Comparative Metagenomics Reveals Microbial Diversity and Biogeochemical Drivers in Deep-Sea Sediments of the Marcus-Wake and Magellan Seamounts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Read-Based Phylogenetic Annotation
2.4. Gene Function Annotation Based on Unique-Gene
2.5. Metagenome Sequence Assembly, Binning and Genome Annotations
2.6. Metabolic Interaction Analysis Based on Metagenomic Sequencing Data
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Community Composition from the Sediments in the Western Pacific
3.2. Uncultured Diversity and Novel Lineages in Metagenome-Assembled Genomes
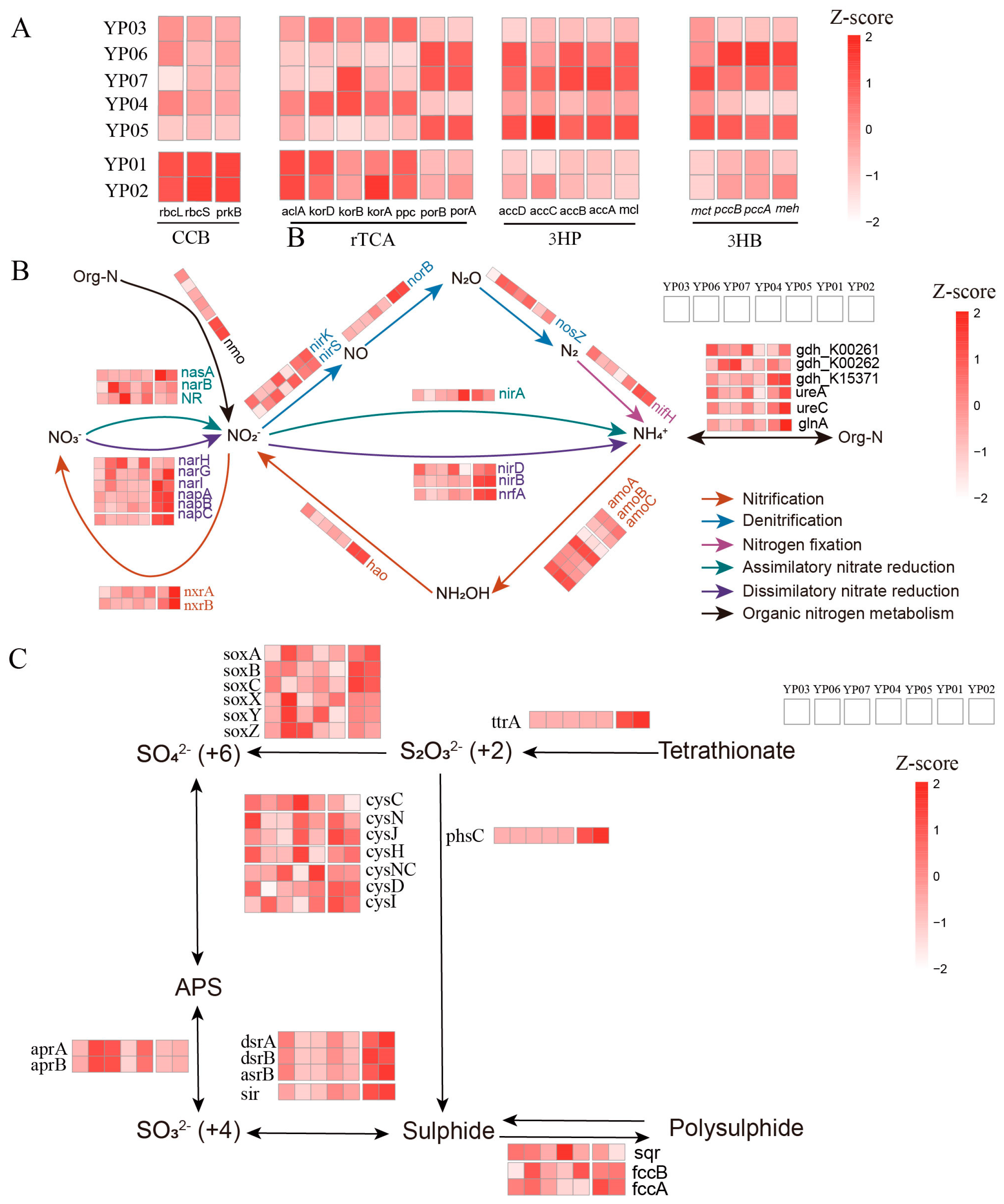
3.3. Metabolic Partitioning of Biogeochemical Cycles Across Deep-Sea Ecosystems
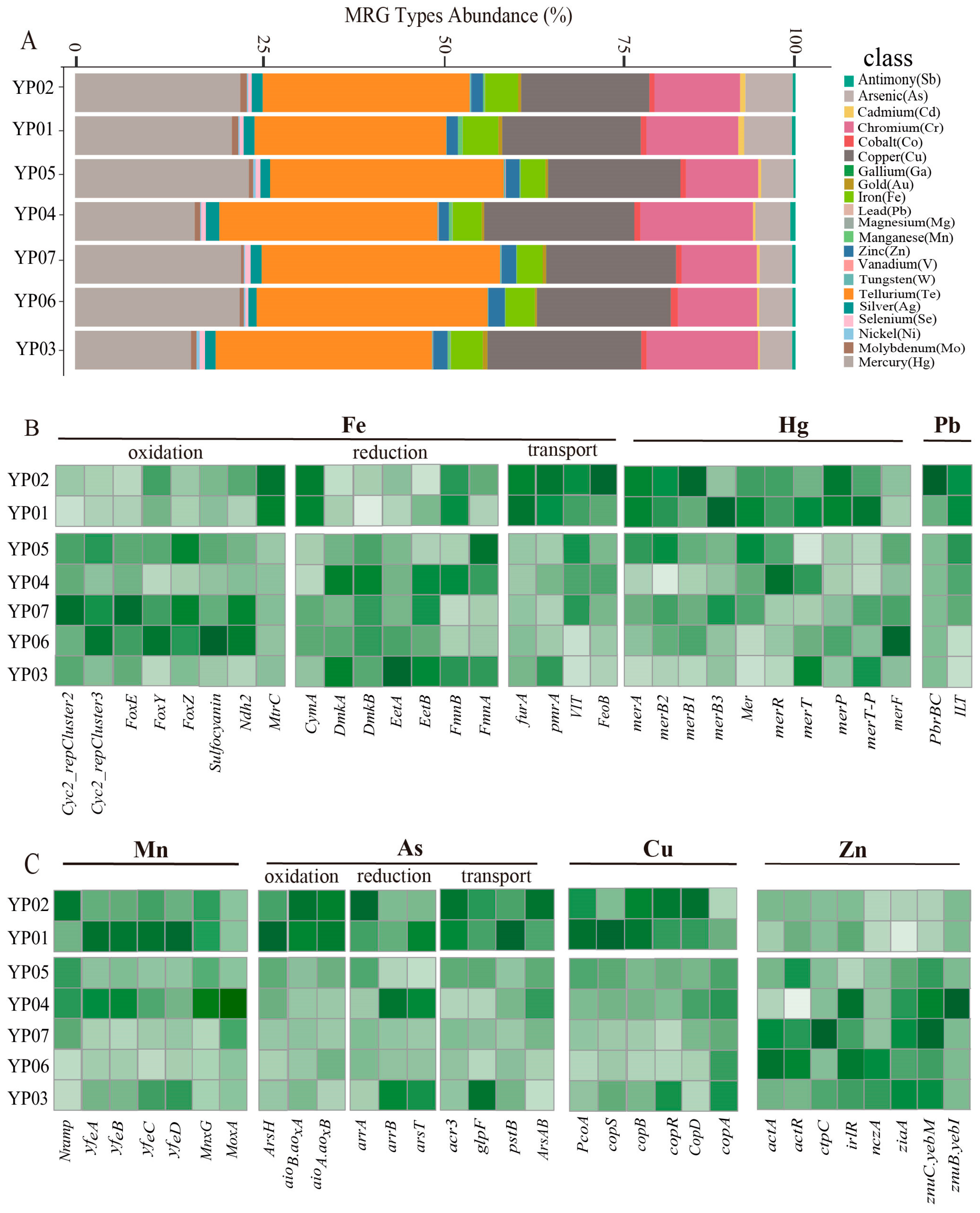
3.4. Metal Resistance and Cycling Analysis of Microbes Across Deep-Sea Ecosystems
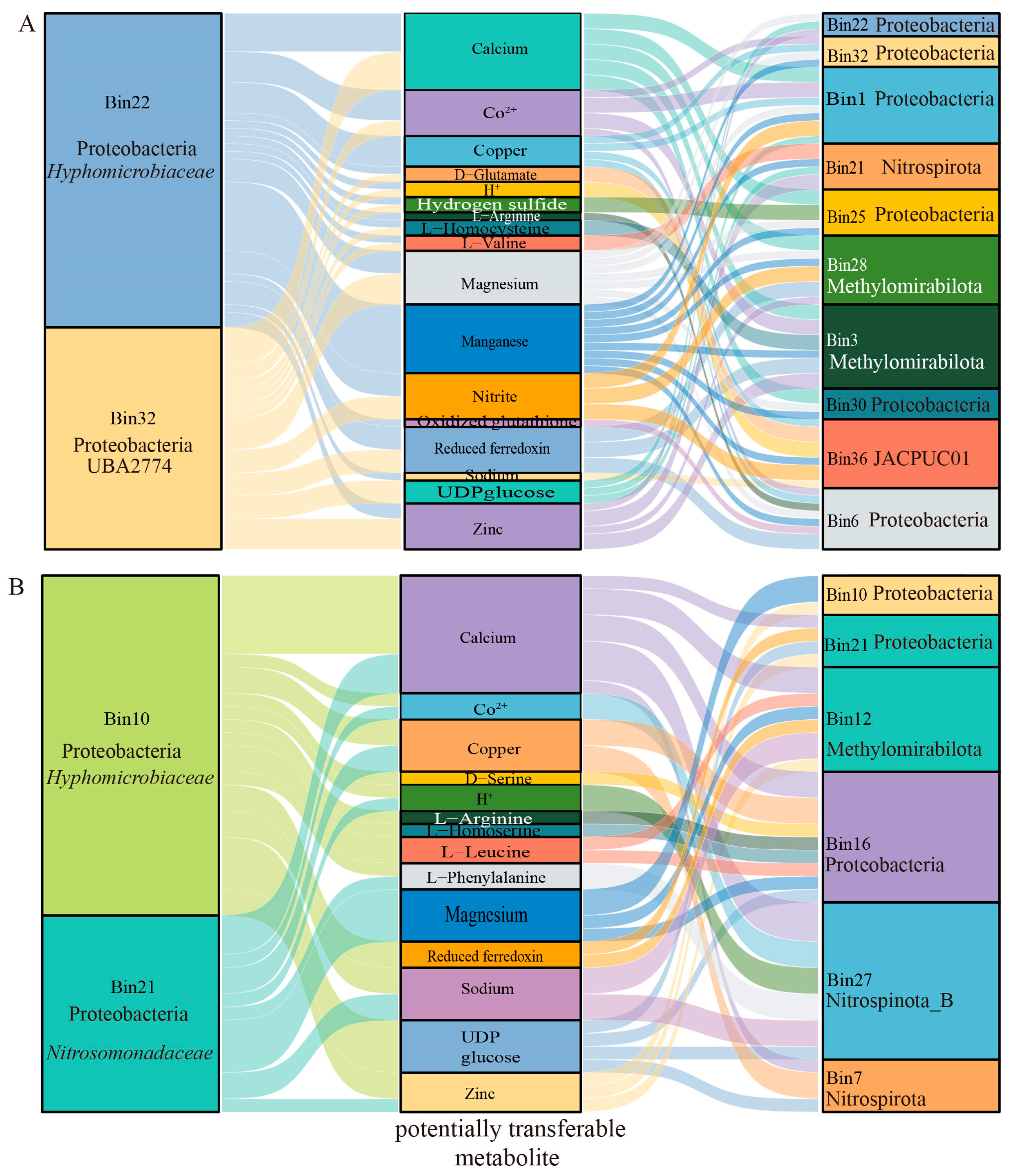
3.5. Metabolic Interdependencies of Sulfur-Metabolizing Bacteria Using Random Matrix Theory Analysis in Nazuna Seamount
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingole, B.; Koslow, J.A. Deep-sea ecosystems of the Indian Ocean. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 34, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- McNichol, J.; Stryhanyuk, H.; Sylva, S.P.; Thomas, F.; Musat, N.; Seewald, J.S.; Sievert, S.M. Primary productivity below the seafloor at deep-sea hot springs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6756–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.A.; Etter, R.J.; Rex, M.A.; Gooday, A.J.; Smith, C.R.; Pineda, J.; Stuart, C.; Hessler, R.; Pawson, D. Environmental influences on regional deep-sea species diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Adams, A.M.; Kieft, K.; Breier, J.A.; Fortunato, C.S.; Sheik, C.S.; Huber, J.A.; Li, M.; Dick, G.J.; et al. Sulfur cycling connects microbiomes and biogeochemistry in deep-sea hydrothermal plumes. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, I.; Dobson, K.; Josso, P.; Pearce, R.; Howarth, S.; Lusty, P.; Le Bas, T.; Murton, B. Assessment of the mineral resource potential of Atlantic ferromanganese crusts based on their growth history, microstructure, and texture. Minerals 2018, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, M.; Pletnev, S.P. Age and formation conditions of the Co-rich manganese crust on guyots of the Magellan seamounts. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2013, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel’nikov, M.E.; Pletnev, S.P.; Anokhin, V.M.; Sedysheva, T.E.; Ivanov, V.V. Volcanic edifices on guyots of the Magellan Seamounts (Pacific Ocean). Russ. J. Pac. Geol. 2016, 10, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.; Koschinsky, A.; Kuhn, T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, Z.; Best, J.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, J. Using multibeam backscatter strength to analyze the distribution of manganese nodules: A case study of seamounts in the Western Pacific Ocean. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, A.B.; Neuheimer, A.B.; Drazen, J.C. Evidence for long-term seamount-induced chlorophyll enhancements. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, Z.H. Fungal diversity in deep-sea sediments from Magellan seamounts environment of the western Pacific revealed by high-throughput Illumina sequencing. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Zhang, T.; Fang, H. Sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification: Diversity, biochemistry, and engineering applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Song, F.; Zhang, G.; Ma, L.; Yang, N. Proteomic insights into the response of Halomonas sp. MNB13 to excess Mn(II) and the role of H2S in Mn(II) resistance. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, F.; Zhang, G.; Ma, L.; Yang, N. Genomic insights into the alphaproteobacterium Georhizobium sp. MAB10 revealed a pathway of Mn (II) oxidation-coupled anoxygenic photoautotrophy: A novel understanding of the biotic process in deep-sea ferromanganese nodule formation. mBio 2025, 16, e0267524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molari, M.; Janssen, F.; Vonnahme, T.; Wenzhoefer, F.; Boetius, A. Microbial communities associated with sediments and polymetallic nodules of the Peru Basin. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 3203–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jing, H.; Xia, X.; Cheung, S.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, H. Metagenomic insights into the microbial community and nutrient cycling in the western Subarctic Pacific Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Jing, H. Metagenome sequencing and 982 microbial genomes from Kermadec and Diamantina Trenches sediments. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Doi, H.; Uramoto, G.I.; Wörmer, L.; Adhikari, R.R.; Xiao, N.; Morono, Y.; D’hondt, S.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Inagaki, F. Global diversity of microbial communities in marine sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27587–27597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, D.; Rowden, A.A.; Glud, R.N.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Kitazato, H.; Clark, M.R. Comparison between in faunal communities of the deep floor and edge of the Tonga Trench: Possible effects of differences in organic matter supply. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 116, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Dong, X. Deep-sea microbial genetic resources: New frontiers for bioprospecting. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Swain, S.; Sahoo, M.; Mishra, S.; Das, A.P. Microbial colonization and degradation of Microplastics in aquatic ecosystem: A review. Geomicrobiol. J. 2022, 39, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, B.; Peng, Y.; Dai, D.; Sha, Z.; Zheng, J. Microbe-driven elemental cycling enables microbial adaptation to deep-sea ferromanganese nodule sediment fields. Microbiome 2023, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.D. The Biology of Seamounts: 25 Years on. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2018, 79, 137–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.R.; Rowden, A.A.; Schlacher, T.; Williams, A.; Consalvey, M.; Stocks, K.I.; Rogers, A.D.; O’hara, T.D.; White, M.; Shank, T.M.; et al. The ecology of seamounts: Structure, function, and human impacts. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeston, M.A.; Cragg, S.M.; Linse, K. Hydrological features above a Southern Ocean seamount inhibit larval dispersal and promote speciation: Evidence from the bathyal mytilid Dacrydium alleni sp. nov. (Mytilidae: Bivalvia). Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Heller, D.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Forslund, S.K.; Cook, H.; Mende, D.R.; Letunic, I.; Rattei, T.; Jensen, L.J.; et al. eggNOG 5.0: A hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D309–D314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.; Irizarry, R.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, B. BBMap: A Fast, Accurate, Splice-Aware Aligner; Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL): Berkeley, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uritskiy, G.V.; Diruggiero, J.; Taylor, J. MetaWRAP-a flexible pipeline for genome-resolved metagenomic data analysis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olm, M.R.; Brown, C.T.; Brooks, B.; Banfield, J.F. dRep: A tool for fast and accurate genomic comparisons that enables improved genome recovery from metagenomes through de-replication. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; Locascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.I.; Nealson, K.H.; Okamoto, A.; Mcallister, S.M.; Chan, C.S.; Barco, R.A.; Merino, N. FeGenie: A comprehensive tool for the identification of iron genes and iron gene neighborhoods in genome and metagenome assemblies. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. KofamKOALA: KEGG Ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Feng, K.; He, Q.; Yang, X.; Hou, W.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, B.; et al. Metabolic interdependencies in thermophilic communities are revealed using co-occurrence and complementarity networks. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogin, M.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Huber, J.A.; Mark Welch, D.; Huse, S.M.; Neal, P.R.; Arrieta, J.M.; Herndl, G.J. Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12115–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Qin, S.; Zeng, Z.; Dang, H.; Qin, Y. Vertical distribution of bacterial and archaeal communities along discrete layers of a deep-sea cold sediment sample at the East Pacific Rise (approximately 13 degrees N). Extremophiles 2008, 12, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’hondt, S.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Miller, D.J.; Batzke, A.; Blake, R.; Cragg, B.A.; Cypionka, H.; Dickens, G.R.; Ferdelman, T.; Hinrichs, K.U.; et al. Distributions of microbial activities in deep subseafloor sediments. Science 2004, 306, 2216–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulse, C.; Maillot, B.; Smith, C.; Church, M. Polymetallic nodules, sediments, and deep waters in the equatorial North Pacific exhibit highly diverse and distinct bacterial, archaeal, and microeukaryotic communities. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergo, N.M.; Bendia, A.G.; Ferreira, J.C.N.; Murton, B.J.; Brandini, F.P.; Pellizari, V.H. Microbial diversity of deep-sea ferromanganese crust field in the Rio Grande Rise Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 82, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jing, C. Depth-Dependent distribution of prokaryotes in sediments of the manganese crust on Nazimov guyots of the Magellan seamounts. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 3027–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Cron, B.R.; Toner, B.M.; Anantharaman, K.; Breier, J.A.; Dick, G.J.; Li, M. Gammaproteobacteria mediating utilization of methyl-, sulfur- and petroleum. ISME J. 2020, 14, 3136–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, R.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, R.; Hou, Y.; Kuang, F.; Feng, X.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Diversity and potential host-interactions of viruses inhabiting deep-sea seamount sediments. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Leadbetter, J.R. Bacterial chemolithoautotrophy via manganese oxidation. Nature 2020, 583, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettwig, K.F.; Speth, D.R.; Reimann, J.; Wu, M.L.; Jetten, M.S.; Keltjens, J.T. Bacterial oxygen production in the dark. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Karwautz, C.; Andrei, S.; Klingl, A.; Pernthaler, J.; Lueders, T. A novel Methylomirabilota methanotroph potentially couples methane oxidation to iodate reduction. mLife 2022, 1, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawat, P.; Higuchi-Takeuchi, M.; Numata, K. Microbial autotrophic biorefineries: Perspectives for biopolymer production. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.L.; Xu, L.; Cui, L.; Fu, G.Y.; Xu, X.W. Metagenome-based analysis of carbon-fixing microorganisms and their carbon-fixing pathways in deep-sea sediments of the southwestern Indian Ocean. Mar. Genom. 2023, 70, 101045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Shi, L.D.; Wei, G.; Hubert, C.R.J.; Wang, Y.; Greening, C. Phylogenetically and catabolically diverse diazotrophs reside in deep-sea cold seep sediments. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Dong, X.; Lu, R.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zheng, P.F.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y. Microbial ecology of sulfur cycling near the sulfate–methane transition of deep-sea cold seep sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6844–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, B.; Mishra, R.; Dutta, S.; Thatoi, H. Sulphur oxidising bacteria in mangrove ecosystem: A review. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar]
- Thatoi, H.; Das, S.; Mishra, J.; Rath, B.P.; Das, N. Bacterial chromate reductase, a potential enzyme for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krout, I.N.; Scrimale, T.; Vorojeikina, D.; Boyd, E.S.; Rand, M.D. Organomercurial lyase (MerB)-Mediated demethylation decreases bacterial methylmercury resistance in the absence of mercuric reductase (MerA). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0001022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.V.; Dellwig, O.; Pollehne, F.; Herlemann, D.P.R.; Leipe, T.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N. A bacterial isolate from the Black Sea oxidizes sulfide with manganese (IV) oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12153–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, Y.; Nelson, N. The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, H.; Helmann, J.D. Ferrous iron efflux systems in bacteria. Metallomics 2017, 9, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmohammad, S.; Fuentealba, N.A.; Marriott, R.A.; Goetze, T.A.; Edwardson, J.M.; Barrera, N.P.; Venter, H. Structural model of FeoB, the iron transporter from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, predicts a cysteine lined, GTP-gated pore. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlovits, T.C.; Haase, W.; Herrmann, C.; Aller, S.G.; Unger, V.M. The membrane protein FeoB contains an intramolecular G protein essential for Fe(II) uptake in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16243–16248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, H.; Yin, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.H.; Yu, M. Deciphering microbial communities and distinct metabolic pathways in the Tangyin hydrothermal fields of Okinawa Trough through metagenomic and genomic analyses. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Cong, B.; Zhang, W.; Lu, T.; Guo, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S. Comparative Metagenomics Reveals Microbial Diversity and Biogeochemical Drivers in Deep-Sea Sediments of the Marcus-Wake and Magellan Seamounts. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071467
Li C, Cong B, Zhang W, Lu T, Guo N, Zhao L, Zhang Z, Liu S. Comparative Metagenomics Reveals Microbial Diversity and Biogeochemical Drivers in Deep-Sea Sediments of the Marcus-Wake and Magellan Seamounts. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071467
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengcheng, Bailin Cong, Wenquan Zhang, Tong Lu, Ning Guo, Linlin Zhao, Zhaohui Zhang, and Shenghao Liu. 2025. "Comparative Metagenomics Reveals Microbial Diversity and Biogeochemical Drivers in Deep-Sea Sediments of the Marcus-Wake and Magellan Seamounts" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071467
APA StyleLi, C., Cong, B., Zhang, W., Lu, T., Guo, N., Zhao, L., Zhang, Z., & Liu, S. (2025). Comparative Metagenomics Reveals Microbial Diversity and Biogeochemical Drivers in Deep-Sea Sediments of the Marcus-Wake and Magellan Seamounts. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071467





