Temperature-Driven Divergence in Microbial Consortia and Physicochemical Functionality: A Comparative Study of High- and Medium-Temperature Daqu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activity Analysis
2.3. Sample DNA Extraction and Microbial Community Structure Analysis
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Alpha Diversity Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
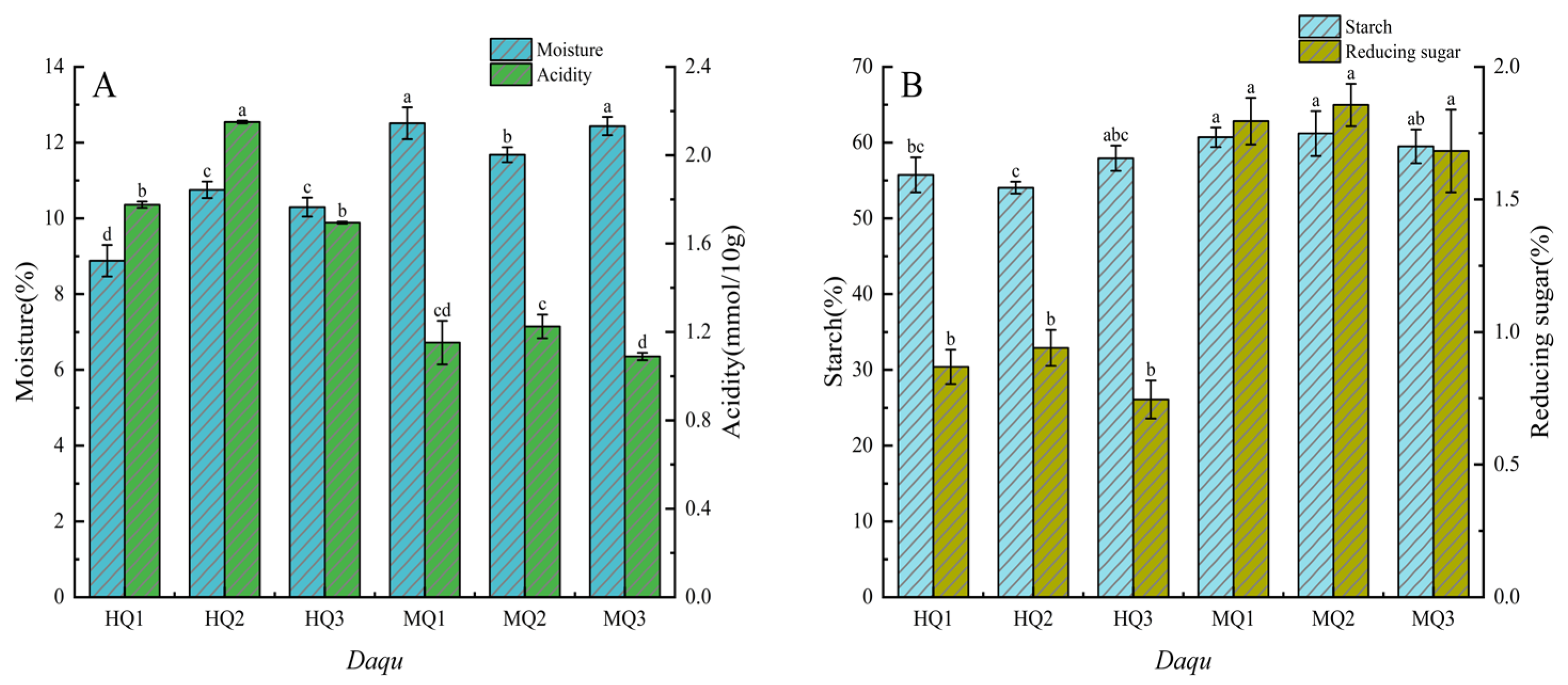
3.1. Daqu-Making Temperature Modulates Physicochemical Properties
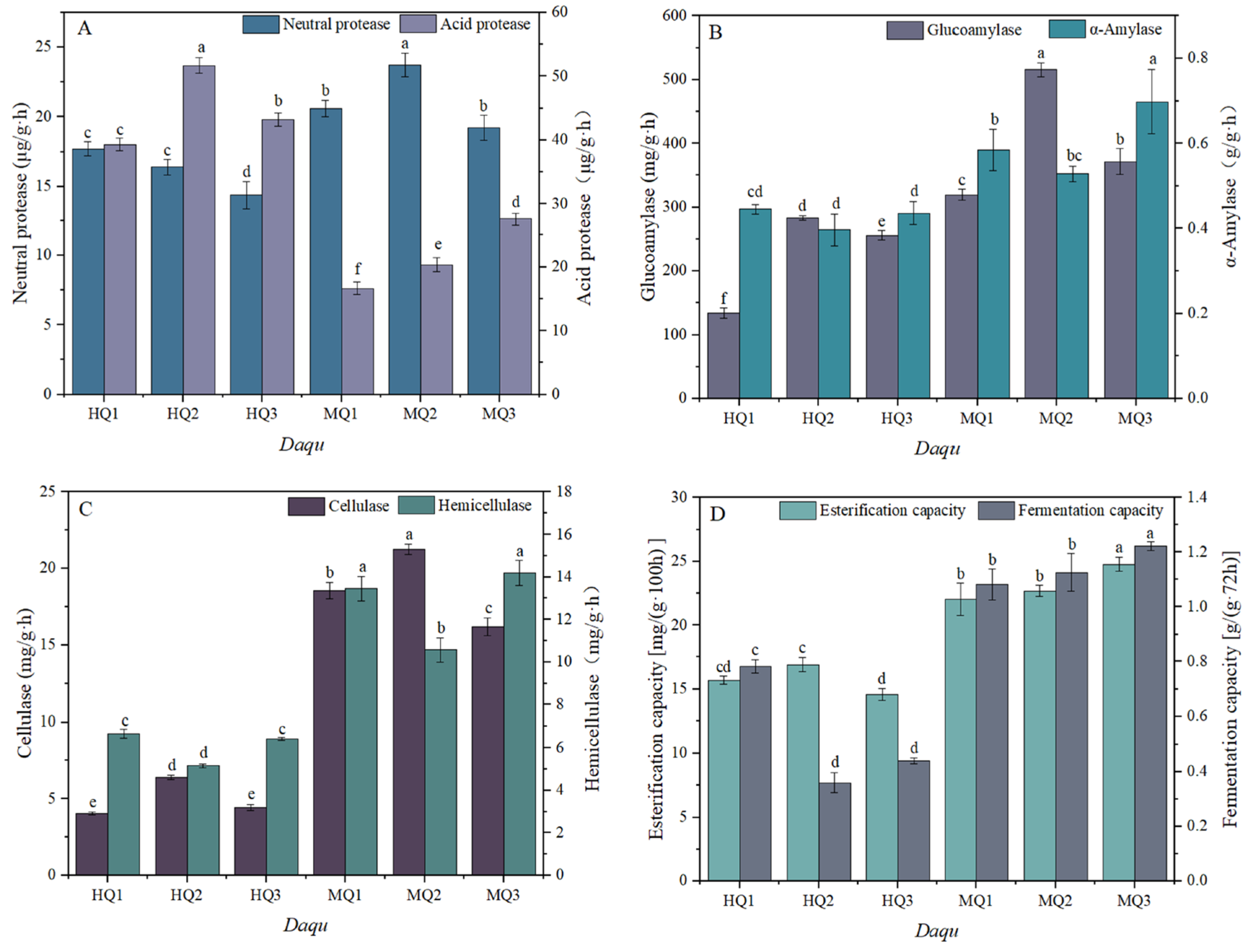
3.2. Temperature-Driven Regulation of Enzymatic Activities
3.3. Daqu-Making Temperature Shapes α-Diversity
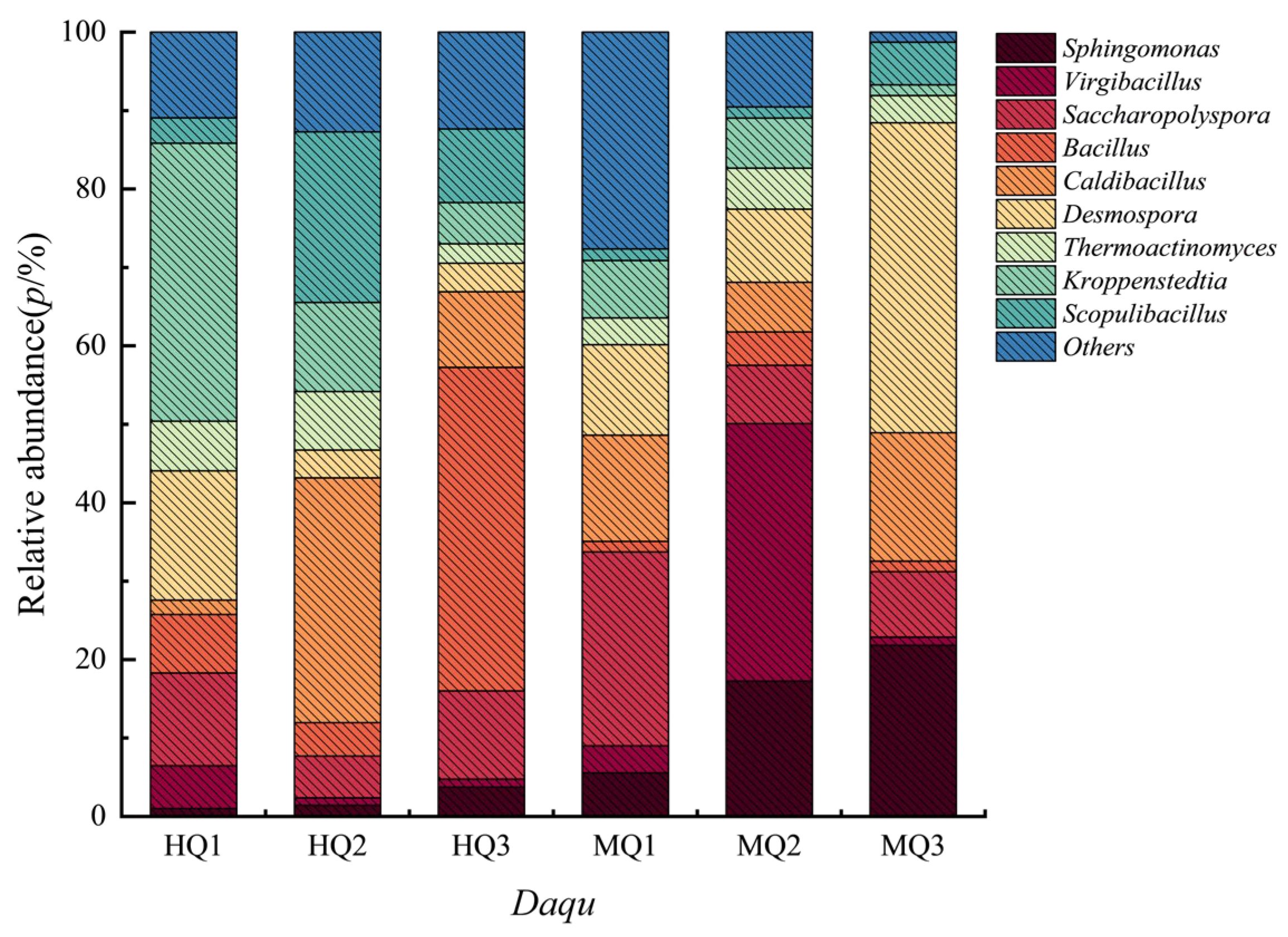
3.4. Genus-Level Abundance Dynamics Driven by Qu-Making Temperature
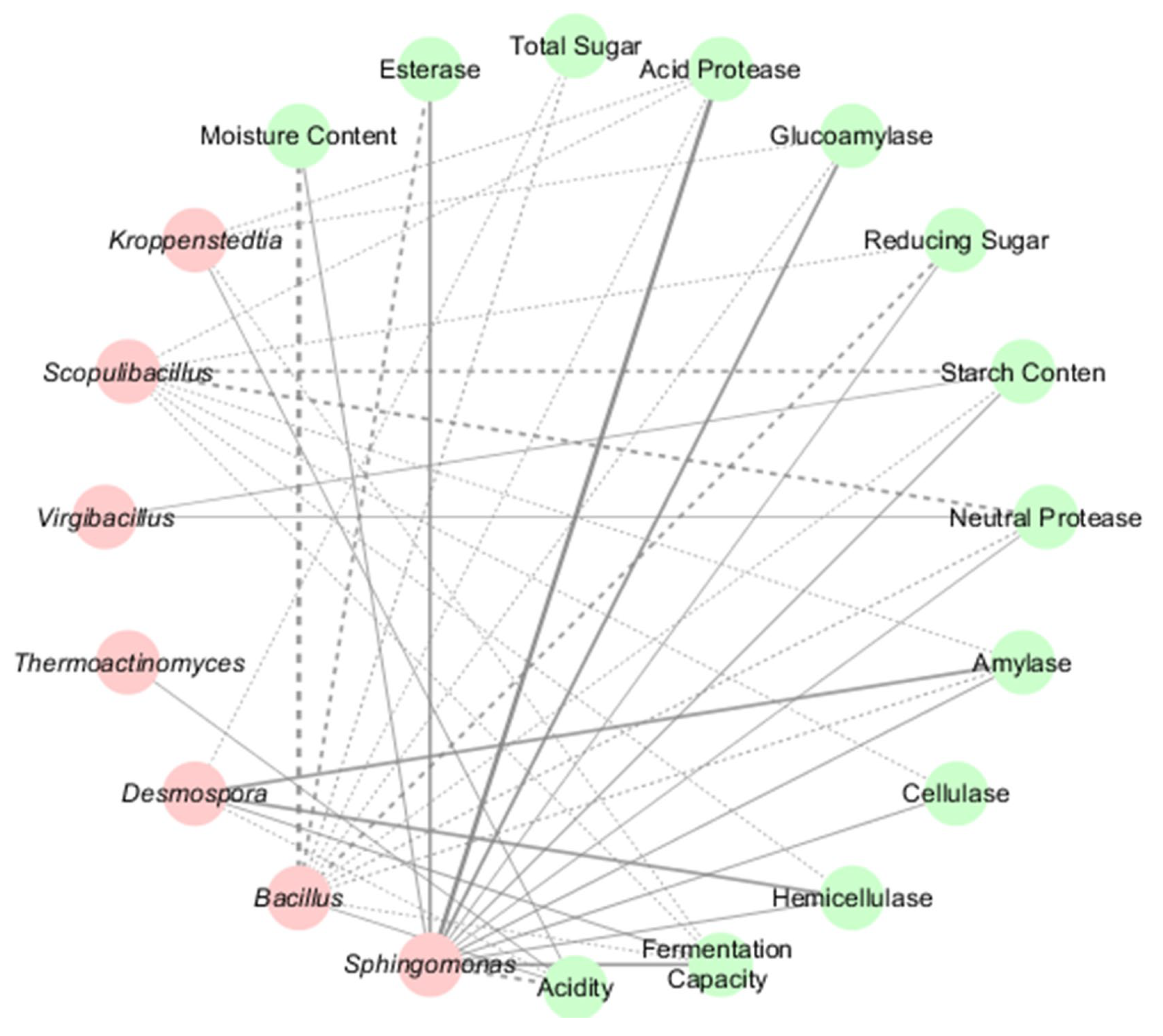
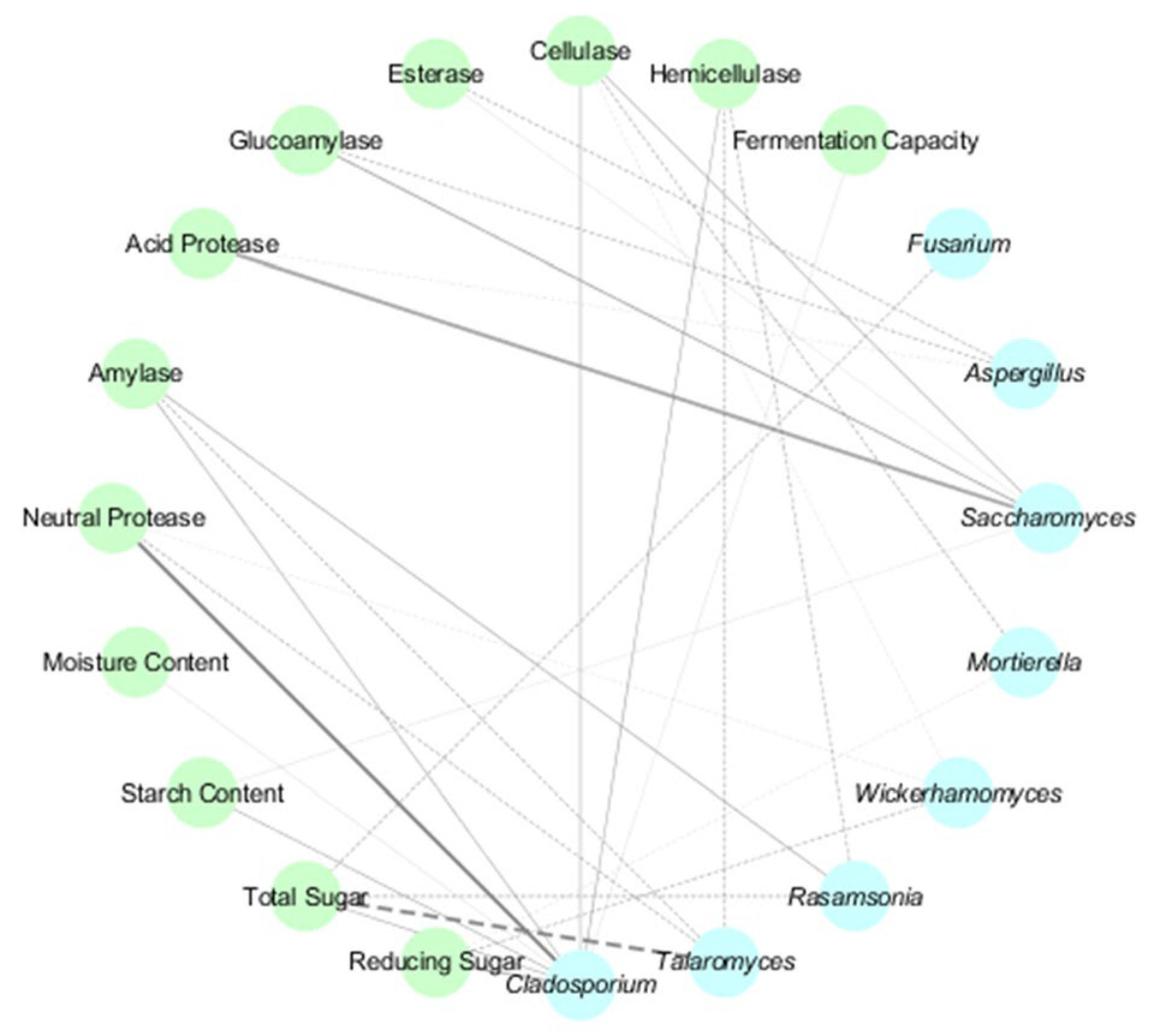
3.5. Microbial-Physicochemical Correlations in HT- and MT-Daqu
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.Y.; Yang, J.G.; Zhao, Q.S.; Zhang, K.Z.; Su, C. Research Progress on Flavor Compounds and Microorganisms of Maotai Flavor Baijiu. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Zheng, J.; Xie, J.; Zhou, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Huang, J.; Wu, C. Effects of Environmental Factors on the Microbial Community Changes during Medium-High Temperature Daqu Manufacturing. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.T.; Lu, Z.M.; Shi, W.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, X.J.; Chai, L.J.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Effects of Different Culture Temperatures on Microbial Community Structure, Enzyme Activity, and Volatile Compounds in Daqu. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2021, 27, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Jin, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C. Research Progress in Microbial Community Structure in Nongxiangxing Daqu. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 3170–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Microbial Diversity in Jiuqu and Its Fermentation Features: Saccharification, Alcohol Fermentation and Flavors Generation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Lu, Z.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, S.T.; Ao, L.; Shen, C.H.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Bio-Heat Is a Key Environmental Driver Shaping the Microbial Community of Medium-Temperature Daqu. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01550-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T.; Lv, N.; Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Bai, B.; Tian, X.; Fan, S. Research Progress on Microbial Communities and Functions during Daqu Fermentation for Baijiu Production. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Han, S.; Hou, J.; Pan, C. Combined Microbiome and Metabolomics Analysis of Taorong-Type Baijiu High-Temperature Daqu and Medium-Temperature Daqu. PeerJ 2024, 12, e16621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Han, S.; Pan, C. Taorong-Type Baijiu Starter: Analysis of Fungal Community and Metabolic Characteristics of Middle-Temperature Daqu and High-Temperature Daqu. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gai, J.; Hou, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Yu, Q.; Chang, X.; Dong, X.; Chen, M.; Li, P.; et al. Ultra-High-Depth Macrogenomic Sequencing Revealed Differences in Microbial Composition and Function Between High Temperature and Medium-High Temperature Daqu. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Mu, Y.; Su, W. Exploring the Heterogeneity of Community and Function and Correspondence of “Species-Enzymes” among Three Types of Daqu with Different Fermentation Peak-Temperature via High-Throughput Sequencing and Metagenomics. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QB/T 4257-2011; General Analysis Methods for Brewing Daqu. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- DB 34/T 3085-2018; Operating Procedures for Testing Strong-Flavor Daqu. Anhui Provincial Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision: Hefei, China, 2018.
- NY/T 912-2020; Determination of Cellulase Activity in Feed Additives—Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 23874-2009; Determination of Xylanase Activity in Feed Additives—Spectrophotometric Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB 5009.7-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Reducing Sugars in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Dueholm, M.S.; Andersen, K.S.; McIlroy, S.J.; Kristensen, J.M.; Yashiro, E.; Karst, S.M.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H. Generation of Comprehensive Ecosystem-Specific Reference Databases with Species-Level Resolution by High-Throughput Full-Length 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Automated Taxonomy Assignment (AutoTax). mBio 2020, 11, e01557-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Walder, F.; Büchi, L.; Meyer, M.; Held, A.Y.; Gattinger, A.; Keller, T.; Charles, R.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Agricultural Intensification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and the Abundance of Keystone Taxa in Roots. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan v2.6: Community Ecology Package. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Xing, G.; Ao, Z.; Wang, S.; Deng, B.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z. Analysis of the Change in Physiochemical Indexes during the Production Process of Daqu of Different Temperature. Liquor-Making Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Wan, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, C.; Fu, G. Effect of Peak Temperature on the Succession of Physicochemical Index and Microbial Community of Special-Flavor Daqu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Li, W.; Hao, J.; Xu, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; et al. Correlational Analysis of the Physicochemical Indexes, Volatile Flavor Components, and Microbial Communities of High-Temperature Daqu in the Northern Region of China. Foods 2023, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Liang, J.; Zhou, W. Study on Physicochemical Indexes and Microbial Succession Law during Fermentation of Medium/High-Temperature Daqu. Liquor-Making Sci. Technol. 2024, 8, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.Y.; Li, X.D.; Xie, S.K.; Yu, P.B.; Chen, J.X. Interactions between Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeasts in Light-Aroma Baijiu. Microbiol. Bull. 2017, 44, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Jia, X.; Zhu, K.; Ling, Z.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.; Ao, Z.; Song, C.; Shen, C.; Chai, L.; et al. Dynamic Changes and Potential Correlations between Microbial Diversity and Volatile Flavor Compounds in Chinese Medium-Temperature Daqu during Manufacturing. Molecules 2024, 29, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Deng, M.; Chen, K.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, S.; Wan, Y. Peak-Temperature Effects of Starter Culture (Daqu) on Microbial Community Succession and Volatile Substances in Solid-State Fermentation (Jiupei) during Traditional Chinese Special-Flavour Baijiu Production. LWT 2021, 152, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.; Tian, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z. Microbial Communities, Functional, and Flavor Differences among Three Different-Colored High-Temperature Daqu: A Comprehensive Metagenomic, Physicochemical, and Electronic Sensory Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Mao, X.; Liu, D.; Ning, X.Q.; Shen, Y.; Chen, B.; Luo, H.B. Comparative Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Composition in High-Temperature Daqu with Different Colors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 588117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shen, L.; Yang, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Microbial Composition and Dynamic Succession during the Daqu Production Process of Northern Jiang-Flavored Liquor in China. aBiotech 2021, 11, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.J.; Song, L.; Wen, Z.; Zhu, H.Y.; Wei, Y.H.; Wang, J.W.; Bai, M.; Luo, L.J.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, S.X.; et al. Species-Level Understanding of the Bacterial Community in Daqu Based on Full-Length 16S rRNA Gene Sequences. Food Microbiol. 2024, 123, 104566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.H.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhao, T.; Mao, H.; Fang, S.L.; Chen, M.B.; Liu, S.L. Changes in the Microbial Community Structure during the Digitally Managed Fermentation of Medium-Temperature Daqu. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e87122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Gao, R.J.; Zhao, Y.W.; Miao, L.H.; Wang, M.K.; Liu, P.L.; Fan, P.W. Relationship between Sensory Indexes, Physicochemical Indexes, Microbial Community, and Volatile Compounds in High-Temperature Daqu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zheng, J.; Huang, D.; Huang, Z.; Ye, G.; Luo, H. Characterization of Physicochemical Properties, Volatile Compounds and Microbial Community Structure in Four Types of Daqu. LWT 2023, 184, 115064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-W.; Tabrizi, M.R.; Nout, M.J.R.; Han, B.-Z. Daqu—A Traditional Chinese Liquor Fermentation Starter. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, M.S.; Dai, Q.L.; Li, S.; Shen, C.H.; Wang, S.T. Comparative Study on Physicochemical Properties and Fungal Community Composition of Medium and High-Temperature Daqu from the Same Region. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.D.; Feng, W.C.; Sun, W.; Chen, H.; Liao, B.; Fang, S.L. Correlation Analysis of Microbial Communities and Physicochemical Indicators in Daqu of Different Flavor Types. China Brew. 2024, 43, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, G.X.; Chen, Y.Q.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.D.; Luo, H.B. Comparative Analysis of Microbial Community Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Different Grades of Strong-Flavor Daqu. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.K.; Xie, J.; Cheng, T.Y.; Wei, C.H.; Huang, Z.G.; Deng, J. Correlation Between Quality Indicators and Bacterial Communities in Strong-Flavor Daqu from Different Regions. Food Res. Dev. 2019, 40, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.Y.; Ran, M.F.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H. Correlation Between Physicochemical Characteristics and Microbial Communities in Highland Barley Daqu with Different Ingredients. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.F.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.Q.; Qin, H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Dong, Y. Effects of Spatial Heterogeneity on Microbial Communities and Quality of Medium-High Temperature Daqu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | ASV Count | Chao1 Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ1 | 961 | 396.36 ± 2.81 c | 7.83 ± 0.07 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 99.99 |
| HQ2 | 736 | 427.51 ± 0.17 f | 4.81 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 d | 99.97 |
| HQ3 | 795 | 242.61 ± 0.30 e | 5.64 ± 0.03 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 99.97 |
| MQ1 | 642 | 642.03 ± 0.02 a | 4.35 ± 0.01 d | 0.98 ± 0.00 a | 99.97 |
| MQ2 | 322 | 322.07 ± 0.04 d | 2.17 ± 0.05 e | 0.92 ± 0.00 b | 99.96 |
| MQ3 | 77 | 577.12 ± 0.01 b | 1.76 ± 0.04 f | 0.94 ± 0.00 ab | 99.94 |
| Samples | ASV Count | Chao1 Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ1 | 368 | 122.24 ± 3.73 d | 2.01 ± 0.01 d | 0.37 ± 0.01 d | 99.93 |
| HQ2 | 297 | 47.83 ± 5.14 f | 1.53 ± 0.05 e | 0.63 ± 0.00 b | 99.91 |
| HQ3 | 331 | 49.03 ± 2.22 e | 1.91 ± 0.04 e | 0.51 ± 0.03 c | 99.93 |
| MQ1 | 2037 | 209.79 ± 0.00 c | 8.44 ± 0.02 a | 0.99 ± 0.00 a | 99.99 |
| MQ2 | 948 | 952.11 ± 0.00 a | 7.63 ± 0.01 b | 0.98 ± 0.00 a | 99.97 |
| MQ3 | 635 | 636.34 ± 0.00 b | 3.72 ± 0.00 c | 0.64 ± 0.00 b | 99.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Zheng, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Xie, T.; Nan, G.; Li, L.; Lou, K. Temperature-Driven Divergence in Microbial Consortia and Physicochemical Functionality: A Comparative Study of High- and Medium-Temperature Daqu. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061312
Yuan H, Zheng J, Ding L, Wang H, Jiang Q, Zhang C, Xie T, Nan G, Li L, Lou K. Temperature-Driven Divergence in Microbial Consortia and Physicochemical Functionality: A Comparative Study of High- and Medium-Temperature Daqu. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061312
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Huawei, Jia Zheng, Liping Ding, Hong Wang, Qin Jiang, Chao Zhang, Tingna Xie, Guohui Nan, Li Li, and Kai Lou. 2025. "Temperature-Driven Divergence in Microbial Consortia and Physicochemical Functionality: A Comparative Study of High- and Medium-Temperature Daqu" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061312
APA StyleYuan, H., Zheng, J., Ding, L., Wang, H., Jiang, Q., Zhang, C., Xie, T., Nan, G., Li, L., & Lou, K. (2025). Temperature-Driven Divergence in Microbial Consortia and Physicochemical Functionality: A Comparative Study of High- and Medium-Temperature Daqu. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061312




