Fogging with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hypochlorous Acid: An Option for Disinfection and Reuse of Disposable Isolation Gowns in Medical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
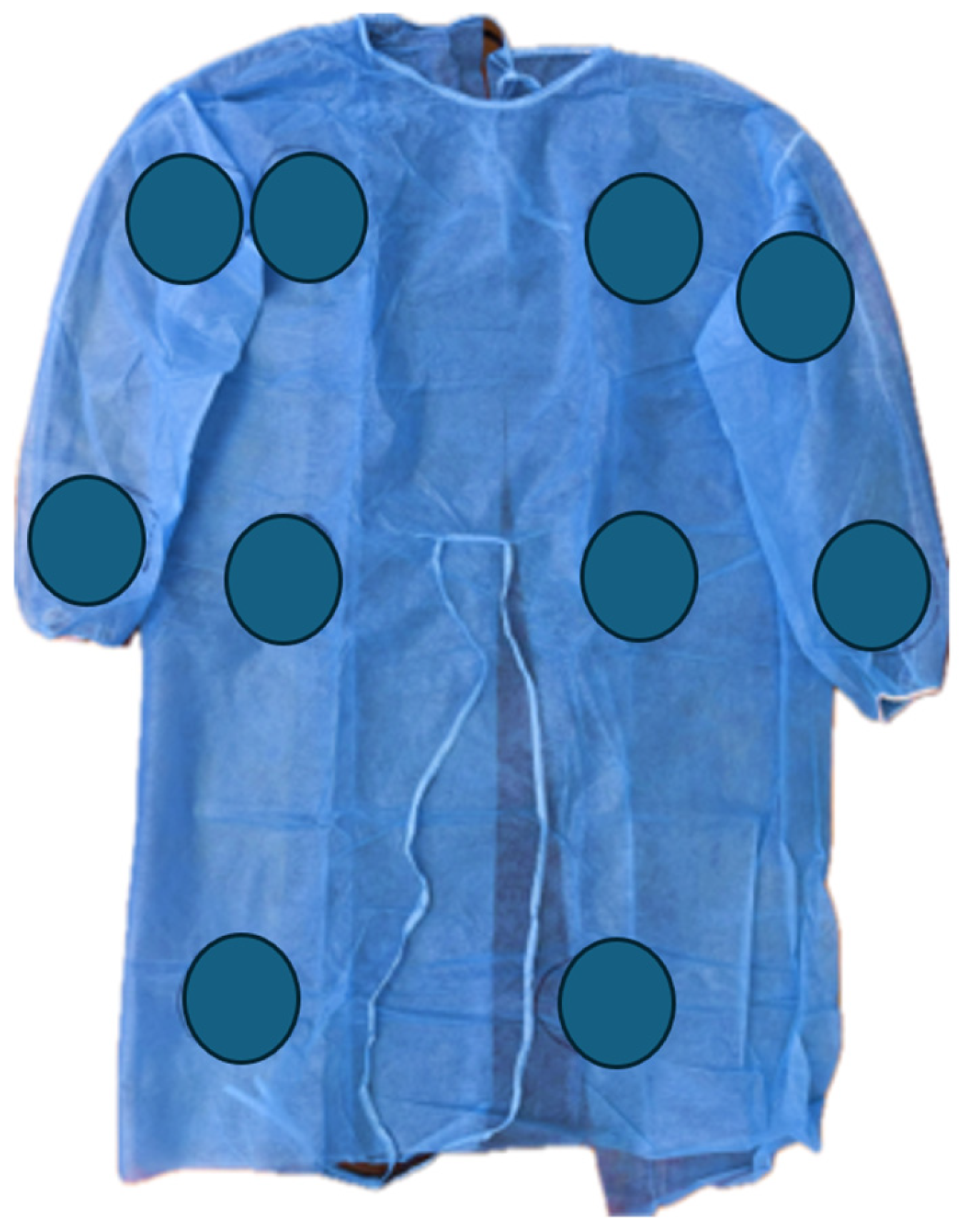
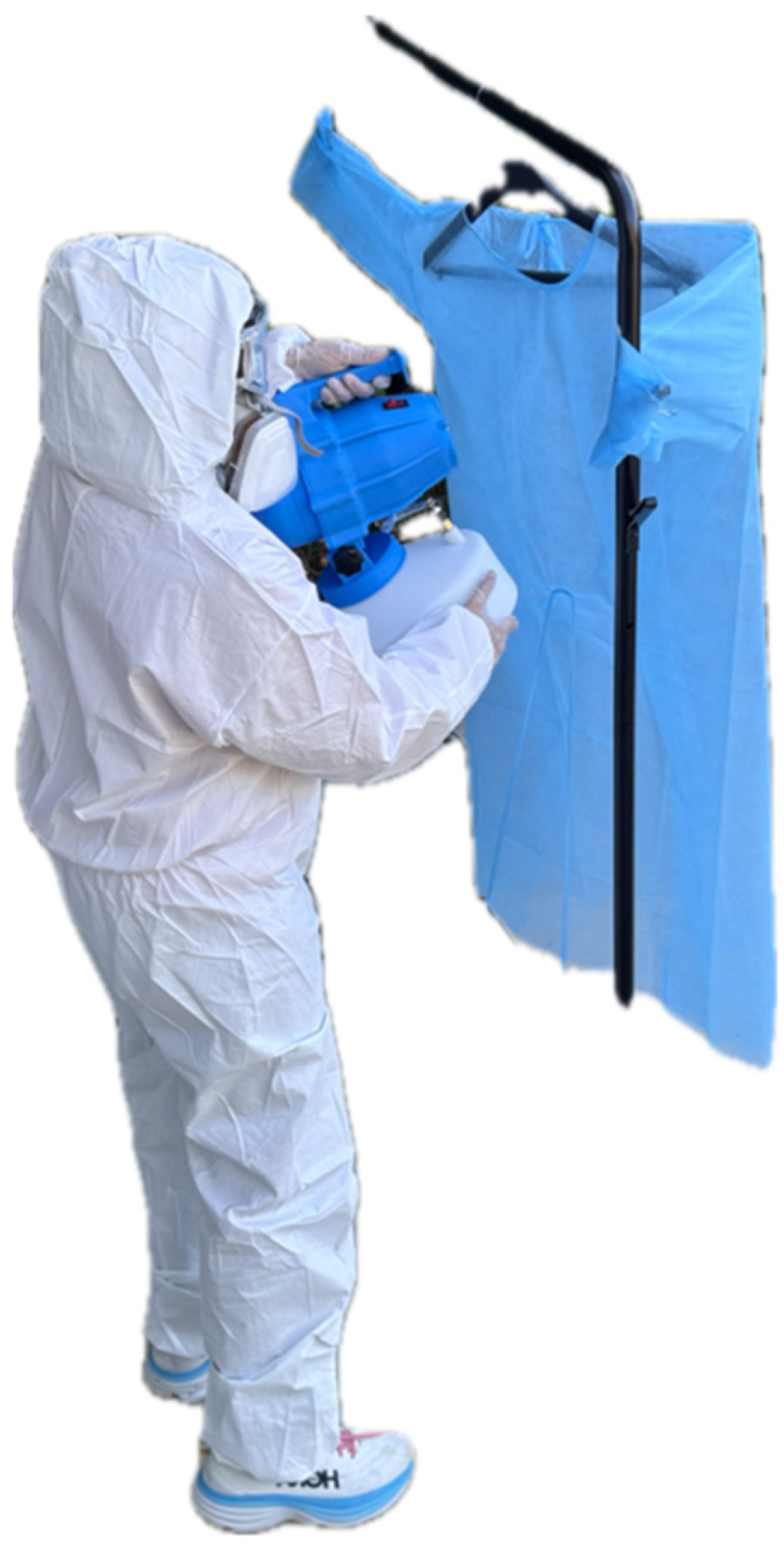
2.1. Methodology
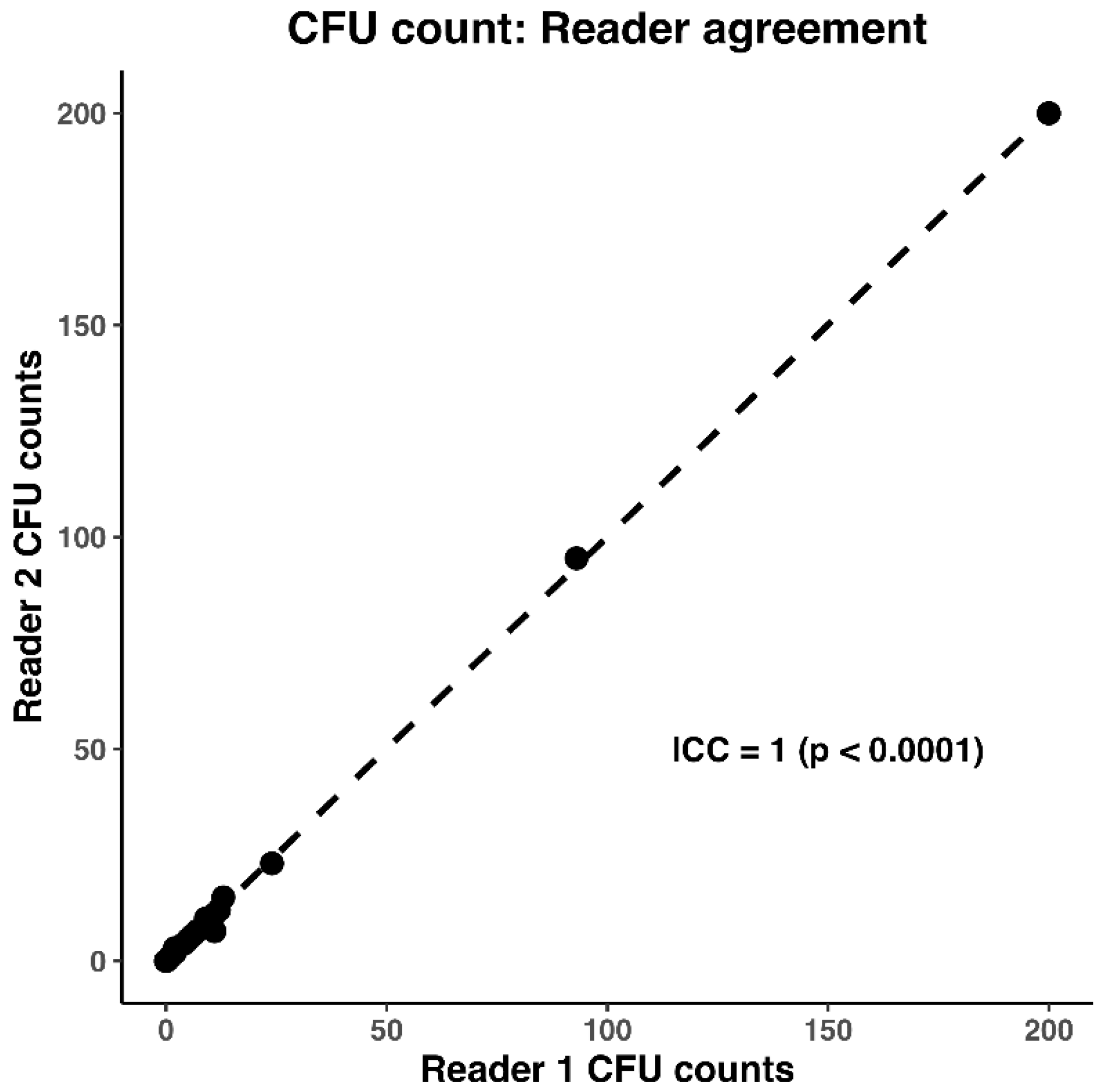
2.2. Statistical Analysis
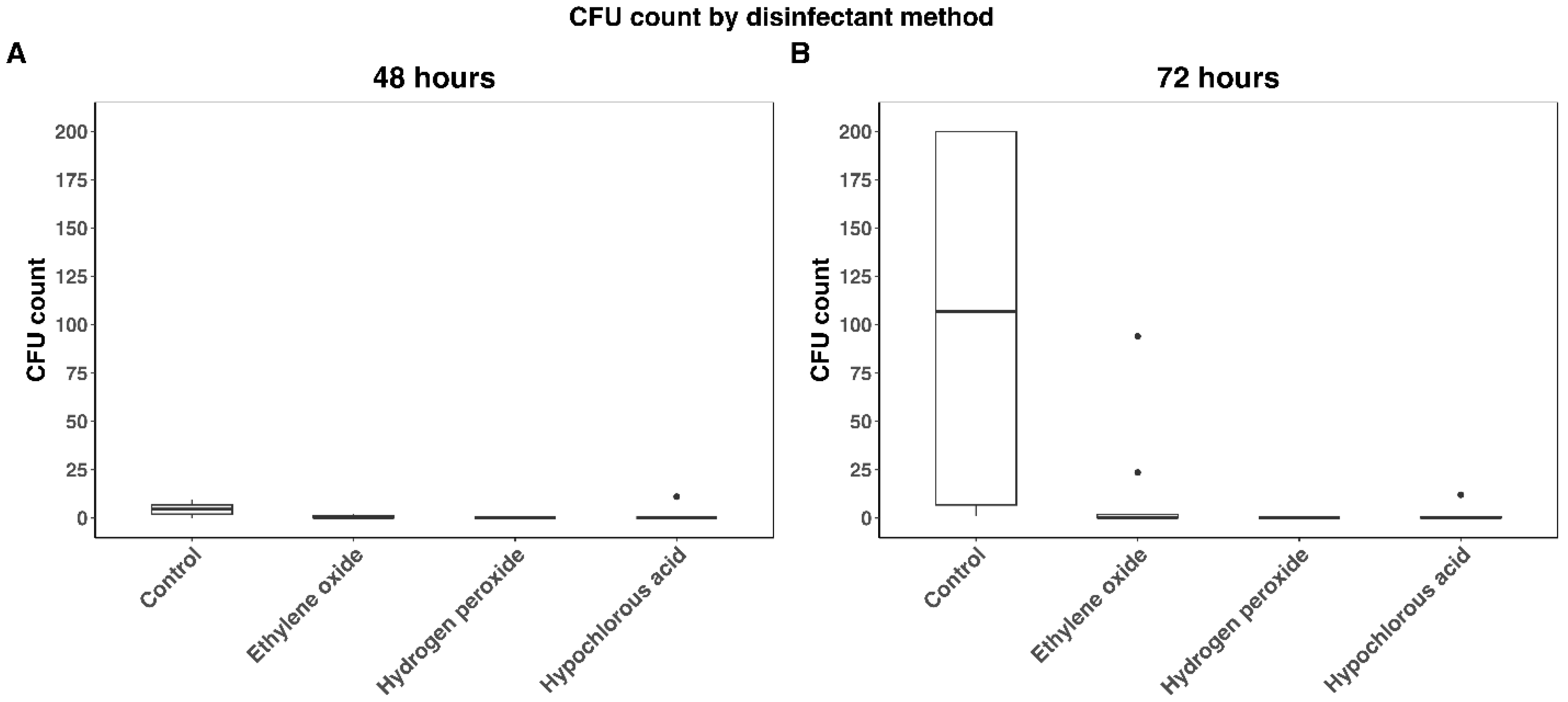
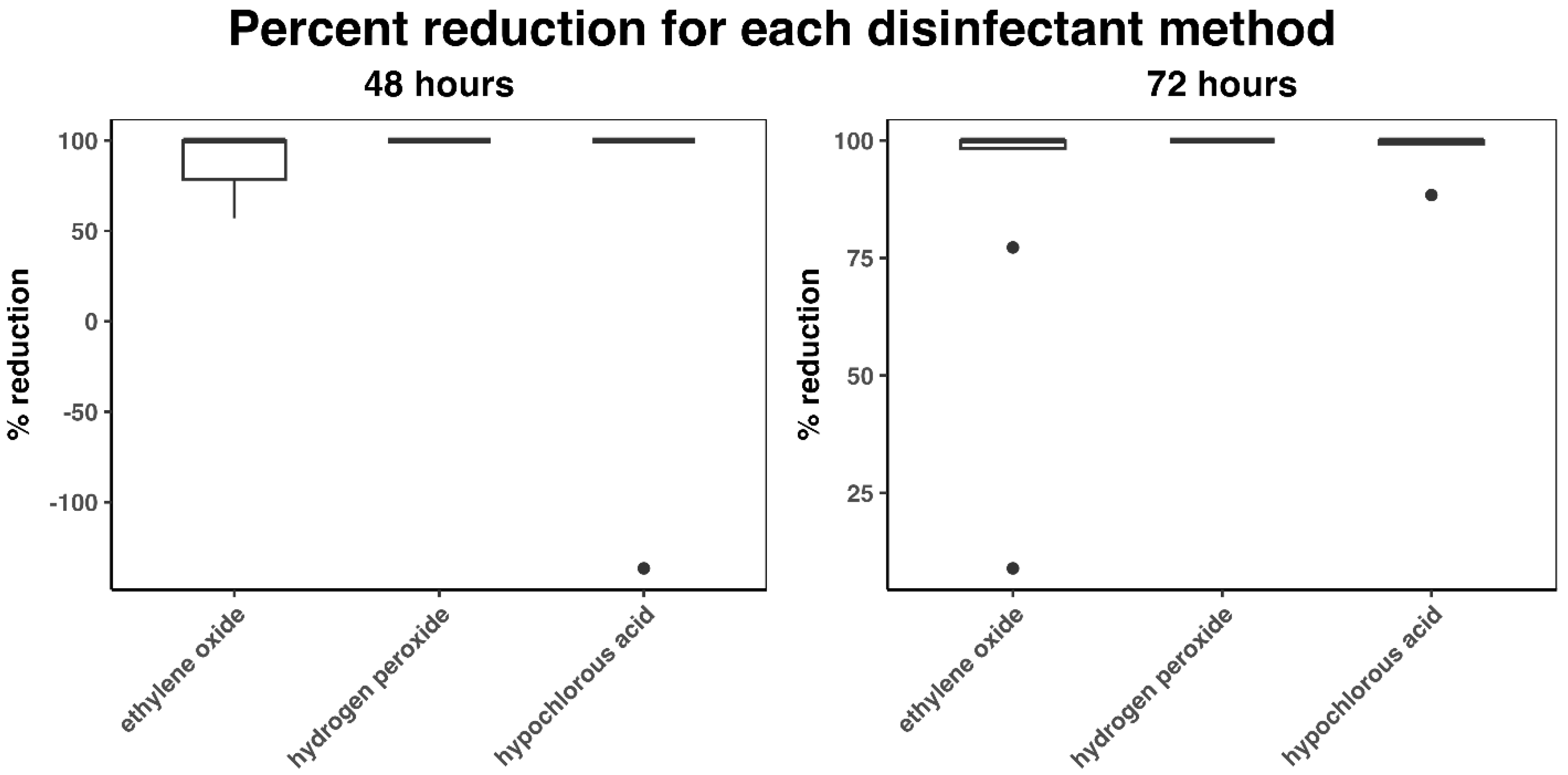
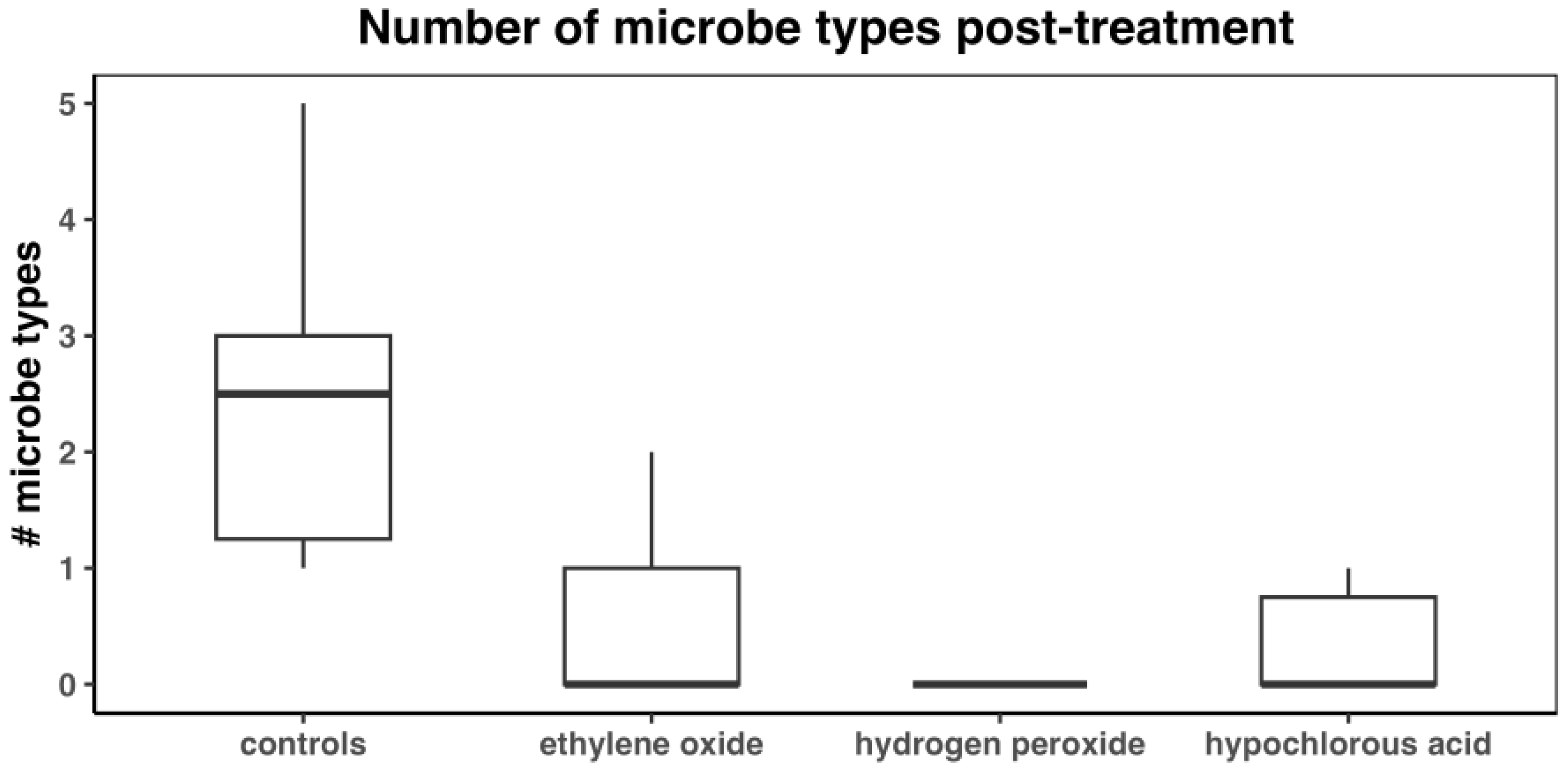
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPE | Personal protective equipment |
| MNP | Micro- and nanoplastic |
| PPM | Parts per million |
| HP | Hydrogen peroxide |
| HC | Hypochlorous acid |
| EO | Ethylene oxide |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
References
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Infection Control: The Role of Disinfection and Sterilization. J. Hosp. Infect. 1999, 43, S43–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities, 2008 (Updated June 2024). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/disinfection-and-sterilization/index.html (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Saber, D.A.; Howlett, B.; Waterman, T.; de Tantillo, L. Solid Waste and Disposal Processes for Isolated Patients with Infectious Disease. Online J. Issues Nurs. 2018, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Saber, D.A.; Neivandt, D.J. Engineering a Compostable Isolation Gown to Reduce Hospital-Derived Synthetic Waste Accumulation in Landfill. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, D.A.; Norris, A.E.; Reinking, J.; Trompeter, G.; Sanford, D. Analyzing the Cost of Hospital Contact Isolation Practices. JONA J. Nurs. Adm. 2022, 52, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Bromley-Dulfano, R.; Chan, J.; Gupta, A.; Herman, L.; Jain, N.; Taylor, A.L.; Lu, J.; Pannu, J.; Patel, L.; et al. COVID-19 Solutions Are Climate Solutions: Lessons from Reusable Gowns. Front. Public. Health 2020, 8, 590275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.P.; Sharma, D.; Saha, S.; Satapathy, B.K. From Outbreak of COVID-19 to Launching of Vaccination Drive: Invigorating Single-Use Plastics, Mitigation Strategies, and Way Forward. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55811–55845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Box, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, H.; Amato, S. Microplastic Pollution in the Surface Waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubas, A.L.V.; Moecke, E.H.S.; Provin, A.P.; Dutra, A.R.A.; Machado, M.M.; Gouveia, I.C. The Impacts of Plastic Waste from Personal Protective Equipment Used during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Polymers 2023, 15, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.-G.; Nguyen, M.-K.; Lin, C.; Nguyen, H.-L.; Nguyen, T.Q.H.; Hue, N.K.; Truong, Q.-M.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, X.H.; Nguyen, D.D. Review on Personal Protective Equipment: Emerging Concerns in Micro(Nano)Plastic Pollution and Strategies for Addressing Environmental Challenges. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Shah, I.A.; Hossain, M.F.; Akther, N.; Zhou, Y.; Khan, M.S.; Al-shaeli, M.; Bacha, M.S.; Ihsanullah, I. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Disposal during COVID-19: An Emerging Source of Microplastic and Microfiber Pollution in the Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, K.K.; Thilagam, H.; Muthukumar, T.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Govarthanan, M. Impact of Microfiber Pollution on Aquatic Biota: A Critical Analysis of Effects and Preventive Measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 163984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.-S.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, D.B.J. Typical Pollutants in Bottom Ashes from a Typical Medical Waste Incinerator. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disinfectants for Emerging Viral Pathogens (EVPs): List Q. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-registration/disinfectants-emerging-viral-pathogens-evps-list-q (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Chemical Disinfectants Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities. 2008. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/disinfection-sterilization/chemical-disinfectants.html#toc (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Patiño-Marín, N.; Villa García, L.D.; Aguirre López, E.C.; Medina-Solís, C.E.; Martínez Zumarán, A.; Martínez Rider, R.; Márquez Preciado, R.; Rosales García, P.; Salas Orozco, M.F. Sterilization and Disinfection: Ensuring Infection Control in Dental Practices. Cureus 2025, 17, e79041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.S.; Adak, A. Physicochemical Methods for Disinfection of Contaminated Surfaces—A Way to Control Infectious Diseases. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destrez, P.; Beysens, D. Disinfection by Hydrogen Peroxide at Low Concentration in Air: The Key Role of Condensation. Anal. Biochem. 2025, 701, 115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, A.; Cheong, Y.K.; Castro, J.C.; Cumberlege, O.; Chrysanthou, A. Use of Hydrogen Peroxide Vapour for Microbiological Disinfection in Hospital Environments: A Review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walawska, A.; Olak-Kucharczyk, M.; Kaczmarek, A.; Kudzin, M.H. Environmentally Friendly Bleaching Process of the Cellulose Fibres Materials Using Ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide in the Gas Phase. Materials 2024, 17, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, A.N.; Maley, M.P. THE 1999 LINDBERG AWARD 3% Hydrogen Peroxide for the Gram–Positive Disinfection of Fabrics. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 1999, 20, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.-C.; Ghai, A.; Liu, H.; Salerno, A.; Miller, C.; Liu, J.; Manesh, S.; Cymerman, J.; Simon, M.; Walker, S.G.; et al. Efficacy of Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) Fog in Sanitizing Surfaces against Enterococcus Faecalis. Am. J. Infect. Control 2022, 50, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzaki, S. Uses of Gaseous Hypochlorous Acid for Controlling Microorganisms in Indoor Spaces. J. Microorg. Control 2023, 28, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, S.; Omura, S.; Fukuzaki, S. Volatilization and Disinfection Efficacy of Gaseous Hypochlorous Acid from an Air Washer-Type Humidifier in a Large Space. J. Microorg. Control 2024, 29, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.S.; Rowan, B.G. Hypochlorous Acid: A Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, W.C. Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles. Aerosol Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, G.E. Antisepsis, Disinfection, and Sterilization: Types, Action, and Resistance; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Mou, S.; Jiang, R.; Zhu, W. Association between Ethylene Oxide Exposure and Osteoarthritis Risk: An Analysis of NHANES Data (2013–2014 and 2017–2018). Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1511215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Xie, S. Association of Ethylene Oxide Exposure and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2025, 30, 24–00248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Lei, D.; Peng, D.; Zong, K.; Li, K.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z. Associations between Ethylene Oxide Exposure and Liver Function in the US Adult Population. Toxics 2024, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, Z.R. Ethylene Oxide: Toxicology Review and Field Study Results of Hospital Use. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. 1979, 2, 173–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rudometkin, N.J.; Wessels, I.F.; Hedayi, R.S.; Choe, J.E.; Roeske, R.E. Culture Plate Temperature and Delayed Incubation Effect on Bacterial Recovery. Cornea 2003, 22, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, H. Ethylene Oxide Gas Sterilization of Medical Devices. Biocontrol Sci. 2017, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.C.C.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Silva, C.L.M. Ethylene Oxide Sterilization of Medical Devices: A Review. Am. J. Infect. Control 2007, 35, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha Mendes, G.C.; da Silva Brandão, T.R.; Miranda Silva, C.L. Ethylene Oxide Potential Toxicity. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2008, 5, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutala, W.A.; Gergen, M.F.; Sickbert-Bennett, E.E.; Williams, D.A.; Weber, D.J. Effectiveness of Improved Hydrogen Peroxide in Decontaminating Privacy Curtains Contaminated with Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijan, S.; Škerget, M.; Knez, Ž.; Šostar-Turk, S.; Neral, B. Determining the Disinfection of Textiles in Compressed Carbon Dioxide Using Various Indicator Microbes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, G. Hydrogen Peroxide Fogging/Fumigation. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 62, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümin, D.; Albert, M.G.; Weber, B.; Summermatter, K. The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Hydrogen Peroxide Fumigation, Part 1: Introduction to Hydrogen Peroxide Fumigation. Appl. Biosaf. 2020, 25, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Lapolla, B.; Bair, T.; Grinstead, F.; Hislop, M.; Greene, C.; Bigham, M.T. Enhanced Disinfection with Hybrid Hydrogen Peroxide Fogging in a Critical Care Setting. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Ilbert, M.; Graf, P.C.F.; Özcelik, D.; Jakob, U. Bleach Activates a Redox-Regulated Chaperone by Oxidative Protein Unfolding. Cell 2008, 135, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.W.; Boston, D.M.; Kase, J.A.; Sampson, M.N.; Sobsey, M.D. Evaluation of Liquid- and Fog-Based Application of Sterilox Hypochlorous Acid Solution for Surface Inactivation of Human Norovirus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4463–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiłowska, B.; Włodarski, M.; Kaliszewski, M.; Bogdanowicz, Z.; Krzowski, Ł.; Kopczyński, K.; Witkowski, G.; Czeczott-Urban, A.; Bombalska, A.; Urbańska, M.; et al. Decontamination Effect of Hypochlorous Acid Dry Mist on Selected Bacteria, Viruses, Spores, and Fungi as Well as on Components of Electronic Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medical Management Guidelines for Hydrogen Peroxide. Available online: https://www.webpoisoncontrol.org/-/media/files/pdf-for-article-dowloads-and-refs/medical-management-guidelines-for-hydrogen-peroxide.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Sun, X.; Peng, Y.; Deng, J. Comparative Performance of Contact Plate Metod and Swab Method for Surface Microbial Contamination on Medical Fabrics. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obee, P.; Griffith, C.J.; Cooper, R.A.; Bennion, N.E. An Evaluation of Different Methods for the Recovery of Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus from Environmental Surfaces. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 65, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmen, S.W.; Häfner, H.; Zolldann, D.; Amedick, G.; Lutticken, R. Comparison of Two Sampling Methods for the Detection of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria in the Environment: Moistened Swabs versus Rodac Plates. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2001, 203, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, W. Development and Validation of a Neutralizer System for in Vitro Evaluation of Some Antiseptics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 19, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Comparison | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|
| @48H | @72H | |
| control vs. ethylene oxide | 0.0124 | 0.0065 |
| control vs. hydrogen peroxide | 0.0001 | 0.0000 |
| control vs. hypochlorous acid | 0.0007 | 0.0008 |
| ethylene oxide vs. hydrogen peroxide | 0.4680 | 0.3383 |
| ethylene oxide vs. hypochlorous acid | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| hydrogen peroxide vs. hypochlorous acid | 1.0000 | 0.9512 |
| Comparison | p-Values |
|---|---|
| control vs. ethylene oxide | 0.0006 |
| control vs. hydrogen peroxide | <0.0001 |
| control vs. hypochlorous acid | 0.0001 |
| ethylene oxide vs. hydrogen peroxide | 0.0669 |
| ethylene oxide vs. hypochlorous acid | 0.3188 |
| hydrogen peroxide vs. hypochlorous acid | 0.1520 |
| Group | Gown # | Fogging Time (min: s) |
|---|---|---|
| HP | 1 | 1:15 |
| HP | 6 | 1:14 |
| HP | 7 | 1:11 |
| HP | 8 | 1:07 |
| HP | 9 | 1:05 |
| HC | 1 | 1:14 |
| HC | 2 | 1:03 |
| HC | 7 | 1:09 |
| HC | 9 | 1:13 |
| HC | 10 | 1:16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iyer, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Vinayak, A. Fogging with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hypochlorous Acid: An Option for Disinfection and Reuse of Disposable Isolation Gowns in Medical Practice. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071537
Iyer S, Ouyang Z, Vinayak A. Fogging with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hypochlorous Acid: An Option for Disinfection and Reuse of Disposable Isolation Gowns in Medical Practice. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071537
Chicago/Turabian StyleIyer, Shay, Zenhwa Ouyang, and Arathi Vinayak. 2025. "Fogging with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hypochlorous Acid: An Option for Disinfection and Reuse of Disposable Isolation Gowns in Medical Practice" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071537
APA StyleIyer, S., Ouyang, Z., & Vinayak, A. (2025). Fogging with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hypochlorous Acid: An Option for Disinfection and Reuse of Disposable Isolation Gowns in Medical Practice. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071537





