Abstract
Revealing soil microbial diversity and metabolic limitations in different land uses and soil depths is essential to understanding the regulation processes of soil nutrients. Here, bacterial and fungal microbial diversity and metabolic restriction in the 0–50 cm soil layers of four land uses, namely farmland, grassland, Betula platyphylla secondary forest, and Larix principis-rupprechtii-planted forest in the mountainous forest-grass ecotone of northern China, were determined. The results showed that soil microbial diversity in farmland was the lowest. Soil microorganisms from all land uses are limited by nitrogen, with the highest nitrogen limitation in planted forest. However, microbial nitrogen limitation in farmland increased with increasing soil depth, while microbial nitrogen limitation in grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest decreased with increasing soil depth. The bacterial and fungal community composition was influenced by soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, soil organic carbon:total phosphorus ratio, soil water content, soil organic carbon, and total nitrogen:total phosphorus ratio. The soil organic carbon:total phosphorus ratio has an impact on microbial metabolic limitation. This study shows that soil microbial communities were more affected by land-use type than soil depth. Land use changes the input of soil nutrients from aboveground plants, which affects the physical and chemical properties of soil, microbial community diversity, and microbial metabolic limitation. The vertical filtration effect between soil layers reduces soil nutrients, making the microbial diversity and enzyme activity of surface soil greater than those of deep soil. Our study helps to understand the function of soil microorganisms under different land use types in the forest-grass ecotone of northern China and provides a basis for predicting biogeochemical cycle dynamics in the ecotone in the context of global warming.
1. Introduction
Nutrient cycling in soil is facilitated by soil microbes, and an unbalanced nutrient supply in the soil will impact the metabolic state of these microorganisms [1]. By creating and secreting a variety of extracellular enzymes, soil microorganisms break down macromolecular organic compounds into smaller molecules. These enzymes are then used to obtain energy and nutrients for the growth of the microorganisms [2,3,4]. Because extracellular enzymes can respond to the availability of nutrients in the environment, it is believed that extracellular enzymes constitute a critical link between biological metabolism and biostoichiometry [5,6]. Soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) acquisition enzymes are divided according to the nutrient conversion function of extracellular enzymes [7]. The relative activity of these three types of enzymes, i.e., extracellular enzyme activity (EEA), is regulated by soil nutrients. As a result, EEA reflects the stoichiometric balance of microbial nutrient and resource demand [8]. In addition, EEA is often used to reflect changes in soil microbial cellular metabolism due to nitrogen deposition, land use change, nutrient addition, and climate change. It also illustrates the connection between the environment’s nutrient availability and the distribution of soil microbial resources [9,10,11,12]. Therefore, to quantify the microbial resource restrictions and the nutrient limitation of ecosystems, most studies have employed soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry [13,14]. In order to shed more light on the metabolic characteristics of bacteria, Moorhrad et al. [15] employed vector length and angles to characterize C, N, and P limitations in the ecosystem. Cao et al. [5] used enzyme activity vector analysis to investigate the metabolic limitations of microbes in the rhizosphere soil of Quercus aquifolioides. In order to investigate the geographical distribution of microbial nutrient limitation in alpine meadows and desert regions, Sun et al. [16] employed vector analysis and enzyme stoichiometry.
Land use change represents a key driver of soil nutrient dynamics and subsequent shifts in soil microbial community structure [17]. Different land use types showed differences in the nutritional composition of the soil, which affects the relative abundance of soil microorganisms [18]. A study revealed that pH value, organic matter, and N, P, and potassium (K) contents significantly affect soil microbial communities [19]. Similar findings were discovered by Li et al. [20] regarding differences in bacterial community composition and diversity, as well as nutritional components, across various land use types. The varying concentrations of soil nutrients across different land use categories could be linked to the metabolic limitations faced by soil microbes, which stem from the restricted availability of these nutrients [21]. Consequently, this kind of research is very meaningful. In a study focused on Robinia pseudocacia plantations in hilly and gully regions of loess [22], N was observed to be the limiting factor for soil microbial metabolism. Similarly, it was discovered that both N and phosphorus hindered microbial metabolism in several desert types in northwest China [23]. Yao et al. [24] studied constraints on microbial metabolism in the forest and farmland of the hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau. Some studies have found that restoration of forest vegetation is mainly hindered by phosphorus, while grassland and farmland are mainly limited by nitrogen. Natural grassland has the lowest microbial restriction of C and P, which is conducive to ecological restoration [4].
One important factor influencing nutrient conditions and soil microbial communities is environmental heterogeneity. Furthermore, soil microbial community composition, diversity, and metabolic limitations generally vary across spatial scales. In a recent study, spatial distribution patterns of soil microbial nutrient restriction in 31 ecosystems in China were studied. Due to variations in the spatial distribution of ecosystems, nearly half of the ecosystems showed differences in microbial nutrient limitations (mainly P limitation), exhibiting an important relationship between microbial nutrient restriction characteristics and soil pH [25]. According to Nottingham et al. [26], as altitude increased, microbial nutrient constraint changed from P limitation to N limitation. These results imply that geographical location affects microbial metabolic restriction. Consequently, in order to comprehend the soil nutrient status in tiny regions, it is crucial to carry out an exhaustive examination.
The soil’s nutrient status, as well as the microbial community’s structure, are influenced by soil depth. Understanding the connection between soil conditions and environmental variability has been hampered in the majority of studies to date, which have mostly concentrated on the nutrients and microbial characteristics of surface soil, while paying less attention to changes in deep soil [27]. Chu et al. [28] found that differences in bacterial communities at a soil depth of 30 cm remain almost unchanged compared with those in deeper soils. In a recent study, soil bacteria existing at a 2 m soil depth under different tree species exhibited greater depth sensitivity in the soil than fungal communities [29]. Depth-dependent patterns of microbial resource restrictions are caused by the depth of the soil. Research has indicated that, as soil depth increases, microbial P limitation increases as well [30]. However, the effect of soil depth on microbial nitrogen restriction is unclear, due to spatial heterogeneity. A thorough comprehension of metabolic limitation in the soil can be helpful in developing strategies for the rational use of land resources. Therefore, investigating microbial nutrient limitation in different soil layers of this region is crucial.
A forest-grass ecotone is an area where forest and grassland ecosystems are interleaved on a certain spatial and temporal scale. These areas have high species richness and high productivity. However, forest-grass ecotones are unstable, as their structure and function are easily affected by natural and human interferences [31]. The northern mountains of Hebei are an important ecological multi-functional area in the forest-grass ecotone of northern China. This region not only has a staggered forest-grass ecotone, but also has staggered areas of agriculture and animal farming. This region coexists with a variety of land use types, including farmland, grassland, and forest, and the nutrient status is complicated and variable. Previously, soil nutrients in the northern mountains of Hebei have been investigated by the researchers; however, soil microbial metabolic limitation has been rarely explored in this region. It is imperative to explore the variety and metabolic limits of soil microbial communities and identify potential influencing factors in order to lay down a scientific basis for land management in this region.
The goals of this study were to better understand soil microbial functions under different land use types in the forest-grass ecotone of northern China and to provide a fundamental basis for predicting the dynamics of biogeochemical cycles in this ecotone in the context of climate warming. For this research, we collected soil samples from farmland, grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest in northern Hebei Province. ITS and 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing were used to examine the bacterial and fungus communities present in the soil. The objectives of our research were to determine (1) any differences in soil microbial community composition and diversity among different land use types and soil depth in the forest-grass ecotone of northern China, (2) if soil metabolic limitations vary with land use, and (3) what environmental factors most strongly influence microbial community structure, diversity, and nutrient limitation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sample Collection
The research site is situated in Laowopu Township, Weichang County, Chengde City, northern Hebei Province (42°2′7.439′′ N, 116°59′39.372′′ E). The average elevation of the site is 1021 m. The yearly average temperature is 5.1 °C, with 373 mm of precipitation on average. It is located in the boundary zone of the Inner Mongolia Plateau and North China, between the forested northern mountains of Hebei and the grasslands of Inner Mongolia. A geographical location map of the study area is shown in Figure 1.
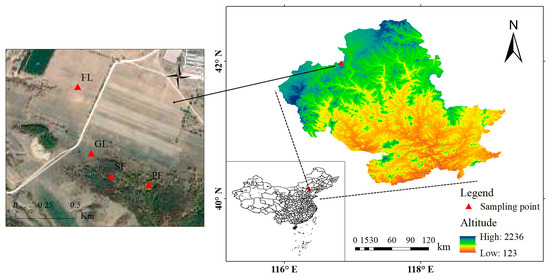
Figure 1.
Location of the studied area.
From July to August 2023, four typical land use types (farmland, grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest) in the typical forest and grassland transition belt in Laowopu were investigated. The basic overview of the sample plot is shown in Table 1. The area was originally a secondary forest of Betula platyphylla. In the late 1970s, due to the living and production needs of the residents in this area, different parts were transformed into farmland, grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest.

Table 1.
Basic overview of the sample plot.
There were three 20 × 30 m sample plots created for each type of land use. At each sample plot’s four corners and center, soil samples were collected from five distinct soil strata (0–10, 10–20, 20–30, 30–40, and 40–50 cm). A total of 60 samples were collected. These soil samples were manually cleaned by removing stones, litter, and roots. Subsequently, the soil samples were sieved through a 2 mm sieve. After collecting the soil samples, they were immediately stored at −80 °C to ensure the activity of soil microorganisms. Then, the microbial genomes were isolated and subjected to high-throughput sequencing. For soil physicochemical property analysis, a portion of each soil sample was kept in a polyethylene plastic bag and kept at room temperature.
2.2. Analysis of the Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
Soil pH and soil water content (SWC) were determined by pH meter at a 2.5:1 soil to water ratio by the mass ratio method and ring knife method, respectively. Soil organic carbon (SOC): potassium dichromate external heating method; total nitrogen (TN): Kjeldahl method with sulfuric acid digestion; total phosphorus (TP): molybdenum-antimony colorimetry after sulfuric acid digestion [32].
2.3. Analysis of Microbial Metabolic Restriction
Microplate fluorescence quantification was used to quantify the extracellular enzyme activities of the soil. The C-acquiring enzymes are represented by β-1,4-glucosidase (BG) and β-D-cellobiose hydrolase (CBH); β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminosidase (NAG) and leucine aminopeptidase (S-LAP) are examples of N-acquiring enzymes; and the P-acquiring enzyme is acid phosphatase (AP). Microbial C metabolic restriction was characterized using vector length [6]:
The variables x and y represent the relative activity of enzymes acquiring C and N and C and P, respectively. The longer the vector, the higher the microorganism’s C limitation.
N and P metabolic limitations were characterized using vector angles:
The vector angles of N and P were the cut-off for the line, where the drawing origin extends to the point (x, y). When the vector angle was less than 45°, microorganisms were constrained by N, and when it was more than 45°, by P. As the angle widened, the P limitation went up and the N limitation went down.
2.4. Extraction of Soil Microbial DNA and High-Throughput Sequencing
Using a DNA extraction kit (TiangenDP812), we first extracted the genomic DNA of soil microorganisms. The primers used for amplification of the V3-V4 regions of 16SrRNA of soil bacterial DNA were F: ACTCCTTACGGGAGGCAGCA and R: GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT. The primers used for targeting the ITS 1-F regions of soil fungi were F: CCTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA and R: GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC. To create qualified sequencing libraries, amplicons underwent purification, quantification, and homogenization. To obtain the raw sequences (reads), we used an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform for high-throughput sequencing. Trimmomatic v0.33 was used to filter these raw reads. To obtain clean reads, primer sequences were found and eliminated using Cutadapt 1.9.1. DADA 2 in QIIME2 2020.6 was used for denoising and clustering of sequences at 100% similarity to obtain amplicon sequence variants (ASVs). The SILVA and UNITE databases were utilized for annotation of related bacterial and fungal species, respectively.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Based on the ASV classification results, the diversity and richness indices of bacteria and fungi (ACE, Chao1 richness index, Shannon–Wiener index, and Simpson index) were calculated. R (v.3.6.1) and SPSS (v.20.0) were used for statistical and differential analyses of bacterial and fungal diversity indices. The Bray–Curtis method was used to conduct PCoA analysis in order to evaluate differences in the soil microbial community structure at different soil depths and for different land use types. We employed one-way ANOVA to assess variations in soil extracellular enzyme activities across different land use types and within various soil layers. SPSS (v.20.0) was used for plotting.
Spearman correlation analysis was employed to assess the relationships among the α diversity of soil microorganisms, environmental factors, and extracellular enzyme-related indices. Additionally, a Mantel test was conducted and visualized using the R “vegan” package. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was further utilized to explore these relationships in greater depth, with visualization performed using Canoco 5.0 software.
3. Results
3.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
The soil pH for the four land use types was weakly acidic (Figure 2). The soil water content (SWC) for planted forest was the highest, the SWC for farmland was the lowest, and the SWC gradually decreased with increasing soil depth. The contents of soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) in the four land use types were grassland > secondary forest > planted forest > farmland and showed a decreasing trend with increasing soil depth. The SOC/TN value for grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest decreased with increasing soil depth, while the SOC/TN value for farmland increased first, then decreased, then increased. The SOC/TP value showed a decreasing trend among soil layers of the four land use types.
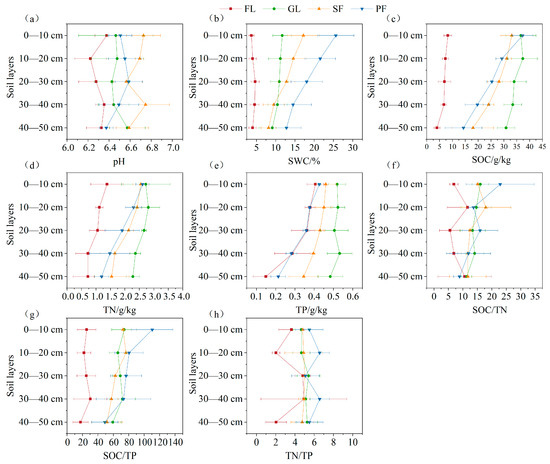
Figure 2.
Soil physical and chemical properties under different land use types and at different soil depths. Note: (a) pH content (b) Soil water content; (c) Organic carbon content; (d) Total nitrogen content; (e) Total phosphorus content; (f) Organic carbon: Total nitrogen content; (g) Organic carbon: Total phosphorus content; (h) Total nitrogen: Total phosphorus content. FL: farmland, GL: grassland, SF: secondary forest, PF: planted forest. The same below.
3.2. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities
Following high-throughput sequencing, soil samples from four different land use types contained 24,910 fungal ASVs and 106,988 bacterial ASVs. At the phylum level, 14 dominant bacterial phyla with relative abundance >1% and 7 dominant fungal phyla were detected. Bacterial taxa with relative abundance <1% were classified as “Other” (Figure 3a). For the four land use types, the abundances of Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteriota were relatively high. The highest abundances of Proteobacteria (28.57%) and Actinobacteria (17.56%) were observed in farmland soil, while the abundance of Acidobacteriota (19.40%) was highest in planted forest soil. Similarly, Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were the most dominant fungal phyla (Figure 3b). The highest abundance of Ascomycota was observed in grassland soil, while the highest abundance of Basidiomycota was witnessed in farmland soil.
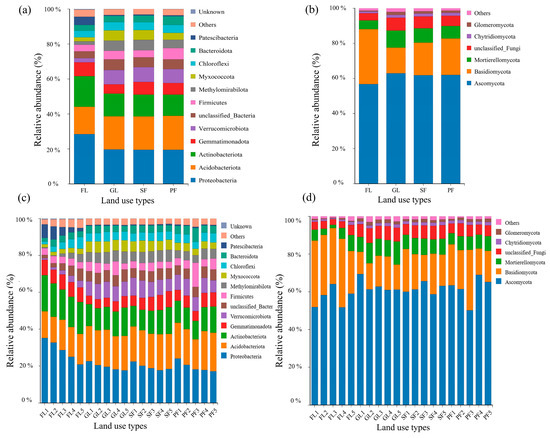
Figure 3.
Composition of soil bacterial and fungal communities for different land use types and soil depths. Note: (a) Relative abundances at the bacterial phylum level under different land use types; (b) Relative abundances at the fungal phylum level under different land use types; (c) Relative abundances at the bacterial phylum level under different soil depths; (d) Relative abundances at the fungal phylum level under different soil depths.
In each soil layer, Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteria were observed to be the top three dominant bacterial phyla with relative abundance >1%. For all four land use types, the abundance of Proteobacteria decreased with soil depth (Figure 3c). Similarly, Ascomycota and Basidiomycota showed the highest abundance in each soil layer. However, no clear pattern of change in abundance was observed with soil depth for the four land use types (Figure 3d).
The Shannon index and Simpson index of bacteria and fungi showed basically no significant differences in the different soil layers, and the Chao1 index and ACE index also exhibited the same results (Figure 4). Bacteria had greater species diversity and richness than fungi. Farmland had the lowest levels of fungal species diversity and richness. The diversity and abundance of bacteria in the surface soil layers (0–10 cm, 10–20 cm) of farmland are usually significantly lower than those for other land use types (p < 0.05).
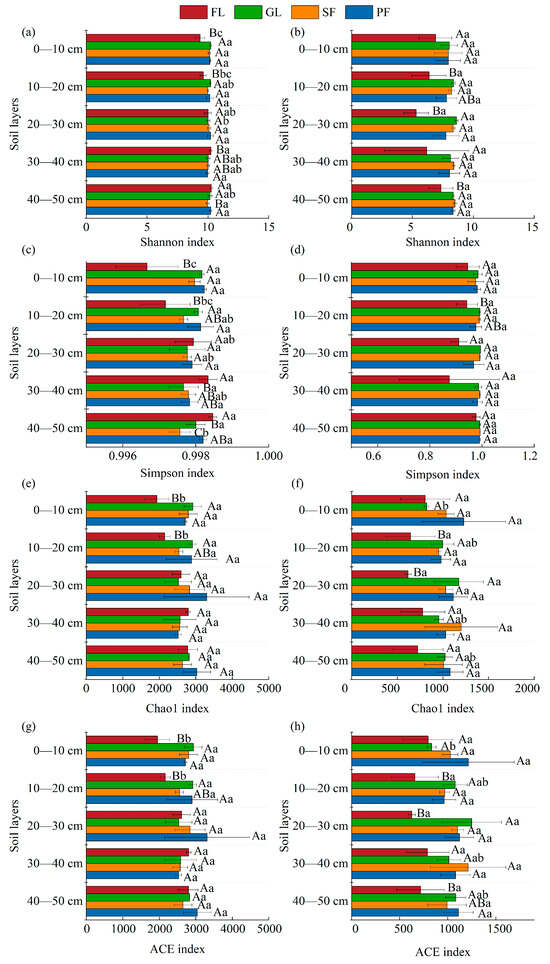
Figure 4.
Shannon index (a,b), Simpson index (c,d), Chao1 index (e,f), and ACE index (g,h) of bacteria and fungi under different land use patterns. Note: Different uppercase letters indicate statistically significant differences among different land use types (p < 0.05), while different lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences among different soil depths (p < 0.05).
PCoA of the ASVs of bacteria and fungi for different land use types and different soil layers was performed (Figure 5). Regarding bacterial β diversity, the first axis contributed 25.26%, while the second axis contributed 7.99%, with the two axes explaining 33.25% of the variance. Regarding the fungal community, the first axis contributed 19.23%, while the second axis contributed 8.32%, with the two axes explaining 27.55% of variance. Both bacterial and fungal communities were significantly affected by land use type (p < 0.01) (Figure 5a,b). On the first coordinate axis, the distance between farmland and the other three land use types is large. This indicated a significant difference between the bacterial community structures of farmland and the other three land use types. The distribution of samples in each group of fungal communities was relatively clustered, and the similarity of the fungal communities was high. Figure 5c,d show that the bacterial community structure in each soil layer is similar, and the soil layer has no significant effect on bacterial and fungal community structure.
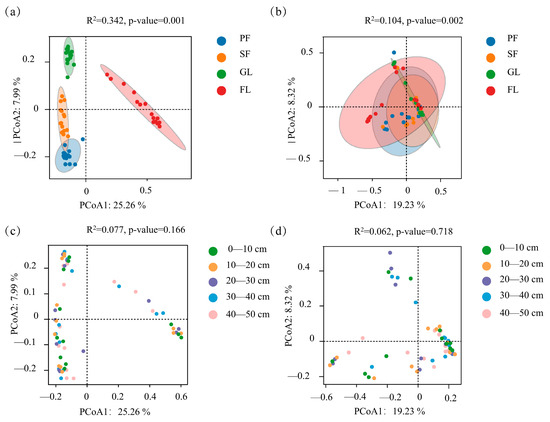
Figure 5.
Results of the PCoA analysis based on a Bray–Curtis heterogeneity matrix, representing changes in bacterial (a,c) and fungal (b,d) communities for different land use types and at different soil depths.
3.3. Stoichiometric Changes and Metabolic Limitations of Microbial Enzymes in Soil
Except for farmland, the activities of C-, N-, and P-related enzymes in the surface soil of the other land use types were higher than those in deep soil, and the activities of three enzymes in farmland were the lowest for all land use types (p < 0.05) (Figure 6). Farmland had the lowest value of the C-acquiring enzyme, whereas grassland had the highest value. Except for the 40–50 cm soil layer, the N-acquiring enzyme activity of planted forest was the highest among the four land use types. The P-acquiring enzyme activity in the 0–50 cm soil layer was substantially lower in farmland than it was in the other three land types.
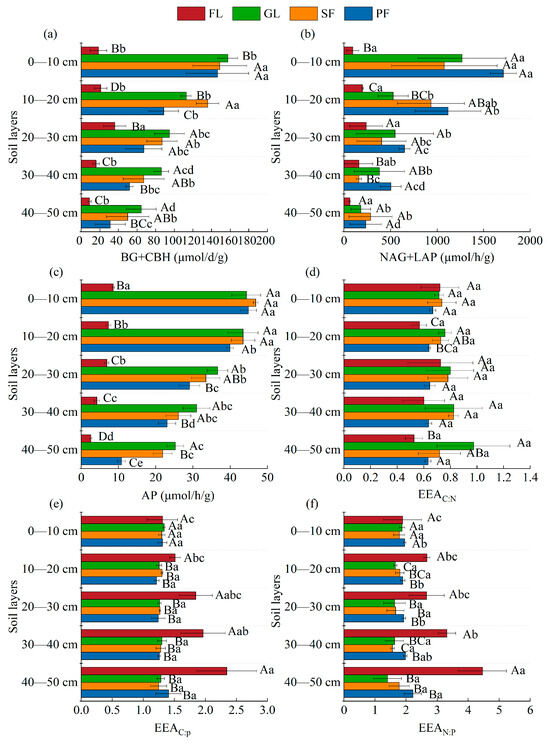
Figure 6.
Effects of different land use types and soil depth on soil extracellular enzyme activities and their stoichiometry in soil. Note: (a) C-acquiring enzymes content; (b) N-acquiring enzymes content; (c) P-acquiring enzymes content; (d) The activity ratio of C and N enzymes; (e) The activity ratio of C and P enzymes; (f) The activity ratio of N and P enzymes. BG, β-1, 4-glucosidase (μmol·d−1·g−1); CBH, β-D-cellosidase (μmol·d−1·g−1); NAG, β-1, 4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (μmol·h−1·g−1); LAP, L leucine aminopeptidase (μmol·h−1·g−1); AP, alkaline phosphatase (μmol·h−1·g−1); EEAC:N-enzyme: LN[(BG + CBH)/(NAG + LAP)], EEAC:P enzyme, LN[(BG + CBH)/AP]; EEAN:P-enzyme, LN[(NAG + LAP)/AP]. Different uppercase letters indicate statistically significant differences among different land use types (p < 0.05), while different lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences among different soil depths (p < 0.05).
The EEAC:N of farmland and plantations was significantly lower than that of grassland in the 10–20 cm soil layer (p < 0.05). The EEAC:P and EEAN:P of farmland were significantly higher than other land use types, except for 0–10 cm soil layer. The EEAC:P of the 40–50 cm soil layer for farmland was significantly higher than that of the 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm soil layers (p < 0.05). The EEAN:P for the 40–50 cm soil layer of farmland was significantly higher than that for the other soil layers (p < 0.05).
The nitrogen restriction on microbial metabolism for the four land use types is explained by the position of most data points below the 1:1 line (Figure 7a). In the 10–20 cm soil layer, the vector length for secondary forest was significantly higher than that for planted forest (Figure 7b). The vector angle for the 0–10 cm soil layer of planted forest was significantly lower than that for other land use types, and the vector angle for the 10–20 cm layer of farmland and planted forest was significantly lower than that of grassland and secondary forest (p < 0.05) The planted forest had a substantially smaller vector angle, but the grassland had the largest angle (Figure 7c). The surface soil of farmland had a higher vector angle than the deep soil, whereas the grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest had the opposite vector angles. Linear regression analysis revealed that the vector length and vector angle of the different land use types correlated positively (Figure 7d).
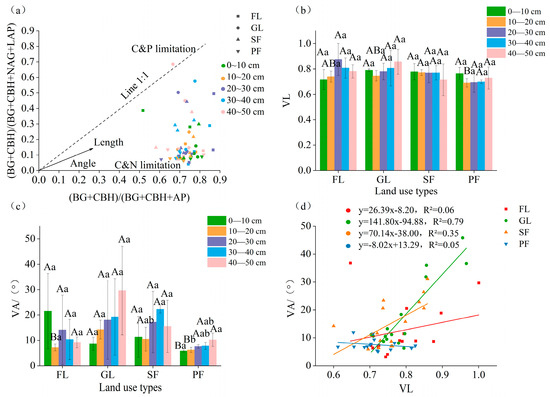
Figure 7.
Enzyme stoichiometry (a), vector lengths (b), vector angles (c), and linear regression fitting (d) of different land use types and for different soil layers. Note: VL: vector length; VA: the vector angle. Different uppercase letters indicate statistically significant differences among different land use types (p < 0.05), while different lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences among different soil depths (p < 0.05).
3.4. Correlation of Soil Properties, Microbial Communities, and Their Metabolic Constraints
Spearman correlation analysis showed that C-, N-, and P-acquiring enzymes and soil properties also showed significant correlations (Figure 8). C-, N-, and P-acquiring enzymes are closely related to each other. C-acquiring enzymes and EAAN:P were found to be significantly and negatively correlated (p < 0.001). Similarly, P-acquiring enzymes showed very significant negative correlations with EAAC:P and EAAN:P (p < 0.001). EAAN:P was significantly negatively correlated with EAAC:N, and EAAN:P was significantly positively correlated with EAAC:P (p < 0.001). Vector length showed very significant positive correlations with EAAC:N and EAAC:P (p < 0.001). Vector angle and N-acquiring enzymes showed very significant negative correlations with EAAN:P (p < 0.001) and significant positive correlations with EAAC:N (p < 0.001). The Mantel test shows that the bacterial community composition was affected by soil SOC, TN, and SOC:TP and had a significant positive correlation with the activities of C- and P-acquiring enzymes. Furthermore, significant correlations of bacterial community composition were observed with EAAC:P and EAAN:P (p < 0.05). In addition, fungal community composition showed weak correlations with most indicators. Fungal community composition only showed very significant positive correlations with SWC (p < 0.01).
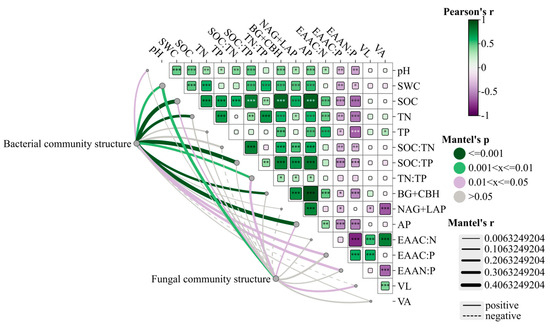
Figure 8.
Spearman correlation analysis of soil physical and chemical properties and dominant community composition at the microbial phyla level. Note: *, **, *** indicated that the differences were statistically significant, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001.
No significant correlations of bacterial α diversity were observed with soil properties, enzymes, and enzyme stoichiometry (Figure 9a). Conversely, it was discovered that fungal α diversity strongly correlated with soil characteristics and enzyme activities. There was strong positive correlation between fungal species diversity and soil SOC and SOC:TP (p < 0.001). It was positively correlated with C-acquiring enzymes and P-acquiring enzymes (p < 0.01). Furthermore, fungi species richness was significantly positively correlated with soil pH, SWC, SOC, SOC:TN, and SOC:TP (p < 0.01) and significantly negatively correlated with EAAC:P and EAAN:P (p < 0.05).
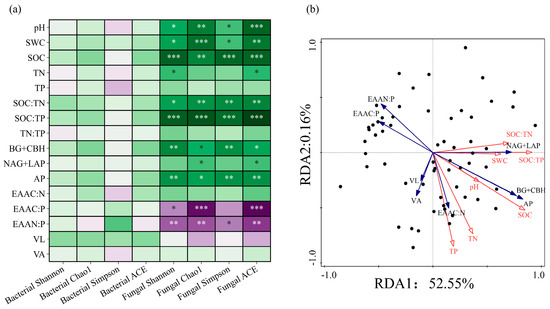
Figure 9.
Spearman correlation analysis of soil physical and chemical properties and microbial diversity at the microbial phyla level (a), restriction of soil enzyme metabolism and redundancy analysis of physical and chemical factors (b). Note: *, **, *** indicated that the differences were statistically significant, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001.
Each environmental variable explained 52.71% of the variation in soil enzyme activity (Figure 9b.). The contributions of the first and second axis variables were 52.55% and 0.16%, respectively. Based on importance in explaining soil enzyme activity and their measurement ratio, the soil environmental factors were ranked as SOC:TP > SWC > SOC > TN > SOC:TN > pH > TP. This suggested that the key soil parameter influencing soil enzyme activity and measurement ratio was SOC:TP (p < 0.01).
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the Composition and Diversity of the Soil Microbial Community
Different land use types have changed the types of surface vegetation, affected the content of soil nutrients and thereby influencing the soil microbial community [33]. The dominant bacterial phyla for all four land use types in the northern mountains of Hebei were Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Acidobacteriota, accounting for more than 50% of the total bacterial sequences. Wang et al. [34] reported similar results. Proteobacteria, which are primarily facultative or aerobic bacteria, exhibit extremely strong adaptability to the surrounding environment and can adapt to multiple ecosystems, which explains their high relative abundance in most land use types [35,36,37]. Proteobacteria in farmland was higher than that in the other three land use types. This may be because Proteobacteria are commonly found in agricultural soil. This outcome was consistent with what Angelo et al. [18] reported. Acidobacteria can grow rapidly in nutrient-deficient environments. Acidobacteria were most abundantly found in planted forest. This might be explained by the deficiency of nutrients and the acidic soil in planted forest, which resulted from planted forest being developed with human intervention. In contrast to this study, Chen et al. [38] found a higher abundance of Acidobacteria in farmland compared with other land use types, which may be due to geographical differences.
Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were the most prevalent fungal phyla at the ASV level in the investigation, which is in line with the findings of numerous other investigations. Soil Ascomycota and Basidiomycota are dominant fungi in the four land use types. Although there are differences in geographical location [39] and aboveground vegetation [40] among the four land use types in this study, the status of the dominant fungi remains unchanged. However, there are still differences in relative abundance and community composition between Ascomycota and Basidiomycota in terms of land use types. For example, studies of soil microorganisms in different land use types in northern mountainous areas have found that the relative abundance of Ascomycota is highest in shrublands, farmlands, and grassland, while the proportion of the relative abundance of Basidiomycota is the highest in forests [41]. This result was consistent with the horizontal distribution of fungal phyla seen in the Pearl River Estuary under various land use scenarios [42].
Microbial α diversity analysis revealed that the microbial (bacterial and fungal) diversity and richness in farmland were lower than those for other land use types. According to certain research, habitat variations may contribute to a decrease in soil microbial diversity, particularly when human activities like tillage, fertilization, and other actions are involved [43]. Nevertheless, other research has revealed the opposite outcome, showing an increase in root exudates and crop residues in soil after fertilization or crop rotation, which further increased the microbial diversity and richness of soil [44]. The farmland in this study adopted a rotation tillage pattern of corn–sunflower–potato, which might be more conducive to an increase in soil microbial diversity compared with the common continuous tillage pattern [45]. Meanwhile, this study found that the soil nutrient content of farmland was the lowest among the four land use types, and the nutrient supply capacity was relatively weak. However, compared with grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest, farmland is affected by human activities, which interferes with its soil structure and nutrient cycling process. The content of organic carbon and total nitrogen in farmland soil is low. Therefore, the microbial diversity of farmland soil in this area is lower than that of other land use types. In forest and grassland areas, the low diversity of soil microorganisms in farmland will have certain impacts on agricultural production in this region, including crop yields, etc. A comparative experiment should be set up to further verify the role of soil microbial diversity in agricultural production in this area.
Overall, the soil’s depth had an impact on the microbial community’s structure. One important environmental factor influencing the richness and complexity of the soil microbial community is the depth of the soil layer [46,47]. Based on the findings of this study, the abundance of some bacterial phyla (like Proteobacteria) declined as soil depth increased. This study found that soil nutrients generally decrease with increasing soil layer depth. Therefore, the energy available for soil bacteria to utilize decreases, and the relative abundance of microorganisms also decreases accordingly [48]. In an earlier investigation, the overall relative abundance of some microbial groups, such as Firmicutes, Chlorendella, and Ascomobacteria, increased with increasing soil depth, reflecting an increase in dominant microbiomes that can maintain the soil nutrient cycle and microbial metabolism with low energy availability [49]. Certain soil microorganisms may find it more difficult to survive in the underlying soil layer due to the filtering of vertical space between soil layers, which further lowers the diversity of soil microbes [50]. However, unlike the other three land use types, the diversity and abundance of bacteria in the 0–10 cm layer of farmland soil are significantly lower than those in the 20–50 cm layer, which is different from the results obtained by most studies. As farmland is a “non-steady-state” environment, it can be affected by human disturbances (such as fertilization and ploughing). The farmland in the study area is often ploughed, which may be one of the reasons for the unstable surface soil conditions of the farmland, which is not conducive to the growth of soil microorganisms and leads to a reduction in bacterial diversity and abundance.
4.2. Differences in Soil Microbial Metabolism Limitations
Aboveground and underground bio-communities, soil properties, and input and output of soil organic matter directly affect soil enzyme activity. In this study, enzyme activity was lowest in farmland. This could be because of the low organic matter content, vegetation litter, and root secretion, which lead to low secretion and activities of soil extracellular enzymes [51]. It may also be related to the farming measures adopted in farmland [52]. The soil nutrient content also reflects microbial enzyme activity, and microbial enzyme activity is different for different land use types. Furthermore, forest also showed a close relationship between soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN). According to studies, NAG is the primary enzyme associated with soil N and is necessary for the circulation of nutrients [53]. Soil microbes may have access to more substrates and energy due to the high SOC and N content of forest soil [54]. Meanwhile, forest vegetation litter and root secretions further stimulate the secretion of extracellular enzymes, thus increasing soil enzyme activity.
The ecological stoichiometric ratio of soil enzyme activity was determined by log-transforming the data, and it was found to be 1:1.46:0.73. This ratio deviates from the global ecosystem soil enzyme stoichiometric ratio of 1:1:1 [6]. This suggested that different land use types had high activity of N-acquiring enzymes, reflecting a relative lack of nitrogen in this region. Most of the land use types had a vector angle of <45°, which indicated nitrogen limitation. Analysis of soil enzyme vector length revealed that there was no discernible variation in carbon restriction among the four land use types. Furthermore, the degree of carbon restriction in secondary forest and planted forest was lower than that in farmland and grassland. Similar findings from other studies have suggested that a higher SOC content in the soil can supply more carbon sources for microbial growth, resulting in weaker carbon limitation [55].
The activities of C-, N-, and P-acquiring enzymes generally decline with increasing soil depth, which aligns with the decreasing trend of soil nutrients with depth. The surface soil’s humus and organic matter accumulation is enhanced by prolonged deposition and breakdown of highly polymerized plant residues, altering the soil’s structure [56]. Deep soil has less enzyme activity than surface soil because it cannot supply microbial enzymes with enough substrates and energy, due to its lower nutrient content [57]. Soil enzyme stoichiometric ratio analysis showed that deep soil was more severely limited by N than top soil. The soil vector angles further confirmed higher N limitation in deep farmland soil compared to surface soil. In contrast, deep soil from secondary forest and plantations, and in grassland soil, had less N limitation than the respective surface soil, with increased P limitation. This could be because, as soil depth increases, the distribution of planted vegetation’s roots decreases relatively. Deep-rooted plant roots in secondary forest and planted forest compete with soil microorganisms for phosphorus, resulting in reduced nitrogen limitation and increased P limitation [58]. In a study by Liu et al. [25] on the nutrient restriction of forest soil in China, it was also found that deep-rooted plants and soil microorganisms compete for nutrient elements, emphasizing their competition for phosphorus. The phosphorus restriction of soil microorganisms increases with increasing soil layer depth, which is consistent with the results obtained in this study. The vector length of enzymes reflects potential hydrolysis of organic carbon in the soil, but it cannot measure carbon restriction in soil microorganisms [59]. Because the carbon content in deep soil is lower than that in the surface layer, which inhibits the growth and metabolism of microorganisms, the medium vector length for secondary forests and planted forests decreases with increasing soil depth [58].
4.3. Key Factors Affecting the Composition and Metabolic Limitation of Soil Microbial Communities
The soil microbial bacterial community composition was mainly influenced by SOC, TN, and SOC:total phosphorus (TP), while the fungal community composition was primarily affected by soil water content (SWC) and TN:TP. These results concurred with those of an earlier study, reporting SOC and TN as key factors affecting soil bacterial communities [60]. Yu et al. [61] studied carbon fixation and microbial regulation mechanisms in grassland soil and observed that the fungal community was more affected by SWC. The environmental parameters influencing fungal diversity in the current study were comparable to those described by Yang et al. [62], who found that soil pH, bulk density, and SOC concentration were the necessary soil factors determining soil microbial diversity. Contrary to the findings of the majority of previous investigations, soil bacterial populations were less impacted by environmental influences. For example, Yan et al. [63] observed that environmental factors were closely related to soil bacterial diversity. This may be due to the heterogeneity of soils in different habitats.
The bioavailability of soil nutrients is mainly based on the microbial community and the environmental conditions in soil [64]. In this study, N limitation of soil microorganisms was found to be related to SOC:TP, SWC, and SOC. Since soil microorganisms are N-limited, they try to obtain as much N as possible from the environment, which leads to higher activity of N-acquiring enzymes. SOC has an important relationship with soil microbial nitrogen limitation. Soils with a high SOC level are better for microbial development and enzyme synthesis because they have a stronger water-holding capacity and a higher effective carbon content [65]. This explains the positive correlations between N-acquiring enzymes and SOC. In this study, N limitation in plantation areas was more severe than that in farmland, grassland, and secondary forest. Due to the higher SOC content in plantation soil, more N-acquiring enzymes are released by microbes to alleviate the N limitation [23]. These plants then compete with microorganisms for N, thus aggravating N limitation in soil. Yuan et al. [66] conducted nitrogen addition experiments in semi-arid grasslands in northern China and found that there is a potential competitive relationship between soil microorganisms and plants, and this competition may be related to soil nitrogen limitation. In addition, plant roots and microorganisms have a certain degree of spatial overlap, and both are significantly related to inorganic nitrogen in the soil. The root systems of plants absorb nitrogen at a faster rate than microorganisms [67].
Cregger et al. [68] found that the increase in SWC is conducive to the growth of plants. Changes in SWC were shown to be negatively connected with carrier length and carrier angle and favorably correlated with enzyme activity in this investigation. SOC:TP was the most significant factor affecting nutrient metabolic limitation in soil microorganisms. Research has demonstrated that the microbial enzyme stoichiometry ratio and enzyme activity in soil can be significantly impacted by the stoichiometric ratio of soil nutrients [69,70]. In the study, the SOC:TP content of the four land use modes was higher, which was closely related to the activity and stoichiometric ratio of the three extracellular enzymes. These findings proved the significant relationships between SOC:TP and microbial nutrient limitation.
5. Conclusions
In this study, changes in soil microbial diversity and metabolic limitation with soil layer depth were investigated in agricultural farmland, grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest in the mountainous forest-grass ecotone of northern China. In summary, the microbial diversity of agricultural land was significantly lower compared to that of other land uses. Soil microorganisms were N-limited regardless of soil texture and depth. Among the four land uses, planted forest exhibited the most severe N limitation. Notably, N limitation in farmland increased with soil depth, whereas grassland, secondary forest, and planted forest showed the opposite trend. This research shows that SOC, TN, and SOC:TP affected bacterial community composition, while SWC, SOC, and TN:TP affected fungal community composition. SOC:TP is closely related to soil microbial nitrogen limitation. This study emphasized that land use types are more influential for soil microbial community than soil depth, and that soil nutrients and their stoichiometric ratios play a key role in microbial metabolic limitation. Land use changes the input of soil nutrients by aboveground plants, which affects the physical and chemical properties of soil, microbial community diversity, and microbial metabolic limitation. The vertical filtration effect between soil layers reduces soil nutrients, making the microbial diversity and enzyme activity of surface soil greater than that of deep soil. In the future, more attention should be paid to the action mechanisms of soil microorganisms in different land use types within the ecologically fragile area of interlaced forests and grasslands, providing a basis for more precisely optimizing land use management strategies. Overall, this study advances the understanding of soil microbial functions under different land use types in the forest-grass ecotone of northern China and emphasizes the need to incorporate vertical changes in microbial properties along the soil layer in future studies to predict the dynamics of biogeochemical cycles within ecosystems in this ecologically critical zone in the context of climate warming.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.M., X.L. and X.X.; methodology, X.M., X.L. and J.W.; software, X.L.; validation, X.M. and X.L.; formal analysis, X.M.; investigation, Y.M., J.L., X.Y., W.W. and J.W.; resources, X.M.; data curation, X.M. and Y.M.; writing—original draft preparation, X.M.; writing—review and editing, X.X.; visualization, X.M.; supervision, X.X.; project administration, X.X.; funding acquisition, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Hebei Provincial Science and Technology Programme, grant number 17236801D-2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to students such as Gao Qingqing, Wang Rui, and Wang Xumin for their assistance in the field sampling.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| SWC | Soil Water Content |
| SOC | Soil Organic Carbon |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
References
- Leff, J.W.; Jones, S.E.; Prober, S.M.; Barberán, A.; Borer, E.T.; Firn, J.L.; Harpole, W.S.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hofmockel, K.S.; Knops, J.M.H.; et al. Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10967–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Manzoni, S.; Moorhead, D.L.; Richter, A. Carbon use efficiency of microbial communities: Stoichiometry, methodology and modelling. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Han, F.; Ju, W.; Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X. Natural grassland as the optimal pattern of vegetation restoration in arid and semi-arid regions: Evidence from nutrient limitation of soil microbes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Chen, M.; Wu, J.; Xu, G.; Xing, H.; Li, F. Carbon and nutrient limitations of soil microbial metabolism in Quercus aquifolioides forest ecosystems along a precipitation gradient on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil. 2023, 488, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, L.R.; Lauber, L.C.; Weintraub, N.M.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, D.S.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, R.A.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, E.M.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, L.R.; Hill, H.B.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, L.R.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, L.R.; Gallo, E.M.; Lauber, C.; Waldrop, P.M.; Zak, R.D. Extracellular enzyme activities and soil organic matter dynamics for northern hardwood forests receiving simulated nitrogen deposition. Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, R.; Fernandez, I.J.; Simon, K.S.; Dail, D.B. Nitrogen and phosphorus regulation of soil enzyme activities in acid forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Duan, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L. Soil moisture mediates microbial carbon and phosphorus metabolism during vegetation succession in a semiarid region. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Rong, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Y. Soil moisture drives the response of soil microbial nutrient limitation to N and P additions in an Inner Mongolian meadow steppe. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 120, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, G.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Feng, Q.; Shi, Z. Effects of slope aspect on soil enzyme activity and microbial nutrient limitation in subalpine region of western Sichuan, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2023, 34, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xue, S.; Xu, Z. Plant-soil-enzyme C-N-P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation responses to plant-soil feedbacks during community succession: A 3-year pot experiment in China. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1009886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Feng, W. Contrasting elevational patterns of microbial carbon and nutrient liitation in soil from alpine meadow to desert. Catena. 2023, 223, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Li, J.; Xiao, N.; Qi, Y.; Fu, G.; Liu, G.; Qiao, M. Urban-Development-Induced Changes in the Diversity and Composition of the Soil Bacterial Community in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, C.M.; Amabel, C.; Ryan, S.D.; Sungwoo, B. Different types of land use influence soil physiochemical properties, the abundance of nitrifying bacteria, and microbial interactions in tropical urban soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161722. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, D.; Yan, X. Effects of heavy metals/metalloids and soil properties on microbial communities in farmland in the vicinity of a metals smelter. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 707786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Prem, P.; Liu, G.; Chen, J. Reclamation of desert land to different land-use types changes soil bacterial community composition in a desert-oasis ecotone. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 32, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Peng, S.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. New insights into the patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry in soil and sediment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of stand age on soil microbial metabolic limitation and enzyme activities in Robinia pseudoacacia L. plantations in the loess hilly-gully region, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2560–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Duan, Y.; Yao, B.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects microbial metabolic limitations in different desert types of northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, F.; Wang, C.; Wei, X.; Song, J. Divergent responses of soil microbial metabolic limitations to cropland revegetation at erosion and deposition topographies in the hilly-gully region of the northern Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil. 2023, 487, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, L.; Qiu, T.; Bing, H.; Cui, Y.; Sardans, J.; Du, E.; Chen, J.; Tan, W.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; et al. Disconnection between plant–microbial nutrient limitation across forest biomes. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, T.A.; Turner, L.B.; Whitaker, J.; Ostle, J.N.; McNamara, P.N.; Bardgett, D.R.; Salinas, N.; Meir, P. Soil microbial nutrient constraints along a tropical forest elevation gradient: A belowground test of a biogeochemical paradigm. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 6071–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, B. Changes in microbial biomass, community composition and diversity, and functioning with soil depth in two alpineecosystems on the tibetan plateau. Plant Soil. 2021, 459, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Sun, H.; Tripathi, B.M.; Adams, J.M.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y. Bacterial community dissimilarity between the surface and subsurface soils equals horizontal differences over several kilometers in the western Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jiao, S.; Bell, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Ma, L.; Chen, J. Depth-dependent effects of tree species identity on soil microbial community characteristics and multifunctionality. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Ji, C.; Shen, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, B. Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munroe, S.J. Physical, Chemical, and Thermal Properties of Soils across a Forest-Meadow Ecotone in the Uinta Mountains. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2018, 44, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Somenahally, A.C.; McLawrence, J.; Chaganti, V.N.; Ganjegunte, G.K.; Obayomi, O.; Brady, J.A. Response of Soil Microbial Communities, Inorganic and Organic Soil Carbon Pools in Arid Saline Soils to Alternative Land Use Practices. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, X.; Pu, L.; Zhang, X. Soil Microbial Succession with Soil Development since Costal Reclamation. Catena 2020, 187, 104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhou, W.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, Y.; Shi, Z.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effects of tillage regime on soil aggregate-associated carbon, enzyme activity, and microbial community structure in a semiarid agroecosystem. Plant Soil. 2024, 498, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yin, S. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Composition in Larix-olgensis Plantations to Disturbance by a Large Outbreak of Bark Beetle. Forests 2024, 15, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yuan, C.; Chen, P.; Rong, Z.; Peng, T.; Farooq, H.T.; Wang, G.; Yan, W.; Wang, J. Soil Microbial Community Composition and Diversity Analysis under Different Land Use Patterns in Taojia River Basin. Forests 2023, 14, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hu, R.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Fan, H.; Deng, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, Q.; Peng, S.; Li, J. Soil Bacterial Community in the Multiple Cropping System Increased Grain Yield within 40 Cultivation Years. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 804527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xue, T.; Yuan, L.; Gao, F.; Hao, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H. The effect of vineyard reclamation on soil properties and microbial communities in desertified land in Hongsibu, Ningxia. Catena 2022, 211, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Fan, X.; Ji, W.; Hai, Z.; Hu, N.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Yu, C.; Chen, Y.; Lian, B.; et al. Soil Fungal Community Composition and Diversity of Culturable Endophytic Fungi from Plant Roots in the Reclaimed Area of the Eastern Coast of China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Jia, G. Soil microorganism regulated aggregate stability and rill erosion resistance under different land uses. Catena 2023, 228, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Z.N.; He, C.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dong, F.F.; Huang, W.J. Effect of soil microbial community structure on the chemical compositions of different soil organic matter fractions in land uses of the Pearl River Estuary. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.L.L.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Börger, L.; Bennett, D.J.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B.; et al. Global Effects of Land Use on Local Terrestrial Biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y. Species Diversity and Drivers of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Communities in a Semi-Arid Mountain in China. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, J.; Du, T.; Ju, X.; Gan, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, L.; Shen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; et al. Diversifying crop rotation increases food production, reduces net greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.S.; Haug, L.A.; Rivera, V.A.; Gonzalez, L.M.H.; Kelly, J.J.; Miller, W.M.; Wells, G.F.; Packman, A.I. Soil hydrology drives ecological niche differentiation in a native prairie microbiome. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiz163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Lin, D.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, N.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Soil microbial communities response to different fertilization regimes in young Catalpa bungei plantation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 948875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, P.; Li, G.; Liu, M.; Alharbi, H.A.; Li, Z. Depth effects on bacterial community assembly processes in paddy soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.M.; DeForest, J.L.; Plante, A.F. Changes in extracellular enzyme activity and microbial community structure with soil depth at the Luquillo Critical Zone Observatory. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, K.G.; Debenport, S.; Anderson, S.; Fierer, N. Digging deeper to find unique microbial communities: The strong effect of depth on the structure of bacterial and archaeal communities in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 50, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Tang, X.; Zhang, A.; Fan, G.; Liu, S. Responses ofsoil specific enzyme activities to short-term land useconversions in a salt-affected region, northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Franco, N.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Goberna, M.; Albaladejo, J. Changes in soil aggregation and micrbial communitystructure control carbon sequestration after afforestaion of semiaridshrublands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; An, S.; Sun, H.; Bhople, P.; Chen, Z. Soil physicochemical and microbial characteristics of contrasting land-use types along soil depth gcadients. Catena 2018, 162, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Long, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, X. Stimulation of nitrogen-hydrolyzing enzymes in soil aggregates mitigates nitrogen constraint for carbon sequestration following afforestation in subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, B.; Zeng, H. Soil extracellular enzymestoichiometry reflects the unique habitat of karst tiankeng and helpsto alleviate the P limitation of soil microbes. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Feng, Z.; Qu, A.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Lai, Y.; Kong, Y. Effects of land-use types on the temporal dynamics of soil active carbon and nitrogen in the rocky mountainous of North China. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Qu, A.; Feng, E.; Chen, R.; Yang, X.; Lai, Y. Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Enzymatic Activity under Different Land-Use Types in Rocky Mountainous Region of North China. Forests 2023, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bing, H.; Moorhead, D.L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ye, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals widespread soil phosphorus limitation to microbial metabolism across Chinese forests. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Belnap, J.; Findlay, S.G.; Shah, J.J.F.; Hill, B.H.; Kuehn, K.A.; Kuske, C.R.; Litvak, M.E.; Martinez, N.G.; Moorhead, D.L. Extracellular enzyme kinetics scale with resource availability. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, A.; Wan, W.; Luo, X.; Zheng, L.; He, G.; Huang, D.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. High Salinity Inhibits Soil Bacterial Community Mediating Nitrogen Cycling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e01366-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Janssens, A.I.; Deng, Y.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Yi, Y.; Xiao, N.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; et al. Divergent rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil microbial structure and function in long-term warmed steppe due to altered root exudation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2024, 30, e17111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Chang, S.X.; Liang, C.; An, S. Negative effects of multiple global change factors on soil microbial diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Dong, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, y. Climatic and edaphic factors affecting soil bacterial community biodiversity in different forests of China. Catena 2021, 207, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Shifts in bacterial diversity, interactions and microbial elemental cycling genes under cadmium contamination in paddy soil: Implications for altered ecological function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: Implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.B.; Niu, D.C.; Weber-Grullon, L.; Fu, H. Nitrogen deposition enhances plant-microbe interactions in a semiarid grassland: The role of soil physicochemical properties. Geoderma 2020, 373, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.Q.; Xie, L.; Chen, Y.M.; Tang, C.D.; Liu, X.F.; Lin, W.S.; Xiong, D.C.; Yang, Y.S. Effects of nitrogen deposition on diversity and composition of soil bacterial community in a subtropical Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2018, 29, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cregger, M.A.; Schadt, C.W.; McDowell, N.G.; Pockman, W.T.; Classen, A.T. Response of the soil microbial community to changes in precipitation in a semiarid ecosystem. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8587–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shangguan, Z. Drivers of soil microbial metabolic limitation changes along a vegetation restoration gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C. Fencing as an effective approach for restoration of alpine meadows: Evidence from nutrient limitation of soil microbes. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).