Medical Comorbidities as the Independent Risk Factors of Severe Adenovirus Respiratory Tract Infection in Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outcome Measurements
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
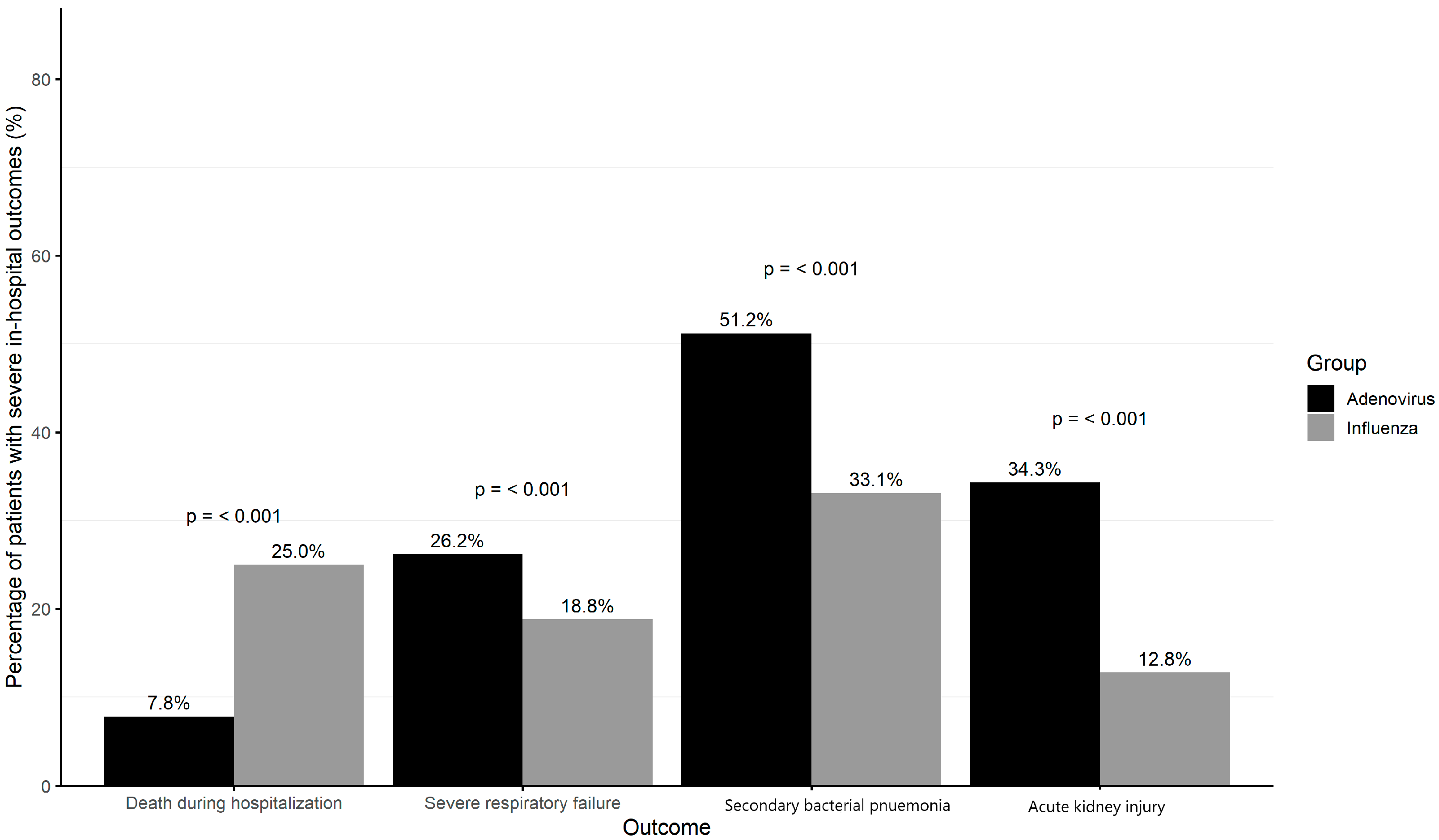
3.2. Severe In-Hospital Outcomes Among Influenza and Adenoviruses Patients
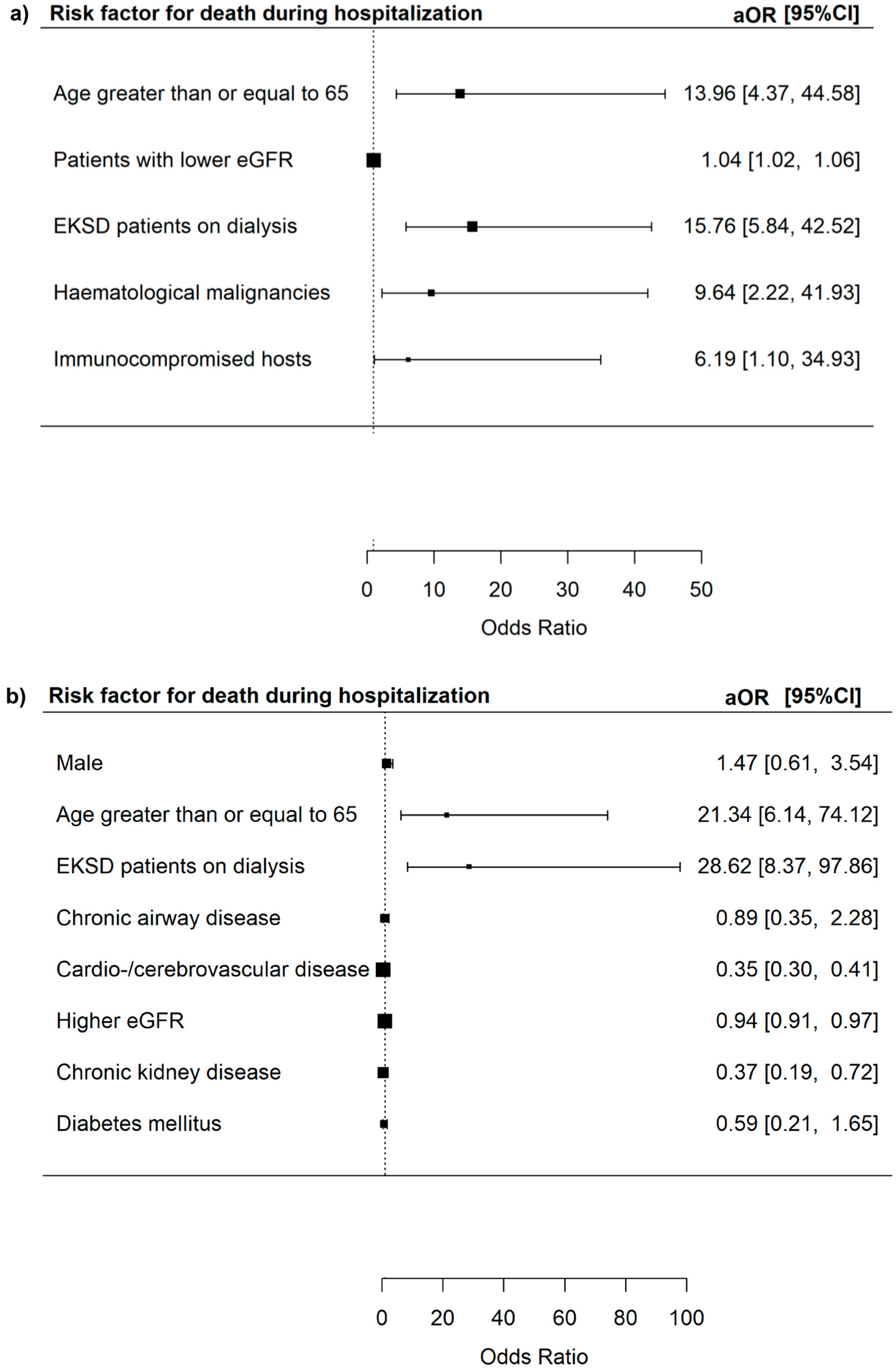
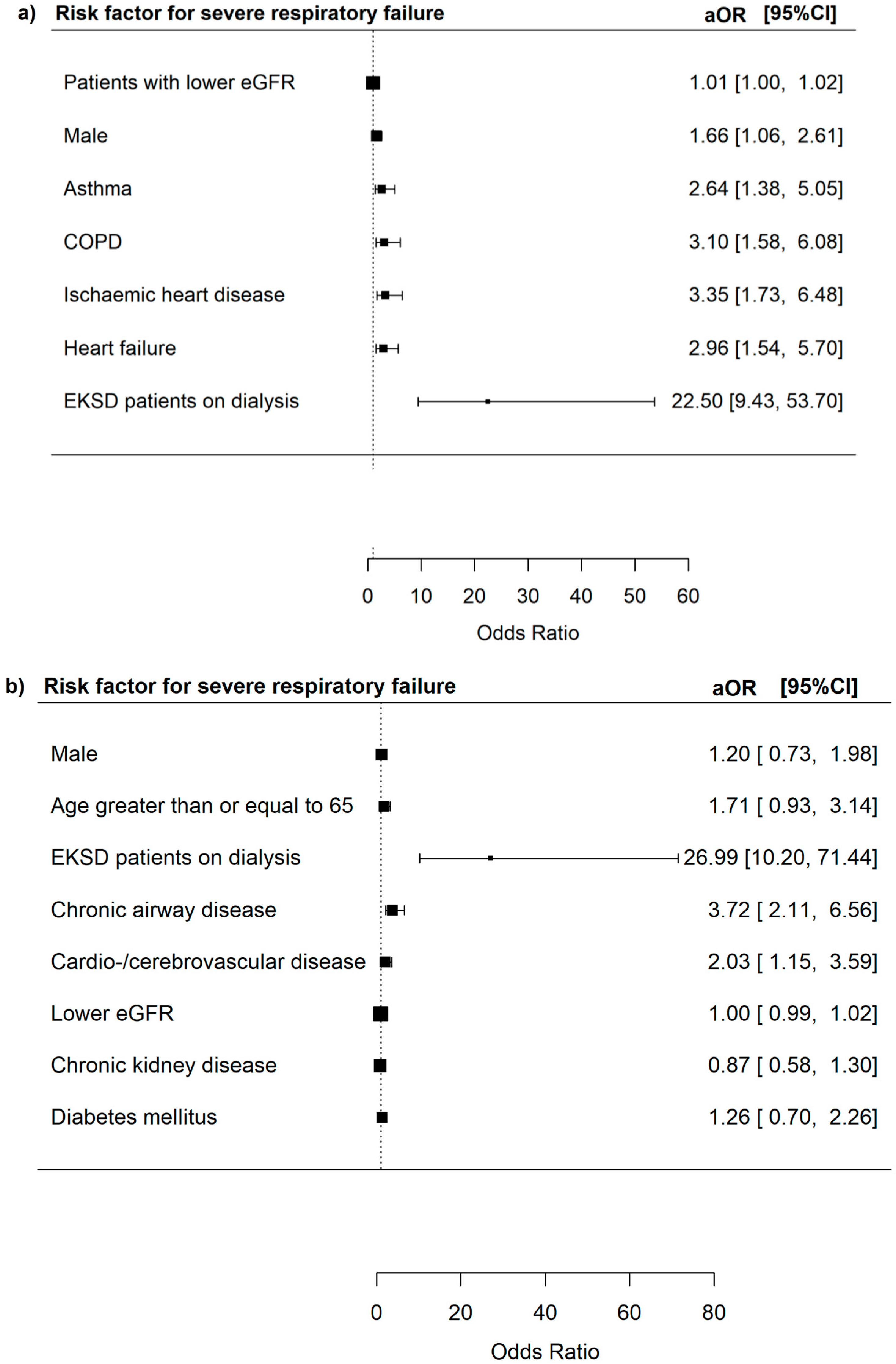
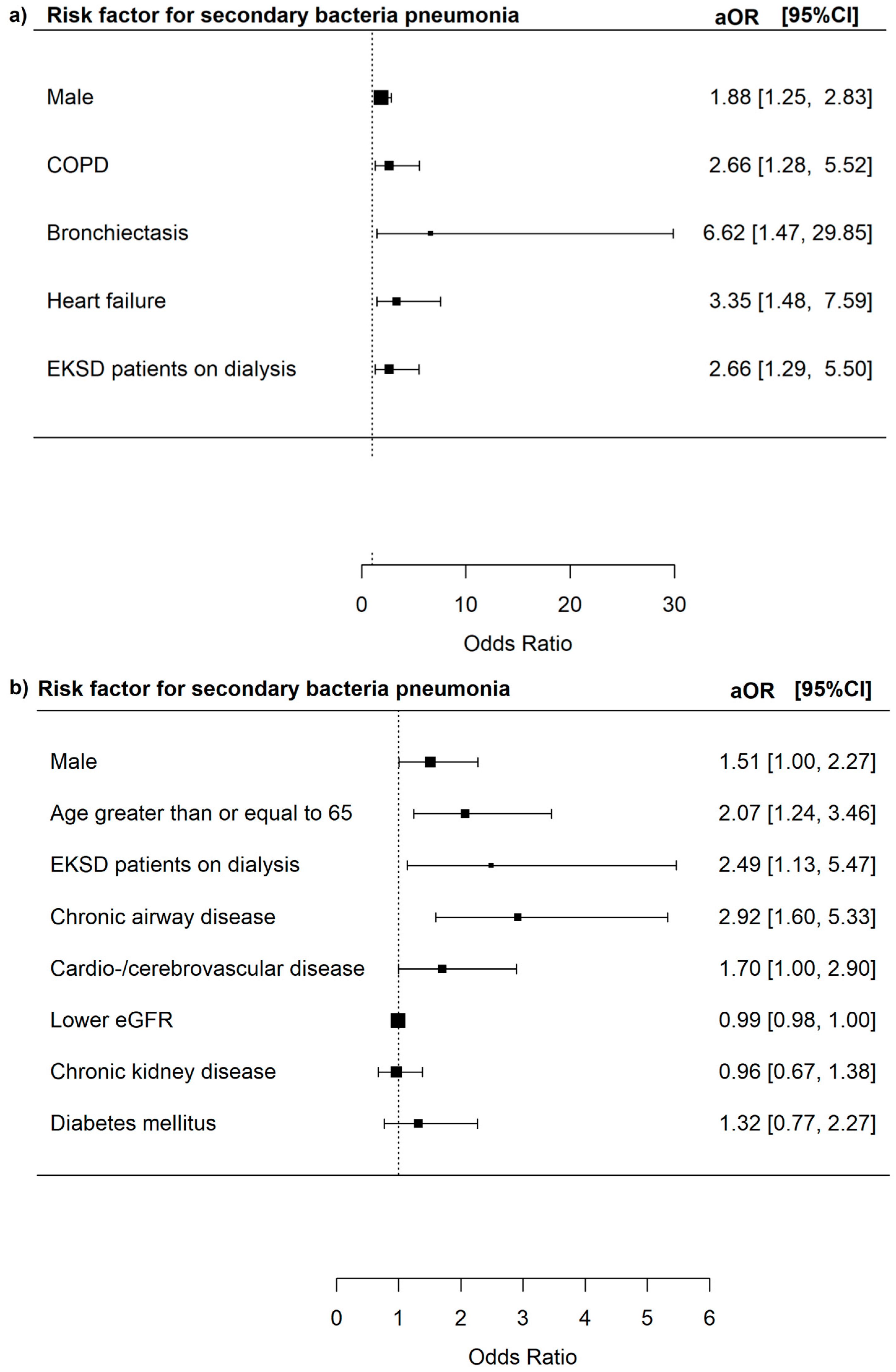
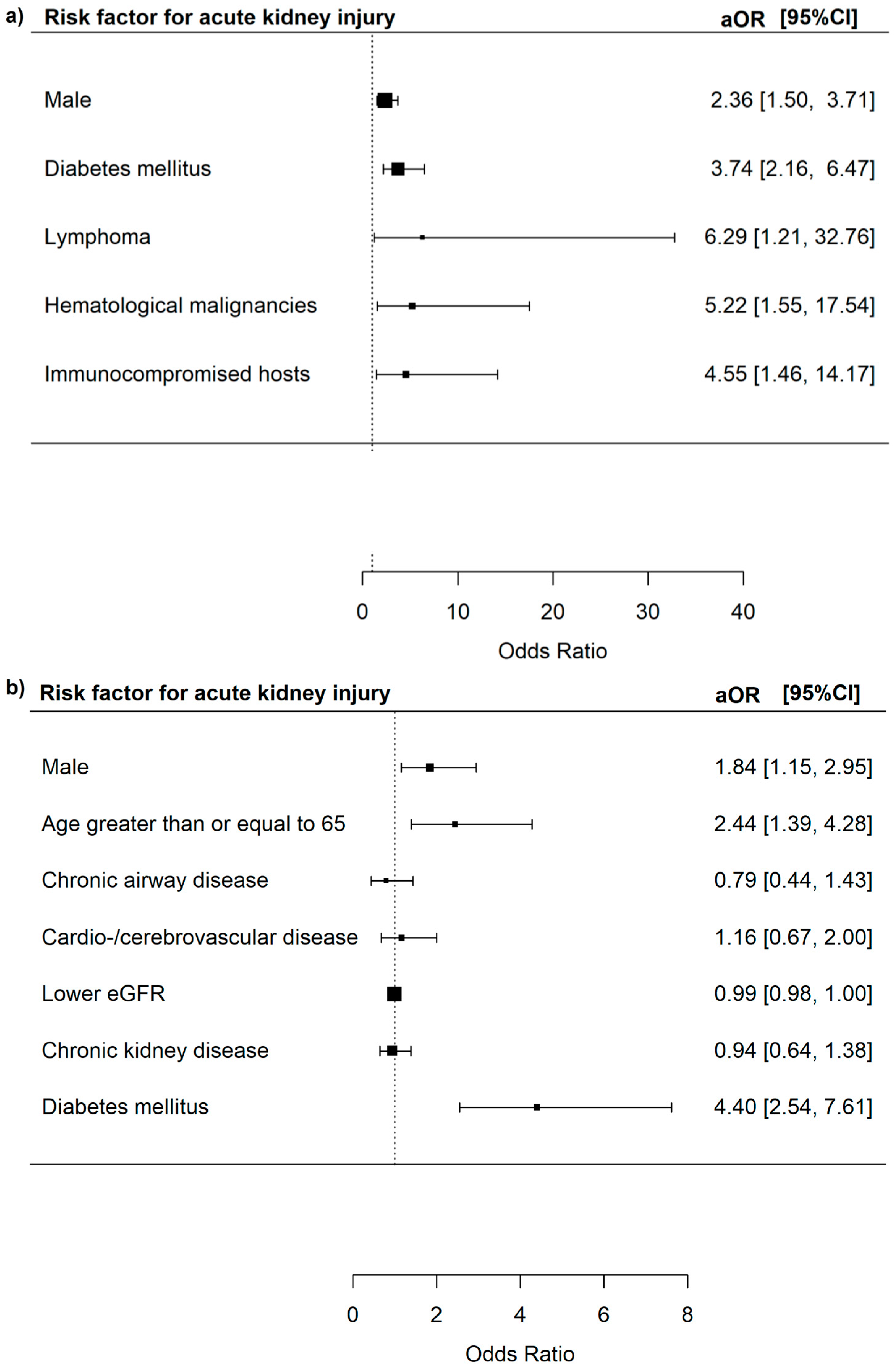
3.3. Risk Factors for Severe In-Hospital Outcomes Among Adenovirus Patients
3.4. Subgroup Analysis in Patients with Adenoviruses Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| CDARS | Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ESKD | End-Stage Kidney Disease |
| HA | Hospital Authority |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| IQR | Inter-Quartile Range |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| RIFLE | Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function, and End-stage kidney disease |
| S.D. | Standard Deviation |
References
- Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Kajon, A.E. Adenovirus: Epidemiology, Global Spread of Novel Serotypes, and Advances in Treatment and Prevention. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajon, A.E.; Lamson, D.M.; St George, K. Emergence and re-emergence of respiratory adenoviruses in the United States. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, K.M.; Dodge, M.J.; Evans, A.M.; Tessier, T.M.; Weinberg, J.B.; Mymryk, J.S. Adenoviruses in medicine: Innocuous pathogen, predator, or partner. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarria, M. Adenoviruses in immunocompromised hosts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, A.M.; Champlin, R.E.; Mirza, N.; Gajewski, J.; Giralt, S.; Rolston, K.V.; Raad, I.; Jacobson, K.; Kontoyiannis, D.; Elting, L.; et al. Adenovirus infections in adult recipients of blood and marrow transplants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humar, A.; Kumar, D.; Mazzulli, T.; Razonable, R.R.; Moussa, G.; Paya, C.V.; Covington, E.; Alecock, E.; Pescovitz, M.D.; Group, P.V.S. A surveillance study of adenovirus infection in adult solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, D.; Falagas, M.E.; Freeman, R.; Rohrer, R.; Fairchild, R.; Colbach, C.; Snydman, D.R. Adenovirus infection in adult orthotopic liver transplant recipients: Incidence and clinical significance. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, N.D.; Spray, T.L.; Collins, M.H.; Bowles, N.E.; Towbin, J.A. Adenovirus infection in the lung results in graft failure after lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1998, 116, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohori, N.P.; Michaels, M.G.; Jaffe, R.; Williams, P.; Yousem, S.A. Adenovirus pneumonia in lung transplant recipients. Hum. Pathol. 1995, 26, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer, J.C. Adenoviruses in the immunocompromised host. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 5, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, M.G. Adenovirus infections in transplant recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.A.; Gray, G.C.; Smith, B.; McKeehan, J.A.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Malasig, M.D. Large epidemic of respiratory illness due to adenovirus types 7 and 3 in healthy young adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.Y.; Lee, C.N.; Lin, P.H.; Huang, H.H.; Chang, L.Y.; Ko, W.; Chang, S.F.; Lee, P.I.; Huang, L.M.; Kao, C.L. A community-derived outbreak of adenovirus type 3 in children in Taiwan between 2004 and 2005. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger, J.R.; Sanchez, M.P.; Curtin, L.A.; Durkin, M.; Matyas, B. Multiple cases of life-threatening adenovirus pneumonia in a mental health care center. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Huang, G.H.; Pu, Z.H.; Qu, J.X.; Yu, X.M.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, J.P.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, X.H.; et al. Emergence of community-acquired adenovirus type 55 as a cause of community-onset pneumonia. Chest 2014, 145, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.L.; Binn, L.N.; Innis, B.L.; Reynolds, R.D.; Lee, T.; Mitchell-Raymundo, F.; Craig, S.C.; Marquez, J.P.; Shepherd, G.A.; Polyak, C.S.; et al. Epidemic of adenovirus-induced respiratory illness among US military recruits: Epidemiologic and immunologic risk factors in healthy, young adults. J. Med. Virol. 2001, 65, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolavic-Gray, S.A.; Binn, L.N.; Sanchez, J.L.; Cersovsky, S.B.; Polyak, C.S.; Mitchell-Raymundo, F.; Asher, L.V.; Vaughn, D.W.; Feighner, B.H.; Innis, B.L. Large epidemic of adenovirus type 4 infection among military trainees: Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symeonidis, N.; Jakubowski, A.; Pierre-Louis, S.; Jaffe, D.; Pamer, E.; Sepkowitz, K.; O’Reilly, R.J.; Papanicolaou, G.A. Invasive adenoviral infections in T-cell-depleted allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: High mortality in the era of cidofovir. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2007, 9, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Boeckh, M.; Englund, J.A. Community respiratory virus infections in immunocompromised patients: Hematopoietic stem cell and solid organ transplant recipients, and individuals with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 28, 222–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, F.A.; Tleyjeh, I.M. Severe adenovirus pneumonia in immunocompetent adults: A case report and review of the literature. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Heeti, O.M.; Cathro, H.P.; Ison, M.G. Adenovirus Infection and Transplantation. Transplantation 2022, 106, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, M.J.; MacNeil, K.M.; Tessier, T.M.; Weinberg, J.B.; Mymryk, J.S. Emerging antiviral therapeutics for human adenovirus infection: Recent developments and novel strategies. Antivir. Res. 2021, 188, 105034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, A.; Gregston, A.; Elwir, S.; Spak, C.W. Treatment of Viral Hepatitis Due to Adenovirus in a Liver Transplantation Recipient: The Clinical Use of Cidofovir and Intravenous Immunoglobulin. Liver Transpl. 2022, 28, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey Garnes, N.J.M.; Ragoonanan, D.; Aboulhosn, A. Adenovirus infection and disease in recipients of hematopoietic cell transplantation. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foss, S.; Jonsson, A.; Bottermann, M.; Watkinson, R.; Lode, H.E.; McAdam, M.B.; Michaelsen, T.E.; Sandlie, I.; James, L.C.; Andersen, J.T. Potent TRIM21 and complement-dependent intracellular antiviral immunity requires the IgG3 hinge. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabj1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskander, J.; Blanchet, S.; Springer, C.; Rockwell, P.; Thomas, D.; Pillai, S. Enhanced Adenovirus Vaccine Safety Surveillance in Military Setting, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, W.C.; Tam, T.C.C.; Sing, C.W.; Chan, E.W.Y.; Cheung, C.L. Validation of diagnostic coding for bronchiectasis in an electronic health record system in Hong Kong. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2023, 32, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, W.C.; Tam, T.C.C.; Sing, C.W.; Chan, E.W.Y.; Cheung, C.L. Validation of Diagnostic Coding for Asthma in an Electronic Health Record System in Hong Kong. J. Asthma Allergy 2023, 16, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Leung, M.T.Y.; Li, X.; Chui, C.S.L.; Wong, R.S.M.; Au Yeung, S.L.; Chan, E.W.W.; Chan, A.Y.L.; Chan, E.W.; Wong, W.H.S.; et al. Linking cohort-based data with electronic health records: A proof-of-concept methodological study in Hong Kong. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P.; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative, w. Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; De Zeeuw, D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, D.; Kim, T.H.; Johnstone, J.; Lam, P.P.; Science, M.; Kuster, S.P.; Fadel, S.A.; Tran, D.; Fernandez, E.; Bhatnagar, N.; et al. Populations at risk for severe or complicated influenza illness: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2013, 347, f5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocoros, N.M.; Lash, T.L.; DeMaria, A., Jr.; Klompas, M. Obesity as a risk factor for severe influenza-like illness. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicembrini, I.; Silverii, G.A.; Clerico, A.; Fornengo, R.; Gabutti, G.; Sordi, V.; Tafuri, S.; Peruzzi, O.; Mannucci, E. Influenza: Diabetes as a risk factor for severe related-outcomes and the effectiveness of vaccination in diabetic population. A meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas, A.; Doris, L.; Frank, K.; Michael, K. Corrigendum to Focusing on severe infections with the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in adults: Risk factors, symptomatology and clinical course compared to influenza A/B and the original SARS-CoV-2 strain: Journal of Clinical Virology, 161 (2023), 105399. J. Clin. Virol. 2023, 164, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.D.; Ding, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.J.; Kursat Azkur, A.; Azkur, D.; Gan, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review. Allergy 2021, 76, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, G.C.; McCarthy, T.; Lebeck, M.G.; Schnurr, D.P.; Russell, K.L.; Kajon, A.E.; Landry, M.L.; Leland, D.S.; Storch, G.A.; Ginocchio, C.C.; et al. Genotype prevalence and risk factors for severe clinical adenovirus infection, United States 2004–2006. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederwall, S.; Pahlman, L.I. Respiratory adenovirus infections in immunocompetent and immunocompromised adult patients. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 147, e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, D.Y.; Fong, C.H.; Zhang, X.; Ip, J.D.; Chan, W.M.; Chu, A.W.; Chen, L.L.; Zhao, Y.; Chan, B.P.; Luk, K.S.; et al. Humoral and cellular immunity against different SARS-CoV-2 variants in patients with chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, P.D.; Gratzl, S.; Simonov, M.; Nachimuthu, S.K.; Goodwin Cartwright, B.M.; Wang, M.D.; Baker, C.; Rodriguez, P.; Bogiages, M.; Althouse, B.M.; et al. Risk of COVID-19 breakthrough infection and hospitalization in individuals with comorbidities. Vaccine 2023, 41, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.M.; Yap, D.Y.H.; Yip, T.P.S.; Hung, I.F.N.; Tang, S.C.W.; Chan, T.M. Vaccination in patients with chronic kidney disease-Review of current recommendations and recent advances. Nephrology 2021, 26, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, N.; Han, M. Characteristics of COVID-19 patients with preexisting CKD history. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 2567–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pio-Abreu, A.; do Nascimento, M.M.; Vieira, M.A.; de Menezes Neves, P.D.M.; Lugon, J.R.; Sesso, R. High mortality of CKD patients on hemodialysis with COVID-19 in Brazil. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akchurin, O.; Meza, K.; Biswas, S.; Greenbaum, M.; Licona-Freudenstein, A.P.; Goyal, P.; Choi, J.J.; Choi, M.E. COVID-19 in Patients with CKD in New York City. Kidney360 2021, 2, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Cheong, H.J.; Song, J.Y.; Noh, J.Y.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, J.; Seo, Y.B.; Lee, J.S.; Wie, S.H.; et al. Analysis of Risk Factors for Severe Acute Respiratory Infection and Pneumonia and among Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Illness during 2011-2014 Influenza Seasons in Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2016, 48, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lion, T. Adenovirus infections in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Dong, X.; Liu, G.H.; Gao, Y.D. Risk and Protective Factors for COVID-19 Morbidity, Severity, and Mortality. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, E.; Kwon, S.H.; Jo, M.W.; Jung, J.; Park, H.; Park, B. Cost-benefit analysis of human adenovirus vaccine development in a Korean military setting. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudding, B.A.; Top, F.H., Jr.; Winter, P.E.; Buescher, E.L.; Lamson, T.H.; Leibovitz, A. Acute respiratory disease in military trainees: The adenovirus surveillance program, 1966–1971. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1973, 97, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radin, J.M.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Blair, P.J.; Faix, D.J.; Raman, R.; Russell, K.L.; Gray, G.C. Dramatic decline of respiratory illness among US military recruits after the renewed use of adenovirus vaccines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoke, C.H., Jr.; Snyder, C.E., Jr. History of the restoration of adenovirus type 4 and type 7 vaccine, live oral (Adenovirus Vaccine) in the context of the Department of Defense acquisition system. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmons, N.S.; McCormic, Z.D.; Gaydos, J.C.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Jordan, N.N. Acute Respiratory Disease in US Army Trainees 3 Years after Reintroduction of Adenovirus Vaccine. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyer, R.N.; Howell, M.R.; Ryan, M.A.; Gaydos, J.C. Cost-effectiveness analysis of reacquiring and using adenovirus types 4 and 7 vaccines in naval recruits. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| All | Whole Cohort | p-Value | ASD | Propensity Score-Matched Cohort | p-Value | ASD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza Virus | Adenovirus | Influenza Virus | Adenovirus | |||||||
| Number of subjects (N) | 41,975 | 41,447 | 528 | 485 | 485 | |||||
| Age, years (Mean (SD)) | 67.20 (19.91) | 67.37 (19.82) | 54.30 (22.47) | <0.001 * | 0.616 | 52.21 (20.95) | 54.33 (22.58) | 0.130 | 0.097 # | |
| Female (N, (%)) | 20,656 (49.2) | 20,336 (49.1) | 320 (60.6) | <0.001 * | 0.233 | 293 (60.4) | 289 (59.6) | 0.844 | 0.017 # | |
| History of malignancies (N, (%)) | 2862 (6.8) | 2794 (6.7) | 68 (12.9) | <0.001 * | 0.207 | 45 (9.3) | 56 (11.5) | 0.293 | 0.074 # | |
| Diabetes mellitus (N, (%)) | 10,223 (24.4) | 10,133 (24.4) | 90 (17.0) | <0.001 * | 0.183 | 85 (17.5) | 83 (17.1) | 0.932 | 0.011 # | |
| Chronic airway diseases (N, (%)) | 6351 (15.1) | 6268 (15.1) | 83 (15.7) | 0.750 | 0.017 # | 76 (15.7) | 76 (15.7) | 1.000 | <0.001 # | |
| Cardiovascular diseases (N, (%)) | 14,063 (33.5) | 13,932 (33.6) | 131 (24.8) | <0.001 * | 0.195 | 119 (24.5) | 114 (23.5) | 0.764 | 0.024 # | |
| CCI (Mean (SD)) | 3.74 (2.57) | 3.75 (2.56) | 3.09 (3.02) | <0.001 * | 0.237 | 2.75 (2.72) | 2.89 (2.91) | 0.419 | 0.052 # | |
| CKD (N, (%)) | 7570 (18.0) | 7470 (18.0) | 100 (18.9) | 0.626 | 0.024 # | 82 (16.9) | 83 (17.1) | 1.000 | 0.005 # | |
| Influenza vaccine (N, (%)) | 12,795 (30.5) | 12,673 (30.6) | 122 (23.1) | <0.001 * | 0.169 | 109 (22.5) | 112 (23.1) | 0.878 | 0.015 # | |
| Pneumococcal conjugated vaccines (N, (%)) | 4787 (11.4) | 4748 (11.5) | 39 (7.4) | 0.004 * | 0.140 | 29 (6.0) | 36 (7.4) | 0.441 | 0.058 # | |
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (N, (%)) | 1574 (3.7) | 1557 (3.8) | 17 (3.2) | 0.596 | 0.029 # | 15 (3.1) | 17 (3.5) | 0.857 | 0.023 # | |
| ESKD on dialysis (N, (%)) | 1431 (3.4) | 1378 (3.3) | 44 (8.3) | <0.001 * | 0.305 | 34 (7.0) | 34 (7.0) | 1.00 | <0.001 # | |
| Leukaemia/Myeloma (N, (%)) | 222 (0.5%) | 213 (0.5) | 9 (1.7) | <0.001 * | 0.164 | 5 (1.%) | 6 (1.2) | 0.762 | 0.064 # | |
| Lymphoma (N, (%)) | 219 (0.5%) | 208 (0.5) | 11 (2.1) | <0.001 * | 0.218 | 11 (2.3) | 8 (1.6) | 0.487 | 0.064 # | |
| HIV infection (N, (%)) | 58 (0.1%) | 54 (0.1) | 4 (0.8) | <0.001 * | 0.168 | 3 (0.6) | 3 (0.6) | 1.00 | 0.064 # | |
| Ethnicity (N, (%)) | <0.001 * | 0.270 | 1.00 | 0.015 # | ||||||
| Chinese | 40,589 (96.7) | 40,093 (96.7) | 496 (93.9) | 460 (94.8) | 458 (94.4) | |||||
| Northeast Asian | 22 (0.1) | 21 (0.1) | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.2) | |||||
| Southeast Asian | 618 (1.5) | 611 (1.5) | 7 (1.3) | 1 (0.2) | 6 (1.2) | |||||
| South Asian | 512 (1.2) | 510 (1.2) | 2 (0.4) | 1 (0.2) | 2 (0.4) | |||||
| Caucasian | 17 (0.0) | 17 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||||
| Others | 217 (0.5) | 195 (0.5) | 22 (4.2) | 23 (4.7) | 18 (3.7) | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwok, W.C.; Leung, I.S.H.; Ho, J.C.M.; Lam, D.C.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Ngai, S.M.; To, K.K.W.; Yap, D.Y.H. Medical Comorbidities as the Independent Risk Factors of Severe Adenovirus Respiratory Tract Infection in Adults. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071670
Kwok WC, Leung ISH, Ho JCM, Lam DCL, Ip MSM, Ngai SM, To KKW, Yap DYH. Medical Comorbidities as the Independent Risk Factors of Severe Adenovirus Respiratory Tract Infection in Adults. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071670
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwok, Wang Chun, Isaac Sze Him Leung, James Chung Man Ho, David Chi Leung Lam, Mary Sau Man Ip, Shuk Man Ngai, Kelvin Kai Wang To, and Desmond Yat Hin Yap. 2025. "Medical Comorbidities as the Independent Risk Factors of Severe Adenovirus Respiratory Tract Infection in Adults" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071670
APA StyleKwok, W. C., Leung, I. S. H., Ho, J. C. M., Lam, D. C. L., Ip, M. S. M., Ngai, S. M., To, K. K. W., & Yap, D. Y. H. (2025). Medical Comorbidities as the Independent Risk Factors of Severe Adenovirus Respiratory Tract Infection in Adults. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071670








