Development of a Broad-Spectrum Antigen-Capture ELISA Using Combined Anti-p26 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies for Detection of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Plasmids and Viruses
2.3. Monoclonal Antibody and Polyclonal Antibody
2.4. Antigen Captured ELISA (AC-ELISA)
2.5. Determination of the Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity of the AC-ELISA
2.6. Reverse Transcriptase Assay
2.7. Real-Time PCR for EIAV-Luc
2.8. Western Blotting
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of the p26 Protein and Validation of Antibody Effectiveness
3.2. Establishment of the AC-ELISA
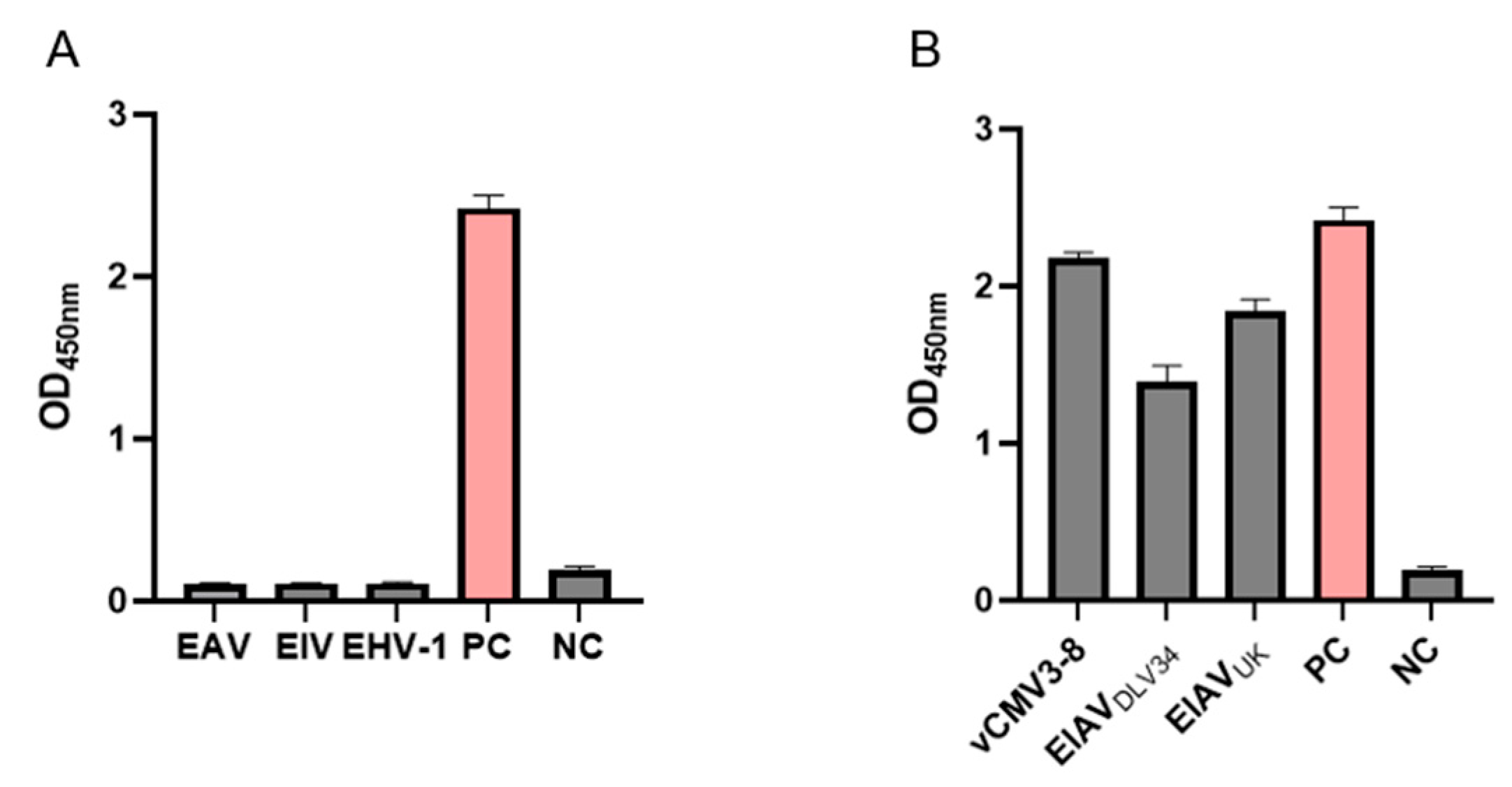
3.3. Specificity of the AC-ELISA
3.4. Analysis of the Sensitivity of the Novel AC-ELISA
3.5. Comparison of the Novel AC-ELISA and Other Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alnaeem, A.A.; Hemida, M.G. Surveillance of the equine infectious anemia virus in Eastern and Central Saudi Arabia during 2014–2016. Vet. World 2019, 12, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malossi, C.D.; Fioratti, E.G.; Cardoso, J.F.; Magro, A.J.; Kroon, E.G.; de Moura Aguiar, D.; Borges, A.M.C.M.; Nogueira, M.F.; Ullmann, L.S.; Araujo, J.P. High Genomic Variability in Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Obtained from Naturally Infected Horses in Pantanal, Brazil: An Endemic Region Case. Viruses 2020, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cursino, A.E.; Vilela, A.P.P.; Franco-Luiz, A.P.M.; de Oliveira, J.G.; Nogueira, M.F.; Pessoa Araújo, J., Jr.; de Aguiar, D.M.; Kroon, E.G. Equine infectious anemia virus in naturally infected horses from the Brazilian Pantanal. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Y. Truncation of cytoplasmic tail of EIAV Env increases the pathogenic necrosis. Virus Res. 2008, 133, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigo, J.; Montelaro, R. Lessons in AIDS Vaccine Development Learned from Studies of Equine Infectious, Anemia Virus Infection and Immunity. Viruses 2013, 5, 2963–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, C.; Cadoré, J.-L.; Montelaro, R.C. Equine Infectious Anemia Virus (EIAV): What has HIV?s country cousin got to tell us? Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 485–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-D.; Na, L.; Fu, L.-H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, C.-H.; Tang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.-F.; et al. Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase 1 (ADAR1) promotes EIAV replication and infectivity. Virology 2015, 476, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigo, J.K.; Barnes, S.; Zhang, B.; Cook, S.J.; Howe, L.; Issel, C.J.; Montelaro, R.C. An EIAV field isolate reveals much higher levels of subtype variability than currently reported for the equine lentivirus family. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-Sáenz, C.I.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Olivas-Holguin, A.; Ramos-Zayas, Y.; Obregón-Macías, N.; González-Ochoa, G.; Zavala-Díaz de la Serna, F.J.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Tamez-Guerra, R.; Gomez-Flores, R. Molecular detection of equine infectious anemia virus in clinically normal, seronegative horses in an endemic area of Mexico. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannai, H.; Kambayashi, Y.; Nemoto, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Tsujimura, K. Comparison of 4 agar gel immunodiffusion kits for serologic detection of equine infectious anemia virus antibodies. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2023, 35, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, K.; Chu, X.; Liu, M.; Du, C.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X. Development and evaluation of a test strip for the rapid detection of antibody against equine infectious anemia virus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupulovic, D.; Savić, S.; Gaudaire, D.; Berthet, N.; Grgić, Ž.; Matović, K.; Deshiere, A.; Hans, A. Identification and genetic characterization of equine infectious anemia virus in Western Balkans. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Rendon, E.; White, L.J.; Olsen, A.; Mitrophanous, K.A.; Mazarakis, N.D. New Methods to Titrate EIAV-Based Lentiviral Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2002, 5, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.-B.; Zhu, W.; Cook, F.R.; Goto, Y.; Horii, Y.; Haga, T. Development of a nested PCR assay to detect equine infectious anemia proviral DNA from peripheral blood of naturally infected horses. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlivan, M.; Cook, R.F.; Cullinane, A. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and PCR assays for a novel European field isolate of equine infectious anaemia virus based on sequence determination of the gag gene. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda Coutinho, L.C.; Santos de Jesus, A.L.; de Paiva Fontes, K.F.L.; Campos Coimbra, E.; Colaço Mariz, F.; de Freitas, A.C.; de Cássia Carvalho Maia, R.; Soares de Castro, R. Production of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus (EIAV) antigen in Pichia pastoris. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 191, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Issel, C.J.; Montelaro, R.C. Serological method using recombinant S2 protein to differentiate equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV)-infected and EIAV-vaccinated horses. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cook, S.J.; Craigo, J.K.; Cook, F.R.; Issel, C.J.; Montelaro, R.C.; Horohov, D.W. Epitope shifting of gp90-specific cellular immune responses in EIAV-infected ponies. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol 2014, 15, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, P.L.; Lv, S.X.; Zhou, J.H.; Liu, X.Q. Cloning, expression and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the equine infectious anaemia virus (EIAV) gp45 ectodomain. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.A.; Dick, R.A.; Xu, C.; Morado, D.R.; Kravchuk, V.; Ricana, C.L.; Lyddon, T.D.; Broad, A.M.; Feathers, J.R.; Johnson, M.C.; et al. Structures of immature EIAV Gag lattices reveal a conserved role for IP6 in lentivirus assembly. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capomaccio, S.; Willand, Z.A.; Cook, S.J.; Issel, C.J.; Santos, E.M.; Reis, J.K.P.; Cook, R.F. Detection, molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of full-length equine infectious anemia (EIAV) gag genes isolated from Shackleford Banks wild horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Wang, Y.; Du, C.; Ren, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Na, L.; Liu, D.; et al. Env diversity-dependent protection of the attenuated equine infectious anaemia virus vaccine. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.-F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. Characterization of EIAV env Quasispecies during Long-Term Passage In Vitro: Gradual Loss of Pathogenicity. Viruses 2019, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.F.; Leroux, C.; Cook, S.J.; Berger, S.L.; Lichtenstein, D.L.; Ghabrial, N.N.; Montelaro, R.C.; Issel, C.J. Development and characterization of an in vivo pathogenic molecular clone of equine infectious anemia virus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.; Chen, K.; Ehrlich, L.S.; Jin, J.; Chen, M.H.; Medina, G.N.; Symons, M.; Montelaro, R.; Donaldson, J.; Tjandra, N.; et al. Phosphoinositides Direct Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Gag Trafficking and Release. Traffic 2011, 12, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaleda, L.; Fuller, F.J.; Payne, S.L. EIAV S2 enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine response in infected macrophages. Virology 2010, 397, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigo, J.K.; Sturgeon, T.J.; Cook, S.J.; Issel, C.J.; Leroux, C.; Montelaro, R.C. Apparent elimination of EIAV ancestral species in a long-term inapparent carrier. Virology 2006, 20, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.F.; Barrandeguy, M.; Lee, P.Y.A.; Tsai, C.F.; Shen, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.L.; Chang, H.F.G.; Wang, H.T.T.; Balasuriya, U.B.R. Rapid detection of equine infectious anaemia virus nucleic acid by insulated isothermal RT-PCR assay to aid diagnosis under field conditions. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 51, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. On the Calculation of TCID50 for Quantitation of Virus Infectivity. Virol. Sin. 2020, 36, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Bai, B.; Lin, Y.; Qi, T.; Du, C.; Song, M.; Wang, X. High-Efficiency Rescue of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus from a CMV-Driven Infectious Clone . Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chang, H.; Ge, M.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, X. Development of antigen capture ELISA for the quantification of EIAV p26 protein. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9073–9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Bai, B.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Simon, V. Truncation of the Cytoplasmic Tail of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Increases Virion Production by Improving Env Cleavage and Plasma Membrane Localization. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0108721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chang, H.; Chu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Identification and characterization of a common B-cell epitope on EIAV capsid proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10531–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-N.; Rao, D.; Fu, X.-Q.; Hu, M.-M.; Dong, J.-G. Equine infectious anemia virus in China. Oncotarget 2017, 21, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielonka, J.; Bravo, I.G.; Marino, D.; Conrad, E.; Perković, M.; Battenberg, M.; Cichutek, K.; Münk, C. Restriction of equine infectious anemia virus by equine APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7547–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.-W.; Du, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.-H. Genetic Evolution during the development of an attenuated EIAV vaccine. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Host cell restriction factors of equine infectious anemia virus. Virol. Sin. 2023, 38, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Schulte, A.; Vogel-Bachmayr, K.; Scheffzek, K.; Geyer, M. Structural insights into the cyclin T1-Tat-TAR RNA transcription activation complex from EIAV. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieulent, C.J.; Carossino, M.; Reis, J.K.P.D.; Vissani, M.A.; Barrandeguy, M.E.; Valle-Casuso, J.-C.; Balasuriya, U.B.R. Equine infectious anemia virus worldwide prevalence: A 24-year retrospective review of a global equine health concern with far-reaching implications. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 306, 110548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.F.; Leroux, C.; Issel, C.J. Equine infectious anemia and equine infectious anemia virus in 2013: A review. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, J.-H.; Wang, X.; Simon, V. Characterization of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Long Terminal Repeat Quasispecies In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02150–e02157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Guo, K.; Du, C.; Sun, J.; Naletoski, I.; Chu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Barrandeguy, M.; Samuel, M.; et al. Development and evaluation of a blocking ELISA for serological diagnosis of equine infectious anemia. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3305–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, A.M.; Chen, F.; Khan, S.B.; Guo, X.; Khan, R.; Khan, F.A.; Zhu, Y.; He, Q. Development and evaluation of polyclonal antibodies based antigen capture ELISA for detection of porcine rotavirus. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohn, O.; Mostafa, S.; Norley, S.; Bannert, N. Development of an antigen-capture ELISA for the detection of the p27-CA protein of HERV-K(HML-2). J. Virol. Methods 2016, 234, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, H.; Zhou, B.; Hu, Z.; Chu, X.; Wang, X.; Du, C.; Wang, X. Development of a Broad-Spectrum Antigen-Capture ELISA Using Combined Anti-p26 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies for Detection of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071500
Liang H, Zhou B, Hu Z, Chu X, Wang X, Du C, Wang X. Development of a Broad-Spectrum Antigen-Capture ELISA Using Combined Anti-p26 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies for Detection of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071500
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Haibing, Bingqian Zhou, Zhe Hu, Xiaoyu Chu, Xuefeng Wang, Cheng Du, and Xiaojun Wang. 2025. "Development of a Broad-Spectrum Antigen-Capture ELISA Using Combined Anti-p26 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies for Detection of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071500
APA StyleLiang, H., Zhou, B., Hu, Z., Chu, X., Wang, X., Du, C., & Wang, X. (2025). Development of a Broad-Spectrum Antigen-Capture ELISA Using Combined Anti-p26 Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies for Detection of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071500




