Diagnostic Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Imaging Protocol
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Diagnostic Classification
3.2. Microbiological and Clinical Findings
3.3. Diagnostic Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT
3.4. Reclassification After 18F-FDG PET/CT
3.5. Detection of Malignancies
3.6. Rejected IE and Alternative Diagnoses
3.7. False-Negative and False-Positive Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anton-Vazquez, V.; Cannata, A.; Amin-Youssef, G.; Watson, S.; Fife, A.; Mulholland, N.; Gunning, M.; Papachristidis, A.; Maccarthy, P.; Baghai, S.; et al. Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in infective endocarditis. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 111, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, E.; Akyel, R. Unexpected septic pulmonary embolism imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT in an infective endocarditis case: Case report. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2022, 53, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajinovic, K.; Lauc, G.; Kralik, S. Dual-Time-Point 18F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis: Impact of delayed imaging in the definitive diagnosis of endocarditis. Biomedicines 2022, 12, 861. [Google Scholar]
- Rewers, K.I.; Scholtens, A.M.; Thomassen, A.; Hess, S. The role of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in infectious endocarditis and cardiac device infection. Curr. Mol. Imaging 2022, 3, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, M.; García, J.; López, J. 18F-FDG PET/CT in infective endocarditis: Indications and approaches for standardization. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Alavi, A. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of infective endocarditis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, J.; Lee, M. Diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/CT in prosthetic valve endocarditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.; Krumholz, H. Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Rodríguez, J. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the assessment of cardiac device infections. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 678–684. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT in infective endocarditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, T.; Alavi, A. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Park, J. Clinical impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with suspected infective endocarditis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4001. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J. The diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in native valve endocarditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 22, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Choi, Y. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: A review. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y. Diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/CT in prosthetic valve endocarditis: A meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 684. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2780–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Li, X. The diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in cardiac device infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 37, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Mylonakis, E.; Calderwood, S. Infective endocarditis in adults: A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Ishida, H. Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: A retrospective study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, A.A.; Elvas, L.; Silva, R.; Gonçalves, L.; Ferreira, M.J. 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of cardiac device-related infective endocarditis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 3093–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzilli, M.; Albano, D.; Lucchini, S.; Peli, A.; Cerudelli, E. New criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis using 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, S.J.; Mediratta, A.; Gillam, L.D.; Slart, R.H.J.A. Cardiovascular imaging in infective endocarditis: A multimodality approach. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e008956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedur, A.; Singh, A. 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of prosthetic valve endocarditis: A review. World J. Cardiol. 2021, 13, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Avesani, S.; De Cesare, S.; Barlascini, S. 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with suspected prosthetic valve endocarditis: A diagnostic aid. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2021, 49, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Garg, A. Clinical role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the early detection of infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L. Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting infective endocarditis: Meta-analysis and systematic review. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3499–3510. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, M.; Rybak, M. Role of imaging, including 18F-FDG PET/CT in diagnosing infective endocarditis: A retrospective study. Heart Lung 2021, 50, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Elbanhawy, S.; El-Kholey, F. Comparative diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/CT and echocardiography in infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 898–906. [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama, A.; Kohno, T. Evaluation of myocardial inflammation in infective endocarditis using FDG PET imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, T.; Tanaka, S.; Fukuoka, T. 18F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: From bacterial detection to treatment planning. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K.; Tsujimoto, H. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting infective endocarditis of the heart valves. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2020, 10, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, H. Evaluation of infective endocarditis using 18F-FDG PET/CT: A systematic review of the literature. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- Eperjesi, T.; Wang, D. The role of hybrid imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis: A review. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Abela, G.S.; Lee, J.W. Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT for identifying aortic valve infective endocarditis. J. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, F.; Sharma, N. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in diagnosing endocarditis: A comprehensive review of clinical studies. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 7, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ogura, T.; Inoue, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosing infective endocarditis: A prospective study. J. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Wu, M. Combined approach of 18F-FDG PET/CT and transthoracic echocardiography in suspected prosthetic valve endocarditis. Heart 2022, 108, 652–659. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, K.; Kobayashi, M. Imaging techniques for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. Heart Vessels 2020, 35, 953–963. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, D.; Botto, G. The diagnostic role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in suspected cases of infective endocarditis: A systematic review of the literature. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Osipova, E.; Frolov, V. PET/CT in infective endocarditis: An emerging imaging modality for clinical management. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkhuizen, M.; Hoffer, P. Comparative evaluation of 18F-FDG PET/CT versus echocardiography in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. The diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/CT in infective endocarditis and its impact on management decisions: A systematic review. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2020, 41, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Prat, A.; Riera, J. Imaging techniques in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis: The emerging role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 28, 276–288. [Google Scholar]
- Lancellotti, P.; Go, Y.Y.; Régis, C. The power of negative metabolic imaging: Negative FDG-PET/CT predicts infective endocard. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 24, 1489–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Bansal, R. Clinical implications of 18F-FDG PET/CT in prosthetic valve endocarditis: A prospective study. Clin. Cardiol. 2022, 45, 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Shah, K. Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in cardiac implantable electronic device infections: A meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 22, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Kawai, H. Diagnostic challenges and solutions in infective endocarditis: Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2022, 36, 881–890. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Takahashi, T. Advances in PET/CT imaging in infective endocarditis: Current status and future perspectives. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
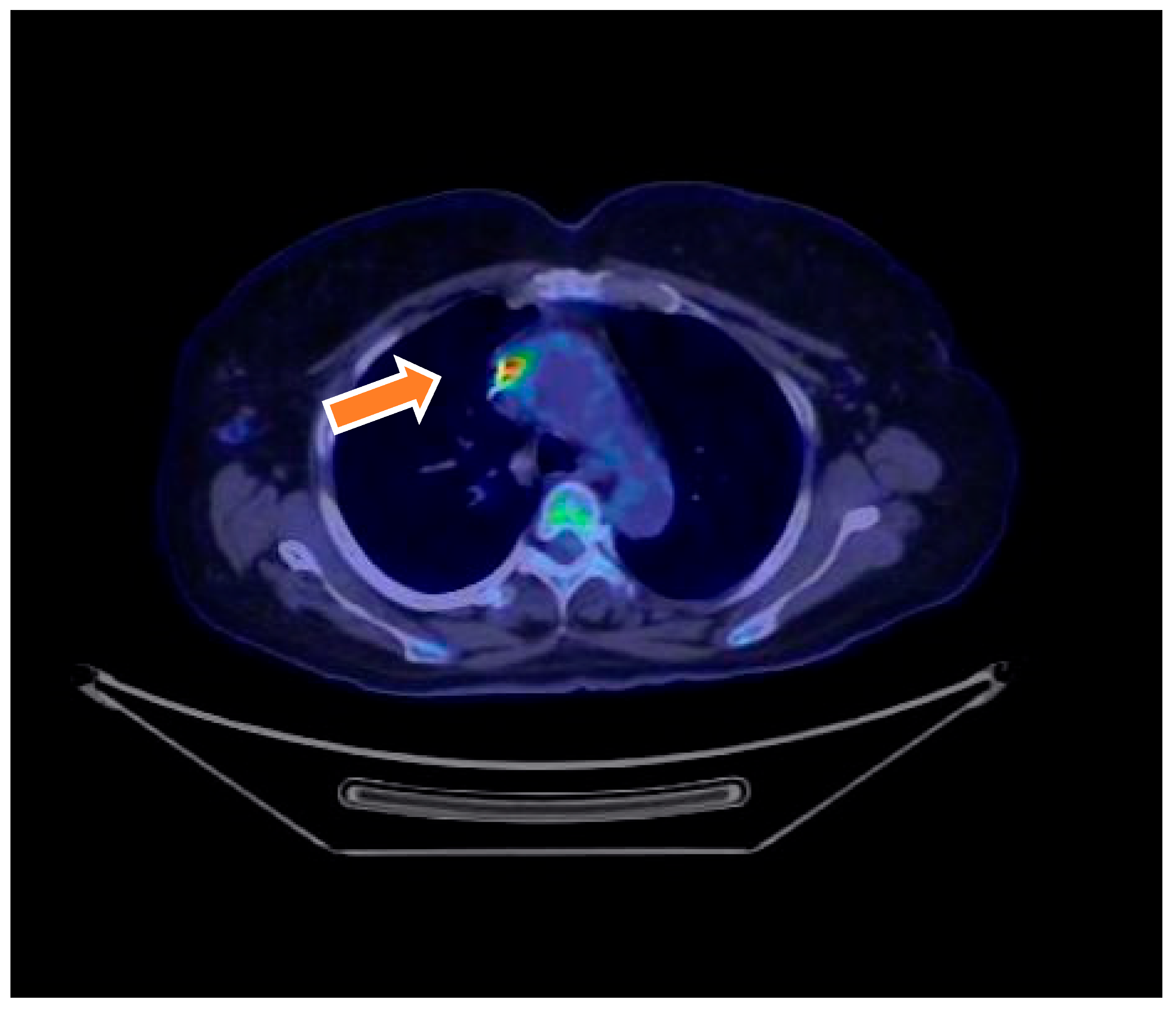
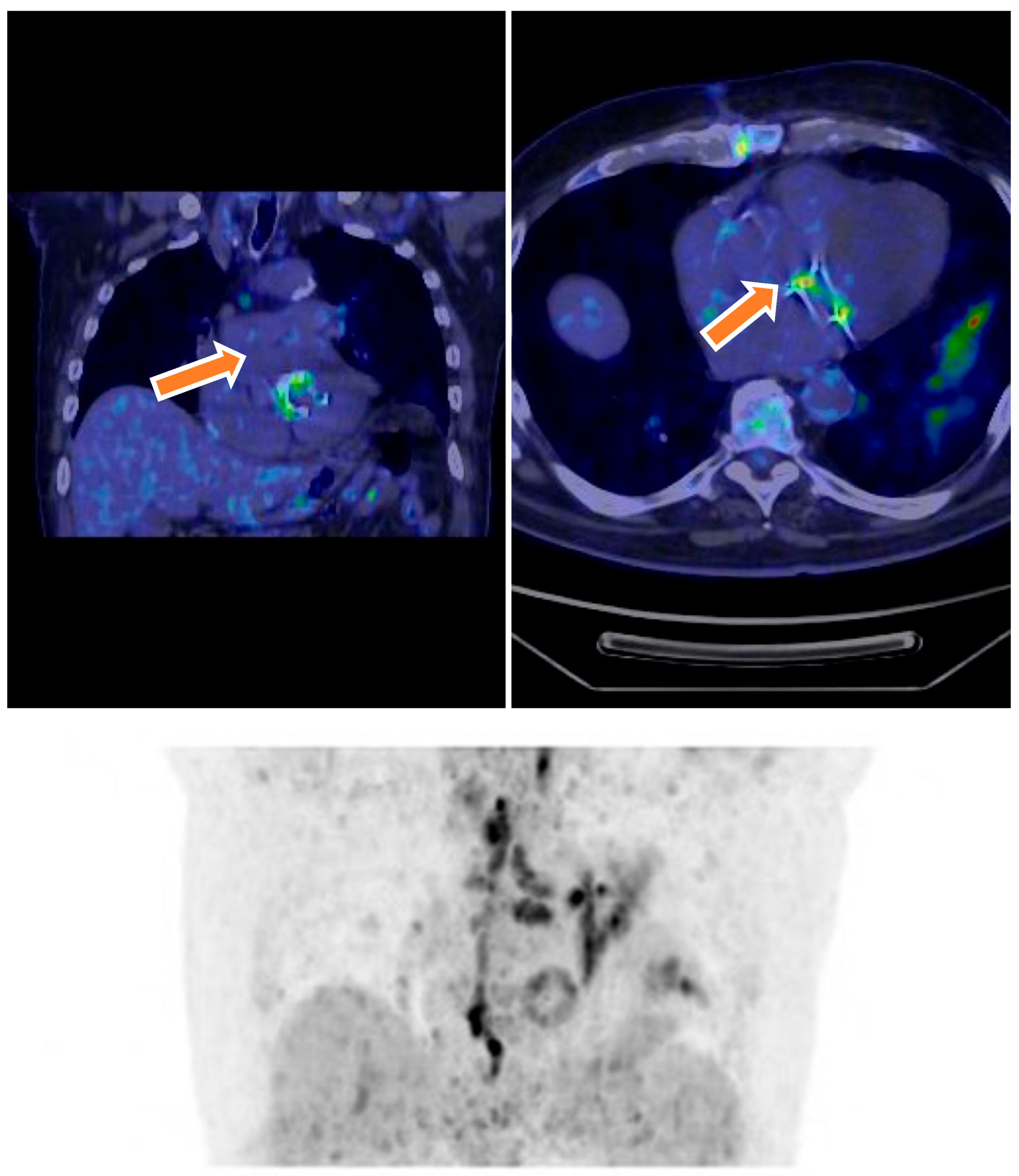
| Characteristic | Total (N = 70) | Definite IE (N = 18) | Possible IE (N = 46) | Rejected IE (N = 6) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Mean ± SD (Years) | 71 ± 11 | 76 ± 15 | 68 ± 12 | 64 ± 13 | 0.002 |
| Sex, N (%) | |||||
| Female | 18 (25.7%) | 4 (22.2%) | 10 (21.7%) | 4 (66.7%) | 0.15 |
| Male | 52 (74.3%) | 14 (77.8%) | 36 (78.3%) | 2 (33.3%) | 0.15 |
| Comorbidities, N (%) | |||||
| Hypertension | 62 (88.6%) | 13 (72.2%) | 45 (97.8%) | 4 (66.7%) | 0.04 |
| Copd | 6 (8.6%) | 4 (22.2%) | 1 (2.2%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0.03 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 34 (48.6%) | 16 (88.9%) | 15 (32.6%) | 3 (50.0%) | <0.001 |
| Cardiac Valve Prosthesis, N (%) | |||||
| Aortic Valve | 16 | 4 | 10 | 2 | 0.88 |
| Mitral Valve | 7 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.71 |
| Echocardiography, N (%) | |||||
| Transthoracic Echo | 70 (100%) | 18 (100%) | 46 (100%) | 6 (100%) | - |
| Transesophageal Echo | 49 (70%) | 9 (38.9%) | 35 (76.1%) | 5 (83.3%) | <0.001 |
| Median Time from Pv Surgery (Days, IQR) | 61 (17–97) | 47 (24–105) | 52 (16–88) | 65 (20–90) | 0.43 |
| <1 Year Since Surgery | 16 (22.9%) | 3 (16.7%) | 11 (23.9%) | 2 (33.3%) | 0.45 |
| ≥1 Year Since Surgery | 54 (77.1%) | 15 (83.3%) | 35 (76.1%) | 4 (66.7%) | 0.07 |
| Days of Antibiotics Before PET/CT (Median, IQR) | 14 (7–34) | 21 (14–31) | 10 (7–25) | 12 (8–20) | 0.02 |
| Category | Finding | N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Fever | 17 (94.4%) |
| Heart failure | 5 (27.7%) | |
| Dyspnea | 3 (16.6%) | |
| Echocardiographic Findings | Vegetations | 16 (88.8%) |
| Valve regurgitation | 5 (27.7%) | |
| No echocardiographic findings | 7 (38.8%) | |
| Etiological Agent | Staphylococcus aureus | 6 (33.3%) |
| Coagulase-negative Staphylococci | 4 (22.2%) | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 3 (16.6%) | |
| Streptococcus bovis | 1 (5.6%) | |
| Candida albicans | 1 (5.6%) | |
| Not identified | 3 (16.6%) | |
| Diagnostic Microbiology | Positive blood cultures | 15 (83.3%) |
| Outcome | Mortality related to IE episode | 1 (5.6%) |
| Initial Duke Classification | Reclassification by PET/CT | Final Duke Classification | Number of Patients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Possible IE | Positive PET/CT (suggesting infection) | Definite IE | 6 |
| Possible IE | Negative PET/CT (no infection signs) | Rejected IE | 7 |
| Not IE | New PET/CT findings suggestive of IE | Possible IE | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anton, C.-I.; Munteanu, A.-E.; Mititelu, M.R.; Alexandru Ștefan, M.; Buzilă, C.-A.; Streinu-Cercel, A. Diagnostic Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061299
Anton C-I, Munteanu A-E, Mititelu MR, Alexandru Ștefan M, Buzilă C-A, Streinu-Cercel A. Diagnostic Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061299
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnton, Corina-Ioana, Alice-Elena Munteanu, Mihaela Raluca Mititelu, Militaru Alexandru Ștefan, Cosmin-Alexandru Buzilă, and Adrian Streinu-Cercel. 2025. "Diagnostic Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061299
APA StyleAnton, C.-I., Munteanu, A.-E., Mititelu, M. R., Alexandru Ștefan, M., Buzilă, C.-A., & Streinu-Cercel, A. (2025). Diagnostic Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061299






