Native Fungi as a Nature-Based Solution to Mitigate Toxic Metal(loid) Accumulation in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Fungal Strains
2.2. Fungal Functional Trait Tests Set-Up
2.3. Secondary Metabolites Production Assessment
2.4. Composition and Enrichment of Bioinoculants
2.5. Greenhouse Experiment Set-Up
2.6. Vitality Tests and Chemical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fungal Identification and Functional Trait Tests
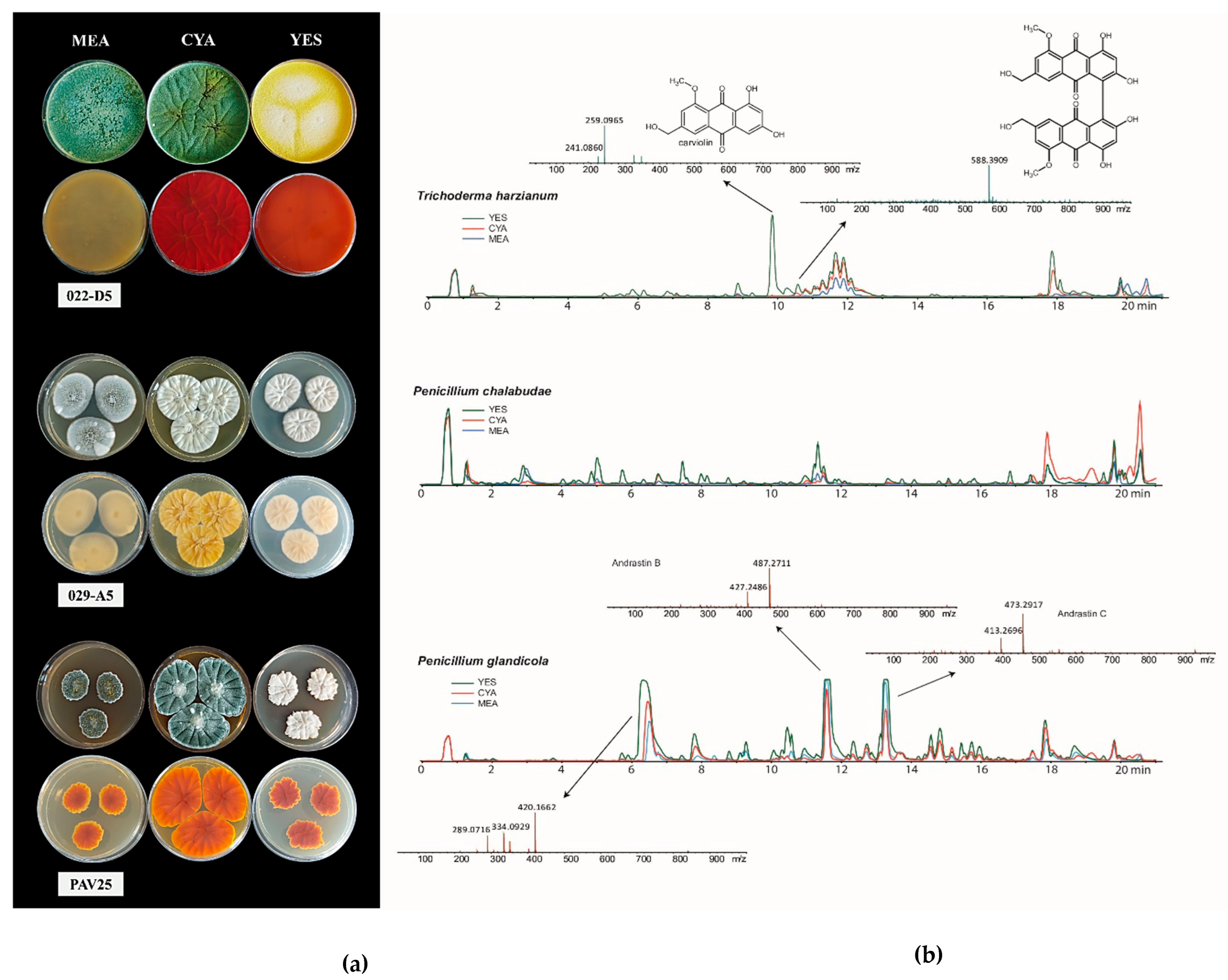
3.2. Secondary Metabolites Production
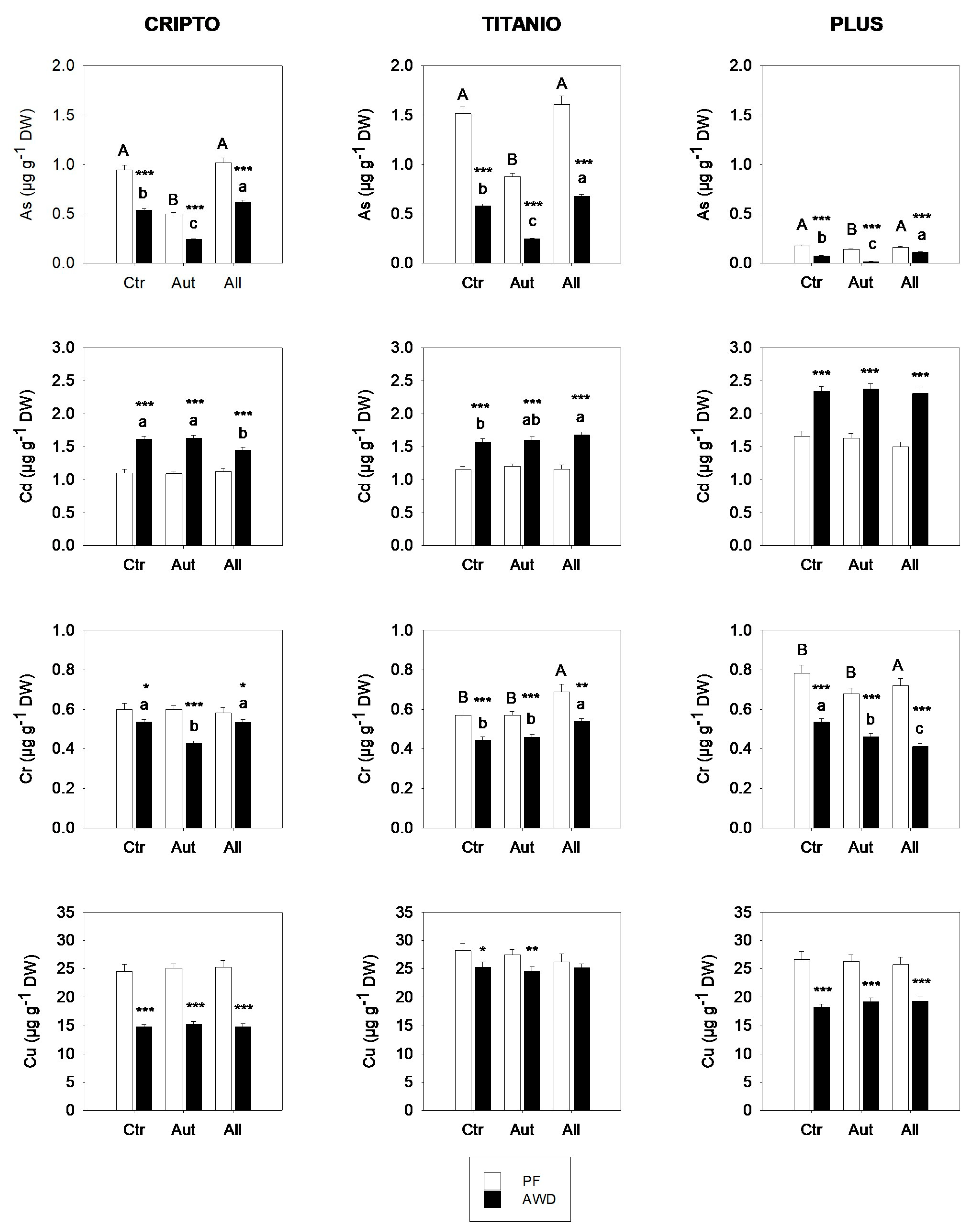
3.3. Greenhouse Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NBS | Nature-based solutions |
| PF | Permanent flooding |
| AWD | Alternate wetting and drying |
| PGPF | Plant growth-promoting fungi |
| PGPB | Plant growth-promoting bacteria |
Appendix A
| Parameter | Value | Confidential Interval |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.51 | 0.19 |
| Sand (% DM) | 55 | 5 |
| Silt (% DM) | 36 | 1 |
| Clay (% DM) | 9 | 2 |
| Soil texture classification | Sandy loam | |
| CEC (cmol(+) kg−1) | 18.85 | 0.95 |
| TOC (g kg−1) | 14.7 | 1.1 |
| SOM (g kg−1) | 25.4 | 1.9 |
| TKN (g kg−1) | 1.78 | 0.17 |
| C/N | 8.3 | 0.2 |
| Available P2O5 (mg kg−1) | 178 | 9 |
| Total Arsenic (As) (mg kg−1) | 24.91 | 1.87 |
| Cadmium (Cd) (mg kg−1) | 0.94 | 0.05 |
| Copper (Cu) (mg kg−1) | 96.86 | 3.55 |
| Lead (Pb) (mg kg−1) | 49.51 | 2.52 |
| Mercury (Hg) (mg kg−1) | <0.1 | |
| Nickel (Ni) (mg kg−1) | 98.19 | 4.43 |
| Selenium (Se) (mg kg−1) | 0.61 | 0.05 |
| Total Chromium (Cr) (mg kg−1) | 114.97 | 5.84 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 359.50 | 9.99 |
References
- Bakhat, H.F.; Zia, Z.; Fahad, S.; Abbas, S.; Hammad, H.M.; Shahzad, A.N.; Abbas, F.; Alharby, H.; Shahid, M. Arsenic uptake, accumulation and toxicity in rice plants: Possible remedies for its detoxification: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9142–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Ohba, H.; Kaneko-Kadokura, A.; Makino, T.; Nakamura, K.; Katou, H. Optimal Soil Eh, pH, and Water Management for Simultaneously Minimizing Arsenic and Cadmium Concentrations in Rice Grains. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4178–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.T.T.; Hang, N.T.T.; Nguyen, X.C.; Nguyen, N.T.M.; Truong, H.B.; Liu, C.; La, D.D.; Kim, S.S.; Nguyen, D.D. Toxic metals in rice among Asian countries: A review of occurrence and potential human health risks. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Du, J.; Zhou, J. Toxic Metals in a Paddy Field System: A Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N.; Blessy, A.; Mathew, B. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ye, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. Adaptation of soil fungi to heavy metal contamination in paddy fields—A case study in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27819–27830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Yao, A.; Qiu, R.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Effects of alkaline and bioorganic amendments on cadmium, lead, zinc, and nutrient accumulation in brown rice and grain yield in acidic paddy fields contaminated with a mixture of heavy metals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23551–23560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, Z.; Zulkafflee, N.S.; Mohd Redzuan, N.A.; Selamat, J.; Ismail, M.R.; Praveena, S.M.; Tóth, G.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Understanding potential heavy metal contamination, absorption, translocation and accumulation in rice and human health risks. Plants 2021, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abtahi, M.; Fakhri, Y.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Keramati, H.; Zandsalimi, Y.; Bahmani, Z.; Hosseini Pouya, R.; Sarkhosh, M.; Moradi, B.; Amanidaz, N.; et al. Heavy metals (As, Cr, Pb, Cd and Ni) concentrations in rice (Oryza sativa) from Iran and associated risk assessment: A systematic review. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Guan, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Zheng, X. Spatial and variety distributions, risk assessment, and prediction model for heavy metals in rice grains in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 7298–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Guo, D.; Mahar, A.; Wang, P.; Shen, F.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Mycoremediation of Potentially Toxic Trace Elements—A Biological Tool for Soil Cleanup: A Review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S. Heavy metals stress, mechanism and remediation techniques in rice (Oryza sativa L.): A review. Pure Appl. Biol. 2020, 9, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government Decree on the Assessment of Soil Contamination and Remediation Needs|214/2007|Translations of Statutes|Finlex. Available online: https://finlex.fi/en/legislation/translations/2007/eng/214 (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Hossain, M.A.; Piyatida, P.; Silva, J.A.T.; da Fujita, M. Molecular Mechanism of Heavy Metal Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants: Central Role of Glutathione in Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species and Methylglyoxal and in Heavy Metal Chelation. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 872875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y. Heavy Metal Stress and Some Mechanisms of Plant Defense Response. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 756120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viehweger, K. How plants cope with heavy metals. Bot. Stud. 2014, 55, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Kumar, A.; Latowski, D.; Kuczynska, P.; Strzałka, K.; Prasad, M.N.V. Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant 2013, 35, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigham, G.E.; Mahfouz, A.Y.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Nofel, M.M.; Attia, M.S. Protective role of plant growth-promoting fungi Aspergillus chevalieri OP593083 and Aspergillus egyptiacus OP593080 as biocontrol approach against Alternaria leaf spot disease of Vicia faba plant. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 23073–23089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, N.H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkunas, I.; Wozniak, A.; Mai, V.C.; Rucinska-Sobkowiak, R.; Jeandet, P. The Role of Heavy Metals in Plant Response to Biotic Stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Shri, M.; Gupta, A.; Rani, V.; Chakrabarty, D. Toxicity and detoxification of heavy metals during plant growth and metabolism. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1169–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Han, F.; Li, J.; Ye, W.; Fu, H.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q. Agronomic management and rice varieties controlling Cd bioaccumulation in rice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y. Co-contamination of Cu and Cd in paddy fields: Using periphyton to entrap heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, L.R.R.; Pomarolli, L.C.; da Veiga, M.A.M.S. From classic methodologies to application of nanomaterials for soil remediation: An integrated view of methods for decontamination of toxic metal(oid)s. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10205–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Ning, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N.; Guo, S. Assemblages of rhizospheric and root endospheric mycobiota and their ecological associations with functional traits of rice. mBio 2024, 15, e0273323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Weller, D.M.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Dwivedi, S.K. Mycoremediation of heavy metals: Processes, mechanisms, and affecting factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 10375–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elnabi, M.K.; Elkaliny, N.E.; Elyazied, M.M.; Azab, S.H.; Elkhalifa, S.A.; Elmasry, S.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Shalamesh, E.M.; Alhorieny, N.A.; Abd Elaty, A.E.; et al. Toxicity of Heavy Metals and Recent Advances in Their Removal: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpasi, S.O.; Anekwe, I.M.S.; Tetteh, E.K.; Amune, U.O.; Shoyiga, H.O.; Mahlangu, T.P.; Kiambi, S.L. Mycoremediation as a Potentially Promising Technology: Current Status and Prospects—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadik, S.P.; Patil, S.V.; Kumudini, B.S. Bioprospecting rhizosphere fungi endowed with multifarious plant growth-promoting potential to enhance finger millet growth under salinity stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 1483–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, A.; Longa, O.; Nicola, L.; Adedayo, A.A.; Babalola, O.O. Fungi That Promote Plant Growth in the Rhizosphere Boost Crop Growth. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Maraghy, S.S.; Tohamy, A.T.; Hussein, K.A. Plant protection properties of the Plant Growth-Promoting Fungi (PGPF): Mechanisms and potentiality. Curr. Res. Environ. Appl. Mycol. 2021, 11, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacchioni, S.; Passato, S.; Ambrosino, P.; Huang, L.; Caldara, M.; Cantale, C.; Hett, J.; Del Fiore, A.; Fiore, A.; Schlüter, A.; et al. Identification of Beneficial Microbial Consortia and Bioactive Compounds with Potential as Plant Biostimulants for a Sustainable Agriculture. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Ali, M.; Aftab, M.; Shakir, S.U.; Qayyum, S.; Haleem, K.S.; Tauseef, I. Mycoremediation: A treatment for heavy metal-polluted soil using indigenous metallotolerant fungi. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koza, N.A.; Adedayo, A.A.; Babalola, O.O.; Kappo, A.P. Microorganisms in Plant Growth and Development: Roles in Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Secondary Metabolites Secretion. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenteno-Alegría, C.O.; Yarzábal Rodríguez, L.A.; Ciancas Jiménez, J.; Álvarez Gutiérrez, P.E.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Batista-García, R.A. Fungi beyond limits: The agricultural promise of extremophiles. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, R.S.; Kim, Y.O.; Woodward, C.J.D.A.; Greer, C.; Espino, L.; Doty, S.L.; Rodriguez, R.J. Increased Fitness of Rice Plants to Abiotic Stress Via Habitat Adapted Symbiosis: A Strategy for Mitigating Impacts of Climate Change. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gao, M.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, J.J. Potential use of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for simultaneous mitigation of arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, B.D.; Lin, A.J.; Smith, S.E.; Smith, F.A. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Contribute to Resistance of Upland Rice to Combined Metal Contamination of Soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekpinar, A.D.; Kalmer, A. Utility of various molecular markers in fungal identification and phylogeny. Nova Hedwig. 2019, 109, 187–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White Thomas, J.; Bruns Thomas, D.; Lee Steven, B.; Taylor John, W. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications—Google Libri. 1990. Available online: https://books.google.it/books?hl=it&lr=&id=Z5jwZ2rbVe8C&oi=fnd&pg=PA315&ots=ICJXMiZS4C&sig=vCtAuY88WQSV5YoJS-bMSu2jmgQ&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Singh, D.P.; Singh, H.B.; Prabha, R. Plant-Microbe Interactions in Agro-Ecological Perspectives; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tatung, M.; Seng Chaupoo, A.; Ranjan Deb, C. Plant Growth Promoting Fungi (PGPF) for Ecologically Plant Growth Promoting Fungi (PGPF) for Ecologically Sound Agriculture and its Market Trend Evolution Sound Agriculture and its Market Trend Evolution. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 2024, 12, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, L.R.L.S.; Senaratne, A.; Wijesinghe, W.R.P. Isolation of a potential rock phosphate solubilizing Aspergillus sp. towards development of biofertilizer. Ceylon J. Sci. 2024, 53, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louden, B.C.; Haarmann, D.; Lynne, A.M. Use of Blue Agar CAS Assay for Siderophore Detection. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2011, 12, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, E.; Di Piazza, S.; Cecchi, G.; Mazzoccoli, M.; Zerbini, M.; Cardinale, A.M.; Zotti, M. Applied Tests to Select the Most Suitable Fungal Strain for the Recovery of Critical Raw Materials from Electronic Waste Powder. Recycling 2022, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C. Physiological Criteria and Mycotoxin Production as Aids in Identification of Common Asymmetric Penicillia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 41, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisvad, J.C. Creatine sucrose agar, a differential medium for mycotoxin producing terverticillate Penicillium species. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 1, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C. Media and growth conditions for induction of secondary metabolite production. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 944, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, K.R.; Muurmann, A.T.; Paulsen, I.E.; Nørgaard, K.T.H.; Overgaard, M.L.; Dall, S.M.; Aalborg, T.; Wimmer, R.; Sørensen, J.L.; Sondergaard, T.E. Who needs neighbors? PKS8 is a stand-alone gene in fusarium graminearum responsible for production of gibepyrones and prolipyrone B. Molecules 2018, 23, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, K.R.; Werner, M.I.H.; Nielsen, K.A.H.; Sørensen, J.L.; Andrushchenko, V.; Winde, J.; Hertz, M.; Jensen, M.A.; Mortensen, M.L.; Bouř, P.; et al. Characterization of Eight Novel Spiroleptosphols from Fusarium avenaceum. Molecules 2019, 24, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.E.R.; Joseph, S.J.; Janssen, P.H. Effects of growth medium, inoculum size, and incubation time on culturability and isolation of soil bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, A.; Malusà, E.; Costa, C.; Pallottino, F.; Mocali, S.; Pinzari, F.; Canfora, L. Current Methods, Common Practices, and Perspectives in Tracking and Monitoring Bioinoculants in Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 698491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baakza, A.; Vala, A.K.; Dave, B.P.; Dube, H.C. A comparative study of siderophore production by fungi from marine and terrestrial habitats. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 311, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.A.; Kazunori, S.; Yoshimiki, A.; Kazuyuki, I. Biocontrol of soilborne Fusarium wilts of tomato and cabbage with a root colonizing fungus, Penicillium sp. EU0013. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Liu, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Q. Talaromyces purpurogenus Isolated from Rhizosphere Soil of Maize Has Efficient Organic Phosphate-Mineralizing and Plant Growth-Promoting Abilities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volante, A.; Desiderio, F.; Tondelli, A.; Perrini, R.; Orasen, G.; Biselli, C.; Riccardi, P.; Vattari, A.; Cavalluzzo, D.; Urso, S.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of japonica rice performance under limited water and permanent flooding conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 301720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M.; Sultana, F.; Islam, S. Plant growth-promoting fungi (PGPF): Phytostimulation and induced systemic resistance. Plant-Microbe Interact. Agro-Ecol. Perspect. 2017, 2, 135–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Kang, S.M.; Baek, I.Y.; Lee, I.J. Characterization of plant growth-promoting traits of Penicillium species against the effects of high soil salinity and root disease. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Motaal, F.; Kamel, N.; El-Zayat, S.; Abou-Ellail, M. Early blight suppression and plant growth promotion potential of the endophyte Aspergillus flavus in tomato plant. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Nakamura, E.; Okuyama, E.; Ishibashi, M. Six Immunosuppressive Features from an Ascomycete, Zopfiella longicaudata, Found in a Screening Study Monitored by Immunomodulatory Activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hind, H.G. The colouring matters of Penicillium carmino-violaceum Biourge, with a note on the production of ergosterol by this mould. Biochem. J. 1940, 34, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizmen, B.; Üner, G.; Küçüksolak, M.; Kırmızıbayrak, P.B.; Bedir, E. Secondary metabolites from endophytic fungus Penicilium roseopurpureum and investigation of their cytotoxic activities. Planta Med. 2022, 88, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Khalil, Z.; Li, L.; Salim, A.A.; Quezada, M.; Kalansuriya, P.; Capon, R.J. Roseopurpurins: Chemical Diversity Enhanced by Convergent Biosynthesis and Forward and Reverse Michael Additions. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 4340–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.F.; Dalsgaard, P.W.; Smedsgaard, J.; Larsen, T.O. Andrastins A-D, Penicillium roqueforti Metabolites consistently produced in blue-mold-ripened cheese. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2908–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez, R.; Fierro, F.; García-Rico, R.O.; Vaca, I. Filamentous fungi from extreme environments as a promising source of novel bioactive secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 154260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrar, M.; Ullah, M.W.; Manan, S.; Farooq, U.; Rafiq, M.; Hasan, F. Fungi from the extremes of life: An untapped treasure for bioactive compounds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2777–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Ouyang, Y.; Wu, L.; Shen, L.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Effects of water management on arsenic and cadmium speciation and accumulation in an upland rice cultivar. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 27, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rob, M.M.; Akhter, D.; Islam, T.; Bhattacharjya, D.K.; Shoaib Khan, M.S.; Islam, F.; Chen, J. Copper stress in rice: Perception, signaling, bioremediation and future prospects. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 302, 154314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Rusyn, I.; Dmytruk, O.V.; Dmytruk, K.V.; Onyeaka, H.; Gryzenhout, M.; Gafforov, Y. Filamentous fungi for sustainable remediation of pharmaceutical compounds, heavy metal and oil hydrocarbons. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. Bioremediation of toxic heavy metals (THMs) contaminated sites: Concepts, applications and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27563–27581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Gadd, G.M. Metal and metalloid biorecovery using fungi. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhamouly, N.A.; Hewedy, O.A.; Zaitoon, A.; Miraples, A.; Elshorbagy, O.T.; Hussien, S.; El-Tahan, A.; Peng, D. The hidden power of secondary metabolites in plant-fungi interactions and sustainable phytoremediation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1044896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, M.; Jiang, T.; Wei, H.; Xu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Bao, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Research Progress of Soil Microorganisms in Response to Heavy Metals in Rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8513–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, P.; Yu, D. Microbial Diversity of Upland Rice Roots and Their Influence on Rice Growth and Drought Tolerance. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.C.; Zheng, Y.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, C.H.; Shen, T.L.; Hsu, Y.C.; Lee, B.H. Investigation of the Microbial Diversity in the Oryza sativa Cultivation Environment and Artificial Transplantation of Microorganisms to Improve Sustainable Mycobiota. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchi, G.; Marescotti, P.; Di Piazza, S.; Zotti, M. Native fungi as metal remediators: Silver myco-accumulation from metal contaminated waste-rock dumps (Libiola Mine, Italy). J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2017, 52, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Annibale, A.; Rosetto, F.; Leonardi, V.; Federici, F.; Petruccioli, M. Role of autochthonous filamentous fungi in bioremediation of a soil historically contaminated with aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
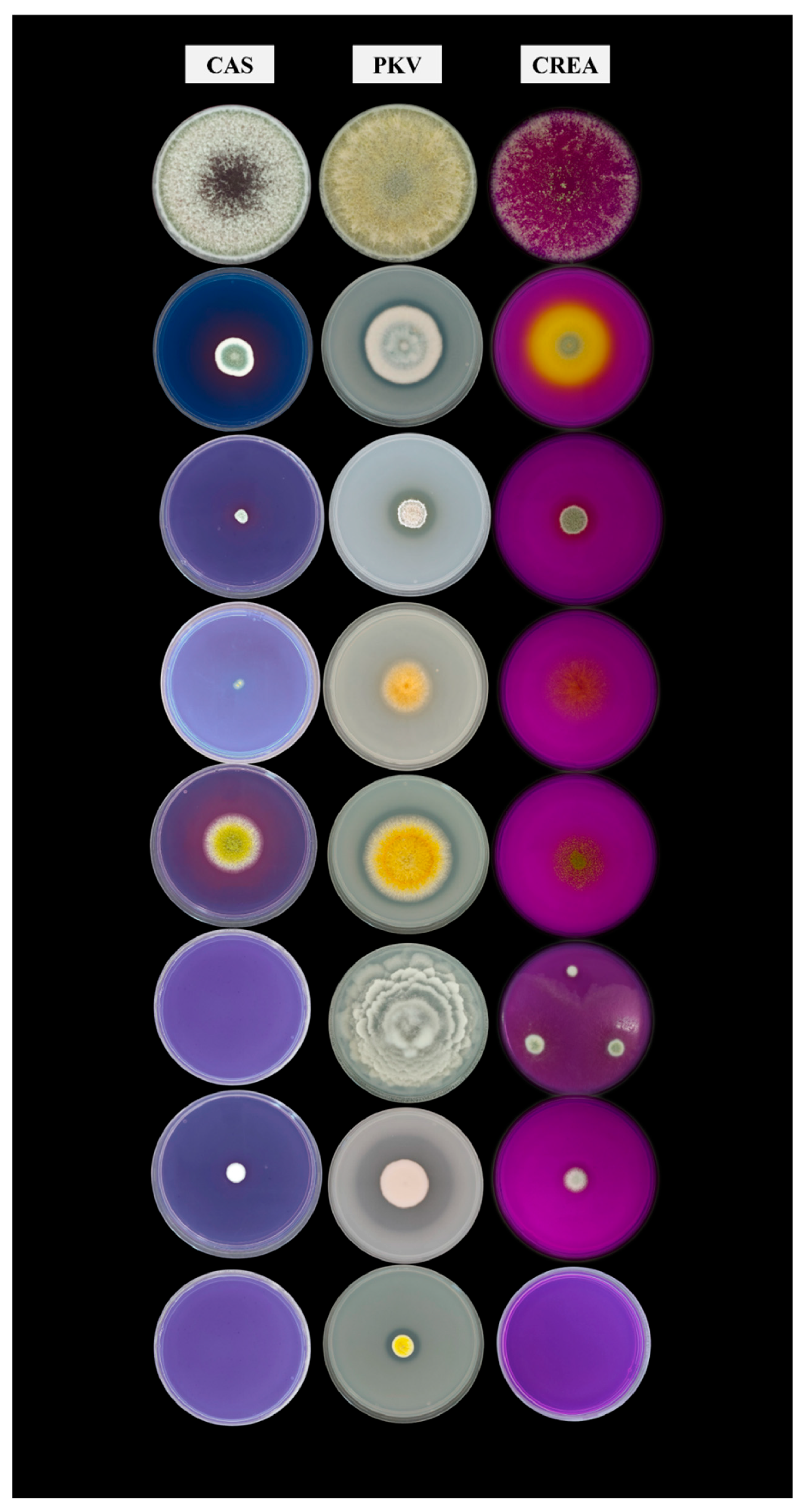
| Fungus | Growth on CAS | Halo Diameter (cm) | Colony Diameter (cm) | Ratio H/C |
| Native fungi | ||||
| Aspergillus flavus | + | 6.43 | 3.63 | 1.77 |
| Mortierella elongata | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | / |
| Penicillium sp. | - | 0.00 | 0.00 | / |
| Penicillium chalabudae | + | 1.78 | 1.05 | 1.69 |
| Allochthonous fungi | ||||
| Acrostalagmus luteoalbus | + | 0.00 | 0.00 | / |
| Penicillium glandicola | + | 1.75 | 0.75 | 2.33 |
| Penicillium piscarium | + | 6.37 | 2.63 | 2.42 |
| Trichoderma harzianum | + | 9.00 | 9.00 | 1.00 |
| Fungus | Growth on PKV | Halo diameter (cm) | Colony diameter (cm) | Ratio H/C |
| Native fungi | ||||
| Aspergillus flavus | + | 6.18 | 5.45 | 1.13 |
| Mortierella elongata | + | 0 | 7.78 | 0.00 |
| Penicillium sp. | + | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.46 |
| Penicillium chalabudae | + | 3.75 | 1.88 | 2.00 |
| Allochthonous fungi | ||||
| Acrostalagmus luteoalbus | + | 0 | 3.33 | 0.00 |
| Penicillium glandicola | + | 2.67 | 1.6 | 1.67 |
| Penicillium piscarium | + | 4.87 | 4.33 | 1.12 |
| Trichoderma harzianum | + | 0 | 9 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canonica, L.; Pesenti, M.; Araniti, F.; Sørensen, J.L.; Muff, J.; Cecchi, G.; Di Piazza, S.; Nocito, F.F.; Zotti, M. Native Fungi as a Nature-Based Solution to Mitigate Toxic Metal(loid) Accumulation in Rice. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071667
Canonica L, Pesenti M, Araniti F, Sørensen JL, Muff J, Cecchi G, Di Piazza S, Nocito FF, Zotti M. Native Fungi as a Nature-Based Solution to Mitigate Toxic Metal(loid) Accumulation in Rice. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071667
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanonica, Laura, Michele Pesenti, Fabrizio Araniti, Jens Laurids Sørensen, Jens Muff, Grazia Cecchi, Simone Di Piazza, Fabio Francesco Nocito, and Mirca Zotti. 2025. "Native Fungi as a Nature-Based Solution to Mitigate Toxic Metal(loid) Accumulation in Rice" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071667
APA StyleCanonica, L., Pesenti, M., Araniti, F., Sørensen, J. L., Muff, J., Cecchi, G., Di Piazza, S., Nocito, F. F., & Zotti, M. (2025). Native Fungi as a Nature-Based Solution to Mitigate Toxic Metal(loid) Accumulation in Rice. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071667








