Composition and Structure of Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive Epinephelus morio via 16S rRNA Analysis and Functional Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Culture Conditions
2.2. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.3. Amplification, Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene, and Sequence Processing
2.4. Diversity Indices
2.5. Gut Microbiota Taxonomy of Wild and Captive E. morio
2.6. Metabolic Functional Prediction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
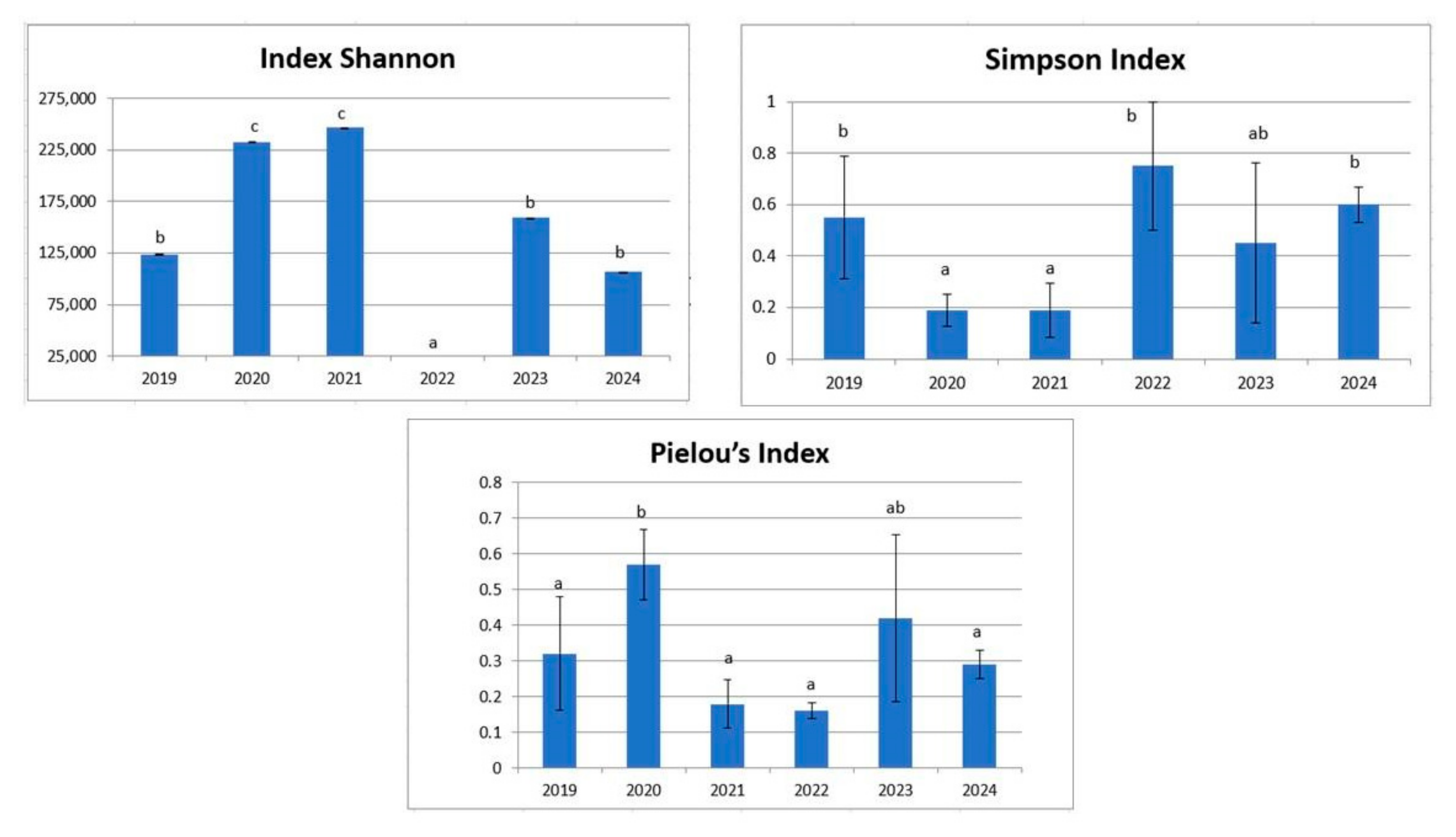
3.1. Alpha Diversity of the Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive E. morio
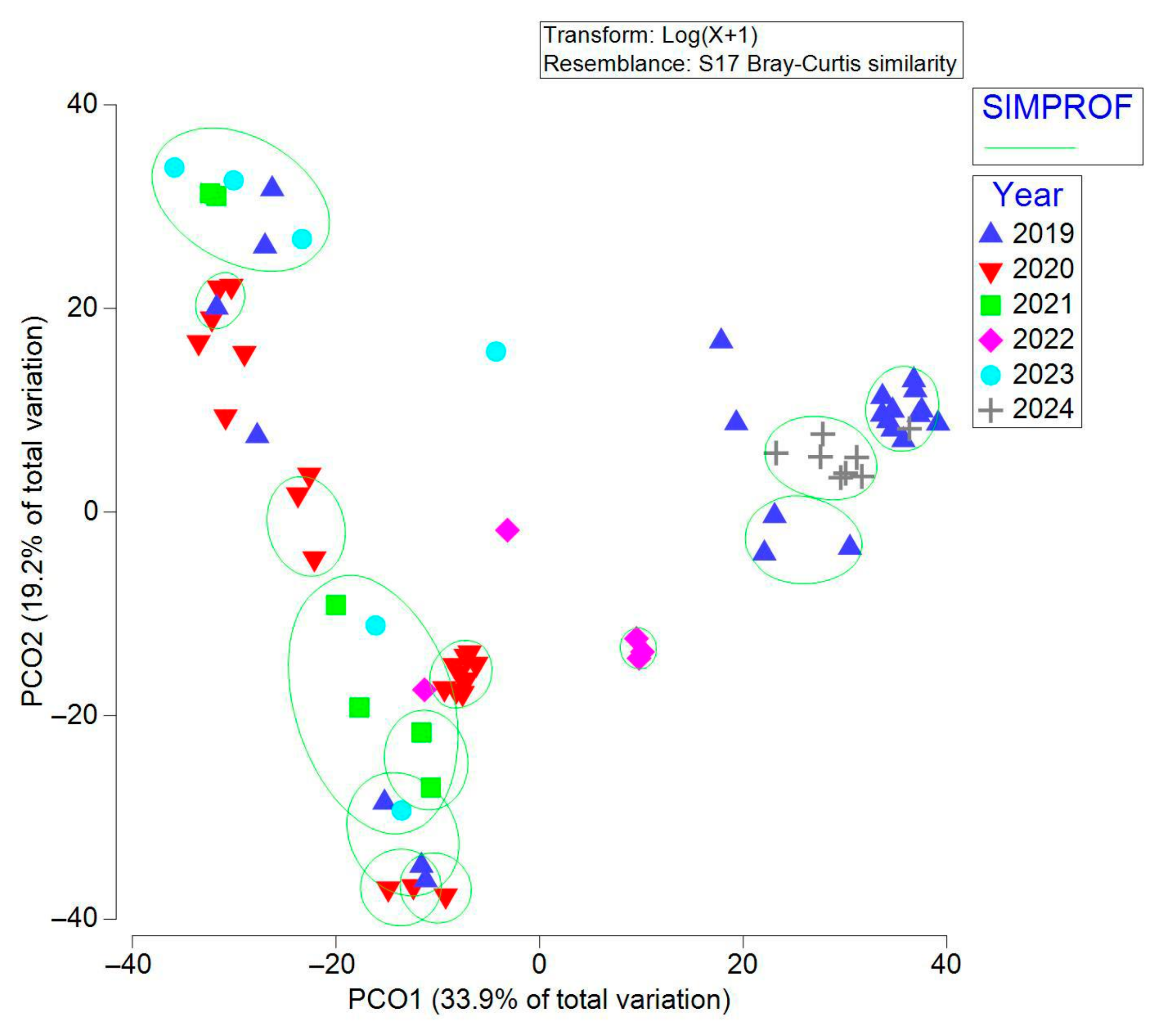
3.2. Beta Diversity Analysis of Wild and Captive E. morio Gut Microbiota
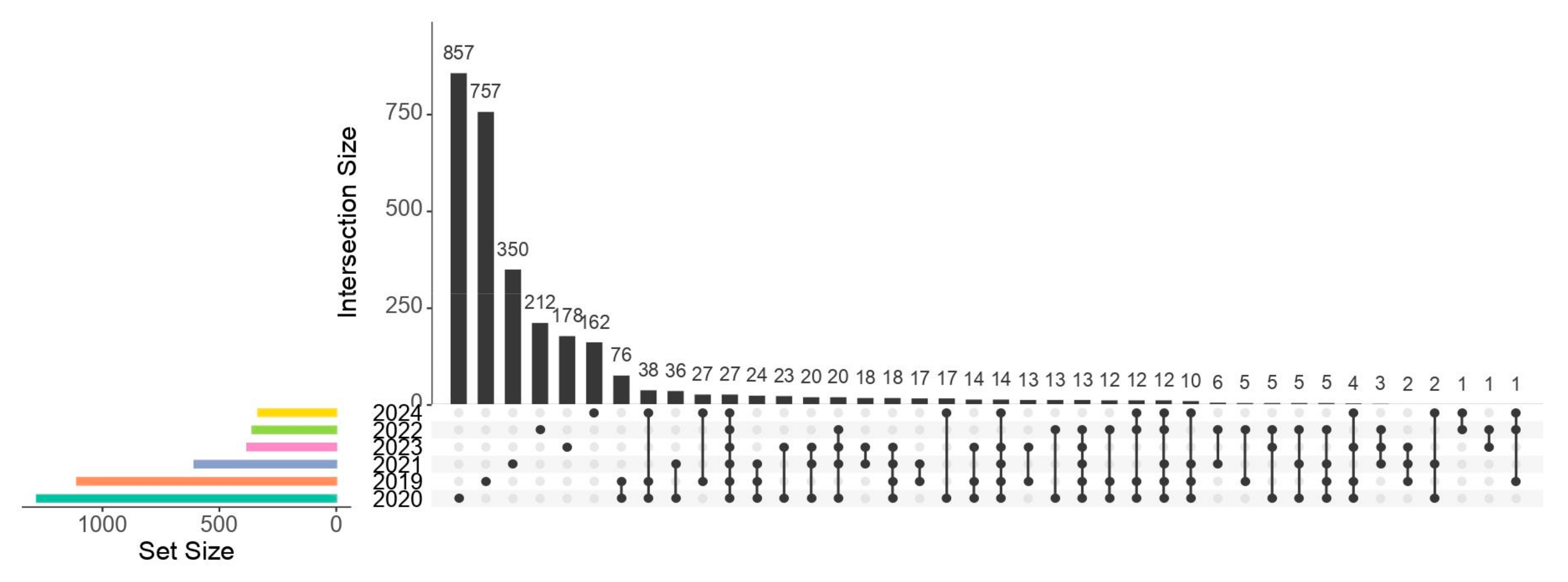
3.3. Changes in the Taxonomy of the Gut Microbiota of Wild E. morio During the Captivity Period
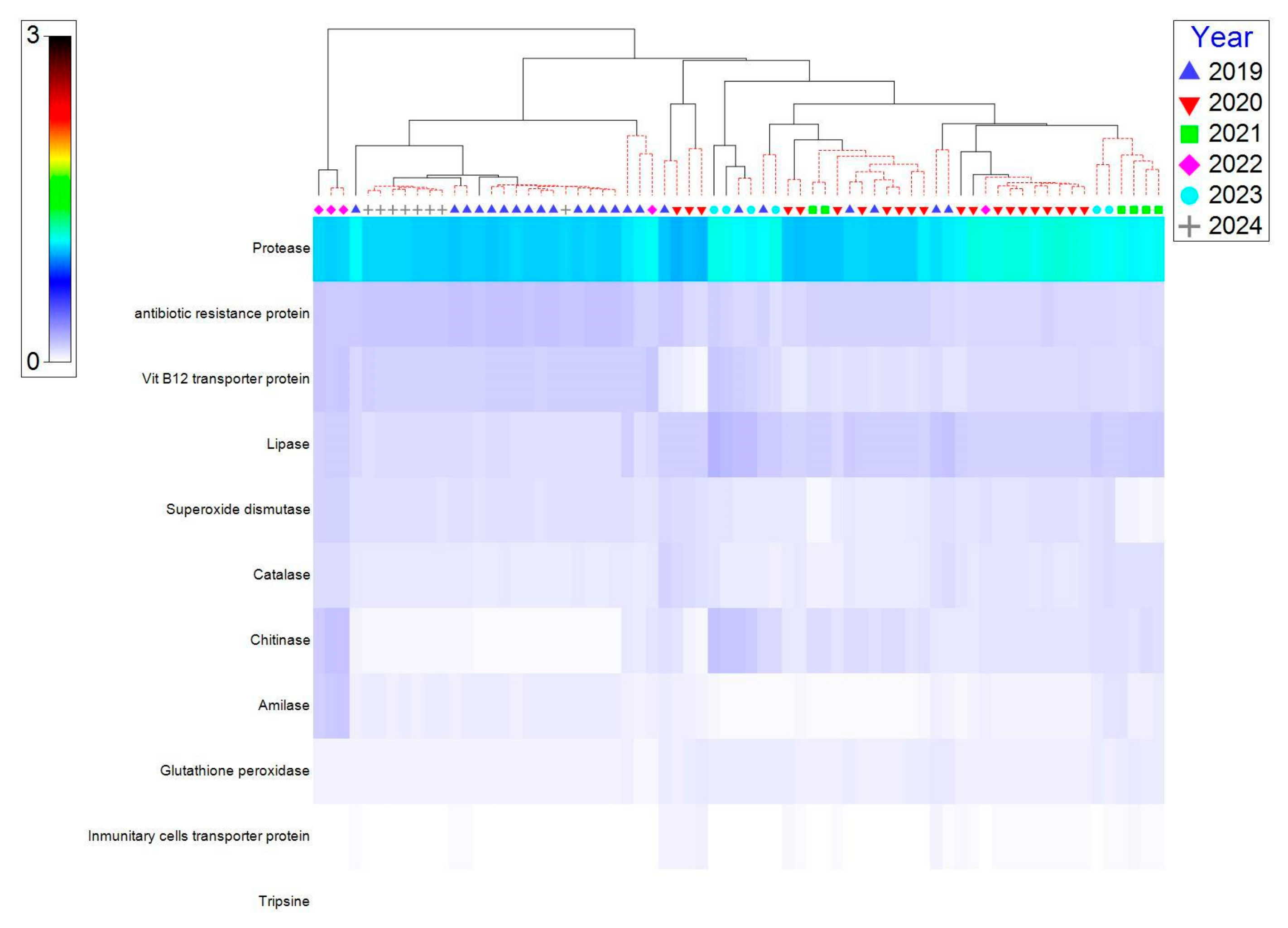
3.4. Functional Predictions of Gut Microbiota of E. morio
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity Findings
4.2. Core Microbiota
4.3. Gut Microbiota Taxonomy of Wild and Captive E. morio
4.4. Functional Implications
4.5. Environmental/Pollution Impact
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The gut microbiota of marine fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.V.; Foster, K.R. Why does the microbiome affect behaviour? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringo, E.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J.L.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, Å.; Merrifield, D.L. Effect of dietary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. A never-ending story? Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, K.T.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Classifying the uncultivated microbial majority: A place for metagenomic data in the Candidatus proposal. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 38, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A.M. Environmental and physiological factors shape the gut microbiota of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2017, 467, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, F.; Zheng, W.; Huang, Y.; Peng, H.; Hao, H.; Wang, K.J. Impact of captivity and natural habitats on gut microbiome in Epinephelus akaara across seasons. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, T.; Natrah, I.; Suyub, I.B.; Edward, M.J.; Kaman, N.; Samsudin, A.A. Comparative study of gut microbiota in wild and captive Malaysian Mahseer (Tor tambroides). Microbiol. Open 2019, 8, e00734. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanasiri, A.K.S.; Brunvold, L.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Korsnes, K.; Bergh, Ø.; Kiron, V. Changes in the intestinal microbiota of wild Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) upon captive rearing. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Mahmoud, A.O.; Dawood, f.; Kuldeep, D.; Hany, M.R.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: An overview. ISFSI 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. 2020. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.; Huttenhower, C. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. J. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gorley, R.N. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: Similarity profiles biota environment linkage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, K.D.; Brun, A.; Magallanes, M.; Brinkerhoff, J.; Laspiur, A.; Acosta, J.C.; Caviedes-Vidal, E.; Bordenstein, S.R. Gut microbial ecology of lizards: Insights into diversity in the wild, effects of captivity, variation across gut regions, and transmission. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, V.J.; Song, S.J.; Delsuc, F.; Prest, T.L.; Oliverio, A.M.; Korpita, T.M.; Alexiev, A.; Amato, K.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Kowalewski, M.; et al. The effects of captivity on the mammalian gut microbiome. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.H.; Lin, G.; Fu, G.H.; Wan, Z.Y.; Lee, M.; Wang, L.; Yue, G.H. The intestinal microbiome of fish under starvation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Fernández, G.; Ortiz-Alcantara, J.M.; Durruty-Lagunes, C.; Arena-Ortiz, L.A. Molecular identification of culturable gut microbiota of Epinephelus morio (red grouper) and its probiotic potential. Bol. Invest. Mar. Cost. 2025, 54, 32–52. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rhman, A.M.A.; Khattab, Y.A.E.; Shalaby, A.M.E. Micrococcus luteus and Pseudomonas species as probiotics for promoting the growth performance and health of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y.; Hlordzi, V.; Sakyi, M.E.; Afriyie, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.X. Mechanisms and the role of probiotic Bacillus in mitigating fish pathogens in aquaculture. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 819–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Geng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Deng, L.; Gan, W.; Wang, K.; Ou, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Zuo, Z.; et al. Acinetobacter lwoffii, an emerging pathogen for fish in Schizothorax genus in China. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszewska, M.; Dabrowska, A.; Murray, G.G.R.; Kett, S.M.; Vick, A.J.A.; Banister, S.C.; Pantoja Munoz, L.H.; Cunningham, P.; Welch, J.J.; Holmes, M.A.; et al. Absence of Staphylococcus aureus in wild populations of fish supports a spillover hypothesis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0485822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runft, D.L.; Mitchell, K.C.; Abuaita, B.H. Vibrio cholerae infection induces strain-specific modulation of the zebrafish intestinal microbiota. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00157-21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.R.; Ran, C.; Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.G. Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, W.B.; Lindsay, E.; Payne, C.J.; Brodie, C.; Kazlauskaite, R. The role of the gut microbiome in sustainable teleost aquaculture. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.J.J.; Tseng, Y.C.; Wu, J.L.; Lu, M.W. The alteration of intestinal microbiota profile and immune response in Epinephelus coioides during pathogen infection. Life 2021, 11, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Leiva, J.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.M.; Teles, A.; Tovar-Ramírez, D. Structure and predictive metabolic contribution of intestinal microbiota of Longfin yellowtail (Seriola rivoliana) juveniles in aquaculture systems. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 9627–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Ghosh, K.; Ringø, E. Enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from fish gut: A review. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 465–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatán, A.E.; Castillo, D.; Castañeda, A.E.; Feria, M.A.; Toledo, E.O.; Aguilar, J.L.; Cueva, M.D.; Motte, E. Characterization of the intestinal microbiota in snook (Centropomus sp.) and isolation of potential probiotic bacteria. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2020, 31, e16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, E.G.; Nealson, K.H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol. Bull. 1979, 151, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.J.; Lemos, L.M.; Osorio, C.R. Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae, a bacterium pathogenic for marine animals and humans. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettengill, E.A.; Pettengill, J.B.; Binet, R. Phylogenetic analyses of Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli for the identification of molecular epidemiological markers: Whole-genome comparative analysis does not support distinct genera designation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Carreno, F.C.; Hernandez-Cortes, P. Use of protease inhibitors in seafood products. In Seafood Enzymes: Utilization and Influence on Postharvest Seafood Quality; Haard, N.F., Simpson, B.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 531–540. [Google Scholar]
- Brulé, T.; Ordaz Avila, D.; Sánchez-Crespo, M.; Déniel, C. Seasonal and diel changes in diet composition of juvenile red grouper (Epinephelus morio) from Campeche Bank. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez, E.; Anderes, B.; Moreno, V.; Burgos, R. Aspectos de la conducta alimentaria del mero (Epinephelus morio) del Banco de Campeche. Cienc. Pesq. 2001, 14, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, F.; Song, K.; Wang, G.; Ling, F. Vitamin B12 produced by Cetobacterium somerae improves host resistance against pathogen infection through strengthening the interactions within gut microbiota. Microbiome 2023, 11, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, H.; Singh, D.N.; Singh, A.; Singh, Y.; La, R.; Negi, R.K. Gut microbiome of endangered Tor putitora (Ham.) as a reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes and pathogens associated with fish health. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, F.M.; Parada, R.B.; Sánchez-Cabrera, M.A.; Marguet, E.R.; Vallejo, M. Capacidad antioxidante de bacterias lácticas aisladas de peces e invertebrados marinos de la provincia de Chubut, Patagonia-Argentina. Rev. Cienc. Mar. Cost. 2023, 15, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Díaz, R.L.; Mercado-Silva, N.; Reynaga-Delgado, E.; Martínez-Rivera, L.M. Bacterial microbiota from wild freshwater fish utilized for subsistence in western Mexico. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2020, 36, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofepris. Available online: https://www.yucatan.com.mx/mexico/2019/07/08/cofepris-pide-no-visitar-estas-playas-por-exceso-de-bacterias-fecales.html (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Cofepris. Available online: https://24horasyucatan.mx/2024/03/25/playas-de-yucatan-declaradas-aptas-para-uso-recreativo-segun-monitoreo-de-cofepris/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 14 May 2025).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalvo-Fernández, G.; Ortiz-Alcantara, J.M.; Durruty-Lagunes, C.; Espinosa-Asuar, L.; Reyes-Sosa, M.B.; Arena-Ortiz, M.L. Composition and Structure of Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive Epinephelus morio via 16S rRNA Analysis and Functional Prediction. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081792
Montalvo-Fernández G, Ortiz-Alcantara JM, Durruty-Lagunes C, Espinosa-Asuar L, Reyes-Sosa MB, Arena-Ortiz ML. Composition and Structure of Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive Epinephelus morio via 16S rRNA Analysis and Functional Prediction. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081792
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalvo-Fernández, Grecia, Joanna M. Ortiz-Alcantara, Claudia Durruty-Lagunes, Laura Espinosa-Asuar, Mariela Beatriz Reyes-Sosa, and María Leticia Arena-Ortiz. 2025. "Composition and Structure of Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive Epinephelus morio via 16S rRNA Analysis and Functional Prediction" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081792
APA StyleMontalvo-Fernández, G., Ortiz-Alcantara, J. M., Durruty-Lagunes, C., Espinosa-Asuar, L., Reyes-Sosa, M. B., & Arena-Ortiz, M. L. (2025). Composition and Structure of Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive Epinephelus morio via 16S rRNA Analysis and Functional Prediction. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081792








