Short-Term Application of Alfalfa Green Manure Increases Maize Yield and Soil Fertility While Altering Microbial Communities in Karst Yellow Clay Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Design
2.2. Field Management
2.3. Sampling and Analyzing
2.4. Calculation of SQI and BCR
2.5. Extraction of Soil DNA and PCR Amplification
2.6. Analysis of the Sequencing Data
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
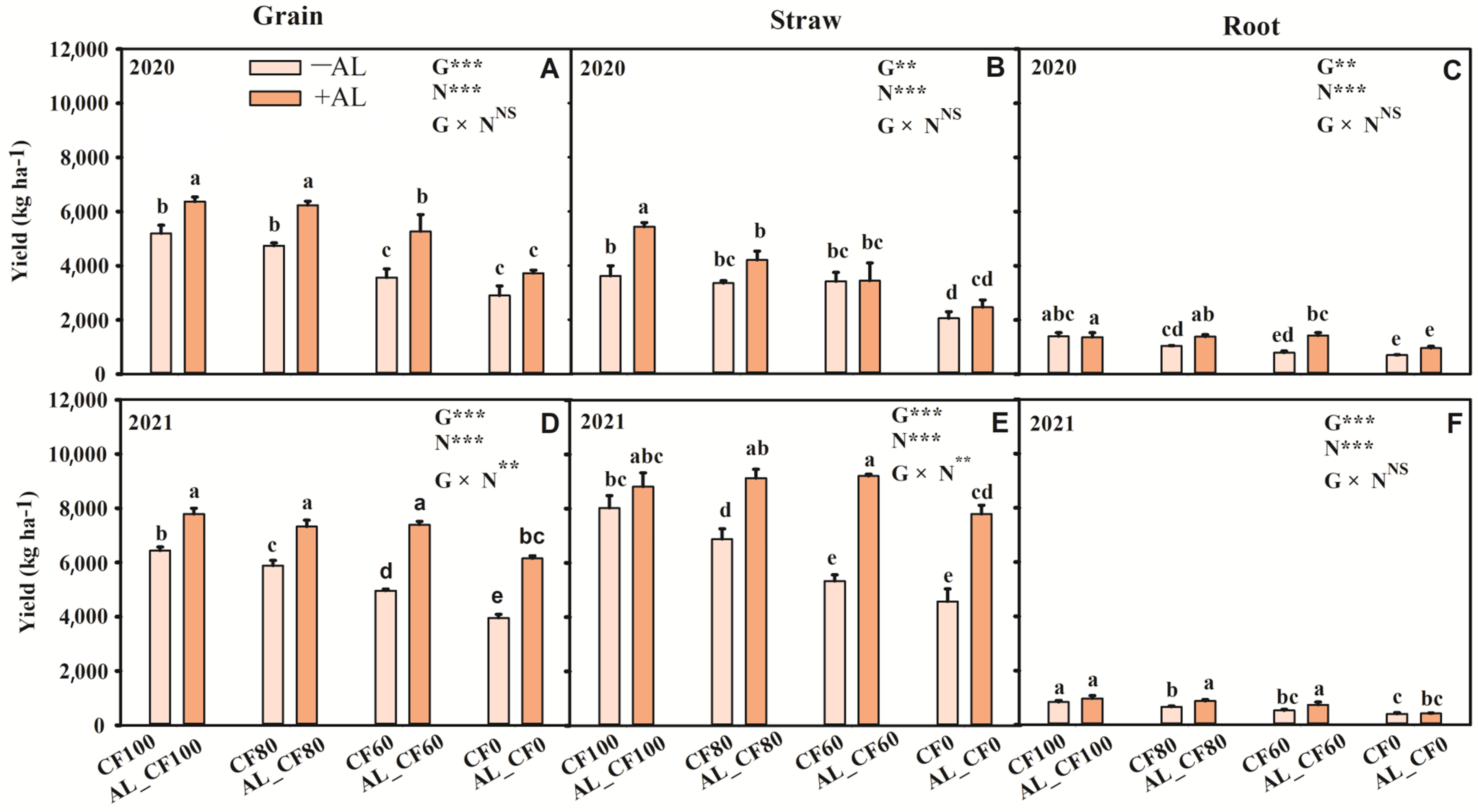
3.1. Maize Production
3.2. Soil Property, Enzyme Activity, and SQI
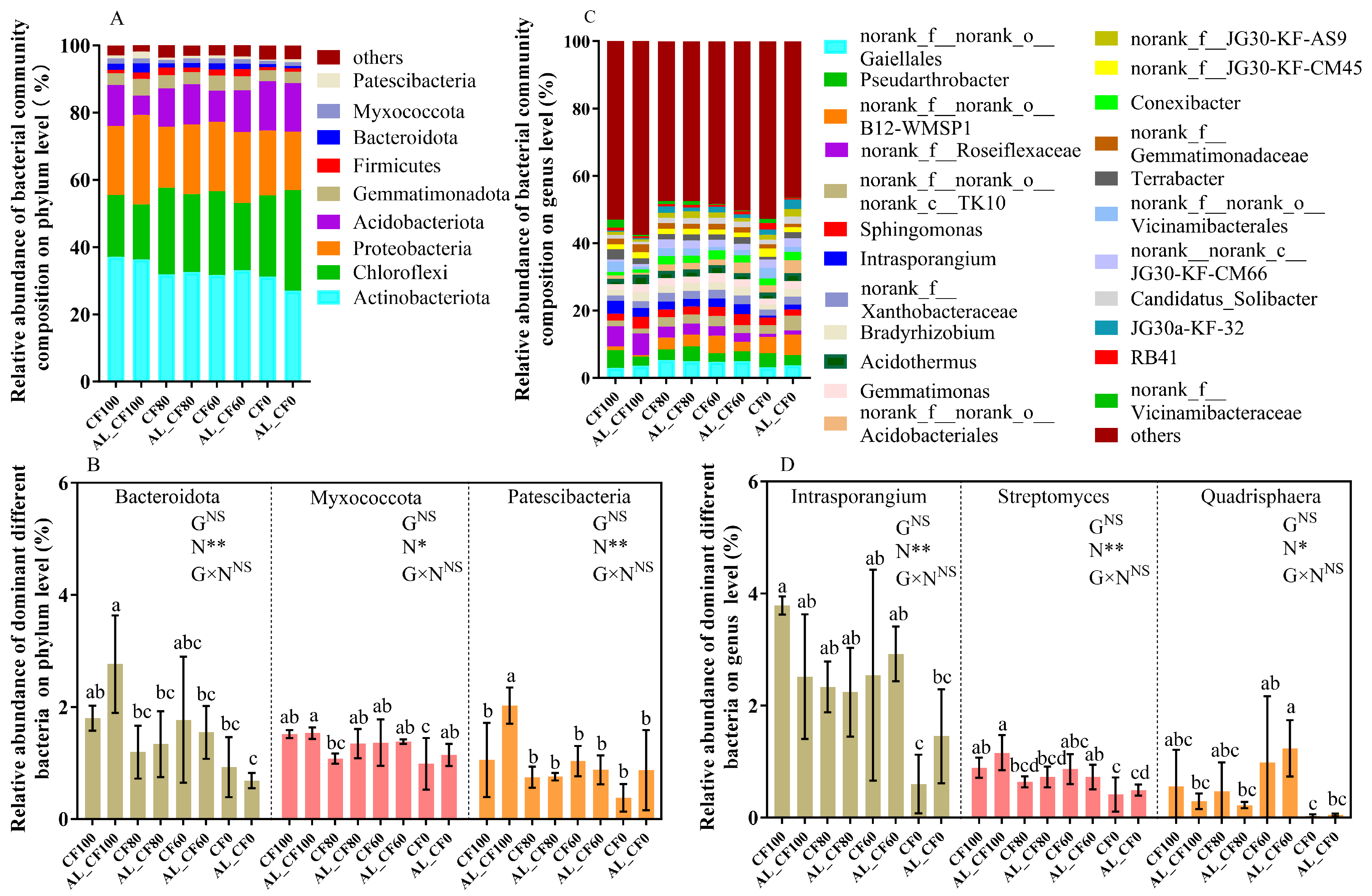
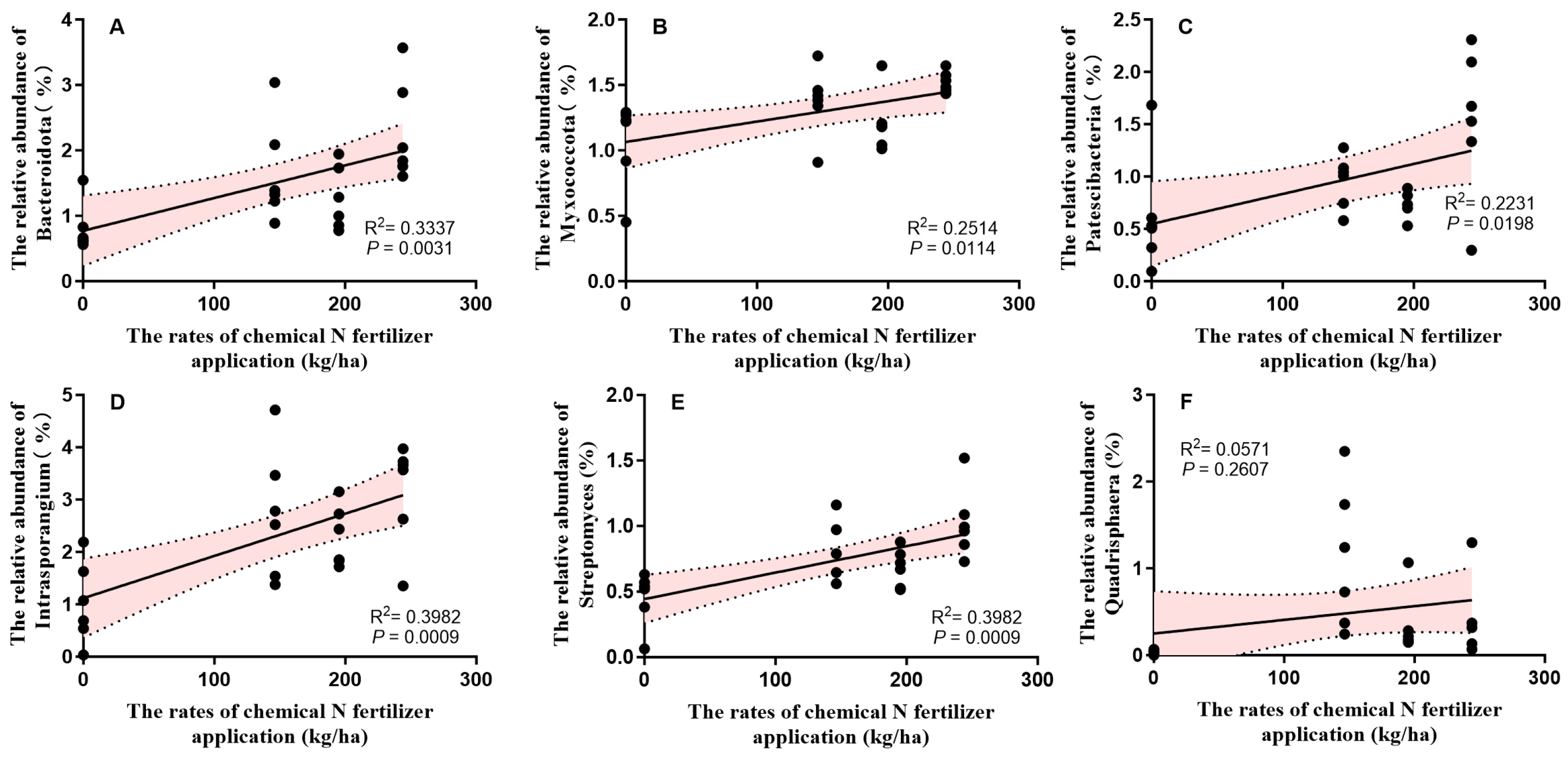
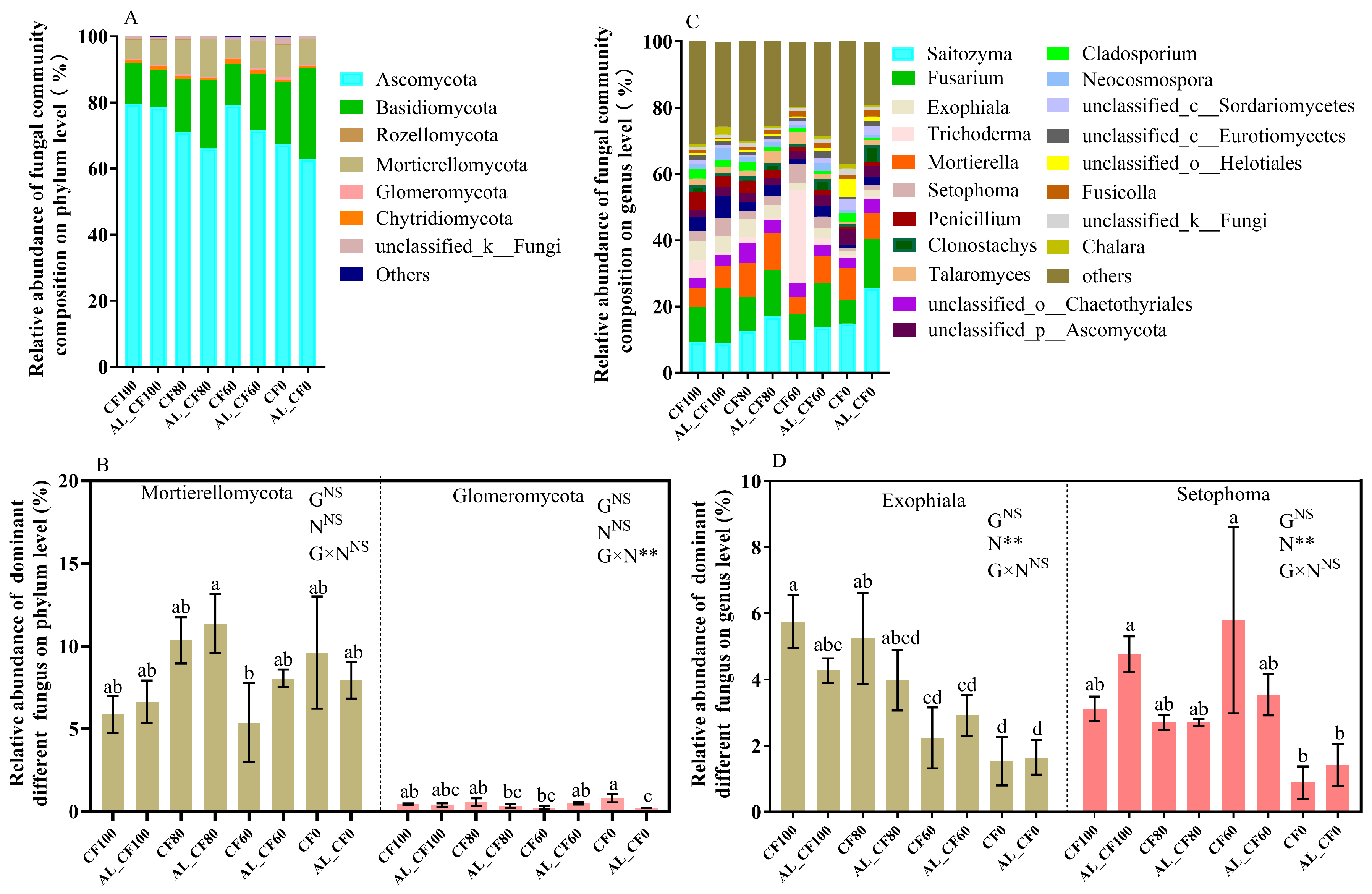
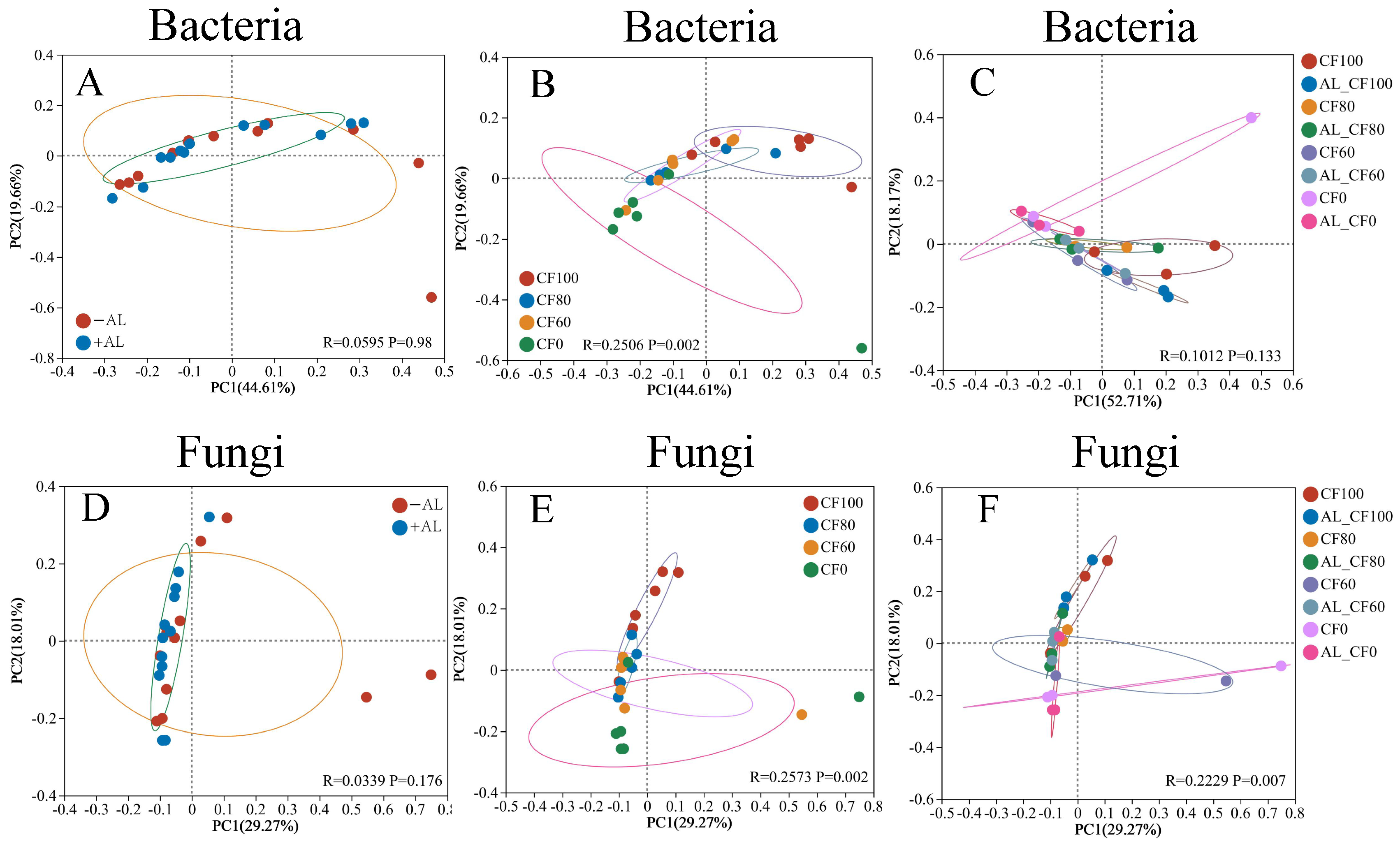
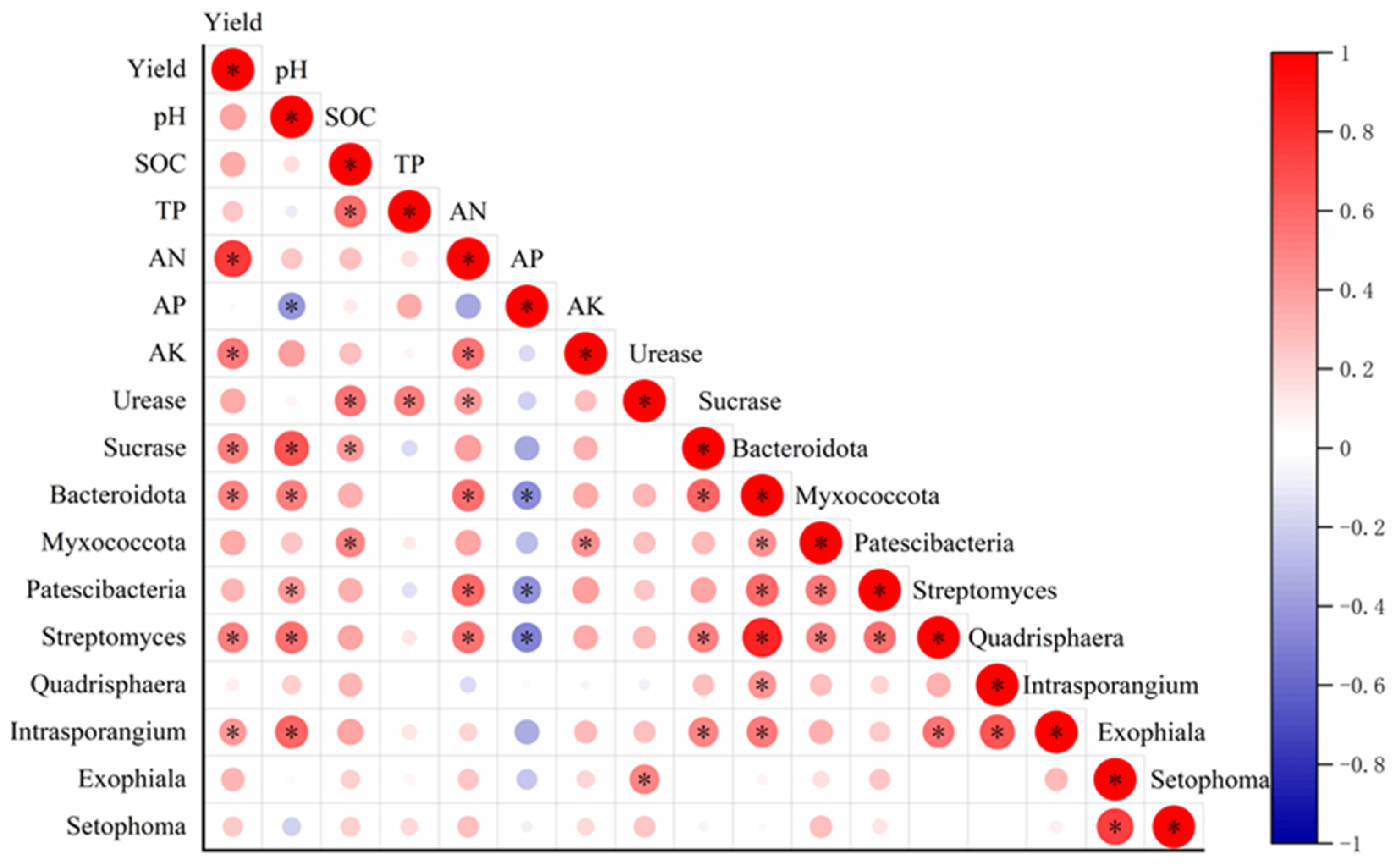
3.3. Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities
3.4. Economic Profitability
4. Discussion
4.1. Partial Substitution of Chemical N Fertilizer with Alfalfa Green Manure on Maize Yield
4.2. Partial Substitution of CF with Alfalfa Green Manure on Soil Fertility and Enzyme Activities
4.3. The Effect of the Partial Substitution of CF with Alfalfa Green Manure on Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities and Diversity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, K.; Xu, C. State-space Prediction of Spring Discharge in a Karst Catchment in Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, K. Subsurface flow in a soil-mantled subtropical dolomite karst slope: A field rainfall simulation study. Geomorphology 2015, 250, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Yu, B.; Xu, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, K. Quantifying the impacts of climate and human activities on water and sediment discharge in a karst region of southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G. Effects of inorganic and organic amendment on soil chemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial community and soil quality in yellow clayey soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeier, M.; Roelcke, M.; Han, Y.; Lan, T.; Bergmann, H.; Böhm, D.; Cai, Z.; Nieder, R. Nitrogen management in a rice–wheat system in the Taihu Region: Recommendations based on field experiments and surveys. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruysschaert, G.; Cougnon, M.; Reheul, D.; Nest, T.; Vanden, M. P availability and P leaching after reducing the mineral P fertilization and the use of digestate products as new organic fertilizers in a 4-year field trial with high P status. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Expósito, A.; Velasco, F. Exploring environmental efficiency of the European agricultural sector in the use of mineral fertilizers. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiong, K.N. Assessing spatial-temporal evolution processes of karst rocky desertification land: Indications for restoration strategies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Tao, R.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X. Controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer application mitigated N losses and modified microbial community while improving wheat yield and N use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 349, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Tu, S.; Shah, F.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.; Han, D.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Muhammad, I.; Cao, W. Substitution of fertilizer-N by green manure improves the sustainability of yield in double-rice cropping system in south China. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 188, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Nie, J.; Geng, M.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Xue, B. Effects of substitution of chemical fertilizer by Chinese milk vetch on distribution and composition of aggregates-associated organic carbon fractions in paddy soils. Plant Soil 2022, 481, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Cao, W.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y. Long-term green manuring to substitute partial chemical fertilizer simultaneously improving crop productivity and soil quality in a double-rice cropping system. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Cao, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Cao, W. Green manure incorporation with reductions in chemical fertilizer inputs improves rice yield and soil organic matter accumulation. J. Soil Sediment. 2020, 20, 2784–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tong, T.; Potcho, P.M.; Huang, S.; Tang, X. Nitrogen effects on yield, quality and physiological characteristics of giant rice. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.S.; Holden, N.M. Quantitative soil quality indexing of temperate arable management systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Ren, T. Rapeseed as a previous crop reduces rice N fertilizer input by improving soil fertility. Field Crops Res. 2022, 281, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.B.; Dsouza, M.; Gilbert, J.A.; Guo, X.S.; Wang, D.Z.; Guo, Z.B.; Ni, Y.Y.; Chu, H.Y. Fungal community composition in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization is most influenced by the type of organic matter. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5137–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Ma, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, C.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y. Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.B.; Li, W.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Cheng, J.K.; Xin, G.R. Effects of Italian ryegrass residues as green manure on soil properties and bacterial communities under an Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.)-rice (Oryza sativa L.) rotation. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caban, J.R.; Kuppusamy, S.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, Y.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.B. Green manure amendment enhances microbial activity and diversity in antibiotic-contaminated soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 129, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Huang, X.; Feng, D.; Xing, S.; Weng, B. Long-term effects of legume mulching on soil chemical properties and bacterial community composition and structure. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misato, T.; Yoshitaka, U. Long-term use of green manure legume and chemical fertiliser affect soil bacterial community structures but not the rate of soil nitrate decrease when excess carbon and nitrogen are applied. Soil Res. 2017, 55, 524–533. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, X.; Adams, J.M.; Qiu, C.; Qin, W.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, J. Nutrient improvement and soil acidification inducing contrary effects on bacterial community structure following application of hairy vetch (Vicia villosa Roth L.) in Ultisol. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 312, 107348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Song, S.; Chen, S.; Du, Z.; Kong, J. Adaptive evaluation of green manure rotation for a low fertility farmland system: Impacts on crop yield, soil nutrients, and soil microbial community. Catena 2023, 222, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yao, Z.; Chen, J.; Yao, P.; Zhao, N.; He, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; et al. Improving soil aggregation, aggregate-associated C and N, and enzyme activities by green manure crops in the Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Gai, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Q.; Jiang, Z. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by green manure increases succeeding maize yield and annual economic benefit in low-yield cropland in the yellow river delta. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, M.; Du, G.; Guo, J.; Ntakirutimana, T. Correlation among soil microorganisms, soil enzyme activities, and removal rates of pollutants in three constructed wetlands purifying micro-polluted river water. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 46, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S. Soil Enzymes and Their Research Methodology; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 274–340. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bastida, F.; Moreno, J.L.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Microbiological degradation index of soils in a semiarid climate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Ling, N.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Zou, J.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Soil fertility and its significance to crop productivity and sustainability in typical agroecosystem: A summary of long-term fertilizer experiments in China. Plant Soil 2014, 381, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.C.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Assessing the soil quality of Bansloi river basin, eastern India using soil-quality indices (SQIs) and Random Forest machine learning technique. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, S. Calculating the economic viability of corporate trainings (Traditional & eLearning) using benefit-cost ratio (BCR) and return on investment (ROI). Int. J. Adv. Corp. Learn. 2019, 12, 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Mago, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic Note: A Place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, R.C.; Henry, P.R.; Ammerman, C.B. Statistical analysis of repeated measures data using SAS procedures. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 1216–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motulsky, H.J. Prism5 Statistics Guide; GraphPad Software, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; Volume 31, pp. 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Yin, L.; Ju, W.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, S. Meta-analysis of green manure effects on soil properties and crop yield in northern China. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 266, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Kumar, M.; Zeng, X. Influence of green manure and rice straw management on soil organic carbon, enzyme activities, and rice yield in red paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Gao, Z. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hao, M.; Wei, X. Soil organic C and N dynamics as affected by 31 years cropping systems and fertilization in highland agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdElgawad, H.; Saleh, A.M.; Al Jaouni, S.; Selim, S.; Hassan, M.O.; Wadaan, M.A.; Shuikan, A.M.; Mohamed, H.S.; Hozzein, W.N. Utilization of actinobacteria to enhance the production and quality of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits in a semi-arid environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Cui, J.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; He, P. Response of potato yield, soil chemical and microbial properties to different rotation sequences of green manure-potato cropping in North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cao, W.; Zhou, G.; Rees, R.M. Bacterial communities in paddy soils changed by milk vetch as green manure: A study conducted across six provinces in South China. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watthier, M.; Antonio, N.P.; Gomes, J.A.; Rocha, S.B.F.; Santos, R.H.S. Decomposition of green manure with different grass: Legume ratios. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pypers, P.; Verstraete, S.; Thi, C.P.; Merckx, R. Changes in mineral nitrogen, phosphorus availability and salt-extractable aluminium following the application of green manure residues in two weathered soils of South Vietnam. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, J.L.; Quemada, M. Replacing bare fallow with cover crops in a maize cropping system: Yield, N uptake and fertiliser fate. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwezor, W. The mineralization of nitrogen and phosphorus in organic materials of varying C:N and C:P ratios. Plant Soil 1976, 44, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, D.; Britto, D.T.; Shi, W.; Kronzucker, H.J. How plant root exudates shape the nitrogen cycle. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y. Nontargeted metabolomic analysis to unravel the impact of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate stress on root exudates of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lambers, H. Root-released organic anions in response to low phosphorus availability: Recent progress, challenges and future perspectives. Plant Soil 2020, 447, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaoka, Y.; Kojima, M.; Sugihara, S.; Yoshihara, T.; Koshino, M.; Ichihara, A. Dissolution of ferric phosphate by alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) root exudates. Plant Soil 1993, 155, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Malav, L.C.; Choudhary, J.; Kannojiya, S.; Kundu, M.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, A.N. Soil microbiomes for healthy nutrient recycling. In Current Trends in Microbial Biotechnology for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, T.; An, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, X. Alfalfa green manure amendment improved P use efficiency and reduced P losses from paddy fields. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2022, 123, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, H.; Sharma, S.; Pandey, R. Phosphorus nutrition: Plant growth in response to deficiency and excess. In Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- de Medeiros, E.V.; Silva, A.O.; Duda, G.P.; Santos, U.J.D.; de Souza Junior, A.J. The combination of Arachis pintoi green manure and natural phosphate improves maize growth, soil microbial community structure and enzymatic activities. Plant Soil 2019, 435, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Gwon, H.S.; Alam, M.A.; Song, H.J.; Das, S.; Kim, P.J. Short term effects of different green manure amendments on the composition of main microbial groups and microbial activity of a submerged rice cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Kandeler, E.; Ruggiero, P. Enzyme activities and microbiological and biochemical processes in soil. In Enzymes in the Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Longa, C.; Nicola, L.; Antonielli, L.; Mescalchin, E.; Zanzotti, R.; Turco, E.; Pertot, I. Soil microbiota respond to green manure in organic vineyards. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpalari, D.F.; Hamani, A.K.M.; Hui, C.; Sogbedji, J.M.; Liu, J.; Le, Y.; Kama, R.; Gao, Y. Soil Bacterial Community and Greenhouse Gas Emissions as Responded to the Coupled Application of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Microbial Decomposing Inoculants in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedling Stage under Different Water Regimes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, T.E.; Kavamura, V.N.; Adriana, T.B.; Smith, M.E.; Mader, A.; Mark, P.; Clark, I.M.; Harris, J.A.; Mauchline, T.H. Agricultural intensification reduces selection of putative plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in wheat. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seveso, A.; Mazurkewich, S.; Banerjee, S.; Poulsen, J.-C.N.; Lo Leggio, L.; Larsbrink, J. Polysaccharide utilization loci from bacteroidota encode CE15 enzymes with possible roles in cleaving pectin-lignin bonds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e01768-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langwig, M.; Anda, V.D.; Dombrowski, N.; Seitz, K.; Rambo, I.; Greening, C.; Teske, A.; Baker, B. Large-scale protein level comparison of Deltaproteobacteria reveals cohesive metabolic groups. ISME J. 2022, 16, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolińska, A.; Kuźniar, A.; Zielenkiewicz, U.; Banach, A.; Błaszczyk, M. Indicators of arable soils fatigue-Bacterial families and genera: A metagenomic approach. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Prakash, O.; Gihring, T.M.; Akob, D.M.; Jasrotia, P.; Jardine, P.M.; Watson, D.B.; Brown, S.D.; Palumbo, A.V.; Kostka, J.E. Denitrifying bacteria isolated from terrestrial subsurface sediments exposed to mixed-waste contamination. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3244–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, X.; Bhople, P.; Jiang, J.; Chater, C.C.C.; Yang, S.; Perez-Moreno, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, D. Enhancing C and N turnover, functional bacteria abundance, and the efficiency of biowaste conversion using Streptomyces-Bacillus inoculation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlatter, D.; Fubuh, A.; Xiao, K.; Hernandez, D.; Hobbie, S.; Kinkel, L. Resource amendments influence density and competitive phenotypes of Streptomyces in soil. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vurukonda, S.S.K.P.; Giovanardi, D.; Stefani, E. Plant growth promoting and biocontrol activity of Streptomyces spp. as endophytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mónica, I.F.D.; Godoy, M.S.; Godeas, A.M.; Scervino, J.M. Fungal extracellular phosphatases: Their role in P cycling under different pH and P sources availability. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Zabalgogeazcoa, I.; Soengas, P.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Cartea, M.E.; Abilleira, R.; Velasco, P. Brassica oleracea var. acephala (kale) improvement by biological activity of root endophytic fungi. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20224. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, S.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Maleki, M.; Molahoseini, H.; Khankahdani, H.; Mohammadi, M. Fungicidal control of onion pink root caused by Setophoma terrestris and effects on soil enzyme activity. J. Phytopathol. 2024, 172, e13349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, D.; Yan, Y.; Yang, C.; Fang, B.; Li, X.; Shao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Short-term application of chicken manure under different nitrogen rates alters structure and co-occurrence pattern but not diversity of soil microbial community in wheat field. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, H.; Yu, A.; Chai, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Shang, Y.; Yang, X. Enhancing soil quality and crop yield by increasing dominant bacterial abundance and reducing bacterial diversity under no-tillage with total green manure incorporation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 378, 109303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Duan, T. Green manure crops affected soil chemical properties and fungal diversity and community of apple orchard in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Item | Unit | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Maize seed | CNY kg−1 | 50 |
| Alfalfa | CNY kg−1 | 60 |
| Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate fertilizer | CNY kg−1 | 4 |
| Urea fertilizer | CNY kg−1 | 2.5 |
| Tillage | CNY ha−1 | 1800 |
| Sowing maize | CNY ha−1 | 1500 |
| Sowing alfalfa | CNY ha−1 | 1000 |
| Fertilizer application | CNY ha−1 | 120 |
| Weeding | CNY ha−1 | 600 |
| Harvesting | CNY ha−1 | 900 |
| Ginning | CNY t−1 | 50 |
| Maize grain | CNY kg−1 | 2.4 |
| Maize straw | CNY kg−1 | 0.2 |
| Year | Treatments | pH | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | NH4+ (mg/kg) | NO3− (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | SQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CF100 | 6.1 ± 0.42 ab | 34.22 ± 0.89 abc | 1.42 ± 0.02 b | 0.86 ± 0.11 bc | 9.04 ± 1.14 c | 10.11 ± 0.26 bc | 10.7 ± 1.1 e | 139.31 ± 3.57 ab | 0.40 ± 0 d |
| AL_CF100 | 6.24 ± 0.35 a | 33.52 ± 0.59 bc | 1.46 ± 0.15 ab | 0.94 ± 0.05 abc | 18.71 ± 1.07 a | 10.95 ± 0.2 abc | 14.62 ± 1.04 de | 152.7 ± 7.8 ab | 0.41 ± 0 bc | |
| CF80 | 5.62 ± 0.14 abc | 37.27 ± 0.6 a | 1.62 ± 0.16 ab | 1.05 ± 0.07 ab | 9.02 ± 0.13 c | 12.76 ± 1.52 a | 19.2 ± 0.83 cd | 133.07 ± 15.3 b | 0.41 ± 0 b | |
| AL_CF80 | 5.74 ± 0.3 abc | 36.01 ± 1.07 ab | 1.8 ± 0.05 a | 1.11 ± 0.03 a | 20.75 ± 1.8 a | 11.7 ± 0.23 ab | 20.27 ± 1.39 bc | 105.87 ± 12.91 c | 0.42 ± 0 a | |
| CF60 | 5.59 ± 0.24 abc | 36.91 ± 2 a | 1.55 ± 0.12 ab | 0.94 ± 0.09 abc | 7.51 ± 0.4 c | 9.69 ± 1.1 bc | 17.99 ± 0.94 cd | 163.24 ± 3.2 a | 0.41 ± 0 bc | |
| AL_CF60 | 5.7 ± 0.11 abc | 35.04 ± 0.31 ab | 1.46 ± 0.23 ab | 1.09 ± 0.05 a | 14.81 ± 0.5 b | 8.58 ± 1.13 c | 28.44 ± 3 a | 93.52 ± 6.08 cd | 0.42 ± 0 a | |
| CF0 | 5.19 ± 0.13 c | 29.8 ± 1.43 d | 1.35 ± 0.04 b | 0.8 ± 0.08 c | 6.41 ± 0.55 c | 9.58 ± 0.27 bc | 19.8 ± 1.59 bcd | 88.34 ± 7.97 cd | 0.41 ± 0 cd | |
| AL_CF0 | 5.42 ± 0.11 bc | 31.02 ± 1.11 cd | 1.43 ± 0.02 b | 0.91 ± 0.05 abc | 8.52 ± 1.01 c | 9.39 ± 0.51 bc | 23.63 ± 2.62 ab | 76.41 ± 5.06 d | 0.41 ± 0 bc | |
| G | NS | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | ** | ** | *** | |
| N | * | *** | NS | * | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | |
| G × N | NS | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | NS | ** | NS | |
| 2021 | CF100 | 6.45 ± 0.24 a | 39.42 ± 1.01 bcd | 1.41 ± 0.1 abc | 0.84 ± 0.05 b | 11.14 ± 0.25 cd | 10.89 ± 0.57 ab | 7.42 ± 0.99 c | 135.07 ± 18.13 b | 0.41 ± 0 d |
| AL_CF100 | 6.14 ± 0.32 ab | 42.23 ± 0.65 ab | 1.8 ± 0.19 a | 0.98 ± 0.07 ab | 30.85 ± 0.58 a | 11.77 ± 0.15 a | 10.52 ± 0.92 c | 146.78 ± 2.77 b | 0.43 ± 0 a | |
| CF80 | 5.78 ± 0.24 ab | 44.11 ± 0.71 a | 1.61 ± 0.07 ab | 1.12 ± 0.11 a | 9.71 ± 0.35 d | 8.75 ± 0.47 c | 18.89 ± 1.24 b | 61.9 ± 5.58 d | 0.42 ± 0 abc | |
| AL_CF80 | 5.86 ± 0.37 ab | 42.93 ± 0.96 ab | 1.57 ± 0.1 ab | 1.17 ± 0.01 a | 16.24 ± 0.3 b | 9.36 ± 0.15 bc | 27.19 ± 1.44 a | 177.33 ± 8.2 a | 0.43 ± 0 a | |
| CF60 | 5.87 ± 0.23 ab | 41.39 ± 2.49 abc | 1.44 ± 0.05 abc | 1.03 ± 0.14 ab | 6.59 ± 0.56 e | 9.19 ± 1.47 bc | 19.86 ± 1.92 b | 81.78 ± 10.07 cd | 0.42 ± 0 cd | |
| AL_CF60 | 5.93 ± 0.11 b | 41.73 ± 0.98 ab | 1.53 ± 0.13 abc | 1.00 ± 0.08 ab | 12.77 ± 1.21 c | 8.33 ± 0.93 c | 27.13 ± 1.09 a | 93.74 ± 11.96 c | 0.42 ± 0 ab | |
| CF0 | 5.51 ± 0.18 ab | 37.4 ± 0.6 cd | 1.29 ± 0.11 bc | 0.82 ± 0.06 b | 3.27 ± 0.36 f | 9.9 ± 0.59 abc | 20.43 ± 1.92 b | 92.26 ± 5.99 c | 0.41 ± 0 d | |
| AL_CF0 | 5.74 ± 0.12 bc | 35.52 ± 2.15 d | 1.13 ± 0.26 c | 0.93 ± 0.06 ab | 11.36 ± 1.12 cd | 9.79 ± 0.16 abc | 22.25 ± 0.26 b | 73.87 ± 5.28 cd | 0.42 ± 0 cd | |
| G | NS | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | *** | ** | *** | |
| N | NS | *** | * | * | *** | ** | *** | *** | * | |
| G × N | NS | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | NS | ** | NS |
| Treatments | Urease (mg/g) | Phosphatase (mg/g) | Sucrase (mg/g) | Catalase (mg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| CF100 | 0.50 ± 0.03 b | 0.46 ± 0.05 ab | 1.87 ± 0.24 b | 5.35 ± 0.51 ab | 6.27 ± 0.77 a | 5.07 ± 0.3 a | 2.04 ± 0.25 a | 2.54 ± 0.05 a |
| AL_CF100 | 0.37 ± 0.03 b | 0.49 ± 0.03 a | 2.27 ± 0.39 ab | 5.94 ± 0.45 a | 7.08 ± 0.64 a | 5.27 ± 0.35 a | 2.35 ± 0.12 a | 2.77 ± 0.26 a |
| CF80 | 0.67 ± 0.11 a | 0.50 ± 0.07 a | 2.75 ± 0.42 a | 5.58 ± 0.43 ab | 5.66 ± 0.83 ab | 4.07 ± 1.49 ab | 2.33 ± 0.31 a | 2.52 ± 0.08 a |
| AL_CF80 | 0.47 ± 0.08 b | 0.48 ± 0.03 ab | 2.21 ± 0.09 ab | 5.95 ± 0.18 a | 6.41 ± 0.75 a | 3.47 ± 0.41 ab | 2.13 ± 0.32 a | 2.5 ± 0.18 a |
| CF60 | 0.41 ± 0.01 b | 0.40 ± 0.03 ab | 2.03 ± 0.05 b | 5.05 ± 0.4 ab | 3.75 ± 0.49 cd | 3.25 ± 0.91 ab | 1.99 ± 0.04 a | 2.81 ± 0.07 a |
| AL_CF60 | 0.44 ± 0.04 b | 0.39 ± 0.02 ab | 1.99 ± 0.06 b | 5.07 ± 0.15 ab | 5.98 ± 0.44 ab | 4.51 ± 0.95 ab | 2.02 ± 0.02 a | 2.59 ± 0.14 a |
| CF0 | 0.52 ± 0.04 ab | 0.35 ± 0.02 b | 1.71 ± 0.06 b | 4.72 ± 0.12 b | 1.83 ± 0.57 d | 2.35 ± 0.42 b | 1.99 ± 0.01 a | 2.36 ± 0.1 a |
| AL_CF0 | 0.46 ± 0.03 b | 0.38 ± 0.07 ab | 1.96 ± 0 b | 4.53 ± 0.37 b | 4.23 ± 0.66 bc | 2.64 ± 0.73 b | 2.02 ± 0.1 a | 2.57 ± 0.02 a |
| G | * | NS | NS | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS |
| N | NS | * | NS | * | *** | *** | NS | NS |
| G × N | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Treatments | Bacteria | Fungi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | Chao | Shannon | Ace | Chao | Shannon | |
| CF100 | 3335.3 ± 218.19 abc | 2991.21 ± 77.09 b | 6.17 ± 0.06 bc | 1057.49 ± 68.37 ab | 1058.92 ± 71.15 ab | 4.10 ± 0.22 a |
| AL_CF100 | 3029.11 ± 189.29 bc | 2941.4 ± 70.75 b | 6.12 ± 0.03 c | 954.17 ± 51.41 abc | 946.13 ± 49.73 abc | 3.98 ± 0.1 a |
| CF80 | 3177.14 ± 89.43 abc | 2927.21 ± 204.77 b | 6.16 ± 0.07 bc | 941.12 ± 0.78 abc | 937.89 ± 2.38 abc | 4.06 ± 0.05 a |
| AL_CF80 | 3241.27 ± 146.9 abc | 2952.03 ± 142.83 b | 6.14 ± 0.03 c | 873.74 ± 52.01 abc | 870.89 ± 57.23 abc | 3.80 ± 0.19 a |
| CF60 | 3389.01 ± 127.28 abc | 3301.92 ± 247.59 ab | 6.27 ± 0.15 abc | 755.47 ± 141.27 c | 754.6 ± 145.97 c | 3.06 ± 0.95 a |
| AL_CF60 | 3575.97 ± 208.63 a | 3574.7 ± 192.35 a | 6.48 ± 0.1 a | 1068.54 ± 40.01 a | 1067.27 ± 35.06 a | 4.13 ± 0.11 a |
| CF0 | 2909.75 ± 200.33 c | 2938.62 ± 188.12 b | 6.27 ± 0.07 abc | 835.95 ± 119.72 bc | 833.81 ± 116.65 bc | 3.92 ± 0.27 a |
| AL_CF0 | 3516.28 ± 34.86 ab | 3522.07 ± 69.95 a | 6.40 ± 0.08 ab | 875.33 ± 29.53 abc | 873.02 ± 25.31 abc | 3.40 ± 0.13 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Yang, S.; He, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, T. Short-Term Application of Alfalfa Green Manure Increases Maize Yield and Soil Fertility While Altering Microbial Communities in Karst Yellow Clay Soil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071445
Gao X, Yang S, He Y, Zhao Q, Zhang T. Short-Term Application of Alfalfa Green Manure Increases Maize Yield and Soil Fertility While Altering Microbial Communities in Karst Yellow Clay Soil. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071445
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiaoye, Shimei Yang, Yan He, Qiumei Zhao, and Tao Zhang. 2025. "Short-Term Application of Alfalfa Green Manure Increases Maize Yield and Soil Fertility While Altering Microbial Communities in Karst Yellow Clay Soil" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071445
APA StyleGao, X., Yang, S., He, Y., Zhao, Q., & Zhang, T. (2025). Short-Term Application of Alfalfa Green Manure Increases Maize Yield and Soil Fertility While Altering Microbial Communities in Karst Yellow Clay Soil. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071445






