Abstract
The aim of this study was to examine the genetic characteristics that could be associated with the virulence characteristics of Escherichia coli collected from clinical samples. A collection of 100 non-repetitive E. coli isolates was analyzed. All isolates were typed by MLST. String production, biofilm formation and serum resistance were examined for all isolates. Twenty E. coli isolates were completely sequenced Illumina platform. The results showed that the majority of E. coli isolates (87%) produced significant levels of biofilm, while none of the isolates were positive for string test and resistance to serum. Additionally, the presence of CRISPR/Cas systems (type I-E or I-F) was found in 18% of the isolates. Analysis of WGS data found that all sequenced isolates harbored a variety of virulence genes that could be implicated in adherence, invasion, iron uptake. Also, WGS data confirmed the presence of a wide variety of resistance genes, including ESBL- and carbapenemase-encoding genes. In conclusion, an important percentage (87%) of the E. coli isolates had a significant ability to form biofilm. Biofilms, due to their heterogeneous nature and ability to make microorganisms tolerant to multiple antimicrobials, complicate treatment strategies. Thus, in combination with the presence of multidrug resistance, expression of virulence factors could challenge antimicrobial therapy of infections caused by such bacteria.
1. Introduction
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative bacterium colonizing the intestines of various animals including humans. Despite E. coli usually being a harmless bacterium, some isolates are pathogenic. E. coli can be the etiological agent of intestinal and extra-intestinal diseases, such as urinary tract infections, septicemia, peritonitis and pneumonia [1]. Annually, pathogenic E. coli (PEC) is estimated to cause over 2 million deaths globally [2]. PECs mainly include the enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC), the Shiga toxin–producing E. coli (STEC) and the enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) [3]. Additionally, among PECs, uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) is responsible for up to 50% of hospital-acquired UTIs and for 90% of community UTIs in both men and women [4].
Pathogenicity is expedited by virulence factors like adhesion, iron acquisition, hemolysin, aerobactin’s and serum resistance encoded by genes found on plasmids and/or chromosome [5]. Furthermore, Shiga toxin (Stx) is considered a major virulence factor, associated with STEC infections [6]. The EPEC pathotype harbors the intimin (eae) gene [7], while the ETEC isolates harbor the plasmid-encoded heat-labile LT or heat-stable ST enterotoxins [8]. UPEC isolates have various virulence factors, including fimbriae and adhesins, biofilm formation ability, iron-acquisition factors, flagella, and toxins such as hemolysin [9,10]. These virulence factors provide the pathogen with the potential to evade or overwhelm host defense mechanisms, invade host cells, and induce inflammation in the host [11].
Furthermore, the growing problem of antimicrobial-resistance (AMR), associated with the presence of multiple resistance genes, complicates the antimicrobial treatment of infections. E. coli isolates have been reported to produce ESBLs, carbapenemases and/or MCRs conferring resistance to cephalosporins, carbapenems and polymyxins [12,13,14], respectively. These resistance genes are usually localized on mobile genetic elements, like plasmids, carrying additional resistance genes conferring resistance to multiple antimicrobial categories [15], such as aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, etc. Thus, treatment options of infections caused by these bacteria are limited to few choices with unpredictable effect [16].
Another interesting feature found in almost 40% of bacterial species is CRISPR/Cas (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated genes or proteins) systems [17]. CRISPR/Cas systems, which were firstly detected on the E. coli K-12 chromosome, in 1987, are a defense mechanism against foreign invaders such as plasmids and viruses [18]. In addition, further studies have demonstrated that many Cas proteins from diverse CRISPR/Cas systems and organisms are involved in various functions, including gene regulation [19,20], DNA repair [21], and cell dormancy [22]. Interestingly, in 2009, CRISPR/Cas systems were shown to affect biofilm formation and swarming in P. aeruginosa [23,24].
Therefore, the aim of the current study was to examine the genetic characteristics that could be associated with virulence characteristics of E. coli isolates collected from clinical samples.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Isolates, Identification and Susceptibility Testing
A collection of 100 nonrepetitive E. coli, isolated from January 2020 to October 2020, from patients treated in UHL, which is a 650-bed tertiary care hospital in Thessaly (Central Greece), serving a population of 1,000,000 inhabitants, was studied. For each month, the ten first isolates were selected. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacterial isolates was performed by the VITEK-2 system (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Étoile, France). E. coli ATCC25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 were used as control strains [25]. Data were interpreted according to the criteria (version 15.0) of the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) (www.eucast.org, accessed on 1 February 2025).
2.2. Detection of ESBL-Encoding Genes
All isolates were screened, by PCR amplification, for the presence of genes encoding SHV and CTX-M β-lactamases, using specific primers [12].
2.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing
All E. coli isolates were typed by multilocus sequence typing (MLST), as described previously [26]. Sequence types (STs) and clonal complexes (CCs) were assigned at the E. coli MLST database (https://pubmlst.org/organisms/escherichia-spp, accessed on 1 February 2025).
2.4. String Test
All E. coli isolates were grown on blood agar plates overnight at 37 °C and stretched using an inoculation loop. The string was manually measured with a ruler. Isolates that produced colonies that could be stretched into a viscous string of >5 mm in all cases were considered string test positive.
2.5. Hemolysin Production
The ability of E. coli to induce hemolysis on blood agar was evaluated to detect the hemolysin-producing isolates. The isolates were inoculated into 5% sheep blood agar plates and incubated overnight at 37 °C. Hemolysin production was detected by the presence of a complete clearing zone of the erythrocytes around the colonies.
2.6. Microtiter Plate (MTP) Assay
The biofilm formation of E. coli was quantitatively estimated using the MTP assay as described earlier with minor modifications [27]. Briefly, 1% overnight culture of the test isolate was dispensed into 96-well MTP containing 200 μL of tryptone soya broth (TSB). The plate was incubated without agitation, for 24 h at 37 °C, to facilitate the adherence of the bacteria cells onto the surface of the MTP. Following incubation, the broth medium was discarded and the wells were gently washed twice with PBS to remove loosely attached planktonic cells. Each well was stained with 200 μL of 0.4% crystal violet (CV) solution for 1 min and the excess stain was removed by rinsing the wells thrice with sterile distilled water. The CV bound to the biofilm mass was then solubilized with 200 μL of 95% ethanol and quantified. Then, the absorbance was measured at 650 nm. The results were interpreted based on the recommendations published previously [28]. Specifically, isolates were classified as non-biofilm producers with OD650 values < 0.1, weak biofilm producers with OD650 = 0.1–0.2, moderate biofilm producers with OD650 = 0.2–0.4, and strong biofilm producers with OD650 values > 0.4.
2.7. Serum Resistance Assay
The recalcification method, as described previously [29,30], was used to prepare pooled human serum from at least 5 different people. Isolates were grown in BHI medium overnight at 37 °C with shaking. The isolates were spun down, washed two times with PBS, and adjusted to a final concentration of 1 × 107 CFU/mL with PBS. A total of 1 × 105 CFU was added to 5 mL of 80% NHS (normal human serum) in PBS and 80% heat-inactivated NHS in PBS. The samples were incubated with shaking at 37 °C for 0 and 3 h. After incubation, the cell count was determined using 10-fold serial dilutions and conventional plating in Luria Bertani agar. The log values of CFU counts at time 3 hrs normalized to CFU counts at time zero were calculated. The interpretation of the results was carried out based on the recommendation shown below. Isolates with log values < −0.7 were serum-sensitive, isolates with log values = −0.7–0.3 exhibited intermediate resistance to serum, and isolates with log values > 0.3 were serum-resistant.
2.8. CRISPR/Cas Typing and CRISPR Amplification
To perform CRISPR/Cas typing, we used the cas2 gene to examine the presence of type I-E systems, and the I-F specific cas1 gene to examine the presence of type I-F systems. Then, for all E. coli isolates, CRISPR arrays were PCR-amplified using specific primers. Primers were designed using WGS data of E. coli, harboring type I-E or I-F CRISPR/Cas systems, which were downloaded from the CRISPRCasdb database (https://crisprcas.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/MainDb/StrainList, accessed on 1 February 2025). Primers and references are shown in Table 1. PCR amplicons were sequenced on both strands using an ABI 3500 sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). CRISPRFinder was chosen to confirm the CRISPR sequences obtained. Furthermore, the BLAST algorithm (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST, accessed on 1 February 2025) was employed for the sequence analysis of the spacers identified.

Table 1.
Primers used for amplification in the present study.
2.9. Whole-Genome Sequencing
Twenty E. coli isolates, selected based on different susceptibility profiles, STs, virulence profiles and epidemiological data, were further analyzed with whole-genome sequencing (WGS). The genomic DNAs of the E. coli isolates, extracted using the DNA-Sorb-B kit (Sacace Biotechnologies S.r.l., Como, Italy), were sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Initial paired-end reads, which were quality trimmed using Trimmomatic tool v0.32 (22 January 2022), were assembled via de Bruijn graph-based de novo assembler SPAdes v3.14.0 (31 December 2019).
2.10. Analysis of WGS Data
Antibiotic resistance genes were identified using the ResFinder 4.6 tool (http://genepi.food.dtu.dk/resfinder, accessed on 1 February 2025) with a threshold for minimum identity of 90% and for minimum coverage of 60% [32]. PlasmidFinder 2.1 (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/PlasmidFinder/, accessed on 1 February 2025), using a threshold for minimum identity of 95% and for minimum coverage of 60%, was used for detecting plasmid replicons in the sequenced isolates [33]. Additionally, WGS data were analyzed with VirulenceFinder 2.0 (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/VirulenceFinder/, accessed on 1 February 2025), with a threshold for minimum identity of 90% and for minimum coverage of 60% [34], to detect virulence factors that could be involved in the pathogenicity of the isolates. The SerotypeFinder 2.0 tool (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/SerotypeFinder/, accessed on 1 February 2025) with a threshold for minimum identity of 85% and for minimum coverage of 60% was also used to identify the serotype of E. coli [35].
2.11. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
Whole-genome assemblies of E. coli were deposited in NCBI under accession number PRJNA1257349.
3. Results
3.1. Metadata and Susceptibility Info
Among our collection, the majority of E. coli isolates were recovered from urine samples (n = 65), while 29 isolates were collected from blood samples. The remaining six E. coli were isolated from pus (n = 3), swab (n = 1) and sputum (n = 1) samples, while one isolate was of unknown source. Most of the samples were collected from the emergency medicine department (n = 45), indicating a community origin of the samples. Nevertheless, other samples were collected from different departments, including internal medicine (n = 28), urology (n = 8), pediatric (n = 5), surgery (n = 4), neurology, ICU (n = 3), outpatient (n = 2), orthopedics (n = 1), rheumatology (n = 1) and endocrinology (n = 1) (Table S1).
Additionally, the clonal relatedness of the E. coli isolates, which was studied by MLST, showed the presence of 39 different STs among our collection. However, a significant number of isolates belonged to clonal complex 131 (CC131) (n = 45) (Table 2), including sequence types (STs) 131 (n = 30), 1195 (n = 1), 7399 (n = 7), 7597 (n = 5) and 10,605 (n = 2). Most of CC131 isolates were recovered from urine (n = 26) and blood (n = 14) samples. Thirty-two isolates were assigned to STs 69 (n = 2), 104 (n = 5), 390 (n = 2), 410 (n = 2), 476 (n = 2), 501 (n = 2), 569 (n = 2), 646 (n = 4), 922 (n = 3), 4560 (n = 3) and 9612 (n = 4), whereas the remaining 23 isolates belonged to unique STs (Table S1). An analysis, using the eBURST algorithm [36], showed that most of the detected STs were not related to each other (Figure S1), while it confirmed that ST195, ST7399, ST7597 and ST10605 belonged to CC31.

Table 2.
Epidemiological characteristics of 100 E. coli isolates included in this study.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed that the frequency of resistance to ampicillin was 77%, while 61% of the E. coli isolates were resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, 38% were resistant to cefepime, 35% were resistant to ceftazidime, 27% were resistant to piperacillin/tazobactam, and 12% were resistant to carbapenems. Additionally, 51% of the E. coli isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin, 45% were resistant to co-trimoxazole, 21% of the isolates were resistant gentamicin, and only 14% of the isolates were resistant to amikacin. Based on their susceptibility profiles, 44 isolates were classified as MDR (multi-drug resistance). PCR screening showed that 15 E. coli isolates carried genes encoding enzymes of CTX-M-1 family. In addition, eleven isolates carried genes encoding enzymes of CTX-M-9 family, while twelve other isolates were positive for both blaCTX-M-1-like and blaCTX-M-9-like genes. The majority of blaCTX-M-positive isolates belonged to CC131 (n = 27).
3.2. Virulence Characteristics
In regard to virulence characteristics, none of the isolates were positive for string test. Similarly, hemolysin production was observed only in 9% of the E. coli isolates. Isolates showing hemolysin production belonged to diverse STs and were recovered from urine (n = 6) and blood samples (n = 3) (Table S1). The remaining isolates showed no hemolysis. From the biofilm quantification assay, we observed that the majority (n = 71) of E. coli isolates produced moderate levels of biofilm (0.4 > OD > 0.2). High production of biofilm was quantitatively estimated for 16 E. coli isolates, while the remaining 13 isolates produced weak levels of biofilm (0.2 > OD > 0.1). The majority of ST131 isolates (25 out of 30) produced moderate levels of biofilm. Isolates with high production of biofilm were recovered from urine (n = 8), blood (n = 6), pus (n = 1) and swab (n = 1) samples. Of note, all ST922 (n = 3) isolates showed high production of biofilm. Moreover, the serum-killing assay showed that no E. coli isolates were resistant to serum. The majority (91%) of E. coli isolates were serum-sensitive. The nine remaining E. coli exhibited intermediate levels of resistance to serum (Table S1).
3.3. CRISPR/Cas Systems
Among 100 clinical E. coli isolates, CRISPR/Cas systems were detected in 18 isolates. Type I-E systems were found in 12 isolates. Isolates with I-E systems belonged to distinct STs (ST58, ST69, ST156, ST216, ST501, ST648, ST708, ST744, ST1011, ST9312) (Table 3). Two of the ST69 isolates harbored identical CRISPR arrays (Figure 1). Also, six isolates harbored a type I-F system. Three isolates carrying I-F systems were assigned to CC95, including STs 95 (n = 1) and 390 (n = 2) (Table 3). The three remaining type I-F-positive isolates were distributed in STs 569, 2371 and 5328. Of note was that none of the isolates, even of the same ST, harbored identical CRISPR arrays (Figure 1), indicating an ongoing evolution of the CRISPR/Cas systems. None of the CRISPR/Cas-positive isolates were found to be positive for more than one system.

Table 3.
Characteristics of CRISPR/Cas-positive E. coli isolates of Greek origin.

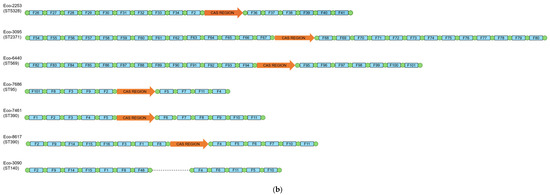
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the spacers’ arrangement in type I-E (a) and I-F (b) CRISPR/Cas-positive E. coli isolates, characterized during this study.
For all CRISPR/Cas-positive isolates, CRISPR arrays were PCR-amplified and sequenced. In addition, type I-F CRISPR loci were amplified from one cas-negative isolate. These loci were determined as orphan CRISPR arrays. Unique spacers were named (Table S2) and the arrangement of the spacers in each strain is shown in Figure 1. In isolates carrying type I-E systems, the CRISPR1 array ranged from 5 to 23 spacers, while the CRISPR2 array carried from 4 to 16 spacers. Of note, in two isolates (Eco-2194 [ST501] and Eco-2258 [ST708]), the CRISPR2 array was not amplified. On the other hand, in type I-F-positive isolates, the CRISPR1 array carried from 4 to 14 spacers, while the CRISPR2 array comprised from 4 to 14 spacers. Furthermore, among our collection, 290 unique spacers were found, with 212 spacers originating from type I-E systems, and 78 of them originating from type I-F systems. In order to determine the origin of the sequences of our spacers, a BLASTn analysis of spacers was carried out. Only results with high identity scores (100% coverage, ≥90% identity) were considered. A total of 257 (88.6%) spacers matched E. coli chromosomal sequences (n = 38) or CRISPR sequences (n = 219). Twelve (4.2%) spacers exhibited no significant similarity with sequences submitted to the NCBI database, which was expected, as a high number of spacers are still of unknown origin. The BLASTn search showed that 18 (6.2%) spacers matched to plasmids like pAVS0973-C (GenBank accession No. CP124474), pF7386-2 (GenBank accession No. CP038361) and p24C171-1 (GenBank accession No. LC501671) that were isolated from E. coli strains. Four of the later spacers were identical to regions involved in conjugative transfer, while another spacer was identical to a region implicated in plasmid replication. None of the identified plasmids carried antimicrobial resistance genes. We also identified three (1.0%) spacers that matched bacteriophages like isolates 3509_17389 (GenBank accession No. OP075566), 3121_76502 (GenBank accession No. OP075223) and vB_EcoM-813R1 (GenBank accession No. ON470617) (Table S2).
3.4. WGS Data
For all isolates, Illumina sequencing resulted in sequences with a Pred quality score of >20. Additionally, following assembly, the obtained genomes were composed of contigs with a length-weighted coverage ranging from 18.5x to 88.1x, and N50 statistics ranging from 2165-bp to 30215-bp. An analysis of WGS data with ResFinder confirmed the presence of ESBL-encoding genes, blaCTX-M-15, blaCTX-M-14 and blaCTX-M-27, in eight of the sequenced isolates (Table 4). Additionally, WGS data showed that one ST9312 isolate carried the blaNDM-1 metallo-β-lactamase-encoding gene, and one ST648 isolate carried the blaKPC-2 crabapenemase-encoding gene, while one ST156 isolate harbored the colistin-resistance gene, mcr1.1. Furthermore, the majority of the isolates exhibited additional genes for resistance to aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, rifampicin, macrolides and quinolones. However, five of the sequenced E. coli isolates carried no resistance genes.

Table 4.
Characteristics of 20 E. coli isolates characterized by Illumina sequencing.
An analysis of WGS data with VirulenceFinder showed the presence of several different virulence genes in all isolates (Table 4). Different combinations of virulence genes were found even in isolates belonging to the same ST (Figure 2). However, the virulence genes nlpI encoding lipoprotein NlpI, csgA encoding the maor curlin subunit formed during biofilm formation, terC involved in tellurium ion resistance, and yehC associated with YHD fimbriael cluster were detected in all isolates. A significant number of isolates was positive for genes encoding adhesins (fimH [n = 18], fdeC [n = 15], and papC [n = 4]) [37]. The genes kpsE and kpsM, involved in biosynthesis of capsular polysaccharides, were detected in 12 isolates. Six isolates were positive for lpfA encoding long polar fimbriae, an adherence factor. The mcbA gene encoding a predicted periplasmic protein-encoding gene, YbiM, involved in the regulation of biofilm formation, was found in the ST10 isolate (Eco-7827). Interestingly, 16 isolates were positive for the iss gene associated with increased serum survival [38]. Several genes, like gad (n = 5; glutamate decarboxylase, which synthesizes Gamma-aminobutyric acid [GABA] from l-glutamic acid), neuC (n = 3; N-Acetylneuraminic acid [NeuAc] synthetic pathway) and sat (n = 4; encoding the serine acetyltransferase) involved in various metabolic pathways were also detected. Additionally, genes were found among the sequenced isolates, such as tsh (n = 6; encoding a temperature-sensitive hemagglutinin), dnaK (n = 3; encoding DnaK, also known as HSP70, that belongs to the superfamily of Heat shock proteins) and clpK1 (n = 1; encoding a heat-resistant plasmid-borne ATPase), involved in the synthesis of stress-specific proteins [39]. Sequenced isolates also carried genes (iutA [n = 12], ireA [n = 4], iucC [n = 12], iroN [n = 11], and aer [n = 1]) encoding siderophore systems. In addition, sixteen isolates harbored the sitA gene encoding the ABC cassette importer SitABCD/MntABC for bacterial Mn homeostasis systems. The genes fyuA (n = 13; pyelonephritis-associated pilus [P fimbriae or pap] Yersinia bactin receptor), vat (n = 3; vacuolating autotransporter toxin), chuA (n = 14; heme receptor) and yfcV (n = 8; encoding the major subunit of a putative chaperone-usher fimbria), which are associated with UPEC isolates [40], were also found. The estC gene encoding an esterace that could be implicated in the ethyl acetate and/or ethyl lactate biosynthesis was detected in nine isolates. Twelve isolates carried genes encoding the HlyE (Hemolysin/cytolysin A) toxin. Also, the hylF encoding hemolysin F was found in 10 isolates. Four isolates were positive for gene tia encoding a determinant invasion previously described in ETEC isolates [41], while two isolates were positive for astA coding an Enteroaggregative heat-stable enterotoxin [42]. Additionally, three isolates carried genes encoding the Usp (Colicin-like Usp) toxin. Genes encoding colicins V (CvaV) and E4 (ColE4) were also found in nine and one isolates, respectively. Two isolates (Eco-3096 and Eco-6440) included a gene expressing SenB Enterotoxin. The three ST131 isolates carried the genes ibeA (an invasion actor of brain endothelium) and iha (which is associated with the Locus of Adhesion and Autoaggregation). Of note was that the ST501 isolate (Eco-2194) carried the aap and aatA genes, and the agg operon associated with EAEC pathotype [43].

Figure 2.
SNP-based phylogeny of the 20 E. coli isolates characterized by Illumina sequencing. The colored squares indicate the presence of selected virulence genes, which were detected by VirulenceFinder 2.0.
Furthermore, an analysis of WGS data with PlasmidFinder detected a huge variety of plasmid replicons among the sequenced isolates (Table 4), with most of the replicons belonging to the IncF-type. However, in an ST69 E. coli isolate, which carried no resistance genes, no plasmid replicons were found. Despite the use of short-read sequencing technology, an analysis of WGS data found an association of the IncFIB (AP001918) replicon with the hlyF and estC virulence genes.
4. Discussion
In the current study, we examined the virulence characteristics of clinical E. coli isolates. The majority of the isolates were collected from urine and blood samples, indicating the infectivity and pathogenicity of the studied isolates. Our results showed that the majority (87%) of E. coli isolates had a significant ability to form biofilm. The biofilm EPS matrix protects bacteria from host immune responses and increases their resistance to antimicrobial agents, making infections difficult to treat. Biofilms can harbor persistent cells that enter an inactive state, which helps them overcome antibiotic treatments without genetic changes. These cells can re-establish active infections after the end of the treatment [44]. Furthermore, biofilms complicate treatment strategies due to their heterogeneous nature and ability to evade conventional therapeutic approaches [45,46].
A previous study has shown that 110 genes were associated with biofilm formation [47]. Those genes were involved in various functions, like for cell surface structures and cell membrane. The genes fimH, csgA, nlpI and fdeC, which were previously associated with biofilm formation [47], were observed in almost all E. coli isolates sequenced during this study (Figure 1). Of note, dnaK, which was also highlighted as an important gene for biofilm formation [47], was found in three isolates with moderate levels of biofilm formation. Another interesting observation was the fact that yfcV (a major subunit of a putative chaperone-usher fimbria), fyuA (P fimbriae), chuA (heme receptor), lpfA (long polar fimbriae), and genes involved in capsular biosynthesis (kpsE and kpsM) were mostly found among isolates that were not weak biofilm producers. Previous studies have shown that capsular polysaccharides also contribute to UPEC biofilm formation in the bladder [48,49].
On the other hand, none of the studied isolates formed a viscous string of >5 mm and were resistant to killing by complement. String phenotypes are associated with capsule production [30]. Complement is a critical part of the innate immune response, serving as a first line of defense to eliminate a diverse range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses and parasites. In a previous study, 31.6% of K. pneumoniae isolates tested were resistant to killing by complement [50], which is in disagreement with the current data, indicating a diverse behavior among different species. However, only in nine isolates was hemolytic activity observed. Hemolysis, which is the lysis of red blood cells, is mainly caused by hemolysins, toxins that are produced by pathogenic bacteria. Isolate Eco-3092, which was positive for hemolysin production, carried the hlyE gene. On the other hand, two isolates (Eco-2253 and Eco-6371) carried the operon hylABCD-encoding Alpha-hemolysin but were negative for hemolysin production on blood agar. These contradictory results indicate that further experiments are needed to elucidate this mechanism.
Furthermore, an analysis of WGS data found that all sequenced isolates harbored a variety of virulence genes. A significant number of isolates was positive for genes (fimH, fdeC, and papC) for adhesion. Several genes, like gad, neuC and sat, involved in various metabolic pathways were also detected. Additionally, genes (tsh, dnaK and clpK1) involved in the synthesis of stress-specific proteins were found. Sequenced isolates also carried genes (iutA, ireA, iucC, iroN, and aer) encoding siderophore systems. Finally, E. coli isolates were positive for genes (astA, usp, cvaC, colE4 and senB) encoding several toxins. These results highlight the huge armamentarium of virulence genes that can be involved in the pathogenicity of E. coli isolates. An association between the virulence genes and the STs or the virulence characteristics was not observed. However, the above findings show only the presence of the genes involved in the pathogenicity of E. coli. Discrepancies between virulence phenotypes and genotypes could be explained by frameshift mutations, truncations and/or incomplete loci.
In addition, our results showed that a significant number of E. coli isolates were resistant to β-lactam antibiotics (77% ampicillin, 35% cephalosporins, 12% carbapenems), complicating treatment strategies. Also, resistance to other antimicrobial classes, like aminoglycosides and fluroquinolones, was observed among the studied isolates. WGS data confirmed the presence of a wide variety of resistance genes, including ESBL-encoding genes, in most of the sequenced isolates. Interestingly, two isolates harbored a carbapenemase-encoding gene, blaNDM-1 or blaKPC-2, while the mcr1.1 colistin-resistance gene was detected in an ST156 isolate. Although the majority of the E. coli isolates belonged to CC131, the wide variety of resistance genes that were observed could be explained by the fact that most of the isolates were of community origin.
Another interesting characteristic of our collection was the presence of CRISPR/Cas systems in 18% of the isolates. Type I-E systems were found in 12 isolates, and type I-F systems were present in 6 other isolates. None of the CRISPR/Cas-positive isolates were found to be positive for more than one system. Of note, the percentage of CRISPR/Cas-positive E. coli isolates was low compared to percentages observed in other bacterial species, like P. aeruginosa [51]. The low percentage of CRISPR/Cas-positive isolates might be associated with the wide variety of plasmid replicons observed in the sequenced isolates (Table 4). Several previous studies have reported that plasmids have been involved in the spread of resistance genes [52]. Also, several studies have demonstrated the critical role of plasmids in the dissemination of virulence factors [53,54]. Such examples were also observed during this study, referring to the association of IncFIB (AP001918) replicon with the hlyF and estC virulence genes. The hlyF encodes hemolysin F, a functional ortholog of CrpA, which is a short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) that contributes to resistance against colistin and antimicrobial peptides. SDRs also induce the production of OMVs, which block autophagic flux. Previous studies have shown that HlyF is encoded by virulence plasmids of E. coli [53]. The estC gene encodes an esterase that could be implicated in the ethyl acetate and/or ethyl lactate biosynthesis. Previous studies have shown that the ester biosynthesis capacity by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) is of great interest in view of fruity flavor formation during sourdough and sourdough bread productions [55].
PCR amplification and sequencing of CRISPR loci identified 290 unique spacers. However, CRISPR loci were also amplified from one Cas-negative isolate. This finding may indicate that cas genes have been deleted through recombination events during the evolutionary history of bacteria. These orphan loci may provide info regarding the interaction history of the isolates with ‘invading molecules’ until the deletion event. Additionally, the presence of spacer sequences in these orphan loci may provide an adaptive immune memory to their hosts if they are found concurrently with complete CRISPR/Cas systems, enhancing their protection against infections by competitor phages [56]. The BLASTn analysis of unique spacers showed that the majority (88.6%) of them matched E. coli chromosomal sequences. Regarding the acquisition of self-targeting spacers, previous studies have proposed the potential role of the CRISPR/Cas system to regulate bacterial virulence. In P. aeruginosa, the CRISPR/Cas system enables modulation of biofilm formation, which is an important virulence factor for various pathogenic microorganisms [24]. A significant number of spacers (4.2%) exhibited no significant similarity with sequences submitted to the GenBank database, supposing that a significant number of genetic features have not yet been sequenced. The remaining 21 spacers matched to plasmids (n = 18) and phages (n = 3). However, none of the latter plasmids showed significant similarity with the plasmid sequences characterized during this study.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the analysis of virulence characteristics showed that an important percentage (87%) of E. coli isolates had a significant ability to form biofilm. Biofilms complicate treatment strategies due to their heterogeneous nature and ability to evade conventional therapeutic approaches. Also, E. coli isolates harbored a variety of virulence genes that could be implicated in adherence, invasion, and iron uptake. Despite further experiments being needed to elucidate the association of specific virulence genes with respective virulence phenotypes, the expression of several virulence factors, in combination with the presence of multidrug resistance, could challenge the antimicrobial therapy of infections caused by such bacteria.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13071488/s1, Table S1: Characteristics of 100 E. coli isolates included in this study. Table S2: Sequences of spacers characterized from E. coli isolates of Greek origin. Figure S1: An eBURST diagram showing the relationships between the detected sequence types of E. coli isolates included in this study.
Author Contributions
L.A.G., E.K. and C.G. carried out experimental work. I.B. assisted in the obtention of data. I.B. and C.C.P. played an important role in interpreting the results and writing the manuscript. C.C.P. supervised the experiments and revised the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by funding from the Research Committee of the University of Thessaly, and the project of National Institute of Virology and Bacteriology (Program EXCELES, ID project No. LX22NPO5103) funded by the European Union–Next Generation EU.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Whole-genome assemblies of E. coli were deposited in NCBI [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/?term=PRJNA1257349] (accessed on 30 April 2025) under accession number PRJNA1257349.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Da Silva, G.J.; Mendonça, N. Association between antimicrobial resistance and virulence in Escherichia coli. Virulence 2012, 3, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Hur, H.G.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Byappanahalli, M.; Yan, T.; Ishii, S. Environmental Escherichia coli: Ecology and public health implications—A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Cuadrado, D.; Moreno, M.A.; Ugarte-Ruíz, M.; Domínguez, L. Antimicrobial resistance in the food chain in the European union. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 86, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toval, F.; Köhler, C.-D.; Vogel, U.; Wagenlehner, F.; Mellmann, A.; Fruth, A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Karch, H.; Bielaszewska, M.; Dobrindt, U. Characterization of Escherichia coli isolates from hospital inpatients or outpatients with urinary tract infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, M.; Luitel, H.; Devkota, B.; Bhattarai, R.K.; Phuyal, S.; Panthi, P.; Shrestha, A.; Chaudhary, D.K. Antibiotic resistance pattern and virulence genes content in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) from broiler chickens in Chitwan, Nepal. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.; Fuenzalida, V.; Ramos, R.; Escobar, B.; Neira, V.; Borie, C.; Lapierre, L.; Lopez, P.; Venegas, L.; Dettleff, P. Genomic features and antimicrobial resistance patterns of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from food in Chile. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhi, S.; Guo, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Lv, J. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and whole genome sequencing analysis of shiga toxinproducing Escherichia coli (STEC) and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) from imported foods in China during 2015–2021. Toxins 2022, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.H.; Michalski, J.; Luo, Q.; Shetty, A.C.; Daugherty, S.C.; Fleckenstein, J.M.; Rasko, D.A. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics of Escherichia coli isolates carrying virulence factors of both enteropathogenic and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, B.R.; Abebe, T.; Zhang, L.; Mihret, A.; Abebe, W.; Amogne, W. Distribution of virulence genes and phylogenetics of uropathogenic Escherichia coli among urinary tract infection patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasi, M.; Asadi Karam, M.R.; Habibi, M.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Bouzari, S. Phenotypic assays to determine virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) isolates and their correlation with antibiotic resistance pattern. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015, 6, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadah Sheikh, A.; Goodarzi, H.; Yadyad, M.J.; Aslani, S.; Amin, M.; Jomehzadeh, N.; Ranjbar, R.; Moradzadeh, M.; Azarpira, S.; Akhond, M.R.; et al. Virulence-associated genes and drug susceptibility patterns of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infection. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Študentová, V.; Jakubů, V.; Španělová, P.; Urbášková, P.; Žemličková, H.; Hrabák, J. High prevalence of ST131 among CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli from community-acquired infections, in the Czech Republic. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudejova, K.; Sourenian, T.; Palkovicova, J.; Stredanska, K.; Nechutna, L.; Vlkova, K.; Studentova, V.; Working Group for Monitoring of Antibiotic Resistance; Hrabak, J.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; et al. Genomic characterization of ST38 NDM-5-producing Escherichia coli isolates from an outbreak in the Czech Republic. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 68, e0013324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelendova, M.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Valcek, A.; Medvecky, M.; Bitar, I.; Hrabak, J.; Gelbicova, T.; Barakova, A.; Kutilova, I.; Karpiskova, R.; et al. Characterization of the Complete Nucleotide Sequences of mcr-1-Encoding Plasmids from Enterobacterales Isolates in Retailed Raw Meat Products from the Czech Republic. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 604067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinon, C.; Miriagou, V.; Carattoli, A.; Luzzaro, F.; Rossolini, G.M. Characterization of the IncA/C plasmid pCC416 encoding VIM-4 and CMY-4 beta-lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.; Huprikar, S.; Factor, S.H.; Jenkins, S.G.; Calfee, D.P. Outcomes of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection and the impact of antimicrobial and adjunctive therapies. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008, 29, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwen, R.; Staals, R.H.; Endtz, H.P.; van Baarlen, P.; van der Oost, J. The role of CRISPR-Cas systems in virulence of pathogenic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.R.; Lee, S.Y. CRISPR technologies for bacterial systems: Current achievements and future directions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1180–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, F.F.; Cianciotto, N.P. The CRISPR-associated gene cas2 of Legionella pneumophila is required for intracellular infection of amoebae. mBio. 2013, 4, e00074-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwen, R.; Horst-Kreft, D.; de Boer, A.G.; van der Graaf, L.; de Knegt, G.; Hamersma, M.; Heikema, A.P.; Timms, A.R.; Jacobs, B.C.; Wagenaar, J.A.; et al. A novel link between Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage defence, virulence and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.; Beloglazova, N.; Flick, R.; Graham, C.; Skarina, T.; Nocek, B.; Gagarinova, A.; Pogoutse, O.; Brown, G.; Binkowski, A.; et al. A dual function of the CRISPR-Cas system in bacterial antivirus immunity and DNA repair. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 484–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Anantharaman, V.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Live virus-free or die: Coupling of antivirus immunity and programmed suicide or dormancy in prokaryotes. Biol. Direct 2012, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegans, M.E.; Wagner, J.C.; Cady, K.C.; Murphy, D.M.; Hammond, J.H.; O’Toole, G.A. Interaction between bacteriophage DMS3 and host CRISPR region inhibits group behaviors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum-Aslan, A.; Marraffini, L.A. Impact of CRISPR immunity on the emergence and virulence of bacterial pathogens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayne, P.A. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. In CLSI 2013, 23rd International Supplement, CLSI document M100-S23; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, R.D.; Lan, F.; Colles, P.; Mensa, L.H.; Wieler, H.; Karch, P.R.; Reeves, M.C.; Maiden, H.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: An evolutionary perspective. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Djukić, S.; Cirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. APMIS 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, P.A. Phenotypic and Molecular Detection of Biofilm Formation in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated from Different Clinical Sources in Erbil City. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 15, e2023016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.; Goldsmith, K.L.; Kerwick, R.A. The preparation of blood grouping serum from human citrated plasma. Vox Sang 1971, 20, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakovitsky, N.; Lurie-Weinberger, M.N.; Hameir, A.; Wulffhart, L.; Keren Paz, A.; Schwartz, D.; Carmeli, Y. Phenotypic and Genomic Characterization of Nine String-Positive Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Israel. Microbiol Spectr. 2023, 11, e0300222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchon, M.; Charpentier, S.; Clermont, O.; Rocha, E.P.; Denamur, E.; Branger, C. CRISPR distribution within the Escherichia coli species is not suggestive of immunity-associated diversifying selection. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malberg Tetzschner, A.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Lund, O.; Scheutz, F. In Silico Genotyping of Escherichia coli isolates for extraintestinal virulence genes by use of Whole-Genome Sequencing data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01269-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and Easy In Silico Serotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feil, E.J.; Li, B.C.; Aanensen, D.M.; Hanage, W.P.; Spratt, B.G. eBURST: Inferring patterns of evolutionary descent among clusters of related bacterial genotypes from multilocus sequence typing data. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Kamar, A.M.; Mustafa, A.A.; Al-Madboly, L.A. Purified α-Amylase from Bacillus cereus exhibits antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing activities against uropathogenic Escherichia coli, Downregulating fimH, and papC virulence genes: Implications for urinary tract infections. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Fan, C. Different loci and mRNA copy number of the increased serum survival gene of Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Fierro-Castro, C.; Santillán-Araneda, M.J.; Goldstein, M.; Reyes-Cerpa, S.; Balasch, J.C.; Khansari, A.R.; Dierckens, K.; Bossier, P.; Tort, L.; et al. The Administration of Heat Shock Protein-70 Bacterial Homolog (DnaK) Improves the Cumulative Survival and the Expression of Immune-Related Genes in Gnotobiotic Full-Sibling Sea Bass Larvae Challenged with Vibrio anguillarum. Animals 2025, 15, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurbeck, R.R.; Dinh, P.C., Jr.; Walk, S.T.; Stapleton, A.E.; Hooton, T.M.; Nolan, L.K.; Kim, K.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Mobley, H.L. Escherichia coli isolates that carry vat, fyuA, chuA, and yfcV efficiently colonize the urinary tract. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondì, R.; Chiani, P.; Michelacci, V.; Minelli, F.; Caprioli, A.; Morabito, S. The Gene tia, Harbored by the Subtilase-Encoding Pathogenicity Island, Is Involved in the Ability of Locus of Enterocyte Effacement-Negative Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains To Invade Monolayers of Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00613-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, A.J.; Tokach, M.D.; Carrender, B.; Amachawadi, R.G.; Labbé, A.; Heuser, W.; Coble, K.; DeRouchey, J.M.; Woodworth, J.C.; Goodband, R.D.; et al. Evaluation of a Lactococcus lactis-based dried fermentation product administered through drinking water on nursery pig growth performance, fecal Escherichia coli virulence genes and pathotypes, antibiotic usage, and mortality. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2023, 7, txad093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, C.A.; Rodrigues, B.O.; Elias, W.P.; Abe, C.M. Adhesin related genes as potential markers for the enteroaggregative Escherichia coli category. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 997208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Han, W.; Gu, J.; Qiu, C.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, J.; Lei, L.; Li, F. Recent advances on the regulation of bacterial biofilm formation by herbal medicines. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1039297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendhe, S.; Badge, A.; Ugemuge, S.; Chandi, D. Impact of Biofilms on Chronic Infections and Medical Challenges. Cureus 2023, 15, e48204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zahra, A.; Kamthan, M.; Husain, F.M.; Albalawi, T.; Zubair, M.; Alatawy, R.; Abid, M.; Noorani, M.S. Microbial Biofilms: Applications, Clinical Consequences, and Alternative Therapies. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.L.; Ulett, G.C.; Mabbett, A.N.; Beatson, S.A.; Webb, R.I.; Monaghan, W.; Nimmo, G.R.; Looke, D.F.; McEwan, A.G.; Schembri, M.A. Identification of type 3 fimbriae in uropathogenic Escherichia coli reveals a role in biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.G.; Palermo, J.J.; Schilling, J.D.; Roth, R.; Heuser, J.; Hultgren, S.J. Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections. Science 2003, 301, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, D.S.; Sundsbak, J.L.; Mulvey, M.A. Actin-gated intracellular growth and resurgence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagaletsios, L.A.; Tagkalegkas, A.; Bitar, I.; Papagiannitsis, C.C. Exploring virulence characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates recovered from a Greek hospital. Mol. Genet. Genomics. 2025, 300, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagaletsios, L.A.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Petinaki, E. Prevalence and analysis of CRISPR/Cas systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Greece. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I. Evolutionary Genomics of Defense Systems in Archaea and Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goman, A.; Ize, B.; Jeannot, K.; Pin, C.; Payros, D.; Goursat, C.; Ravon-Katossky, L.; Murase, K.; Chagneau, C.V.; Revillet, H.; et al. Uncovering a new family of conserved virulence factors that promote the production of host-damaging outer membrane vesicles in gram-negative bacteria. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2025, 14, e270032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Molecular and genetic characteristics of highly virulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in respiratory infection. Chin. J. Hosp. Infect. Dis. 2020, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pradal, I.; Weckx, S.; De Vuyst, L. The production of esters by specific sourdough lactic acid bacteria species is limited by the precursor concentrations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0221624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shayeb, B.; Sachdeva, R.; Chen, L.X.; Ward, F.; Munk, P.; Devoto, A.; Castelle, C.J.; Olm, M.R.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Amano, Y.; et al. Clades of huge phages from across earth’s ecosystems. Nature 2020, 578, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).