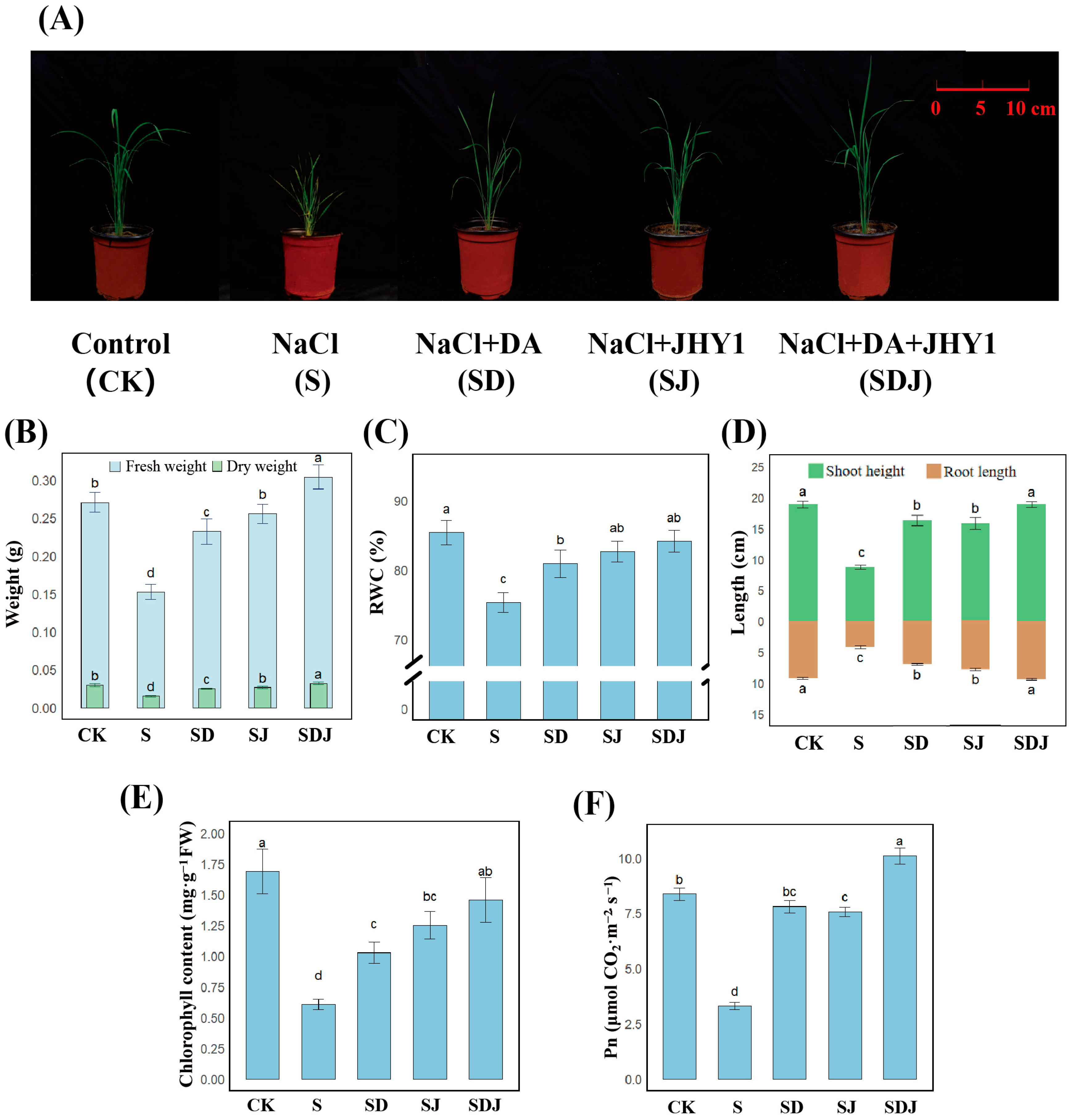
3.3. Effects of Individual and Co-Application of DA and Strain JHY1 on Growth Parameters of Rice Under Salt Stress
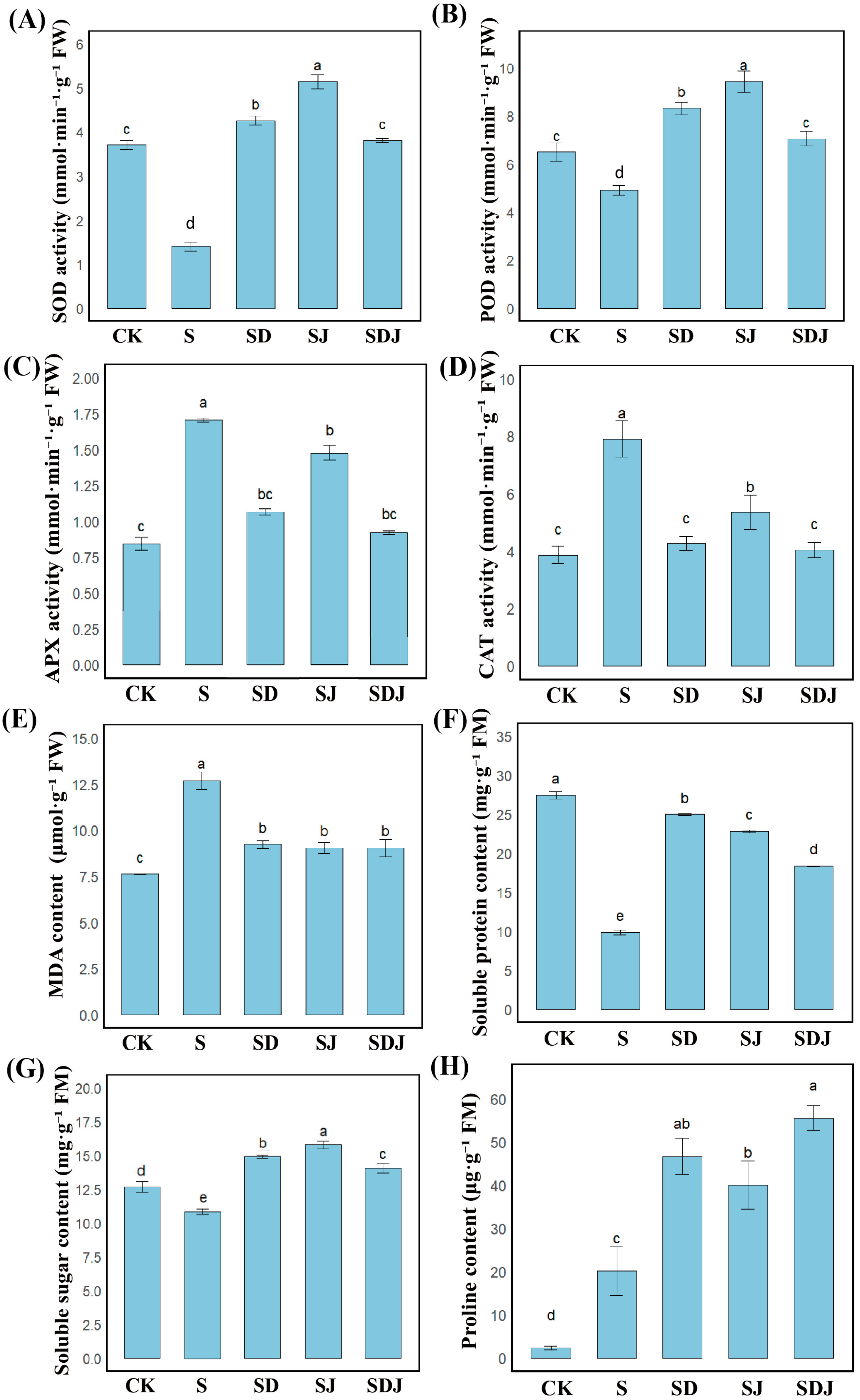
3.4. Effects of Individual and Co-Application of DA and Strain JHY1 on Antioxidant Enzymes and Osmotic Substances of Rice Under Salt Stress
3.5. Effects of Individual and Co-Application of DA and Strain JHY1 on Soil Nutrient Dynamics and Enzymatic Activity in Rice Under Salt Stress
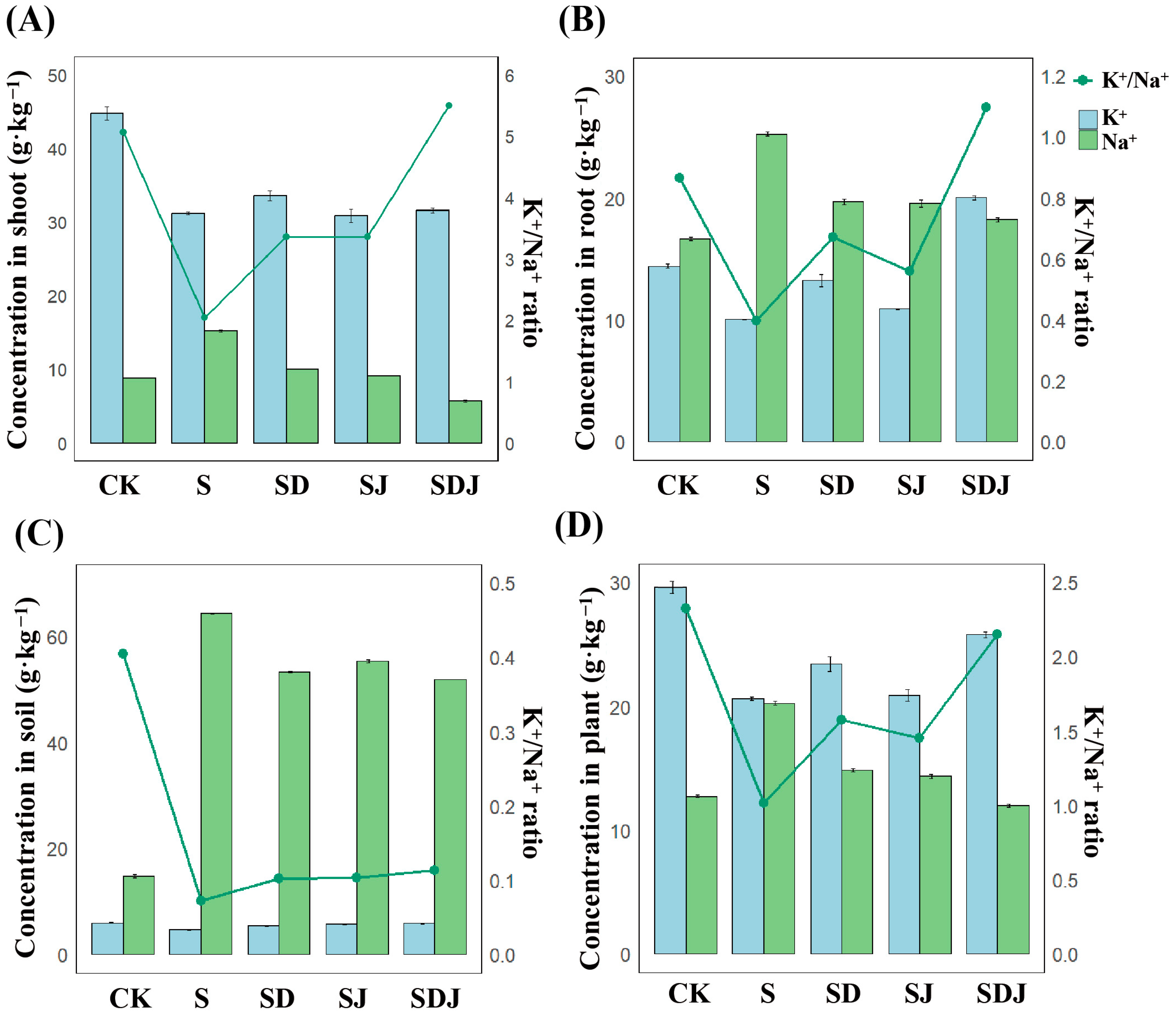
3.6. Na+ and K+ Ionic Regulation Under Salt Stress in Rice and Soil
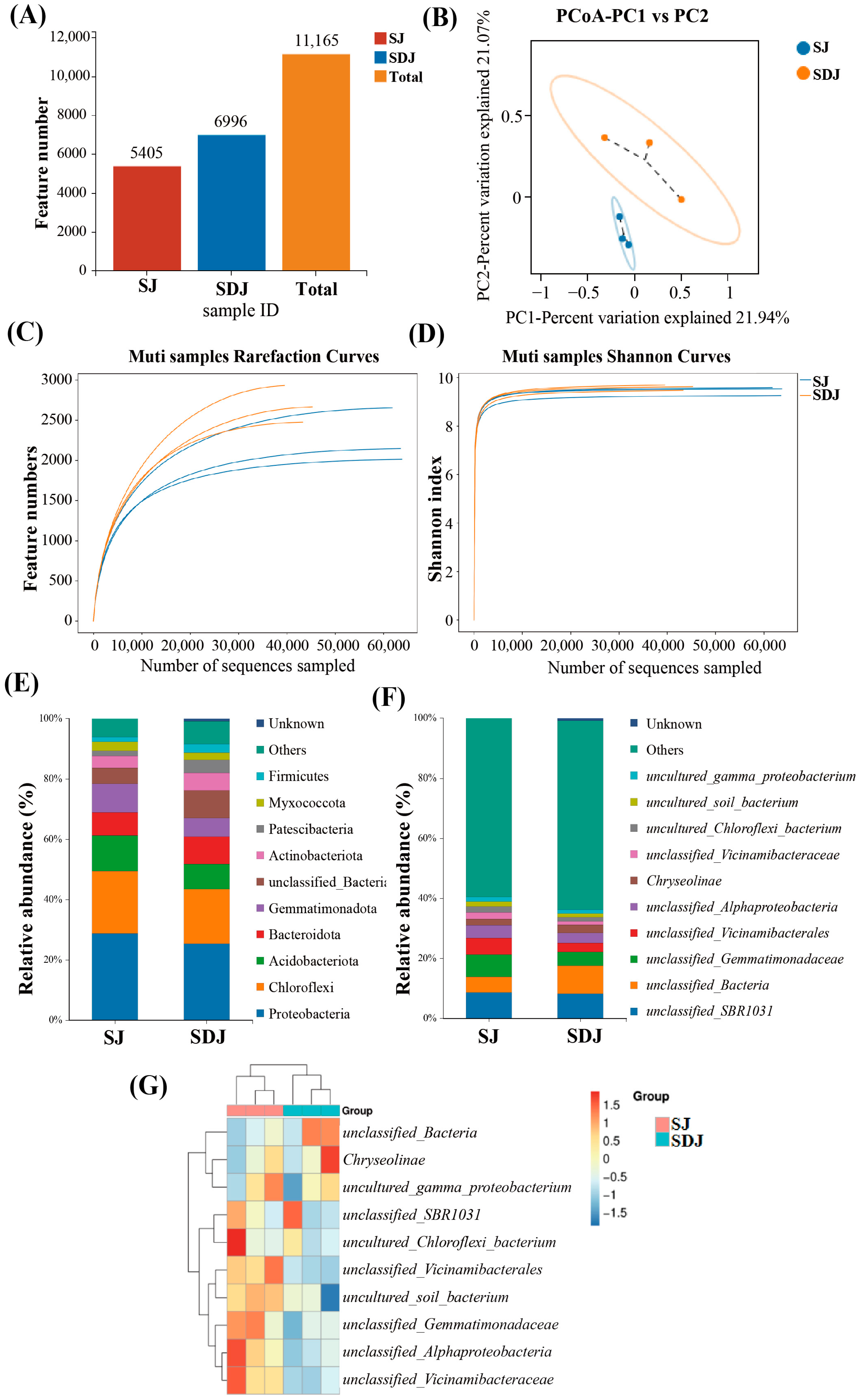
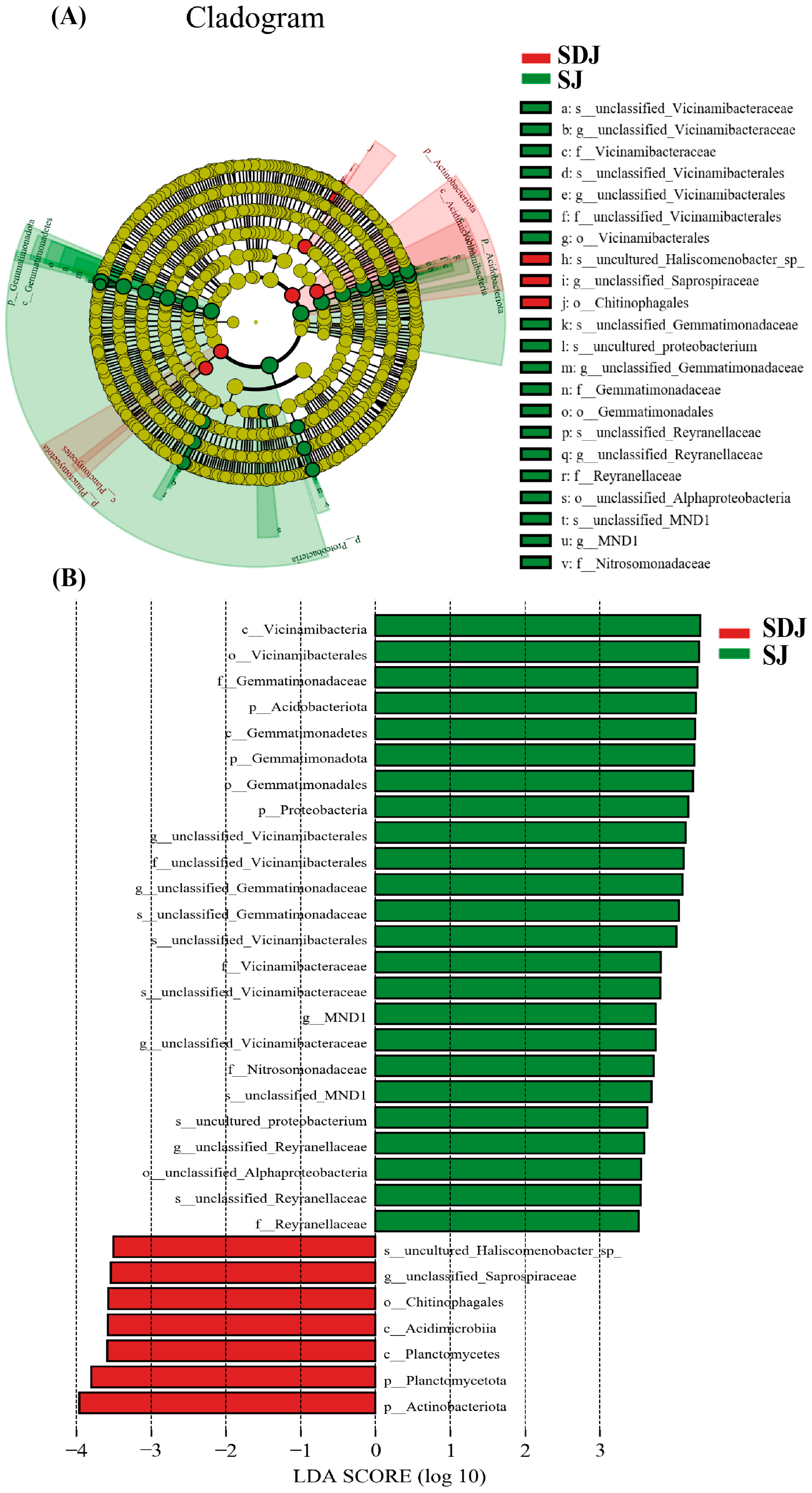
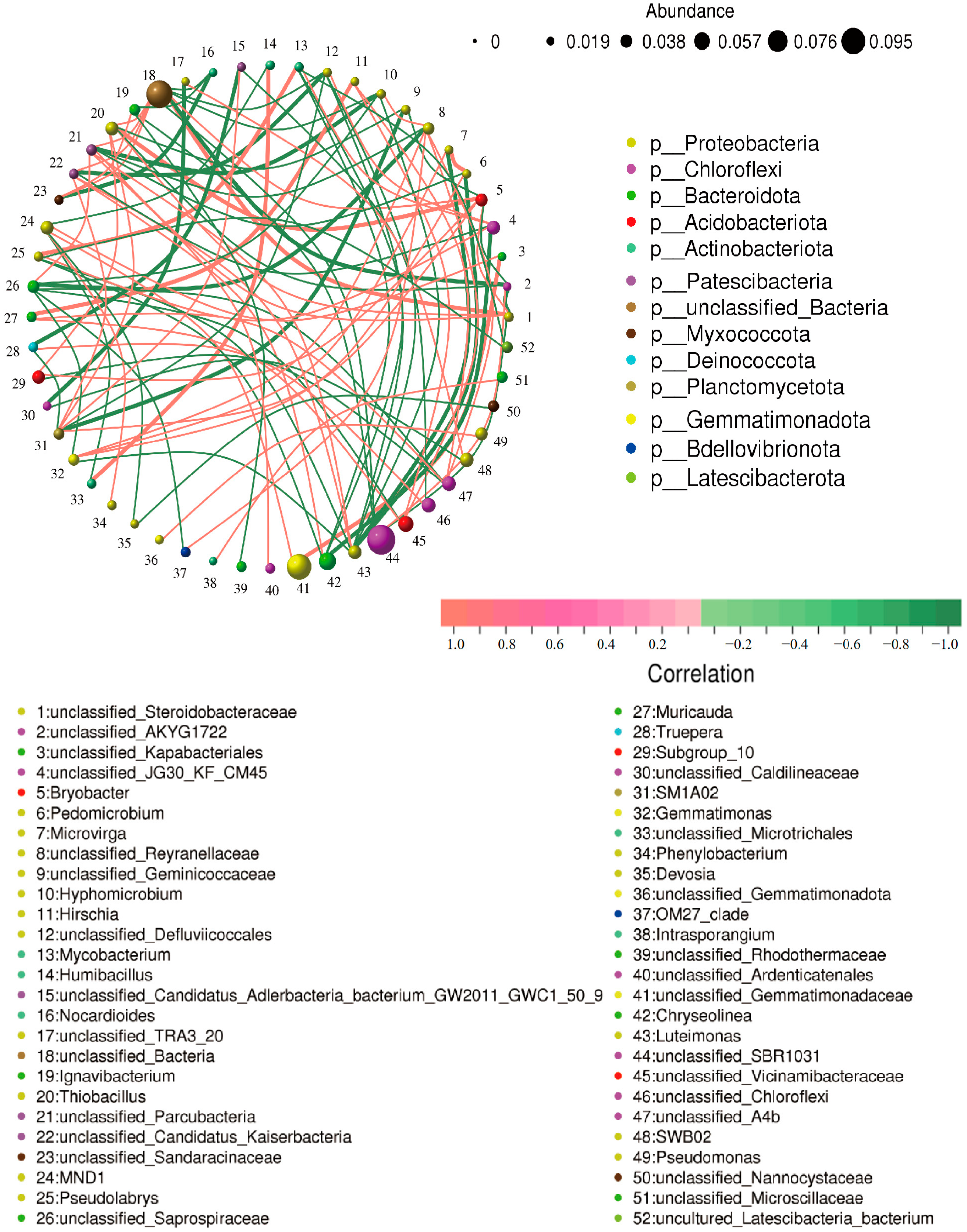
3.7. Rhizosphere Microbial Community in the Soil of the Strain JHY1-Treated Group and the DA-JHY1 Co-Treated Group
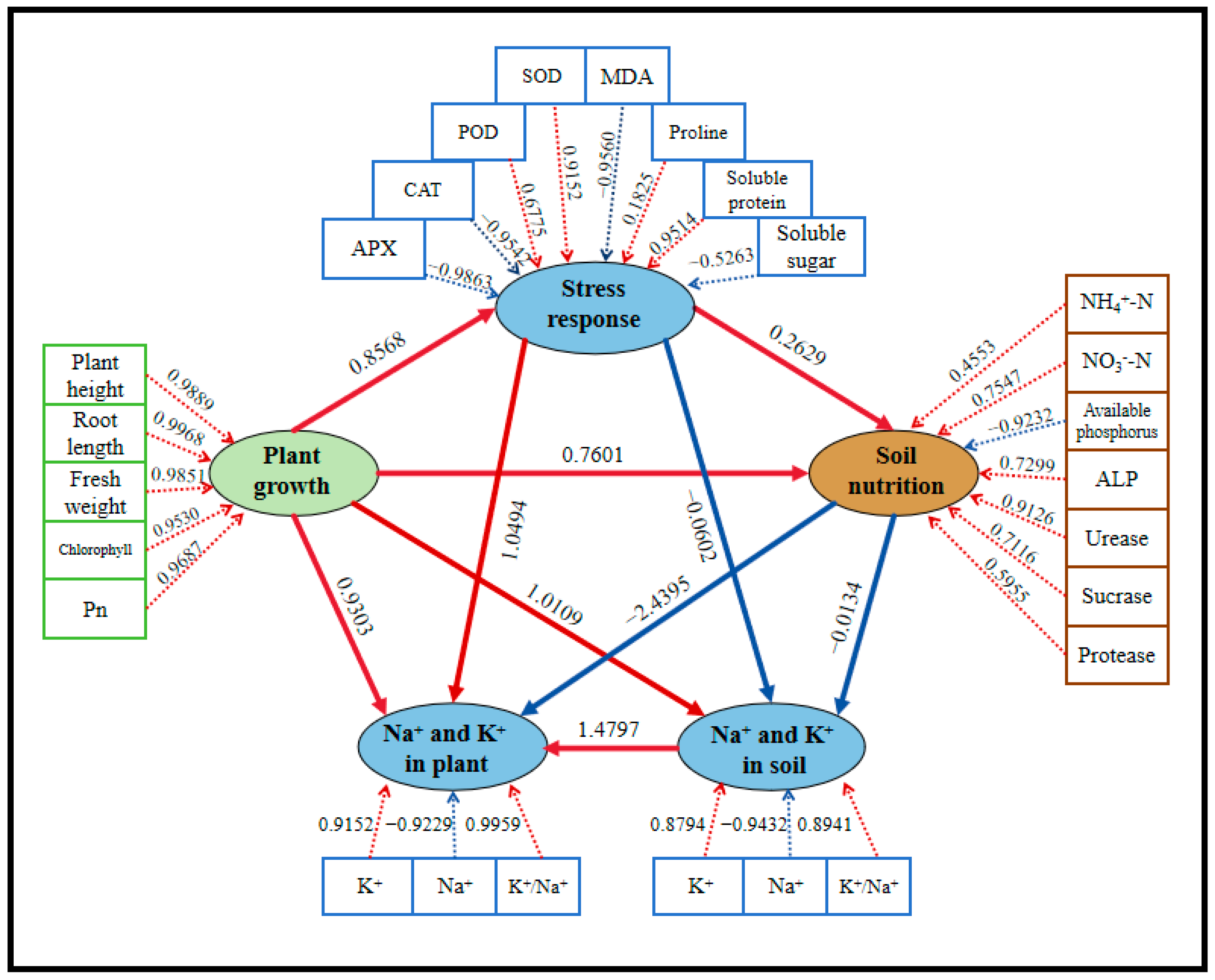
3.8. PLS-PM Analysis of Plant and Rhizosphere Soil Responses to Salt Stress and DA-JHY1 Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of DA on Growth Promotion Characteristics of Strain JHY1 Under Salt Stress
4.2. The Combined Application of DA and Strain JHY1 Has Synergistic Promoting Effect on Rice Growth Under Salt Stress
4.3. DA and Strain JHY1 Coordinate Salt Resistance Through Antioxidant Enzymes, Osmotic Substances, Lipid Peroxidation, and Ion Homeostasis
4.4. The Combined Application of DA and Strain JHY1 Improved Soil Fertility and Regulated Microbial Community Structure
4.5. DA and PGPR: Safety and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, B.; Huang, B. Mechanism of Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Characterization. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 701596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Gaurav, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Verma, J.P. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Biological Tools for the Mitigation of Salinity Stress in Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.J.; Drechsel, P.; Noble, A.D. Economics of Salt-Induced Land Degradation and Restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil Salinity and Sodicity in Drylands: A Review of Causes, Effects, Monitoring, and Restoration Measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 712831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrt, C.S.; Munns, R.; Burton, R.A.; Gilliham, M.; Wege, S. Root Cell Wall Solutions for Crop Plants in Saline Soils. Plant Sci. 2018, 269, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Runthala, A.; Khan, S.; Jha, P.N. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Reveals the Tolerance of Wheat to Salt Stress in Response to Enterobacter Cloacae Sbp-8. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Damodaran, P.N.; Roh, K.S. Influence of Salicylic Acid on Rubisco and Rubisco Activase in Tobacco Plant Grown under Sodium Chloride in Vitro. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vocciante, M.; Grifoni, M.; Fusini, D.; Petruzzelli, G.; Franchi, E. The Role of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (Pgpr) in Mitigating Plant’s Environmental Stresses. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Wang, Z.; Sha, W.; Song, S.; Qin, F.; Zhang, W. Role of Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria in Plant Machinery for Soil Heavy Metal Detoxification. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumawat, K.C.; Nagpal, S.; Sharma, P. Potential of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria-Plant Interactions in Mitigating Salt Stress for Sustainable Agriculture: A Review. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Godínez, L.J.; Aguirre-Noyola, J.L.; Martínez-Romero, E.; Arteaga-Garibay, R.I.; Ireta-Moreno, J.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M. A Look at Plant-Growth-Promoting Bacteria. Plants 2023, 12, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, D.; Pande, V.; Pandey, S.C.; Samant, M. Recent Advances in Pgpr and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Drought Stress Resistance. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardharajula, S.; Ali, S.Z.; Grover, M.; Reddy, G.; Bandi, V. Drought-Tolerant Plant Growth Promoting Bacillus Spp.: Effect on Growth, Osmolytes, and Antioxidant Status of Maize under Drought Stress. J. Plant Interact. 2011, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, X.; Chang, C.; Jia, D.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Dopamine Alleviates Salt-Induced Stress in Malus Hupehensis. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 584–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channer, B.; Matt, S.M.; Nickoloff-Bybel, E.A.; Pappa, V.; Agarwal, Y.; Wickman, J.; Gaskill, P.J. Dopamine, Immunity, and Disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 75, 62–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, E.; Ekinci, M.; Turan, M.; Yuce, M.; Ors, S.; Araz, O.; Torun, U.; Argin, S. Exogenous Dopamine Mitigates the Effects of Salinity Stress in Tomato Seedlings by Alleviating the Oxidative Stress and Regulating Phytohormones. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2024, 46, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.F.; El-Khawas, S.; El-Sherif, N.; Hassanein, R.A.; Emam, M.A.; Hassan, R.E. Expression of Aquaporin Gene (Ospip1-3) in Salt-Stressed Rice (Oryzasativa L.) Plants Pre-Treated with the Neurotransmitter (Dopamine). Plant Omics 2012, 5, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Liang, Q.; Wang, G. Effects of Dopamine Priming on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Rice under Salt Stress. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2021, 35, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shanab, W.A.; Diab, R.H. Dopamine Hydrochloride Alleviates the Salt-Induced Stress in Glycine Max (L.) Merr. Plant. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3474–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Overexpression of the Tyrosine Decarboxylase Gene Mdtydc Confers Salt Tolerance in Apple. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 180, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Liu, X.; Shan, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Dopamine and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Act Synergistically to Promote Apple Growth under Salt Stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 178, 104159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Du, P.; Zhang, J.; Ji, J.; Xu, J.; Liang, B. Dopamine Alleviates Cadmium Stress in Apple Trees by Recruiting Beneficial Microorganisms to Enhance the Physiological Resilience Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing and Soil Metabolomics. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B. Dopamine Alleviates Phloridzin Toxicity in Apple by Modifying Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Structure and Function. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 13001–13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Ji, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B. Dopamine Improves Apple Replant Disease Resistance by Regulating Physiological Resilience and Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 3025–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.N.M.R.B.; Zhang, J. Trends in Rice Research: 2030 and Beyond. Food Energy Secur. 2023, 12, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Ge, J.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Dai, Q. Rice Response to Salt Stress and Research Progress in Salt Tolerance Mechanism. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2022, 36, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, C.; Kumar, A.; Parshad, J.; Sharma, S.S.; Patra, A.; Dogra, P.; Yadav, G.K.; Dadhich, S.K.; Verma, R.; Kumawat, G.L. Microbial Diversity and Adaptation under Salt-Affected Soils: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, H.V.T.; Lavane, K.; Ty, T.V.; Downes, N.K.; Hong, T.T.K.; Kumar, P. Evaluation of the Impact of Drought and Saline Water Intrusion on Rice Yields in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Water 2022, 14, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.C. Rapid Analysis of Yeast Transformants Using Colony-Pcr. BioTechniques 1992, 13, 350. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Ji, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Song, W.J.; Guan, C. Combined Application of Allantoin and Strain Jit1 Synergistically or Additively Promotes the Growth of Rice under 2, 4-Dcp Stress by Enhancing the Phosphate Solubility, Improving Soil Enzyme Activities and Photosynthesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 282, 153941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bric, J.M.; Bostock, R.M.; Silverstone, S.E. Rapid in Situ Assay for Indoleacetic Acid Production by Bacteria Immobilized on a Nitrocellulose Membrane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R. Methods for Isolating and Characterizing Acc Deaminase-Containing Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria. Physiol. Plant. 2003, 118, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Ali, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, F.; Deng, H. Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of an Efficient Siderophore Producing Bacterium from Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J.B. Universal Chemical Assay for the Detection and Determination of Siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, E.J. The Colorimetric Determination of Phosphorus. Biochem. J. 1932, 26, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.S. Screening of Free-Living Rhizospheric Bacteria for Their Multiple Plant Growth Promoting Activities. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Usman, J.; Kaleem, F.; Omair, M.; Khalid, A.; Iqbal, M. Evaluation of Different Detection Methods of Biofilm Formation in the Clinical Isolates. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, B.; Lama, L.; Esposito, E.; Manca, M.C.; Improta, R.; Bellitti, M.R.; Duckworth, A.W.; Grant, W.D.; Gambacorta, A. Haloarcula Spp Able to Biosynthesize Exo- and Endopolymers. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 23, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshat, M.; Abbasi, A.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Sarikhani, M.R.; Chavan, D.D.; Rasoulnia, A. Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria (Pgpr) Induce Antioxidant Tolerance against Salinity Stress through Biochemical and Physiological Mechanisms. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2022, 28, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Leite, A.C.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Chlorophylls Extraction from Spinach Leaves Using Aqueous Solutions of Surface-Active Ionic Liquids. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 2, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, F.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F. Modulation of Exogenous Glutathione in Ultrastructure and Photosynthetic Prformance against Cd Stress in the Two Barley Genotypes Differing in Cd Tolerance. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 144, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, T.; Ali, S.; Seleiman, M.F.; Naveed, N.H.; Ali, A.; Ahmed, K.; Abid, M.; Rizwan, M.; Shahid, M.R.; Alotaibi, M.; et al. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Alleviates Drought Stress in Potato in Response to Suppressive Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Enzymes Activities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xu, S.; Zou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, F. Changes of Antioxidative Enzymes and Lipid Peroxidation in Leaves and Roots of Waterlogging-Tolerant and Waterlogging-Sensitive Maize Genotypes at Seedling Stage. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Applications of the Ninhydrin Reaction for Analysis of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins to Agricultural and Biomedical Sciences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barickman, T.C.; Simpson, C.R.; Sams, C.E. Waterlogging Causes Early Modification in the Physiological Performance, Carotenoids, Chlorophylls, Proline, and Soluble Sugars of Cucumber Plants. Plants 2019, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Qi, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Guan, C. Evaluation of Electrokinetic-Assisted Phytoremediation Efficiency of Dibutyl Phthalate Contaminated Soil by Maize (Zea Mays L.) under Different Electric Field Intensities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Song, W.; Ma, B.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Wang, G.; Guan, C.; Gao, X. The Alleviation of Salt Stress on Rice through Increasing Photosynthetic Capacity, Maintaining Redox Homeostasis and Regulating Soil Enzyme Activities by Enterobacter Sp. Jiv1 Assisted with Putrescine. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 280, 127590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Fu, W.; Wang, G.; Ji, J.; Guan, C. Phytoremediation of Dehp and Heavy Metals Co-Contaminated Soil by Rice Assisted with a Pgpr Consortium: Insights into the Regulation of Ion Homeostasis, Improvement of Photosynthesis and Enrichment of Beneficial Bacteria in Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, R.; He, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Effect of Various Phosphorus Levels on the Extraction of Cd, the Transformation of P, and Phosphorus-Related Gene During the Phytoremediation of Cd Contaminated Soil. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.; Guo, Q.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Comparative Analysis of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria’s Effects on Alfalfa Growth at the Seedling and Flowering Stages under Salt Stress. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Zeyad, M.T.; Syed, A.; Singh, U.B.; Mohamed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Elgorban, A.M.; Pichtel, J. Stress-Tolerant Endophytic Isolate Priestia Aryabhattai Bpr-9 Modulates Physio-Biochemical Mechanisms in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) for Enhanced Salt Tolerance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Wu, Y.; Tai, C.; Lin, I.; Wang, W.; Tseng, T.; Chuang, H. Examining the Transcriptomic and Biochemical Signatures of Bacillus Subtilis Strains: Impacts on Plant Growth and Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderlinde, E.M.; Harrison, J.J.; Muszynski, A.; Carlson, R.W.; Turner, R.J.; Yost, C.K. Identification of a Novel Abc Transporter Required for Desiccation Tolerance, and Biofilm Formation in Rhizobium Leguminosarum Bv Viciae 3841. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 71, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunkaew, T.; Kantachote, D.; Nitoda, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Ritchie, R.J. Characterization of Exopolymeric Substances from Selected Rhodopseudomonas Palustris Strains and Their Ability to Adsorb Sodium Ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, B.B.; Gomes, B.R.; Siqueira-Soares, R.d.C.; Soares, A.R.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. The Effects of Dopamine on Root Growth and Enzyme Activity in Soybean Seedlings. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e25477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.R.; Siqueira-Soares, R.C.; Dos-Santos, W.D.; Marchiosi, R.; Soares, A.R.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. The Effects of Dopamine on Antioxidant Enzymes Activities and Reactive Oxygen Species Levels in Soybean Roots. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e977704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berihu, M.; Somera, T.S.; Malik, A.; Medina, S.; Piombo, E.; Tal, O.; Cohen, M.; Ginatt, A.; Ofek-Lalzar, M.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; et al. A Framework for the Targeted Recruitment of Crop-Beneficial Soil Taxa Based on Network Analysis of Metagenomics Data. Microbiome 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Xu, K.; Yin, L.; Rao, Y.; Wang, B.; Jia, A. Dopamine, an Exogenous Quorum Sensing Signaling Molecule or a Modulating Factor in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa? Biofilm 2024, 8, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Plant Salt-Stress Responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhong, C.; Deng, R.; Fan, C. Transcriptome and Structure Analysis in Root of Casuarina Equisetifolia under Nacl Treatment. PeerJ 2021, 09, e12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, A.; Benazir, I.; Kumar, G. Reassessing the Role of Ion Homeostasis for Improving Salinity Tolerance in Crop Plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U. Drought and Salinity: A Comparison of Their Effects on Mineral Nutrition of Plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Raihan, M.R.H.; Masud, A.A.C.; Rahman, K.; Nowroz, F.; Rahman, M.; Nahar, K.; Fujita, M. Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense in Plants under Salinity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Sui, N. Sensitivity and Responses of Chloroplasts to Salt Stress in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1374086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A Review on Plant Responses to Salt Stress and Their Mechanisms of Salt Resistance. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Mishra, J.; Singh, P.; Fatima, T. Salt-Tolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Pseudomonas Atacamensis Kss-6 in Combination with Organic Manure Enhances Rice Yield, Improves Nutrient Content and Soil Properties under Salinity Stress. J. Basic Microbiol. 2024, 64, 2300767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Guan, C.; Ji, J. The Combined Use of a Plant Growth Promoting Bacillus Sp. Strain and Gaba Promotes the Growth of Rice under Salt Stress by Regulating Antioxidant Enzyme System, Enhancing Photosynthesis and Improving Soil Enzyme Activities. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Lin, K.; Gao, M.; Han, X.; Guan, Q.; Ji, X.; Yu, S.; Lu, L. Mitigation of Salt Stress in Rice by the Halotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Enterobacter Asburiae D2. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiedrych, A.; Stachowiak, J.; Szopa, J. The Catecholamine Potentiates Starch Mobilization in Transgenic Potato Tubers. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Cao, H.; Tian, X.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, K.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Dopamine Regulates Its Own Synthesis Via Mdorg2 to Improve Low-Nitrogen Tolerance in Apple Plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Gao, T.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, C.; Chen, Q.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Effects of Exogenous Dopamine on the Uptake, Transport, and Resorption of Apple Ionome under Moderate Drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Steve, N.; Liu, Q.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Physiological and Transcriptome Analyses of the Effects of Exogenous Dopamine on Drought Tolerance in Apple. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulma, A.; Szopa, J. Catecholamines Are Active Compounds in Plants. Plant Sci. 2007, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Exogenous Dopamine Improves Apple Fruit Quality Via Increasing Flavonoids and Soluble Sugar Contents. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 280, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Lan, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y. Dopamine Alleviates Chilling Stress in Watermelon Seedlings Via Modulation of Proline Content, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, and Polyamine Metabolism. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Giraldo, J.P.; Shabala, S. It Is Not All About Sodium: Revealing Tissue Specificity and Signalling Roles of Potassium in Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Plant Soil 2018, 431, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, D.; Feng, S. Chelation and Nanoparticle Delivery of Monomeric Dopamine to Increase Plant Salt Stress Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, A.; Lee, B.H.; Muñoz-Mayor, A.; Sharkhuu, A.; Miura, K.; Zhu, J.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M. Athkt1 Facilitates Na+ Homeostasis and K+ Nutrition in Planta. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2500–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, P. Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, H.U.R.; Zulfiqar, F.; Moosa, A.; Ashraf, M.; Zafar, Z.U.; Zhang, L.; Ahmed, N.; Kalaji, H.M.; Nafees, M.; Hossain, M.A.; et al. Salt Stress Proteins in Plants: An over View. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 999058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Dai, H.; Khan, W.A.; Guo, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Topping Inhibited Potassium Uptake Via Regulating Potassium Flux and Channel Gene Expression in Tobacco. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gan, Y.; Xu, B. Mechanisms of the Iaa and Acc-Deaminase Producing Strain of Trichoderma Longibrachiatum T6 in Enhancing Wheat Seedling Tolerance to Nacl Stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinia, M.; Kazemeini, S.A.; Dadkhodaie, A.; Sepehri, M.; Mahjenabadi, V.A.J.; Amjad, S.F.; Poczai, P.; El-Ghareeb, D.; Bassouny, M.A.; Abdelhafez, A.A. Co-Application of Acc Deaminase-Producing Rhizobial Bacteria and Melatonin Improves Salt Tolerance in Common Bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.) through Ion Homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamalero, E.; Bona, E.; Todeschini, V.; Lingua, G. Saline and Arid Soils: Impact on Bacteria, Plants, and Their Interaction. Biology 2020, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, R.J.L.; Manzanera, M. The Effects of Plant-Associated Bacterial Exopolysaccharides on Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Metabolites 2021, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Che, T.; Li, Y.; Zang, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; et al. The Nutrient Preferences of Rice and Wheat Influence Fluoranthene Uptake. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 987743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtaoui, N.; Rabiu, M.K.; Raklami, A.; Oufdou, K.; Hafidi, M.; Jemo, M. Phosphate-Dependent Regulation of Growth and Stresses Management in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 679916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankati, S.; Podile, A.R. Understanding Plant-Beneficial Microbe Interactions for Sustainable Agriculture. J. Spices Aromat. Crops 2018, 27, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saia, S.; Rappa, V.; Ruisi, P.; Abenavoli, M.R.; Sunseri, F.; Giambalvo, D.; Frenda, A.S.; Martinelli, F. Soil Inoculation with Symbiotic Microorganisms Promotes Plant Growth and Nutrient Transporter Genes Expression in Durum Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, B.A. Enzyme Activities as a Component of Soil Biodiversity: A Review. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavi; Mishra, R.K.; Sahu, P.K.; Mishra, V.; Jamal, H.; Varma, A.; Tripathi, S. Isolation and Characterization of Halotolerant Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria from Mangrove Region of Sundarbans, India for Enhanced Crop Productivity. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1122347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, K.; Shan, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Exogenous Dopamine and Overexpression of the Dopamine Synthase Gene Mdtydc Alleviated Apple Replant Disease. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 1524–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Sun, Y. Exogenous Dopamine Promotes Photosynthesis and Carbohydrate Metabolism of Downy Mildew-Infected Cucumber. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 295, 110842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, S.P.; El Aidy, S. Contributions of Gut Bacteria and Diet to Drug Pharmacokinetics in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Cao, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B. Improved Tolerance of Apple Plants to Drought Stress and Nitrogen Utilization by Modulating the Rhizosphere Microbiome Via Melatonin and Dopamine. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 980327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, R.; Yao, N.; Li, L. Diversity of Iaa-Producing Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from the Roots of Cymbidium Goeringii. Biodivers. Sci. 2010, 18, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Ali, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Mu, G.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.R.; Manghwar, H.; Wu, H.; et al. Salt Tolerant Bacillus Strains Improve Plant Growth Traits and Regulation of Phytohormones in Wheat under Salinity Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhatem, Z.F.; Merabet, C.; Tsaki, H. Plant Growth Promoting Actinobacteria, the Most Promising Candidates as Bioinoculants? Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 849911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, K.; Lv, D.; Jiang, S.; Sun, J.; Lin, H.; Sun, J. Inconsistent Response of Bacterial Phyla Diversity and Abundance to Soil Salinity in a Chinese Delta. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Alkawally, M.; Brady, A.L.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Damste, J.S.S.; Dunfield, P.F. Chryseolinea Serpens Gen. Nov., Sp Nov., a Member of the Phylum Bacteroidetes Isolated from Soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shaibani, M.M.; Mohamed, R.; Sidik, N.M.; Enshasy, H.A.E.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Noman, E.; Al-Mekhlafi, N.A.; Zin, N.M. Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Lin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Long, K.; Xie, Z.; Hu, W. Salt Stress Affects the Bacterial Communities in Rhizosphere Soil of Rice. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1505368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasankari, B.; Daniel, T.; Sobana, C. A Study on the Biopotentials of Bacterial Strains Isolated from Paddy Rhizosphere. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 5, 413–416. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dong, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, M.Z.; Liu, X.H.; Gu, X.L.; Antonietti, M.; Chen, Z.P. Sustainable Production of Dopamine Hydrochloride from Softwood Lignin. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecka, D. Significance and Roles of Proteus Spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaresan, N.; Jayakumar, V.; Kumar, K.; Thajuddin, N. Plant Growth-Promoting Effects of Proteus Mirabilis Isolated from Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum Mill) Plants. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2021, 44, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, J.; Ma, B.; Wang, R.; Li, T. Proteus sp. Strain JHY1 Synergizes with Exogenous Dopamine to Enhance Rice Growth Performance Under Salt Stress. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081820
Ji J, Ma B, Wang R, Li T. Proteus sp. Strain JHY1 Synergizes with Exogenous Dopamine to Enhance Rice Growth Performance Under Salt Stress. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081820
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Jing, Baoying Ma, Runzhong Wang, and Tiange Li. 2025. "Proteus sp. Strain JHY1 Synergizes with Exogenous Dopamine to Enhance Rice Growth Performance Under Salt Stress" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081820
APA StyleJi, J., Ma, B., Wang, R., & Li, T. (2025). Proteus sp. Strain JHY1 Synergizes with Exogenous Dopamine to Enhance Rice Growth Performance Under Salt Stress. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081820






