The Complete Genomes of Microcystis ichthyoblabe Kützing and Microcystis protocystis (Crow) Komárek & Anagnostidis Reveal the Complexity and Plasticity of Microcystis Genomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Collection and Culture Conditions
2.2. DNA Extraction and Library Preparation
2.3. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Gene Cluster and Genome Structure Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Complete Genome Assembly of Three Microcystis Strains
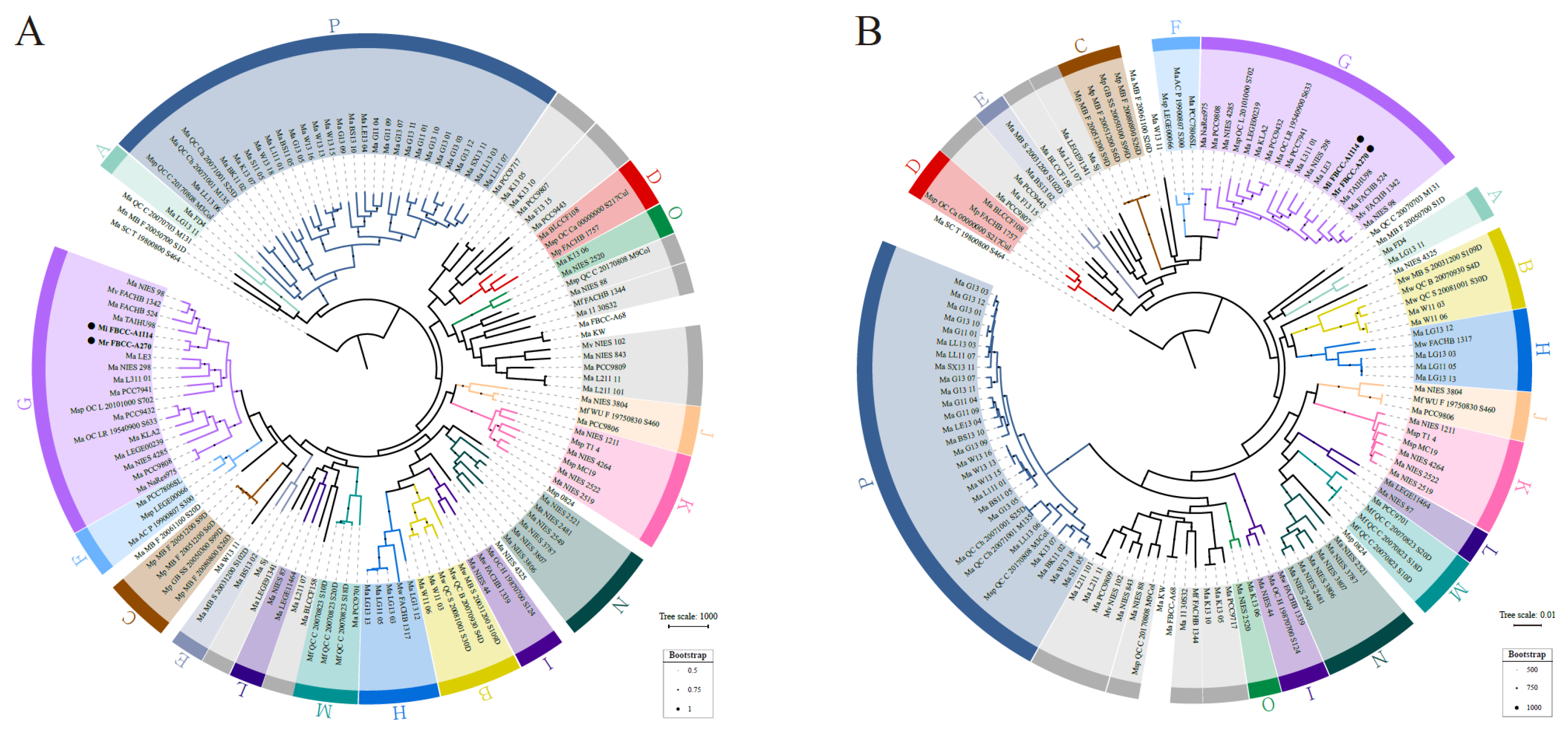
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Assembled Microcystis Strains
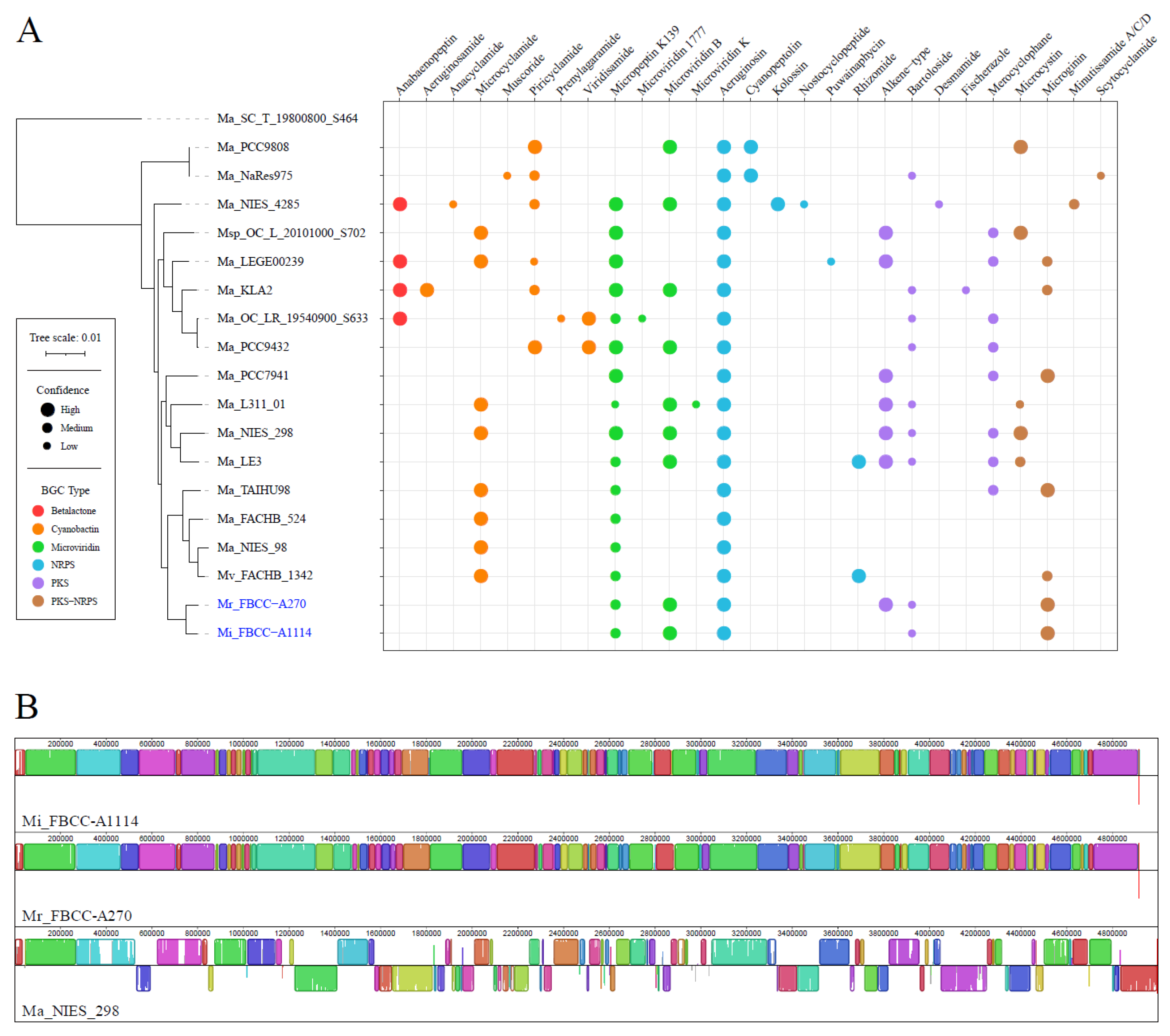
3.3. Functional and Structural Complexity of Microcystis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAB | Harmful Algal Bloom |
| ITS | Internal Transcribed Spacer |
| OGRI | Orthologous average Genome Relatedness Index |
| ANI | Average Nucleotide Identity |
| dDDH | digital DNA-DNA Hybridization |
| BGC | Biosynthesis Gene Cluster |
| CDS | Coding Sequence |
| TCS | Tetra Correlation Search |
| EPS | Extracellular Polysaccharide |
| PEPPAN | Phylogenetic Estimation of Pangenome using PEPPAN |
| BUSCO | Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs |
References
- Harke, M.J.; Steffen, M.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Otten, T.G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wood, S.A.; Paerl, H.W. A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.L. The complicated and confusing ecology of Microcystis blooms. mBio 2020, 11, e00529-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoof, L.; Catherine, A. Appendix 3: Tables of microcystins and nodularins. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 526–537. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, R. The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon 1998, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, X.; Cai, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, P.; Ni, J.; Mo, A.; Peng, C.; Liu, J. Advances in investigating microcystin-induced liver toxicity and underlying mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yi, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Tian, L. A review of nephrotoxicity of microcystins. Toxins 2020, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Massey, I.Y.; Feng, H.; Yang, F. A review of cardiovascular toxicity of microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fan, H.; Xie, P.; He, J. A review of neurotoxicity of microcystins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7211–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, T.; Kagalou, I.; Stalikas, C.; Pilidis, G.; Leonardos, I.D. Assessment of microcystin distribution and biomagnification in tissues of aquatic food web compartments from a shallow lake and evaluation of potential risks to public health. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Kudela, R.M.; Mekebri, A.; Crane, D.; Oates, S.C.; Tinker, M.T.; Staedler, M.; Miller, W.A.; Toy-Choutka, S.; Dominik, C.; et al. Evidence for a novel marine harmful algal bloom: Cyanotoxin (microcystin) transfer from land to sea otters. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Chorus, I. Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merel, S.; Walker, D.; Chicana, R.; Snyder, S.; Baurès, E.; Thomas, O. State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westrick, J.A.; Szlag, D.C.; Southwell, B.J.; Sinclair, J. A review of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal/inactivation in drinking water treatment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komárek, J.; Cepák, V. Cytomorphological characters supporting the taxonomic validity of Cyanothece (Cyanoprokaryota). Plant Syst. Evol. 1998, 210, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Kopecký, J.; Cepák, V. Generic characters of the simplest cyanoprokaryotes Cyanobium, Cyanobacterium and Synechococcus. Cryptogam. Algol. 1999, 20, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. A review of water-bloom forming Microcystis species, with regard to populations from Japan. Algol. Stud. 1991, 64, 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M. Isolation, cultivation and classification of bloom-forming Microcystis in Japan. Toxic Microcystis 1996, 2, 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, S.; Suda, S.; Li, R.; Matsumoto, S.; Watanabe, M.M. Morphological variability of colonies of Microcystis morphospecies in culture. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, M.; Tan, X. Morphological changes of Microcystis aeruginosa colonies in culture. J. Limnol. 2016, 75, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Tan, X.; Parajuli, K.; Upadhyay, S.; Zhang, D.; Shu, X.; Liu, Q. Colony formation in two Microcystis morphotypes: Effects of temperature and nutrient availability. Harmful Algae 2018, 72, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, W.; Xiao, M.; Li, M. Interspecific variation in extracellular polysaccharide content and colony formation of Microcystis spp. cultured under different light intensities and temperatures. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, M.; Reynolds, C.S. Colony formation in the cyanobacterium Microcystis. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1399–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepère, C.; Wilmotte, A.; Meyer, B. Molecular diversity of Microcystis strains (Cyanophyceae, Chroococcales) based on 16S rDNA sequences. Syst. Geogr. Plants 2000, 70, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, S.; Suda, S.; Li, R.; Watanabe, M.; Oyaizu, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Watanabe, M.M. 16S rDNA sequences and phylogenetic analyses of Microcystis strains with and without phycoerythrin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 164, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, S.; Suda, S.; Li, R.; Watanabe, M.; Oyaizu, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Watanabe, M.M. Phylogenetic relationships between toxic and non-toxic strains of the genus Microcystis based on 16S to 23S internal transcribed spacer sequence. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 172, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; da Costa, M.S.; Rooney, A.P.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.-W.; De Meyer, S.; et al. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; McLimans, C.J.; Beyer, J.E.; Krumholz, L.R.; Hambright, K.D. Microcystis pangenome reveals cryptic diversity within and across morphospecies. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, M.; Berkeley, M.R.; Seppey, M.; Simão, F.A.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO update: Novel and streamlined workflows along with broader and deeper phylogenetic coverage for scoring of eukaryotic, prokaryotic, and viral genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4647–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chklovski, A.; Parks, D.H.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM2: A rapid, scalable and accurate tool for assessing microbial genome quality using machine learning. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Oliver Glöckner, F.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Charlesworth, J.; Achtman, M. Accurate reconstruction of bacterial pan-and core genomes with PEPPAN. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kück, P.; Longo, G.C. FASconCAT-G: Extensive functions for multiple sequence alignment preparations concerning phylogenetic studies. Front. Zool. 2014, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, L.; Glover, R.H.; Humphris, S.; Elphinstone, J.G.; Toth, I.K. Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: Soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.; et al. antiSMASH 7.0: New and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W46–W50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, R.A.M.; Chen, Z.J. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, D.O.; Fiore, M.F.; Varani, A.M. A metagenomic approach to cyanobacterial genomics. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, G.J.; Duhaime, M.B.; Evans, J.T.; Errera, R.M.; Godwin, C.M.; Kharbush, J.J.; Nitschky, H.S.; Powers, M.A.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Schmidt, K.C.; et al. The genetic and ecophysiological diversity of Microcystis. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 7278–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ai Nguyen, V.; Tanabe, Y.; Matsuura, H.; Kaya, K.; Watanabe, M.M. Morphological, biochemical and phylogenetic assessments of water-bloom-forming tropical morphospecies of Microcystis (Chroococcales, Cyanobacteria). Phycol. Res. 2012, 60, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yang, Z.; Hu, N.; Xiao, B.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, T. Effect of extracellular polymeric substances on the colony size and morphological changes of Microcystis. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1367205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Okita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Okino, T.; Murakami, M. Aeruginosins, protease inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 10971–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploutno, A.; Shoshan, M.; Carmeli, S. Three Novel Protease Inhibitors from a Natural Bloom of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Qiu, X. Diversity, biosynthesis and bioactivity of aeruginosins, a family of cyanobacteria-derived nonribosomal linear tetrapeptides. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan-Amer, R.; Carmeli, S. Inhibitors of serine proteases from a Microcystis sp. bloom material collected from Timurim reservoir, Israel. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Kato, T.; Murakami, M.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, M.F. Microginins, zinc metalloproteases inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 8643–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodin-Friedman, A.; Carmeli, S. Microginins from a Microcystis sp. bloom material collected from the Kishon Reservoir, Israel. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusébio, N.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Sousa, D.; Preto, M.; D’Agostino, P.; Gulder, T.A.; Leão, P.N. Discovery and heterologous expression of microginins from Microcystis aeruginosa LEGE 91341. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P. Coevolution of the organization and structure of prokaryotic genomes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Wolf, Y.I. Genomics of bacteria and archaea: The emerging dynamic view of the prokaryotic world. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6688–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, O.X.; Polz, M.F. Explaining microbial genomic diversity in light of evolutionary ecology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polz, M.F.; Alm, E.J.; Hanage, W.P. Horizontal gene transfer and the evolution of bacterial and archaeal population structure. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
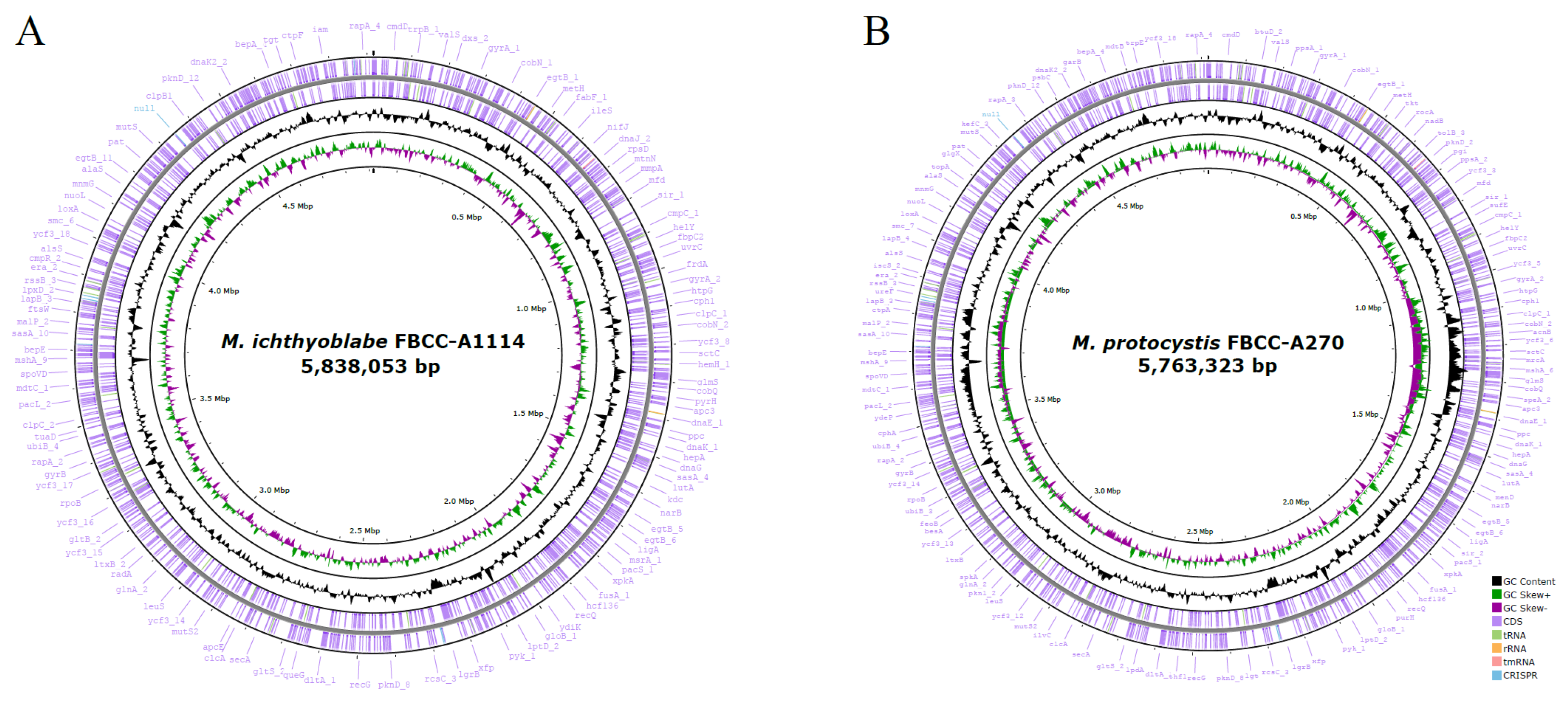
| Strain | FBCC-A1114 | FBCC-A270 |
|---|---|---|
| Species Name | Microcystis ichthyoblabe | Microcystis protocystis |
| NCBI Taxonomy ID | 1125 | |
| Domain | Bacteria | |
| Taxonomy | Bacteria; Bacillati; Cyanobacteriota/Melainabacteria group; Cyanobacteriota; Cyanophyceae; Oscillatoriophycideae; Chroococcales; Microcystaceae; Microcystis | |
| Genome Size (bp) | 5,838,053 | 5,763,323 |
| GC content (mol%) | 42.3 | 42.5 |
| Number of Genome Sequences | 1 Circular (Single chromosomal DNA without plasmid) | |
| Number of Plasmids | 0 | |
| Number of Coding Sequences | 4706 | 4701 |
| Number of rRNAs | 4 | 4 |
| Number of tRNAs (tmRNA) | 46 (1) | 45 (1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Goh, J.; Nam, S.W.; Chung, E.J.; Shin, M.; Seol, D.; Kim, K.H.; Kwak, W. The Complete Genomes of Microcystis ichthyoblabe Kützing and Microcystis protocystis (Crow) Komárek & Anagnostidis Reveal the Complexity and Plasticity of Microcystis Genomes. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071693
Kim J, Kim H, Goh J, Nam SW, Chung EJ, Shin M, Seol D, Kim KH, Kwak W. The Complete Genomes of Microcystis ichthyoblabe Kützing and Microcystis protocystis (Crow) Komárek & Anagnostidis Reveal the Complexity and Plasticity of Microcystis Genomes. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071693
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jina, Hyaekang Kim, Jaeduk Goh, Seung Won Nam, Eu Jin Chung, Miyoung Shin, Donghyeok Seol, Ki Hwan Kim, and Woori Kwak. 2025. "The Complete Genomes of Microcystis ichthyoblabe Kützing and Microcystis protocystis (Crow) Komárek & Anagnostidis Reveal the Complexity and Plasticity of Microcystis Genomes" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071693
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, H., Goh, J., Nam, S. W., Chung, E. J., Shin, M., Seol, D., Kim, K. H., & Kwak, W. (2025). The Complete Genomes of Microcystis ichthyoblabe Kützing and Microcystis protocystis (Crow) Komárek & Anagnostidis Reveal the Complexity and Plasticity of Microcystis Genomes. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071693







