Identification of a Novel Regulatory Gene, trmE, that Orchestrates Salmonella Flagellar Synthesis and Virulence
Abstract
1. Instruction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Cells
2.2. Mice and Animal Ethics
2.3. Construction of SE Transposon Mutant Library
2.4. Motility-Deficient Mutant Screening and Identification using Semi-Solid Plate and U-Tube
2.5. Gene Identification of Sequence Flanking Tn5 Inserted in Bacterial Genome
2.6. Construction of C50041∆trmE and Its Complemented Strain C50041∆ trmE::trmE
2.7. Biological Characteristics of SEΔtrmE
2.7.1. Growth and Biochemical Characteristics
2.7.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibly Test
2.8. mRNA Level of Flagellar Synthesis-Related Gene and Flagella Observation via TEM
2.8.1. mRNA Level of Flagellar Synthesis-Related Gene via qRT-PCR
2.8.2. Flagella Observation via TEM
2.9. In Vitro and In Vivo Assay for Virulence Analysis
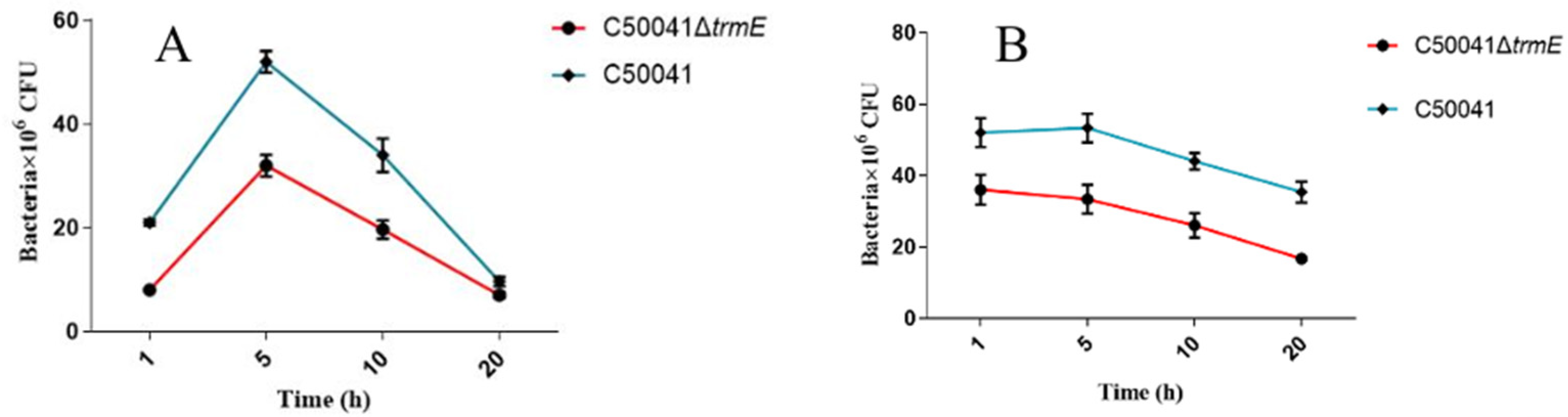
2.9.1. Cell Adhesion, Invasion, and Intracellular Proliferation
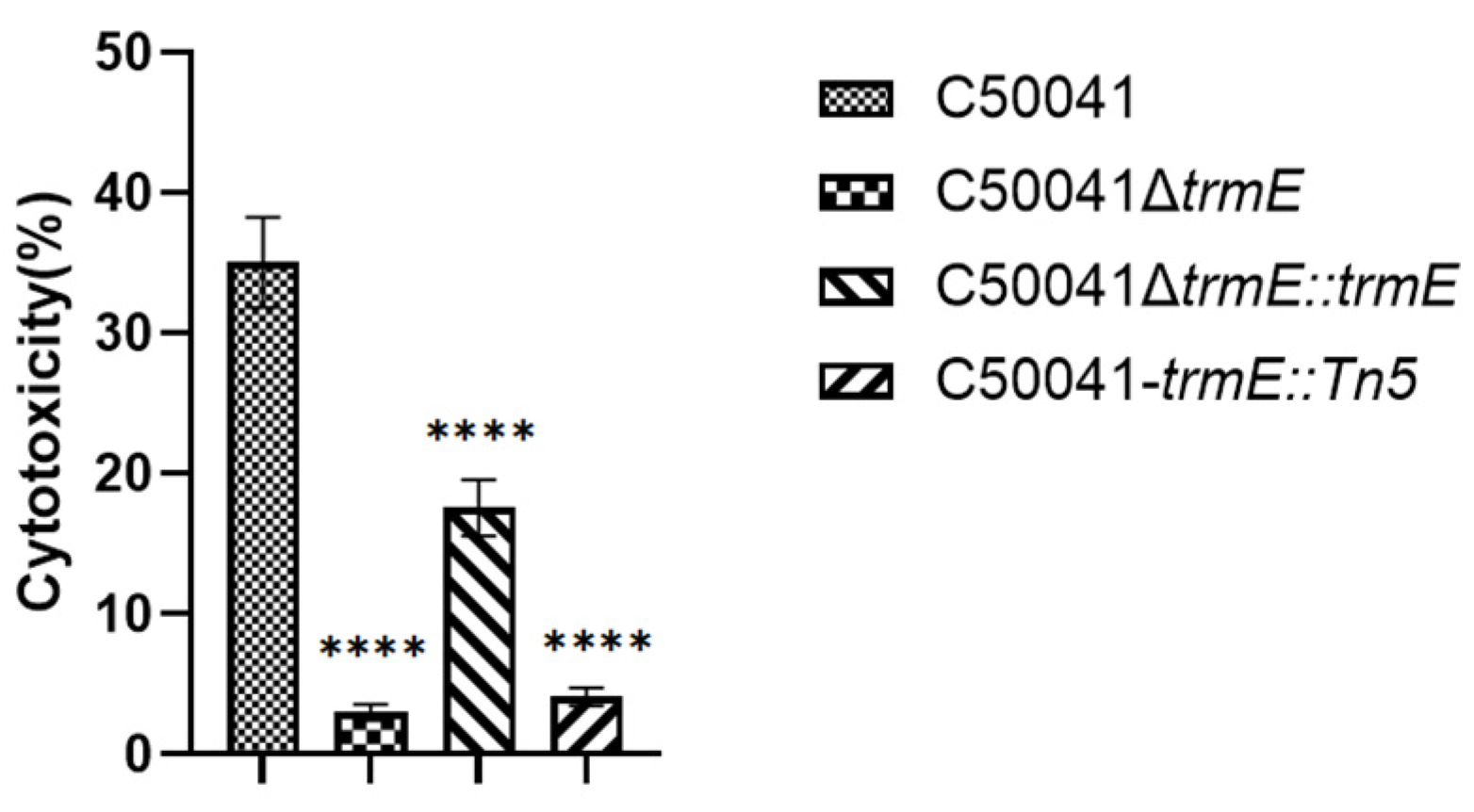
2.9.2. LDH for Cytotoxicity
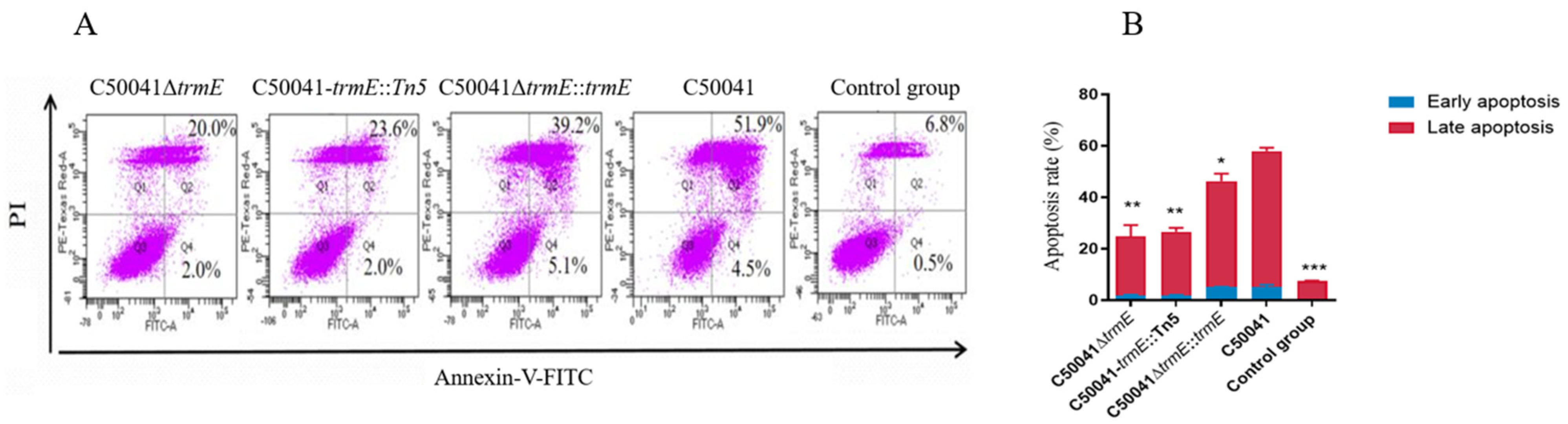
2.9.3. Apoptosis Based on Dual Staining with FITC and PI
2.9.4. Pyroptosis Based on Caspase-1 Protein
2.9.5. LD50 in Mice
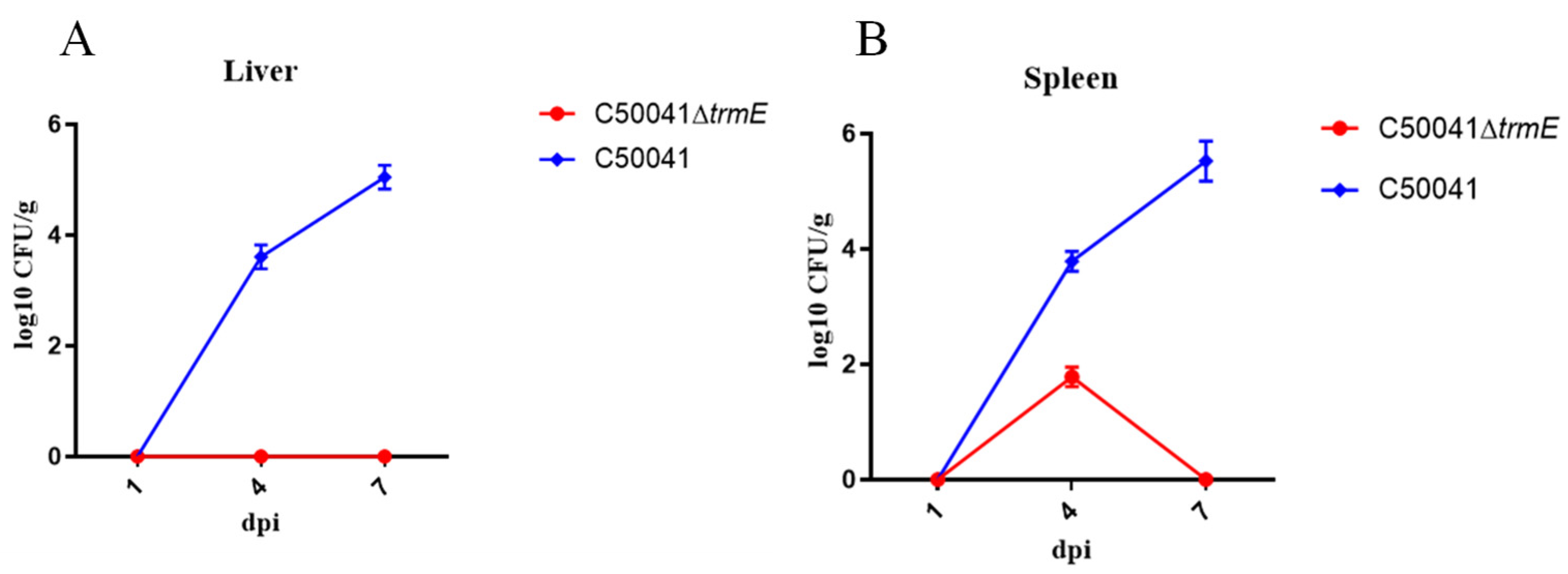
2.9.6. Persistence In Vivo
2.9.7. Lesions and mRNA Level of Inflammatory Cytokine in Murine Spleen
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotype Exhibited trmE::Tn5 Mutant Without Motility
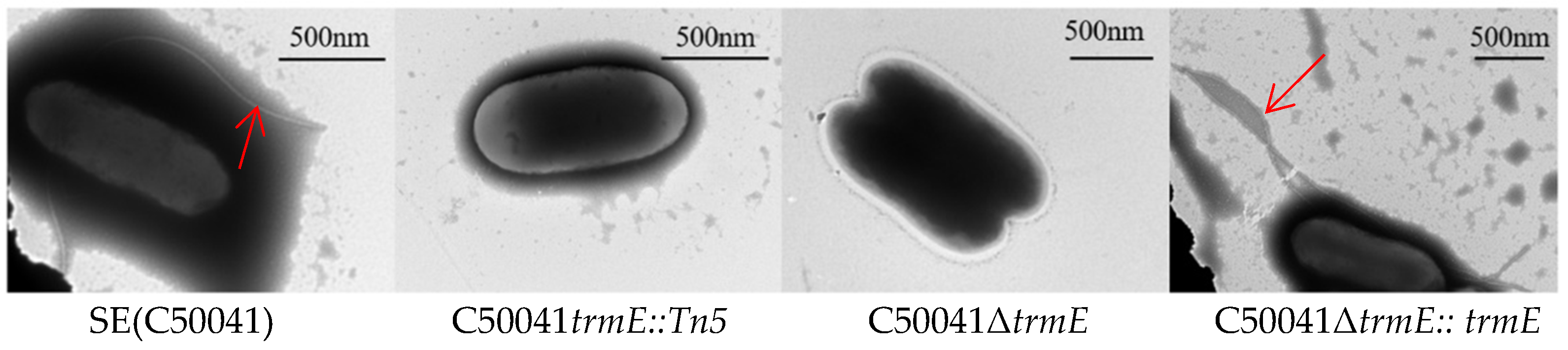
3.2. SE∆trmE Reconfirmed This Phenotype Without Motility
3.3. Biological Characteristics of C50041ΔtrmE Without Flagella
3.3.1. No Change in Biochemical Characteristics
3.3.2. No Change in Antibiotic Resistance
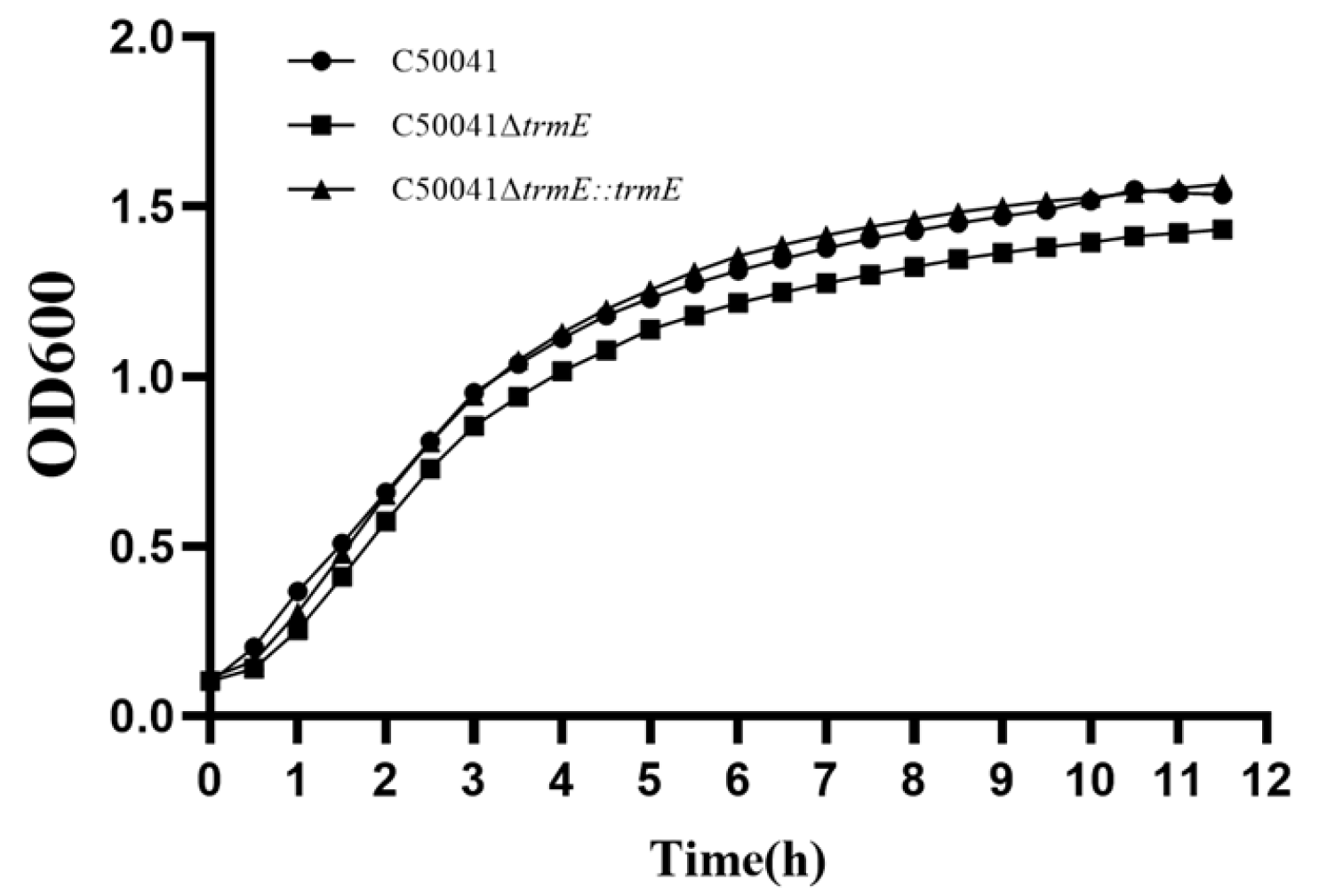
3.3.3. No Change in Bacterial Growth Speed
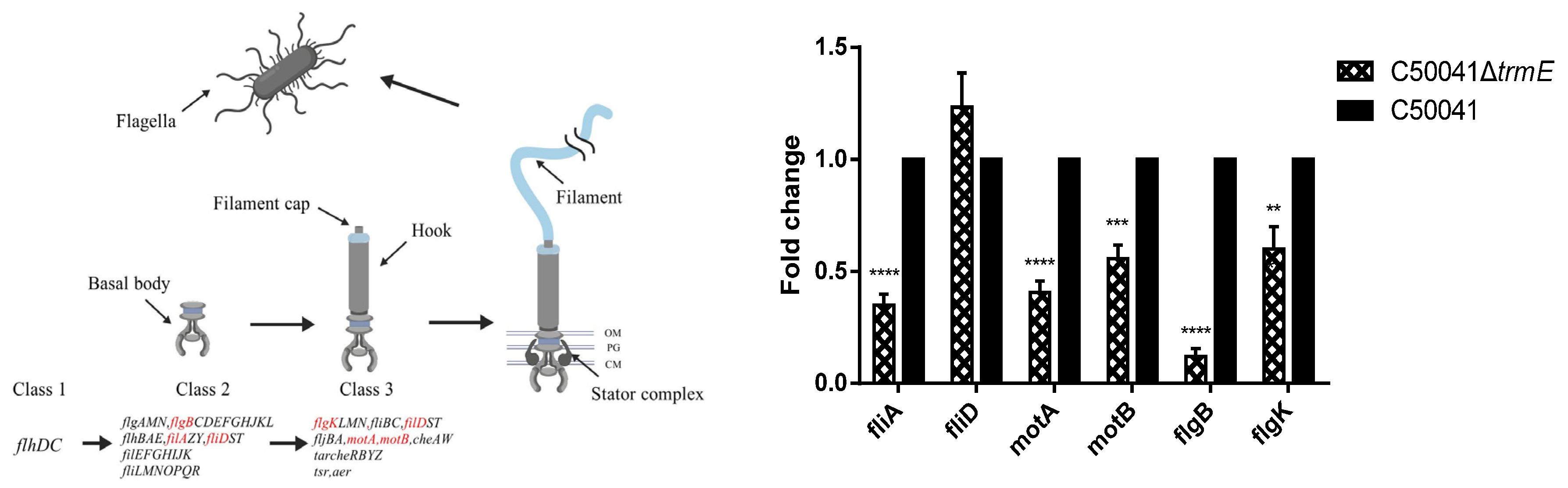
3.4. Low mRNA Level of Flagella Synthesis-Related Genes of C50041ΔtrmE
3.5. Low-Virulence In Vitro and In Vivo Assay of C50041ΔtrmE
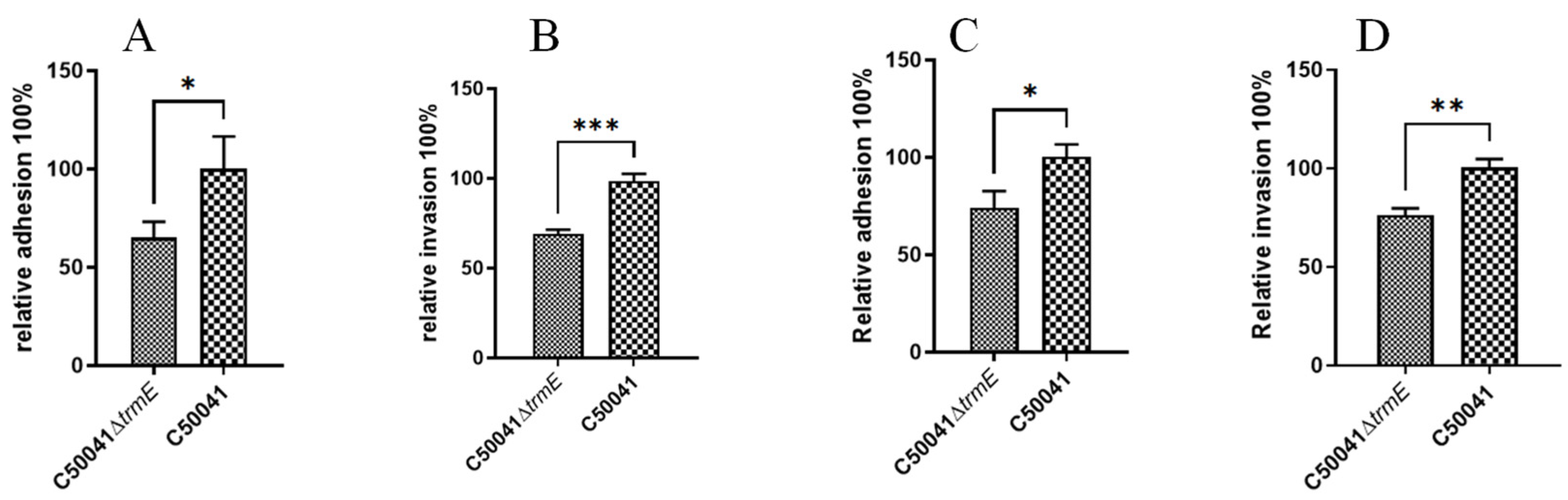
3.5.1. Low Ability to Infect Macrophages
3.5.2. LDH Assay for Cytotoxicity
3.5.3. Decreased Ability to Induce Macrophage Apoptosis
3.5.4. Decreased Ability to Induce Macrophage Pyroptosis Based on Caspase-1 Level
3.5.5. Low Mortality to Mice Based on LD50
3.5.6. Low Persistence Ability In Vivo
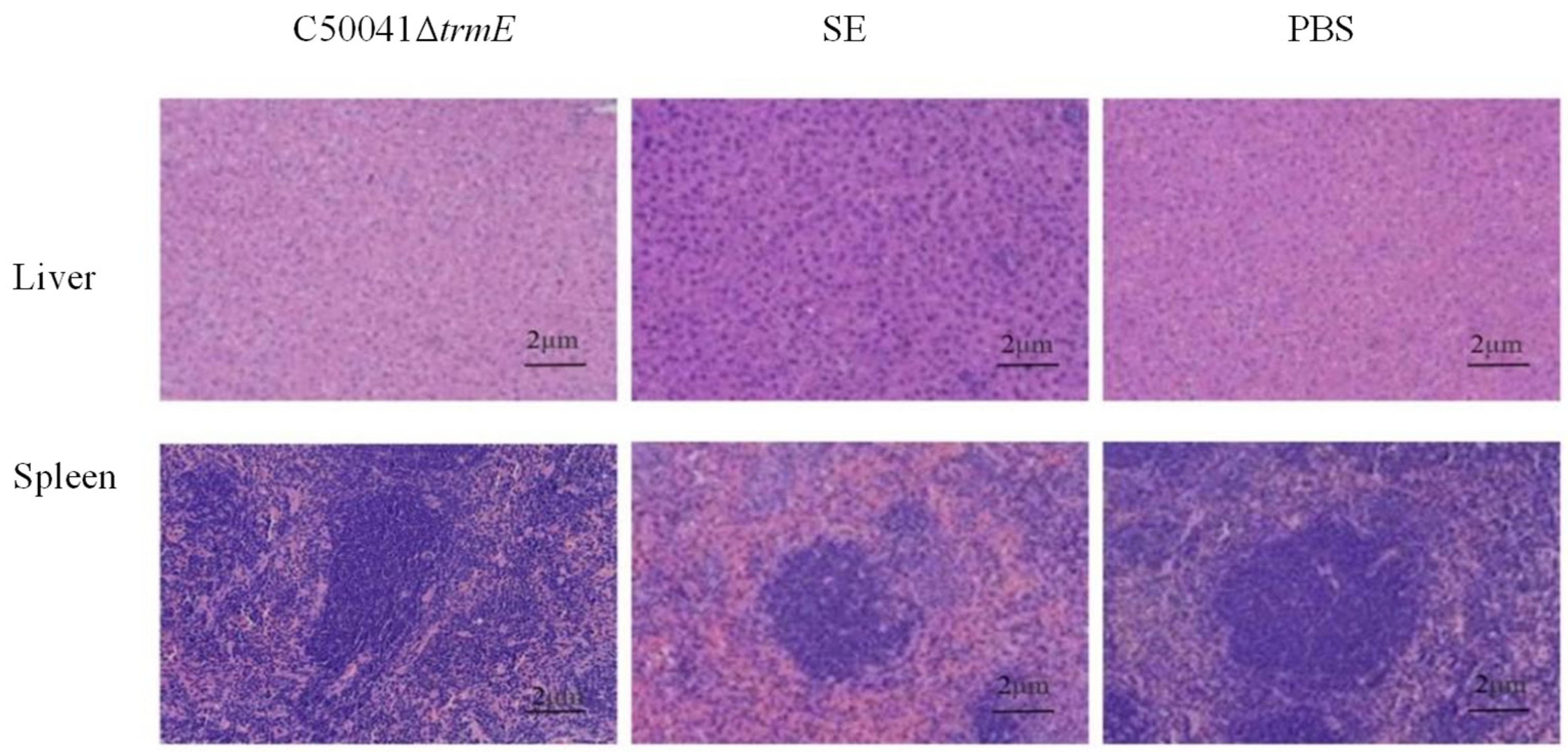
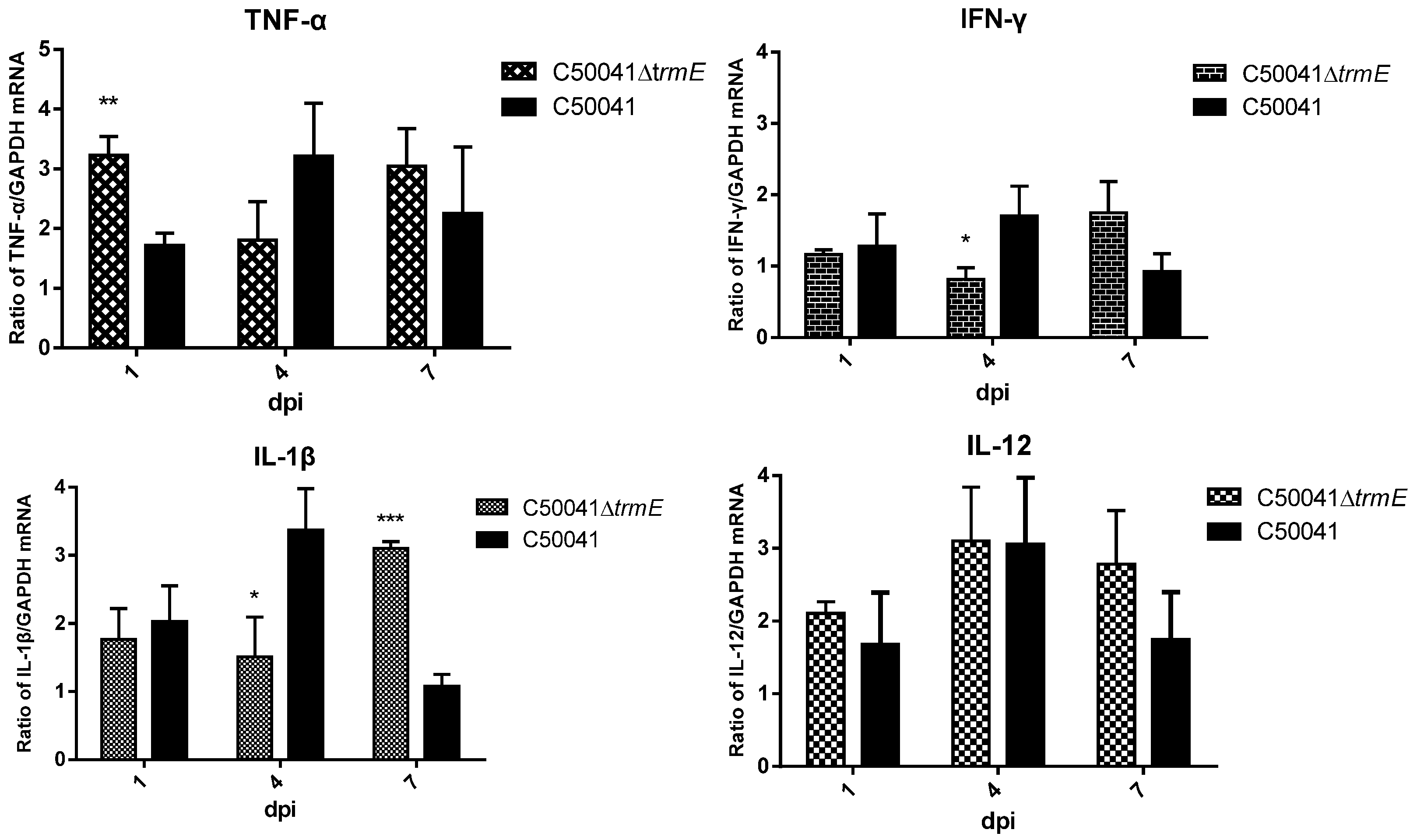
3.5.7. No Obvious Tissue Lesions and Changed mRNA Level of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Strains or Plasmids | Characteristic | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| SE C50041 | Wild-type Salmonella Enteritidis | Lab collection |
| C50041-trmE::Tn5 | C50041 with Tn5 inserted in trmE gene | This study |
| C50041∆trmE | C50041 with a defined deletion of the trmE gene | This study |
| C50041∆trmE::trmE | C50041∆trmE with pBR322 expressing the trmE gene | This study |
| E.coli χ7213 | Its growth for pGMB152 with DAP, as conjugal donor | [15] |
| Plasmids | ||
| pUT mini-Tn5Km2 | Transposon delivery vector, Cmr, Kmr | [17] |
| pGMB152 | pGMB151 derivative, suicide vector, Ampr, Smr, LacZYA | [15] |
| pBR322 | For construction of SE∆trmE::trmE, Cmr | [18] |
| pBR322-trmE | pPR322 derivative containing trmE, Ampr and Tetr | This study |
| Cells | ||
| RAW264.7 | Murine macrophages | This study |
| J774A.1 | Murine macrophages | This study |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Target |
|---|---|---|
| trmE-up-F | CCCCCCCTGCAGGTCGACGTGGTTCCCGTCAGGTCT | Construction for C50041∆ trmE |
| trmE-up-R | CAGCCTACACAATCGCTCAAGGTTAGTCTCAACTTTGTTGCAAT | |
| trmE-Cm-F | ATTGCAACAAAGTTGAGACTAACCTTGAGCGATTGTGTAGGCTG | |
| trmE-Cm-R | TTTGTAGGCCCGGTAAGCATATGGGAATTAGCCATGGTCC | |
| trmE-down-F | GGACCATGGCTAATTCCCATATGCTTACCGGGCCTACAAA | |
| trmE-down-R | CTTATCGATACCGTCGACCAGGTAAACGGAGAAGGCGA | |
| trmE-NYZ-F | AAACTCGTTACAGGGGGCAT | |
| trmE-NYZ-R | TACGCTCAACTTCGTCGCTG | |
| pGMB152-F | CGTGGAGGCCATCAAACCAC | |
| pGMB152-R | CGCGAAATAAACGACCGGGA | |
| C-trmE-F | TTATCATCGATAAGCTTATGAGCCATAACGACACTATCGTC | Construction of complemented mutant C50041∆ trmE:: trmE |
| C-trmE-R | TCCGGCGTAGAGGATCCTTGTAGGCCCGGTAAGCATC |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β-F | TGGCCTTCAAAGGAAAGAATCTATACCTGTCC | 167 |
| IL-1β-R | GTTGGGGAACTCTGCAGACTCAAACTCCAC | |
| IL-12-F | TGCCCCCACAGAAGACGTCTTTGATGAT | 138 |
| IL-12-R | GATGGCCACCAGCATGCCCTTGTC | |
| TNF-α-F | CAGGCCTTCCTACCTTCAGACCTTTCCAGAT | |
| TNF-α-R | ACACCCCGCCCTTCCAAATAAATACATTCAT | 122 |
| IFN-γ-F | GCCAAGACTGTGATTGCGGGGTTGTATCT | |
| IFN-γ-R | TAAAGCGCTGGCCCGGAGTGTAGACA | 198 |
| GAPDH-F | CAGCCTCGTCCCGTAGACAA | |
| GAPDH-R | ACCCCGTCTCCGGAGTCCATCACAAT | 156 |
References
- Shaji, S.; Selvaraj, R.K.; Shanmugasundaram, R. Salmonella Infection in Poultry: A Review on the Pathogen and Control Strategies. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, T.; Qi, W.; Ding, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; et al. Salmonella manipulates macrophage migration via SteC-mediated myosin light chain activation to penetrate the gut-vascular barrier. EMBO J. 2024, 43, 1499–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.L.; Zhang, S.; Tsolis, R.M.; Kingsley, R.A.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. Animal models of Salmonella infections: Enteritis versus typhoid fever. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magariyama, Y.; Sugiyama, S.; Kudo, S. Bacterial swimming speed and rotation rate of bundled flagella. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 199, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas Boas, D.; Castro, J.; Araújo, D.; Nóbrega, F.L.; Keevil, C.W.; Azevedo, N.F.; Vieira, M.J.; Almeida, C. The Role of Flagellum and Flagellum-Based Motility on Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.; Hoede, C.; Scharte, F.; Coluzzi, C.; Cohen, E.; Shomer, I.; Mallet, L.; Holbert, S.; Serre, R.F.; Schiex, T.; et al. Intracellular Salmonella Paratyphi A is motile and differs in the expression of flagella-chemotaxis, SPI-1 and carbon utilization pathways in comparison to intracellular S. Typhimurium. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Qazi, I.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Han, H. Salmonella Virulence and Immune Escape. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamino, T.; Macnab, R.M. Components of the Salmonella flagellar export apparatus and classification of export substrates. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilcott, G.S.; Hughes, K.T. Coupling of flagellar gene expression to flagellar assembly in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2000, 64, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Mokashi, C.; Mande, S.S.; Saini, S. Dynamics and Control of Flagella Assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, P.D.; Wu, C.; Gnerer, J.; Karlinsey, J.E.; Hughes, K.T.; Sachs, M.S. Regulatory protein that inhibits both synthesis and use of the target protein controls flagellar phase variation in Salmonella enterica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11340–11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Song, N.; Jia, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, B. Cooperative Regulation of Flagellar Synthesis by Two EAL-Like Proteins upon Salmonella Entry into Host Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0285922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanna, A.; Sim, M.; Hoskisson, P.A.; Gillespie, C.; Rao, C.V.; Aldridge, P.D. Driving the expression of the Salmonella enterica sv Typhimurium flagellum using flhDC from Escherichia coli results in key regulatory and cellular differences. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz, H.L.; Dehio, C. Signature-tagged mutagenesis: Technical advances in a negative selection method for virulence gene identification. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Tian, Q.; An, S.; Pan, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiao, X. High-Efficiency, Two-Step Scarless-Markerless Genome Genetic Modification in Salmonella enterica. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Kang, X.; Geng, S.; Jiao, X.; Barrow, P. The Loss of focA Gene Increases the Ability of Salmonella Enteritidis to Exit from Macrophages and Boosts Early Extraintestinal Spread for Systemic Infection in a Mouse Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Jiao, X.; Barrow, P.; Pan, Z.; Chen, X. Virulence determinants of Salmonella Gallinarum biovar Pullorum identified by PCR signature-tagged mutagenesis and the spiC mutant as a candidate live attenuated vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Barrow, P.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. The SseL protein inhibits the intracellular NF-κB pathway to enhance the virulence of Salmonella Pullorum in a chicken model. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, H.; Sauer, T.; Becker, H.; Aleksic, S.; Meyer, H. Comparison of systems for identification and differentiation of species within the genus Yersinia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3366–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikler, M.A.; Cockerill, F.R.; Bush, K.; Dudley, M.N.; Eliopoulos, G.M.; Hardy, D.; Hecht, D.W.; Ferraro, M.J.; Swenson, J.M.; Hindler, J.F.; et al. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.C.; Nadeau, K.; Abbasi, M.; Lachance, C.; Nguyen, M.; Fenrich, J. The Ultimate qPCR Experiment: Producing Publication Quality, Reproducible Data the First Time. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, X.; Mu, J.; Zou, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, B.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, X.; et al. Quercetin induces MGMT+ glioblastoma cells apoptosis via dual inhibition of Wnt3a/β-Catenin and Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 118, 154933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boise, L.H.; Collins, C.M. Salmonella-induced cell death: Apoptosis, necrosis or programmed cell death? Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Geng, S.; Jiao, X. Evaluation of the Salmonella enterica Serovar Pullorum Pathogenicity Island 2 Mutant as a Candidate Live Attenuated Oral Vaccine. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2015, 22, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Kinoshita, M.; Namba, K. Multiple Roles of Flagellar Export Chaperones for Efficient and Robust Flagellar Filament Formation in Salmonella. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 756044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiko, J.; Westerlund-Wikström, B. The role of the bacterial flagellum in adhesion and virulence. Biology 2013, 2, 1242–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, A.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, C.; Li, Z.; Wei, Y. Inflammasome activation and pyroptosis mediate coagulopathy and inflammation in Salmonella systemic infection. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 275, 127460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSorley, S.J.; Cookson, B.T.; Jenkins, M.K. Characterization of CD4+ T cell responses during natural infection with Salmonella typhimurium. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyant, T.L.; Tanner, M.K.; Sztein, M.B. Salmonella typhi flagella are potent inducers of proinflammatory cytokine secretion by human monocytes. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3619–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabedo, H.; Macián, F.; Villarroya, M.; Escudero, J.C.; Martínez-Vicente, M.; Knecht, E.; Armengod, M.E. The Escherichia coli trmE (mnmE) gene, involved in tRNA modification, codes for an evolutionarily conserved GTPase with unusual biochemical properties. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 7063–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brégeon, D.; Colot, V.; Radman, M.; Taddei, F. Translational misreading: A tRNA modification counteracts a +2 ribosomal frameshift. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Pindi, P.K.; Dube, S.; Sundareswaran, V.R.; Shivaji, S. Importance of trmE for growth of the psychrophile Pseudomonas syringae at low temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shippy, D.C.; Fadl, A.A. tRNA modification enzymes GidA and MnmE: Potential role in virulence of bacterial pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18267–18280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Ma, Z.; Foster, J.W. The Era-like GTPase TrmE conditionally activates gadE and glutamate-dependent acid resistance in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Identified Gene | Number of Mutant | Gene Function | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| trmE | 1 | tRNA modification GTPase TrmE | 100% |
| fliD | 2 | synthesis of flagellum | 100% |
| fliP | 1 | synthesis of flagellum | 100% |
| rfbK | 1 | synthesis of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) | 100% |
| fliA | 1 | flagellar biosynthesis sigma factor | 100% |
| cpsG | 1 | synthesis of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) | 100% |
| rfaL | 2 | synthesis of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) | 100% |
| csrD | 2 | Global regulation | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, H.; Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Geng, S.; Barrow, P. Identification of a Novel Regulatory Gene, trmE, that Orchestrates Salmonella Flagellar Synthesis and Virulence. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071455
Geng H, Luo L, Zhang J, Gao J, Geng S, Barrow P. Identification of a Novel Regulatory Gene, trmE, that Orchestrates Salmonella Flagellar Synthesis and Virulence. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071455
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Haoyu, Linyan Luo, Jian Zhang, Jingying Gao, Shizhong Geng, and Paul Barrow. 2025. "Identification of a Novel Regulatory Gene, trmE, that Orchestrates Salmonella Flagellar Synthesis and Virulence" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071455
APA StyleGeng, H., Luo, L., Zhang, J., Gao, J., Geng, S., & Barrow, P. (2025). Identification of a Novel Regulatory Gene, trmE, that Orchestrates Salmonella Flagellar Synthesis and Virulence. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071455





