Biodegradation of Cholesterol by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans YS01 Isolated from the Gut of Healthy Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Culture Media
2.2. Isolation of Bacterial Strain for Biodegrading CHOL
2.3. Genome Sequencing of YS01
2.4. Analysis of CHOL and Its In Vitro Biodegradation with HPLC
2.5. Biodegradation of CHOL by YS01
2.6. Biodegradation of CHOL by Extracellular Crude Enzymes of YS01
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
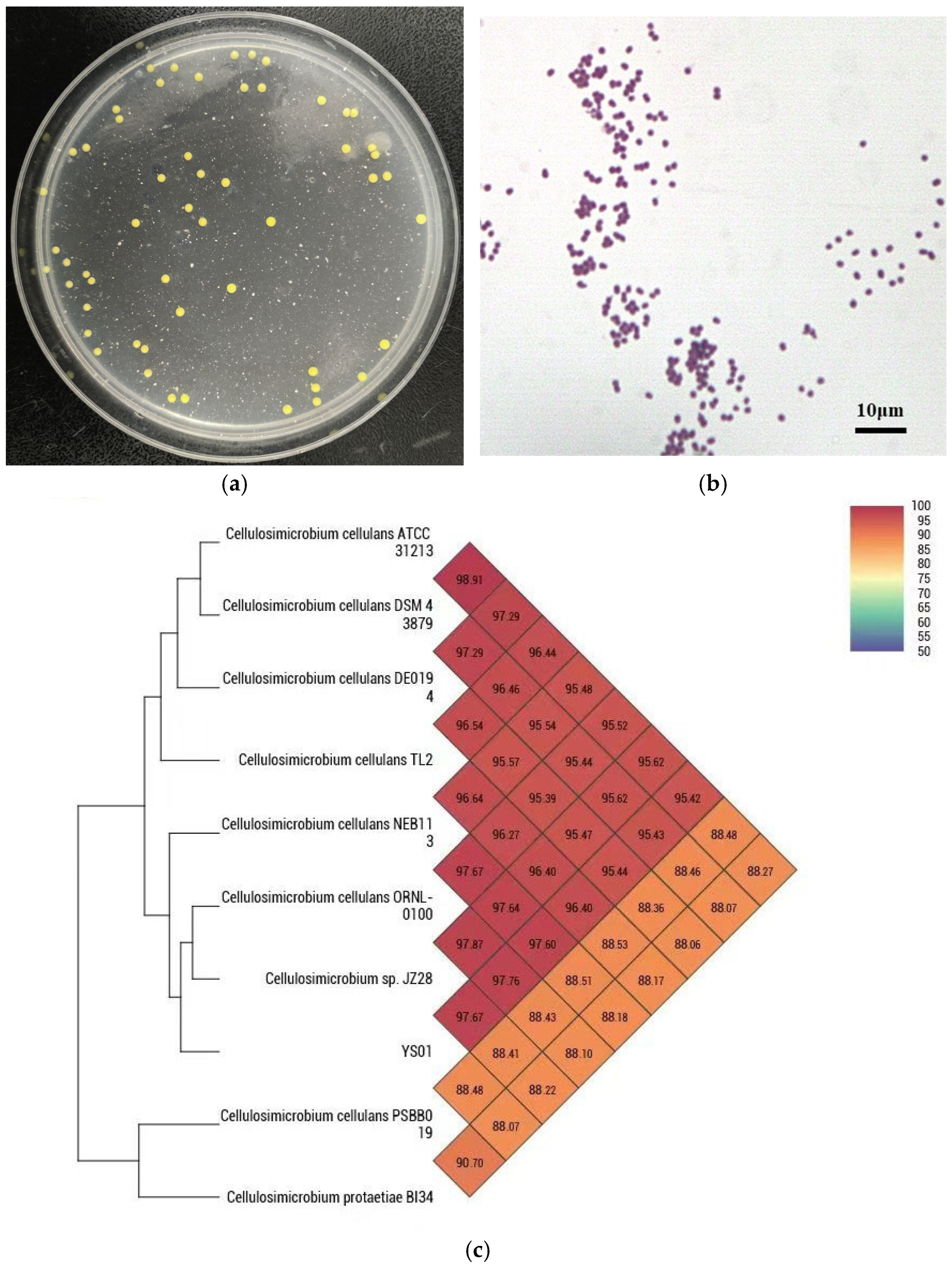
3.1. Isolation and Identification of YS01
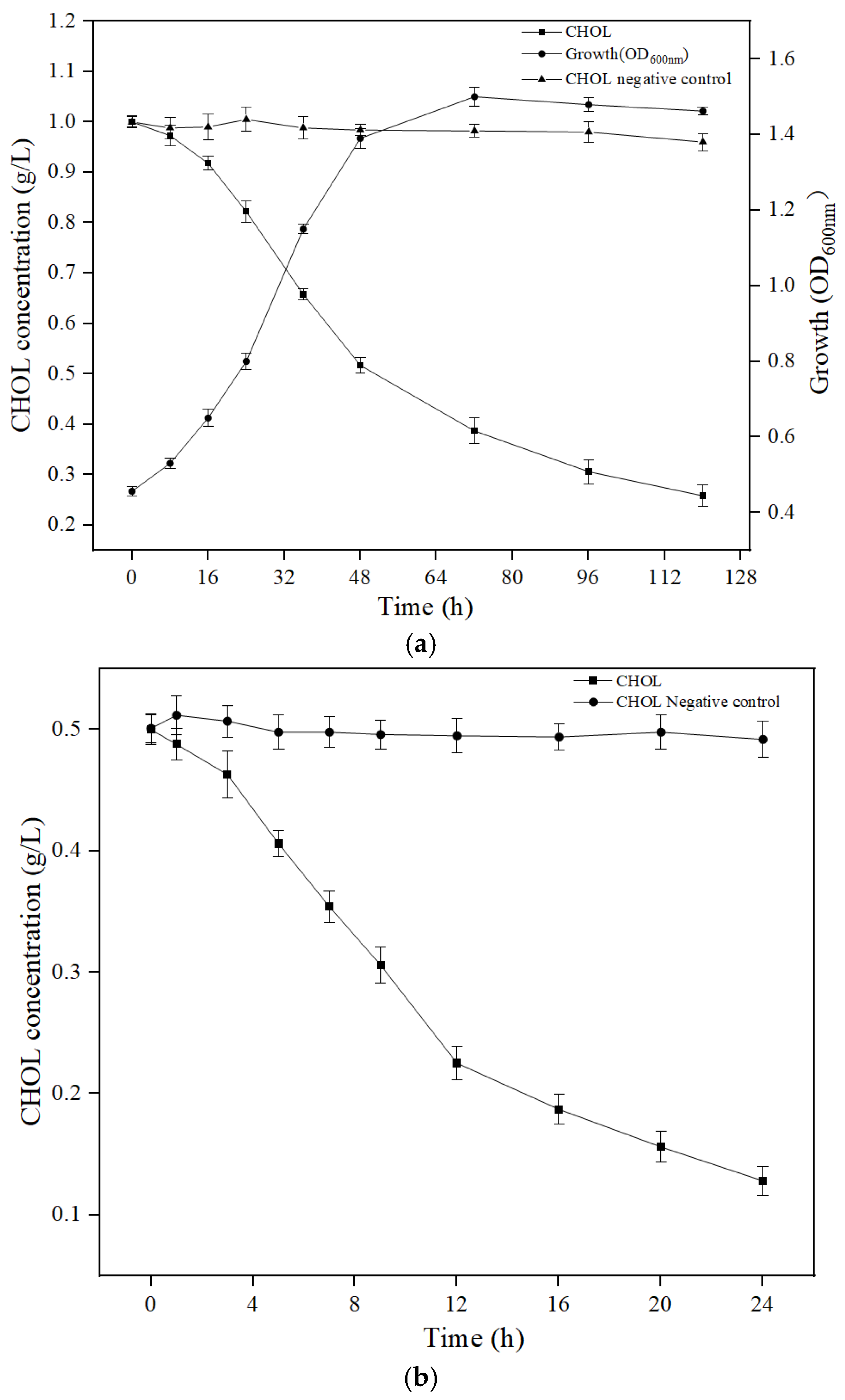
3.2. Biodegradation of CHOL by YS01 and Extracellular Crude Enzymes
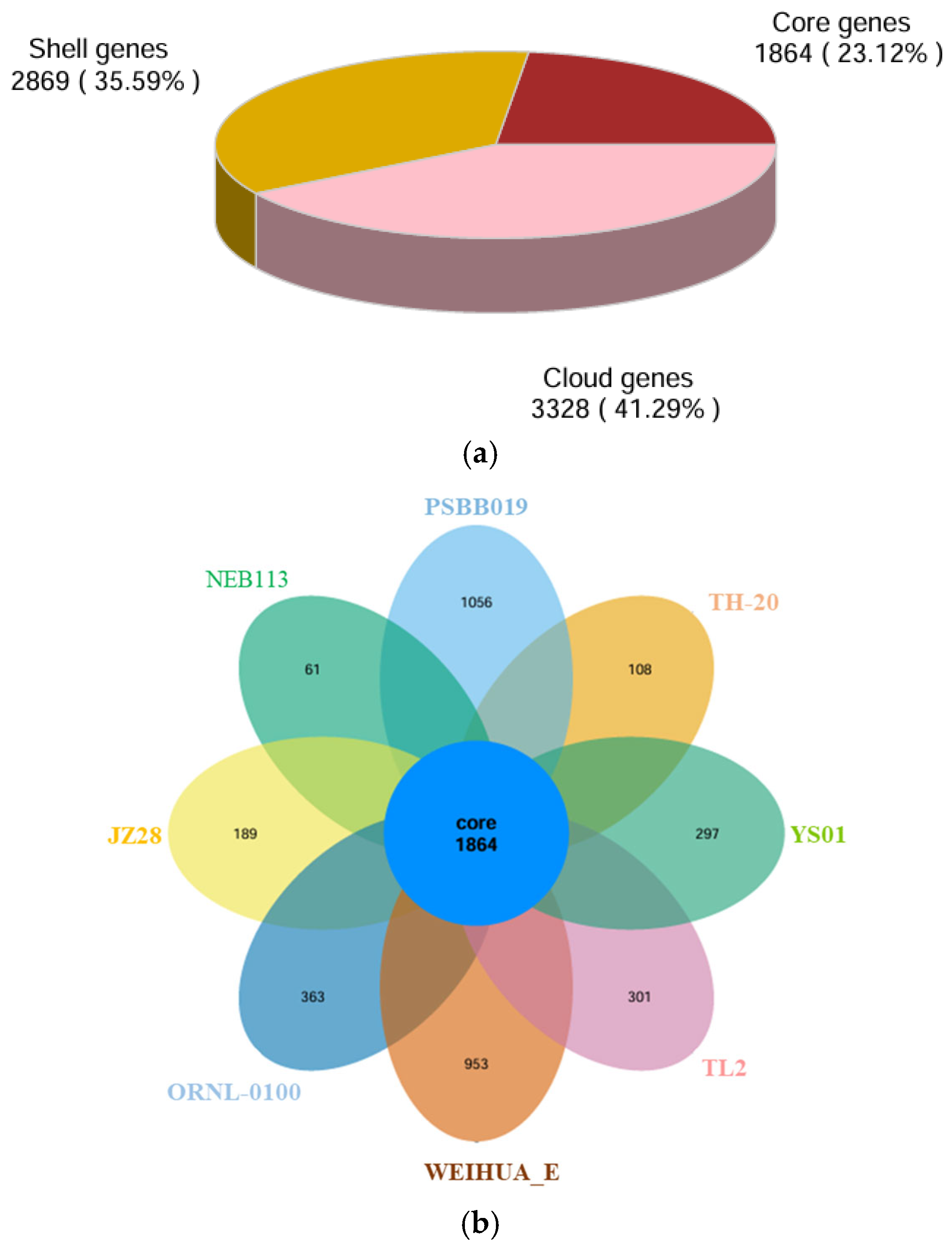
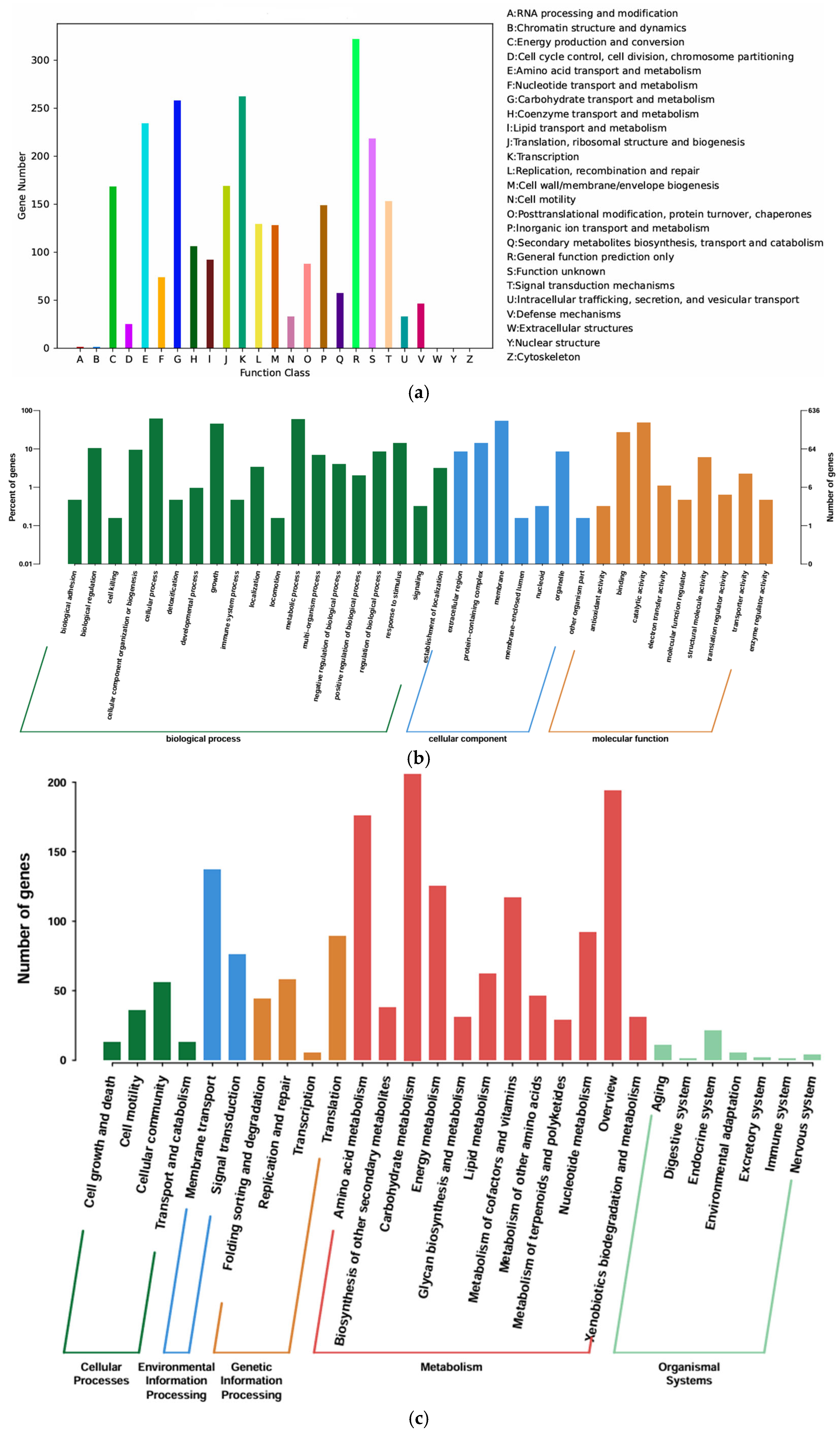
3.3. Genomic Analysis and Functional Annotation of YS01
3.4. Metabolic Pathways and Enzyme of CHOL Biodegradation of YS01
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lye, H.-S.; Rusul, G.; Liong, M.-T. Removal of cholesterol by lactobacilli via incorporation and conversion to coprostanol. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, M.F.; Manuck, S.B.; Matthews, K.A. Lowering cholesterol concentrations and mortality: A quantitative review of primary prevention trials. Br. Med. J. 1990, 301, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civeira, F.; Arca, M.; Cenarro, A.; Hegele, R.A. A mechanism-based operational definition and classification of hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2022, 16, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packard, C.J.; Shepherd, J. The pathophysiology of cholesterol metabolism in man. J. Mol. Med. 1985, 63, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, F.; Roessler, J.; Schmidt, D.; Jasina, A.; Schumann, P.; Gast, M.; Poller, W.; Leistner, D.; Giral, H.; Kränkel, N.; et al. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Atorvastatin Mediated Effects on Blood Lipids. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bäckhed, F.; Cani, P.D. Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: Effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, J.F.; Martín, J.F. Microbial cholesterol oxidases: Bioconversion enzymes or signal proteins? Mol. Biosyst. 2008, 4, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollegioni, L.; Piubelli, L.; Molla, G. Cholesterol oxidase: Biotechnological applications. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6857–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukyu, N. Characteristics and biotechnological applications of microbial cholesterol oxidases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zou, Y.; Han, X.; Bae, J.W.; Jeon, C.O. Gut microbiome-mediated mechanisms for reducing cholesterol levels: Implications for ameliorating cardiovascular disease. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 31, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zou, K.; Zhan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, X.; Qiu, L.; Wei, H. Enterococcus faecium GEFA01 alleviates hypercholesterolemia by promoting reverse cholesterol transportation via modulating the gut microbiota-SCFA axis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1020734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öner, Ö.; Aslim, B.; Aydaş, S.B. Mechanisms of cholesterol-lowering effects of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria strains as potential probiotics with their bsh gene analysis. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kombala, C.J.; Agrawal, N.; Sveistyte, A.; Karatsoreos, I.N.; Van Dongen, H.P.; Brandvold, K.R. Profiling rhythmicity of bile salt hydrolase activity in the gut lumen with a rapid fluorescence assay. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 4028–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T.; Shah, N.P. Acid and Bile Tolerance and Cholesterol Removal Ability of Lactobacilli Strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Grover, S.; Batish, V.K. Hypocholesterolaemic effect of dietary inclusion of two putative probiotic bile salt hydrolase-producing Lactobacillus plantarum strains in Sprague–Dawley rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 105, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, R.; Altermann, E.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Roy, N.C. The Role of Cell Surface Architecture of Lactobacilli in Host-Microbe Interactions in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 237921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.; Majeed, S.; Nagabhushanam, K.; Arumugam, S.; Beede, K.; Ali, F. Evaluation of the in vitro cholesterol-lowering activity of the probiotic strain Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, M.; Yi, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, M.; Xue, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short-chain fatty acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New prospects for short-chain fatty acids as therapeutic targets. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokila, V.; Namasivayam, S.K.R.; Amutha, K.; Kumar, R.R.; Bharani, R.A.; Surya, P. Hypocholesterolemic potential of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens KAVK1 modulates lipid accumulation on 3T3-L1 adipose cells and high fat diet-induced obese rat model. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boetzer, M.; Pirovano, W. Toward almost closed genomes with GapFiller. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, D.A.; Galperin, M.Y.; Tatusov, R.L.; Koonin, E.V. Using the COG database to improve gene recognition in complete genomes. Genetica 2000, 108, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, M.; Kanehisa, M. Using the KEGG database resource. In Current Protocols in Bioinformatics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- López Fernández, O.; Domínguez, R.; Santos, E.M.; Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Campagnol, P.C.B.; Lorenzo, J.M. Comparison Between HPLC-PAD and GC-MS Methods for the Quantification of Cholesterol in Meat. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, G.; Yan, H. Microbial biodegradation of microcystin-RR by bacterium Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yan, H. Biodegradation of Inosine and Guanosine by Bacillus paranthracis YD01. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, C.; Leng, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Y. Overexpression and characterization of a glycoside hydrolase family 1 enzyme from Cellulosimicrobium cellulans sp. 21 and its application for minor ginsenosides production. J. Mol. Catalysis. B Enzym. 2015, 120, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Lin, Z.; Pang, S.; Zhang, W.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Recent Advanced Technologies for the Characterization of Xenobiotic-Degrading Microorganisms and Microbial Communities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 632059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkem, B.M.; Halimoon, N.; Yusoff, F.M.; Johari, W.L.W.; Zakaria, M.P.; Medipally, S.R.; Kannan, N. Isolation, identification and diesel-oil biodegradation capacities of indigenous hydrocarbon-degrading strains of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans and Acinetobacter baumannii from tarball at Terengganu beach, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Sun, H.; Wen, X.; Sobhi, M.; Guo, J.; Dong, R. Urea-assisted ensiling process of wilted maize stover for profitable biomethane production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 757, 143751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narihiro, T.; Hiraishi, A. Microbiology of Fed-batch Composting. Microbes Environ. 2005, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Aljadaani, S.; Khan, J.; Sindi, I.; Aboras, M.; Aly, M.M. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Two Chitinase Producing Bacteria from Marine Shrimp Shell Wastes. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2020, 23, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, D.; Higashitani, A.; Osada, H.; Bito, T.; Shimizu, K.; Arima, J. Chitinolytic proteins secreted by Cellulosimicrobium sp. NTK2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Han, M.K.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, H.-W.; Park, D.-S.; Shin, D.-H.; Bae, K.S.; Son, K.-H.; Park, H.-Y. Isolation and characterization of a cellulase-free endo-β-1,4-xylanase produced by an invertebrate-symbiotic bacterium, Cellulosimicrobium sp. HY-13. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ahmad, S.; Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Yin, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, H. Biodegradation of Cholesterol by Enterococcus faecium YY01. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintakovid, N.; Singkhamanan, K.; Yaikhan, T.; Nokchan, N.; Wonglapsuwan, M.; Jitpakdee, J.; Kantachote, D.; Surachat, K. Probiogenomic analysis of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SPS109: A potential GABA-producing and cholesterol-lowering probiotic strain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, T.; Lin, X.; Liang, H.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ge, L.; Jin, X.; et al. Probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus gasseri TF08-1: A cholesterol-lowering bacterium, isolated from human gut. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 169, 110276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, S.; Giordano, M.; Dolci, P.; Zeppa, G. In vitro cholesterol-lowering activity of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus paracasei strains isolated from the Italian Castelmagno PDO cheese. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2009, 89, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Itoh, N.; Nakao, R.; Yasumoto, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Fukudome, S.I.; Okita, K.; Takano-Ishikawa, Y. Wheat alkylresorcinols suppress high-fat, high-sucrose diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance by increasing insulin sensitivity and cholesterol excretion in male mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, B.; Bernstein, J.; Marchlewicz, M. Dietary alkylresorcinols and cancer prevention: A systematic review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1693–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horáčková, Š.; Plocková, M.; Demnerová, K. Importance of microbial defence systems to bile salts and mechanisms of serum cholesterol reduction. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Cholesterol Oxidase: Source, Properties and Applications. Insights Enzym. Res. 2017, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobharani, P.; Halami, P.M. In vitro evaluation of the cholesterol-reducing ability of a potential probiotic Bacillus spp. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 643–651. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.-X.; Klinman, J.P. Structural bases of hydrogen tunneling in enzymes: Progress and puzzles. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004, 14, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrielink, A.; Ghisla, S. Cholesterol oxidase: Biochemistry and structural features. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6826–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gu, D.F.; Wu, X.G.; Reynolds, K.; Duan, X.F.; Yao, C.H.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Wildman, R.P.; et al. Major causes of death among men and women in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
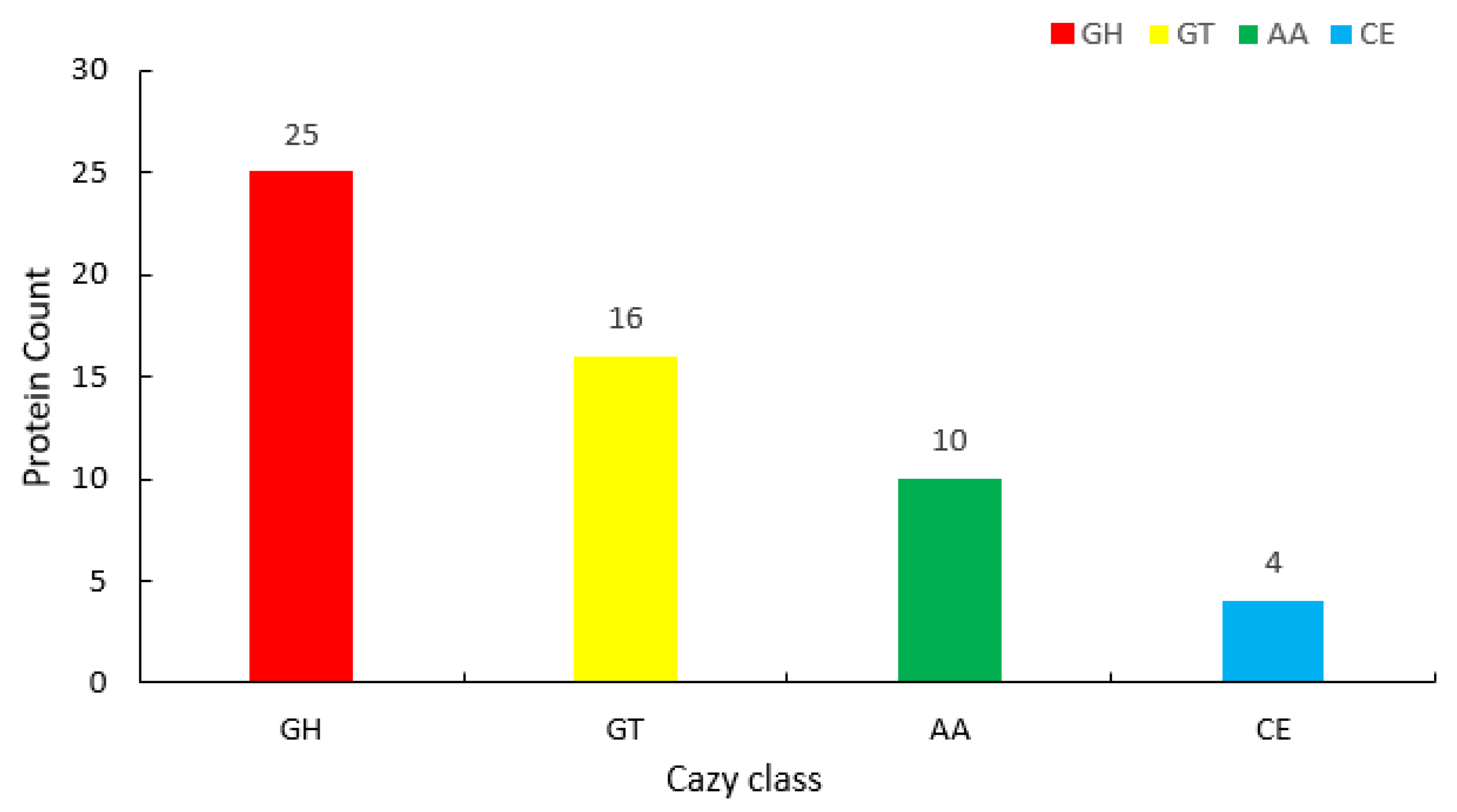
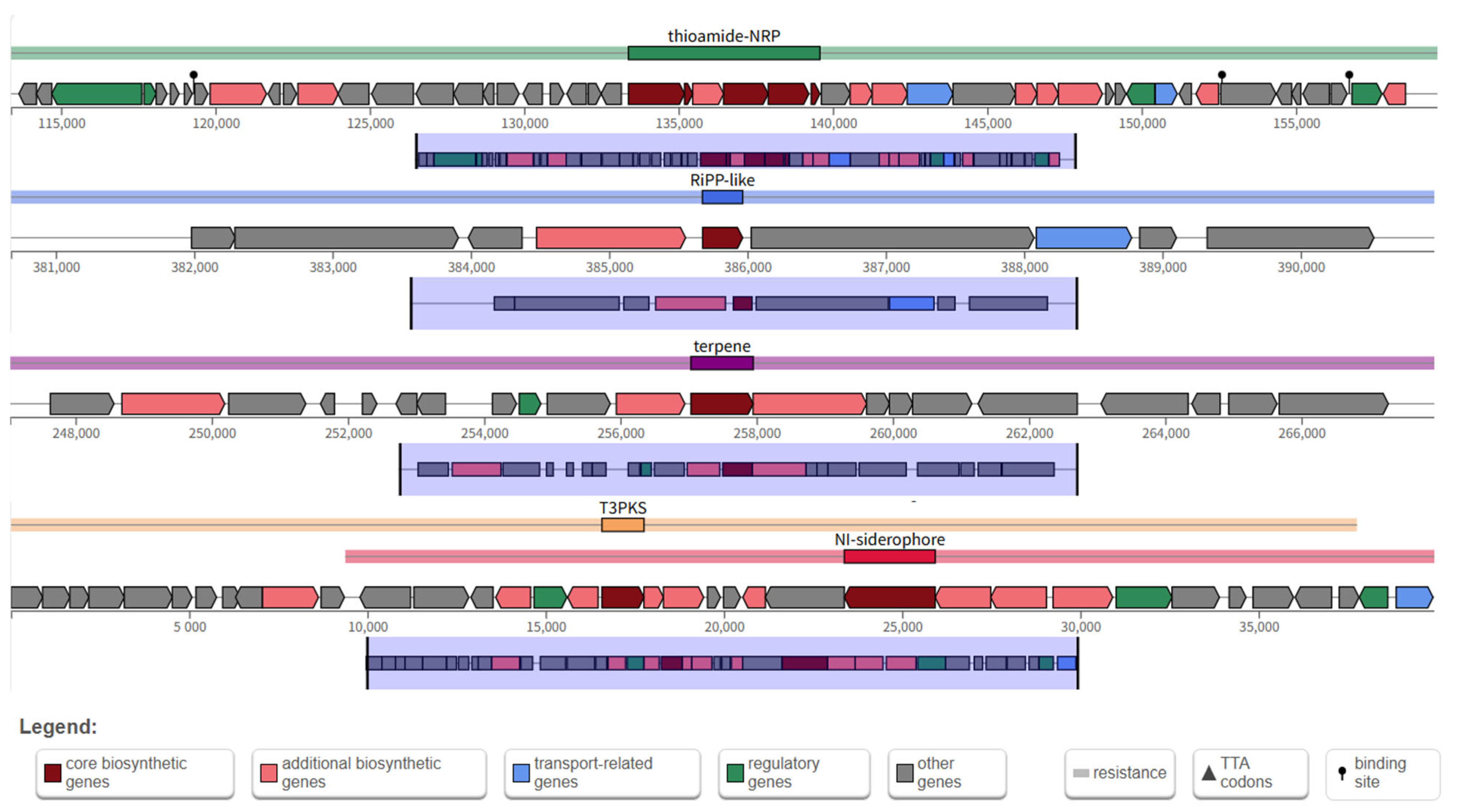
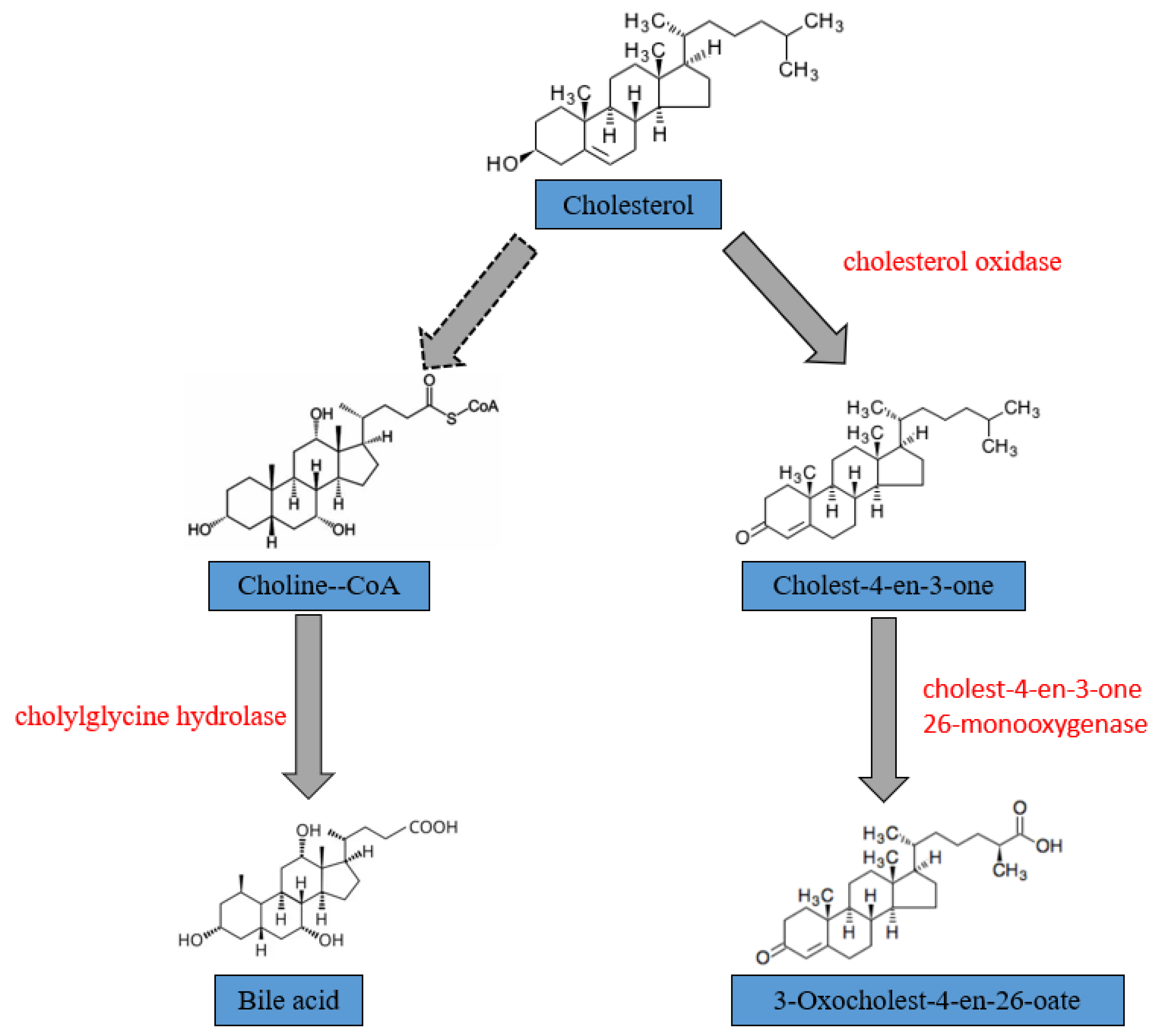
| Database | Number of Genes |
|---|---|
| NR | 3922 |
| COG | 2468 |
| CDD | 1606 |
| PFAM | 2318 |
| GO | 636 |
| KEGG | 1043 |
| Region | Type | From | To | Similarity | Most Similar Known Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.1 | thioamide-NRP | 113,379 | 159,582 | 12% | enteromyic |
| 4.2 | Ripp-like | 380,676 | 390,966 | — | — |
| 5.1 | terpene | 247,037 | 267,951 | 5% | 7-deoxypactamycin |
| 6.1 | T3PKS | 1 | 39,930 | 100% | alkylresorcinols |
| Gene Name | Databes | Enzyme |
|---|---|---|
| choD | KEGG | cholesterol oxidase [EC:1.1.3.6] |
| —— | GO | cholest-4-en-3-one 26-monooxygenase |
| cbh | KEGG | choloylglycine hydrolase [EC:3.5.1.24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, P.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Cao, X.; Du, X.; Lin, K.; Yan, H. Biodegradation of Cholesterol by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans YS01 Isolated from the Gut of Healthy Individuals. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071451
Sheng P, Xu Q, Zhang K, Cao X, Du X, Lin K, Yan H. Biodegradation of Cholesterol by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans YS01 Isolated from the Gut of Healthy Individuals. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071451
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Panqi, Qianqian Xu, Kaige Zhang, Xiaoyu Cao, Xinyue Du, Kun Lin, and Hai Yan. 2025. "Biodegradation of Cholesterol by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans YS01 Isolated from the Gut of Healthy Individuals" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071451
APA StyleSheng, P., Xu, Q., Zhang, K., Cao, X., Du, X., Lin, K., & Yan, H. (2025). Biodegradation of Cholesterol by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans YS01 Isolated from the Gut of Healthy Individuals. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071451



_Di_Marco.png)



