Biosensors in Microbial Ecology: Revolutionizing Food Safety and Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Starter Cultures
3. Composition of Food Microbial Communities
3.1. Microbial Diversity Across Food Types
3.2. Factors Shaping Microbial Ecology
3.3. Tools for Microbial Analysis
4. Microbial Interactions and Their Effects
4.1. Competition
4.2. Cooperation
4.3. Quorum Sensing (QS)
4.4. Fermented Food Examples
5. Case Studies and Regional Focus
5.1. Global and Regional Perspectives
5.1.1. Case Studies from Asia
5.1.2. Case Studies from Africa
5.1.3. Case Studies from Latin America
6. Detection and Monitoring Techniques
6.1. Types of Biosensors by Transduction Mechanism
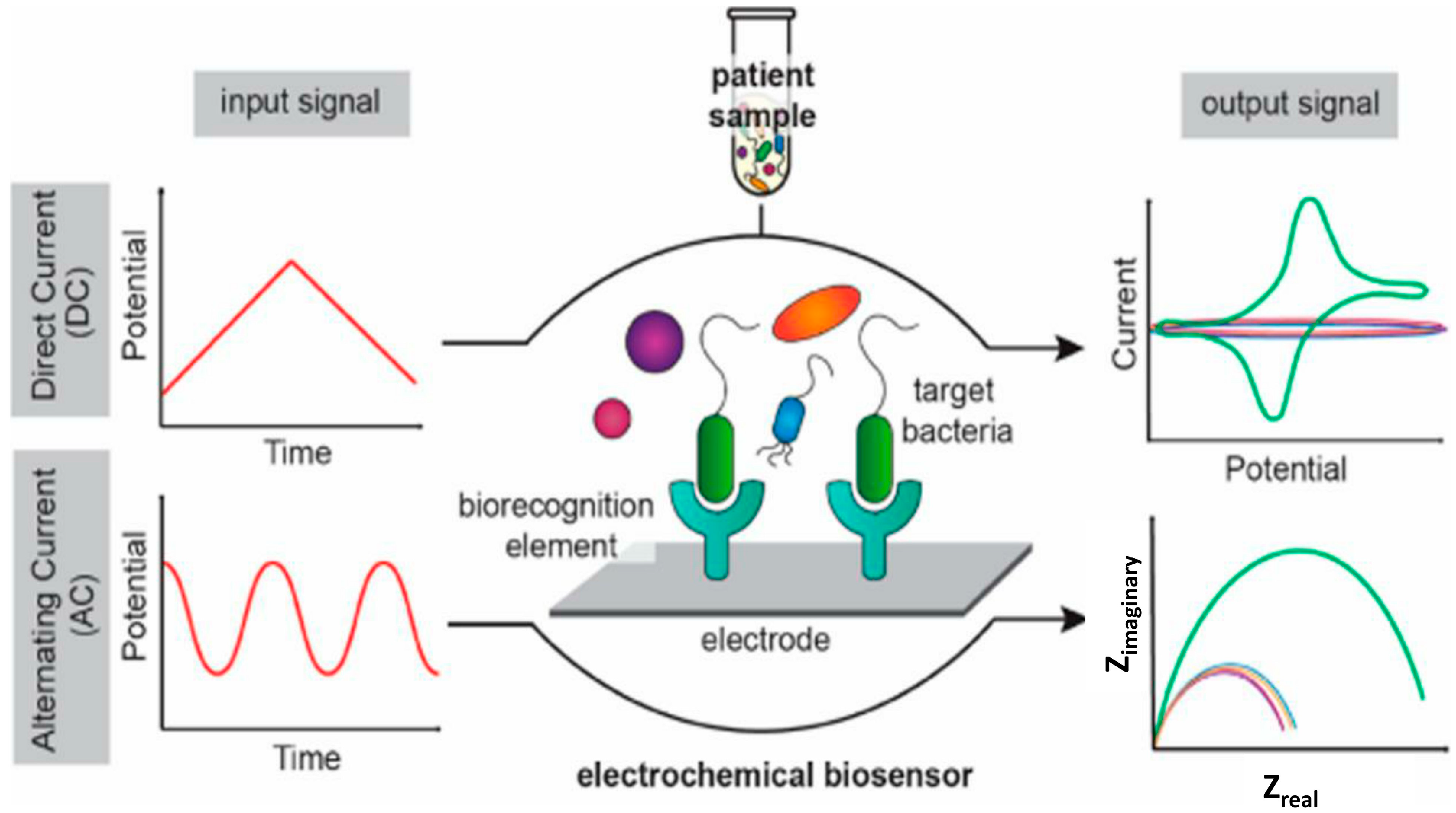
6.1.1. Electrochemical Biosensors
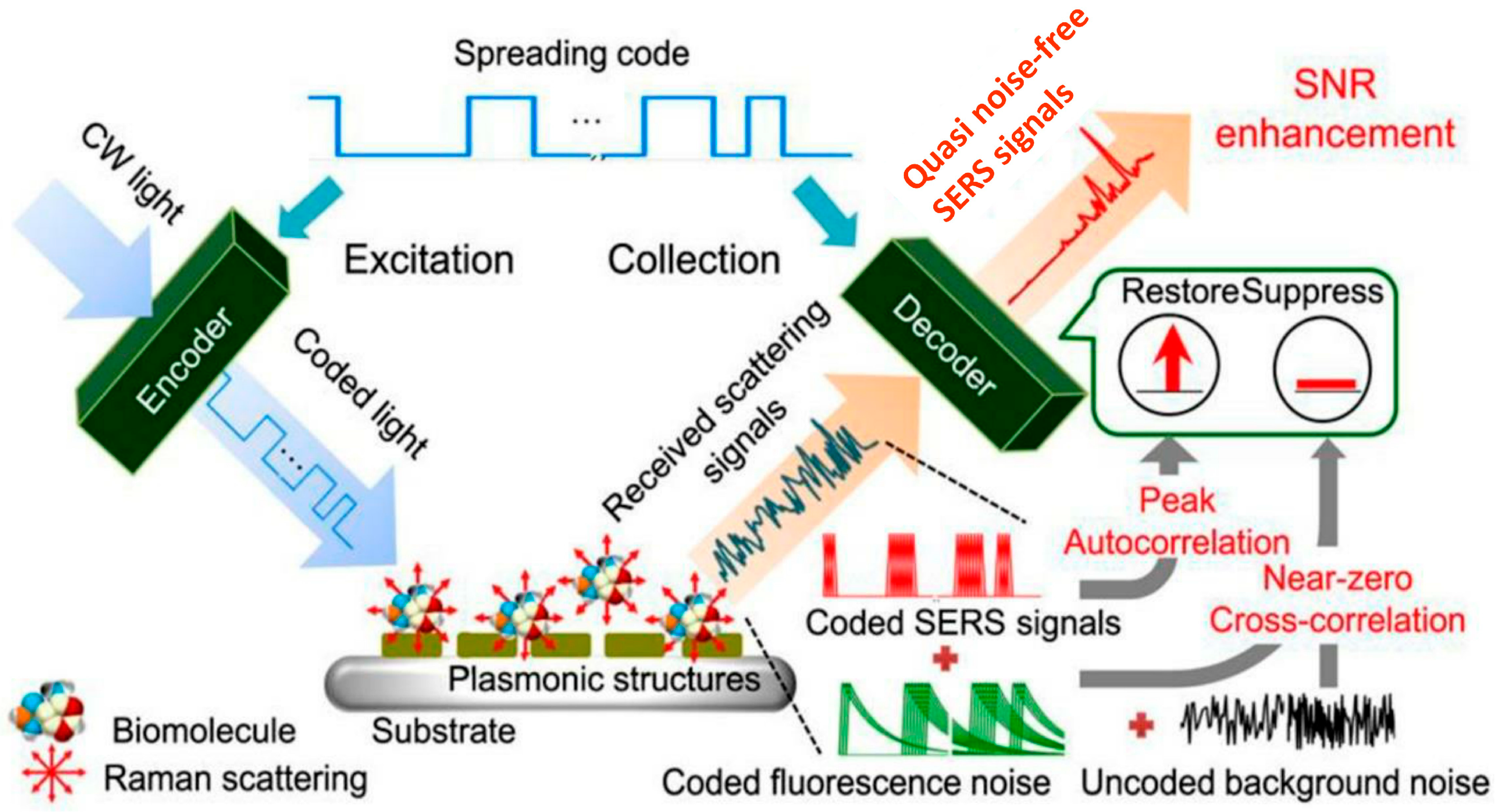
6.1.2. Optical Biosensors
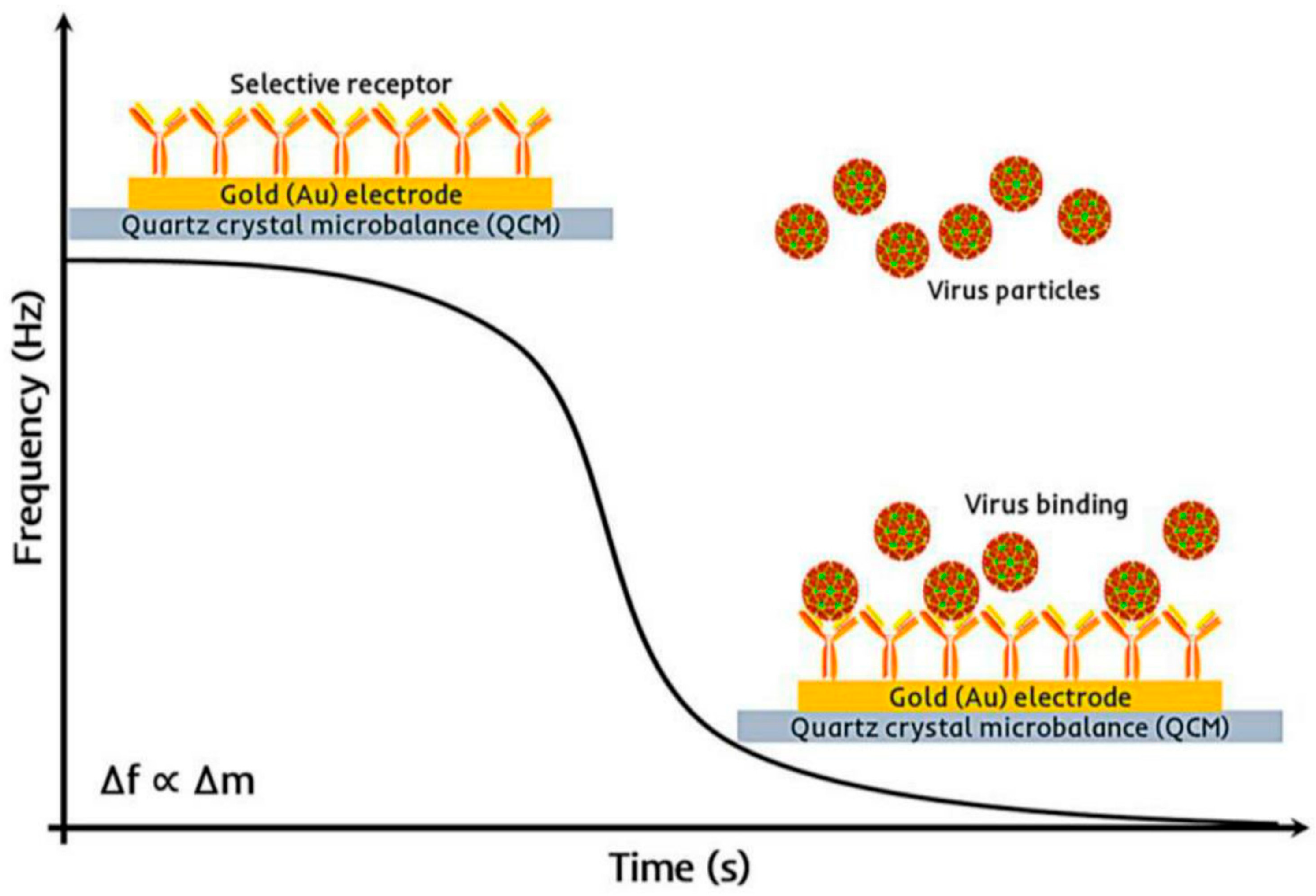
6.1.3. Piezoelectric Biosensors
6.1.4. Thermal Biosensors
6.1.5. Field-Effect Transistor (FET)
6.1.6. Lateral Flow Assay (LFA)
7. Control Strategies Based on Microbial Ecology
7.1. Bacteriocins
7.2. Biofilms
7.3. Probiotics
8. Decontamination Methods
8.1. Thermal Methods
8.2. Non-Thermal Methods
9. Chemical and Biocontrol Agents
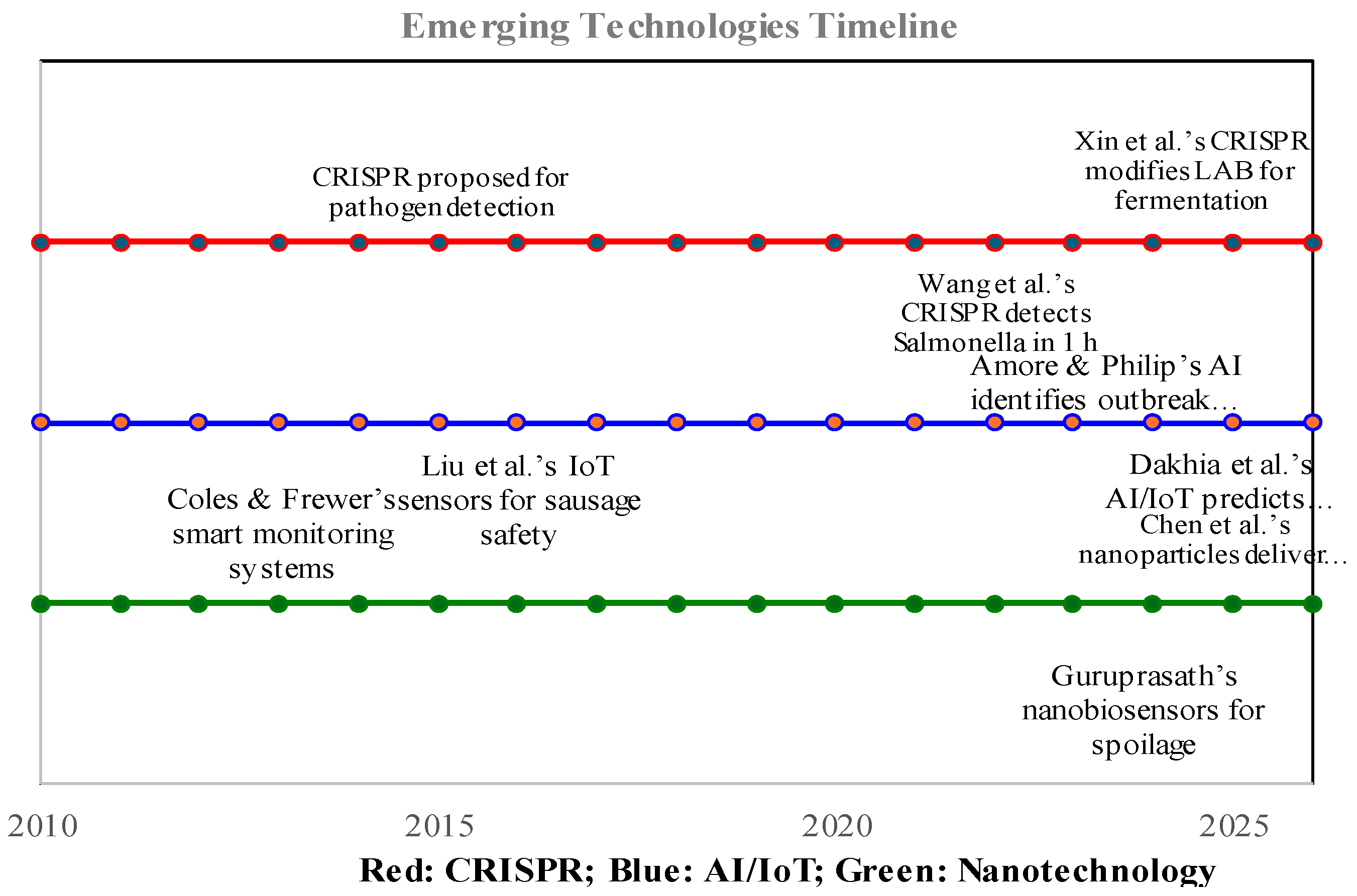
10. Emerging Technologies in Food Microbiology
10.1. CRISPR-Based Assays
10.2. AI and IoT Systems
10.3. Blockchain for Food Traceability
10.4. Nanotechnology-Enhanced Biosensors
11. Challenges and Future Directions
AMR: An Expanding Frontier
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smid, E.J.; Lacroix, C. Microbe–microbe interactions in mixed culture food fermentations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdichon, F.; Casaregola, S.; Farrokh, C.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gerds, M.L.; Hammes, W.P.; Harnett, J.; Huys, G.; Laulund, S.; Ouwehand, A. Food fermentations: Microorganisms with technological beneficial use. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 154, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, J.M.; Loessner, M.J.; Golden, D.A. Modern Food Microbiology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, M.P.; Diez-Gonzalez, F.; Hill, C. Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Law, J.W.-F.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercolini, D. High-throughput sequencing and metagenomics: Moving forward in the culture-independent analysis of food microbial ecology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, S.M.; Alocilja, E.C. A high density microelectrode array biosensor for detection of E. coli O157: H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-M.; Runyon, M.; Herrman, T.J.; Phillips, R.; Hsieh, J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: Aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control 2015, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, C.; Harms, H.; Maskow, T. Rapid calorimetric detection of bacterial contamination: Influence of the cultivation technique. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Xing, D. based bipolar electrode electrochemiluminescence switch for label-free and sensitive genetic detection of pathogenic bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10191–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Brul, S.; De Jong, A.; De Jonge, R.; Zwietering, M.H.; Ter Kuile, B.H. Future challenges to microbial food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, S79–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, O.S.; Doulgeraki, A.; Panagou, E.; Argyri, A.A. Recent advances and future perspective in probiotics isolated from fermented foods: From quality assessment to novel products. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1150175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, X.; Ge, C. Biofilm formation and control of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Molecules 2023, 28, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spacova, I.; Binda, S.; Ter Haar, J.A.; Henoud, S.; Legrain-Raspaud, S.; Dekker, J.; Espadaler-Mazo, J.; Langella, P.; Martín, R.; Pane, M. Comparing technology and regulatory landscape of probiotics as food, dietary supplements and live biotherapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1272754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomakina, G.Y.; Modestova, Y.A.; Ugarova, N. Bioluminescence assay for cell viability. Biochemistry 2015, 80, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farka, Z.k.; Juřík, T.s.; Pastucha, M.j.; Skládal, P. Enzymatic precipitation enhanced surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of Salmonella in powdered milk. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11830–11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.D. Recent findings on the viable but nonculturable state in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kračmarová, M.; Stiborova, H.; Horáčková, Š.; Demnerová, K. Rapid Detection of Microbial Contamination in UHT Milk: Practical Application in Dairy Industry. Czech J. Food Sci. 2018, 36, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Islam, M.S.; Jia, F.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, C. Flexible biosensors for food pathogen detection. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 2300898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmael, A.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Albiheyri, R.S.; Alharbi, M.G.; Filimban, A.A.; Alseghayer, M.S.; Almaneea, A.M.; Alhadlaq, M.A.; Ayubu, J.; Teklemariam, A.D. Fresh produce as a potential vector and reservoir for human bacterial pathogens: Revealing the ambiguity of interaction and transmission. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Adverse effects of thermal food processing on the structural, nutritional, and biological properties of proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 259–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magan, N.; Pavlou, A.; Chrysanthakis, I. Milk-sense: A volatile sensing system recognizes spoilage bacteria and yeasts in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 72, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.K.; Biswas, A.K. Modern techniques for rapid detection of meatborne pathogens. In Meat Quality Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 287–303. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippis, F.; Parente, E.; Ercolini, D. Metagenomics insights into food fermentations. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheryan, Z.; Raoof, J.-B.; Golabi, M.; Turner, A.P.; Beni, V. Diazonium-based impedimetric aptasensor for the rapid label-free detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food sample. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keba, A.; Rolon, M.L.; Tamene, A.; Dessie, K.; Vipham, J.; Kovac, J.; Zewdu, A. Review of the prevalence of foodborne pathogens in milk and dairy products in Ethiopia. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 109, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Wu, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, J.; Su, X. A label-free multi-functionalized graphene oxide based electrochemiluminscence immunosensor for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seawater and seafood. Talanta 2016, 147, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M. QCM immunosensor for the determination of Staphylococcus aureus antigen. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, G.; Rey, A.; Rivera, C.; Iregui, C.; Orozco, J. Amperometric biosensor based on a single antibody of dual function for rapid detection of Streptococcus agalactiae. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieuwerts, S.; Molenaar, D.; van Hijum, S.A.; Beerthuyzen, M.; Stevens, M.J.; Janssen, P.W.; Ingham, C.J.; de Bok, F.A.; de Vos, W.M.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E. Mixed-culture transcriptome analysis reveals the molecular basis of mixed-culture growth in Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7775–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhzadeh, E.; CHamsaz, M.; Turner, A.; Jager, E.; Beni, V. Label-free impedimetric biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium detection based on poly [pyrrole-co-3-carboxyl-pyrrole] copolymer supported aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, A.B.; Martin, N.; Wiedmann, M. Microbial food spoilage: Impact, causative agents and control strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Kidd, M. Rapid and sensitive detection of Campylobacter jejuni in poultry products using a nanoparticle-based piezoelectric immunosensor integrated with magnetic immunoseparation. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security 2023—Avoiding and Reducing Losses Through Investment in Resilience; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023; p. 7900en. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. WAAW/ACT Project is Helping the Plurinational State of Bolivia Tackle the Threat of Foodborne AMR. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/news-and-events/news-details/en/c/1724299/ (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Action to Support Implementation of Codex AMR Texts (ACT) Project: Progress in Cambodia; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2025.
- Somorin, Y.M.; Odeyemi, O.A.; Ateba, C.N. Salmonella is the most common foodborne pathogen in African food exports to the European Union: Analysis of the Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (1999–2019). Food Control 2021, 123, 107849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Z. Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogens: Current perspective and challenges. Foods 2023, 12, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Altemimi, A.B.; Alhelfi, N.; Ibrahim, S.A. Application of biosensors for detection of pathogenic food bacteria: A review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.-C.; Bridgman, R.C. Magnetic nanoparticles enhanced surface Plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in Romaine lettuce. Sensors 2022, 22, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fande, S.; Amreen, K.; Sriram, D.; Goel, S. Microfluidic electrochemical device for real-time culturing and interference-free detection of Escherichia coli. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1237, 340591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forinová, M.; Pilipenco, A.; Lynn, N.S.; Obořilová, R.; Šimečková, H.; Vrabcová, M.; Spasovová, M.; Jack, R.; Horák, P.; Houska, M. A reusable QCM biosensor with stable antifouling nano-coating for on-site reagent-free rapid detection of E. coli O157: H7 in food products. Food Control 2024, 165, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Bodkhe, G.A.; Cong, C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M. Electrohydrodynamic-printed ultrathin Ti3C2Tx-MXene field-effect transistor for probing aflatoxin B1. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Sun, X.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, F. New advances in lateral flow immunoassay (LFI) technology for food safety detection. Molecules 2022, 27, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, S.; Gupta, P.; Yadav, S.P.S.; Raj, D.; Singh, G.; Chauhan, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Martín-Ortega, E.; Chiussi, S.; Kant, K. Lateral flow assays: Progress and evolution of recent trends in point-of-care applications. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 28, 101188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Luo, Q.; Wei, C.; Deng, X.; Liang, H.; Wei, J.; Gong, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Liao, X. Electrochemical biosensing for E. coli detection based on triple helix DNA inhibition of CRISPR/Cas12a cleavage activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1285, 342028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigoli, M.; Krupa, M.P.; Hooyberghs, G.; Lowdon, J.W.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B. Electrochemical Sensors for Antibiotic Detection: A Focused Review with a Brief Overview of Commercial Technologies. Sensors 2024, 24, 5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Ramírez, A.Y.; González-Estrada, R.R.; Chacón-López, M.A.; de Lourdes García-Magaña, M.; Montalvo-González, E.; Álvarez-López, A.; Rodríguez-López, A.; López-García, U.M. Detection of foodborne pathogens in contaminated food using nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 693, 115600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szelenberger, R.; Cichoń, N.; Zajaczkowski, W.; Bijak, M. Application of Biosensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins for the Improvement of Food Safety. Toxins 2024, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbelkar, A.A.; Furst, A.L. Electrochemical diagnostics for bacterial infectious diseases. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashini, M.; Shanmugasundaram, S.; Sunil, C. Surface plasmon biosensing for the detection of foodborne pathogens. In Biosensors for Foodborne Pathogens Detection; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 195–221. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Zu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Qin, X.; Xu, W. An overview of rapid detection methods for Salmonella. Food Control 2024, 167, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.-U.; Sikder, R.; Tripathi, M.; Zahan, M.; Ye, T.; Gnimpieba Z., E.; Jasthi, B.K.; Dalton, A.B.; Gadhamshetty, V. Machine learning-assisted raman spectroscopy and SERS for bacterial pathogen detection: Clinical, food safety, and environmental applications. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.A.; Tran, T.T.V.; Doan, V.D.; Vo, G.N.; Tran, V.H.; Jeong, H.; Vo, T.T.T. Advanced nano engineering of surface-enhanced Raman scattering technologies for sensing applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 38, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Länge, K. Bulk and surface acoustic wave biosensors for milk analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yuan, R.; Fu, H.; Xu, Z.; Wei, S. Foodborne pathogen detection using surface acoustic wave biosensors: A review. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 37087–37103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, A.; Mujahid, A.; Schirhagl, R.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Latif, U.; Feroz, S. Gravimetric viral diagnostics: QCM based biosensors for early detection of viruses. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkovsky, D.B.; Kerry, J.P. Oxygen sensor-based respirometry and the landscape of microbial testing methods as applicable to food and beverage matrices. Sensors 2023, 23, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D. Measuring Metabolism and Bioenergetic Profiles of Biofilm: Isothermal Calorimetry, Differential Scanning Calorimetry, and Future of Chip Calorimetry. Anal. Methodol. Biofilm Res. 2021, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, K.; Danielsson, B. Principles and applications of thermal biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvandi, H.; Asadi, F.; Rezayan, A.H.; Hajghassem, H.; Rahimi, F. Ultrasensitive biosensor based on MXene-GO field-effect transistor for the rapid detection of endotoxin and whole-cell E. coli in human blood serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1348, 343816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyez, T.; Imran, A.B. Electrochemical Nanobiosensors Approaches for Rapid Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. Nano-Biosens. Technol. Diagn. Infect. Dis. 2025, 197–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, P.; Xiao, M.; Li, T.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Recent advances in the detection of pathogenic microorganisms and toxins based on field-effect transistor biosensors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 9161–9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jallow, A.; Nidiaye, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P.; Tang, X. Improvement of the sensitivity of lateral flow systems for detecting mycotoxins: Up-to-date strategies and future perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ren, S.; Gao, Z.; Chen, A. Dual-competitive lateral flow aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B1 in food and feedstuffs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, L.; Xing, K.; Lu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lai, W.; Chen, T. Nanozyme-based lateral flow assay for the sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5770–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.; Xu, Y. Fast detection of Escherichia coli in food using nanoprobe and ATP bioluminescence technology. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5378–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyaina, M.; Rasco, B.; Sablani, S.S. Rapid methods of microbial detection in dairy products. Food Control 2020, 110, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, D.A.; Lei, J.; Rossiana, N.; Syaputri, Y. Biopreservation of Food Using Bacteriocins From Lactic Acid Bacteria: Classification, Mechanisms, and Commercial Applications. Int. J. Microbiol. 2024, 2024, 8723968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujato, S.A.; Mercanti, D.J.; Briggiler Marcó, M.; Capra, M.L.; Quiberoni, A.; Guglielmotti, D.M. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Strategies for the bioprotection of dairy foods. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 1439891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.J.; Teichmann, L.; Fante, N.; Crauwels, P.; Grünberger, A.; Neddermann, T.; Riedel, C.U. High-throughput detection of potential bacteriocin producers in a large strain library using live fluorescent biosensors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1405202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Du, X. Electrochemical biosensors for detection of foodborne pathogens. Micromachines 2019, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozoglu, O.; Uzunoglu, A.; Unal, M.A.; Gumustas, M.; Ozkan, S.A.; Korukluoglu, M.; Altuntas, E.G. Electrochemical detection of lactate produced by foodborne presumptive lactic acid bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2023, 135, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, A.; Ochani, S.; Nazir, A.; Fatima, B.; Ochani, K.; Al Hasibuzzaman, M.; Ullah, K. Rising trends of foodborne illnesses in the US. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 2280–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouhagger, A.; Celiešiūtė-Germanienė, R.; Bakute, N.; Stirke, A.; Melo, W.C. Electrochemical biosensors on microfluidic chips as promising tools to study microbial biofilms: A review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1419570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, A.; Shehzad, A.; Niazi, S.; Zahid, A.; Ashraf, W.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Riaz, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Khan, I.M. Probiotics: Mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. Activity of cecropin P1 and FA-LL-37 against urogenital microflora. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarita, B.; Samadhan, D.; Hassan, M.Z.; Kovaleva, E.G. A comprehensive review of probiotics and human health-current prospective and applications. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1487641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistyakov, V.A.; Prazdnova, E.V.e.; Mazanko, M.S.; Bren, A.B. The use of biosensors to explore the potential of probiotic strains to reduce the SOS response and mutagenesis in bacteria. Biosensors 2018, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazanko, M.; Prazdnova, E.; Kulikov, M.; Maltseva, T.; Rudoy, D.; Chikindas, M. Antioxidant and antimutagenic properties of probiotic Lactobacilli determined using LUX-biosensors. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 155, 109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottinghaus, A.G.; Amrofell, M.B.; Moon, T.S. Biosensing in smart engineered probiotics. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 1900319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra, M.; Danino, T.; Garrido, D. Engineered probiotics for detection and treatment of inflammatory intestinal diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramaniam, V.; Martinez-Monteagudo, S.I.; Gupta, R. Principles and application of high pressure–based technologies in the food industry. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 435–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, N.; Raghavarao, K.; Balasubramaniam, V.; Niranjan, K.; Knorr, D. Opportunities and challenges in high pressure processing of foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 69–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, S.; Karatzas, K.A. Inactivation of Escherichia coli K12 in phosphate buffer saline and orange juice by high hydrostatic pressure processing combined with freezing. LWT 2021, 136, 110313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cap, M.; Paredes, P.F.; Fernández, D.; Mozgovoj, M.; Vaudagna, S.R.; Rodriguez, A. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on Salmonella spp inactivation and meat-quality of frozen chicken breast. LWT 2020, 118, 108873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyamkondan, S.; Jayas, D.; Holley, R. Pulsed electric field processing of foods: A review. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, I.; Raso, J.; Palop, A.; Sala, F.J. Influence of different factors on the inactivation of Salmonella senftenberg by pulsed electric fields. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 55, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, F.J.; Parniakov, O.; Pereira, S.A.; Wiktor, A.; Grimi, N.; Boussetta, N.; Saraiva, J.A.; Raso, J.; Martin-Belloso, O.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. Current applications and new opportunities for the use of pulsed electric fields in food science and industry. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 773–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Yue, Y.; Yang, F. Recent Advances in CRISPR/Cas System-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Li, C.; Yan, C.; Huang, L.; Qin, P. Development of a CRISPR/Cas9-integrated lateral flow strip for rapid and accurate detection of Salmonella. Food Control 2022, 142, 109203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Guo, T.; Qiao, M. Current application and future prospects of CRISPR-Cas in lactic acid Bacteria: A review. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakhia, Z.; Russo, M.; Merenda, M. AI-Enabled IoT for Food Computing: Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions. Sensors 2025, 25, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amore, A.; Philip, S. Artificial intelligence in food biotechnology: Trends and perspectives. Front. Ind. Microbiol. 2023, 1, 1255505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, J.F.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. Future challenges on the use of blockchain for food traceability analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruprasath, N.; Sankarganesh, P.; Adeyeye, S.; Babu, A.S.; Parthasarathy, V. Review on emerging applications of nanobiosensor in food safety. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3950–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, N. Intelligent biosensors promise smarter solutions in food safety 4.0. Foods 2024, 13, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chatterjee, S.; Lian, X.; Traylor, Z.; Sattiraju, S.R.; Xiao, Y.; Dilliard, S.A.; Sung, Y.-C.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.M. In vivo editing of lung stem cells for durable gene correction in mice. Science 2024, 384, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coles, D.; Frewer, L.J. Nanotechnology applied to European food production–A review of ethical and regulatory issues. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelada-Guillén, G.A.; Sebastián-Avila, J.L.; Blondeau, P.; Riu, J.; Rius, F.X. Label-free detection of Staphylococcus aureus in skin using real-time potentiometric biosensors based on carbon nanotubes and aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sui, C.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ai, S. Tungsten disulfide (WS 2) nanosheet-based photoelectrochemical aptasensing of chloramphenicol. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2022–2023. EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
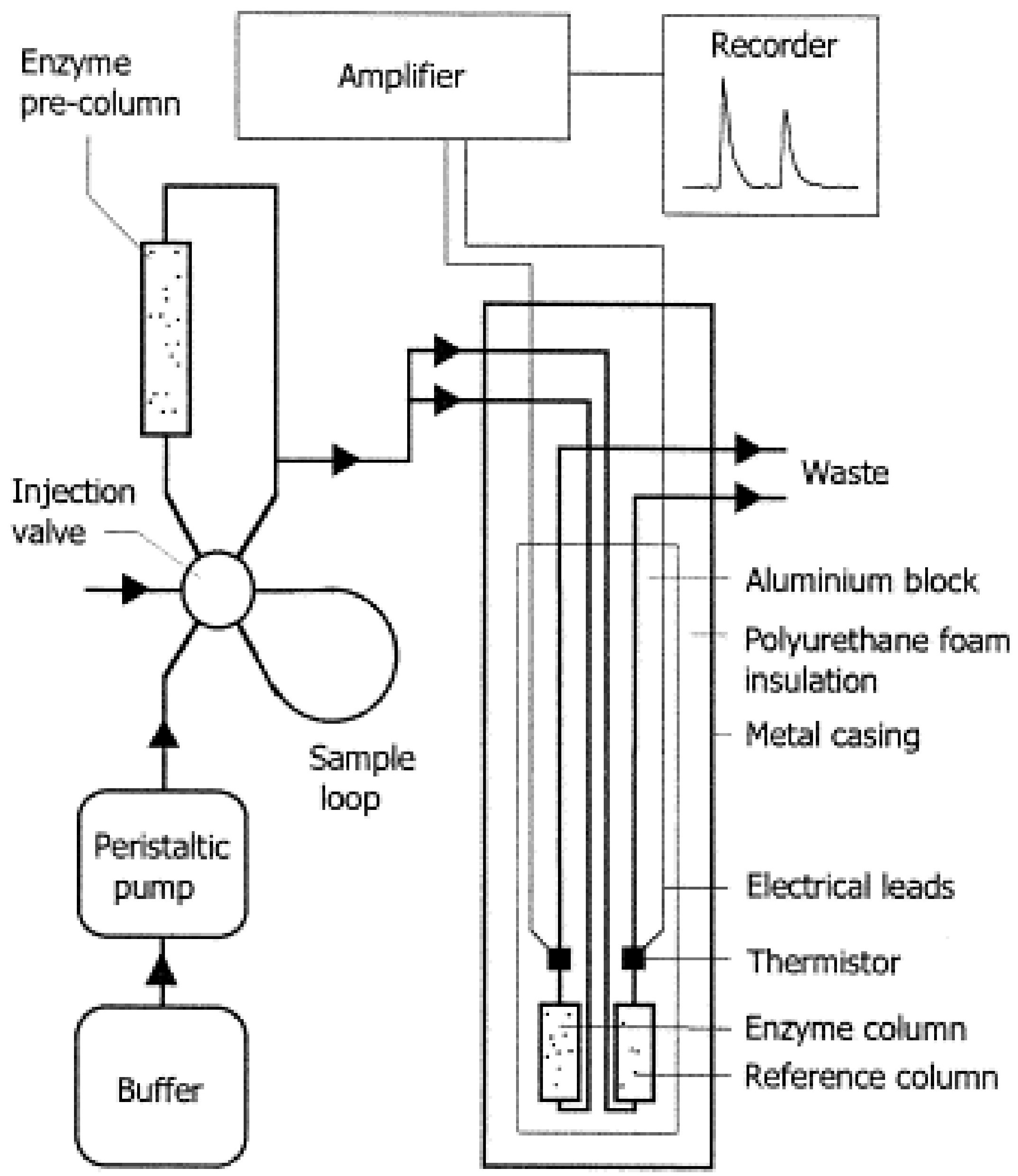
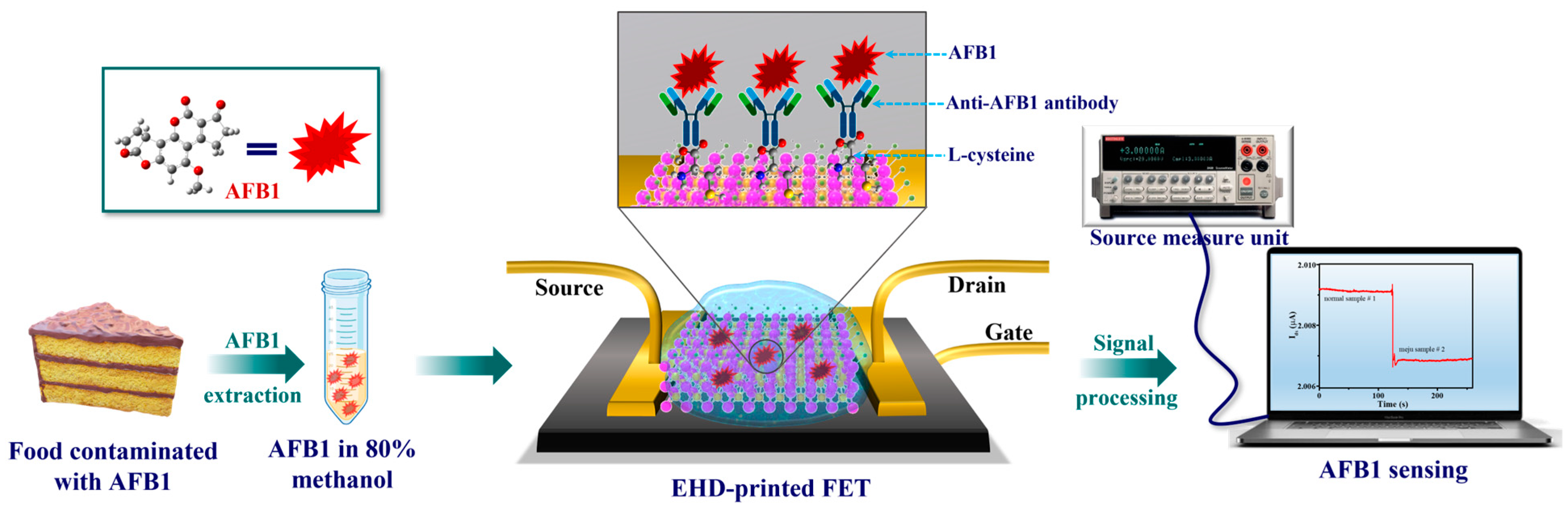
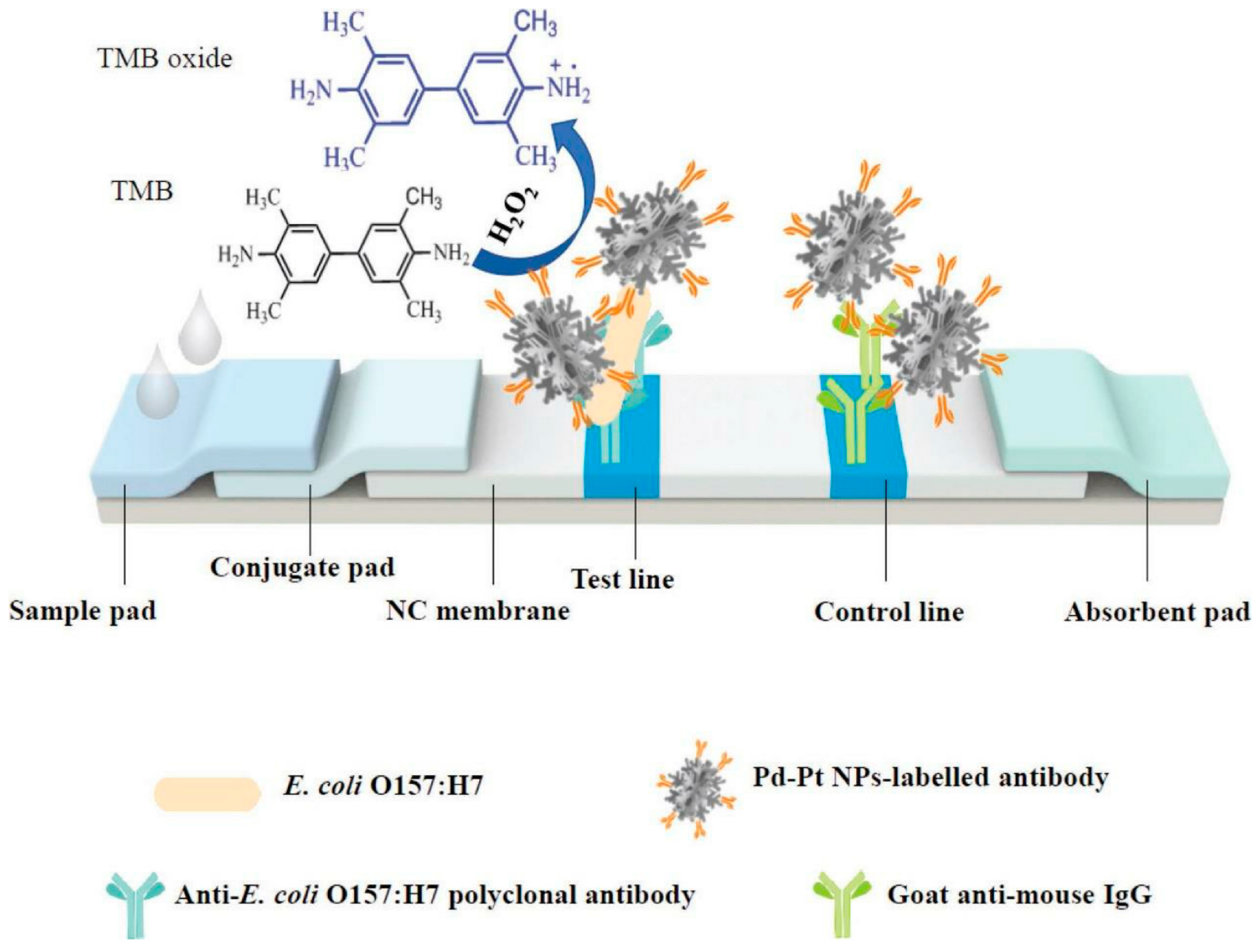
| Food Category | Predominant Microbial Types | Key Roles | Biosensor Detection Examples | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy | LAB (Lactobacillus, Lactococcus), yeasts (Saccharomyces), molds (Penicillium) | Fermentation, flavor development, preservation | pH sensors (LAB), SPR (Listeria) | [2,28] |
| Meat/Poultry | LAB, CNS (Staphylococcus), spoilage bacteria (Pseudomonas, Brochothrix), pathogens (Listeria, Salmonella) | Fermentation, spoilage, safety risks | Amine sensors (Pseudomonas) | [7,18] |
| Fresh Produce | Gram-negative bacteria (Pseudomonas, Enterobacteriaceae), fungi, pathogens (Salmonella, E. coli O157:H7) | Spoilage, safety risks, plant adaptation | SPR (Salmonella) | [19,21,22] |
| Interaction | Food Example | Biosensor Type | Detected Signal | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Competition | Cheese | Electrochemical | Bacteriocins | [2,27] |
| Cooperation | Yogurt | Optical | Volatile compounds | [9,31] |
| Quorum sensing | Meat | QCM | Biofilm mass | [21,32] |
| Biosensor Type | Detection Method | Example Pathogen | LOD (CFU/mL) | Detection Time | Advantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical (SPR) | Surface plasmon resonance | Salmonella | 12 | 20 min | High sensitivity, label-free | [40] |
| Electrochemical | Amperometric/impedimetric | E. coli | 0.35 | 30 min | Cost-effective, rapid | [41] |
| QCM | Mass change detection | E. coli | 102 | 30 min | High sensitivity, label-free | [42] |
| FET-based | Charge-sensitive transistor readout | Aflatoxin B1, | 5.6 ppb | ~2 min | Ultra-sensitive, label-free, scalable electronics | [43] |
| LFA (strip-based) | Lateral capillary flow, colorimetric/SERS | Aflatoxin B1, Listeria, Salmonella | <1 ng/mL; 103 CFU/mL | 10–20 min | Rapid, low-cost, field-deployable | [44,45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodkhe, G.A.; Kumar, V.; Li, X.; Pei, S.; Ma, L.; Kim, M. Biosensors in Microbial Ecology: Revolutionizing Food Safety and Quality. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071706
Bodkhe GA, Kumar V, Li X, Pei S, Ma L, Kim M. Biosensors in Microbial Ecology: Revolutionizing Food Safety and Quality. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071706
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodkhe, Gajanan A., Vishal Kumar, Xingjie Li, Shichun Pei, Long Ma, and Myunghee Kim. 2025. "Biosensors in Microbial Ecology: Revolutionizing Food Safety and Quality" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071706
APA StyleBodkhe, G. A., Kumar, V., Li, X., Pei, S., Ma, L., & Kim, M. (2025). Biosensors in Microbial Ecology: Revolutionizing Food Safety and Quality. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071706