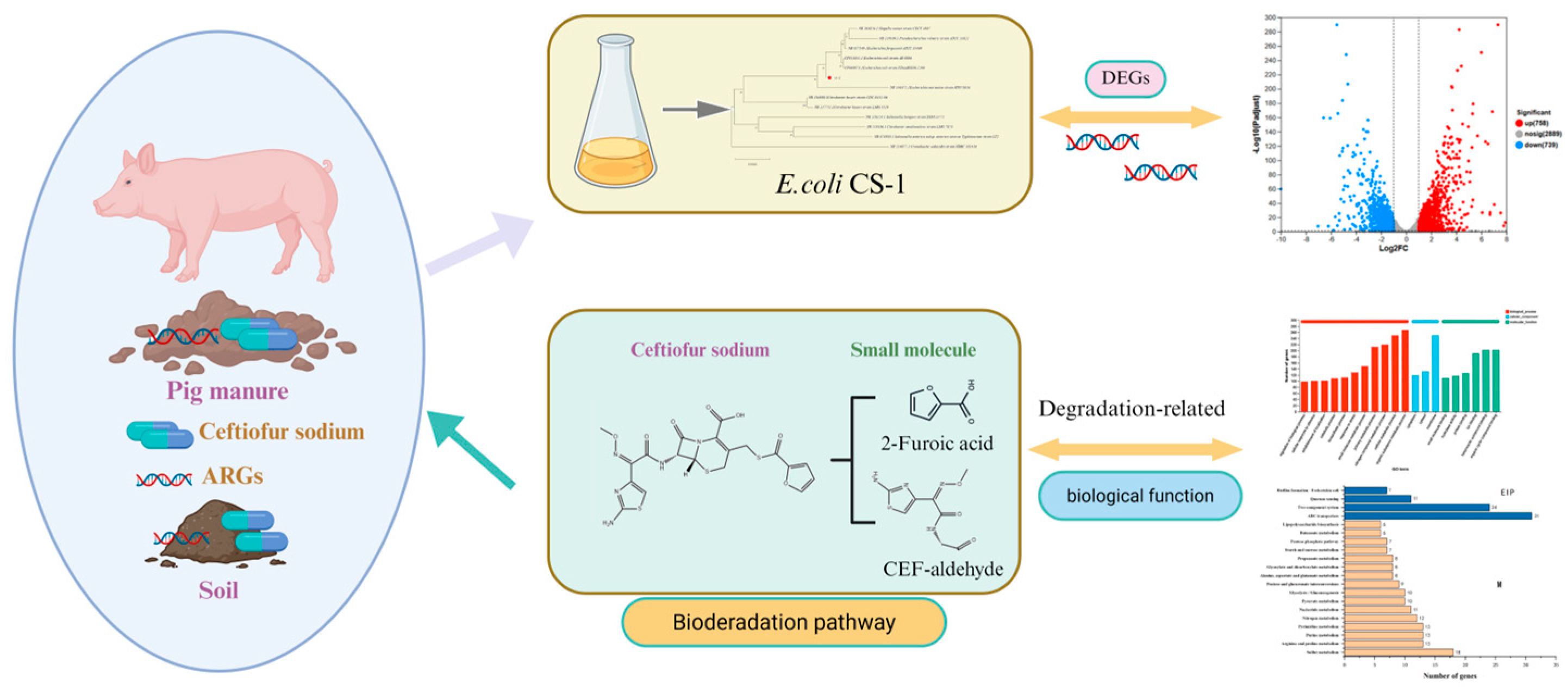
Assessment of Biodegradation Mechanisms of Ceftiofur Sodium by Escherichia sp. CS-1 and Insights from Transcriptomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Media
2.2. Screening and Isolation of CFS-Degrading Bacteria
2.3. Identification of Strain CS-1
2.4. Optimization of Conditions for CFS Degradation by E. coli CS-1
2.5. Identification of Biodegradable Products of E. coli CS-1
2.6. Transcriptome Sequencing of E. coli CS-1
2.6.1. Sample Handling
2.6.2. Transcriptome Analysis
2.6.3. qRT-PCR Validation
3. Results and Discussion
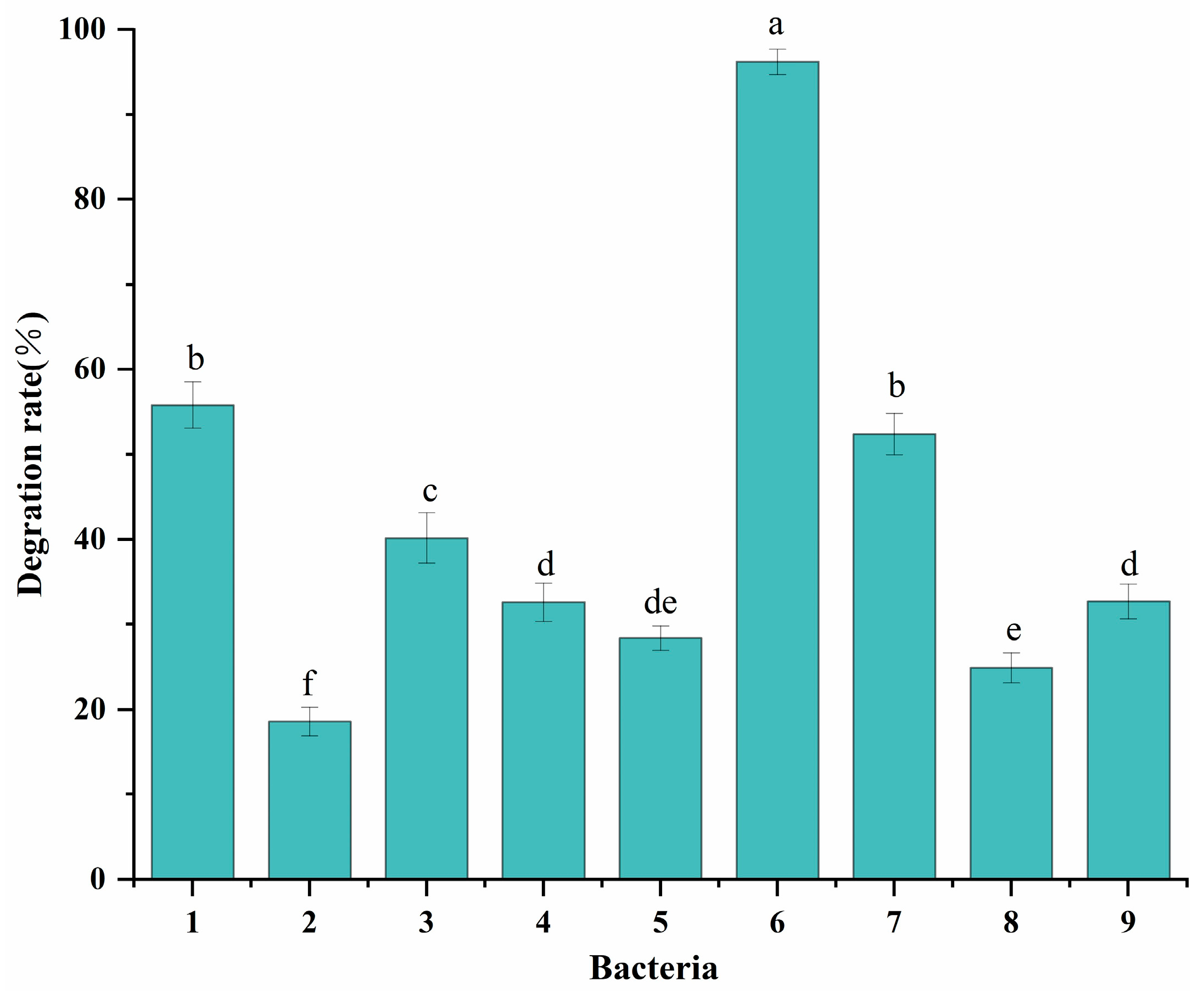
3.1. Screening of CFS-Degrading Strains
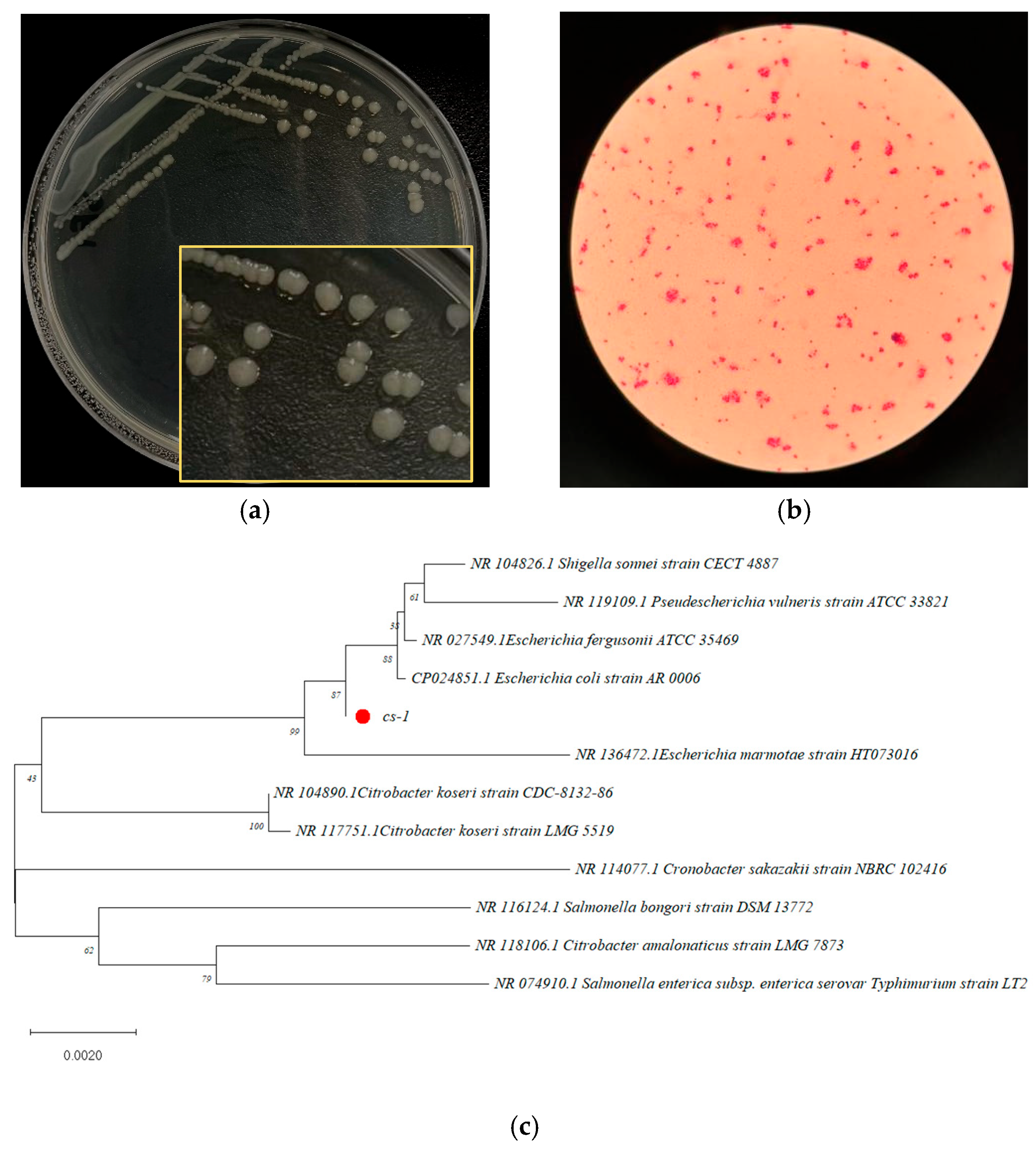
3.2. Identification of Bacterium CS-1, Highly Efficient in Degradation
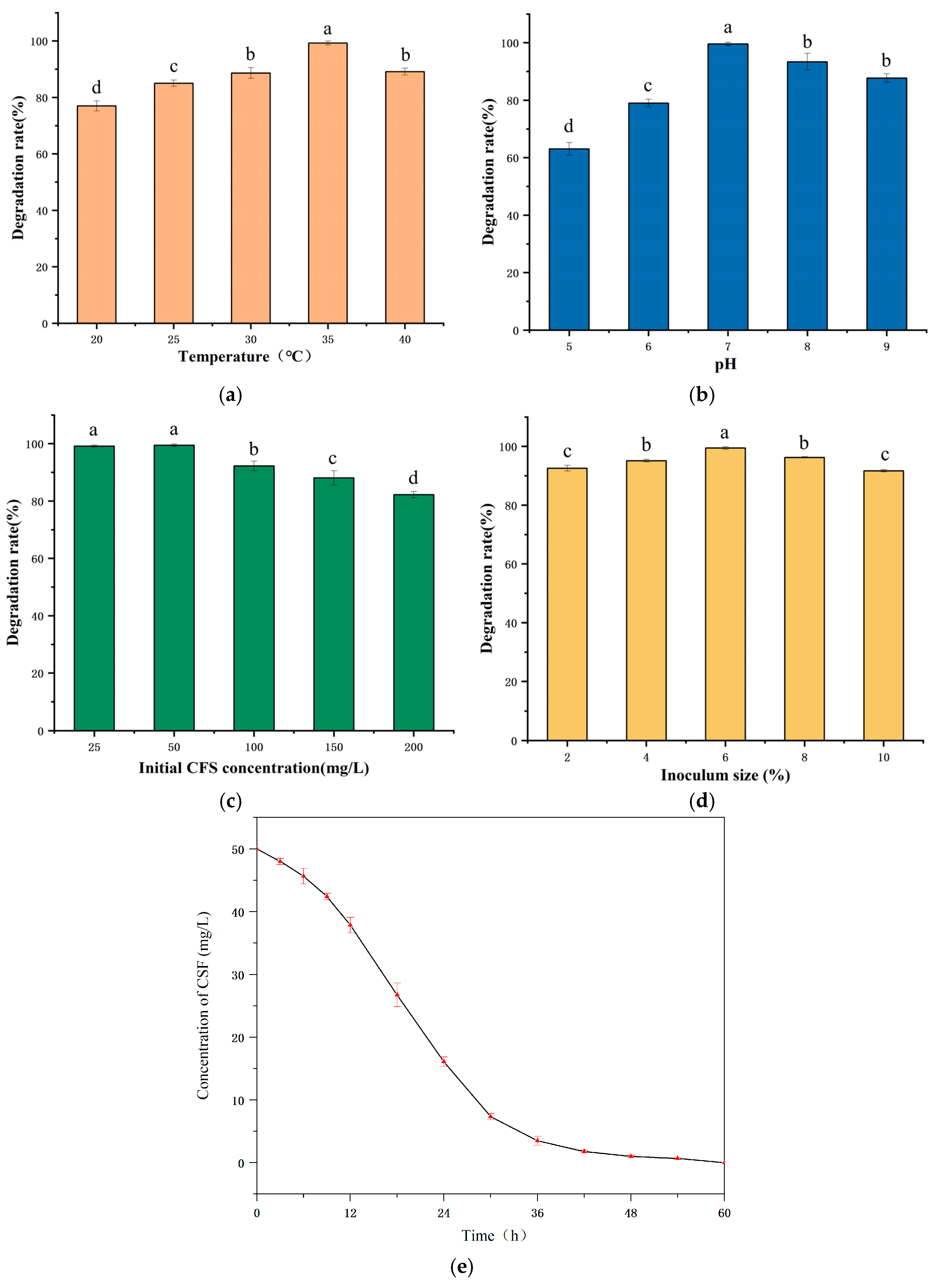
3.3. Optimization of Degradation Conditions of E. coli CS-1
3.4. Analysis of CFS Degradation Products and Degradation Pathways
3.5. DEGs Transcriptome Analysis
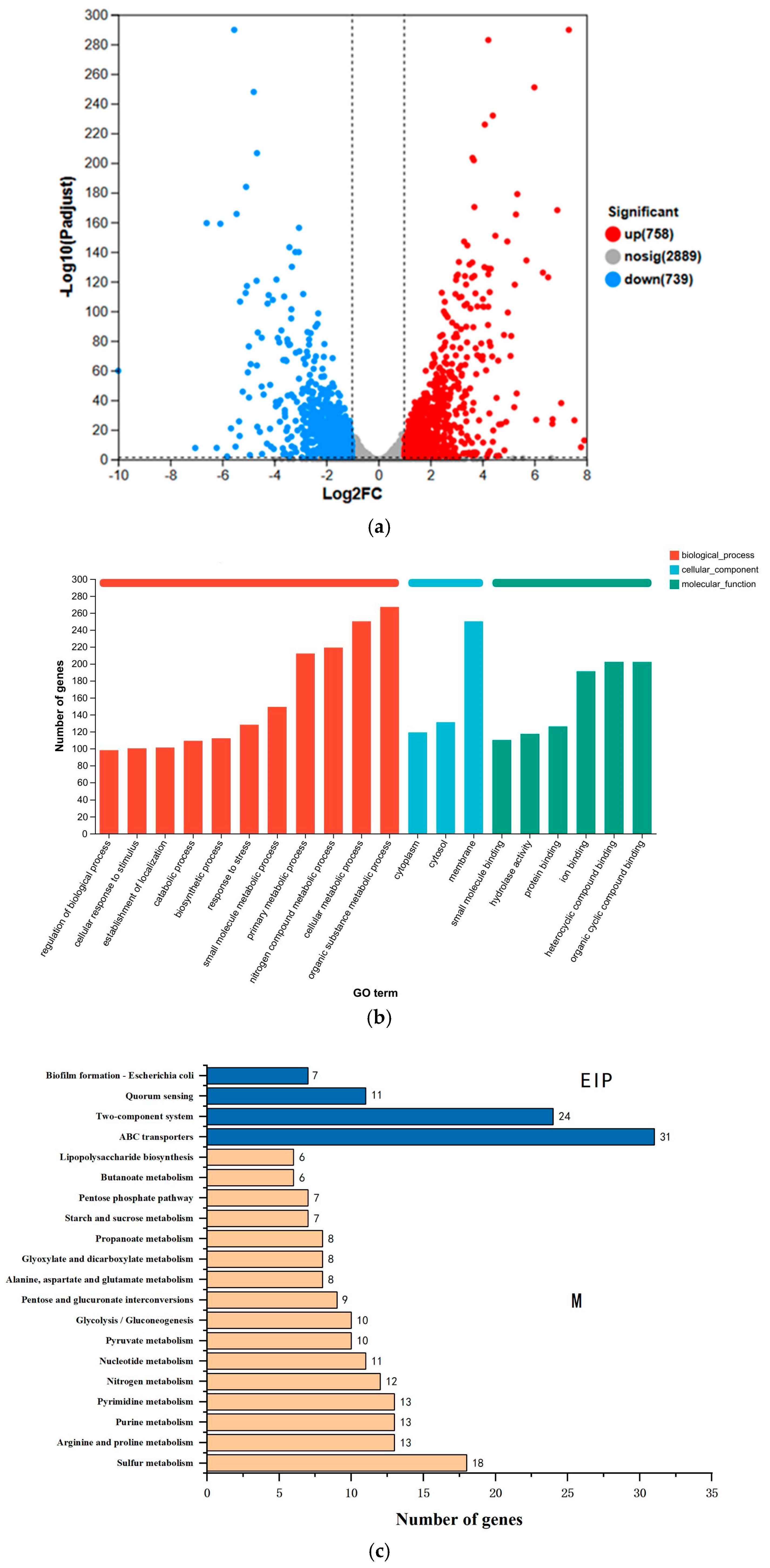
3.5.1. Transcriptomic Characterization
3.5.2. CFS Degradation-Related Genes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Sodhi, K.K.; Shree, P.; Singh, D.K.; Agrawal, P.K.; Shukla, P. Antibiotics bioremediation: Perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttner, A.; Bielicki, J.; Clements, M.N.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Muller, A.E.; Paccaud, J.-P.; Mouton, J.W. Oral amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid: Properties, indications and usage. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 26, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.; Pinto, E.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E. Targeting antimicrobial drug resistance with marine natural products. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, R.L.; Collignon, P.; Larsson, D.G.J.; McEwen, S.A.; Li, X.-Z.; Gaze, W.H.; Reid-Smith, R.; Timinouni, M.; Graham, D.W.; Topp, E. The Scourge of antibiotic Resistance: The important role of the environment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-H.; Ng, C.; Tran, N.H.; Chen, H.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Removal of antibiotic residues, antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater by membrane bioreactor systems. Water Res. 2018, 145, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; Fels, L.E.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, D.K. Insight into the amoxicillin resistance, ecotoxicity, and remediation strategies. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 39, 101858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Xu, X.; Ma, W.; Huo, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, G.; Huang, L. The adsorption-desorption characteristics and degradation kinetics of ceftiofur in different agricultural soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Sures, B.; Schmidt, T.C. Ecotoxicity of the two veterinarian antibiotics ceftiofur and cefapirin before and after photo-transformation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 619–620, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, J. Degradation of cefradine in alga-containing water environment: A mechanism and kinetic study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9184–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafii, F.; Williams, A.J.; Park, M.; Sims, L.M.; Heinze, T.M.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Sutherland, J.B. Isolation of bacterial strains from bovine fecal microflora capable of degradation of ceftiofur. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, S.A.; Watts, J.L.; Yancey, R.J. In Vitro Activity of Ceftiofur and its Primary Metabolite, Desfuroylceftiofur, against Organisms of Veterinary Importance. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1996, 8, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Esmorís, C.; Conde-Cid, M.; Ferreira-Coelho, G.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Arias-Estévez, M. Adsorption/desorption of sulfamethoxypyridazine and enrofloxacin in agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 706, 136015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofts, T.S.; Wang, B.; Spivak, A.; Gianoulis, T.A.; Forsberg, K.J.; Gibson, M.K.; Johnsky, L.A.; Broomall, S.M.; Rosenzweig, C.N.; Skowronski, E.W.; et al. Shared strategies for β-lactam catabolism in the soil microbiome. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Biodegradation of chlortetracycline by Bacillus cereus LZ01: Performance, degradative pathway and possible genes involved. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Cun, D.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Tang, H.; Qiu, L.; Wang, F.; et al. Biodegradation of phthalate acid esters by a versatile PAE-degrading strain Rhodococcus sp. LW-XY12 and associated genomic analysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 170, 105399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wen, S.; Kim, Y.M. Mechanism for biodegradation of sulfamethazine by Bacillus cereus H38. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 809, 152237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, R.; Vass, H.; Dawson, A.; Squires, T.; Tavaddod, S.; Allen, R.J. Stability of β-lactam antibiotics in bacterial growth media. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Li, B. Genomic characterization, kinetics, and pathways of sulfamethazine biodegradation by Paenarthrobacter sp. A01. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wan, J.; Hu, L.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W. Efficient degradation of sulfamethazine in simulated and real wastewater at slightly basic pH values using Co-SAM-SCS /H2O2 Fenton-like system. Water Res. 2018, 138, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Geng, A.; Liu, F.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, X. Insight into Dominant Cellulolytic Bacteria from Two Biogas Digesters and Their Glycoside Hydrolase Genes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cai, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H. Characterization and mechanism analysis of lincomycin biodegradation with Clostridium sp. strain LCM-B isolated from lincomycin mycelial residue (LMR). Chemosphere 2017, 193, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-W.; Wen, Y.-Y.; Niu, Z.-L.; Yin, K.; Xu, D.-X.; Chen, L.-X. Isolation and characterization of sulfonamide-degrading bacteria Escherichia sp. HS21 and Acinetobacter sp. HS51. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, C.; Lartey-Young, G.; Ma, L. Biodegradation of cefalexin by two bacteria strains from sewage sludge. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 220442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Jeon, C.-H.; Kim, W. Tetracycline bioremediation using the novel Serratia marcescens strain WW1 isolated from a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, S.-Y.; Lin, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Barceló, D.; Zheng, H.-B. Efficient degradation of tylosin by Klebsiella oxytoca TYL-T1. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, P.L.; Ren, Y.; Slape, C.M.; Ambike, I.M.; Wallace, A.C.; Fiedler, A.K.; González, J.E.; Biewer, M.C.; Zimmern, P.; Stefan, M.C. Oxidative Degradation of Polypropylene Mesh in E. coli Environment. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Deng, Y.-D.; Chen, Z.-F.; Zuo, Z.-H.; Tian, Y.-S.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Li, Z.-J.; et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for 2,4-dinitrotoluene degradation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Peng, R.; Tian, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Han, H.; Fu, X.; Gao, J.; Yao, Q. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficient degradation of 4-fluorophenol. AMB Express 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, B.D.; Elkins, C.A.; Mullis, L.B.; Heinze, T.M.; Wagner, R.D.; Cerniglia, C.E. A metallo-β-lactamase is responsible for the degradation of ceftiofur by the bovine intestinal bacterium Bacillus cereus P41. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, A.; Salam, J.A.; Das, N. Biodegradation of cefdinir by a novel yeast strain, Ustilago sp. SMN03 isolated from pharmaceutical wastewater. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Lyu, J.; Lyu, X.-J.; Yu, H.-Q.; Hu, Z.; Lam, J.C.W.; Lam, P.K.S. Characterization of cefalexin degradation capabilities of two Pseudomonas strains isolated from activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 282, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2010, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tian, S.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, L. Removal of sulfamethazine antibiotics by aerobic sludge and an isolated Achromobacter sp. S-3. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Chen, F.; Zhao, X.; Guo, T.; Lin, R.; Qu, M.; Liu, Q. Isolation, identification and degrading characteristics of phenol-degrading bacteria B3. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering, Yichang, China, 16–18 September 2011; pp. 3509–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; An, X.; Feng, L.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Q. Genome and transcriptome analysis of a newly isolated azo dye degrading thermophilic strain Anoxybacillus sp. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 111047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, Y.; Bai, B.; Xu, Z.; Ding, L.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, T. Degradation performance and optimal parameters of two bacteria in degrading nonylphenol. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 2657–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniegowski, K.; Bers, K.; Ryckeboer, J.; Jaeken, P.; Spanoghe, P.; Springael, D. Minimal pesticide-primed soil inoculum density to secure maximum pesticide degradation efficiency in on-farm biopurification systems. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Wencewicz, T.A. Tetracycline-Inactivating enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, V.H.A.; Hammond, K.; Chudyk, E.I.; Limb, M.a.L.; Spencer, J.; Mulholland, A.J.; Van Der Kamp, M.W. An efficient computational assay for Β-Lactam antibiotic breakdown by class A Β-Lactamases. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3365–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Machesky, M.L.; Yates, S.R.; Katterhenry, M. Degradation Kinetics and Mechanism of Antibiotic Ceftiofur in Recycled Water Derived from a Beef Farm. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10176–10181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Gupta, P.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist. Updates 2014, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Cai, J.Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhao, Z.H.; Shen, D.N. Research progress on two-component signal transduction systems in Porphyromonas gingivalis. West China J. Stomatol. 2021, 39, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nair, S.K. Quorum sensing: How bacteria can coordinate activity and synchronize their response to external signals? Protein Sci. 2012, 21, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | Product Length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| lhgD | lhgD-F lhgD-R | GTTCCGTGGCGAGTATTT TCCTGAGCGTAGATGGTIT | 265 |
| yghA | YghA-F YghA-R | TTTACTGGACTATGCGGCTAC CCAAACTGCGGGATCTTAT | 132 |
| dkgA | DkgA-F DkgA-R | TCCGCTGGCATCTGGATAG CGCCGAGTTCGTCTTTGTC | 114 |
| ahr | Ahr-F Ahr-R | CCGCAGGCACTGAAAGCAC CGCACCGACCGTATGGAAA | 126 |
| yqjG | YqjG-F YqjG-R | CGGTTGGACCTTTGATGAC TGCGGATGATTTCTGCTGATT | 182 |
| PuuD (Reference gene) | PuuD-F PuuD-R | CGCATGAAGTTCAGGTTGA AGGATGATTGATGACGCTAA | 176 |
| Reactant | Concentration | Volume (μL) |
|---|---|---|
| 2× Taq Plus Master Mix | 2X | 10 |
| Primer F | 5 μM | 0.8 |
| Primer R | 5 μM | 0.8 |
| Template (cDNA) | 1 | |
| ddH2O | 7.4 | |
| Total | 20 |
| Temperature | Time | Number of Cycles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-denaturation | 95 °C | 5 min | 1 |
| Denaturation | 95 °C | 30 s | |
| Annealing | 50 °C | 30 s | 35 |
| Extension | 72 °C | 1 min |
| Gene Name | Gene Description | FC(c/d) | Log2FC(c/d) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lhgD | L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase | 5.941 | 2.570588309 | 1.21 × 10−32 |
| uxaA | D-altronate dehydratase | 5.807 | 2.537895134 | 8.40 × 10−27 |
| astD | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | 4.732 | 2.242575807 | 3.49 × 10−45 |
| yghA | NADP(+)-dependent aldehyde reductase | 18.766 | 4.230028451 | 1.74 × 10−81 |
| dkgA | Methylglyoxal reductase (DkgA) | 9.968 | 3.317306509 | 9.49 × 10−33 |
| yohF | Putative oxidoreductase YohF | 18.735 | 4.227673213 | 4.92 × 10−21 |
| puuD | γ-glutamyl-γ-aminobutyrate hydrolase | 11.686 | 3.546758205 | 6.80 × 10−50 |
| ahr | NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase (Ahr) | 5.957 | 2.574467799 | 2.93 × 10−81 |
| yqjG | Glutathionyl-hydroquinone reductase (YqjG) | 12.939 | 3.693655648 | 3.24 × 10−77 |
| glxR | Tartronate semialdehyde reductase 2 | 12.037 | 3.589455688 | 2.04 × 10−24 |
| puuD | γ-glutamyl-γ-aminobutyrate hydrolase | 11.686 | 3.546758205 | 6.80 × 10−50 |
| rutB | Ureidoacrylate amidohydrolase | 7.695 | 2.943936191 | 3.74 × 10−18 |
| norW | NADH-flavorubredoxin reductase | 6.735 | 2.751693923 | 4.61 × 10−16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, M.-Y.; Zhao, C.-H.; Wu, J.; Mohammad, A.; Li, Y.-T.; Liu, L.-B.; Cao, Y.-B.; Deng, X.-M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Assessment of Biodegradation Mechanisms of Ceftiofur Sodium by Escherichia sp. CS-1 and Insights from Transcriptomic Analysis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061404
Yan M-Y, Zhao C-H, Wu J, Mohammad A, Li Y-T, Liu L-B, Cao Y-B, Deng X-M, Guo J, Zhang H, et al. Assessment of Biodegradation Mechanisms of Ceftiofur Sodium by Escherichia sp. CS-1 and Insights from Transcriptomic Analysis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061404
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Meng-Yang, Cai-Hong Zhao, Jie Wu, Adil Mohammad, Yi-Tao Li, Liang-Bo Liu, Yi-Bo Cao, Xing-Mei Deng, Jia Guo, Hui Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Assessment of Biodegradation Mechanisms of Ceftiofur Sodium by Escherichia sp. CS-1 and Insights from Transcriptomic Analysis" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061404
APA StyleYan, M.-Y., Zhao, C.-H., Wu, J., Mohammad, A., Li, Y.-T., Liu, L.-B., Cao, Y.-B., Deng, X.-M., Guo, J., Zhang, H., He, H.-S., & Sun, Z.-H. (2025). Assessment of Biodegradation Mechanisms of Ceftiofur Sodium by Escherichia sp. CS-1 and Insights from Transcriptomic Analysis. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061404





